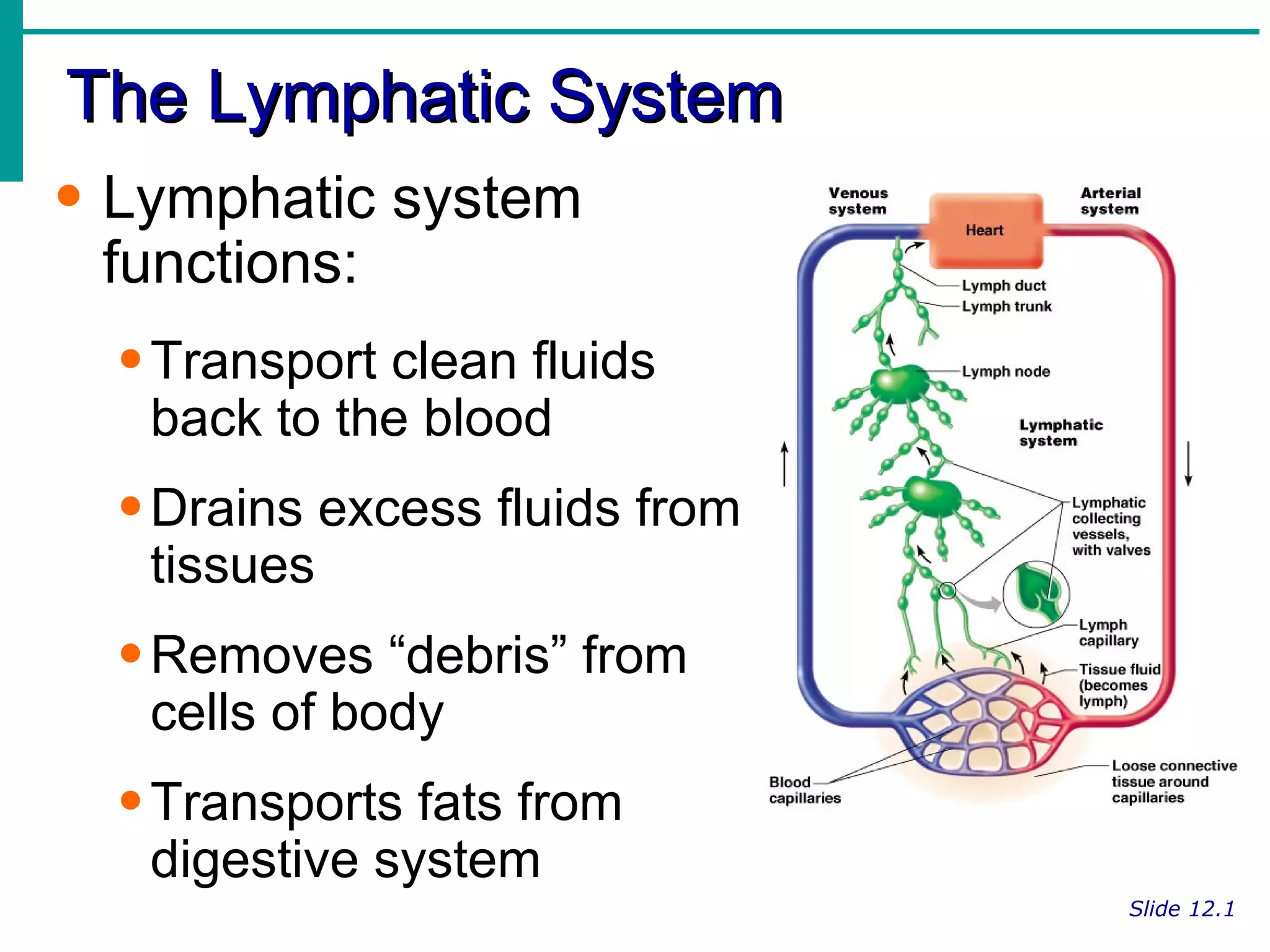
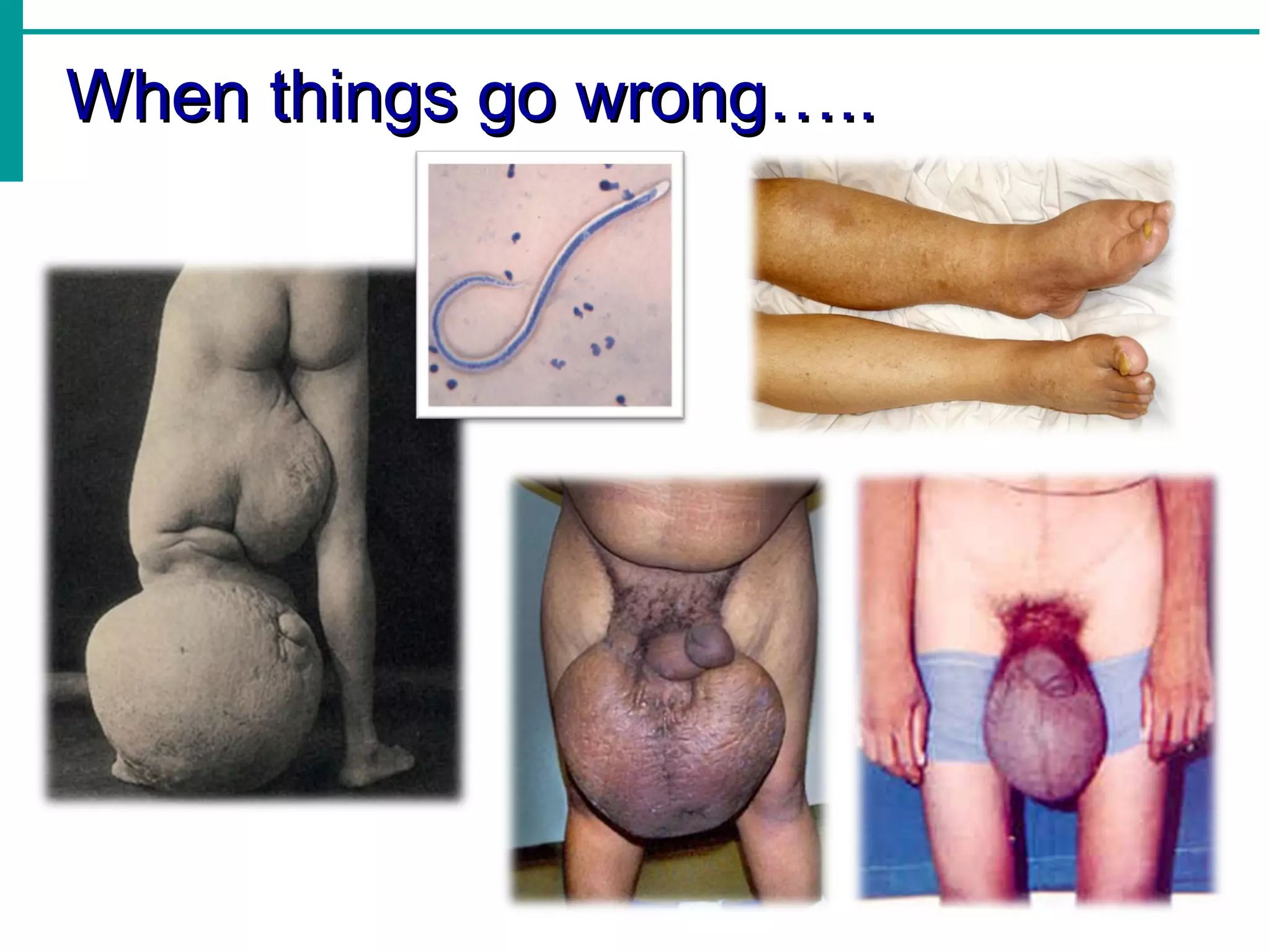
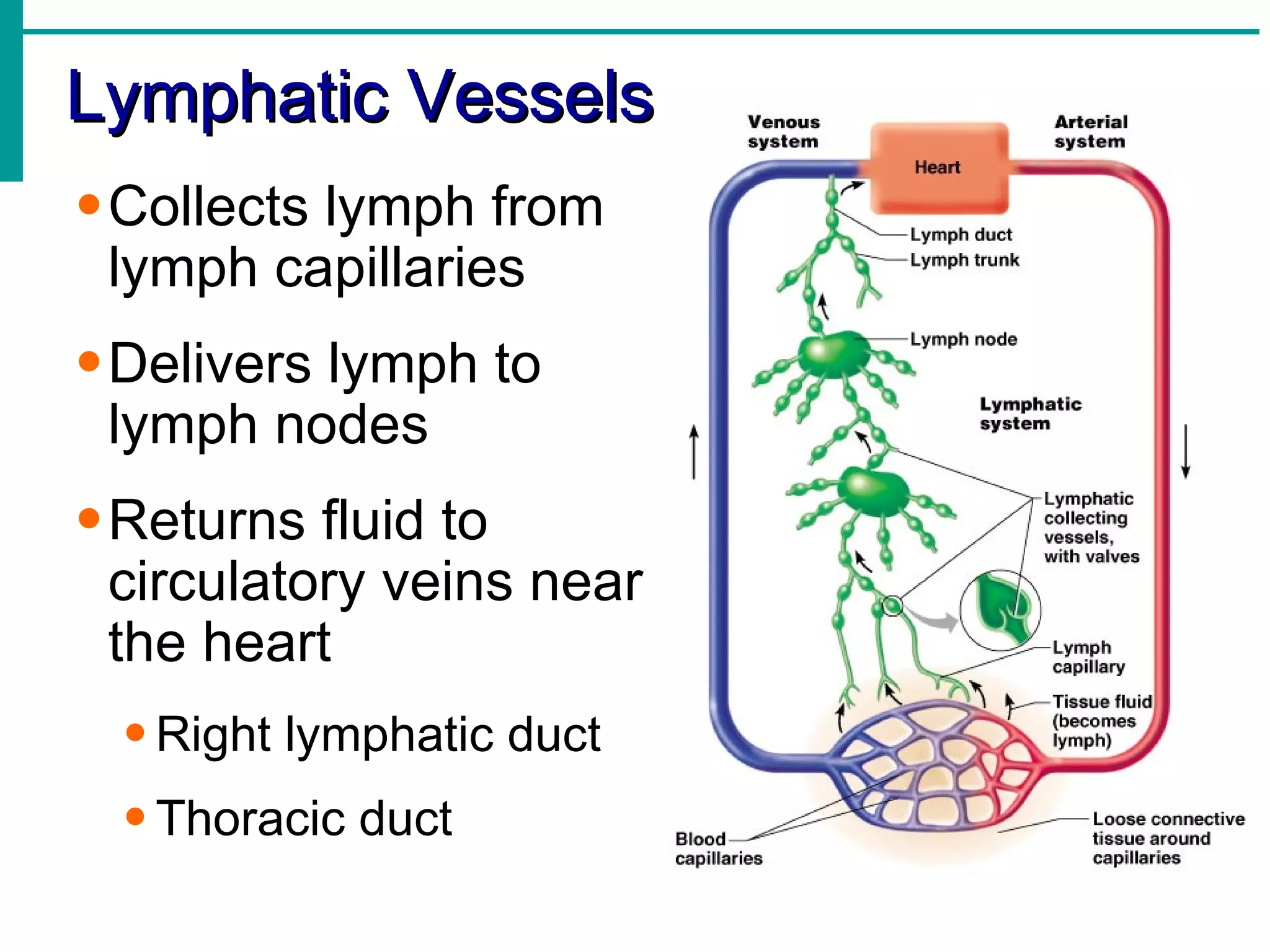
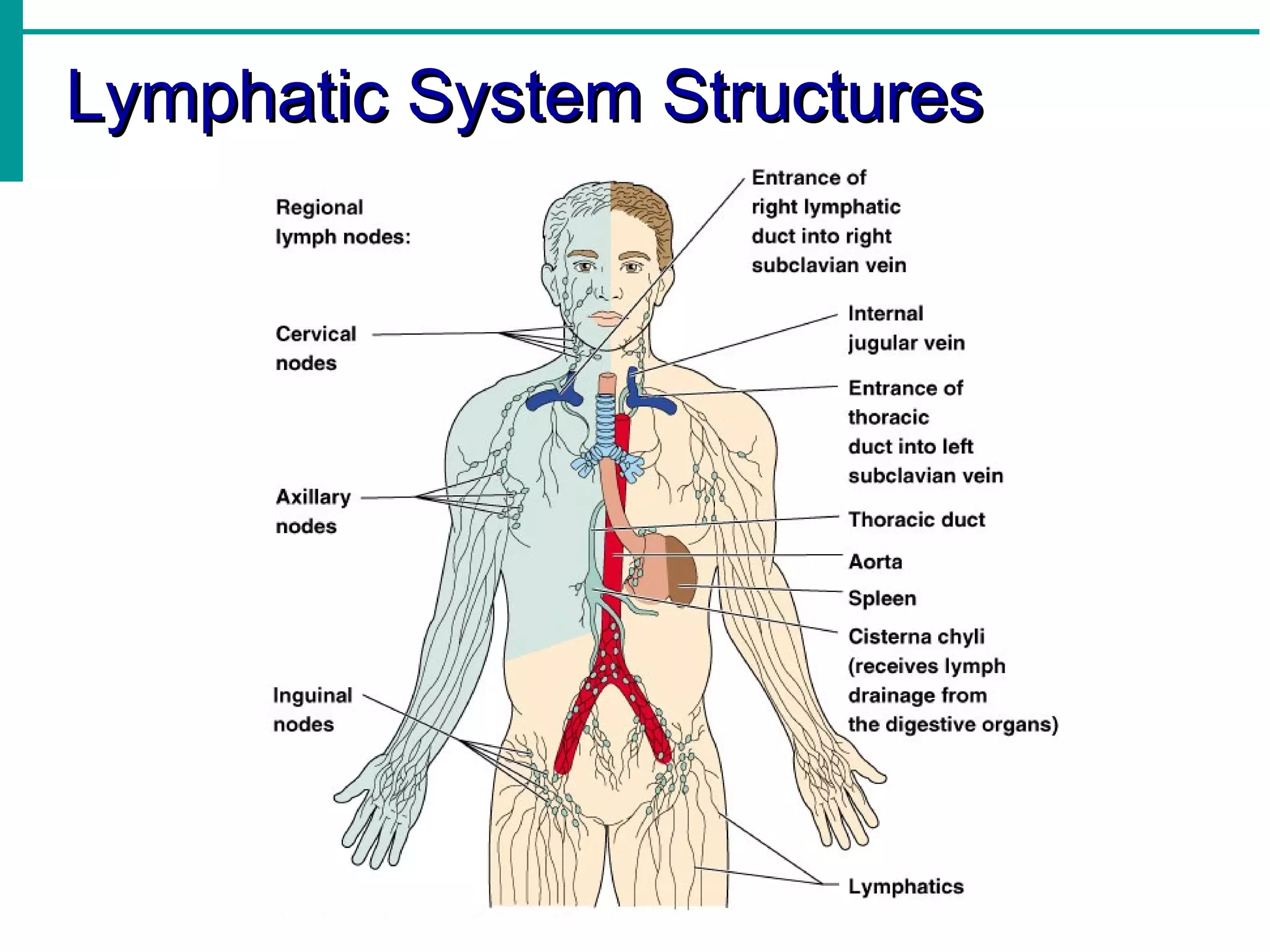
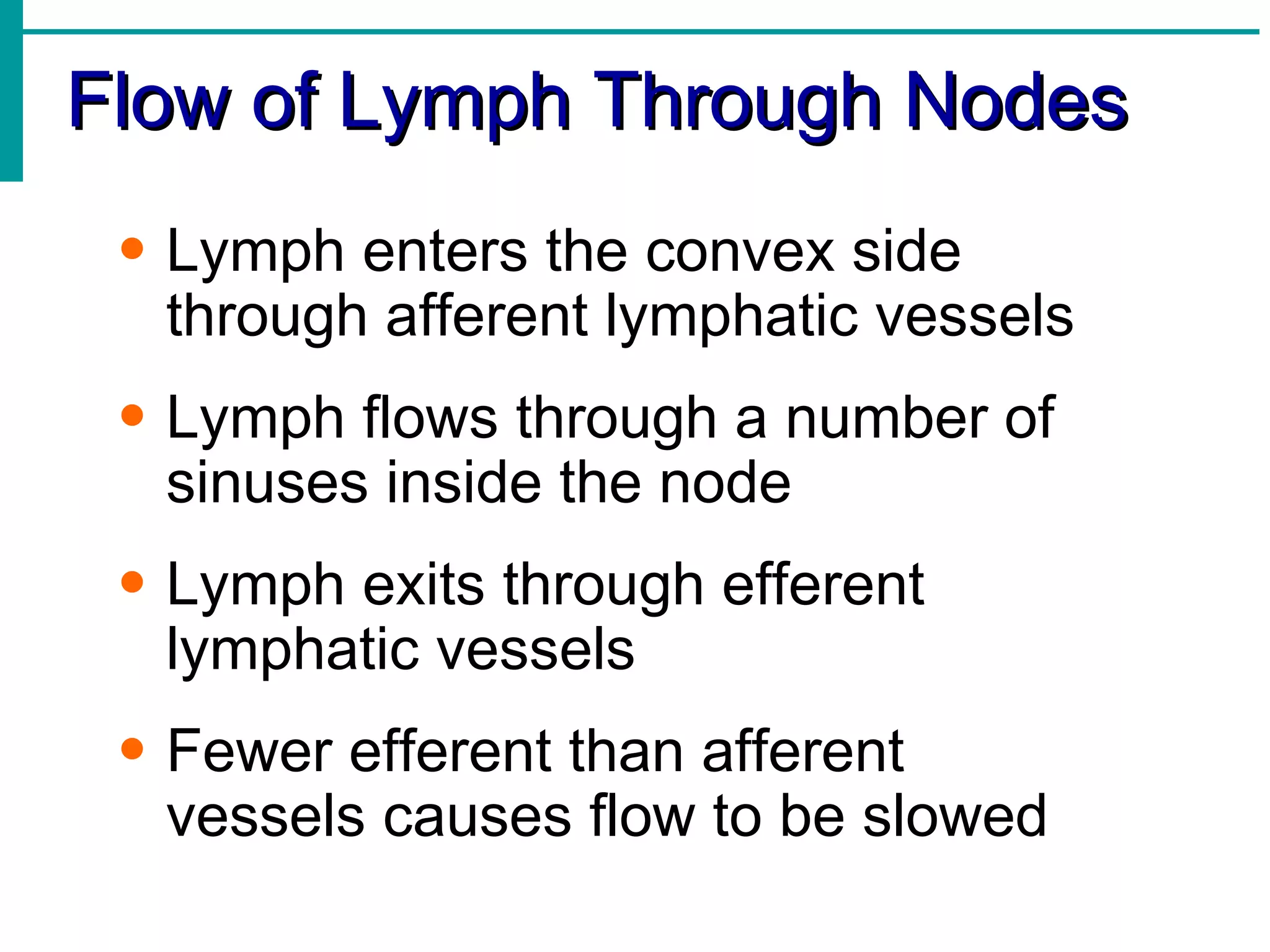
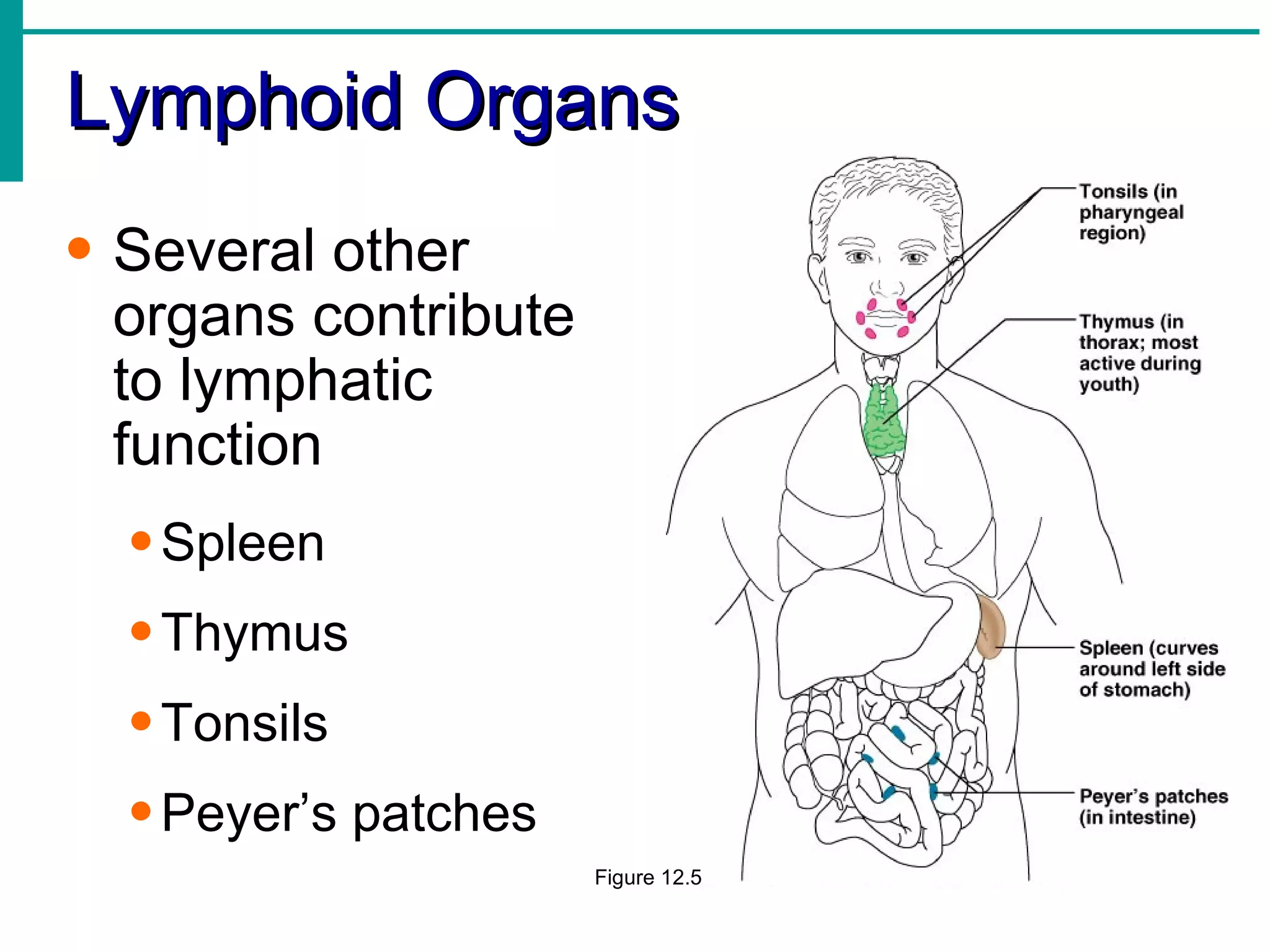
The lymphatic system functions to:
1) Transport clean fluids back to the blood from tissues;
2) Drain excess fluids from tissues; and
3) Remove debris from cells of the body.
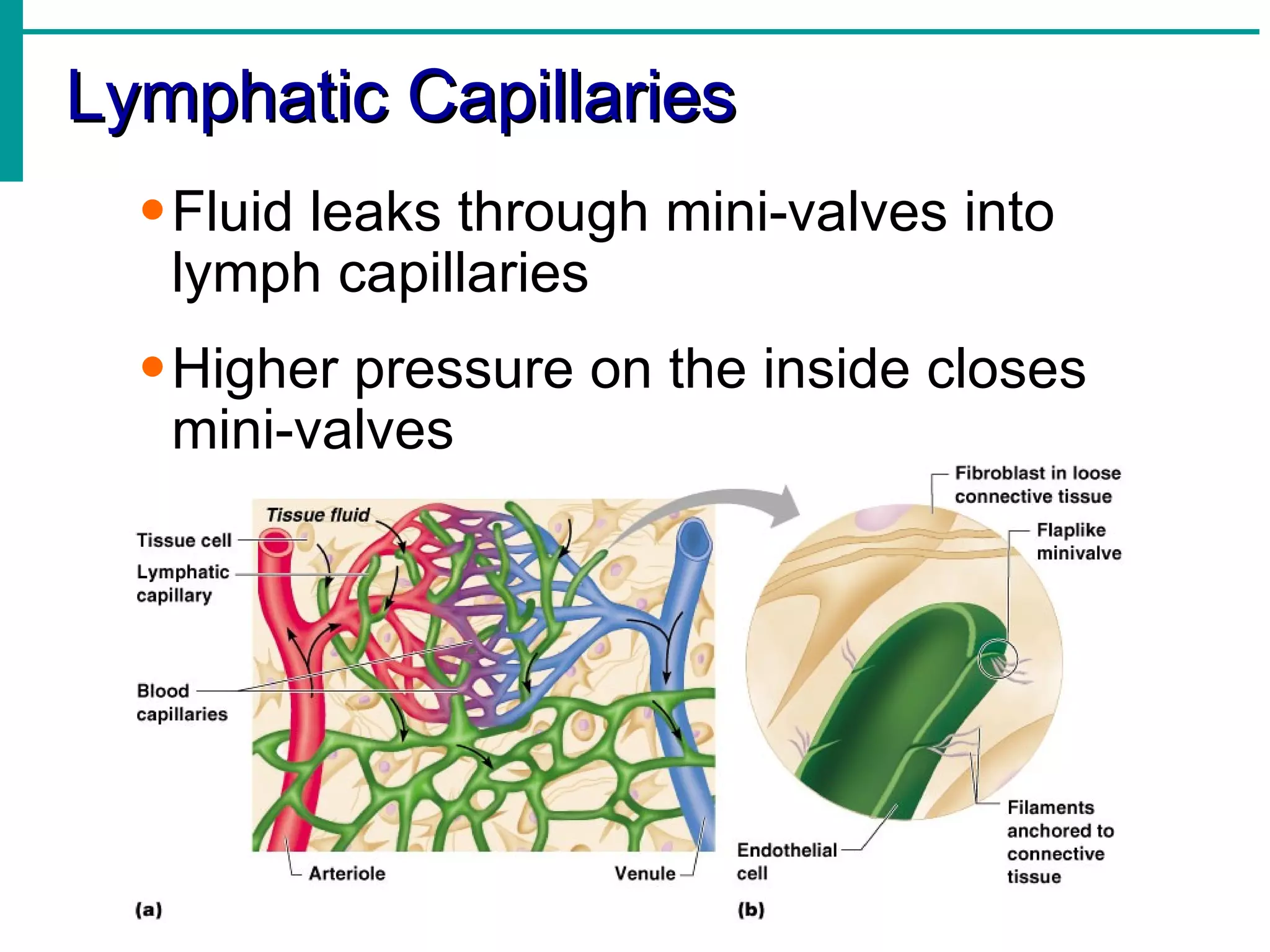
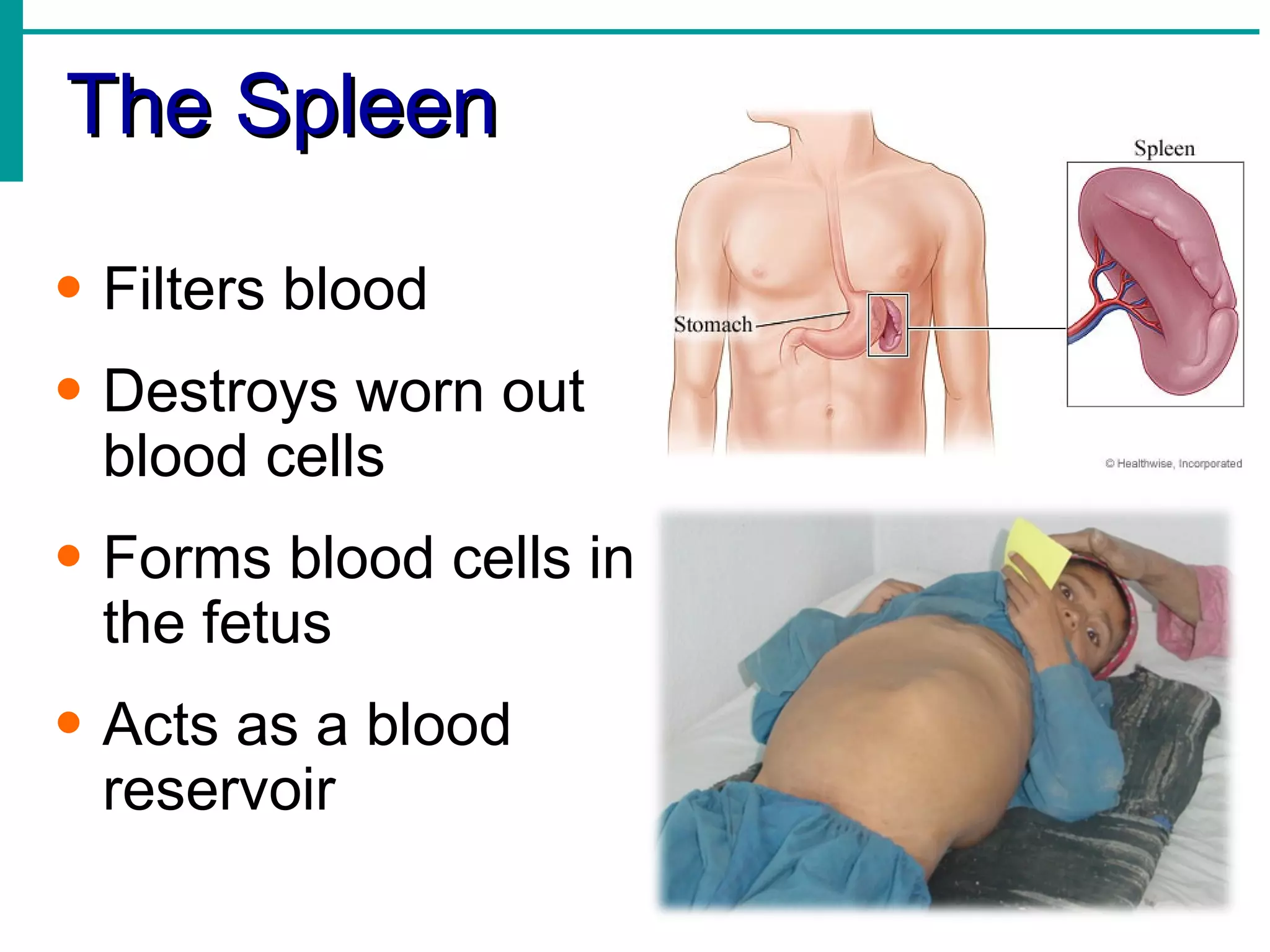
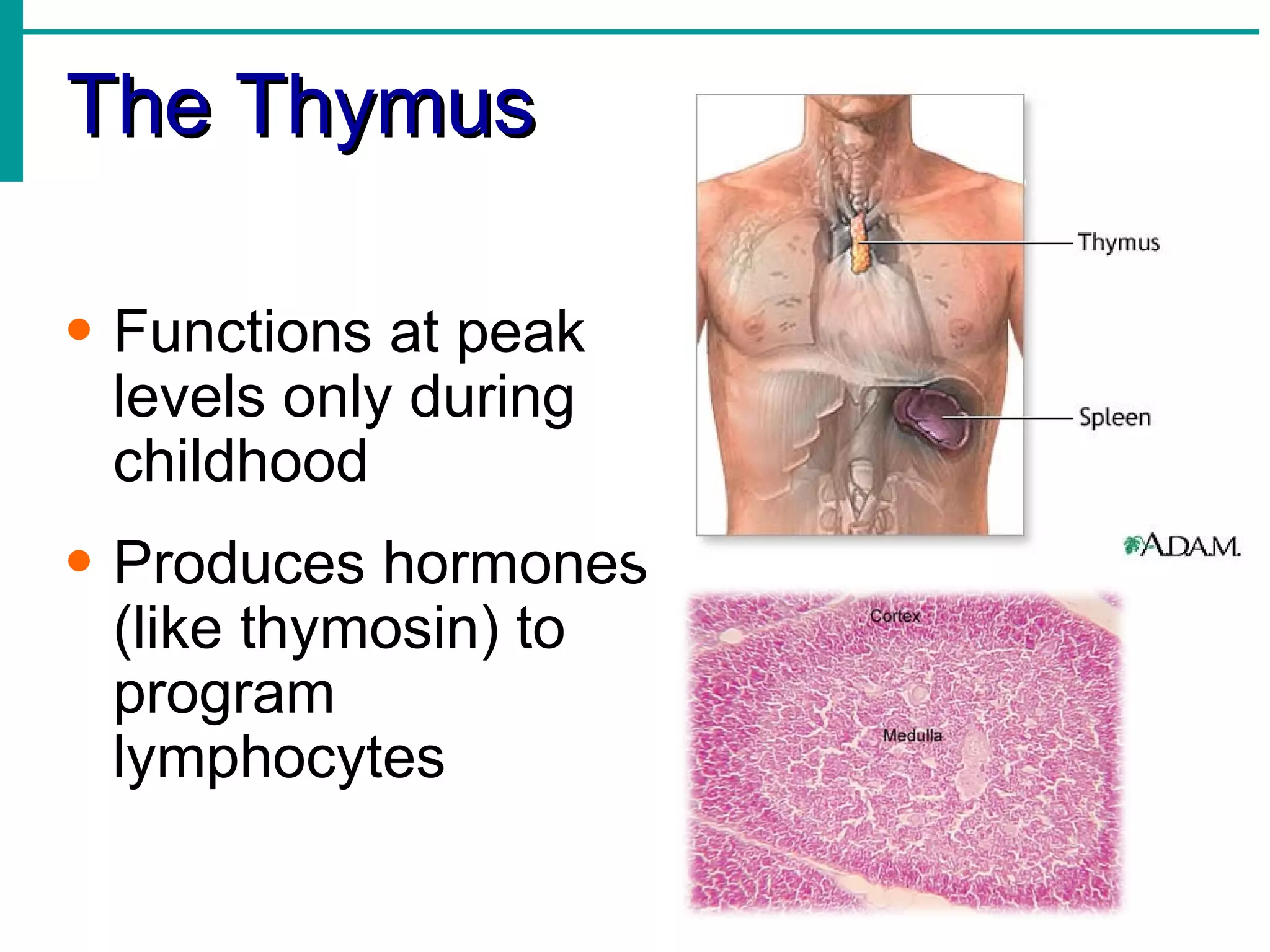
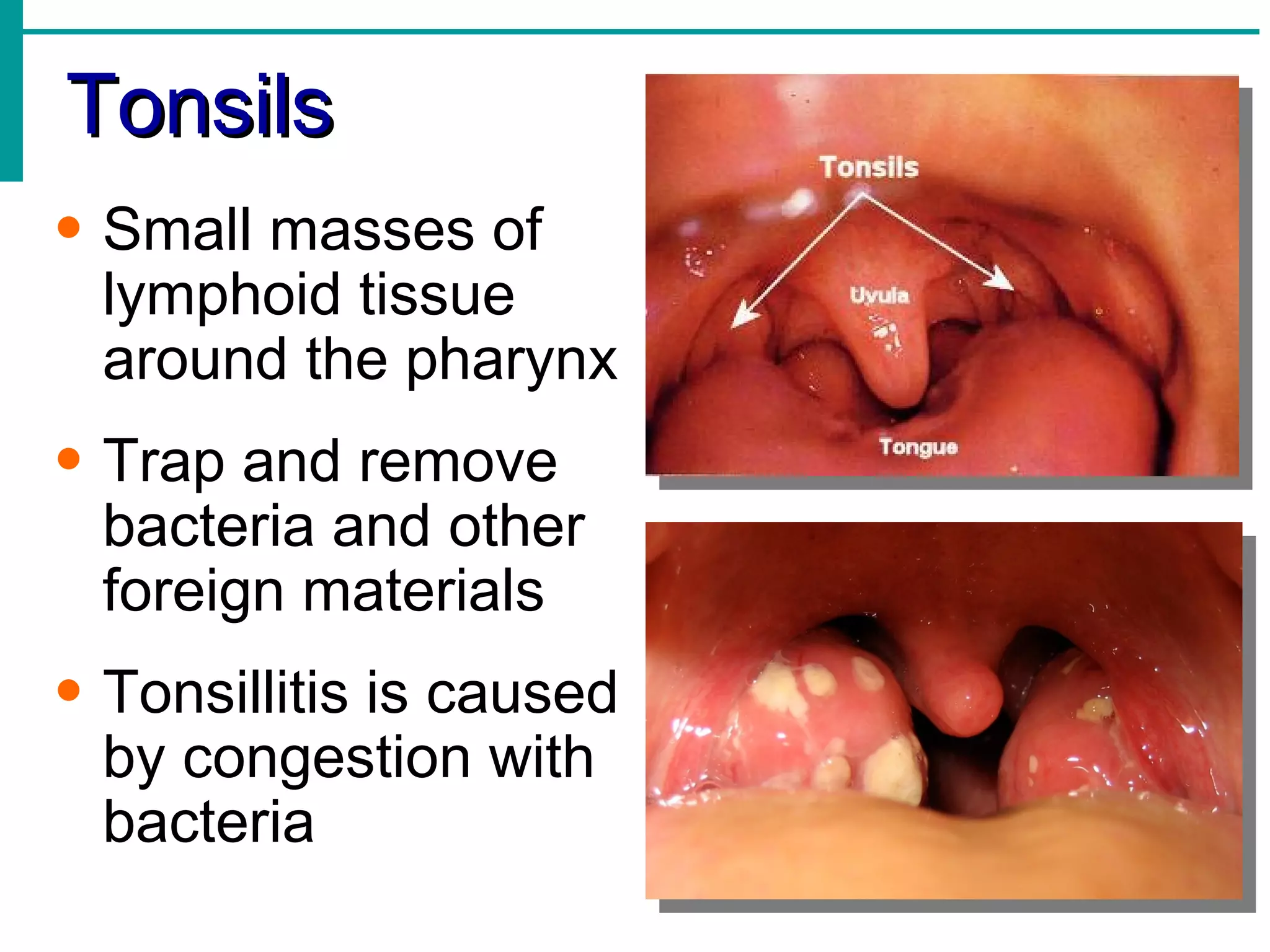
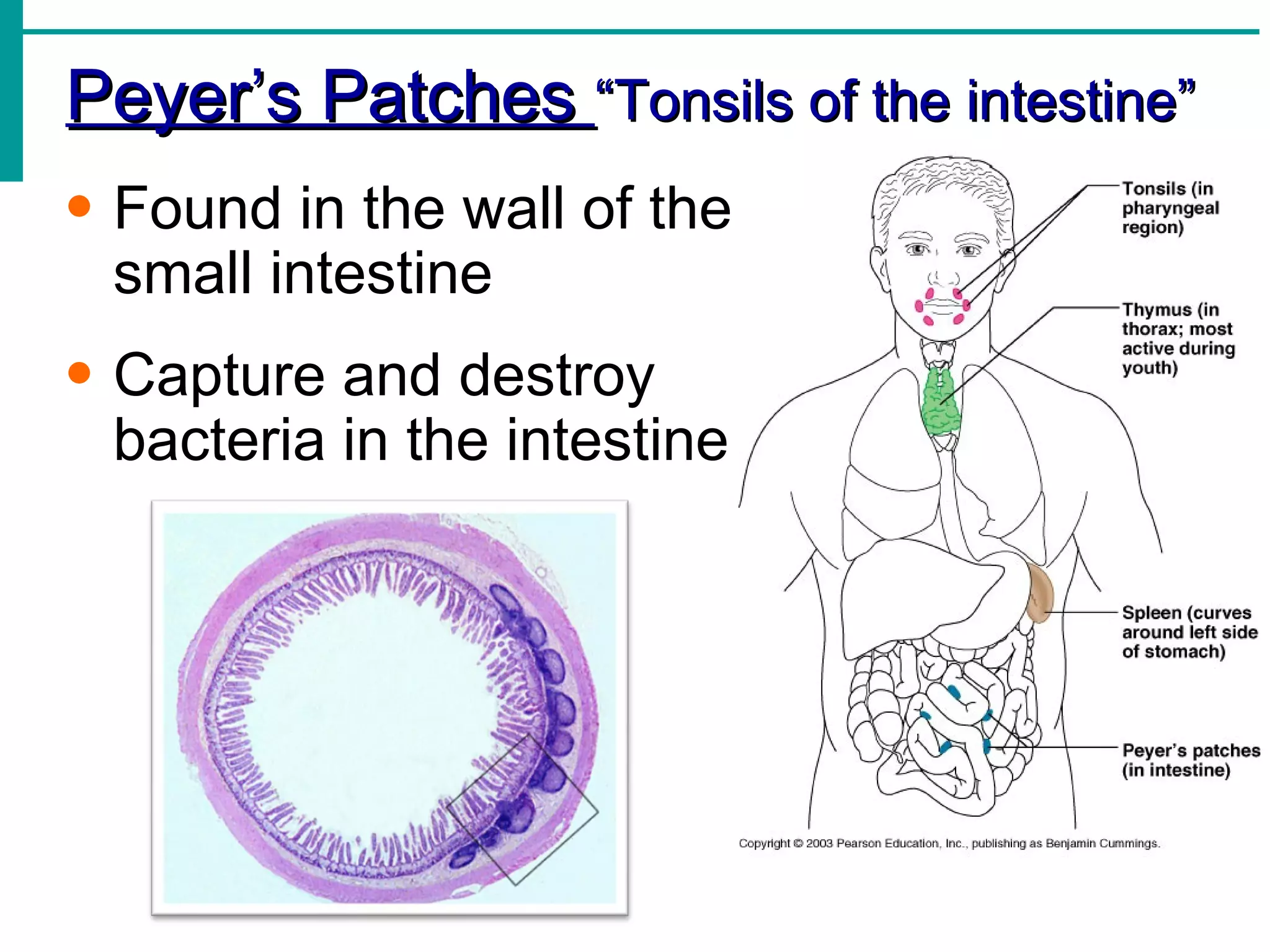
Lymph is transported through lymphatic vessels in a passive, one-way system toward the heart, where it is returned to circulation. Along the way, lymph passes through lymph nodes which filter the lymph and provide an immune response. Other lymphoid organs like the spleen, thymus, tonsils, and Peyer's patches also contribute to lymphatic function and immune defense.