1. MATLAB is a software package for mathematical computation, numerical computation, algorithm development, data analysis, and more. It allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs in other languages.
2. The document introduces basic MATLAB operations like arithmetic operations, variables, matrices, plotting, scripts and functions. It also discusses flow control and logical operations like if/else statements and loops.
3. MATLAB can be used for scientific and engineering applications like modeling, simulation, and prototyping through its implementation of algorithms, data analysis tools, and graphical capabilities for visualizing data.







![MATLAB Variables Scalar A = 4 Vector A = [2 3 4] Matrices A=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-090308235829-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Basic-Tutorial-11-2048.jpg)


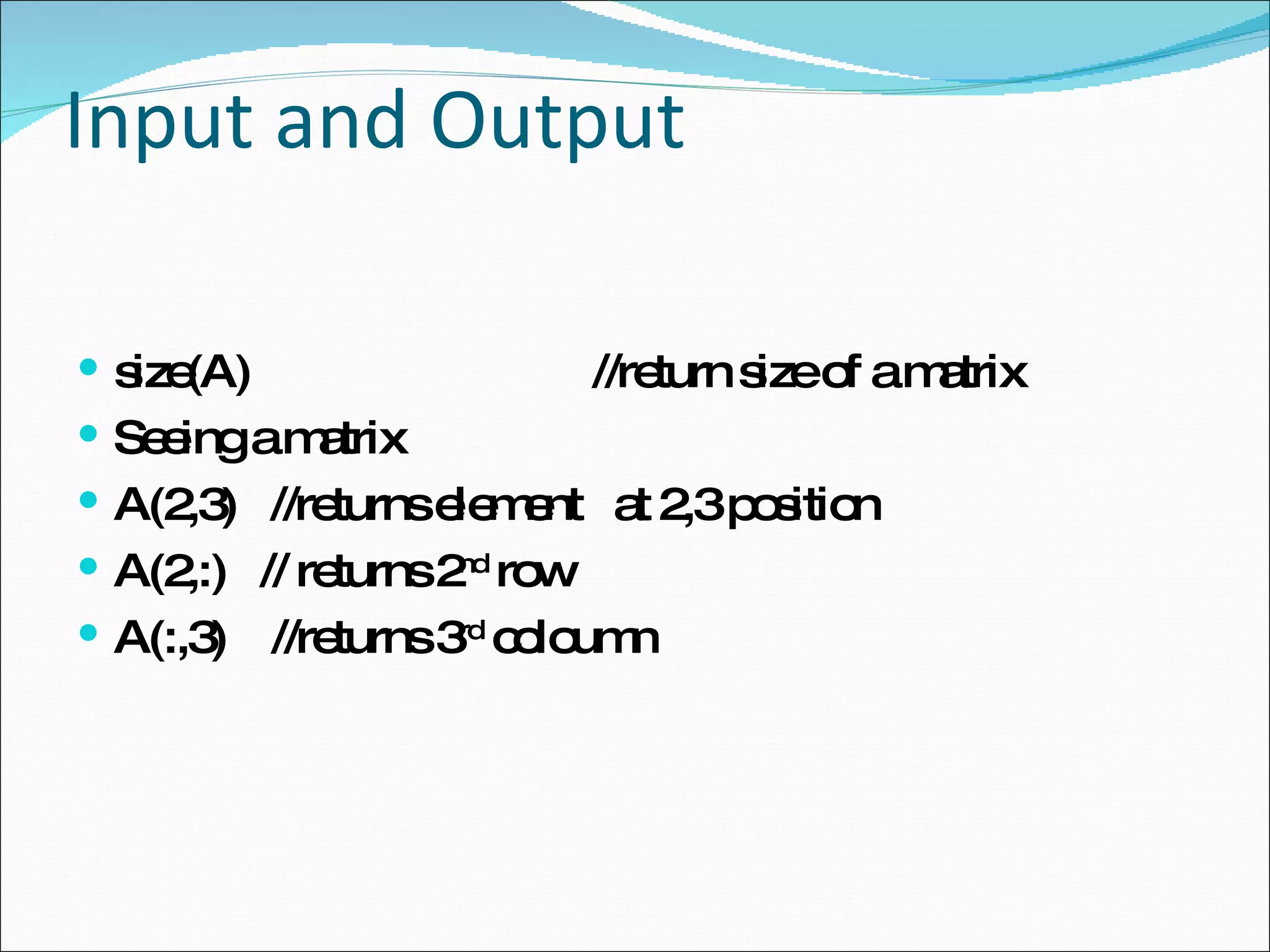
![Input and Output (Contd) V=[1 1/2 1/6 1/12] [1 3 5] row vector [1 3 5]’ [1;3;5] column vector [1;3;5]’ [1 3 5;7 8 4] Matrix](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-090308235829-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Basic-Tutorial-16-2048.jpg)

![Matrix Operations (Contd) Augmented matrix [B b] [A;C] [C A;A C] Diagonal matrix D=diag([1 2 3]) // create diagonal matrix Diag(D) // return diagonal diag(diag(D)) what it can do?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-090308235829-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Basic-Tutorial-19-2048.jpg)










![Functions Format function [x, y] = myfun(a, b, c) % Function definition a , b , c are input parameters and x , y are output parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-090308235829-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Basic-Tutorial-30-2048.jpg)
![Functions function [output_parameter_list] = function_name(input_parameter_list) The first word must always be ``function''. Following that, the (optional) output parameters are enclosed in square brackets [ ]. If the function has no output_parameter_list the square brackets and the equal sign are also omitted. The function_name is a character string that will be used to call the function. The function_name must also be the same as the file name (without the ``.m'') in which the function is stored. In other words the MATLAB function, ``foo'', must be stored in the file, ``foo.m''.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-090308235829-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Basic-Tutorial-31-2048.jpg)