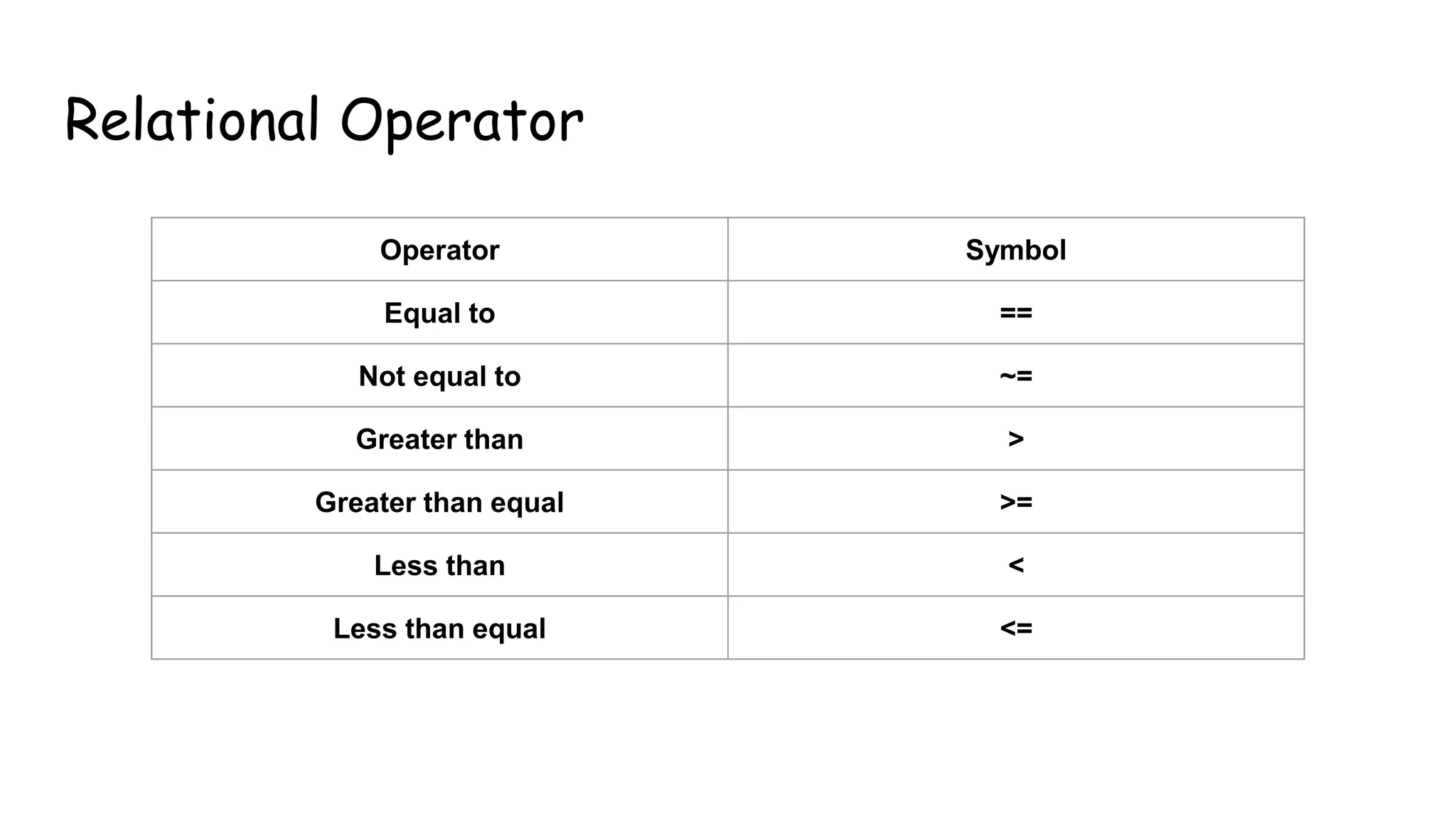
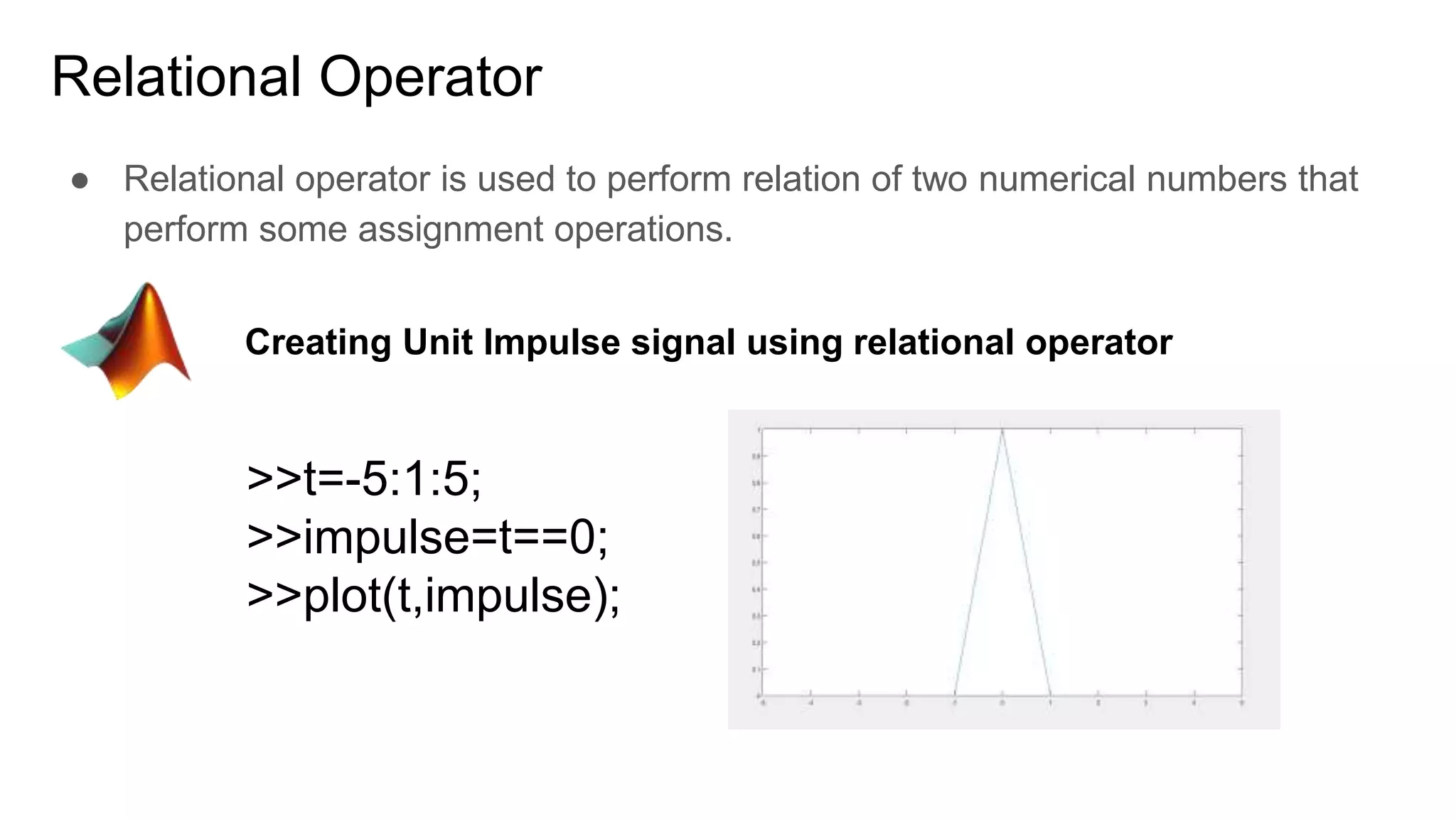
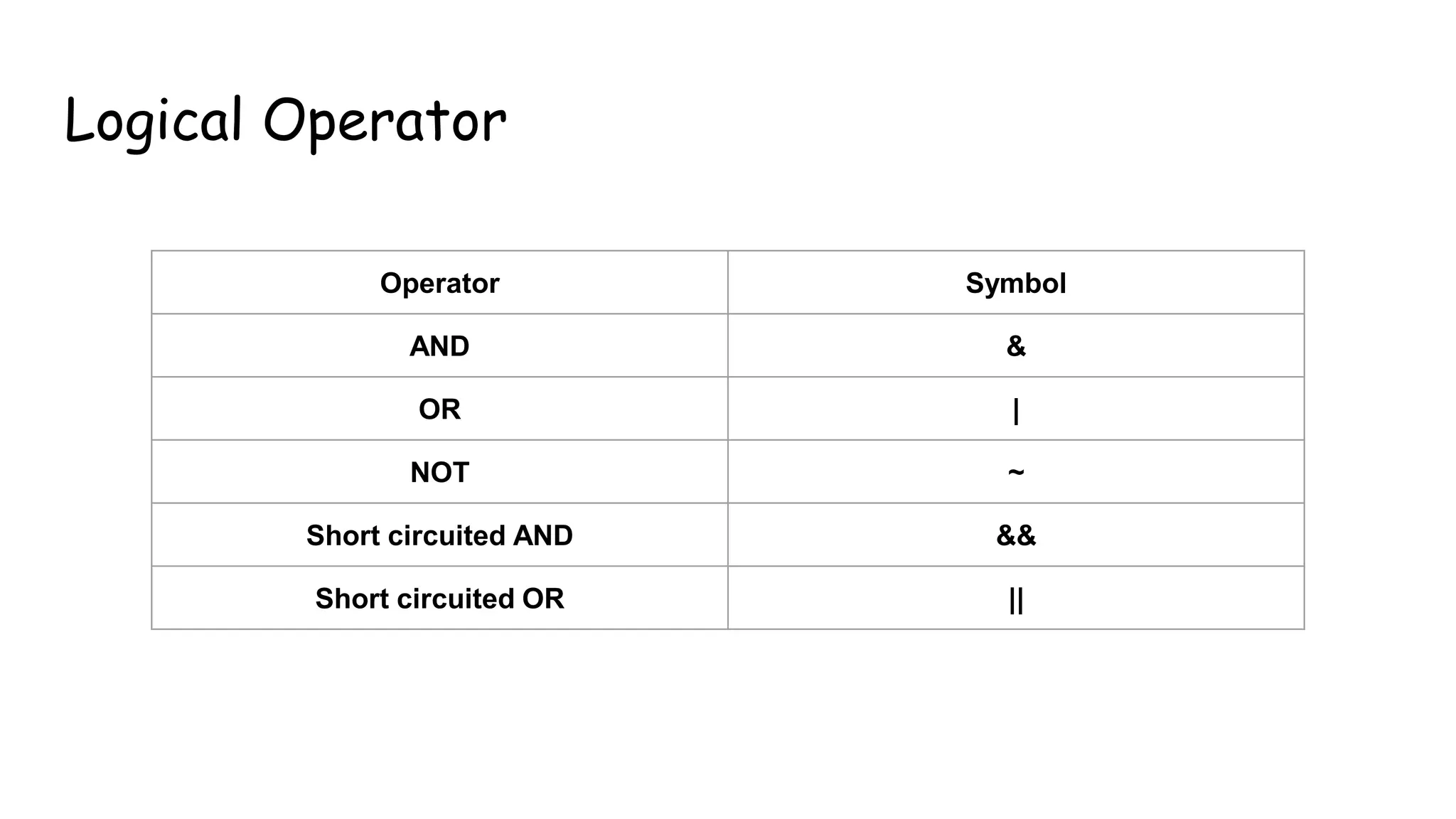
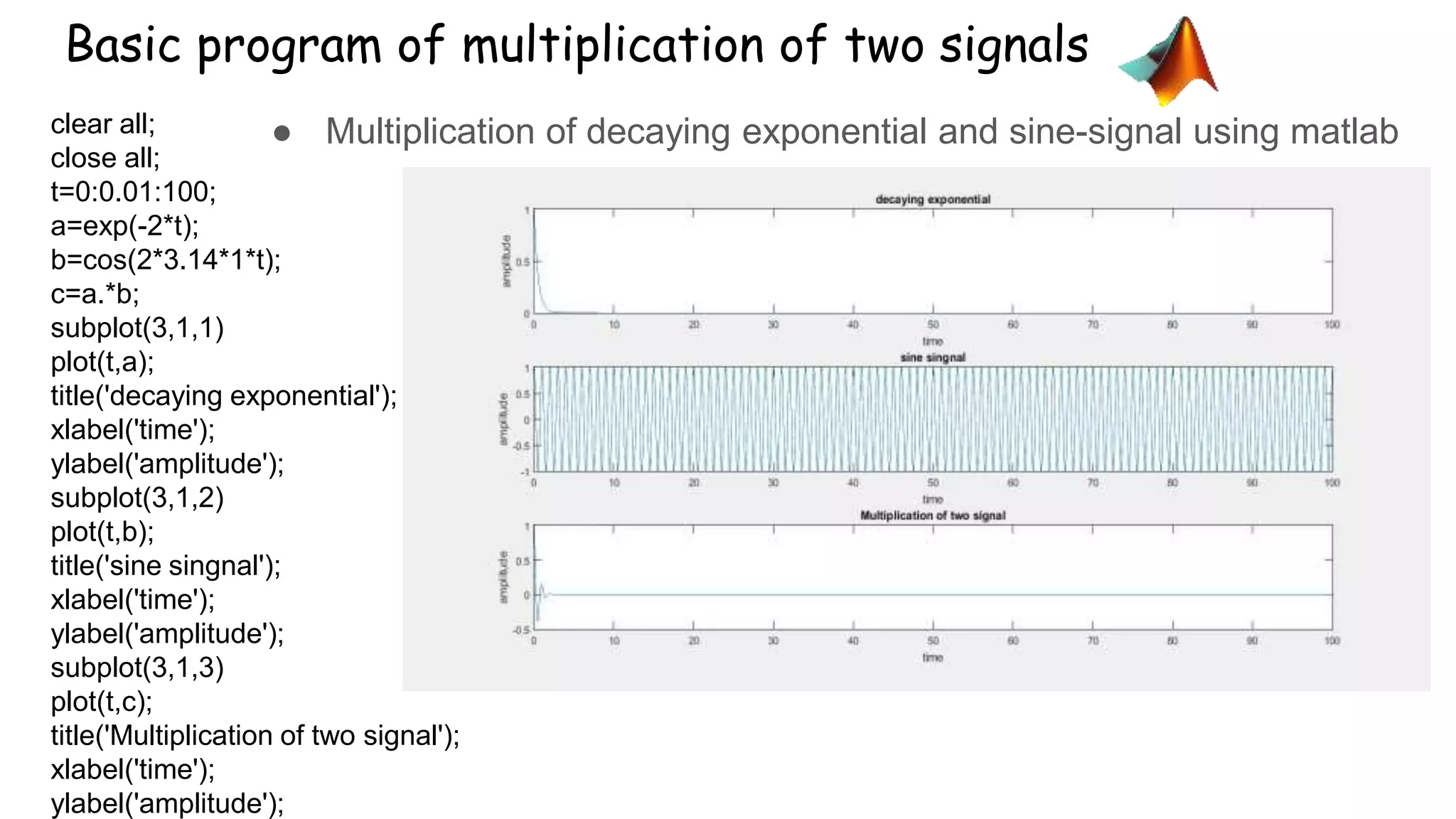
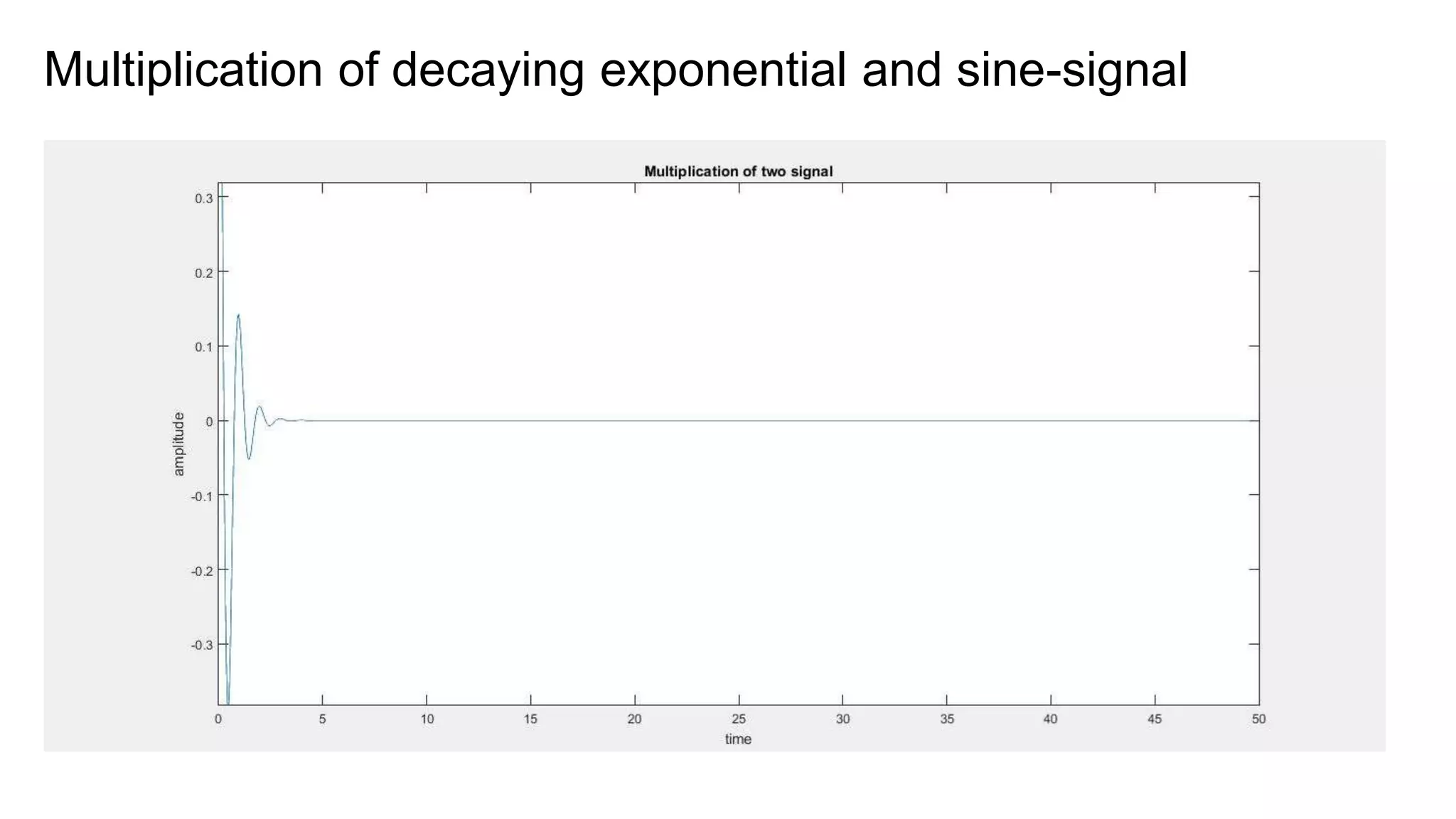
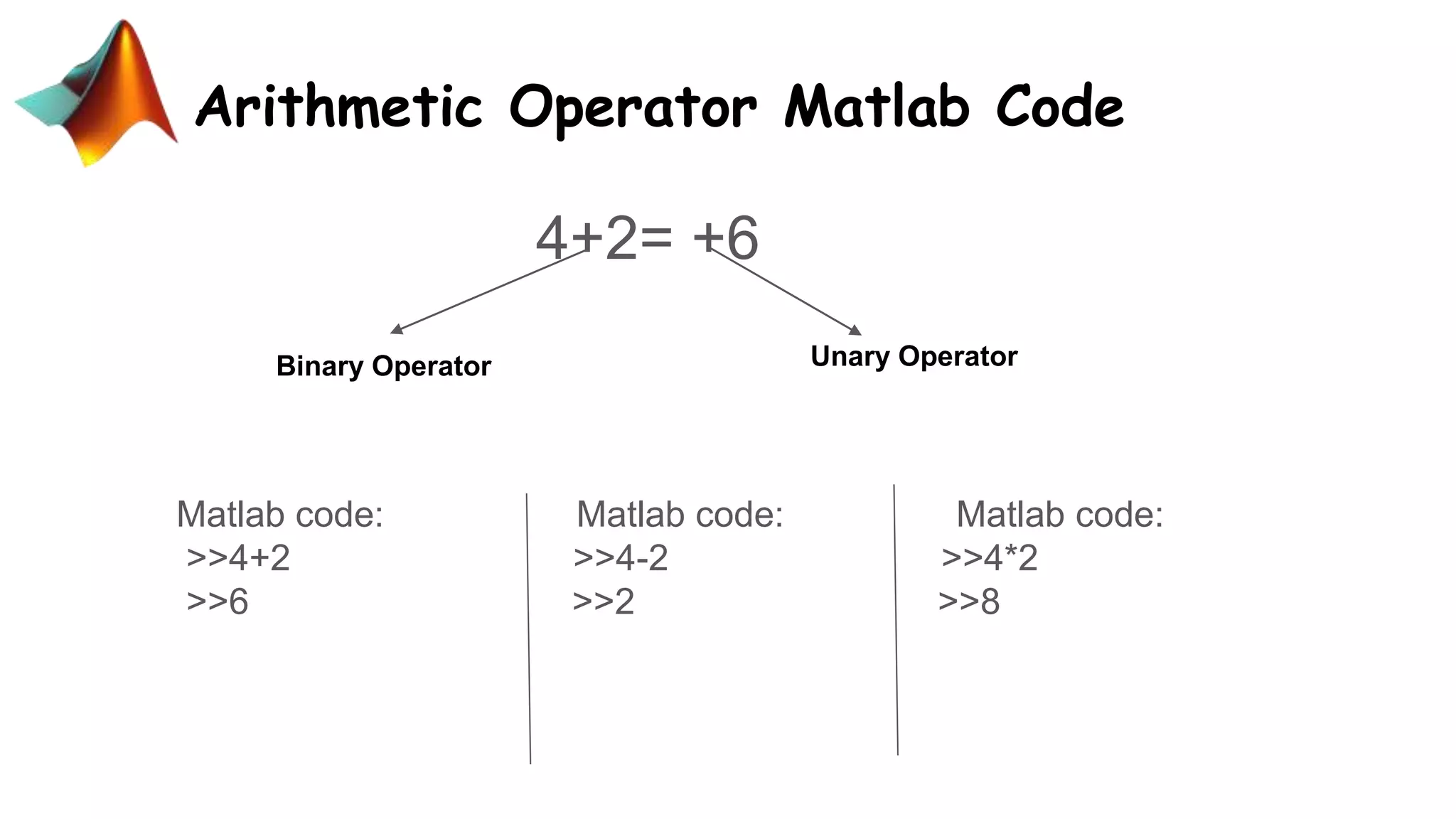
This document discusses basic operators in MATLAB, including arithmetic, relational, and logical operators. It provides examples of using each operator type to perform operations on numbers, matrices, and signals. Arithmetic operators allow mathematical operations like addition and multiplication. Relational operators compare values. Logical operators perform logic operations like AND and OR.



![Creating the Matrix & Multiplication
In MATLAB, you create a matrix by entering elements in each row as comma or space
delimited numbers and using semicolons to mark the end of each row.
Matlab code for Matrix Creation
a = [ 1 1 1; 2 2 2;] Matlab code for multiplication
a = 1 1 1 a = [ 1 1 1; 2 2 2;] ;
2 2 2 b= [ 1 1 1; 2 2 2;] ;
c=a*b;
disp(c);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hmu0h2vustobc1tmskr2-signature-9de5a718353f1c074460b8ceebccf3b30f0e705418235fafc8c65a4918ee7379-poli-190809170608/75/Basic-operators-in-matlab-5-2048.jpg)