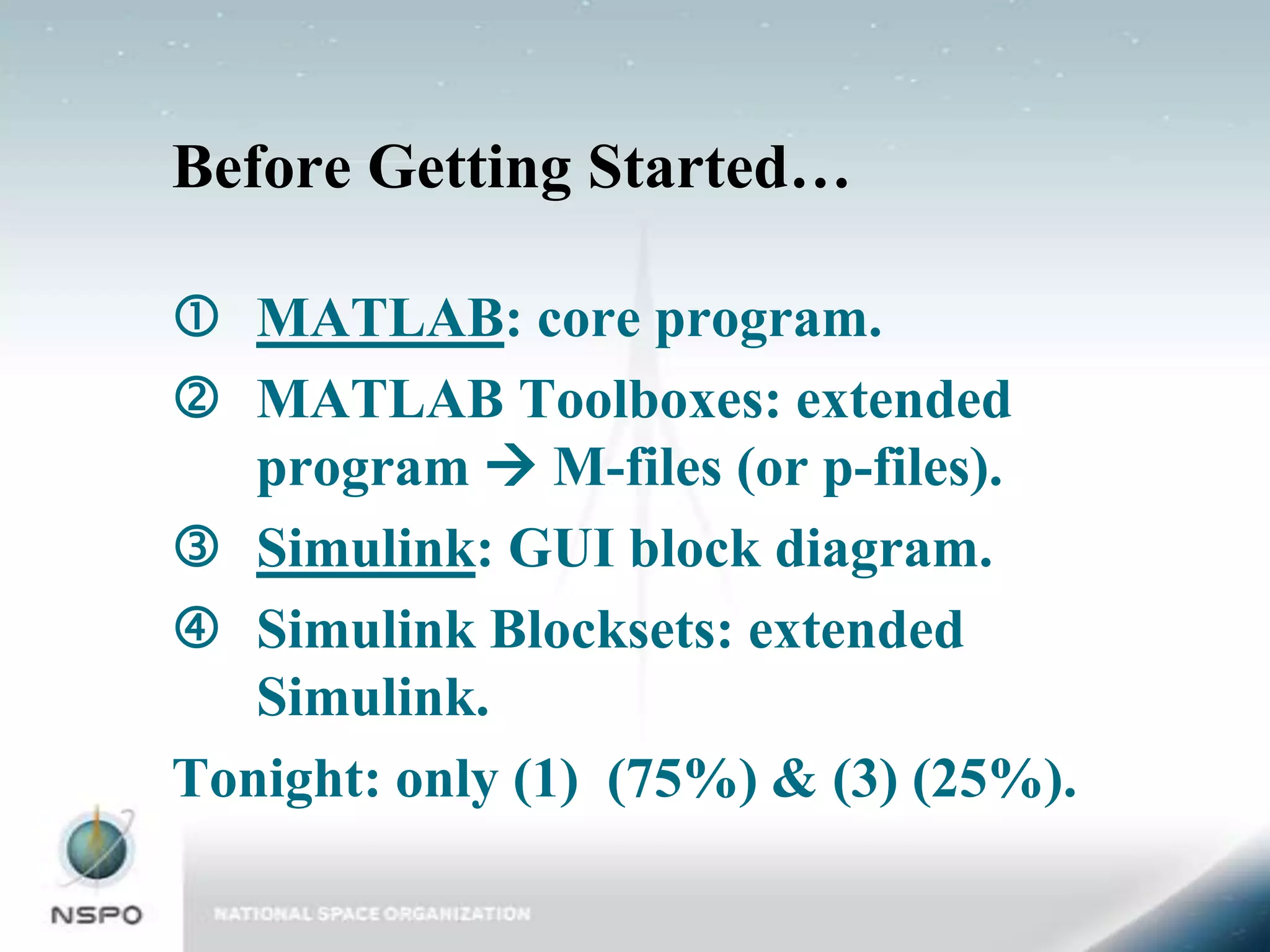
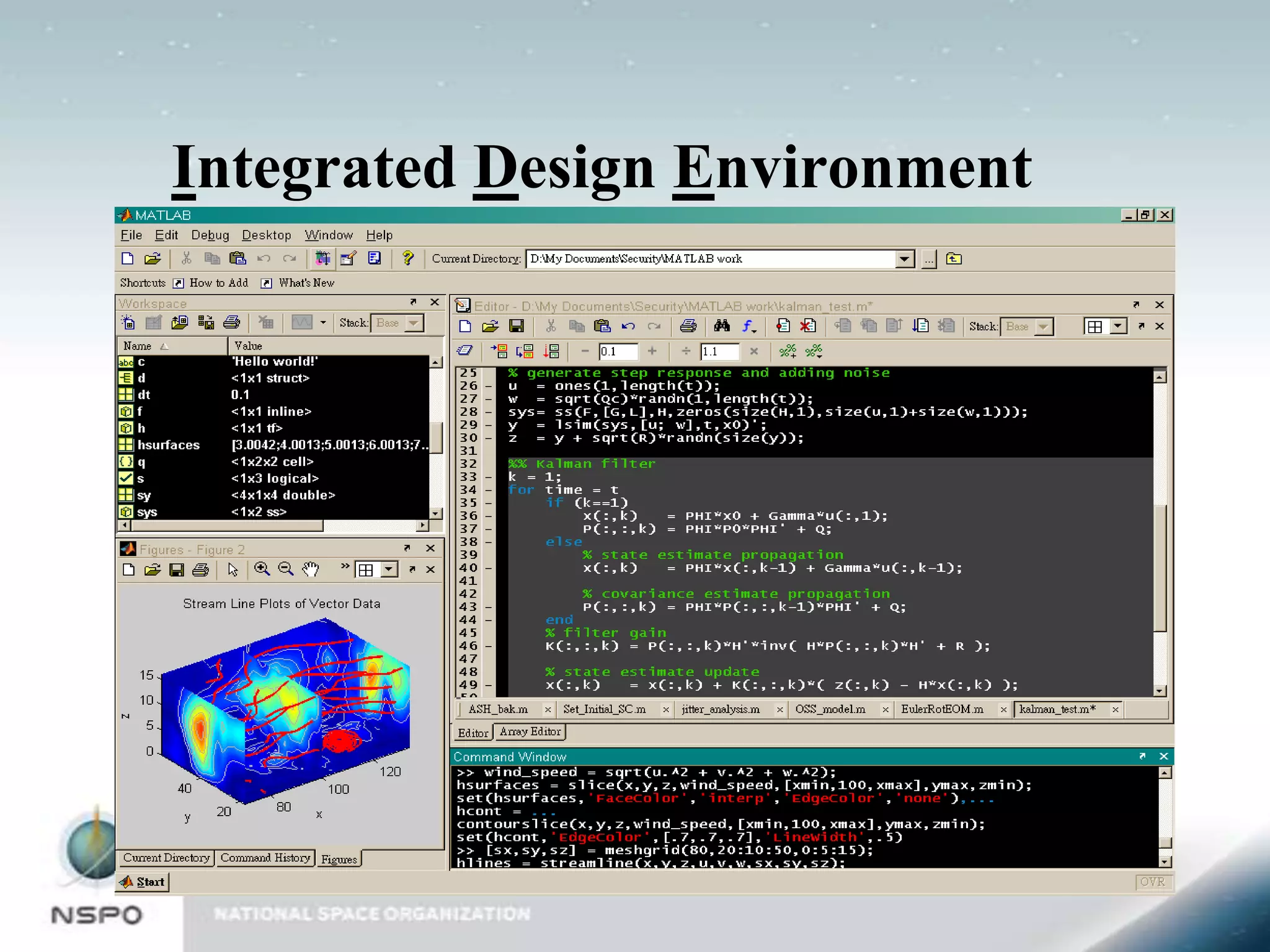
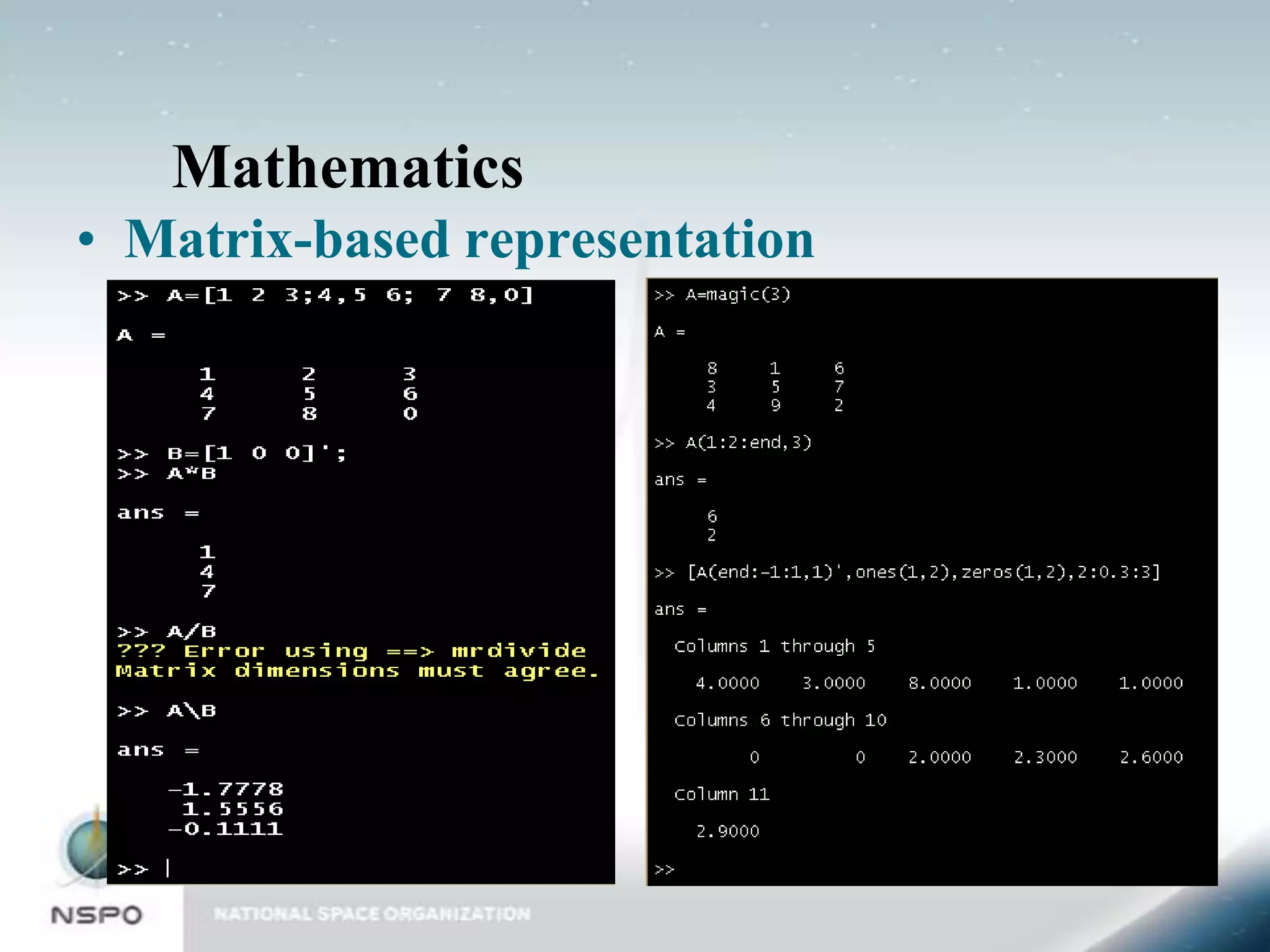
This document provides an introduction to MATLAB and Simulink. It discusses the core functionality of MATLAB, including mathematics, graphics, and programming. It also discusses Simulink, the graphical block diagram modeling environment. Examples are provided for key MATLAB functions like plotting and programming in scripts and functions. An example Simulink model is also shown and described. The document is intended as an overview to get users started with the basics of MATLAB and Simulink.






![Simulink Example
Scope
w
y XY Graph
-C- J RotEOM y dot x
1
T xo s
MOI q
Euler Rotational Integrator y
q tip pos
Eq. of motion
-C- [w0,q0] z
body z-axis
Pulse tip trajectory
Terminator
Generator
[0 0 1]
b3
Matrix
DCM Multiply 1
1 q be
tip
q Product
q2c pos
Masked subsystem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/matlabintro-12741619453306-phpapp01/75/Matlab-Intro-14-2048.jpg)