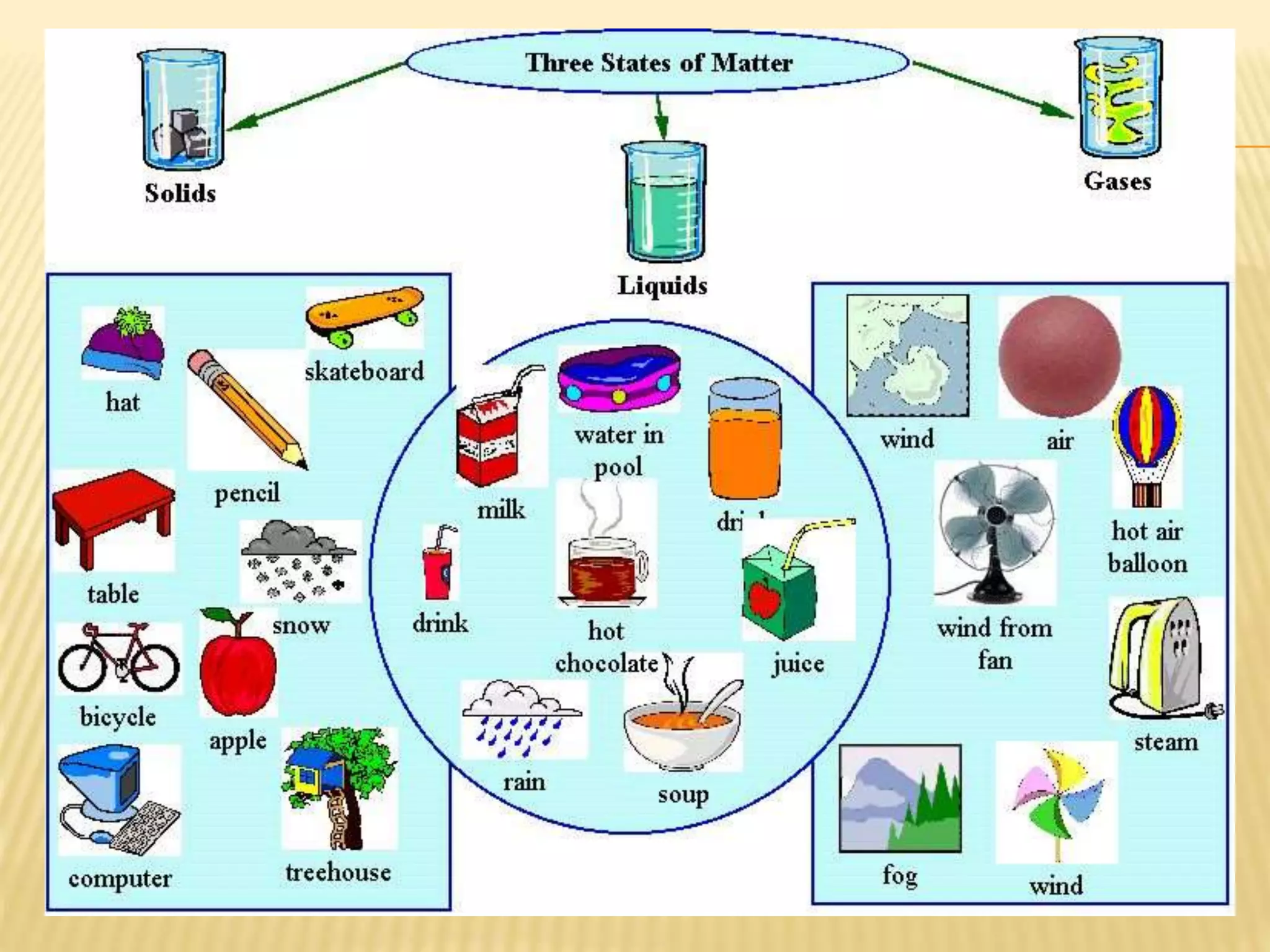
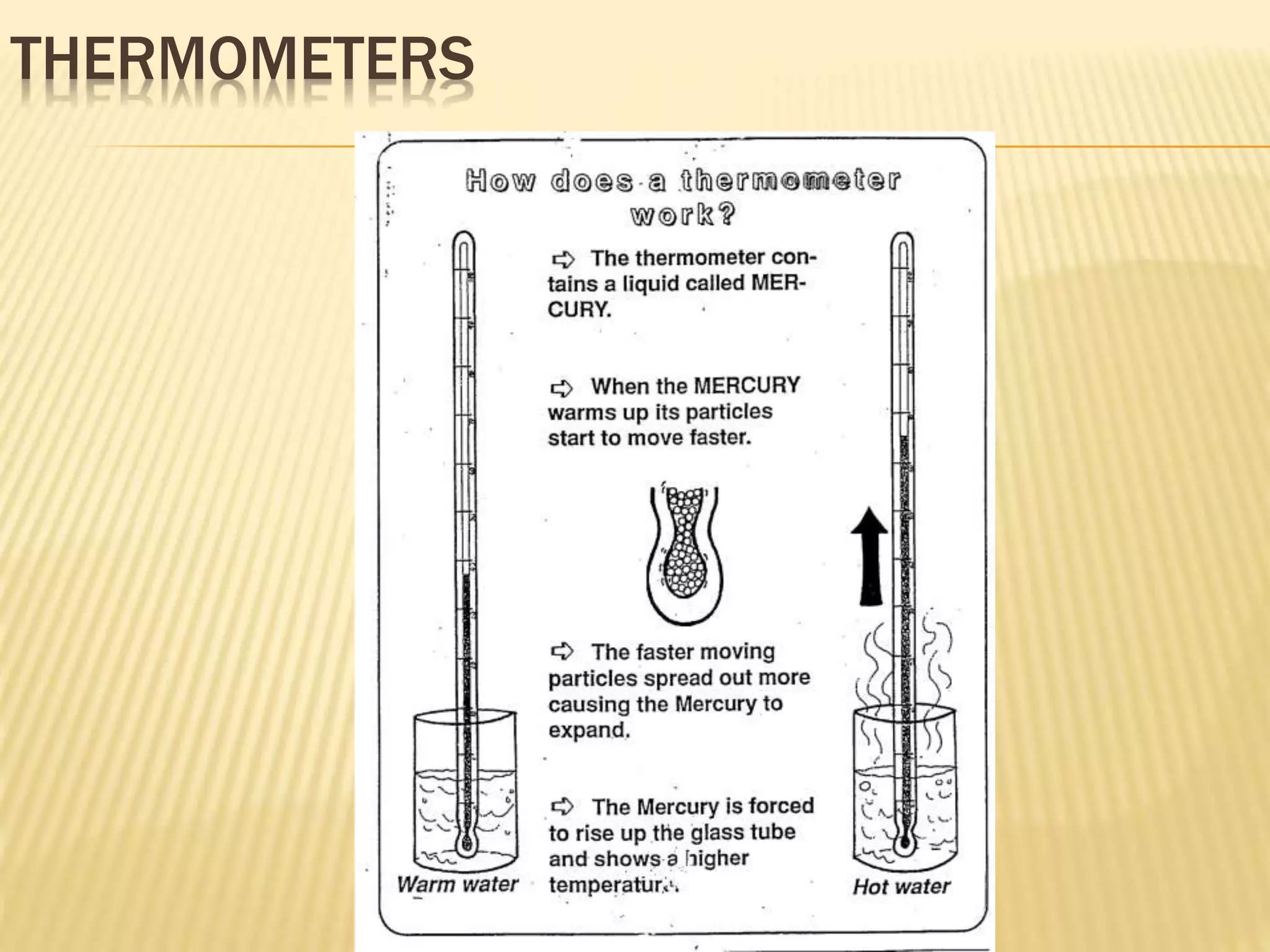
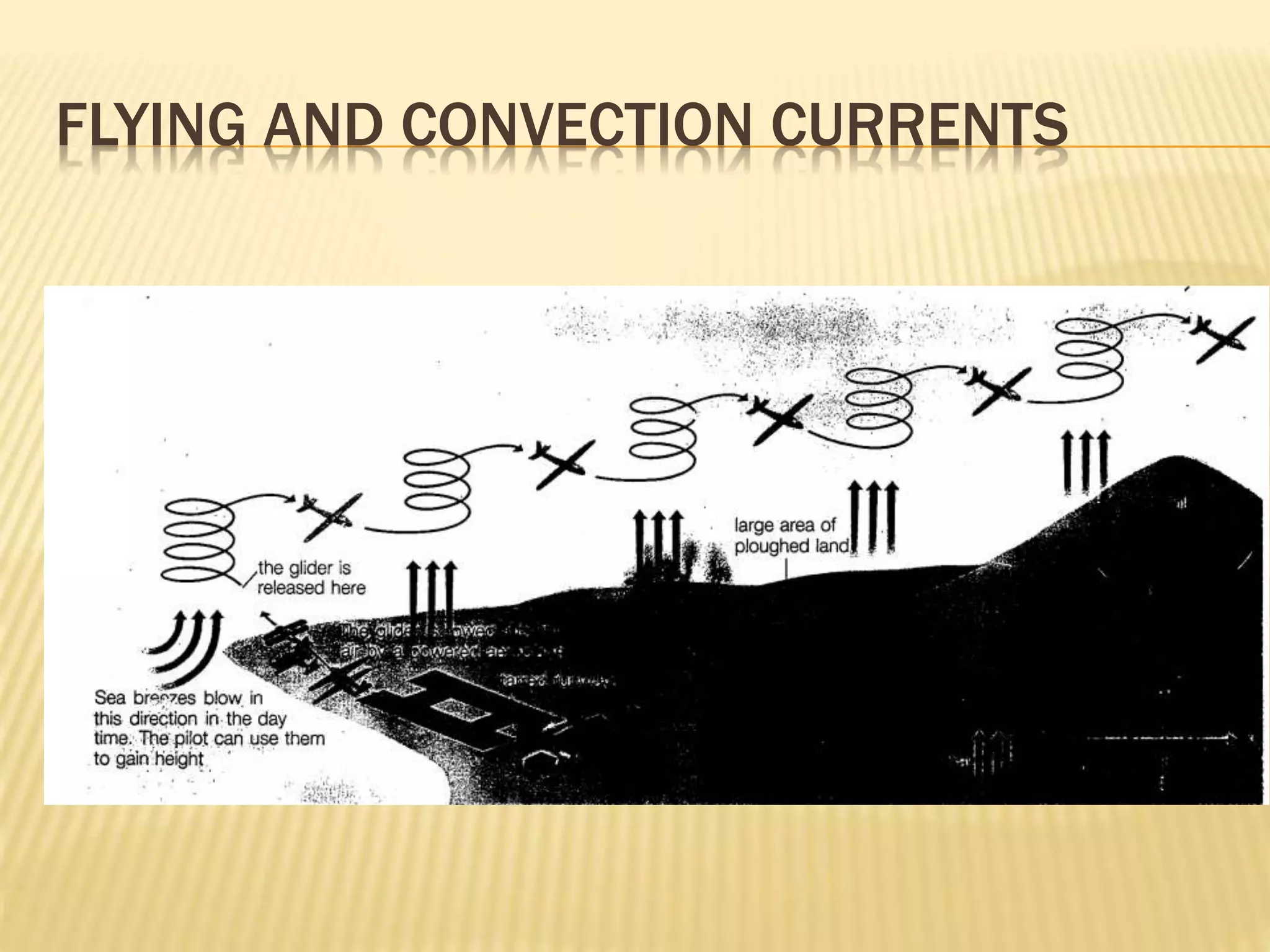
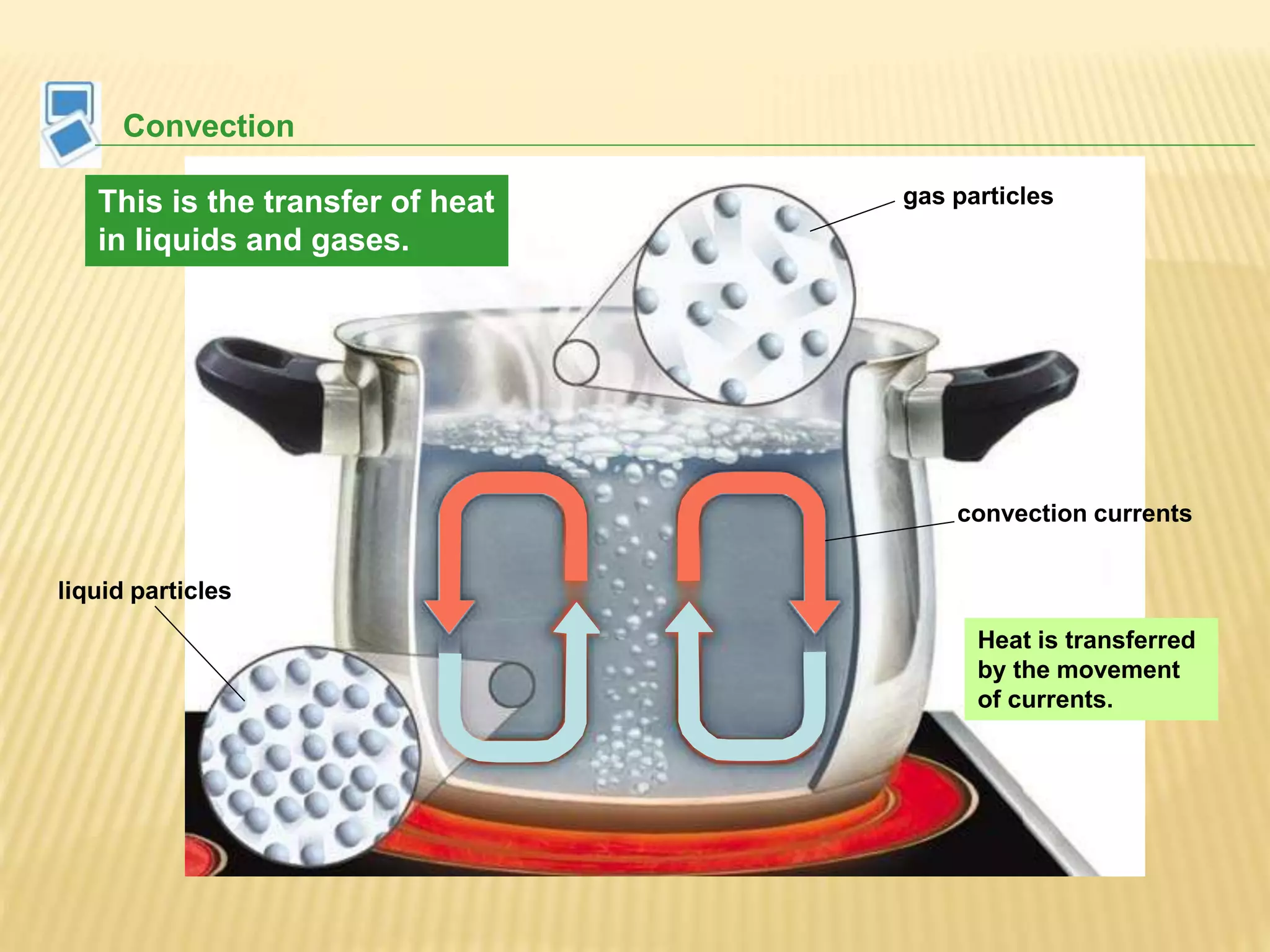
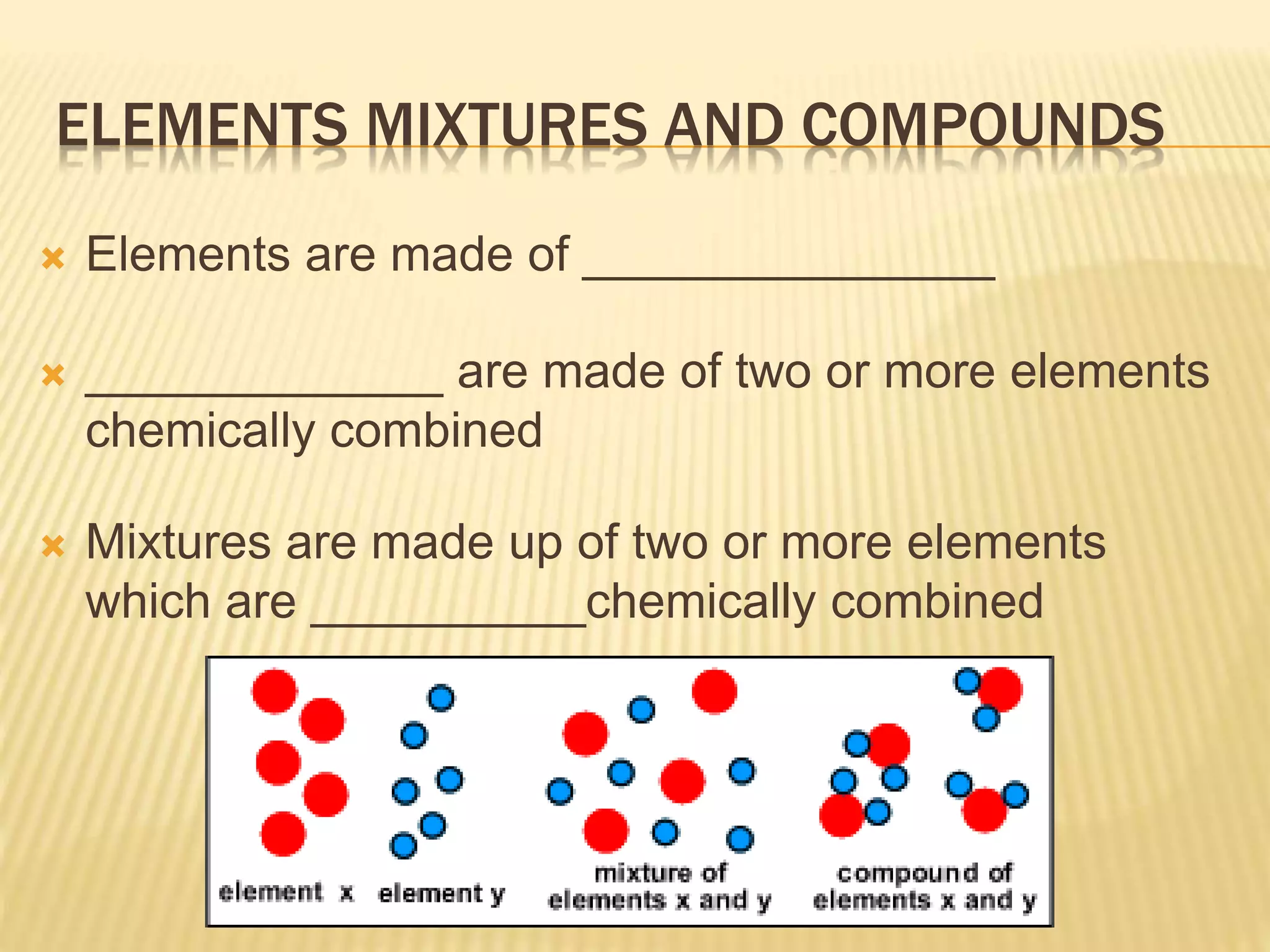
This document outlines the learning outcomes and content covered in a Year 9 unit on matter and atoms. It includes 10 student learning outcomes related to the particle nature of matter, states of matter, density, diffusion, the atomic model, and distinguishing between elements, compounds, and mixtures. Key concepts covered are the particle theory of matter, the three states of matter and how matter changes between states, density and factors that affect floating and sinking, conduction and convection as methods of heat transfer, the structure of the atom including subatomic particles, and writing chemical formulas.