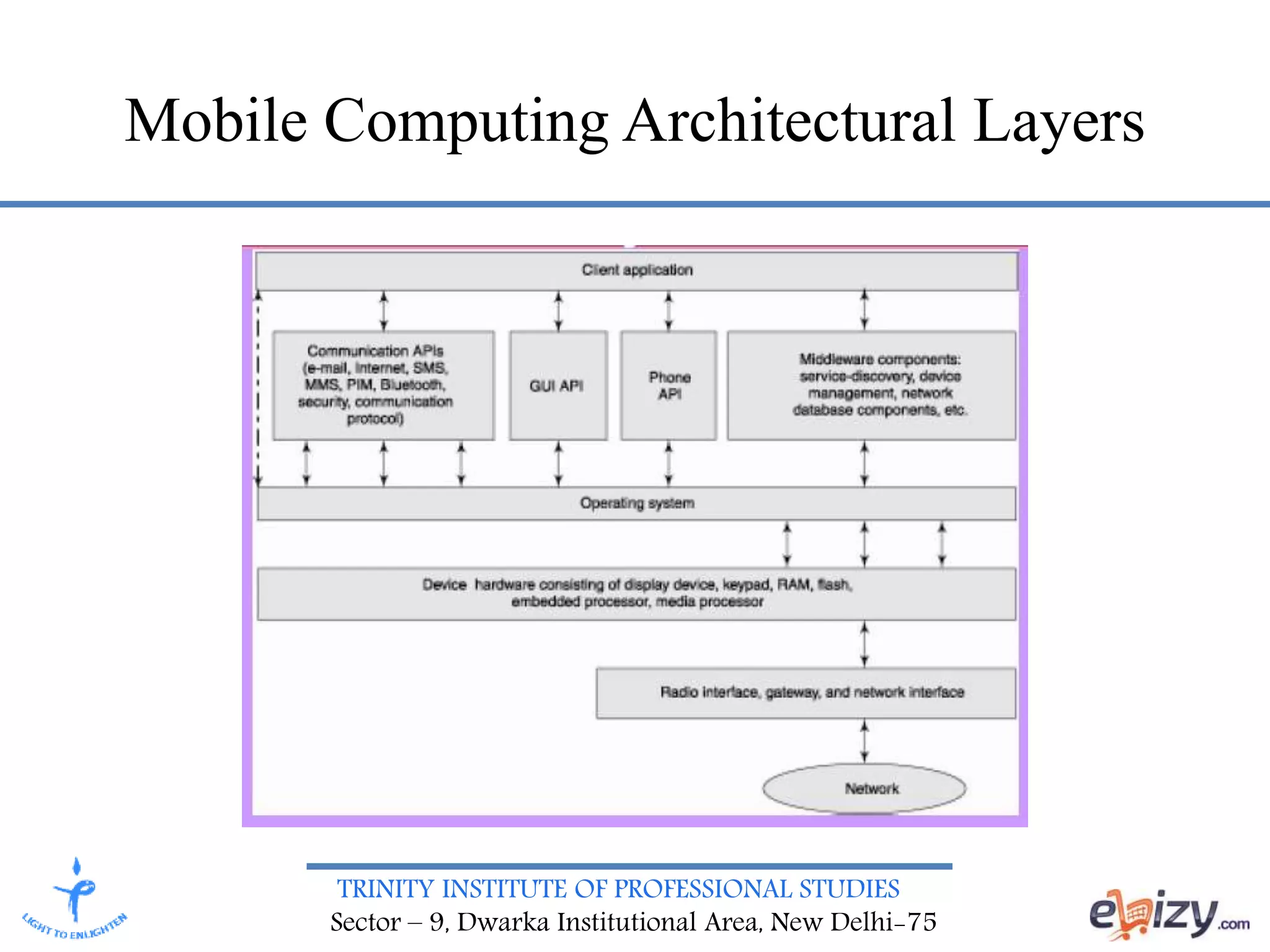
The document discusses mobile computing architecture, detailing programming languages, operating systems, and middleware components essential for mobile systems. It outlines the layered structure of mobile computing and the various protocols used for communication and data transmission. Key programming languages mentioned include Java and C++, while notable operating systems include Symbian OS and Windows CE.