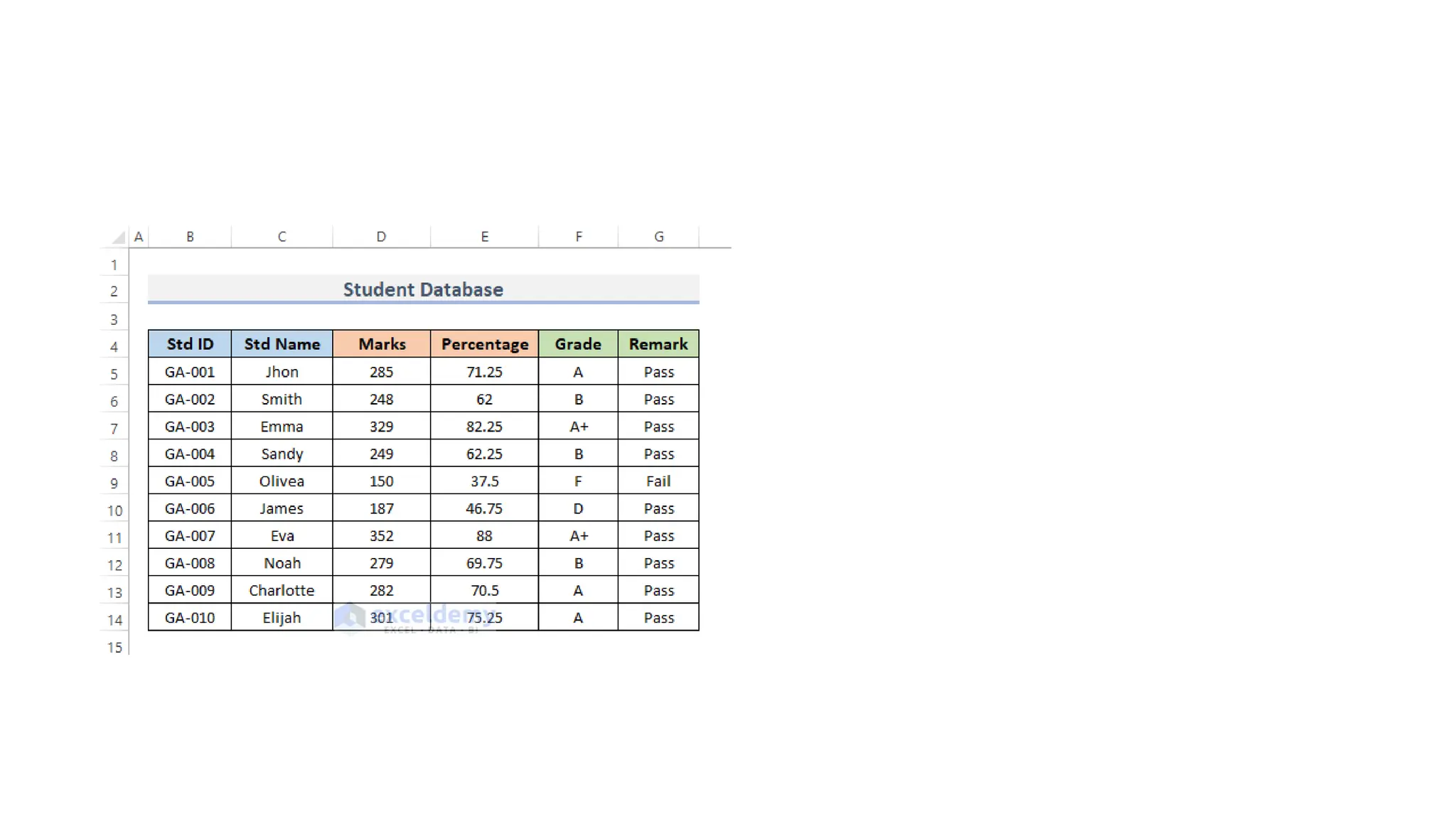
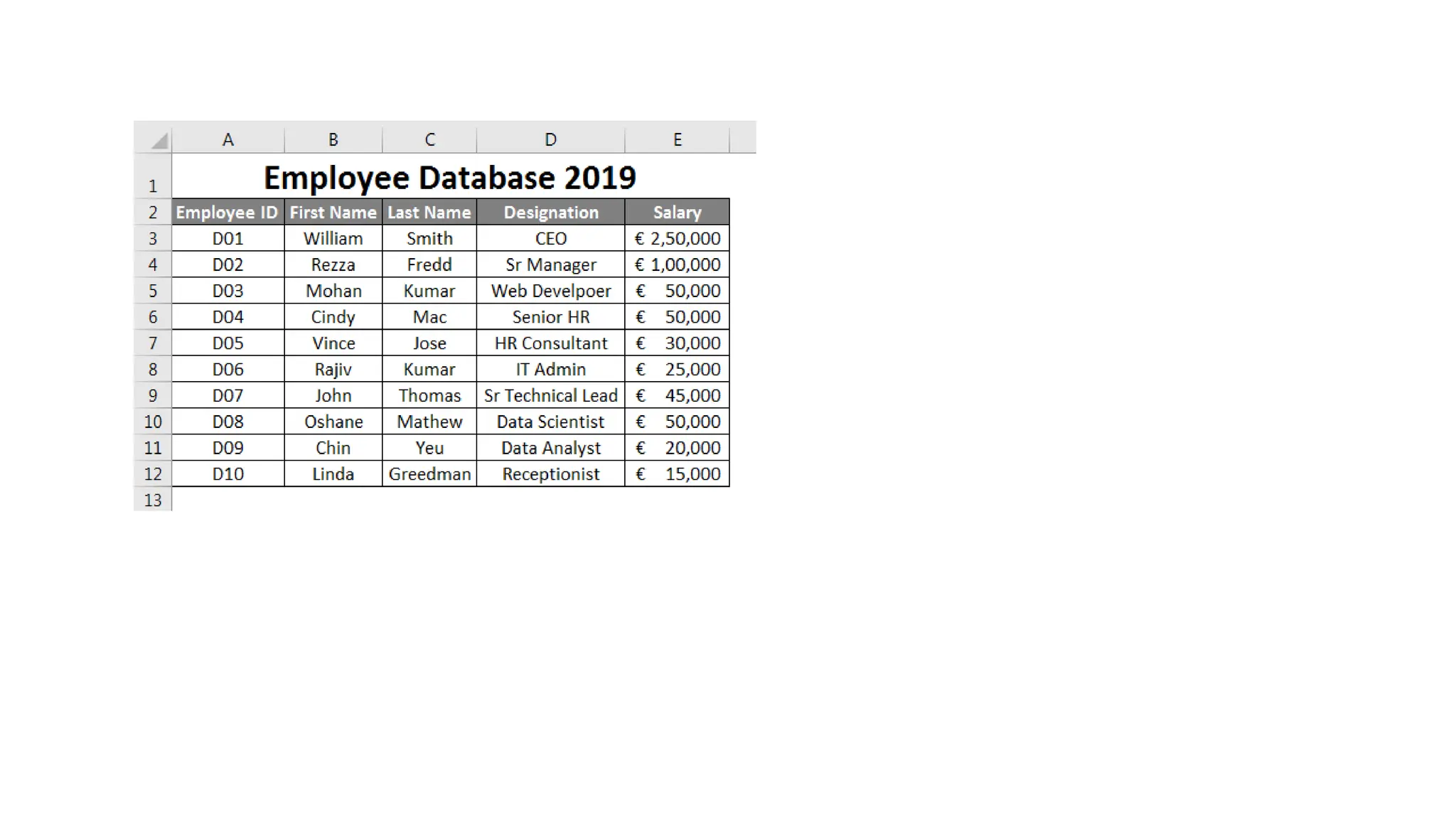
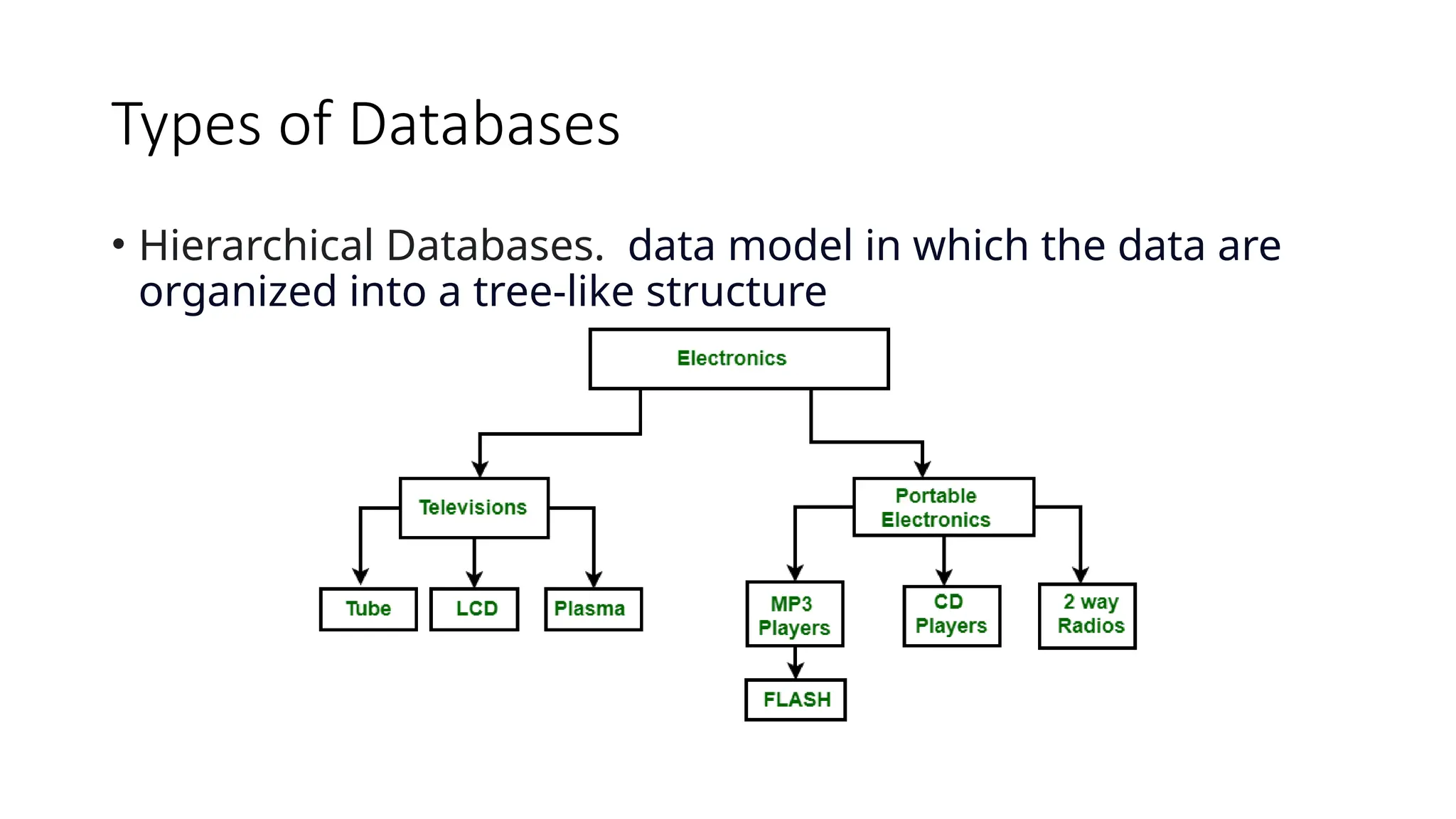
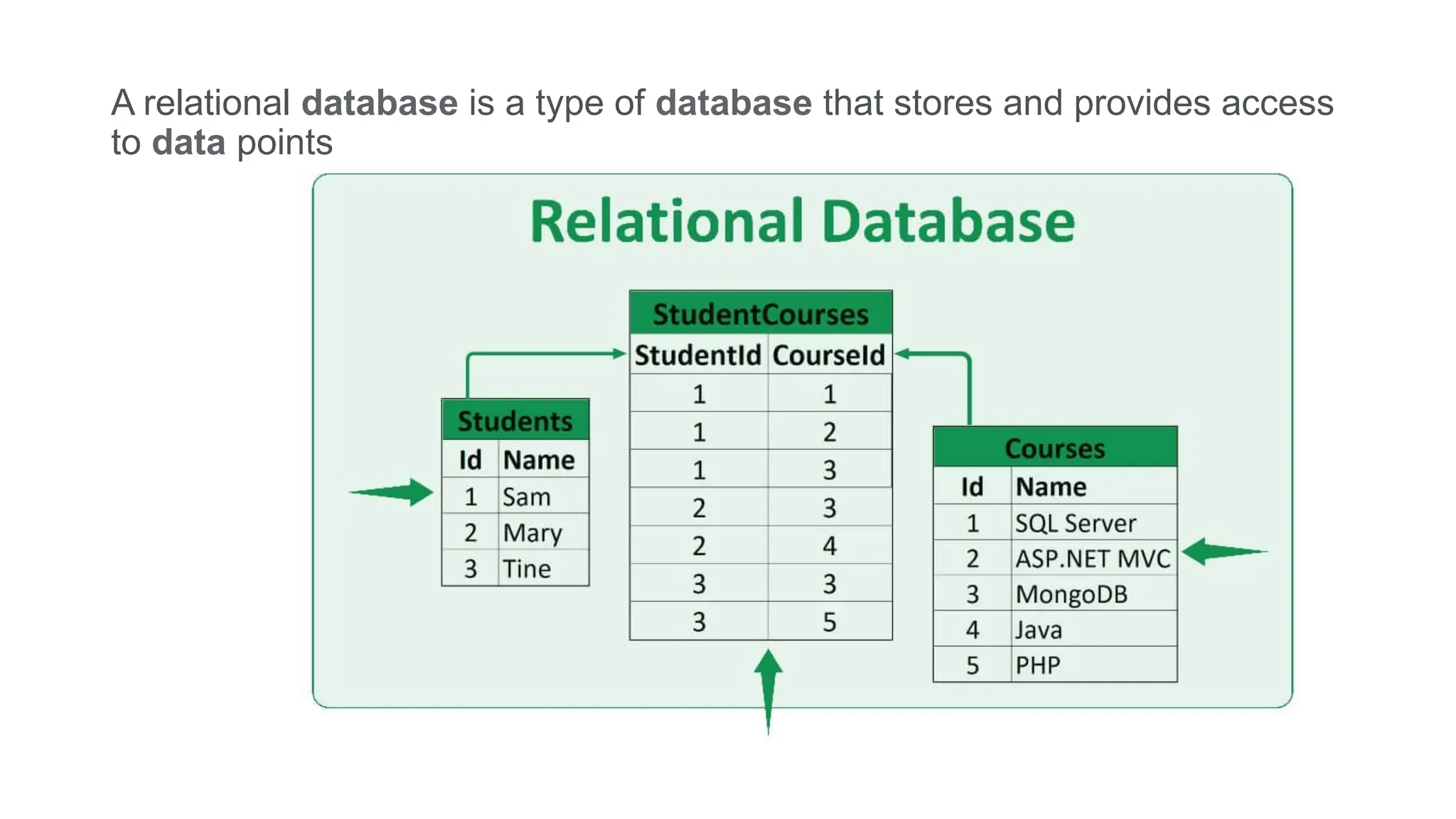
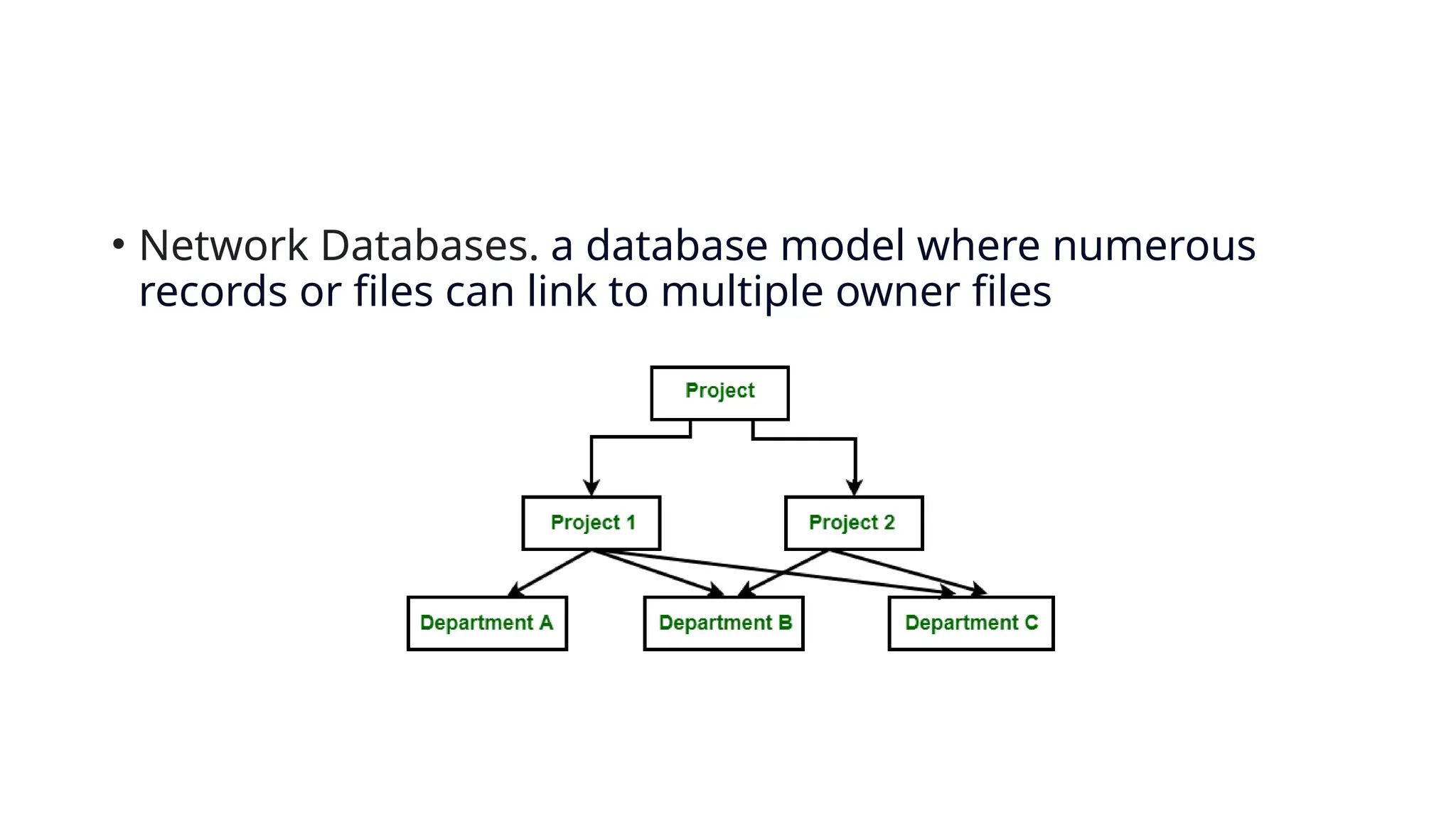
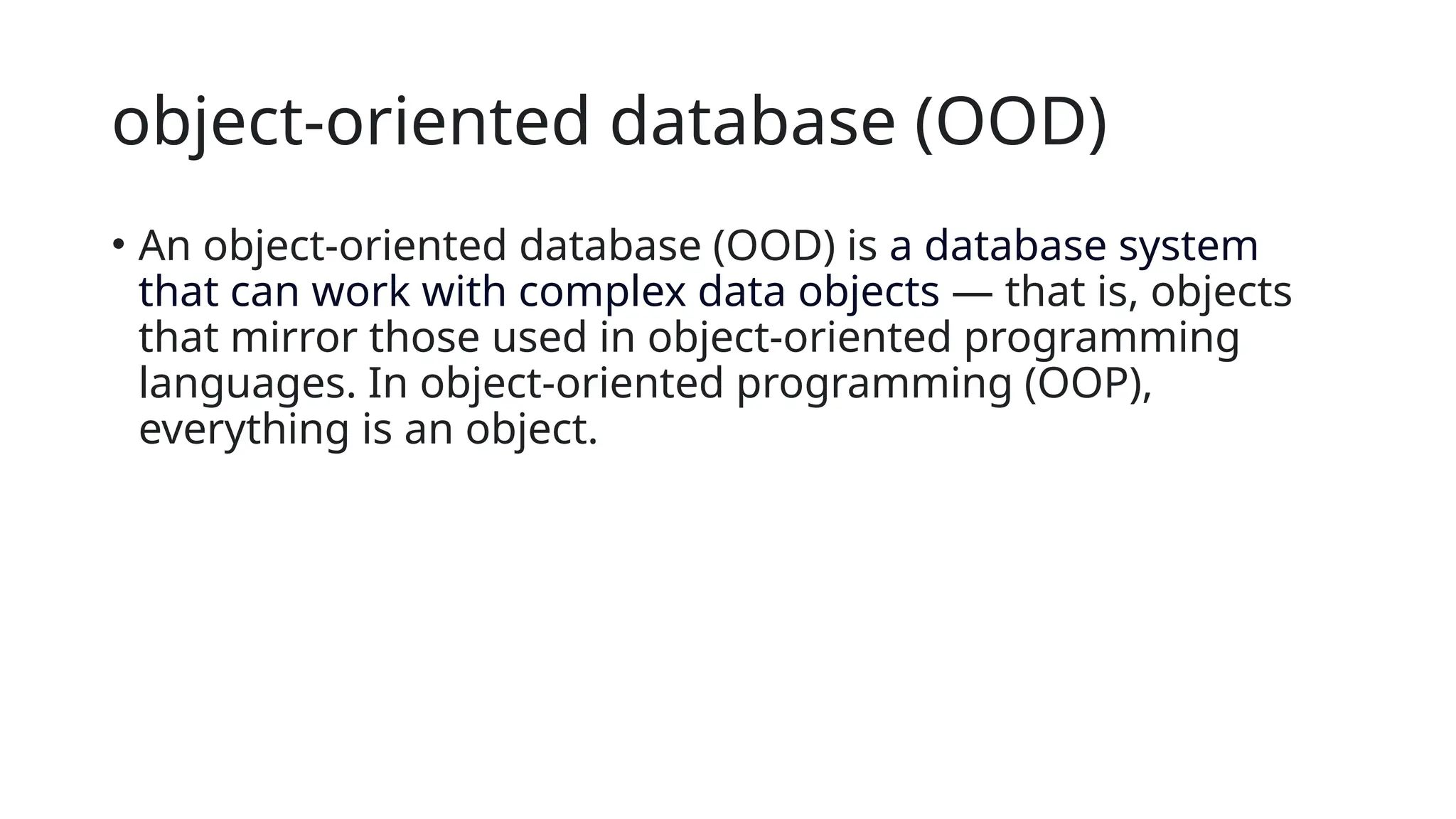
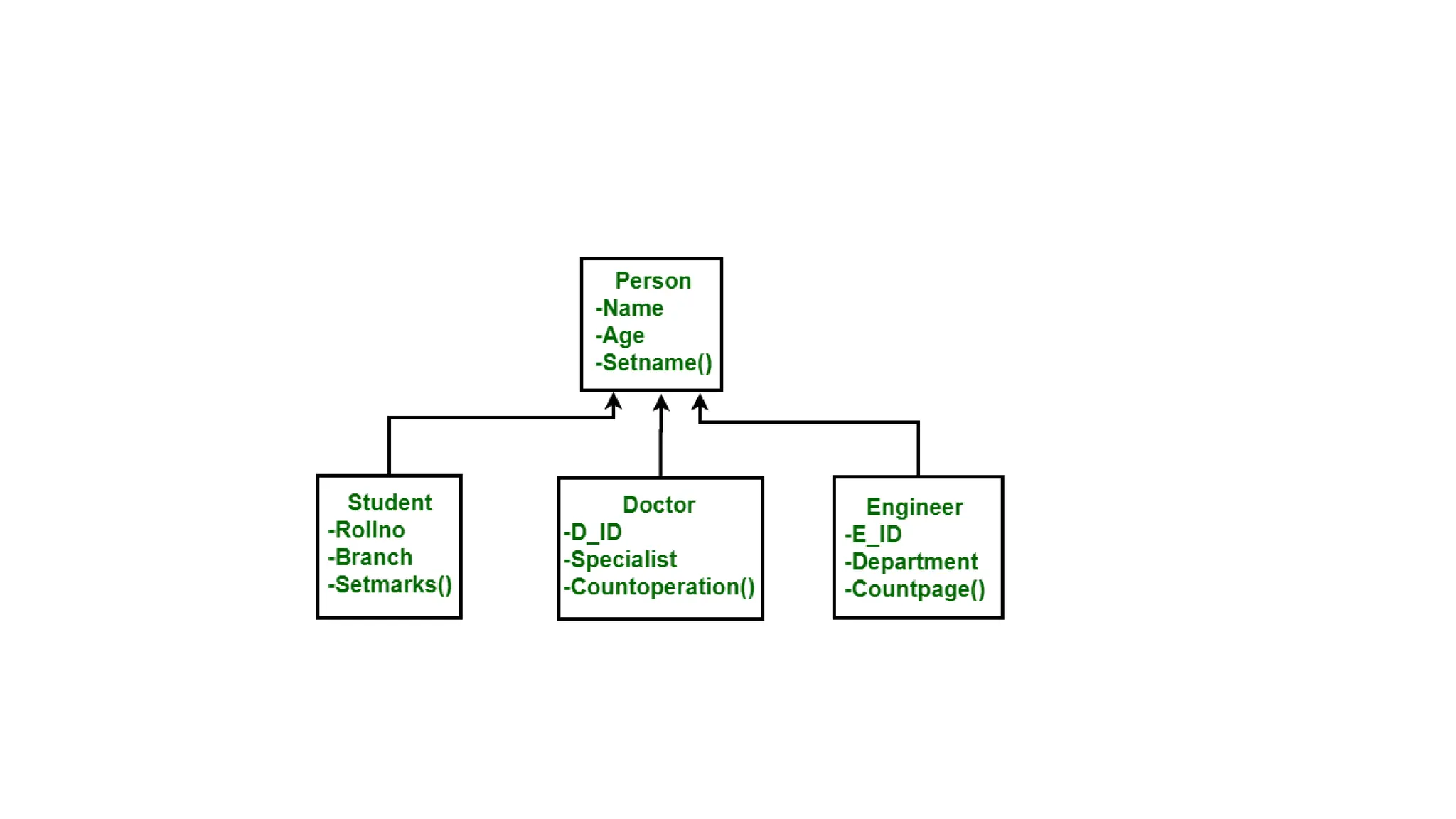
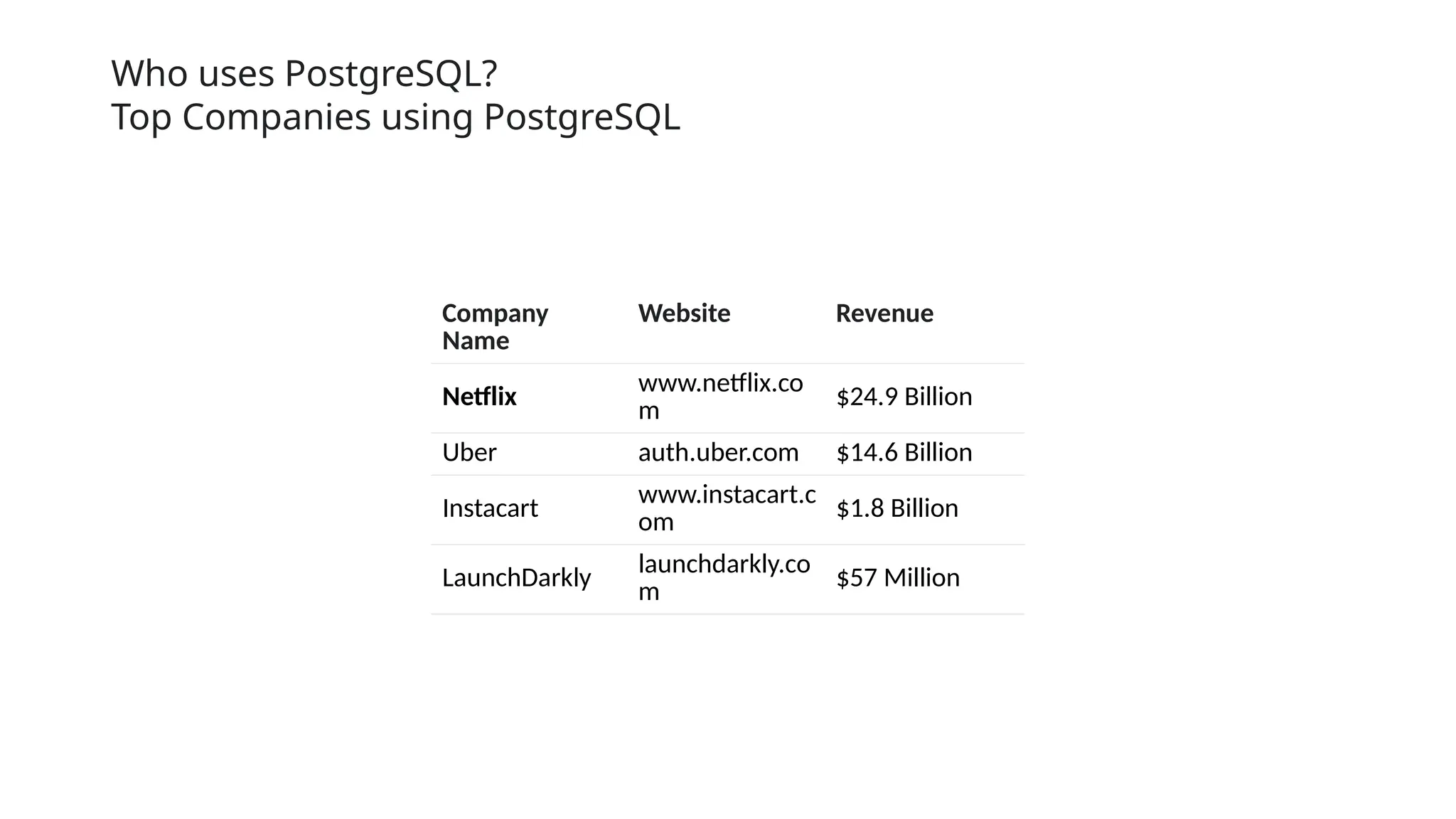
The document outlines the setup and use of PostgreSQL and TypeORM, including technical requirements, database types, management systems, and the features of PostgreSQL. It details the installation process of PostgreSQL and configuring TypeORM for building a repository layer with sample steps for Node.js and TypeScript. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of PostgreSQL, including its open-source nature, reliability, and support for complex data objects.