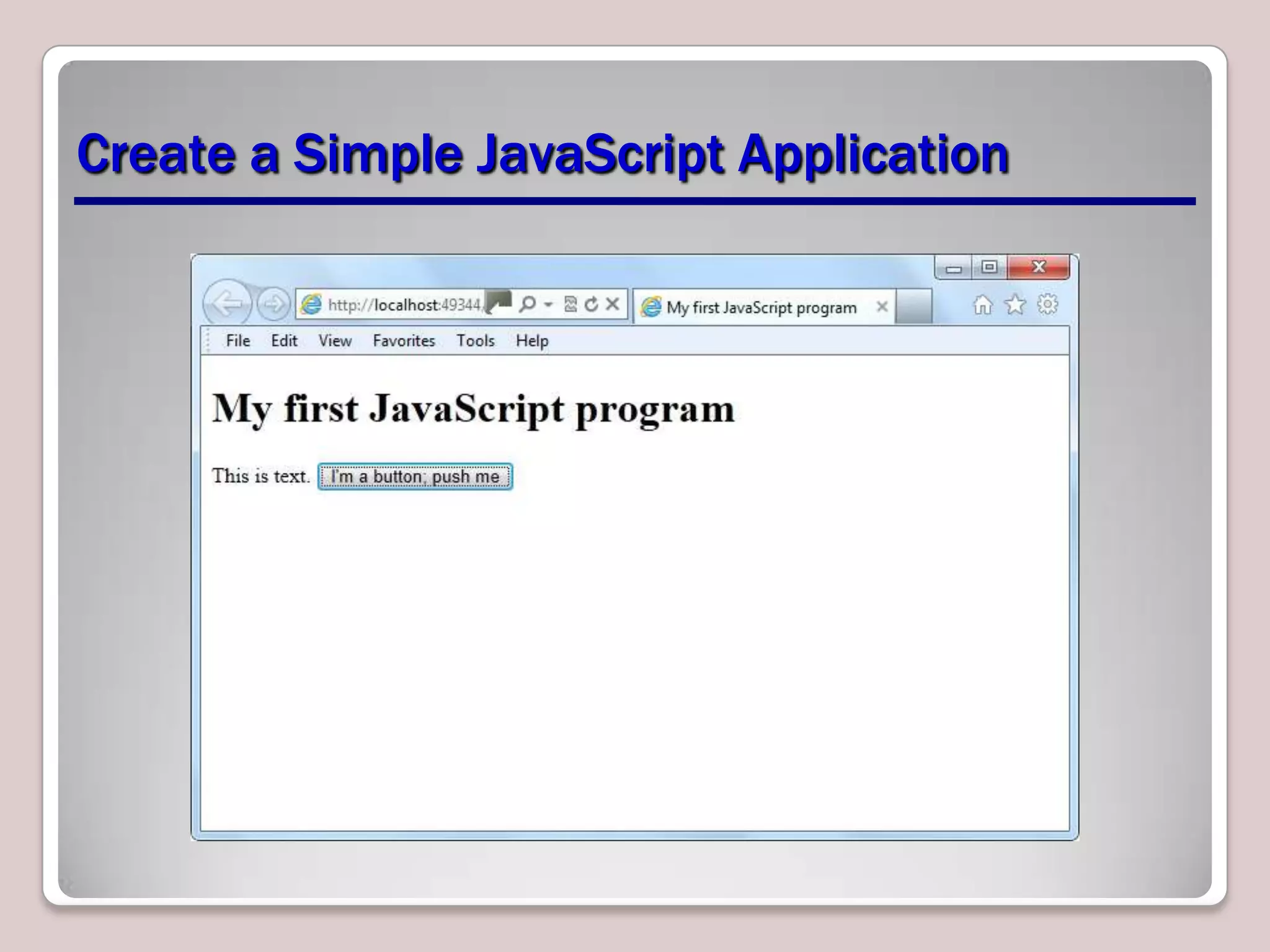
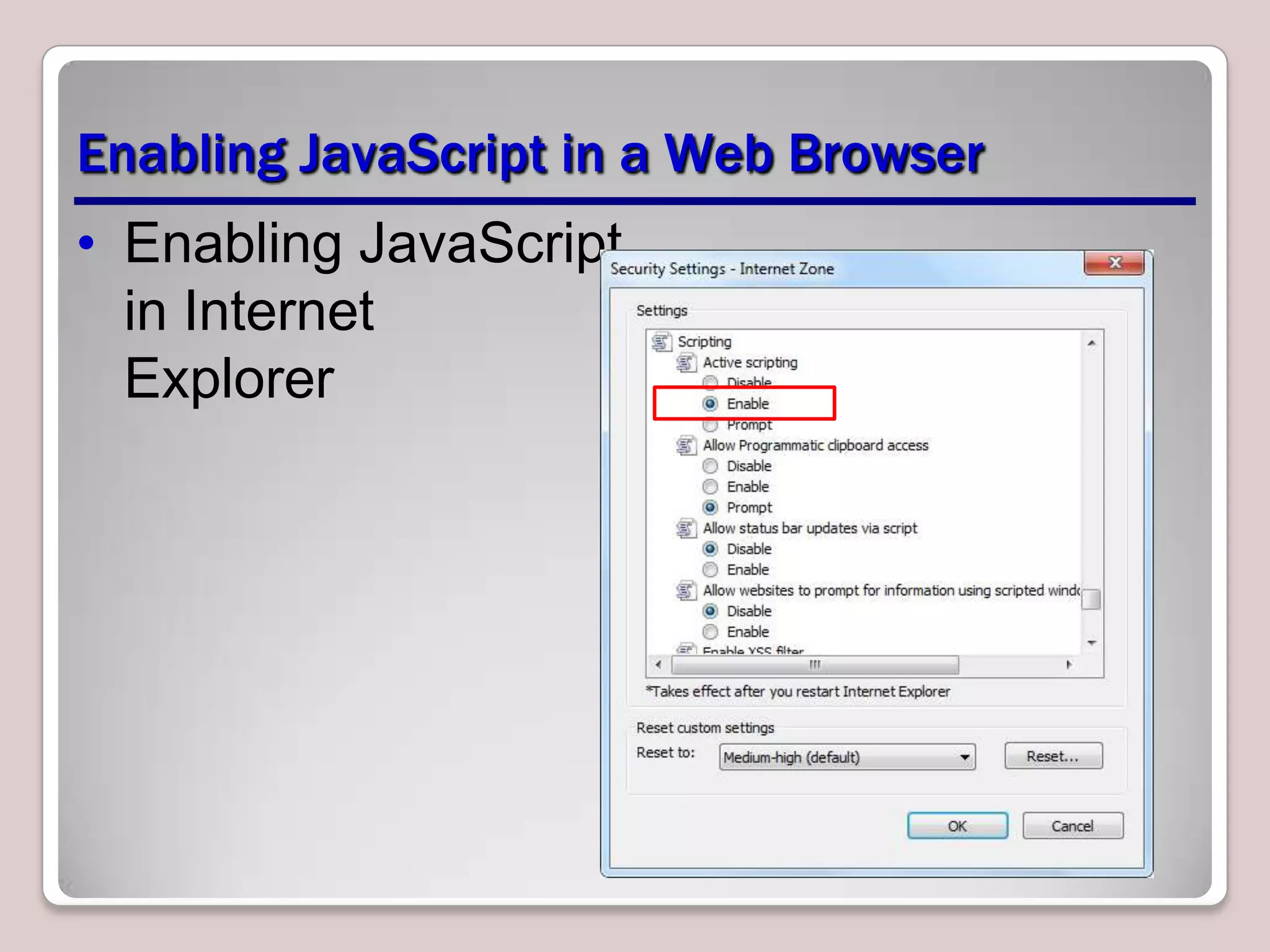
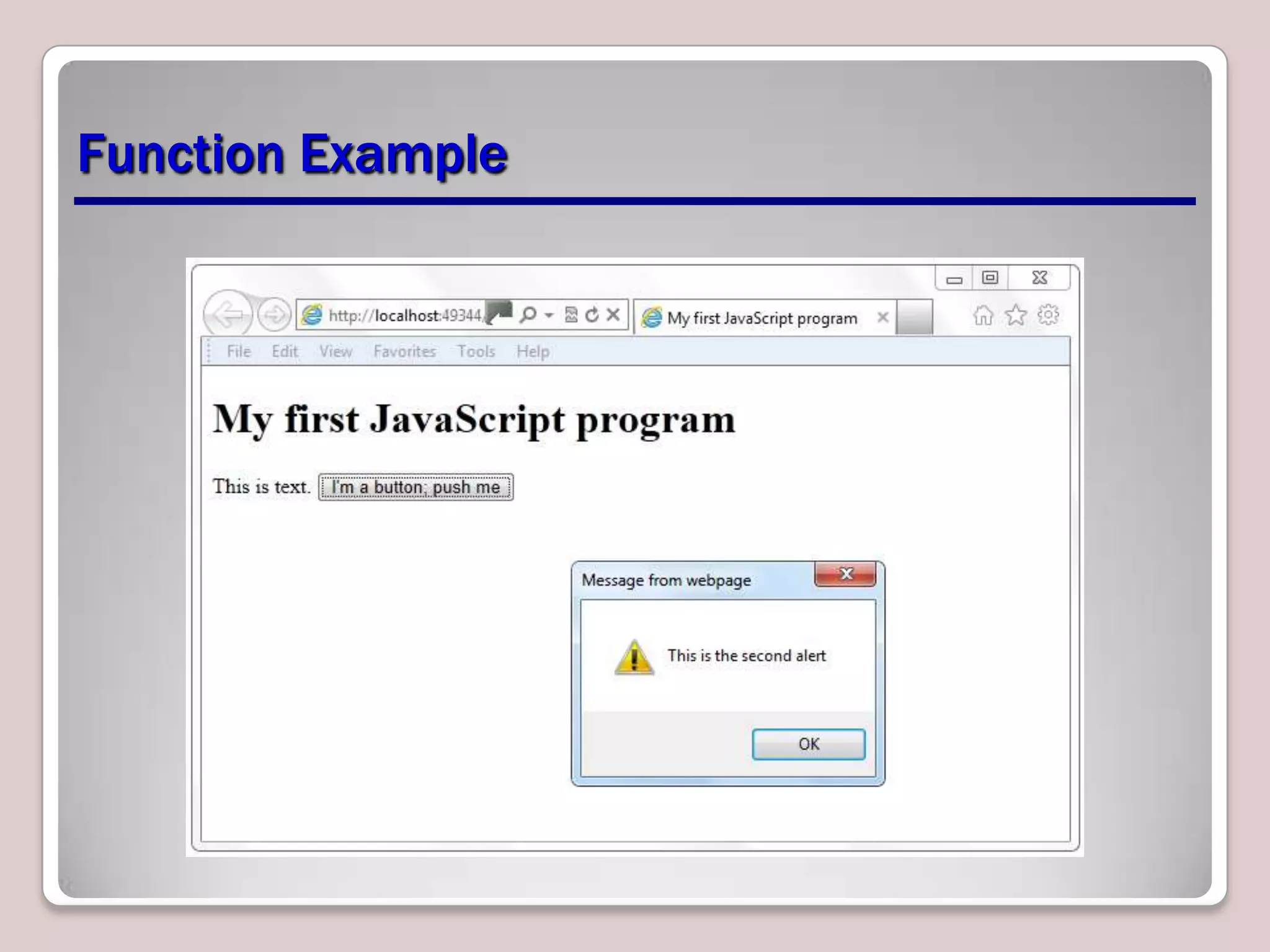
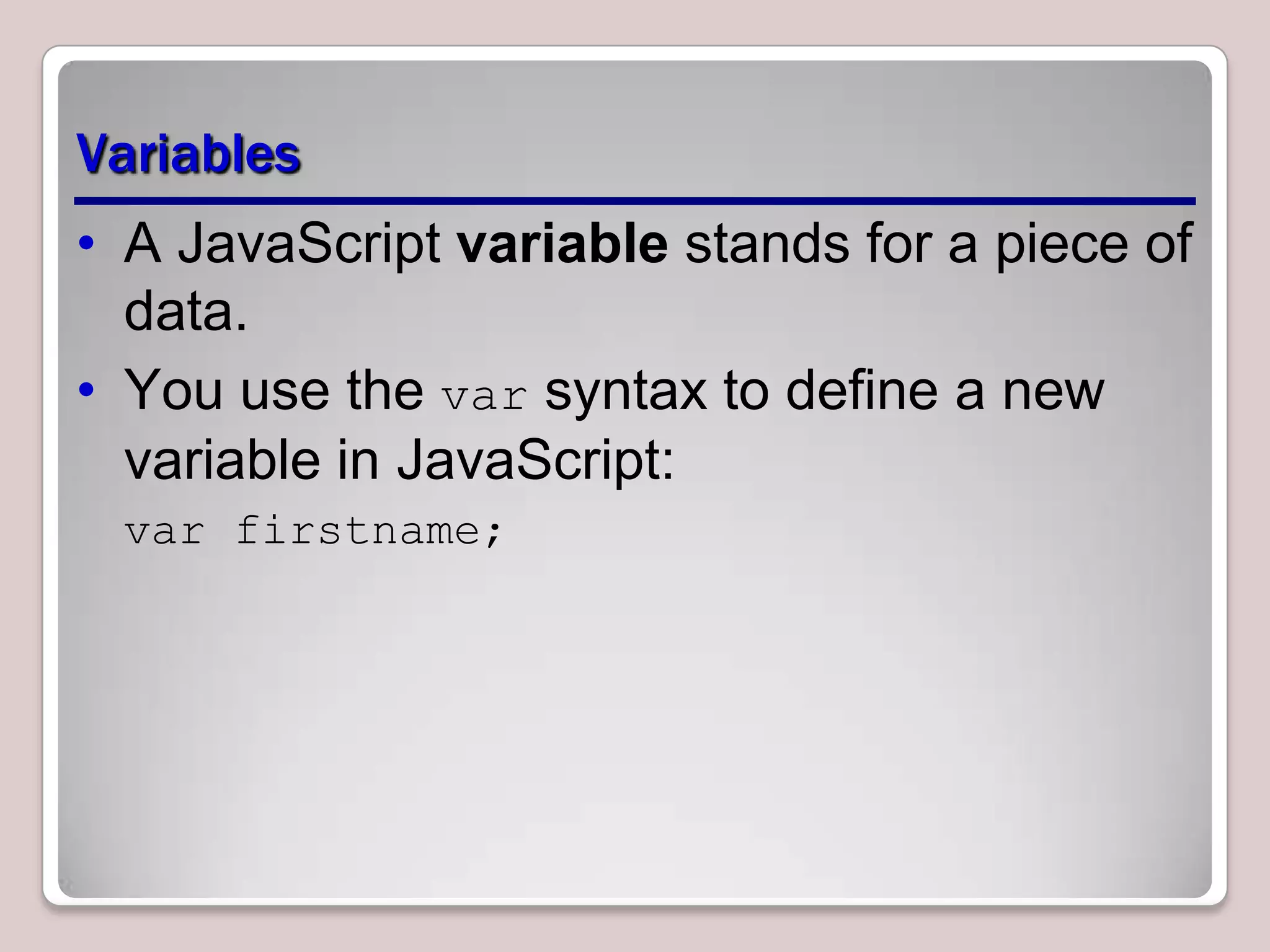
This document provides an overview of JavaScript coding essentials and concepts for managing and maintaining JavaScript and updating the UI. It covers topics such as functions, variables, identifiers, libraries, methods, events, showing/hiding elements, and updating content. Functions are segments of code that execute when invoked, variables store data, and methods are functions associated with objects. Events trigger actions, like onclick handlers. The document also demonstrates how to create simple JavaScript applications and link JavaScript to HTML.