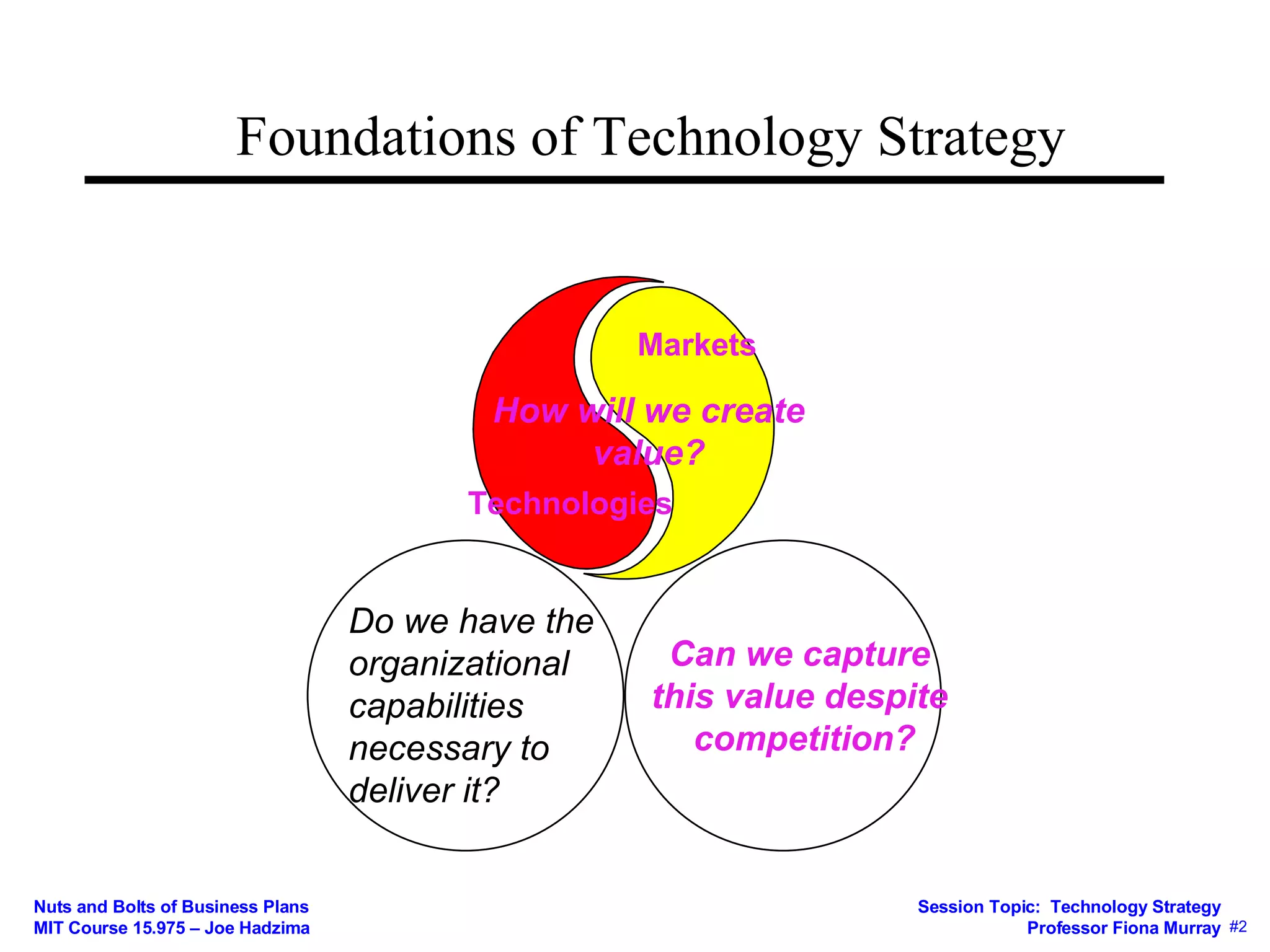
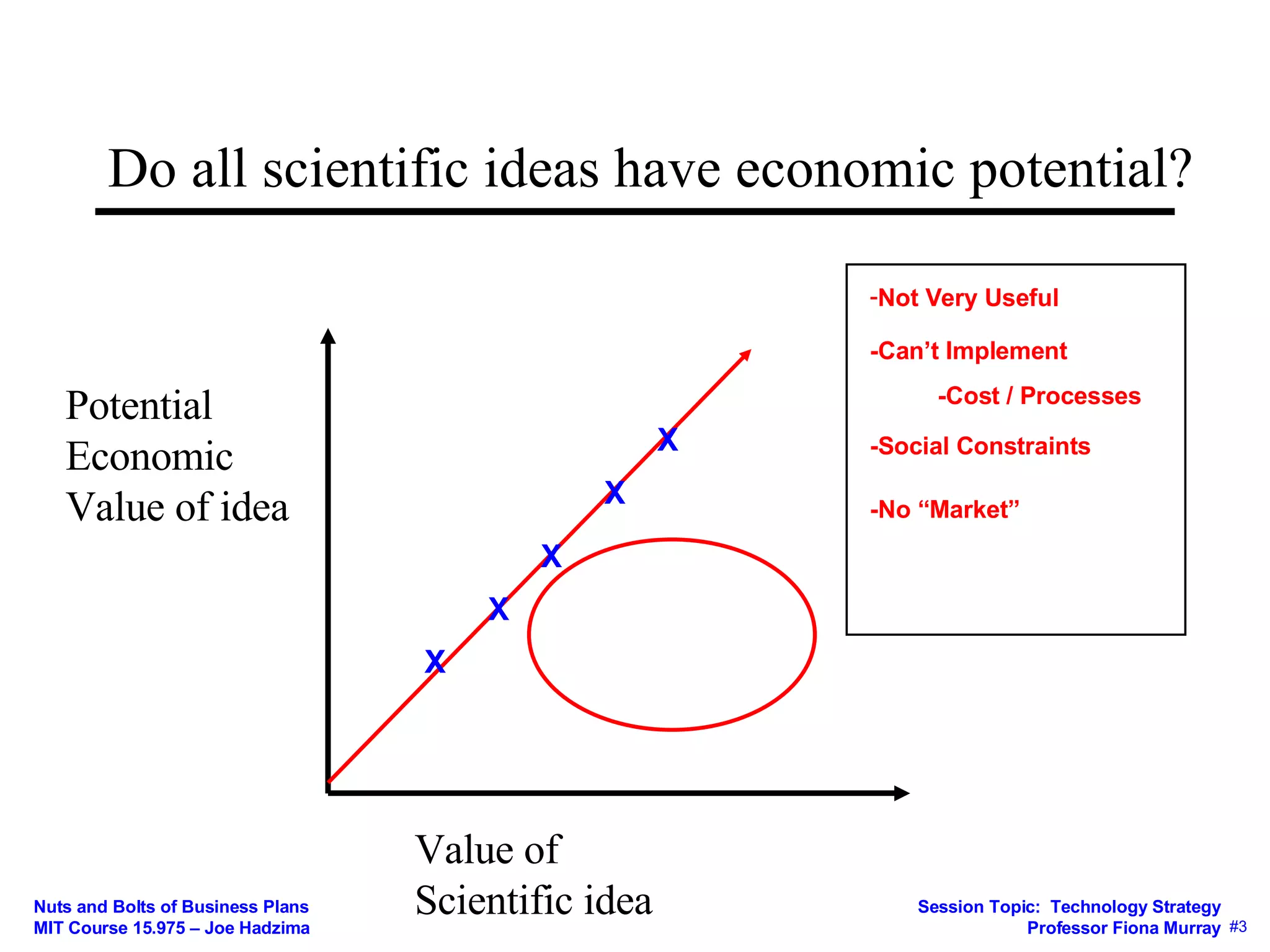
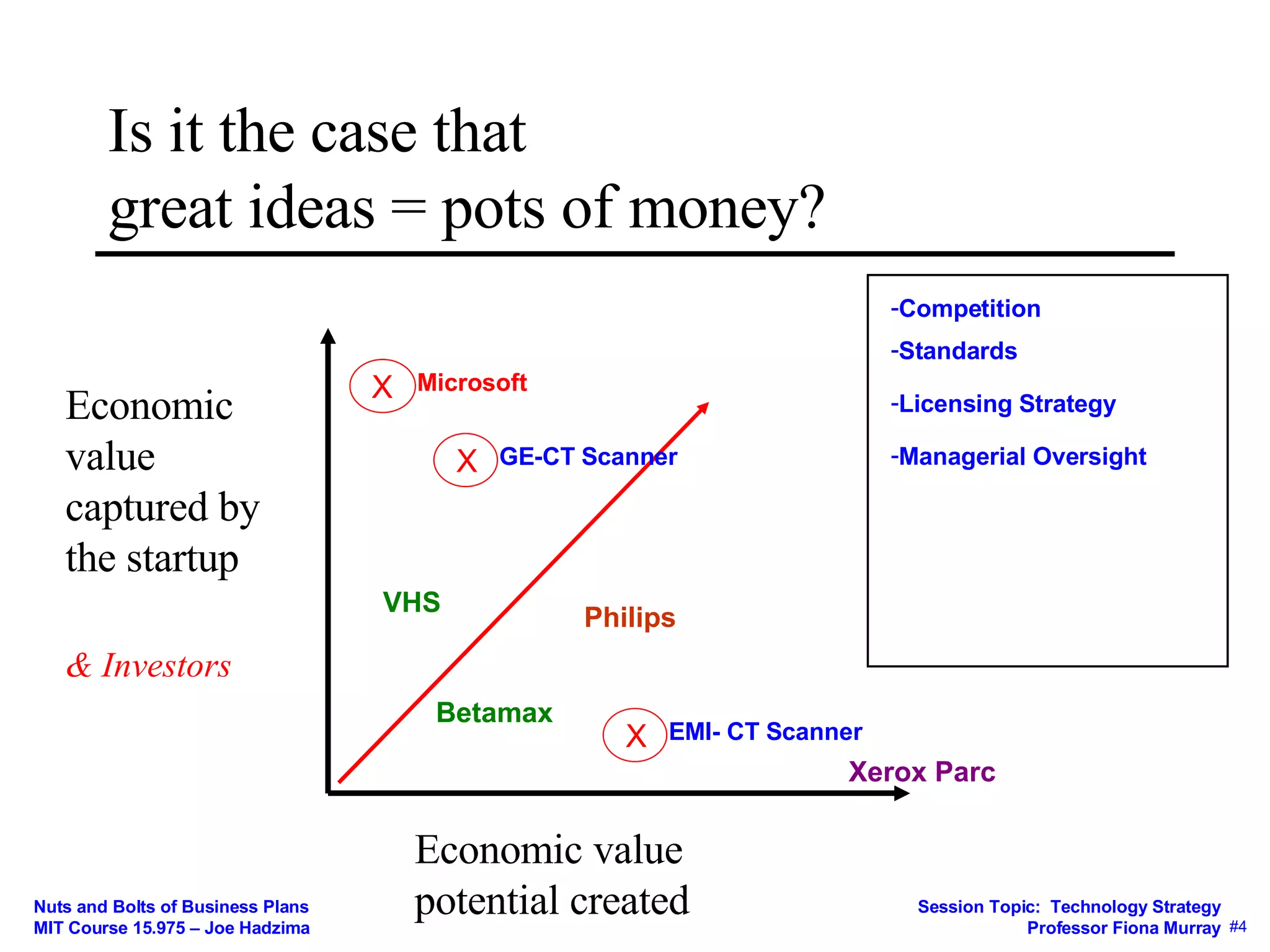
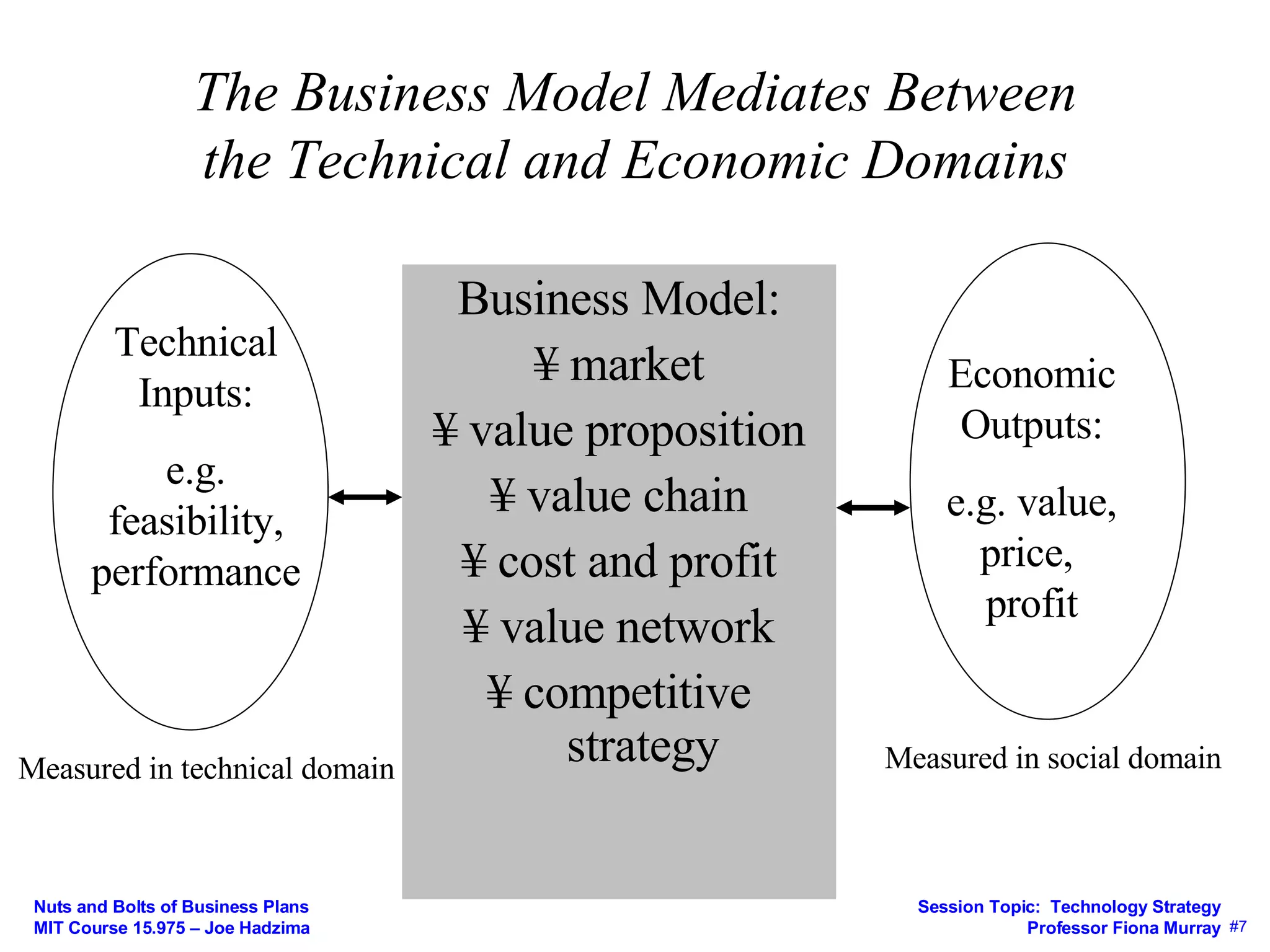
This document discusses key concepts in technology strategy for startups. It addresses questions around value creation and value capture. Specifically, it discusses:
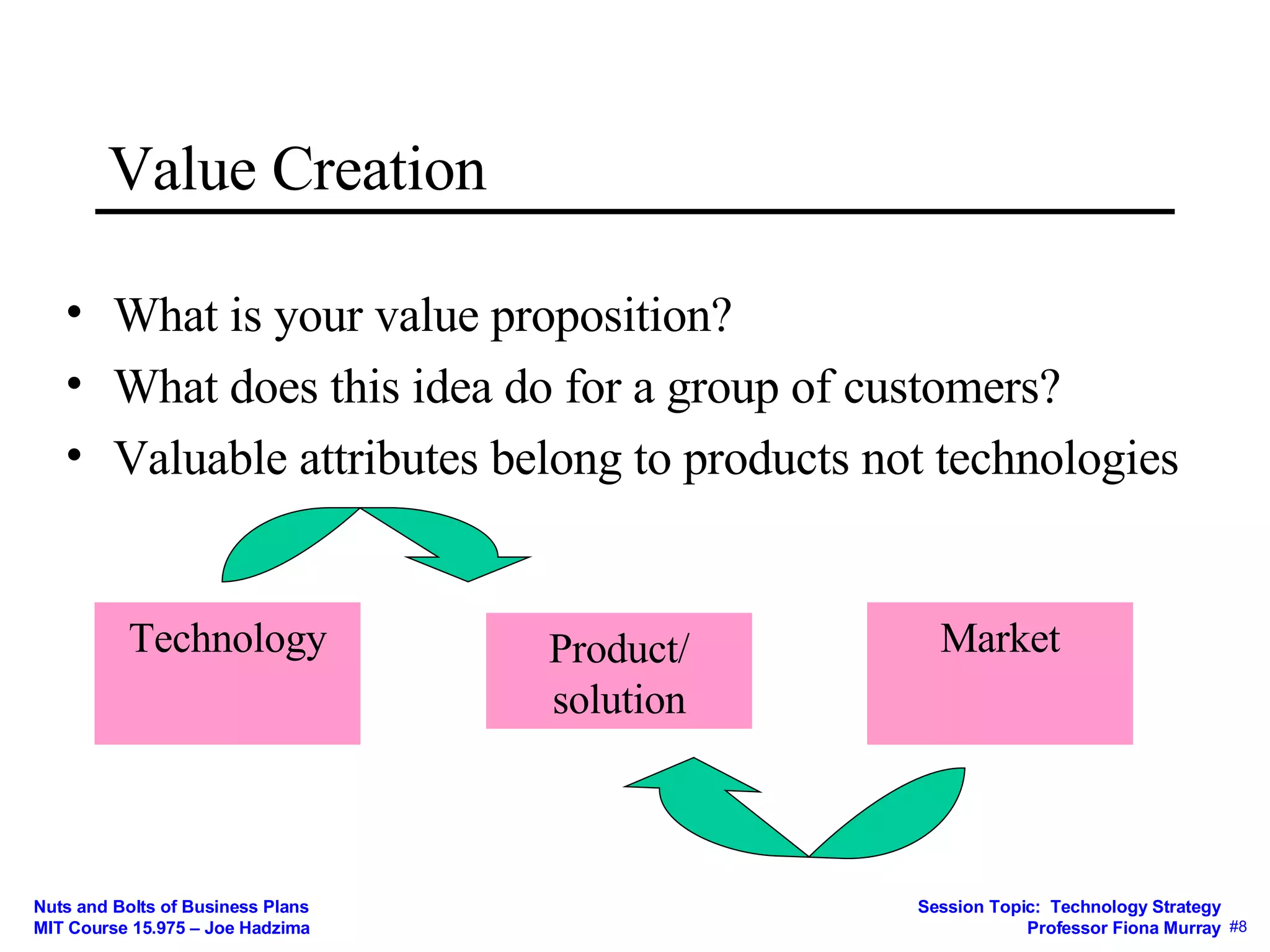
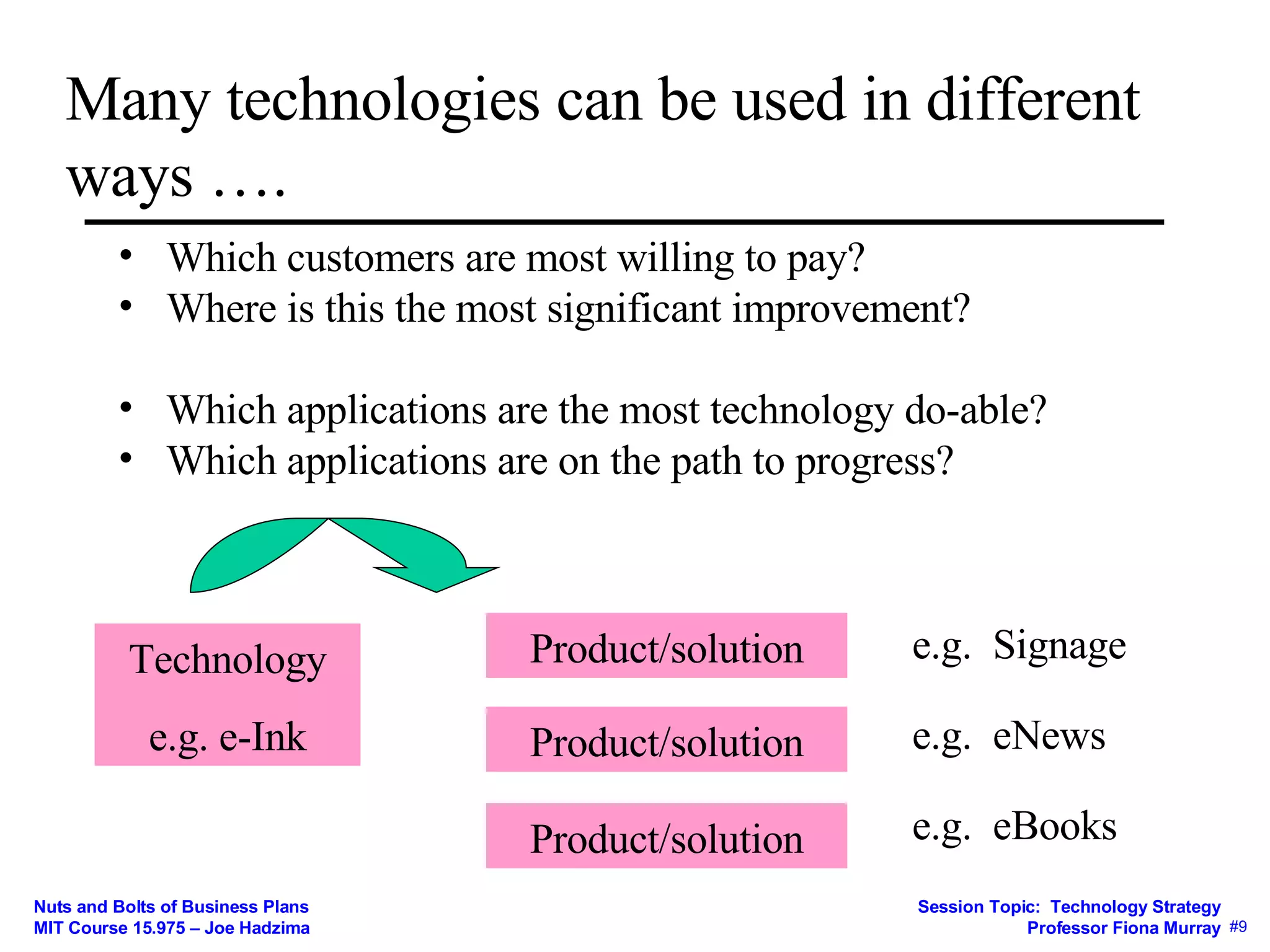
1) Whether a scientific idea has economic potential and how to determine a technology's value proposition for customers.
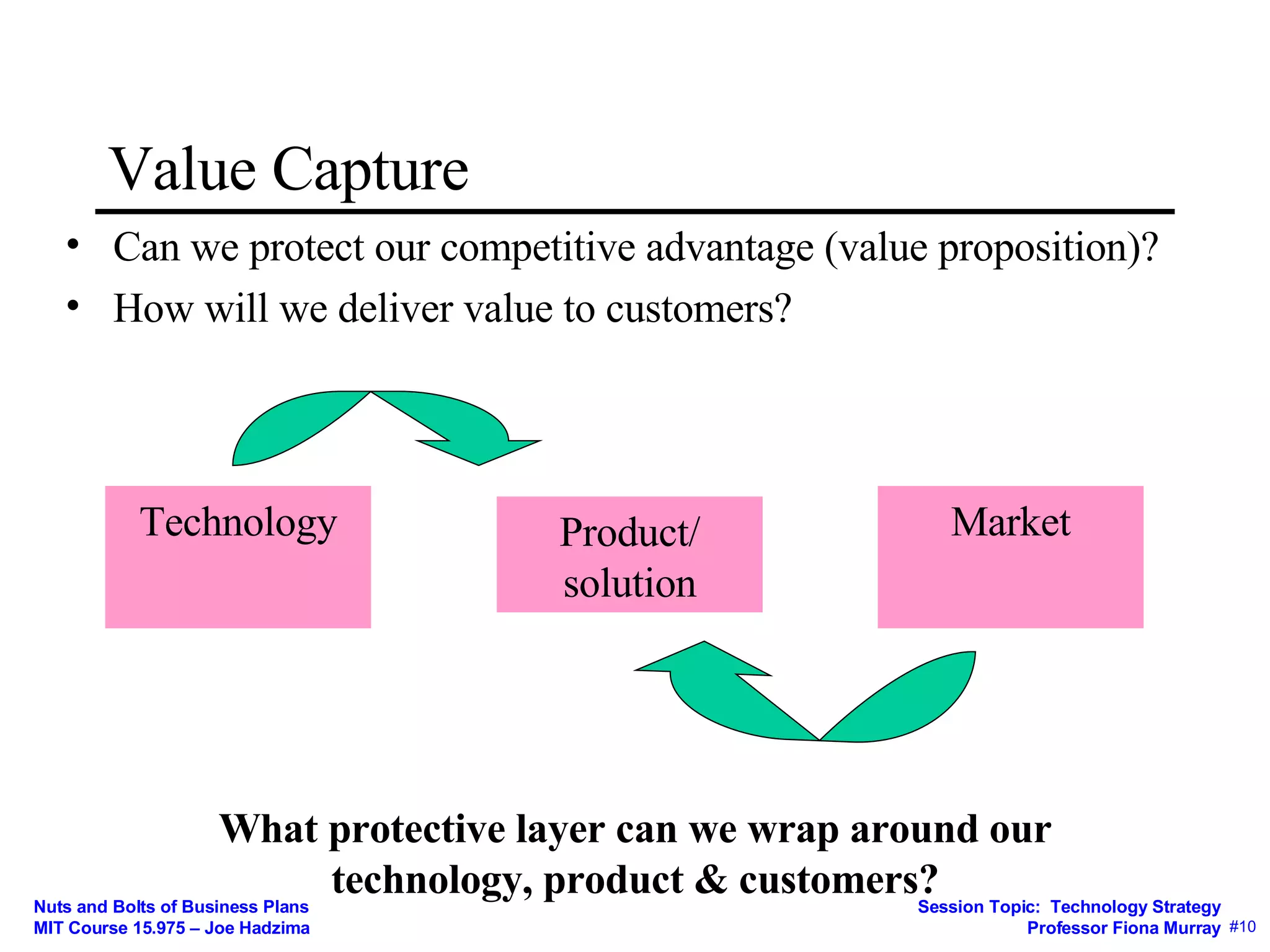
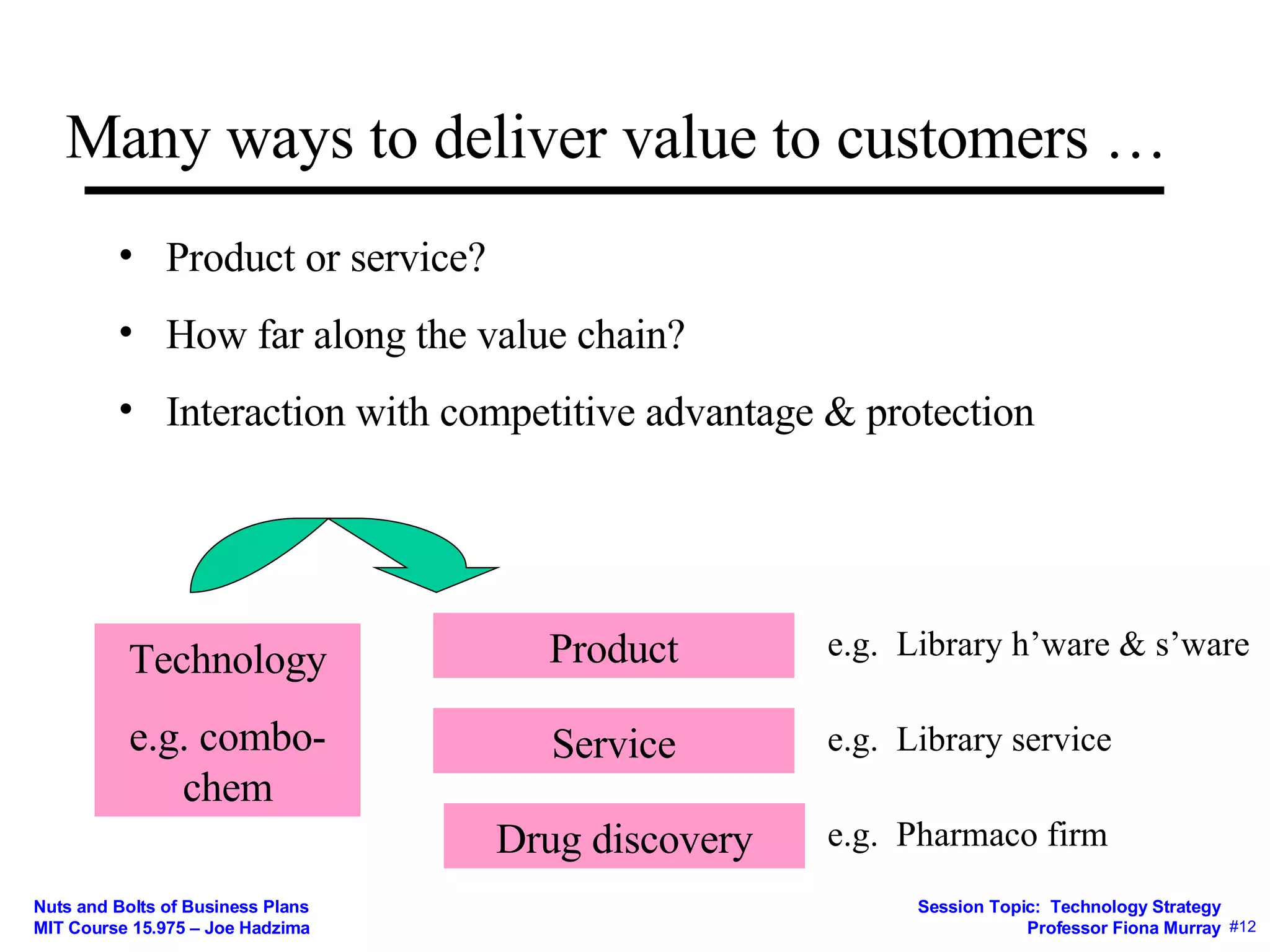
2) The importance of considering competition and having strategies to capture value such as intellectual property protection, secrecy, speed, and lock-in.
3) How the business model mediates between technical and economic domains by defining the market, value proposition, value chain, costs, and competitive strategy.