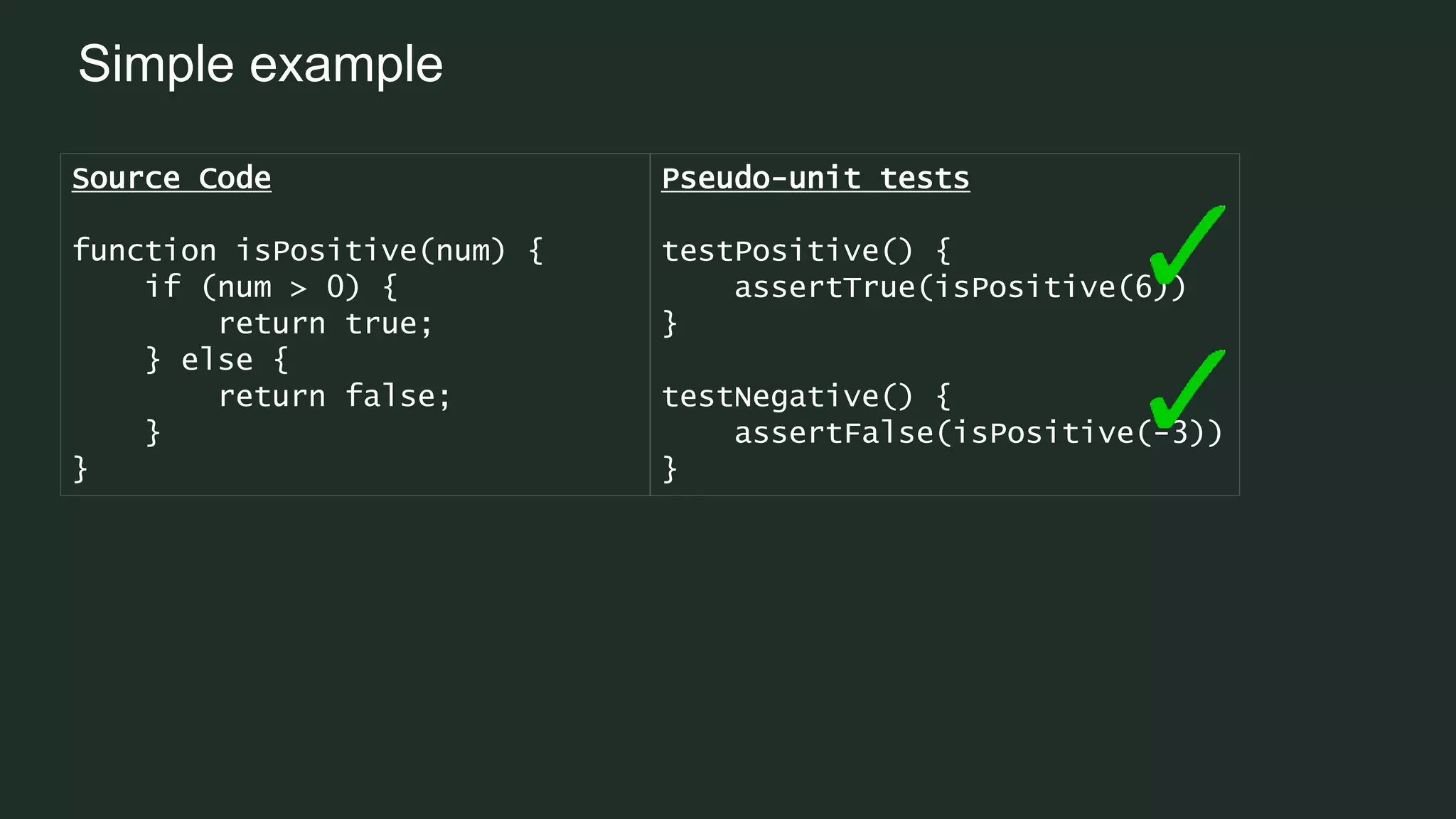
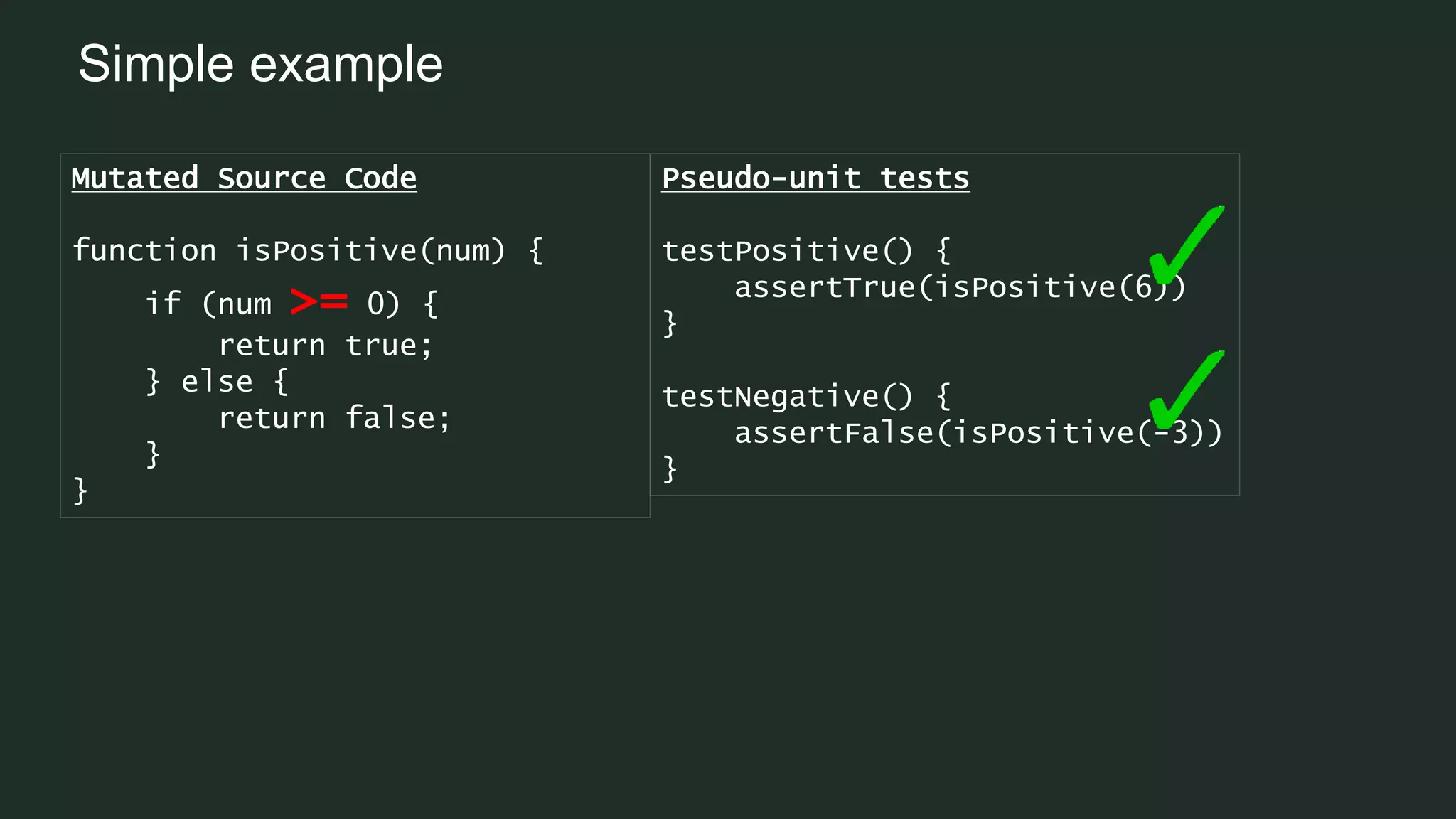
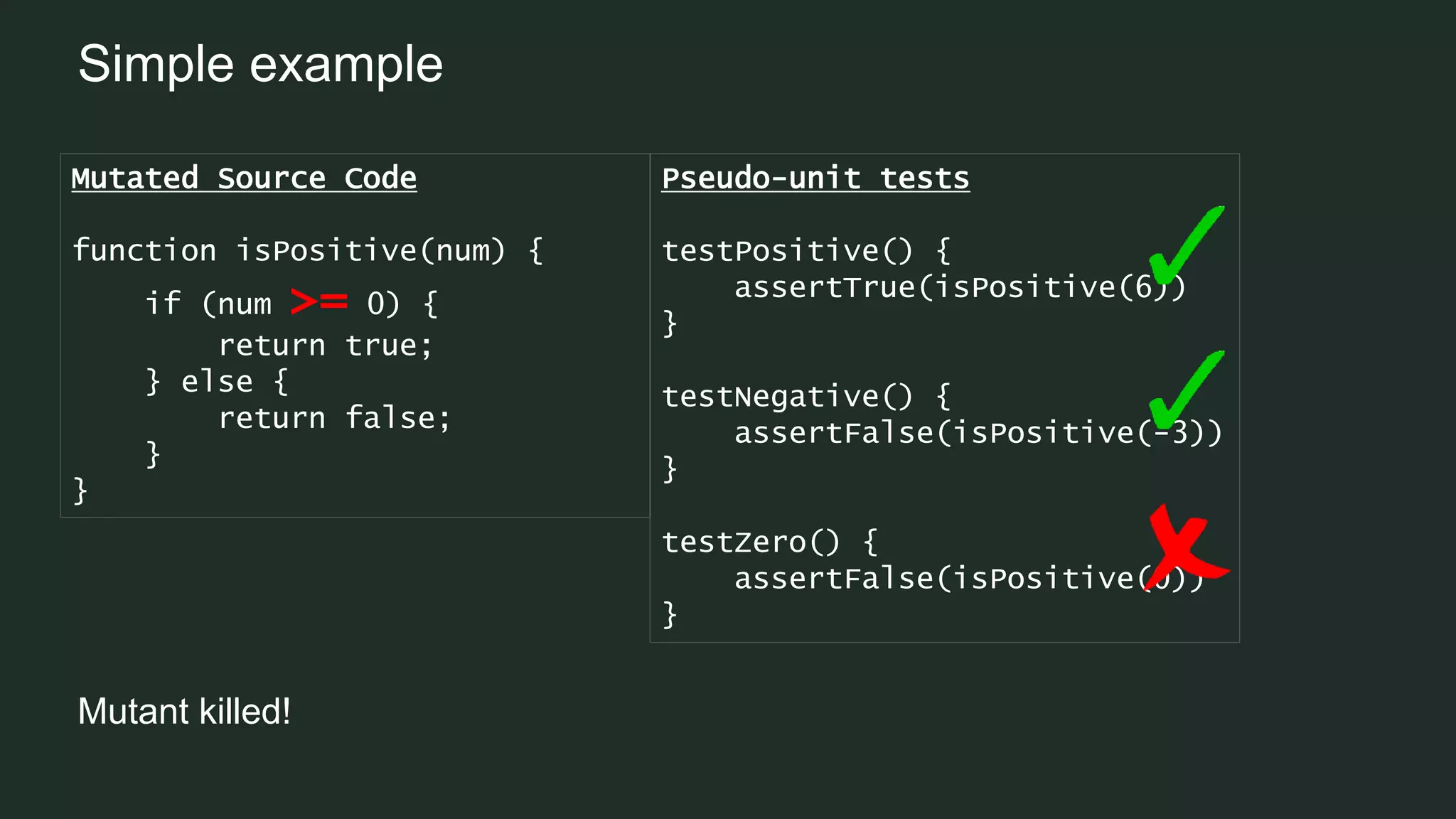
Mutation testing is a technique used to ensure that unit tests effectively validate code functionality by introducing small changes, known as mutants, to the source code. If a unit test fails against a mutant, it indicates that the test is validating the code correctly, while passing tests suggest gaps in coverage. Despite its computational expense and potential signal-to-noise ratio challenges, mutation testing is seen as a more reliable measure than simple line coverage.








![More complex example
Mutated Source Code
function handleLogin(request, response)
const {username, password} =
if (!username) {
return response.status(400)
.json({reason: ‘ERR_NO_USERNAME’})
}
if (false) {
return response.status(400)
.json({reason: ‘ERR_NO_PASSWORD’})
}
}
Pseudo-unit tests
const testRequest = {
body: {} // no username or password
fields
}
const mockResponse = () => ...
testNoUsername() {
handleLogin(testRequest, mockResponse);
expect(mockResponse.calls[0].toBe(400));
}
testNoPassword() {
const testRequestUsername = {
body: {
username: “abc”
}
};
handleLogin(testRequestUsername,
mockResponse);Mutant killed!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutation-testing-sleigh-190330085844/75/Mutation-Testing-Testing-your-tests-12-2048.jpg)

