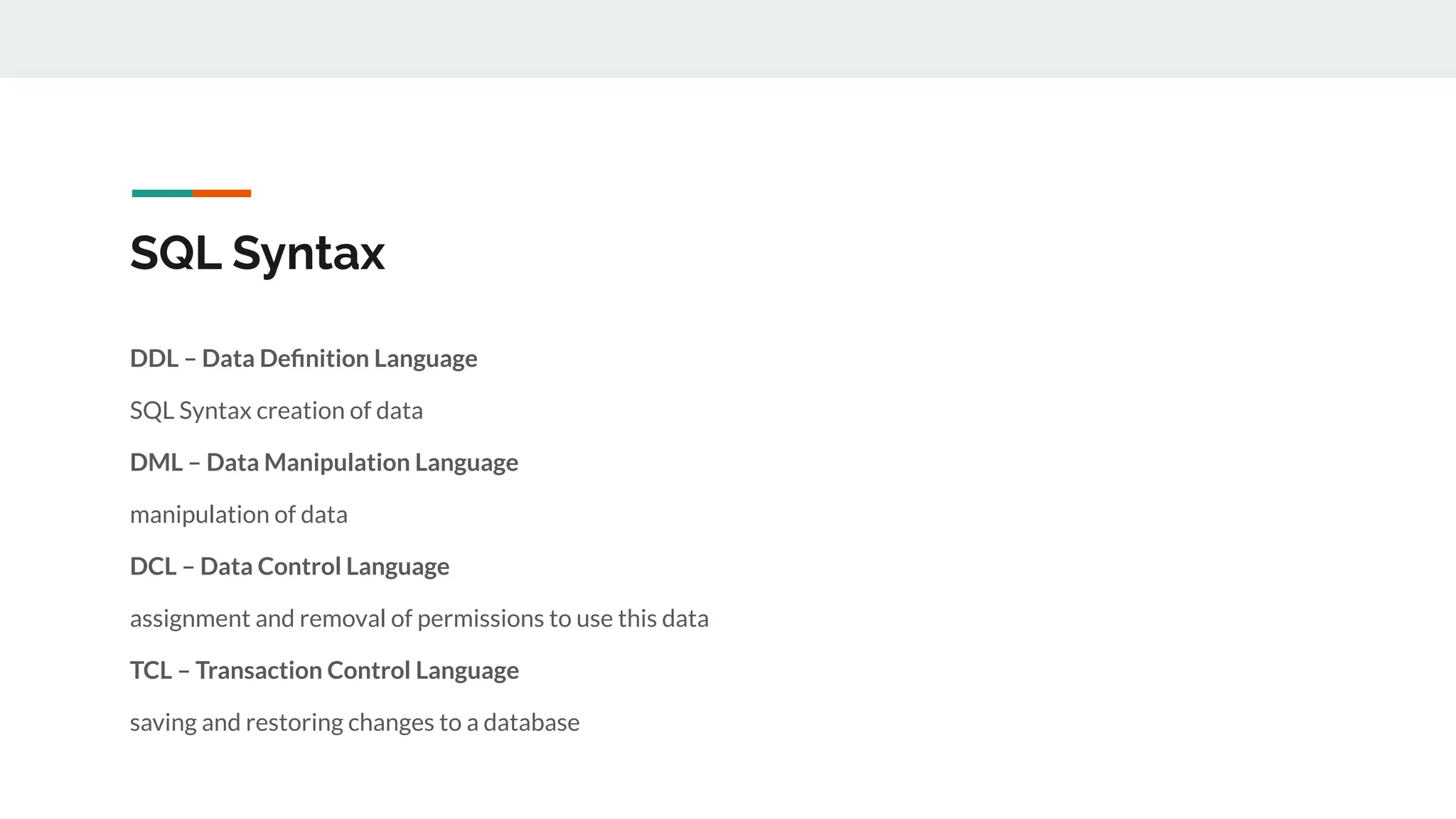
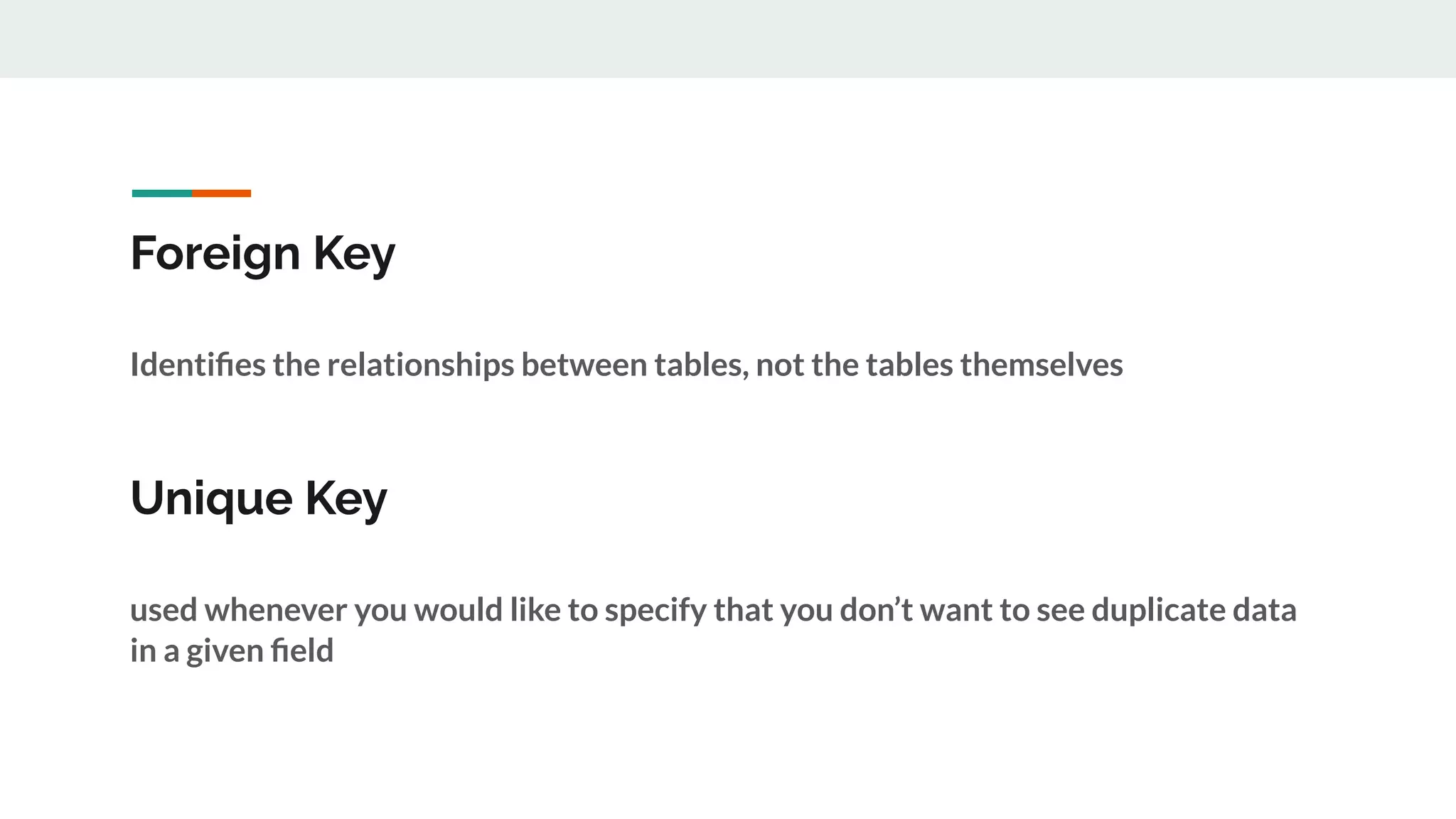
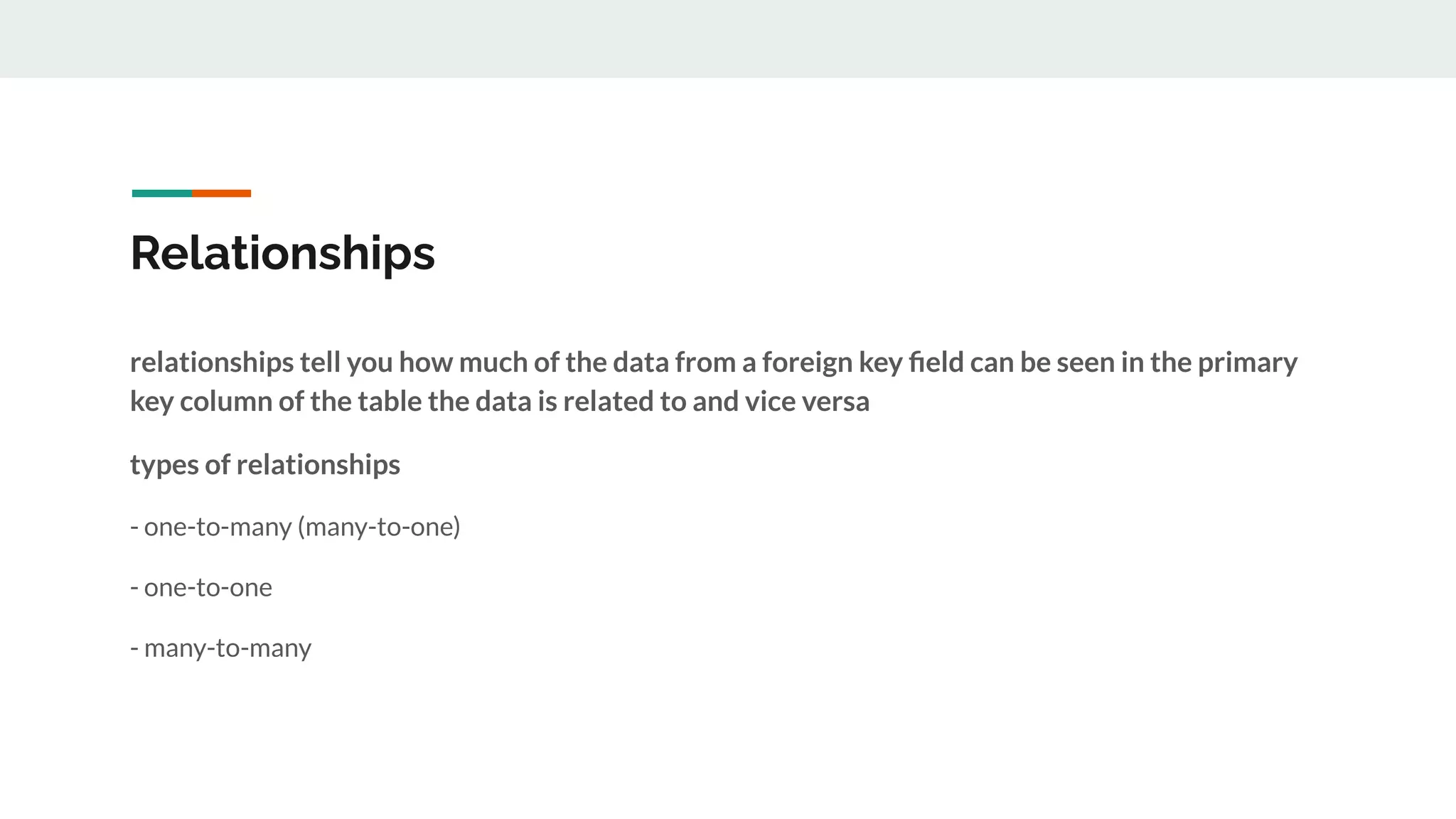
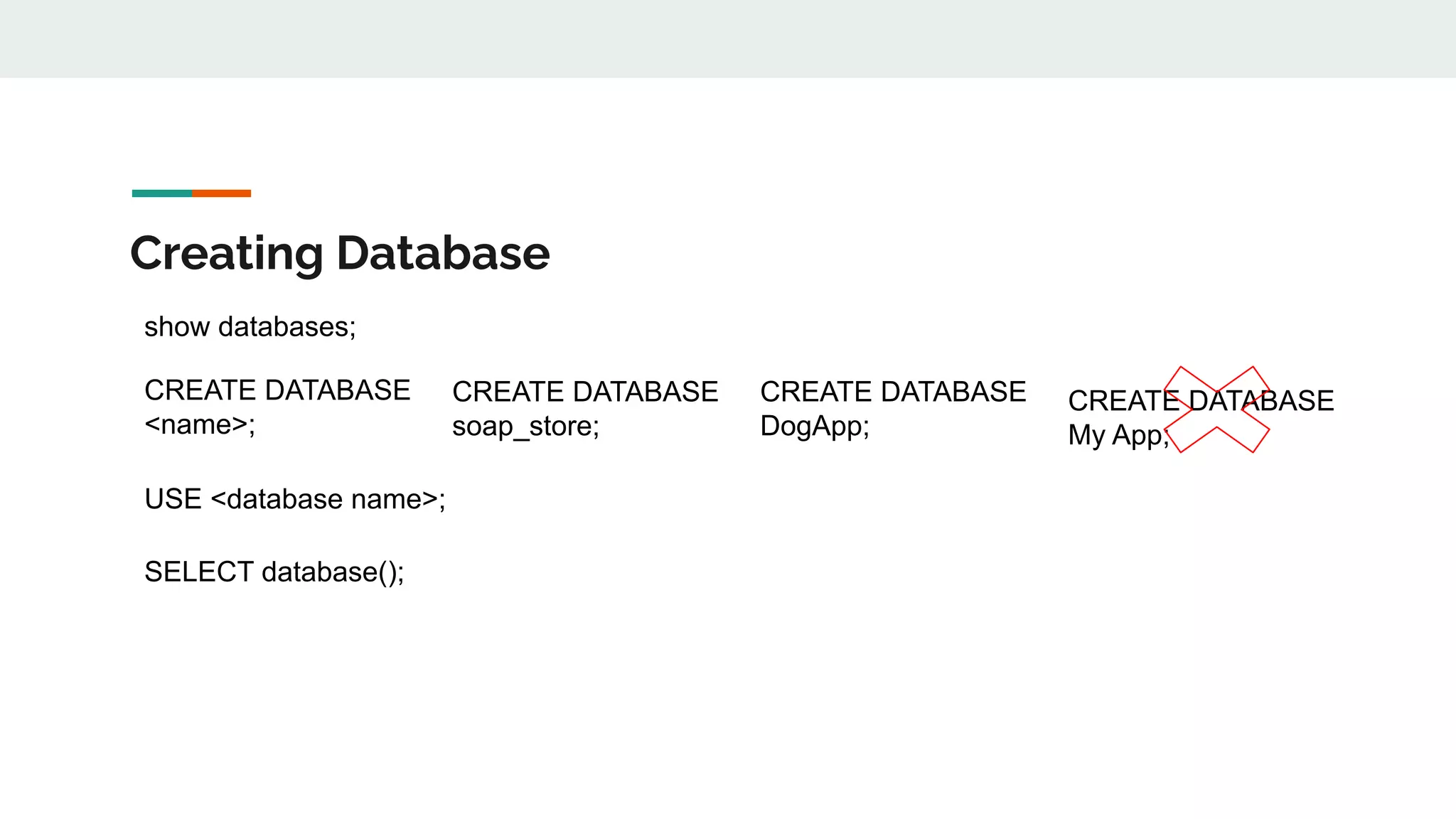
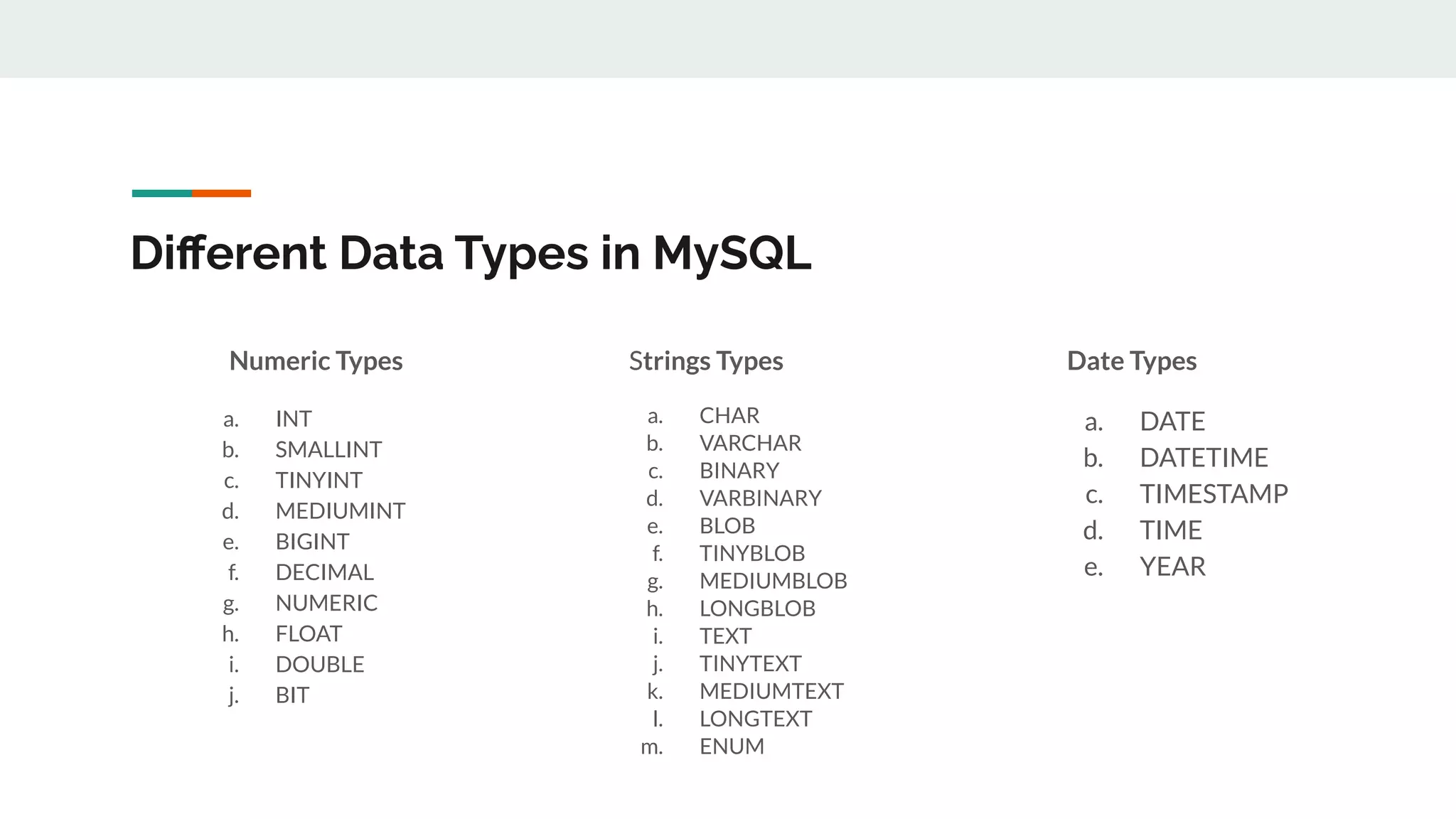
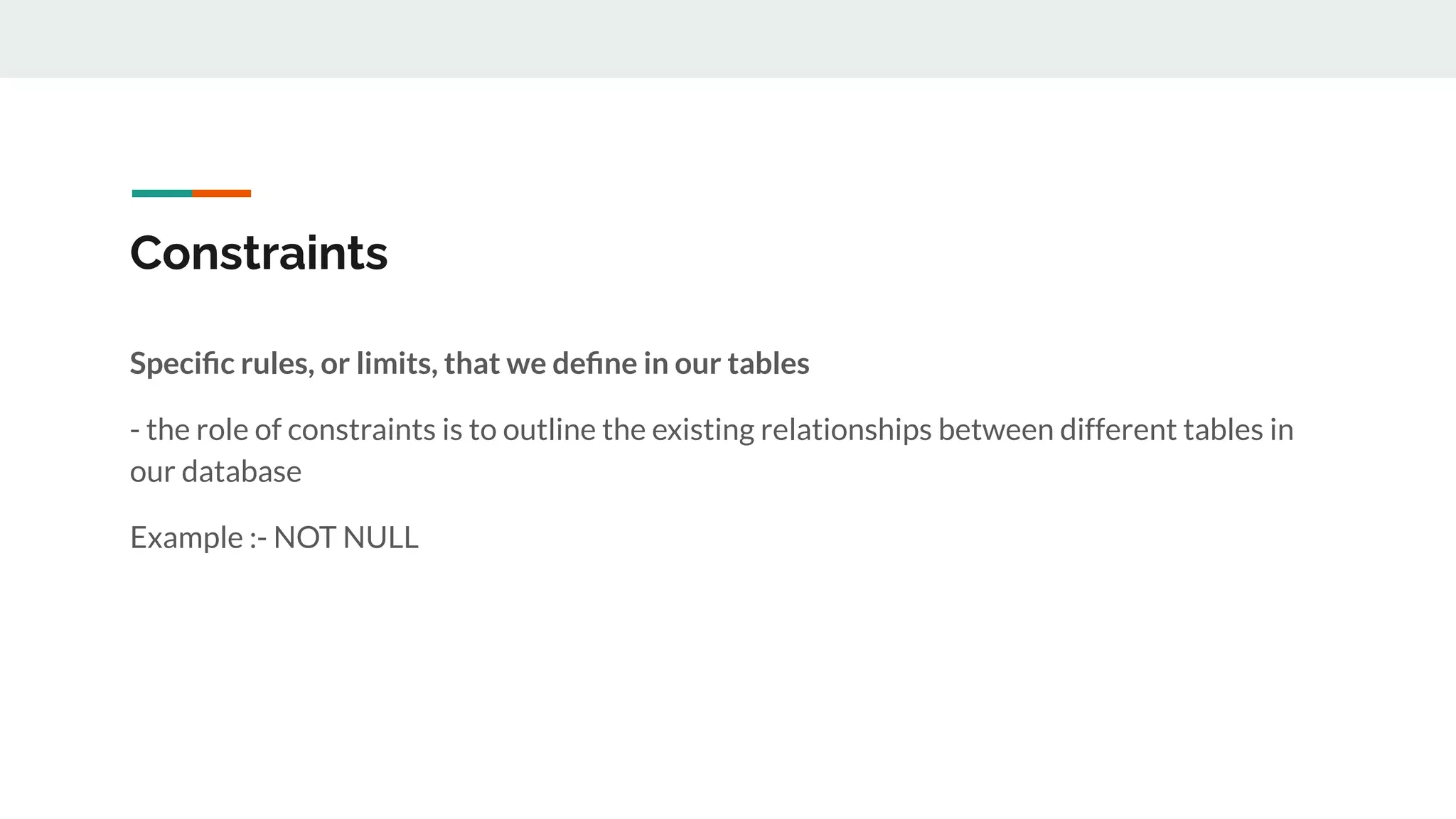
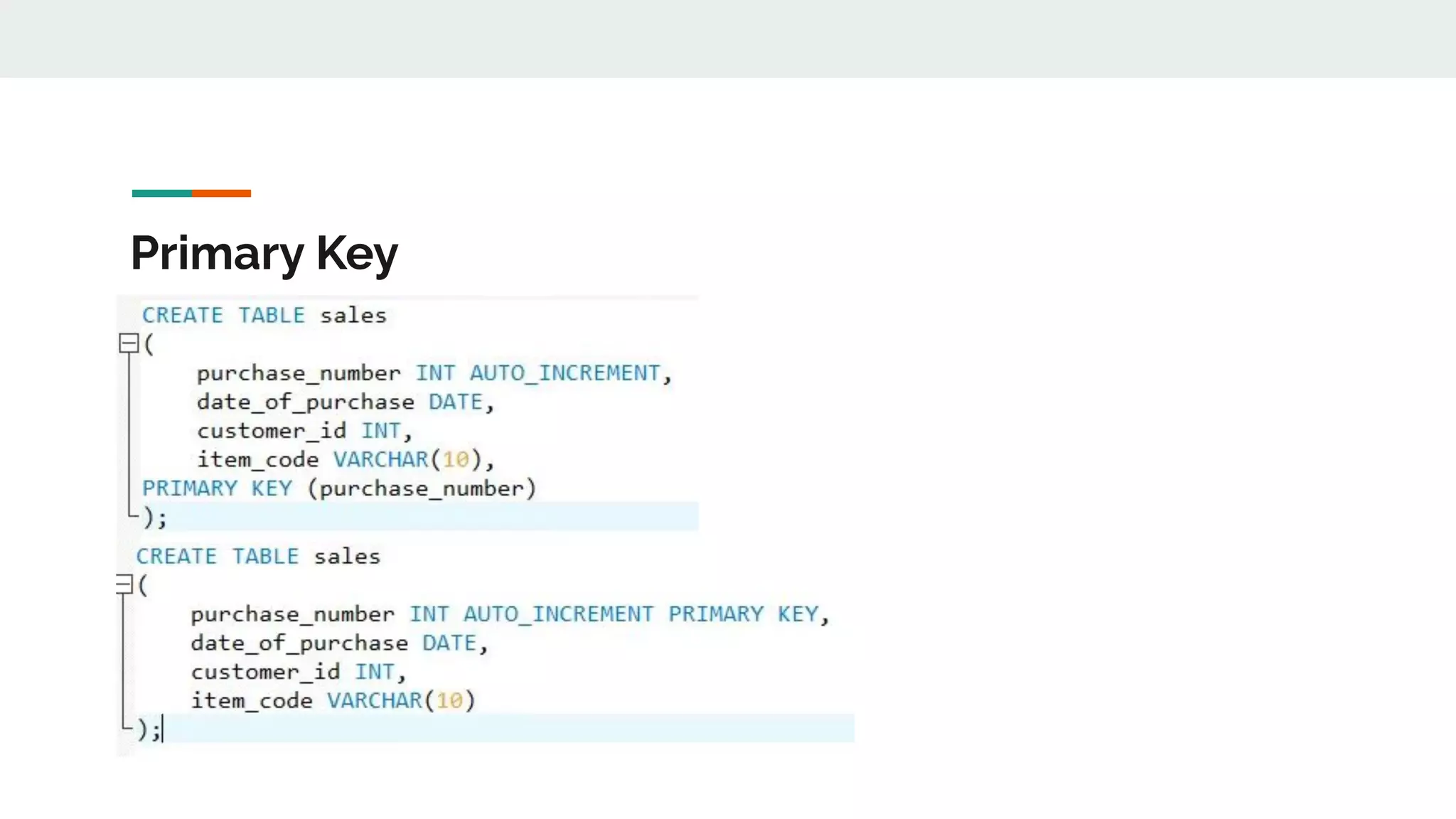
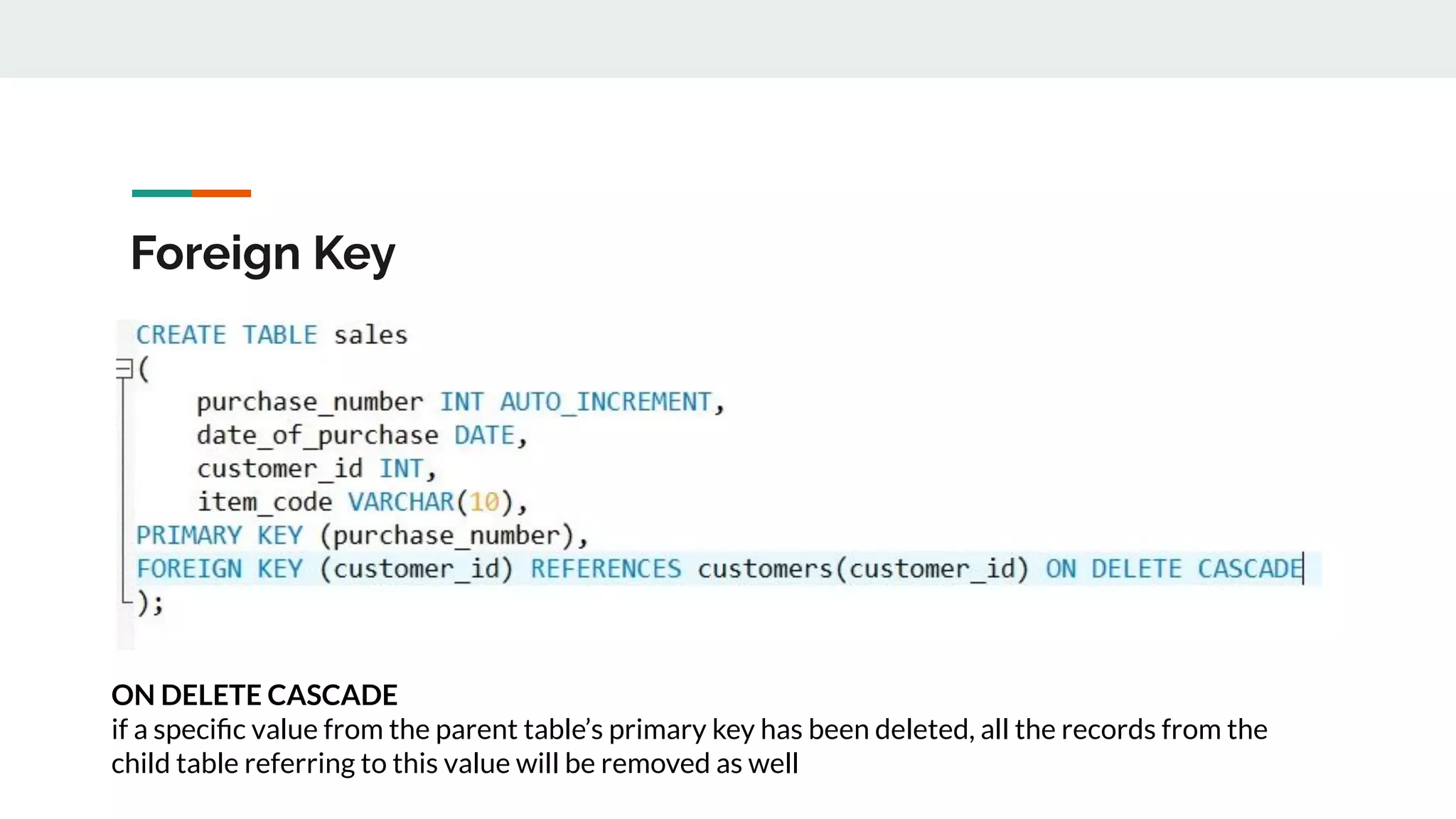
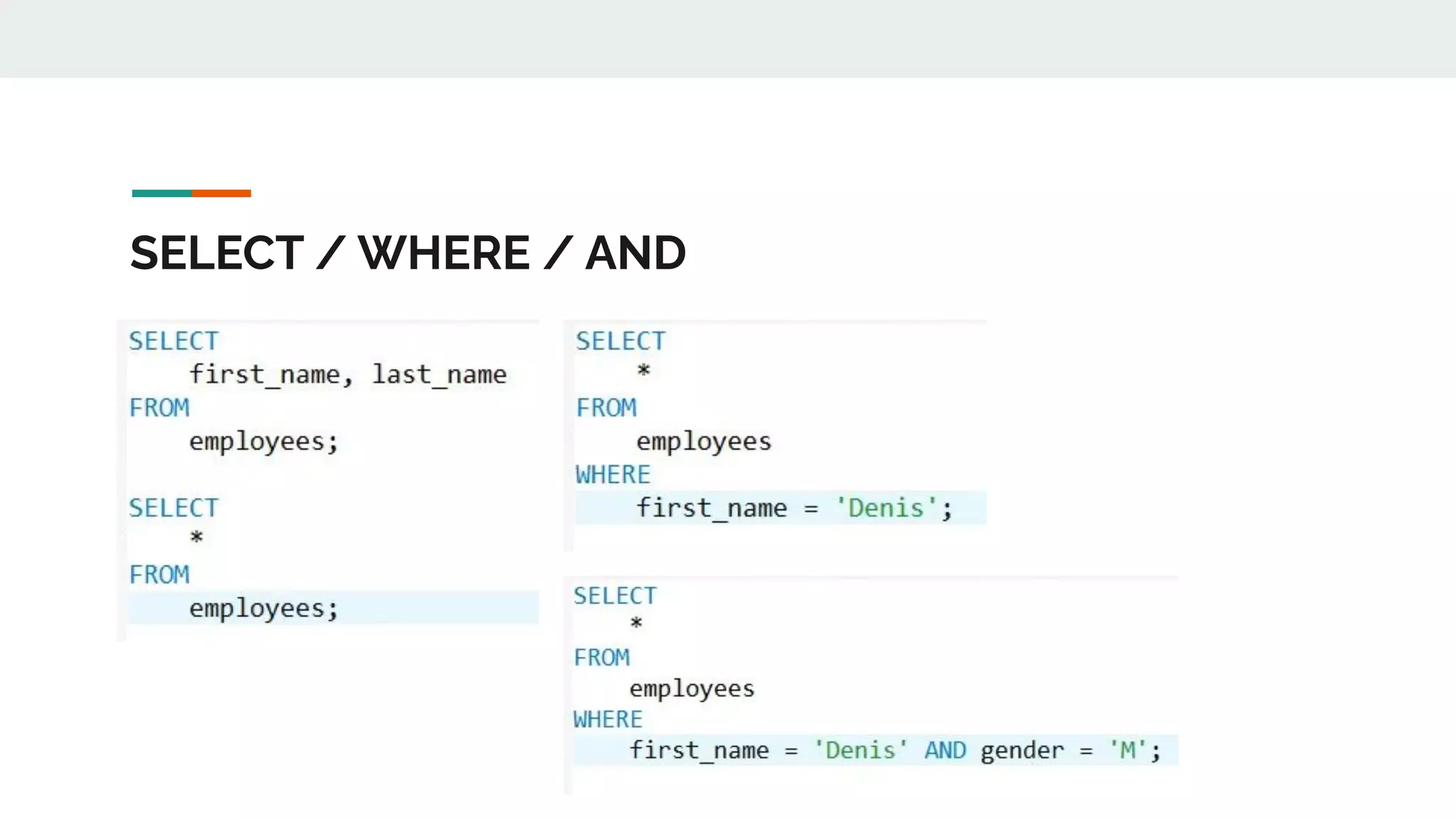
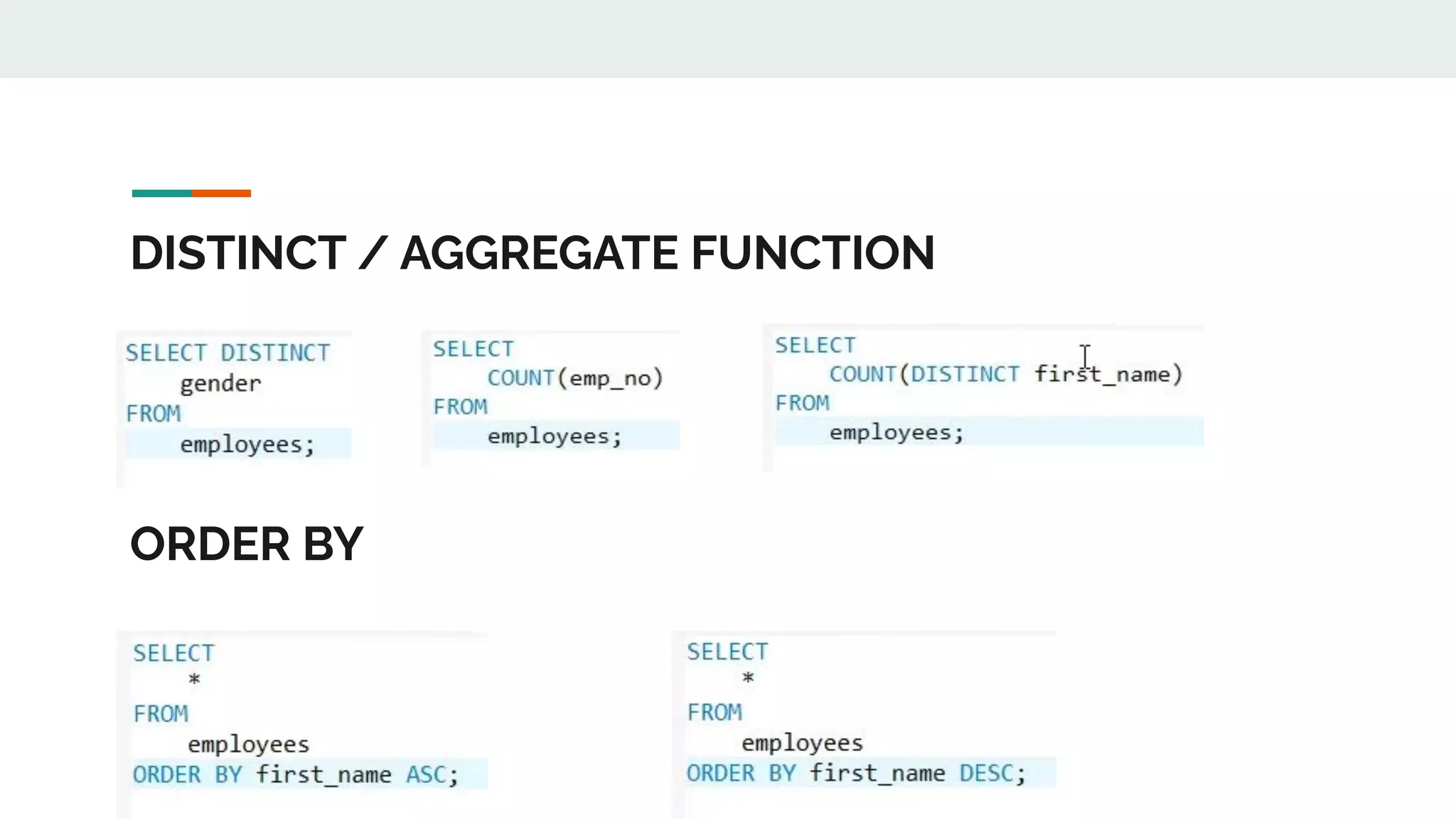
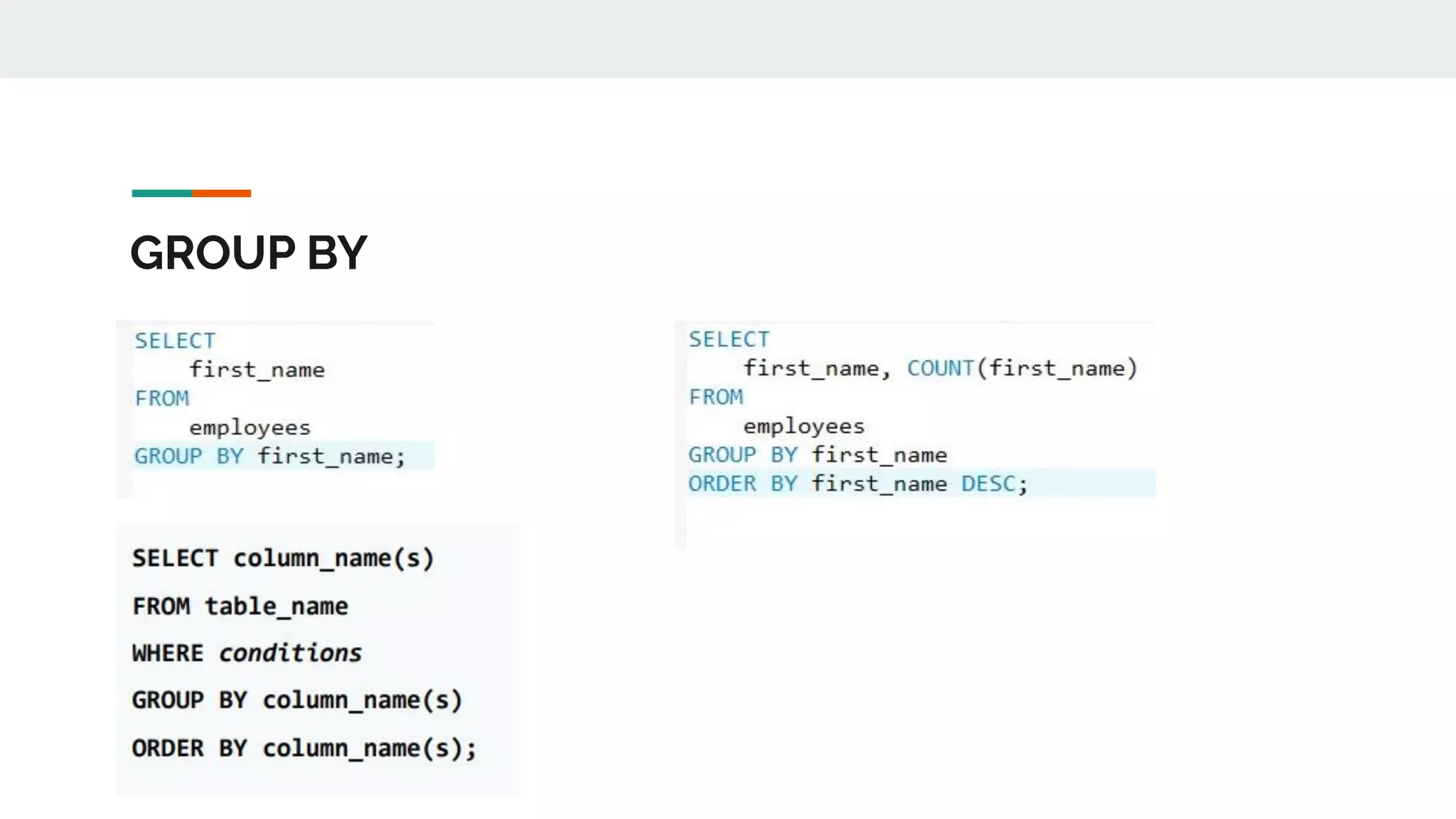
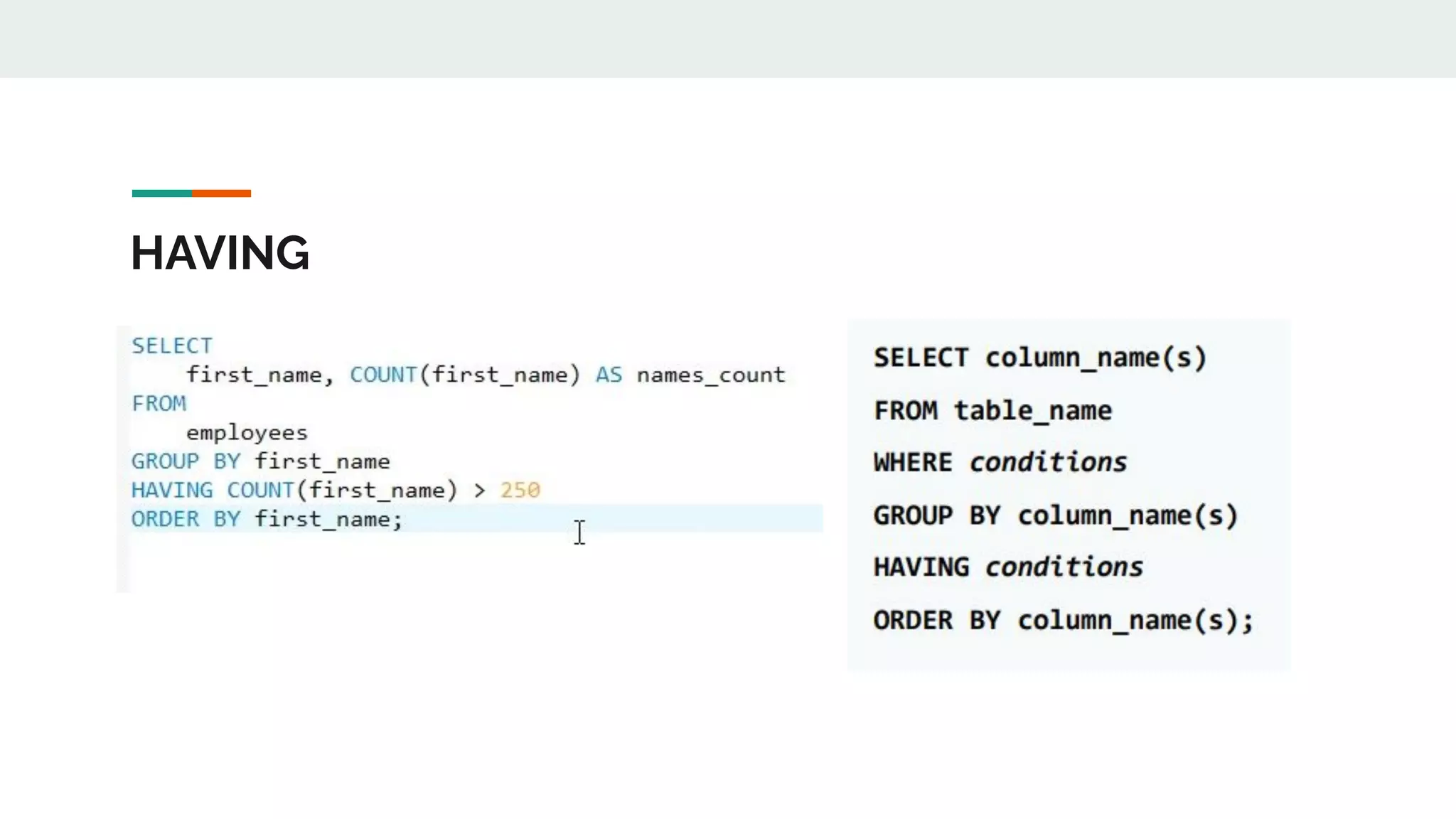
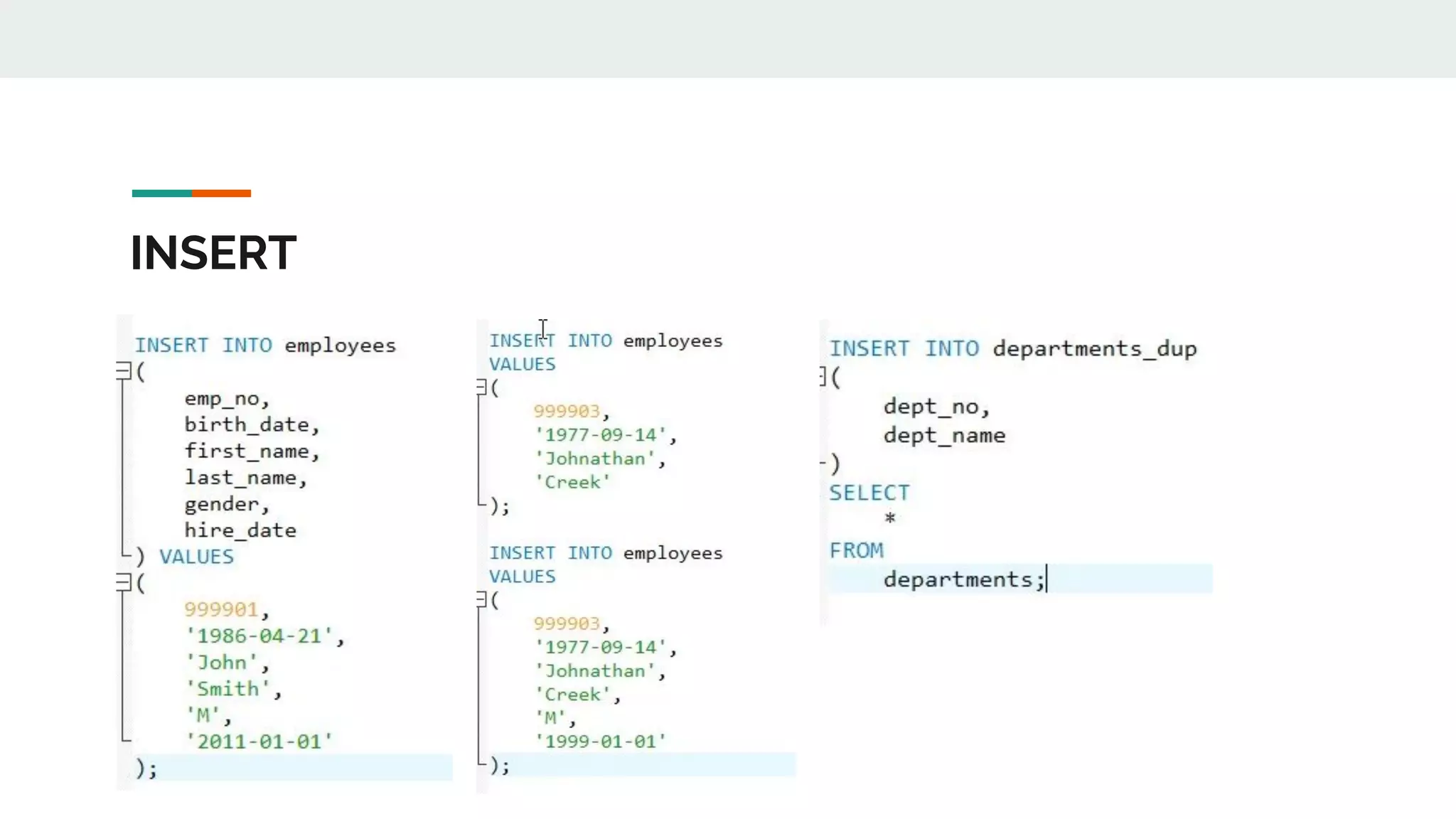
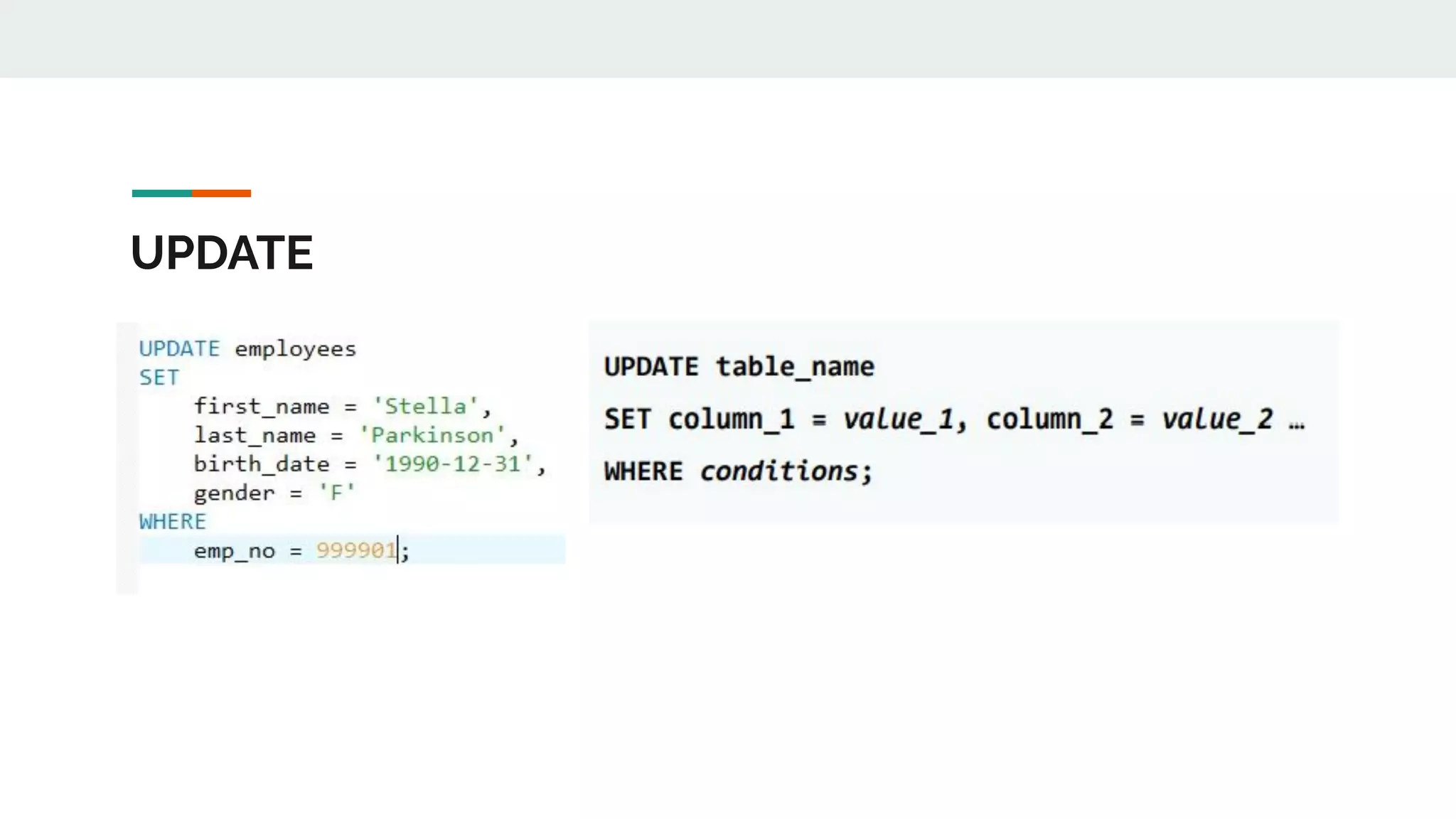
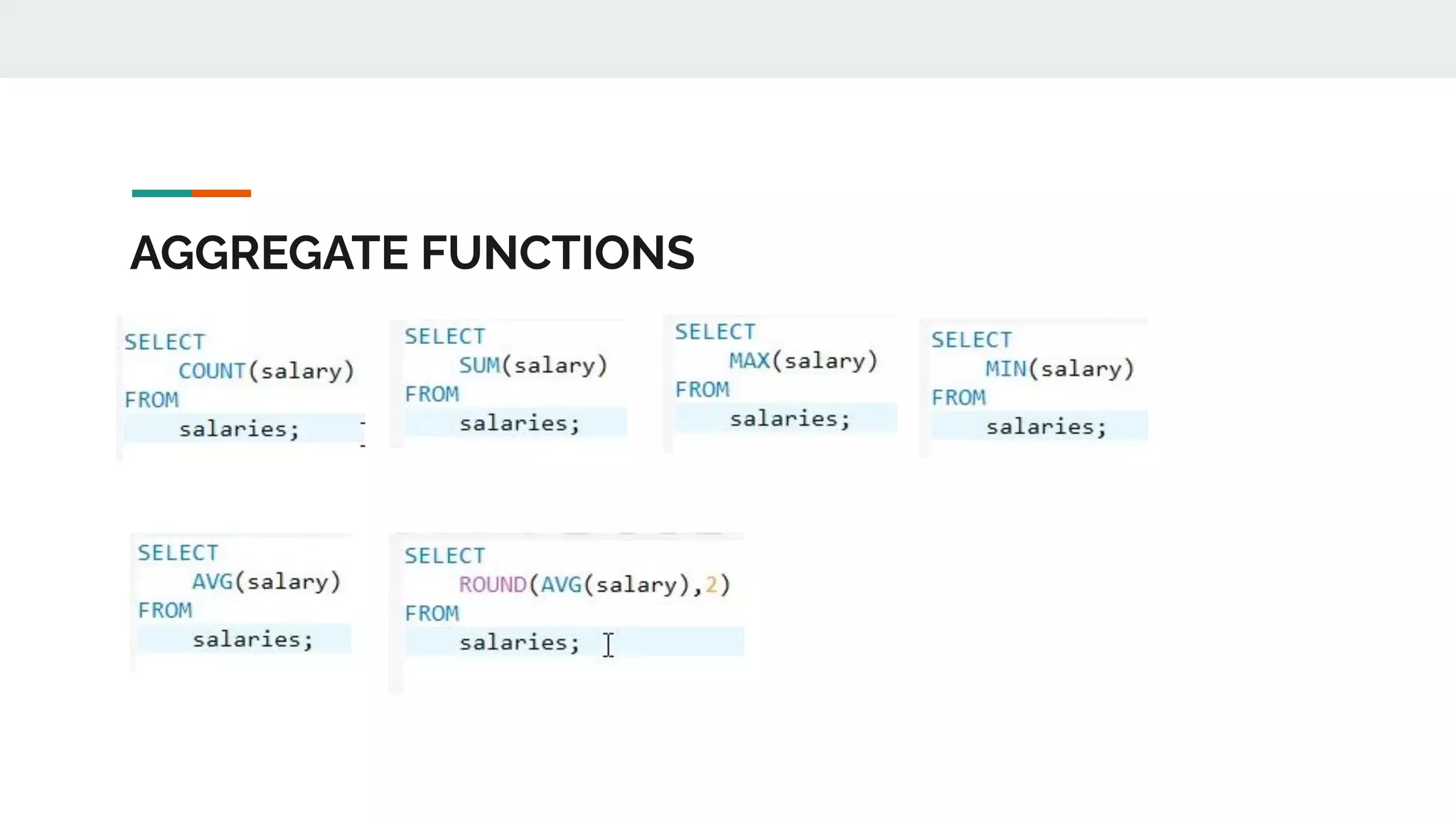
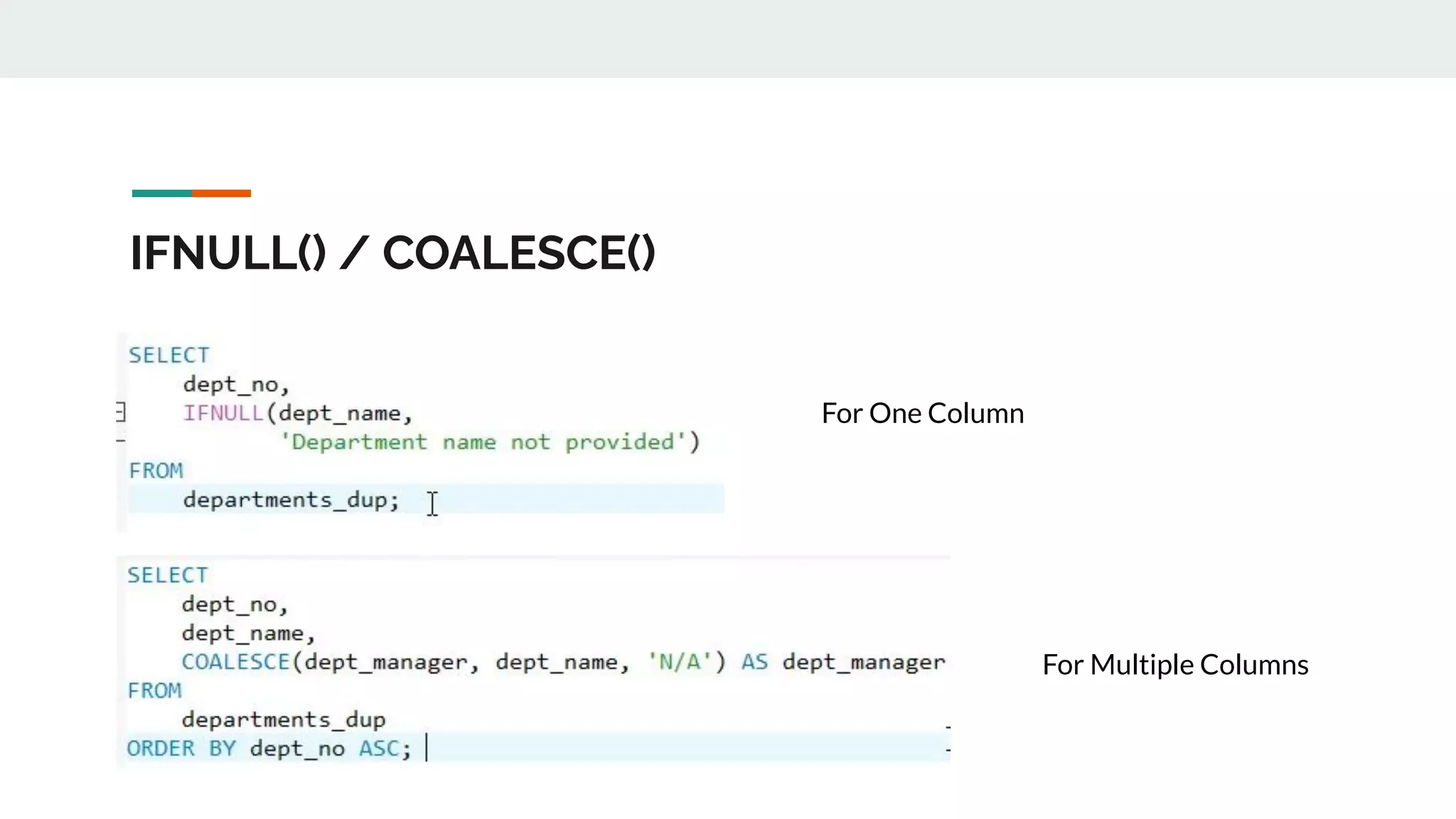
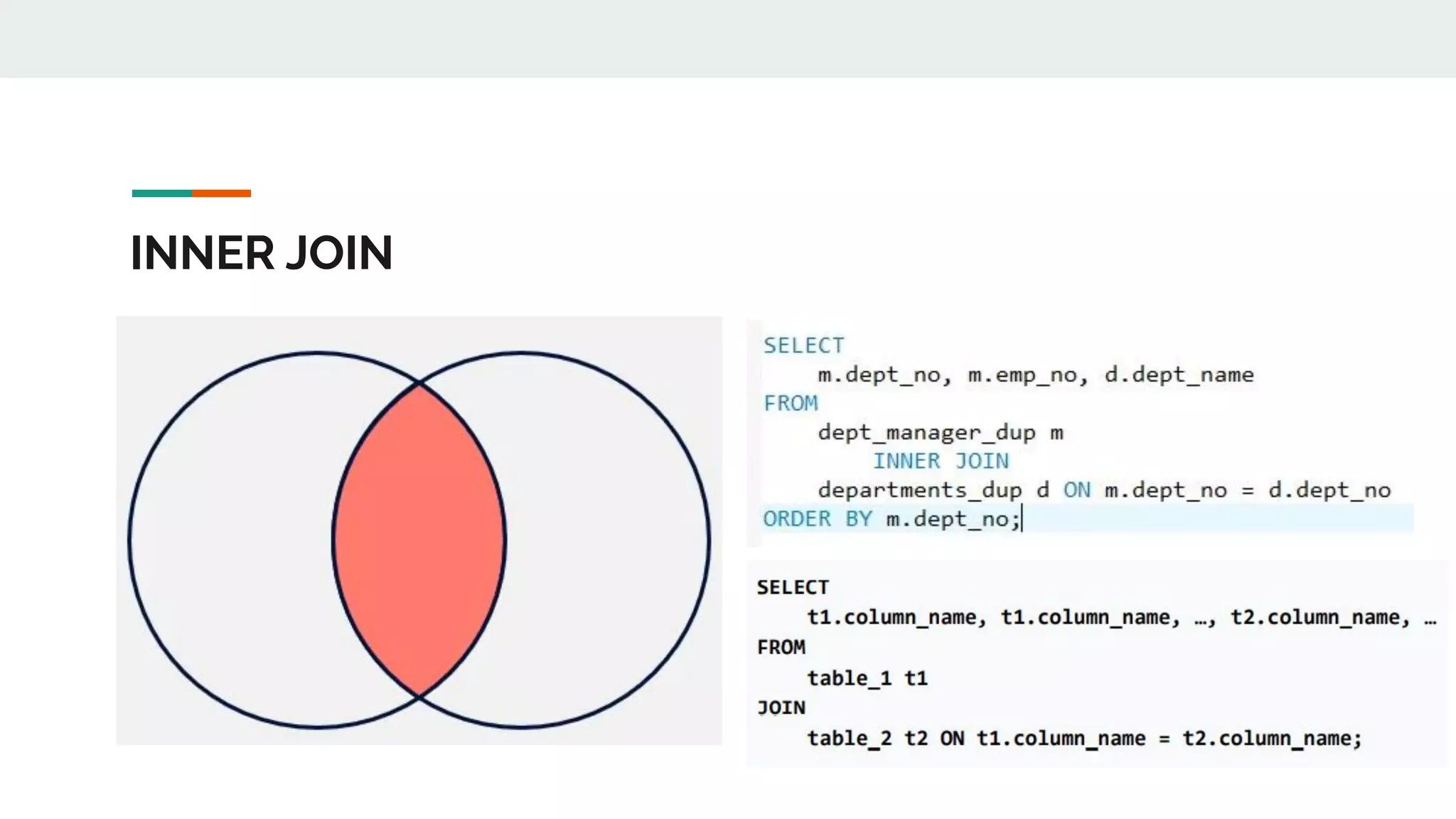
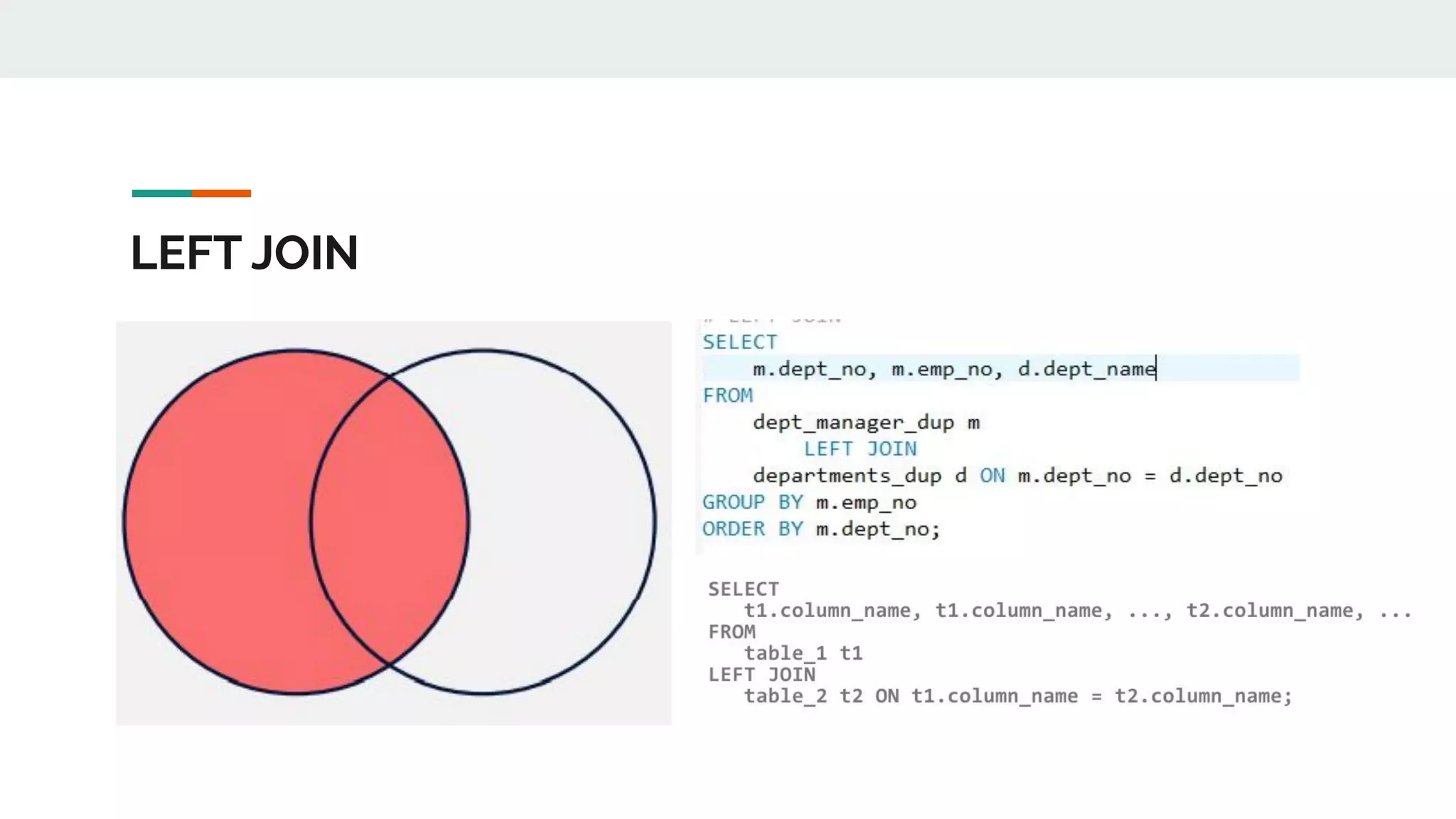
This document provides an overview of MySQL including definitions of database, data definition language, data manipulation language, data control language, transaction control language, data types, table creation, constraints, joins, and views. It defines what a database is and explains DDL for defining structures, DML for manipulating data, DCL for controlling access, and TCL for transactions. It also covers data types, primary keys, foreign keys, relationships, and SQL syntax.