This document provides an overview of nested queries in SQL, including examples and explanations of:
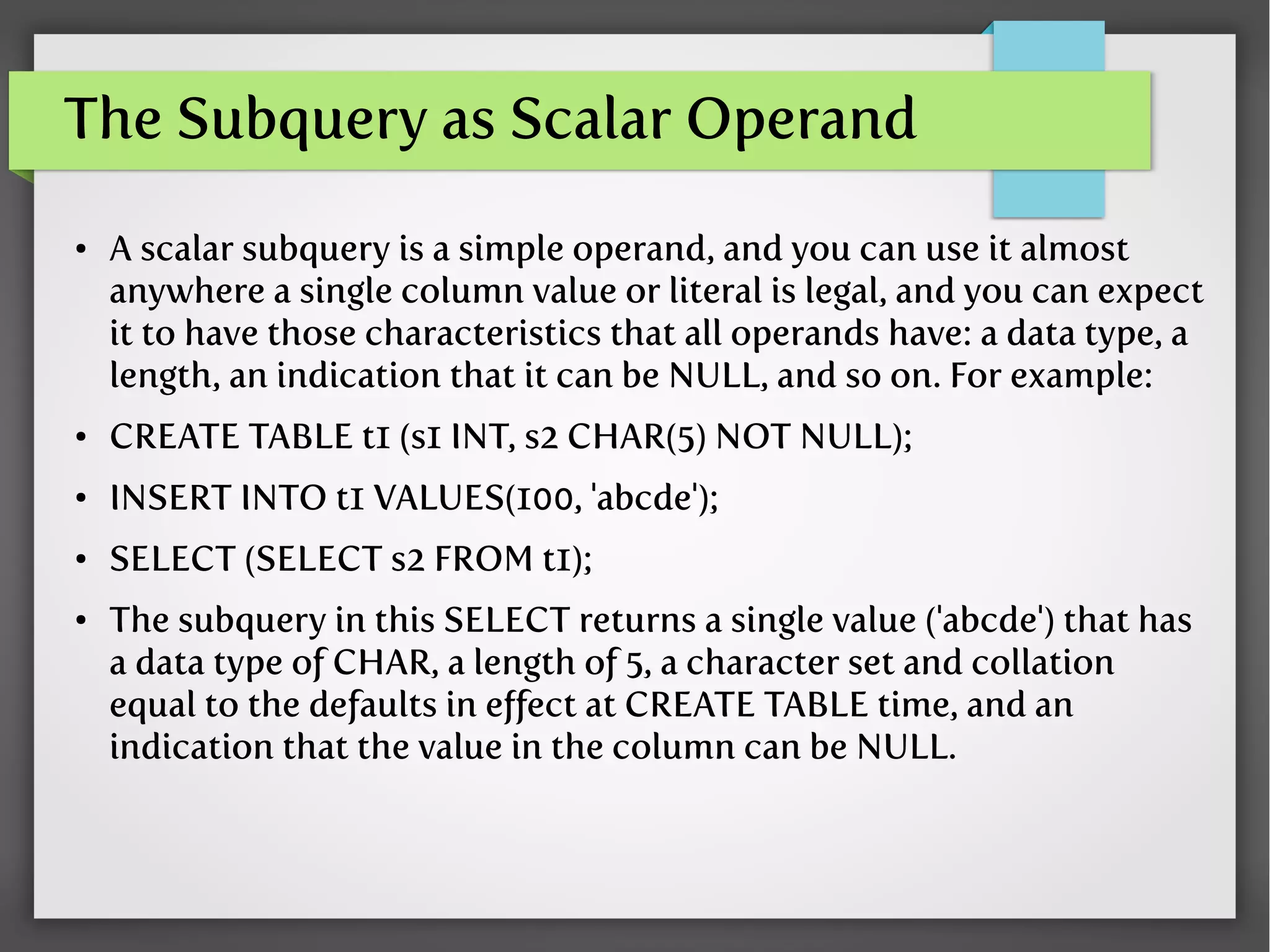
- What nested queries are and how they are structured using subqueries
- How to write nested queries using operators like IN, EXISTS, and correlated subqueries
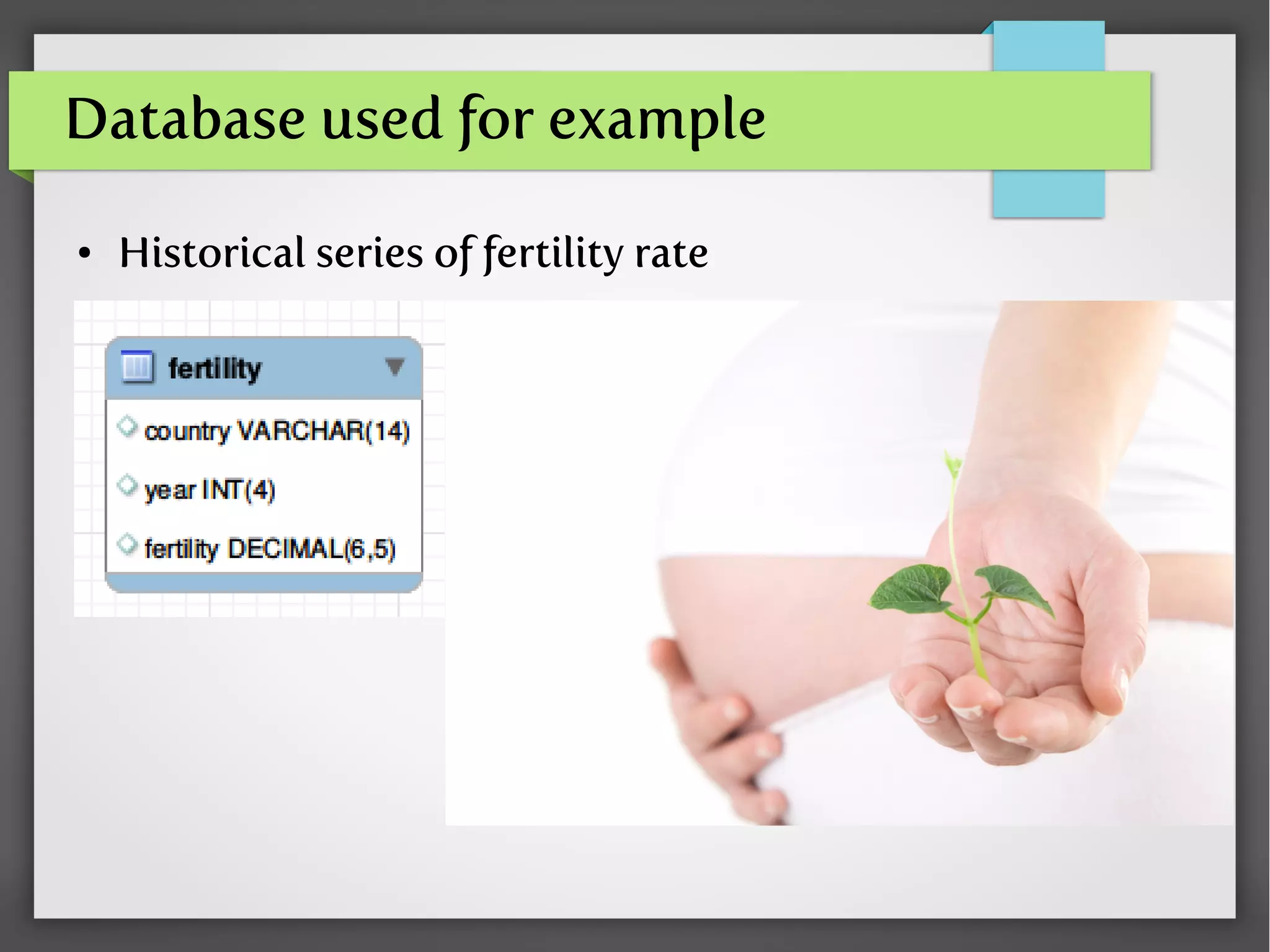
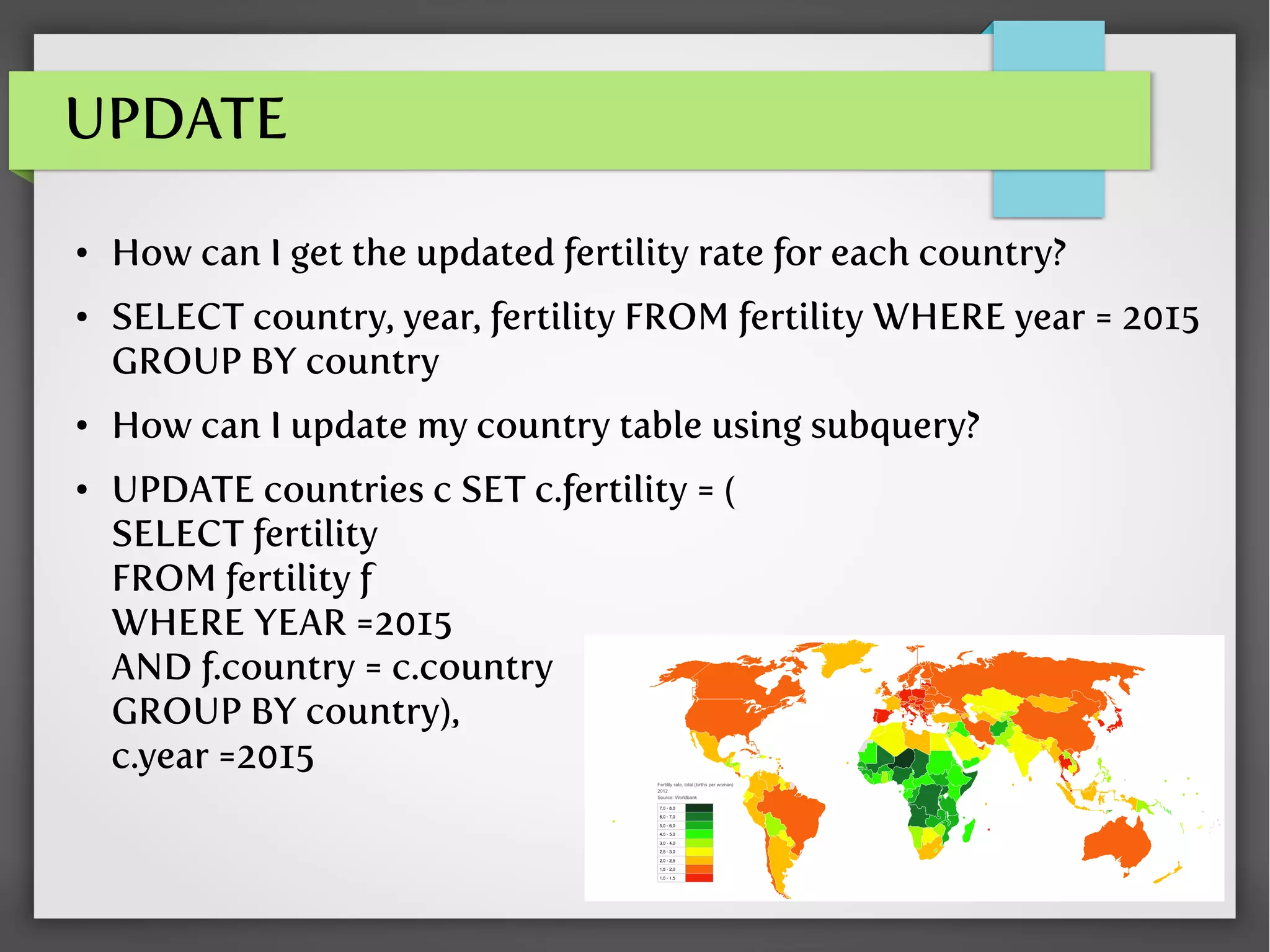
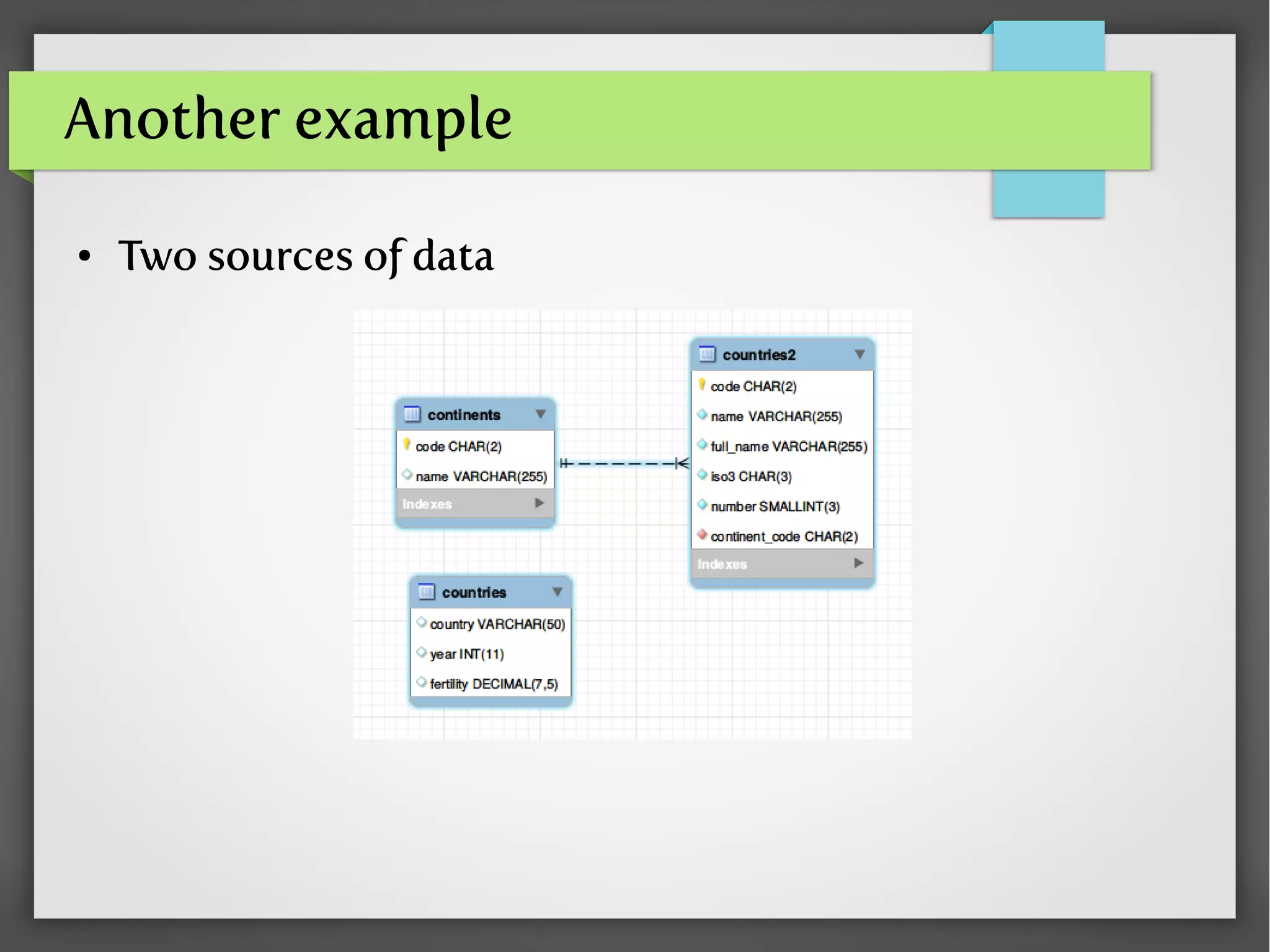
- Examples of nested queries for SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and the FROM clause using data on country fertility rates
- Advantages of nested queries like readability and ability to isolate parts of statements




















![Subqueries in the FROM Clause
● SELECT ... FROM (subquery) [AS] name …
● Average of fertility for each continent using historical average
for each country
●
SELECT continent, AVG(avg_fertility)
FROM
(SELECT AVG(fertility) as avg_fertility, country
FROM fertility f
WHERE year BETWEEN 2000 AND 2015
GROUP BY country) AS avgfert
JOIN countries c ON (c.country = avgfert.country)
GROUP BY continent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nestedqueries-lecture-fcosta-160520124012/75/Nested-Queries-Lecture-26-2048.jpg)