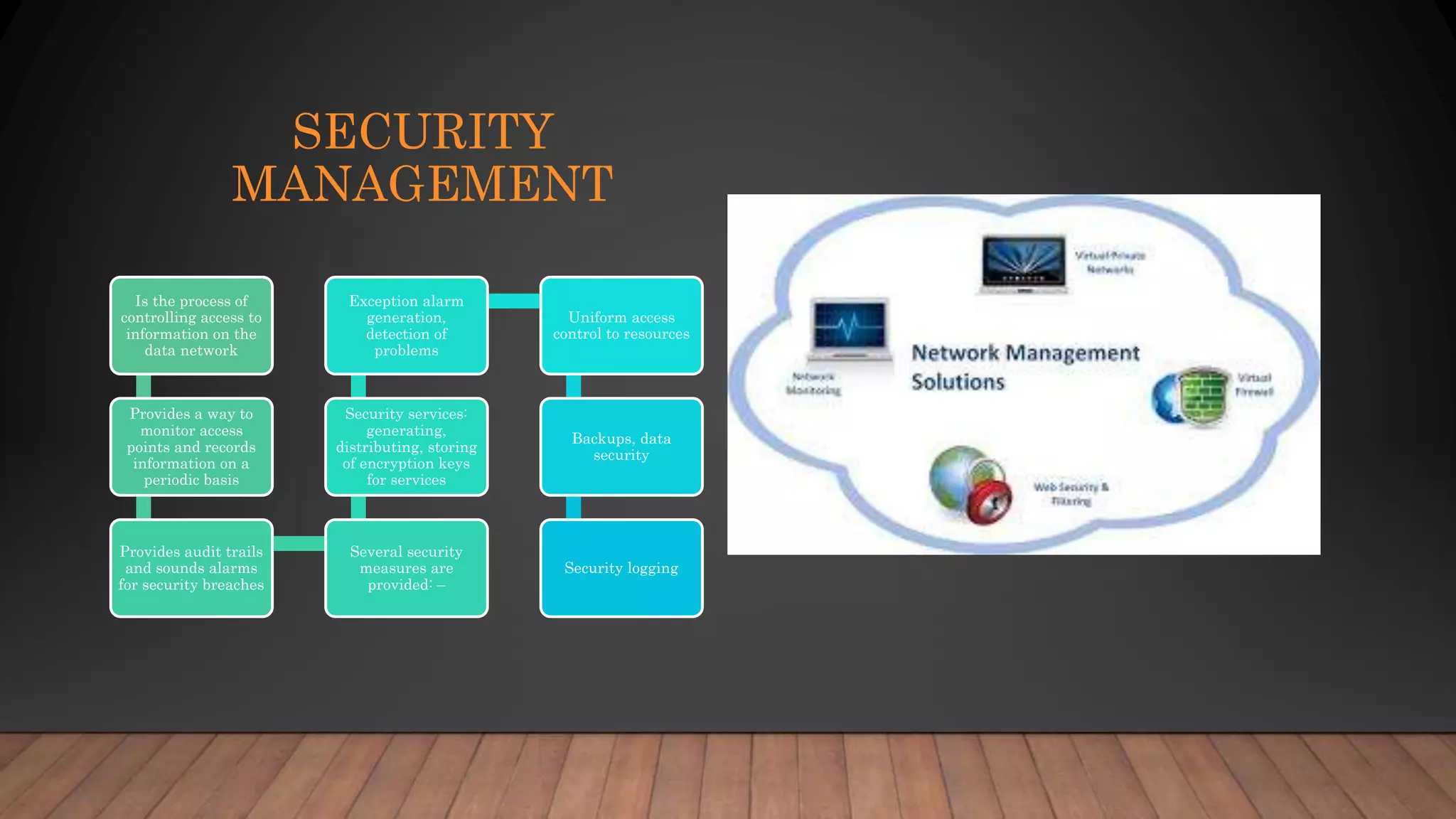
Network management is the process of overseeing a data network to maximize efficiency and productivity, addressing complexity while ensuring optimal data flow. It encompasses five functional areas: fault management, configuration management, security management, performance management, and accounting management, each focusing on different aspects of network control. Key activities include troubleshooting, device configuration, access control, performance measurement, and resource tracking.