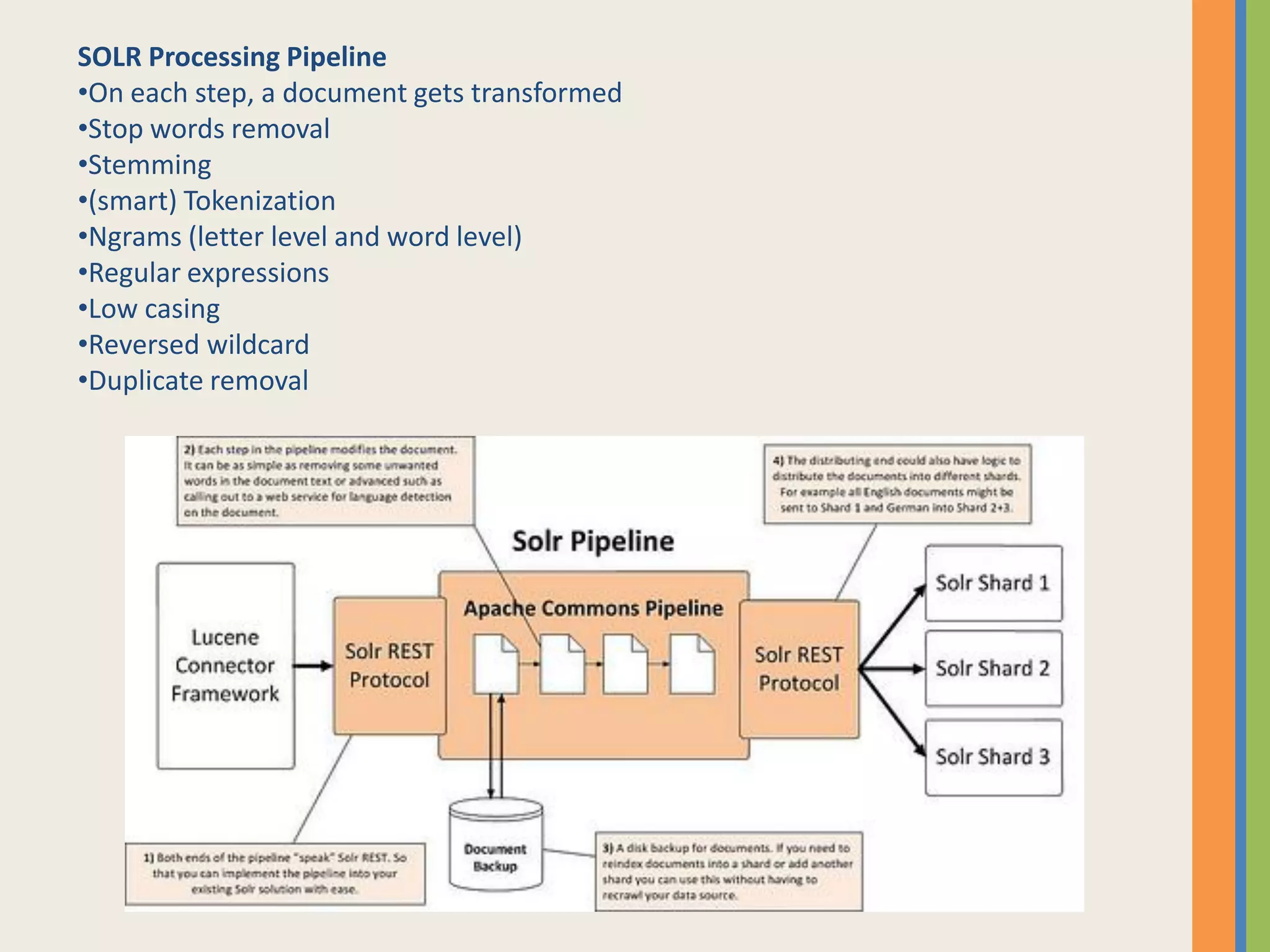
The document discusses NoSQL databases, explaining their origin, key characteristics, and various types, including key-value stores and document databases. It highlights major players in the NoSQL space like Amazon Dynamo and Google Bigtable, and distinguishes NoSQL as a complement to SQL rather than a replacement. Additionally, it provides an overview of Apache Solr, its features for enterprise search, and its integration with big data technologies like Hadoop.
















![References
[1] Tim Perdue: NoSQL: An Overview of NoSQL Databases, About.com Guide
Sarah Pidcock (2011-01-31). http://bit.ly/fFQOYI
[2] "Dynamo: Amazon’s Highly Available Key-value Store".
http://www.cs.uwaterloo.ca/:
WATERLOO. p. 2/22. Retrieved 2011-04-05.
"Dynamo: a highly available and scalable distributed data store"
[3] http://cassandra.apache.org/
[4] http://labs.google.com/papers/bigtable.html
[5] http://aws.amazon.com/ (look for SimpleDB)
[6] http://couchdb.apache.org/
[7] http://neo4j.org/
[8] Information Week: Surprise: 44% Of Business IT Pros Never Heard Of NoSQL
http://bit.ly/go5ios
[9] http://drupal.org/
[10] Mark Miller: Scaling Lucene and Solr // Lucid Imagination
[11] http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SpatialSearch
[12] http://dmitrykan.blogspot.com/2011/01/solr-speed-up-batch-posting.html
[13] http://wiki.apache.org/solr/AnalyzersTokenizersTokenFilters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachesolrapachehadoopdmitrykan-110423092537-phpapp02/75/NoSQL-Apache-SOLR-and-Apache-Hadoop-22-2048.jpg)
![References
[14] Using Nutch with SOLR,
http://www.lucidimagination.com/blog/2009/03/09/nutch-solr/
[15] http://tika.apache.org/
[16] http://lucene.apache.org/solr/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachesolrapachehadoopdmitrykan-110423092537-phpapp02/75/NoSQL-Apache-SOLR-and-Apache-Hadoop-23-2048.jpg)