This document provides a guide for .NET or Java developers transitioning to Objective-C, addressing common concerns such as memory management, syntax, and community perception. It covers key concepts including object and class handling, properties, methods, delegates, categories, and protocols, highlighting similarities and differences with .NET. The conclusion encourages developers to overcome their fears of Objective-C based on outdated perceptions.




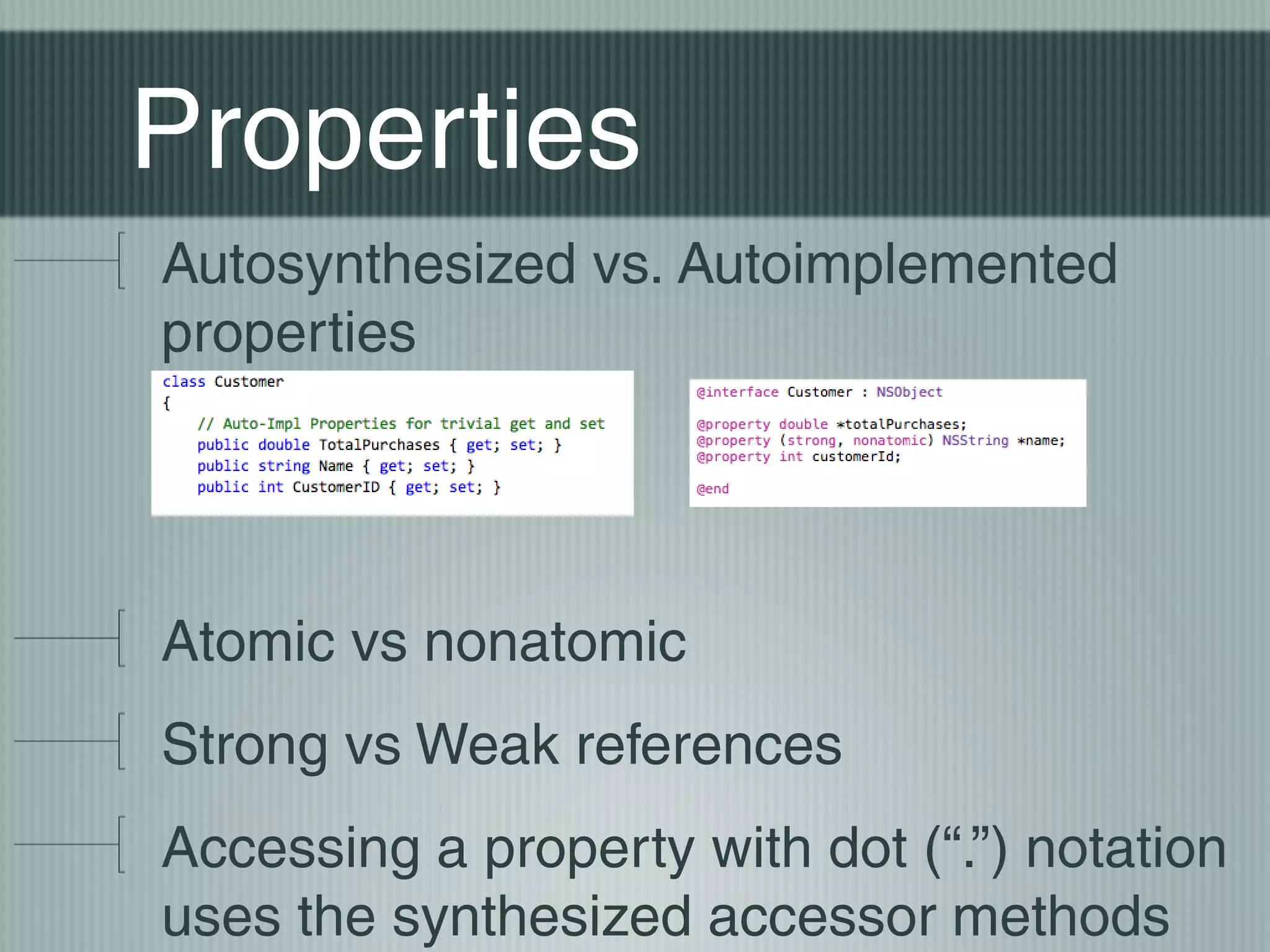

![Why []?
C#
Objective-c](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectivecforthenetdeveloper-131025103112-phpapp02/75/Think-Different-Objective-C-for-the-NET-developer-7-2048.jpg)











