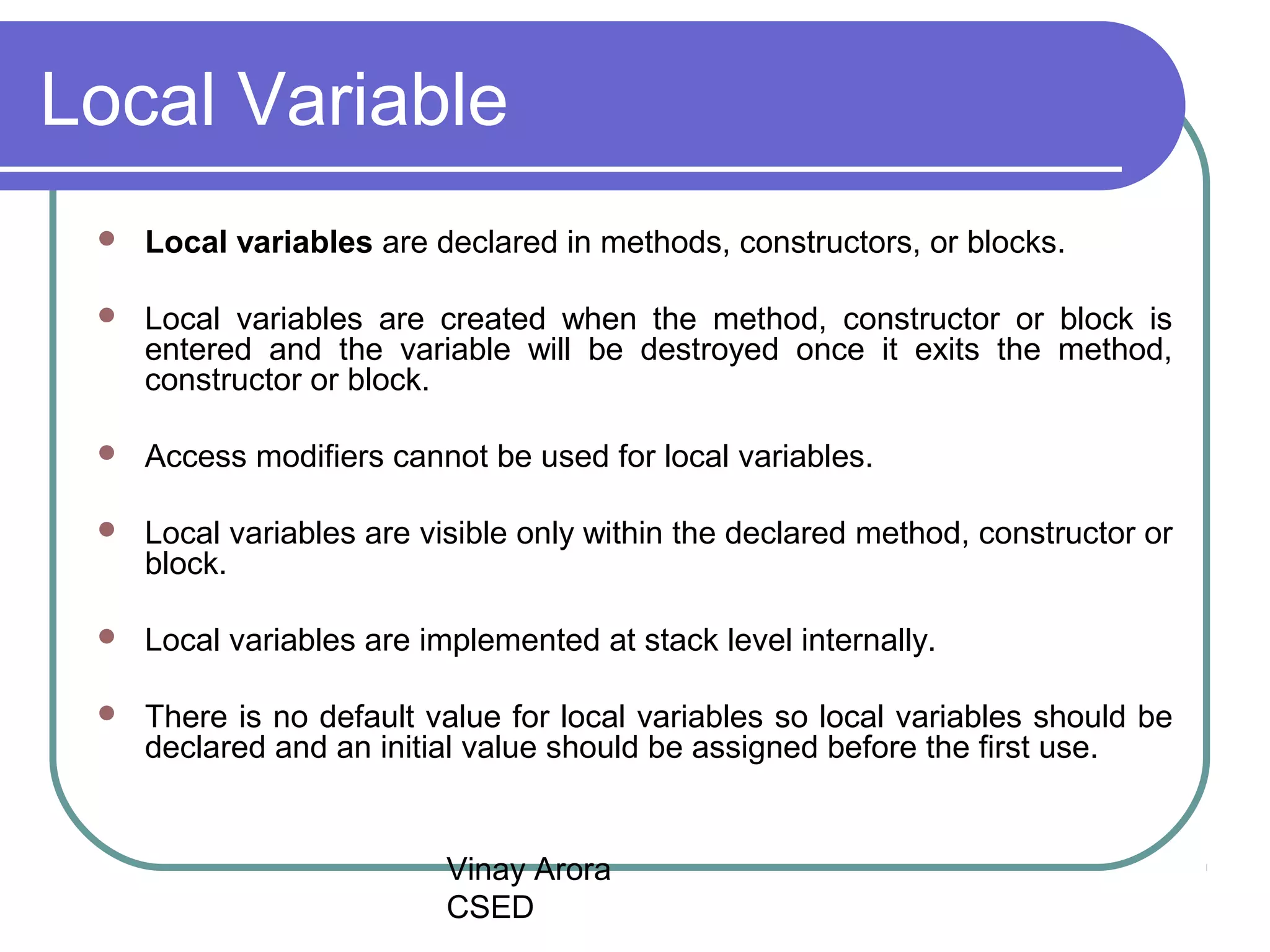
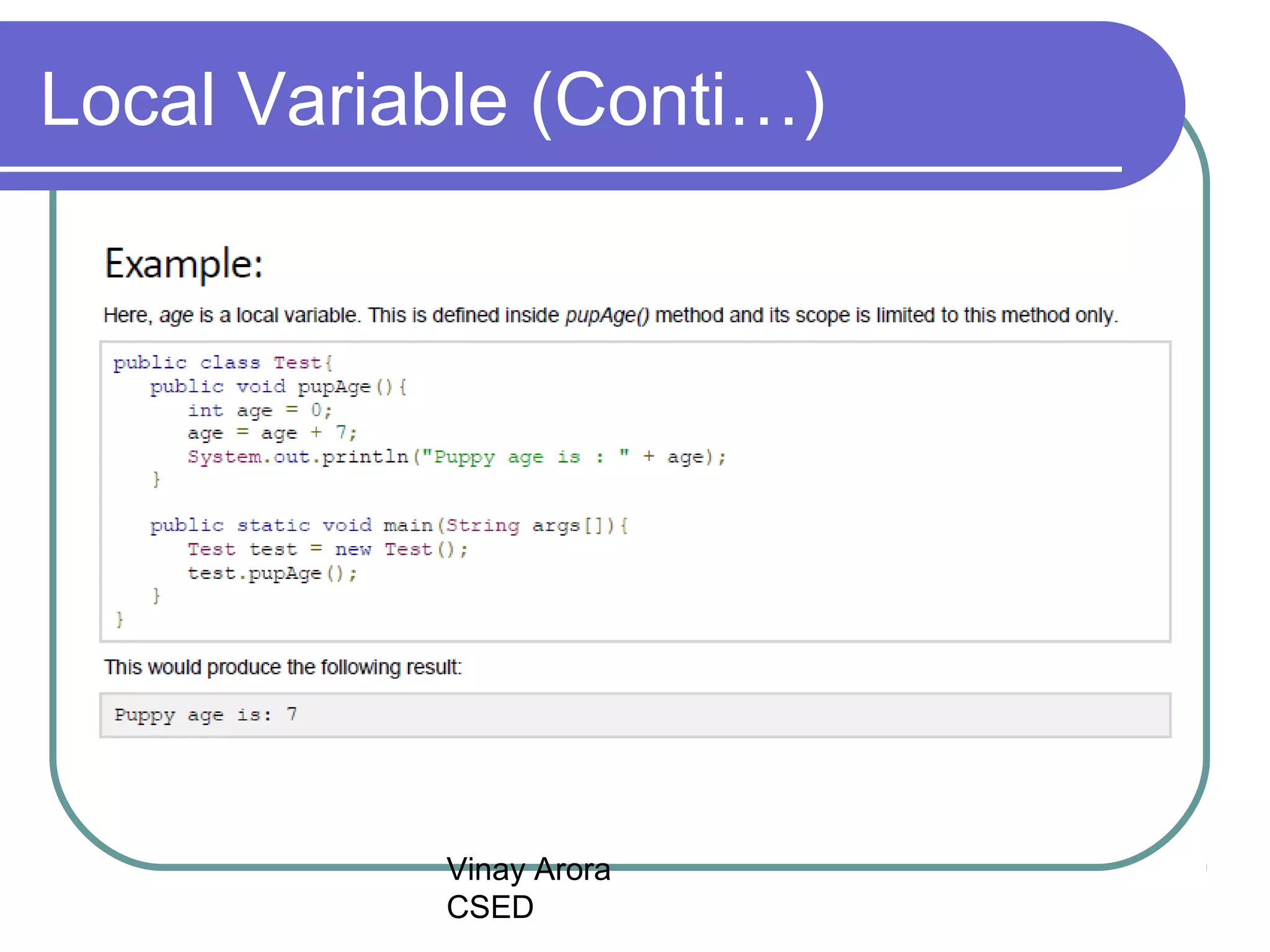
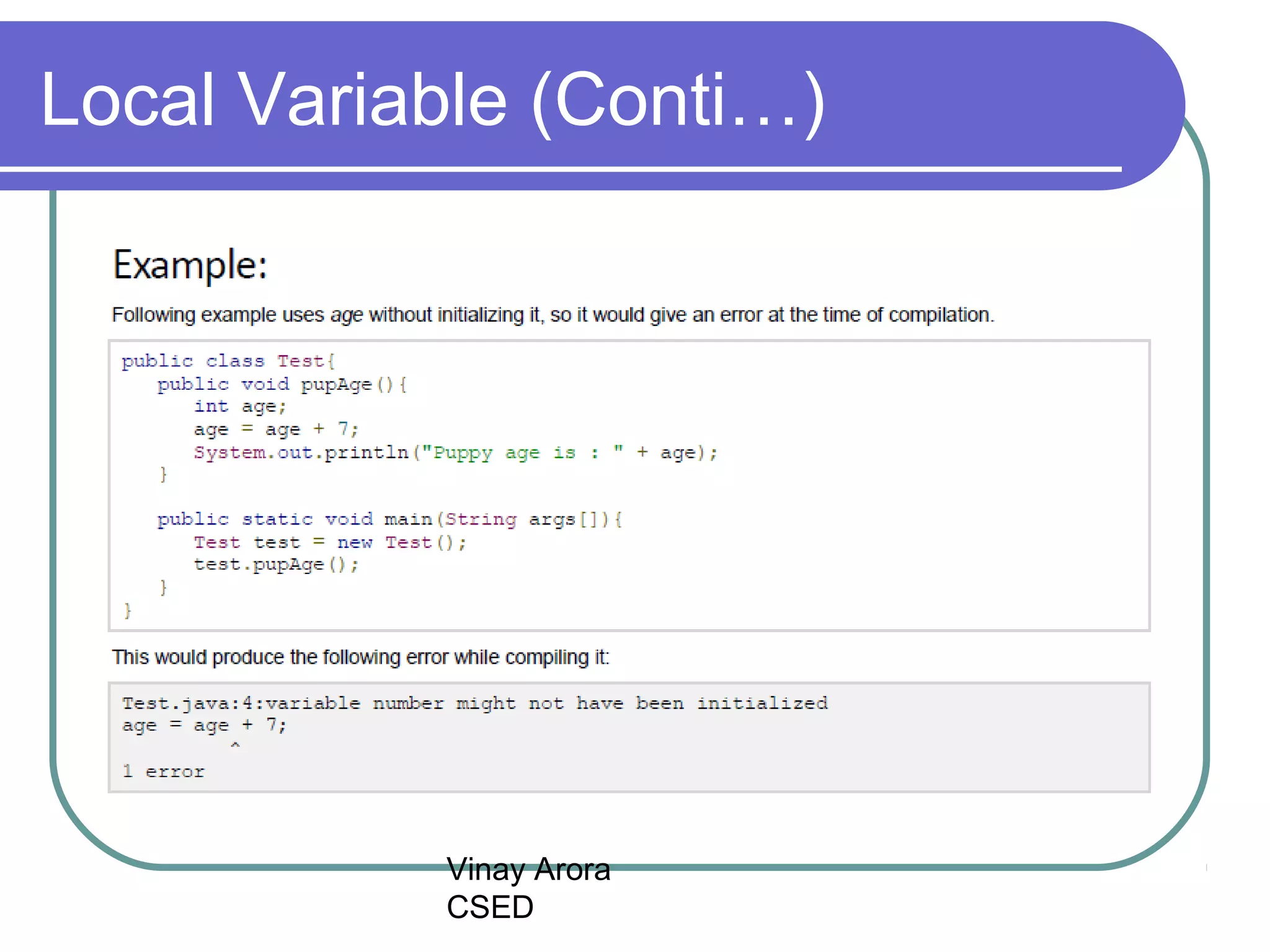
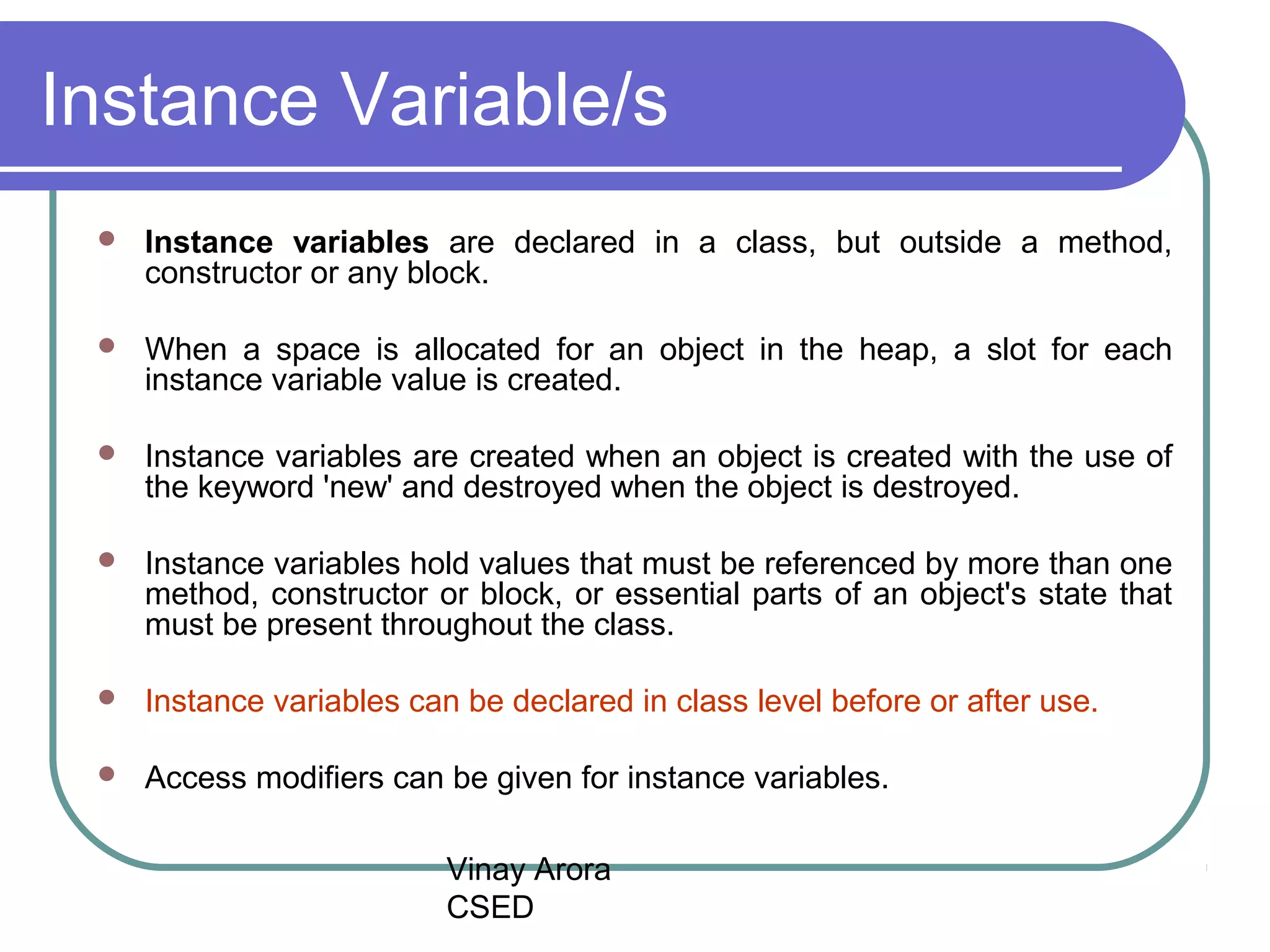
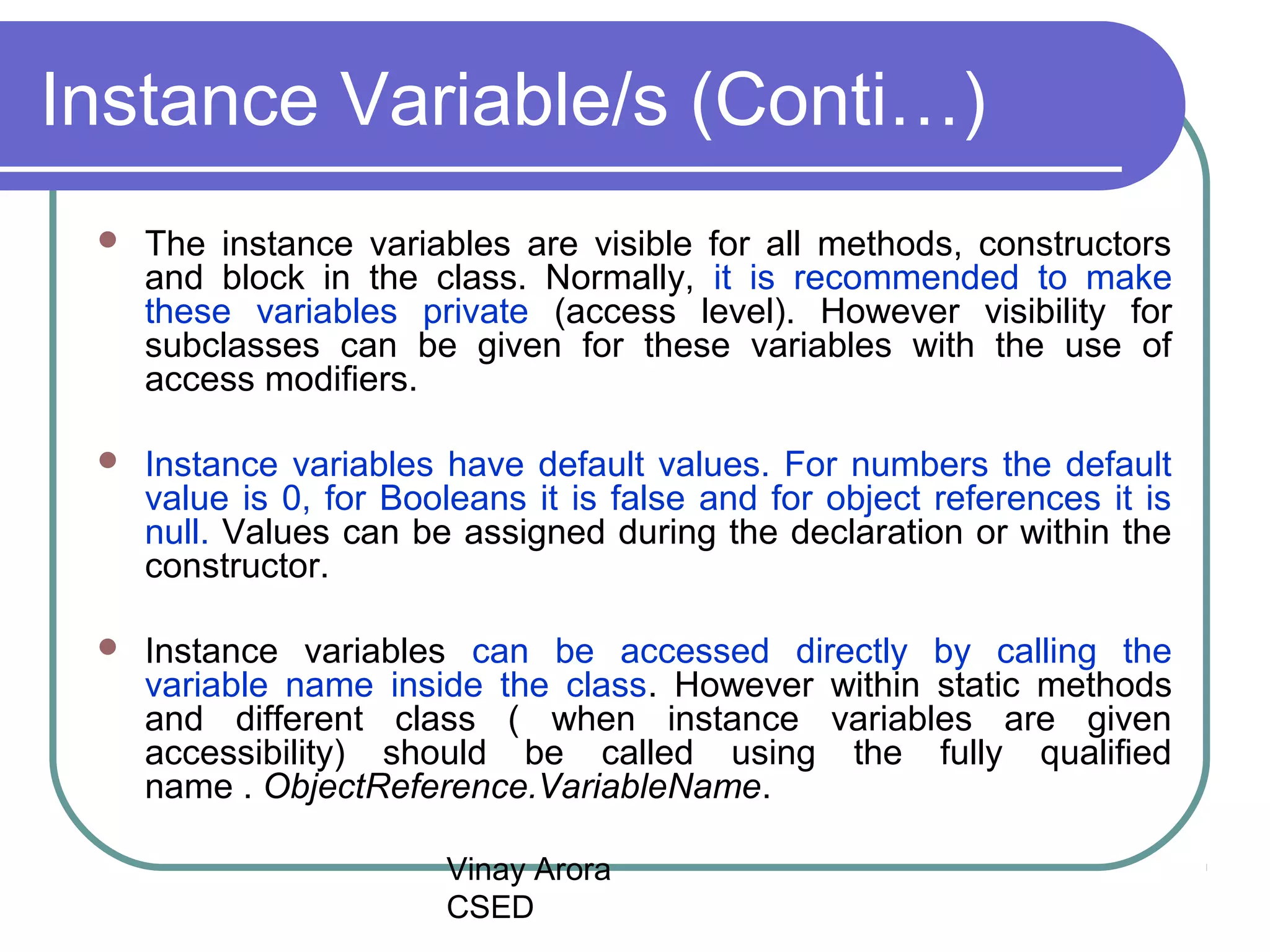
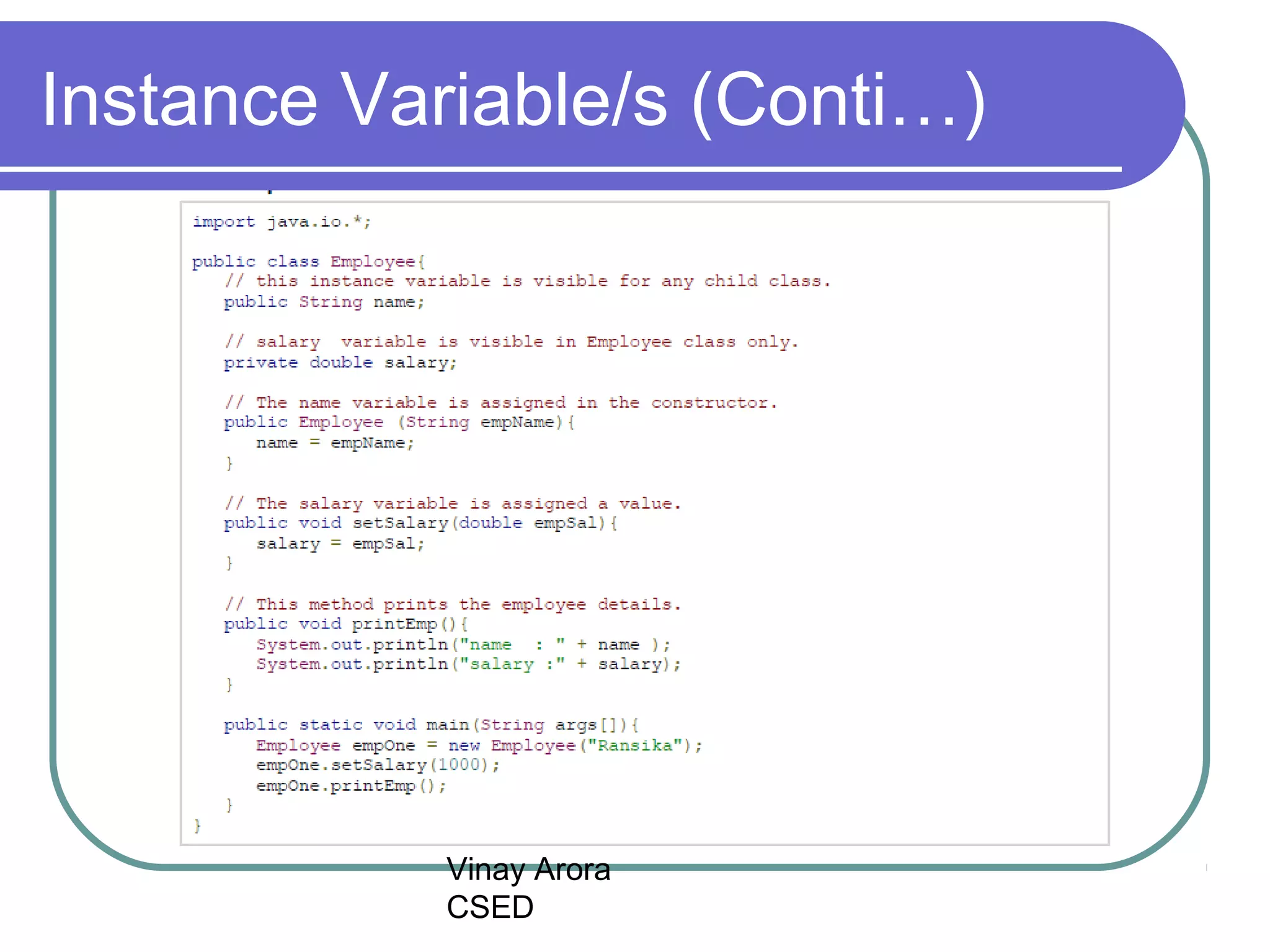
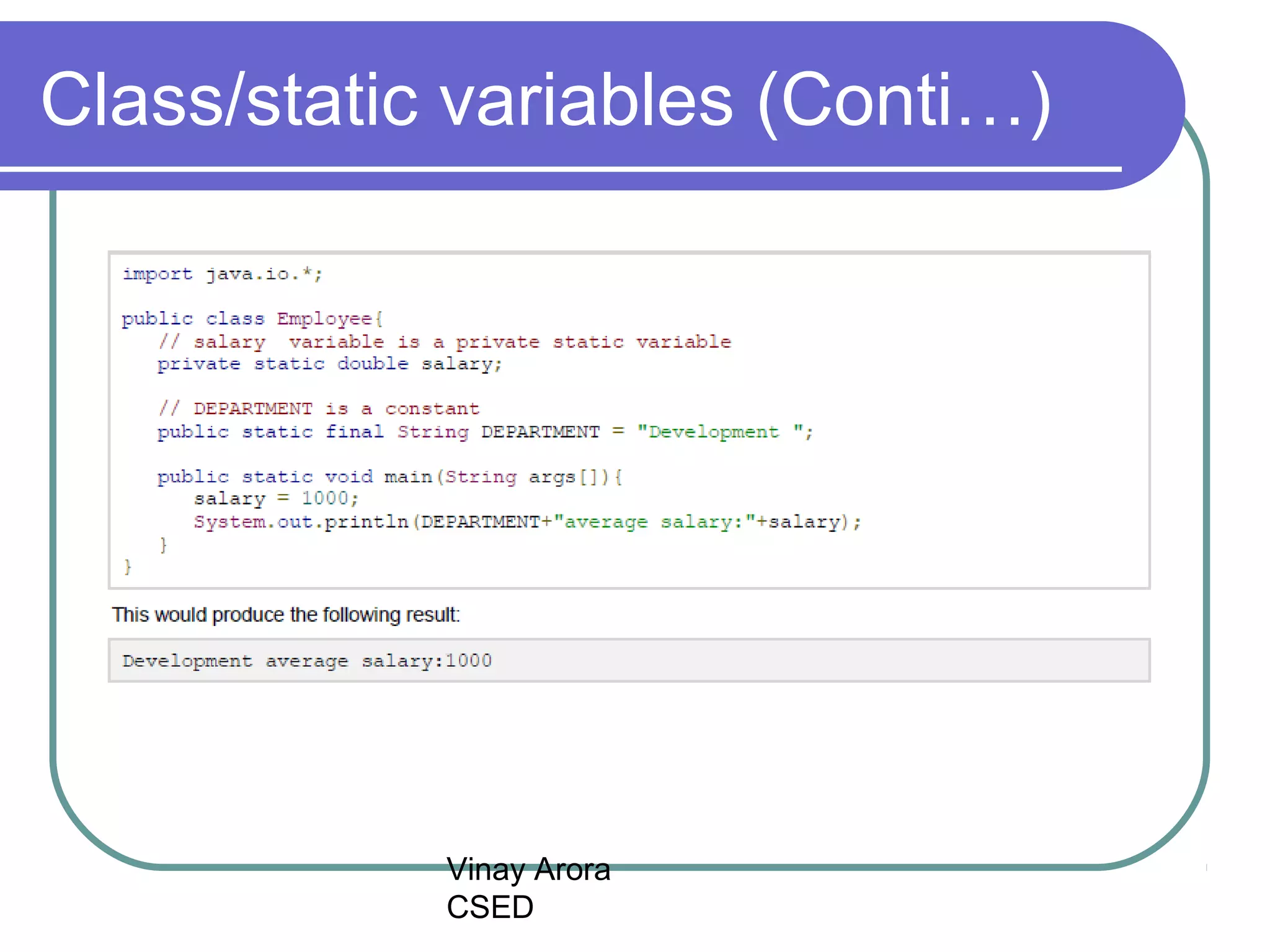
There are three types of variables in Java: local variables, instance variables, and class/static variables. Local variables are declared within methods, constructors, or blocks and exist only within their scope. Instance variables are declared within a class but outside of methods and constructors, and each object instance has its own copy. Class/static variables are declared with the static keyword, and there is only one copy per class regardless of instances. Each variable type has different scopes, lifetimes, and ways of accessing them.