The document discusses different approaches to testing in Odoo including:
1. TransactionCase and SavepointCase - TransactionCase runs each test in its own transaction while SavepointCase runs all tests in a single transaction using savepoints.
2. HttpCase and HttpSavepointCase - Launch the HTTP server and a browser to run JavaScript tests on the client-side form.
3. Server-side forms - A Python implementation of a form to test record creation and editing like a user.
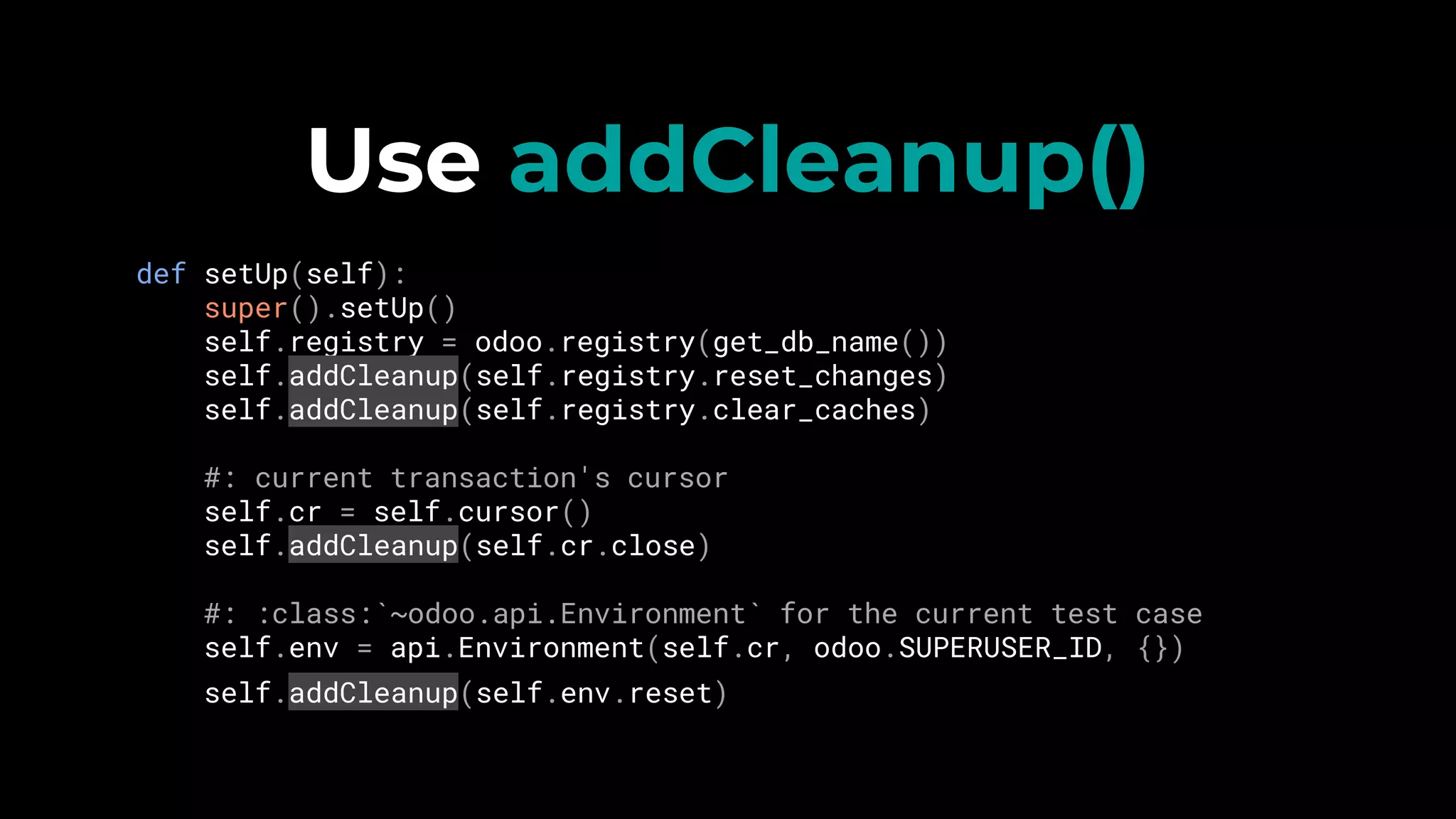
4. Use addCleanup() to reset changes, clear caches, and close cursors after each test.
5. Use unittest.mock to patch values like dates during tests.








![Server-side form
move_form = Form(self.env['account.move'])
move_form.partner_id = partner
...
with move_form.invoice_line_ids.new() as line_form:
line_form.product_id = product
...
invoice = move_form.save()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/odoostestframeworklearnbestpractices-201102095408/75/Odoo-s-Test-Framework-Learn-Best-Practices-9-2048.jpg)