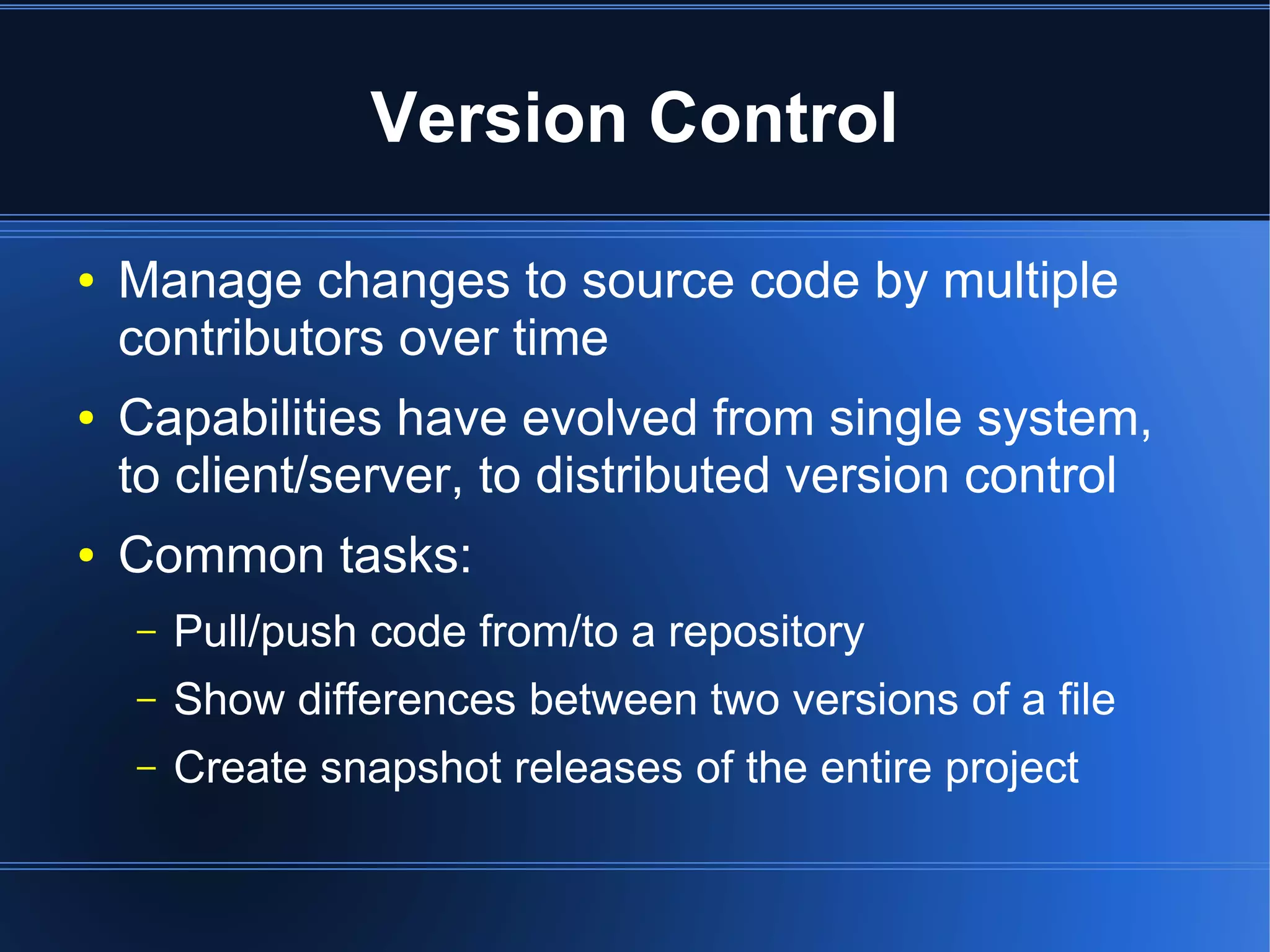
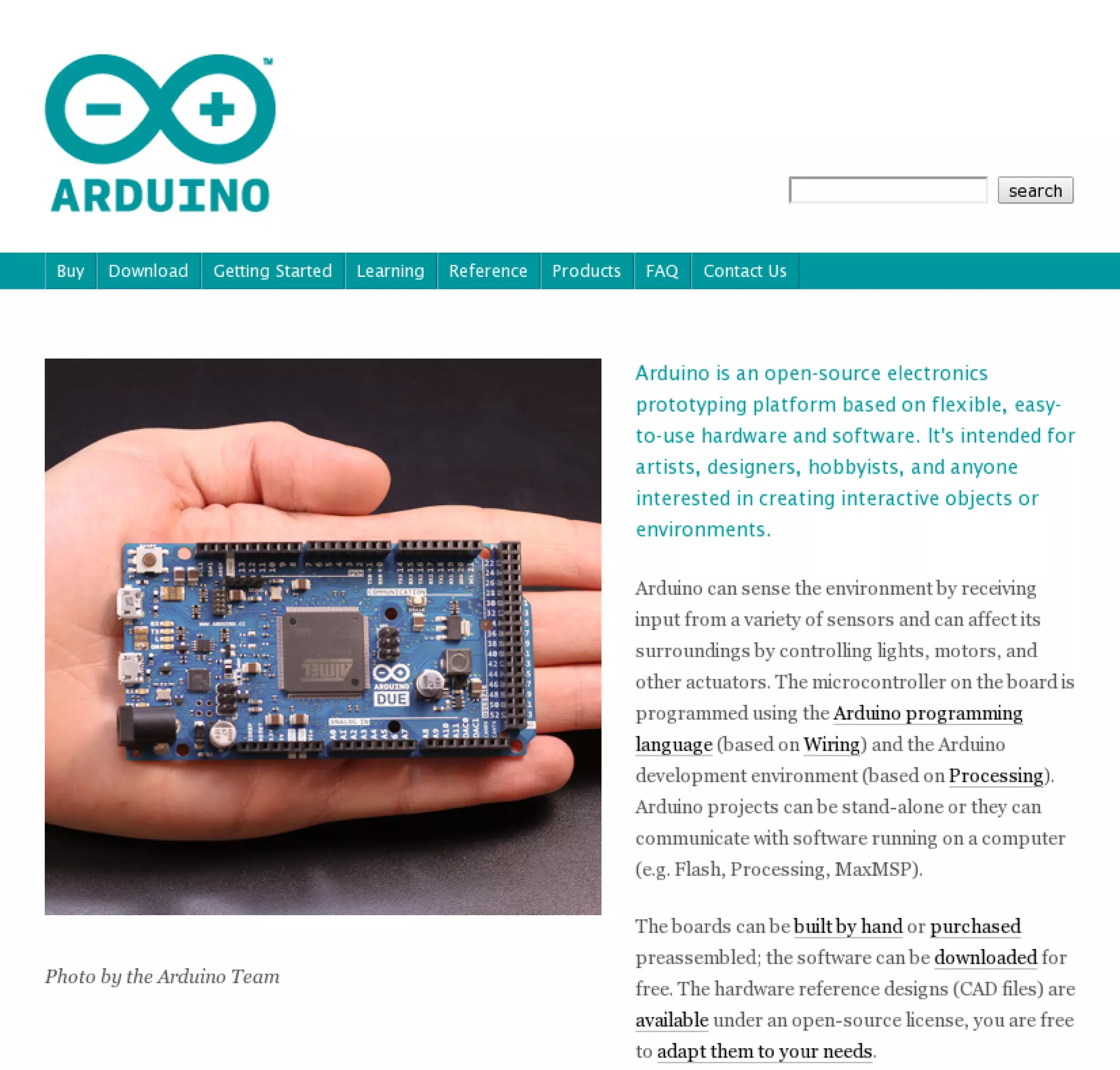
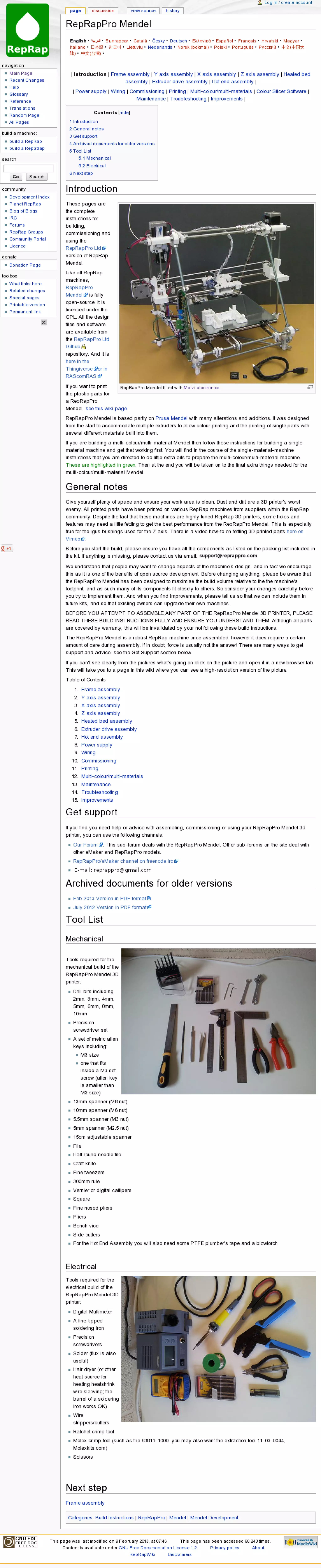
The document provides an overview of open source software, its principles, and how open source projects operate, including the necessary platforms and tools for development. It discusses the motivations for open source collaboration, highlights companies and individuals that contribute to it, and mentions the benefits of using and contributing to open source software. Additionally, it notes various educational resources and government initiatives that promote open source collaboration.