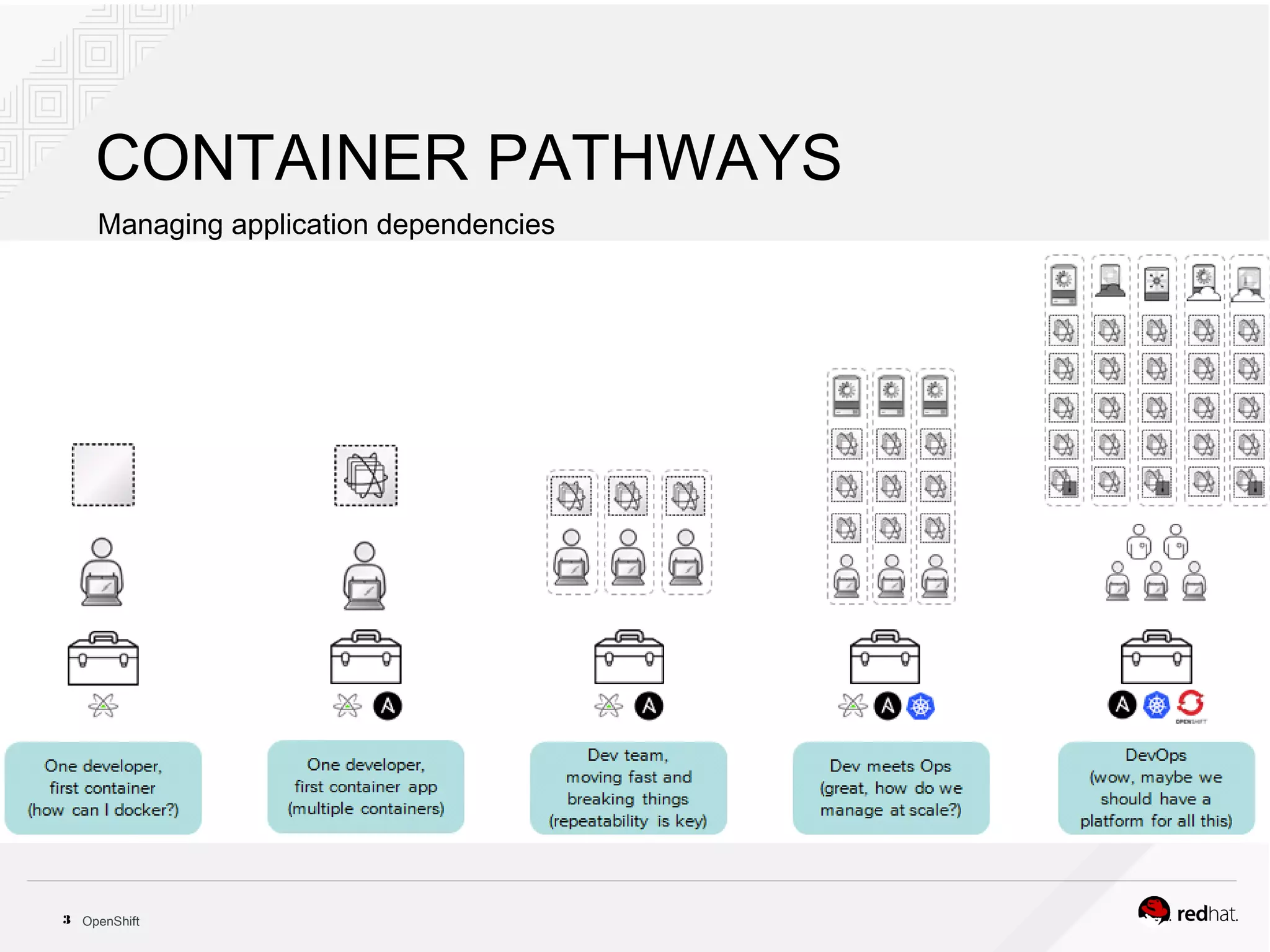
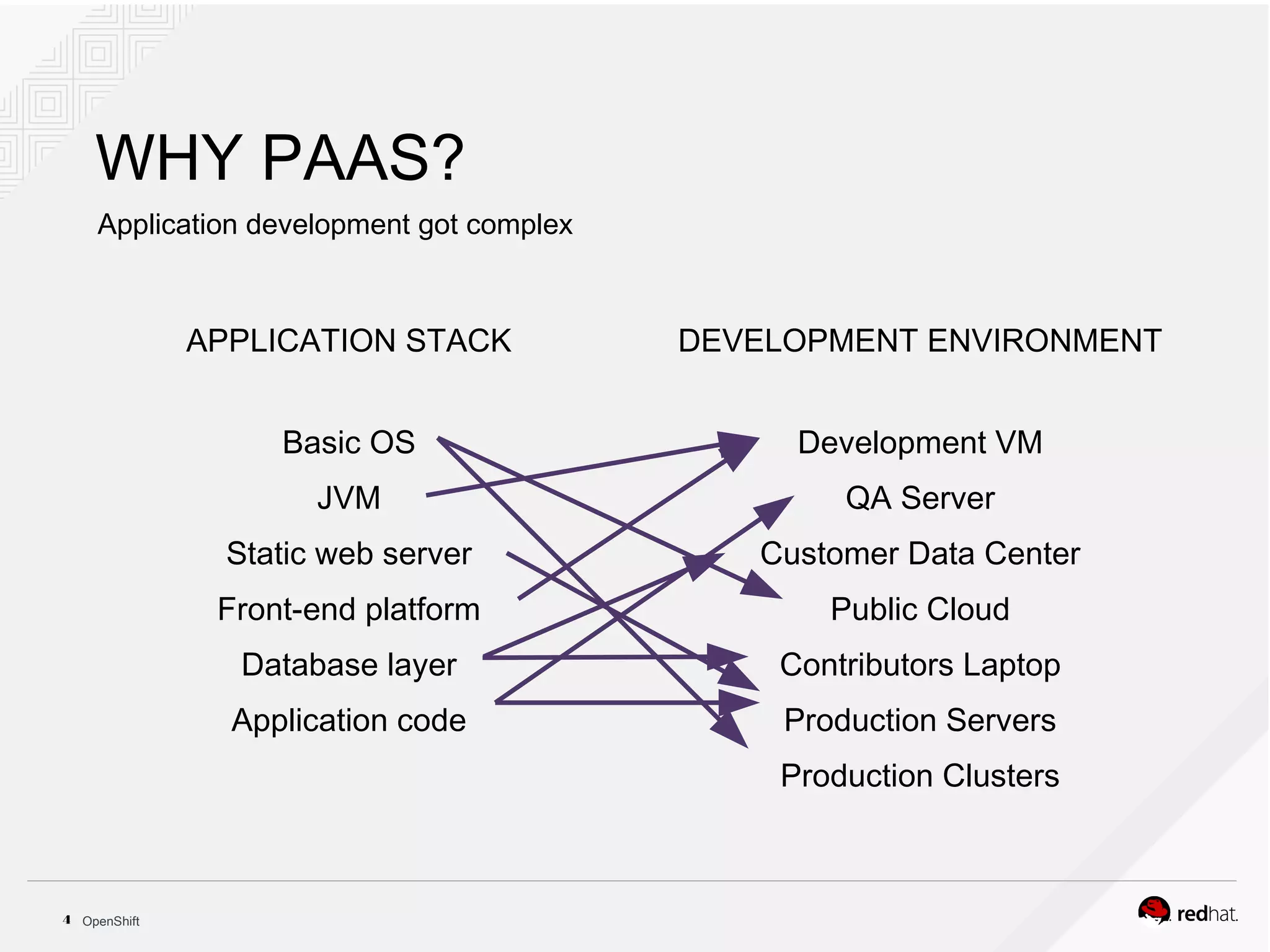
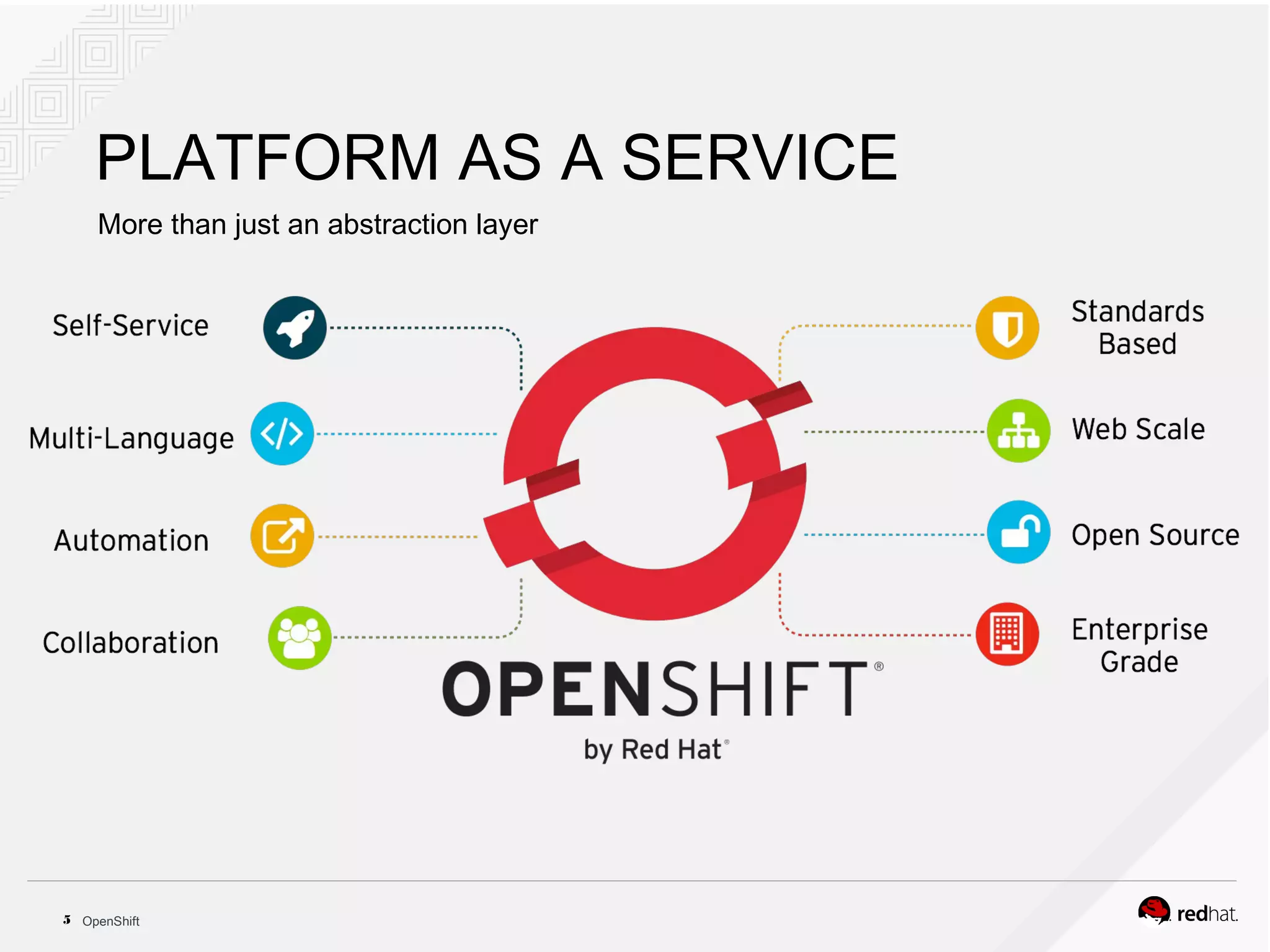
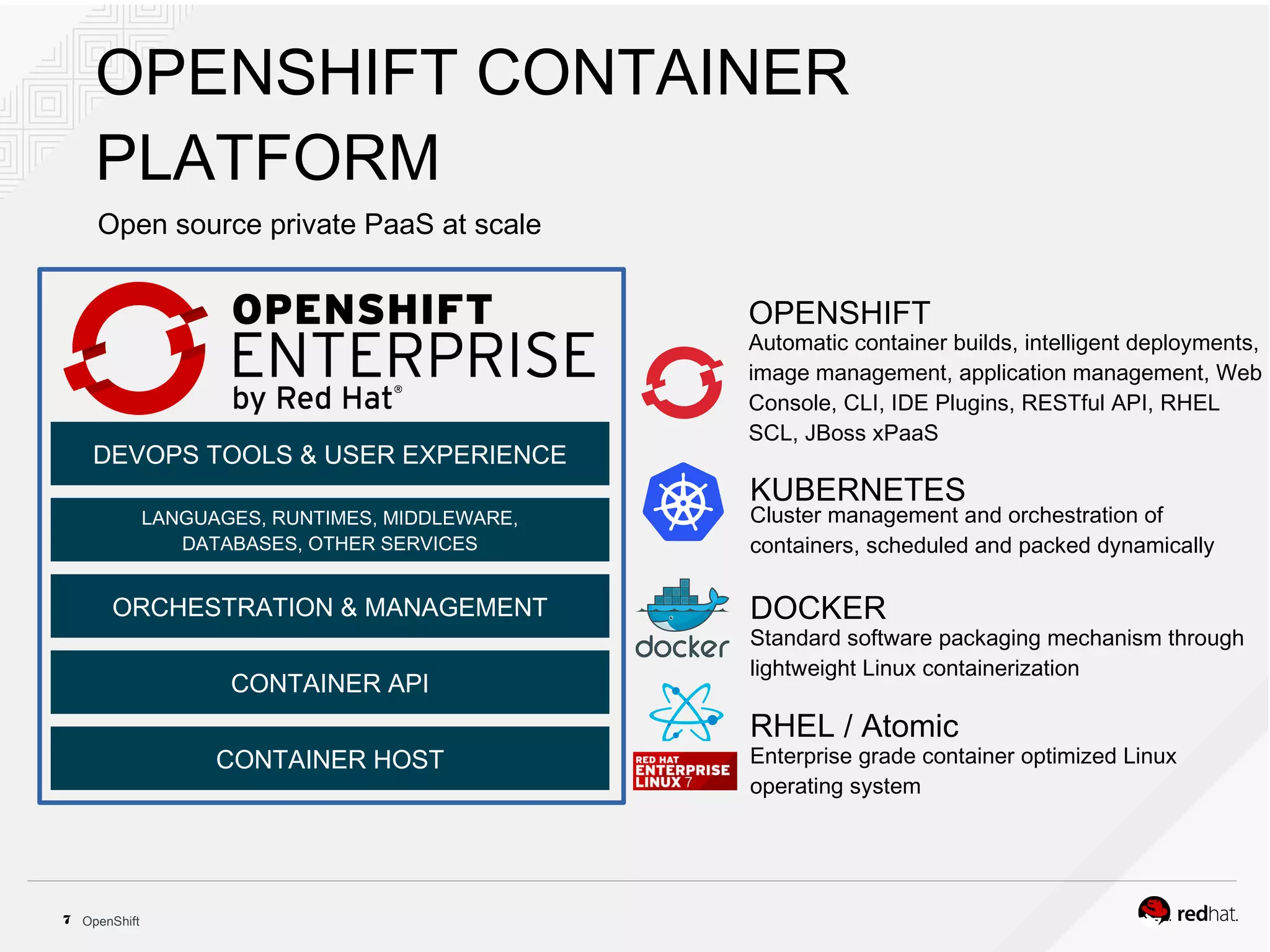
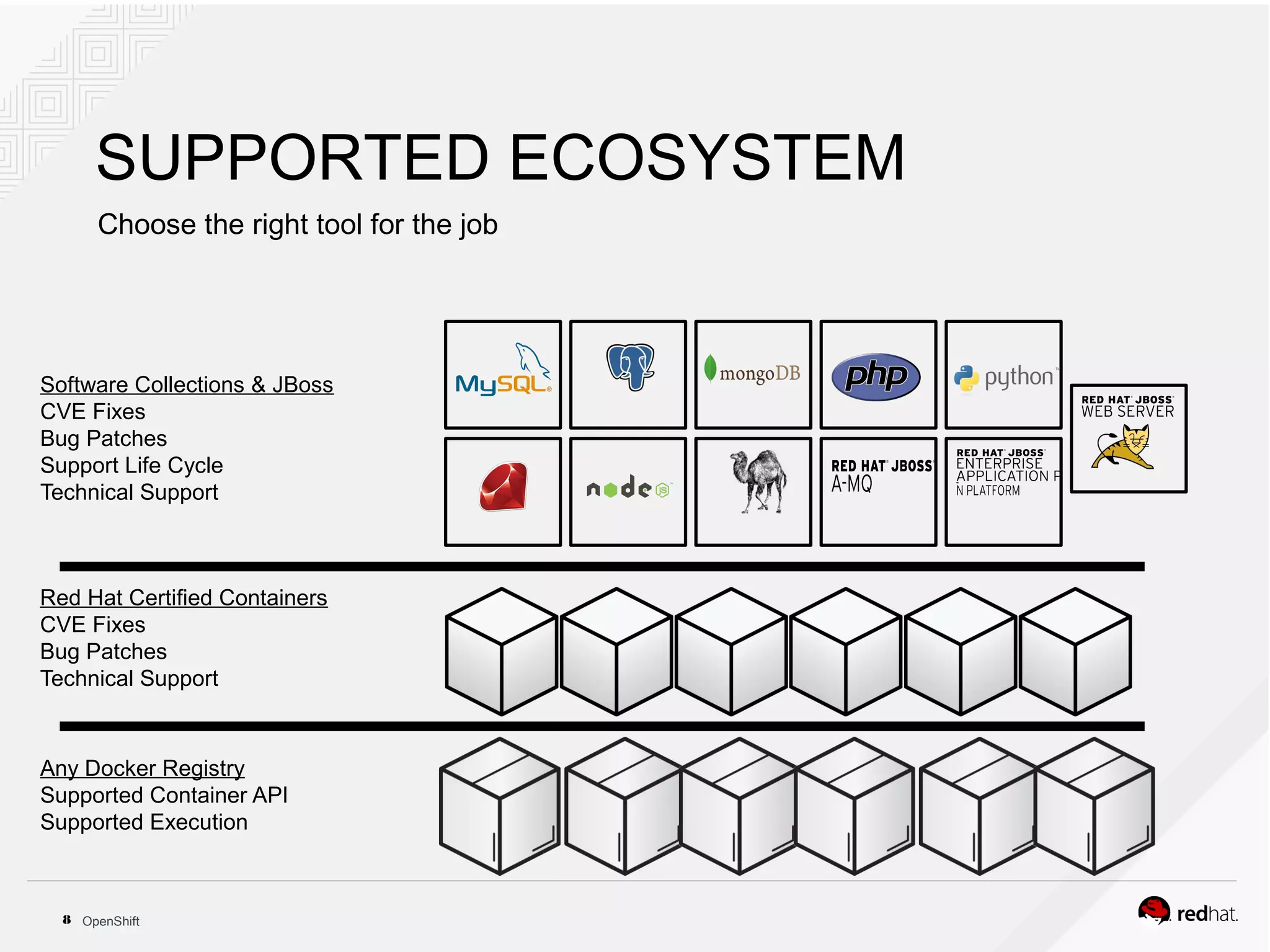
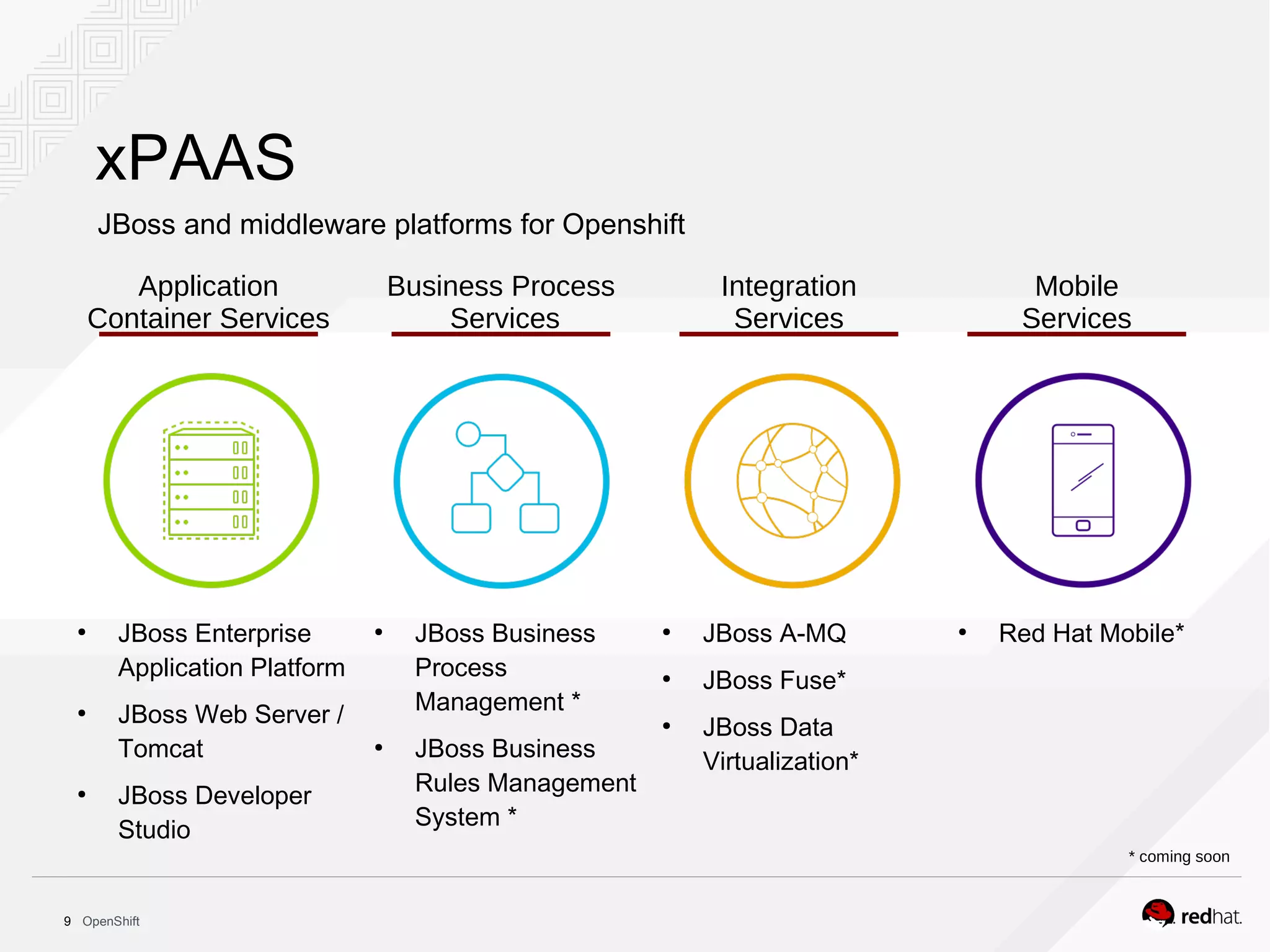
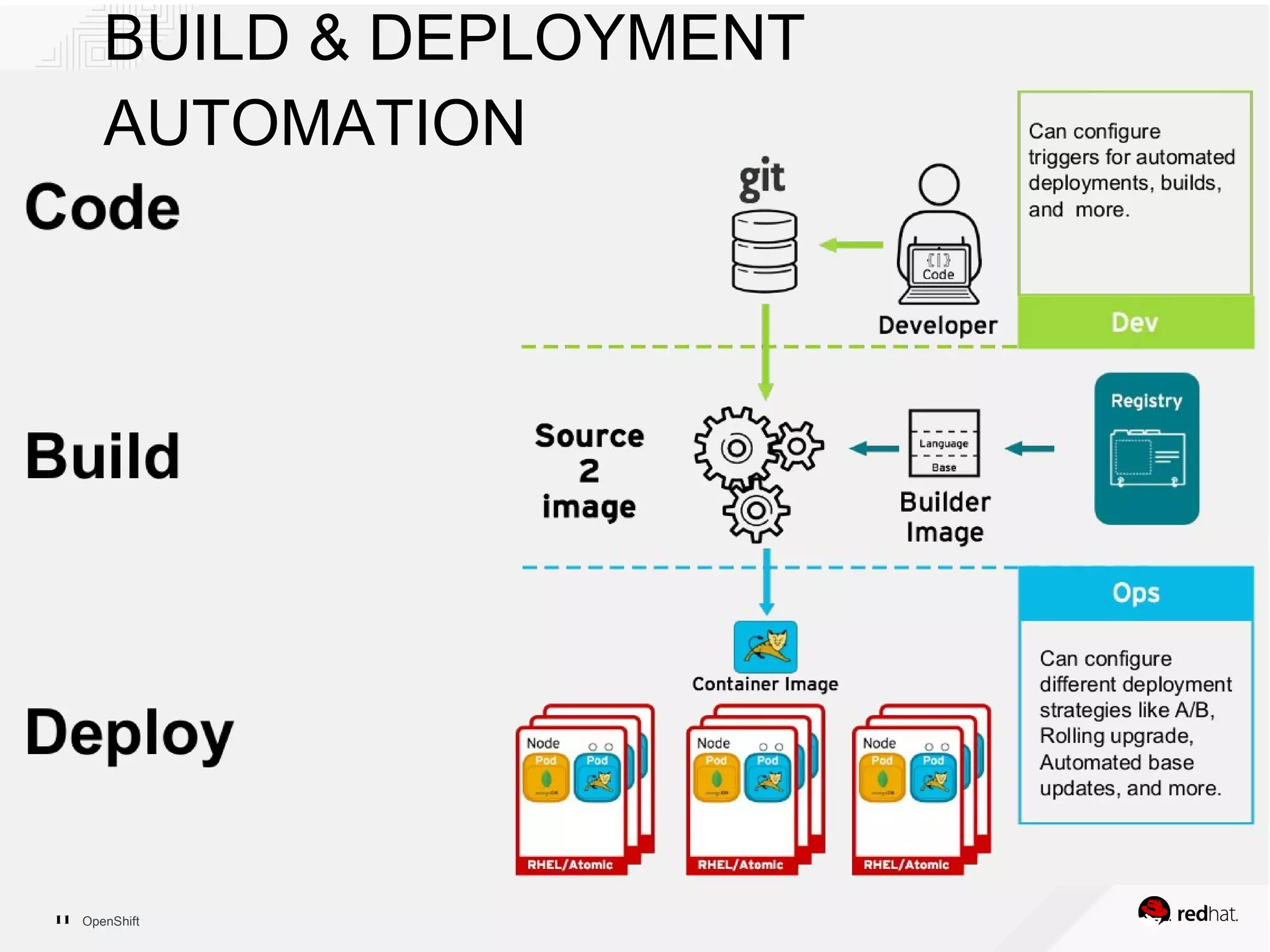
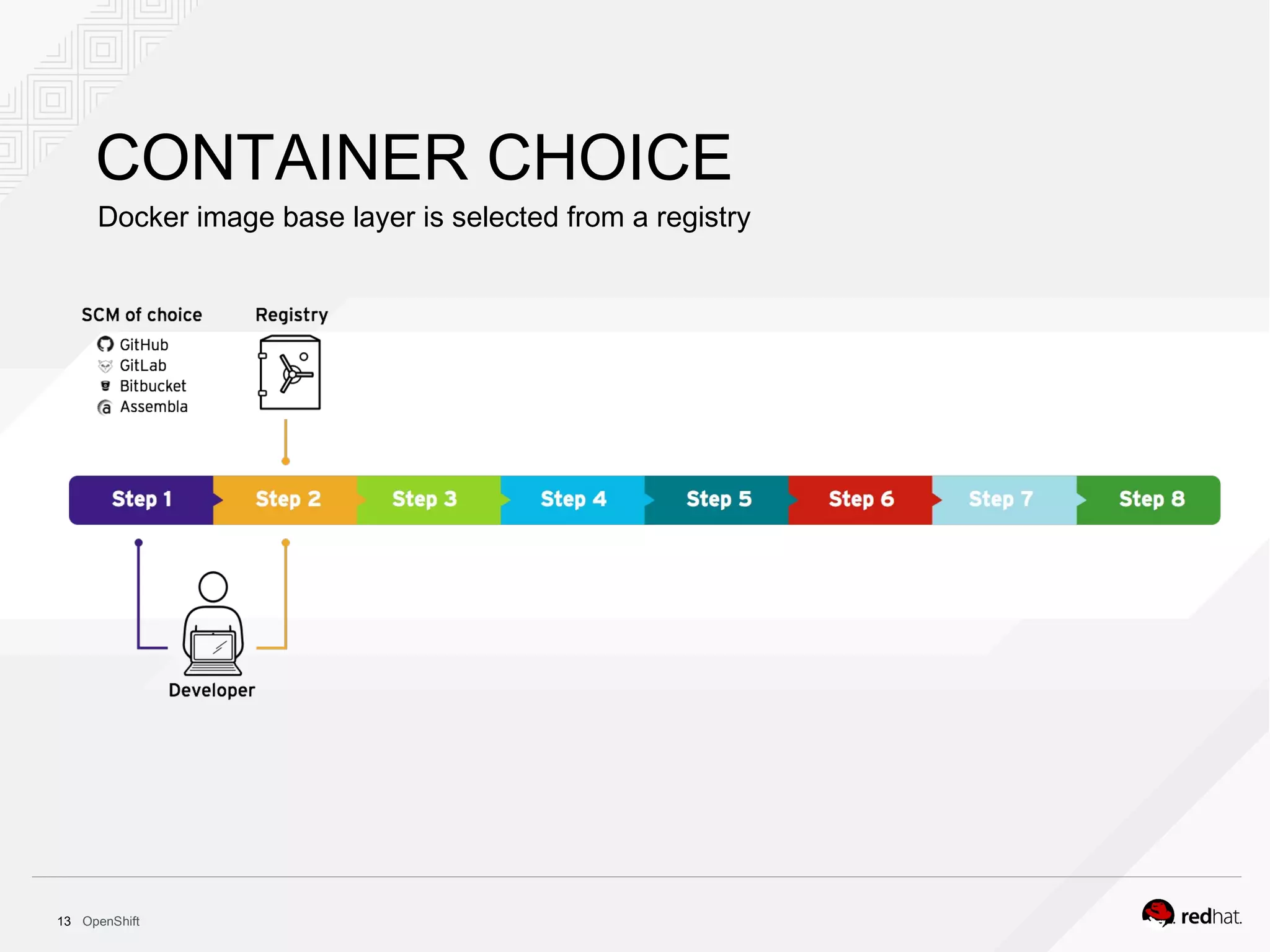
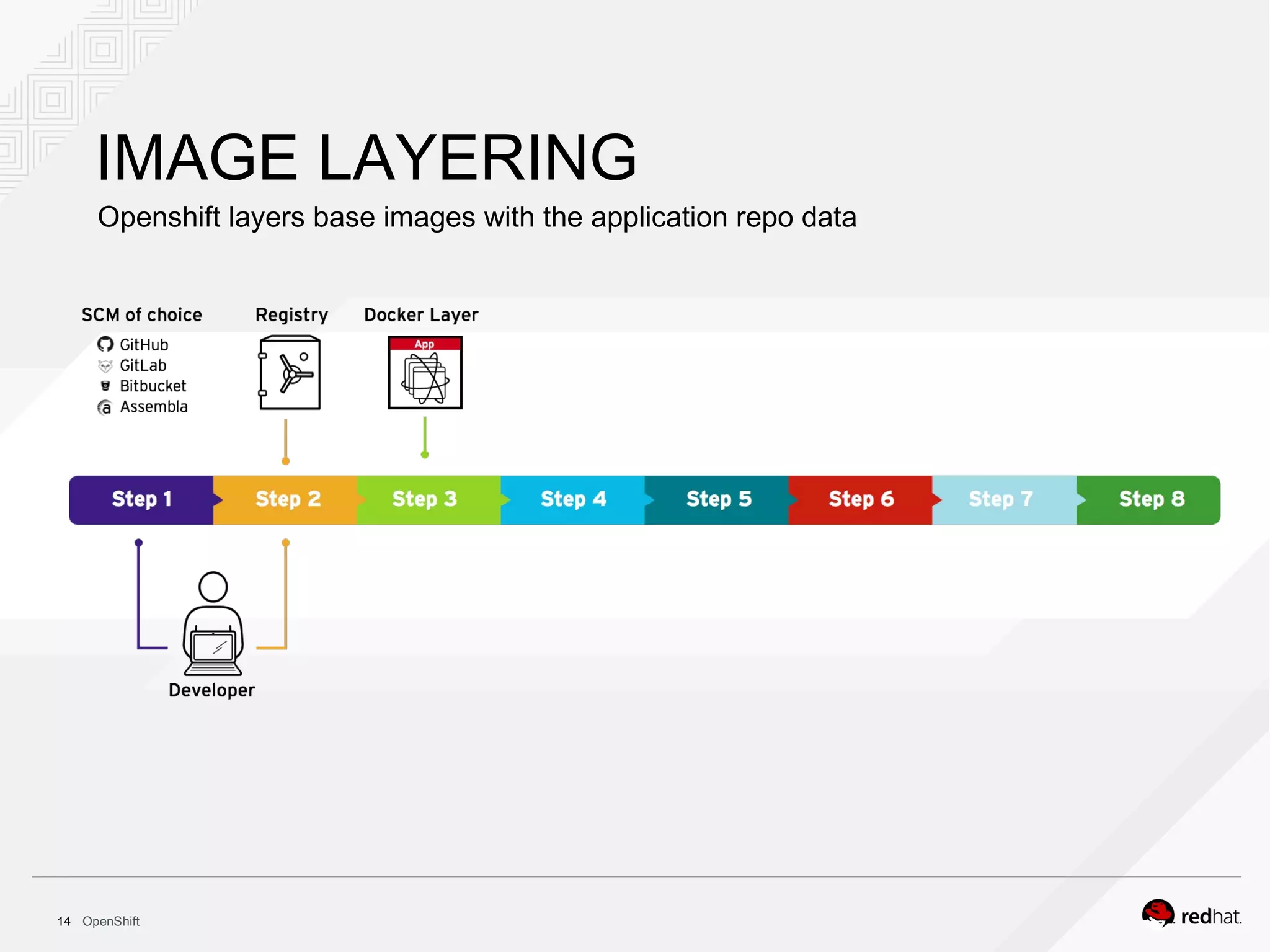
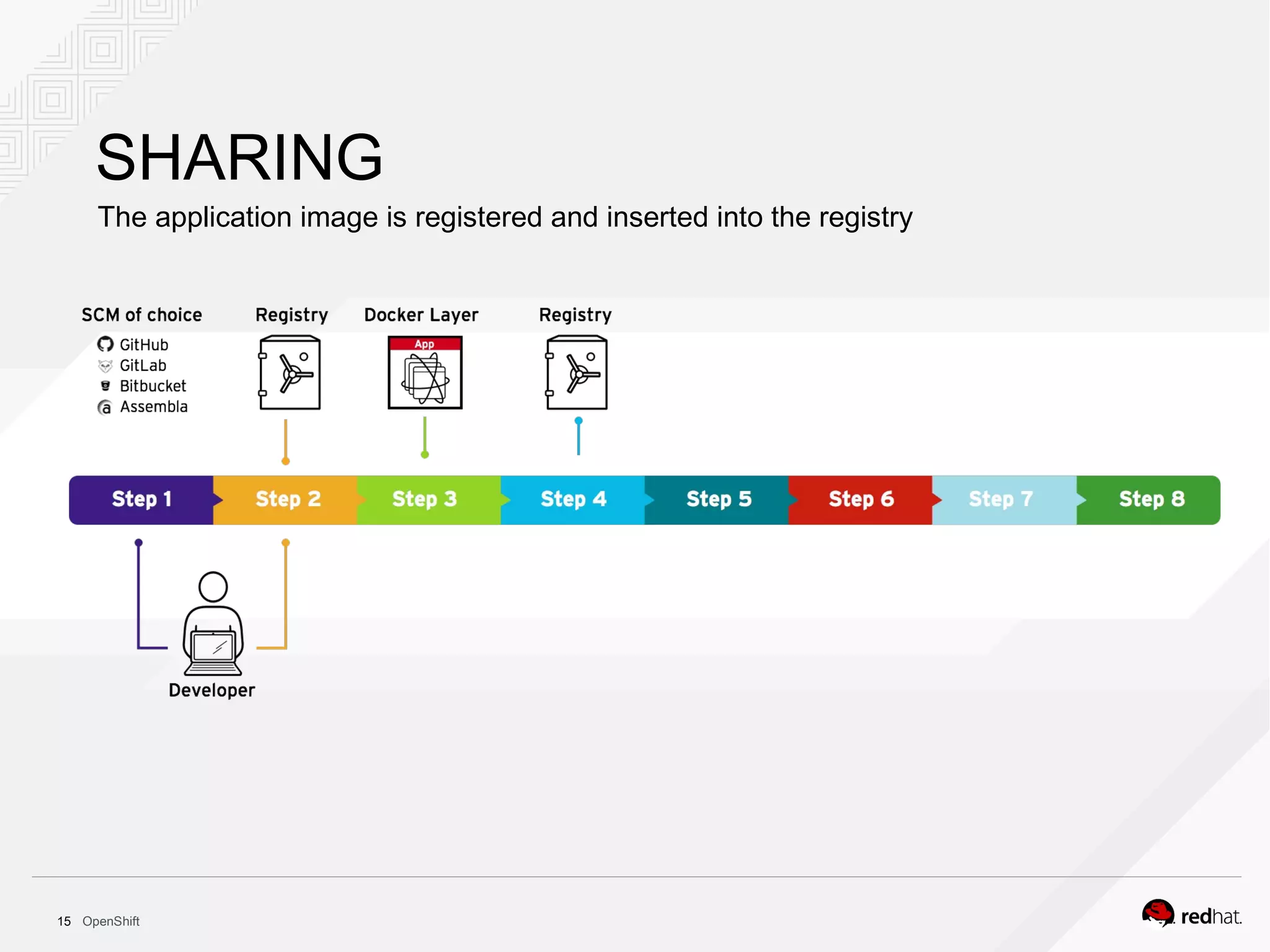
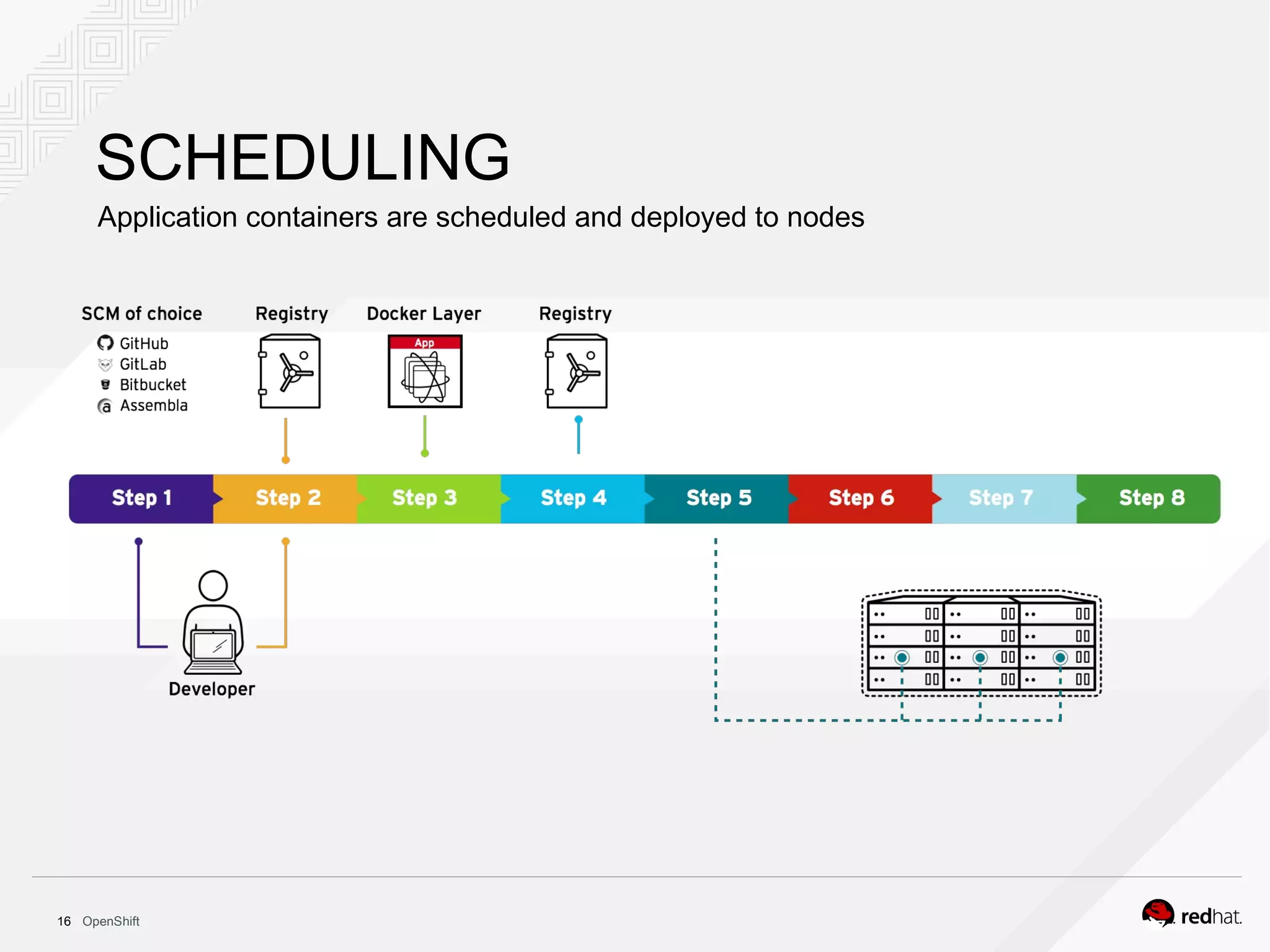
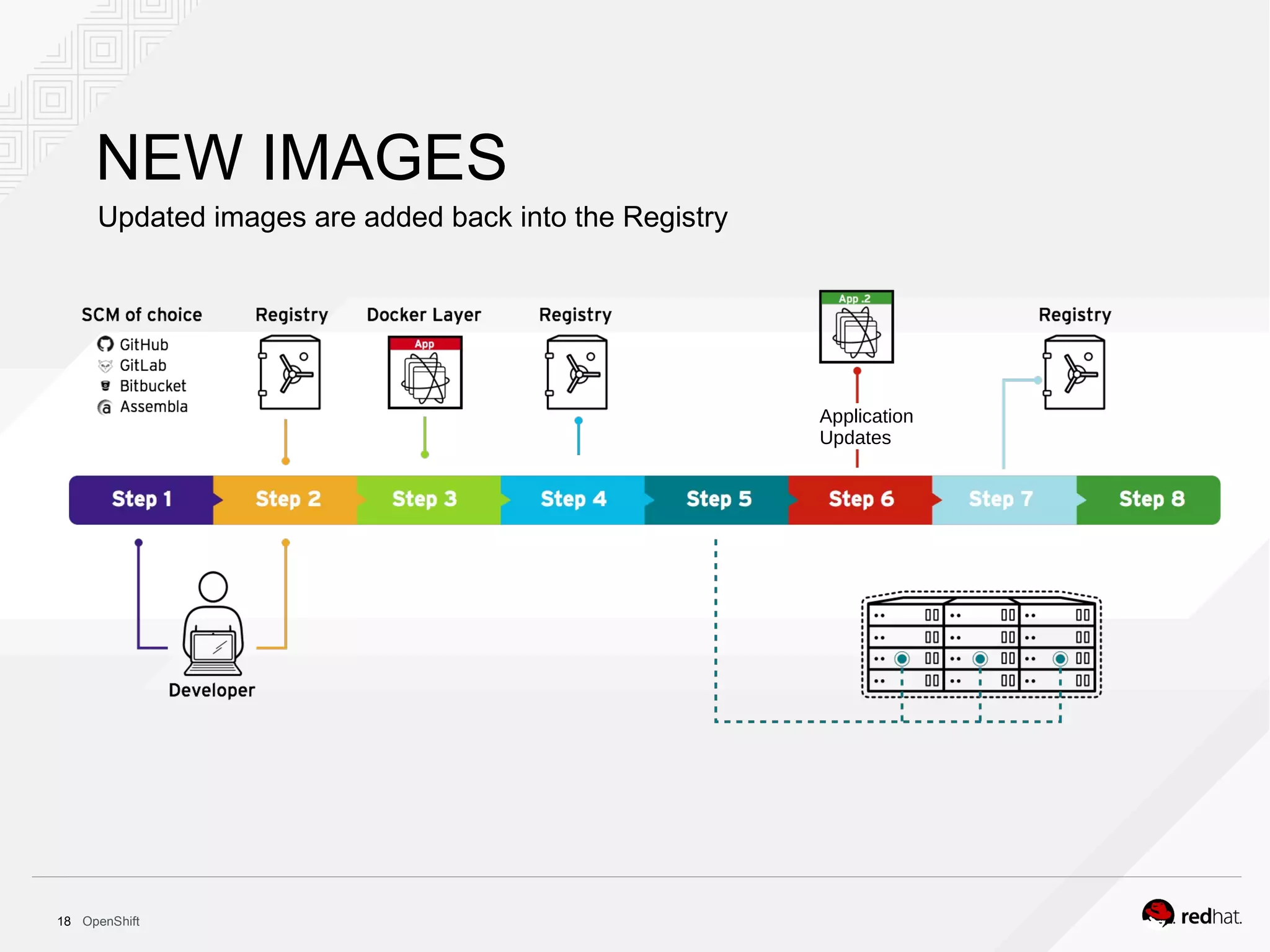
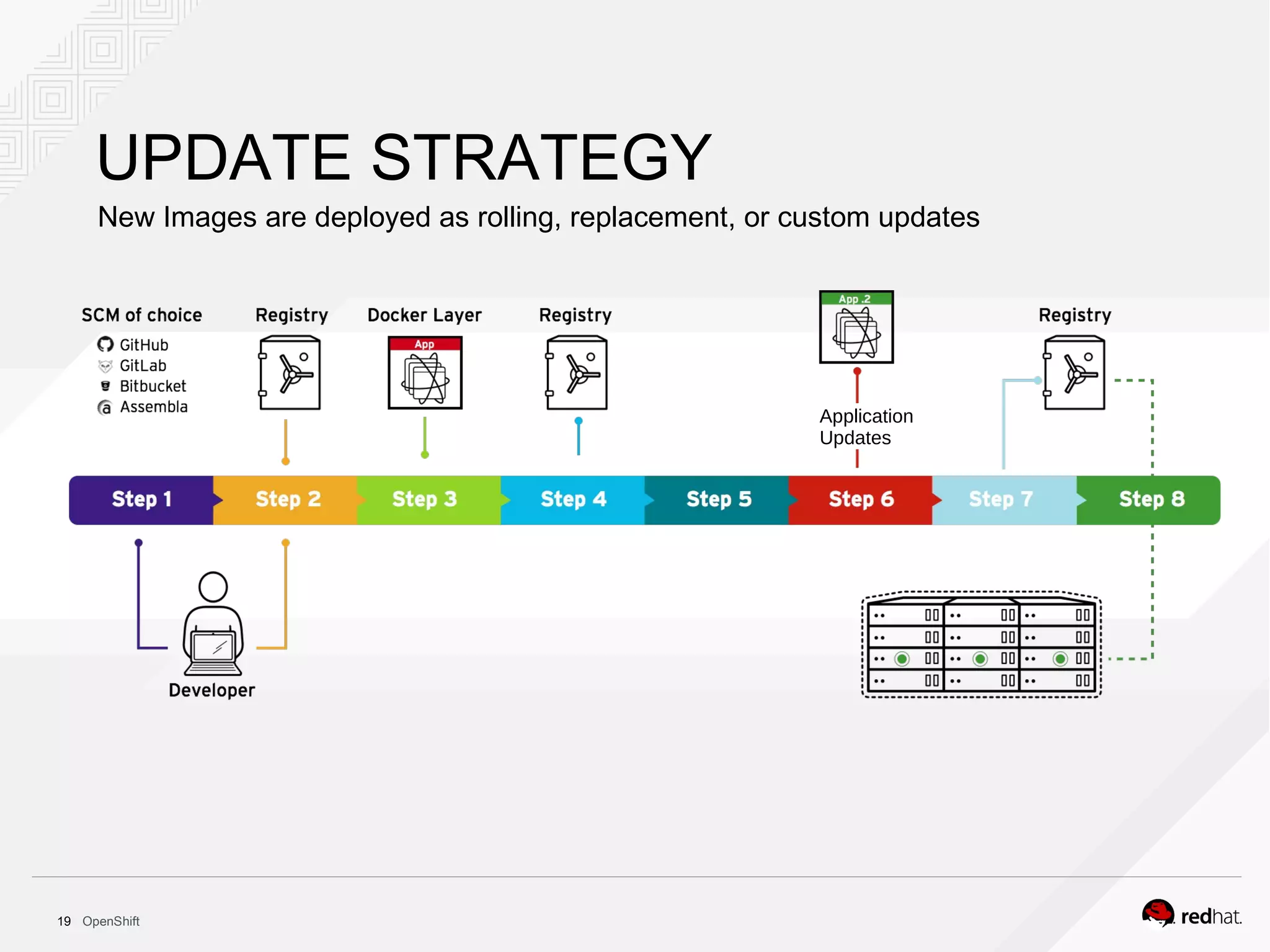
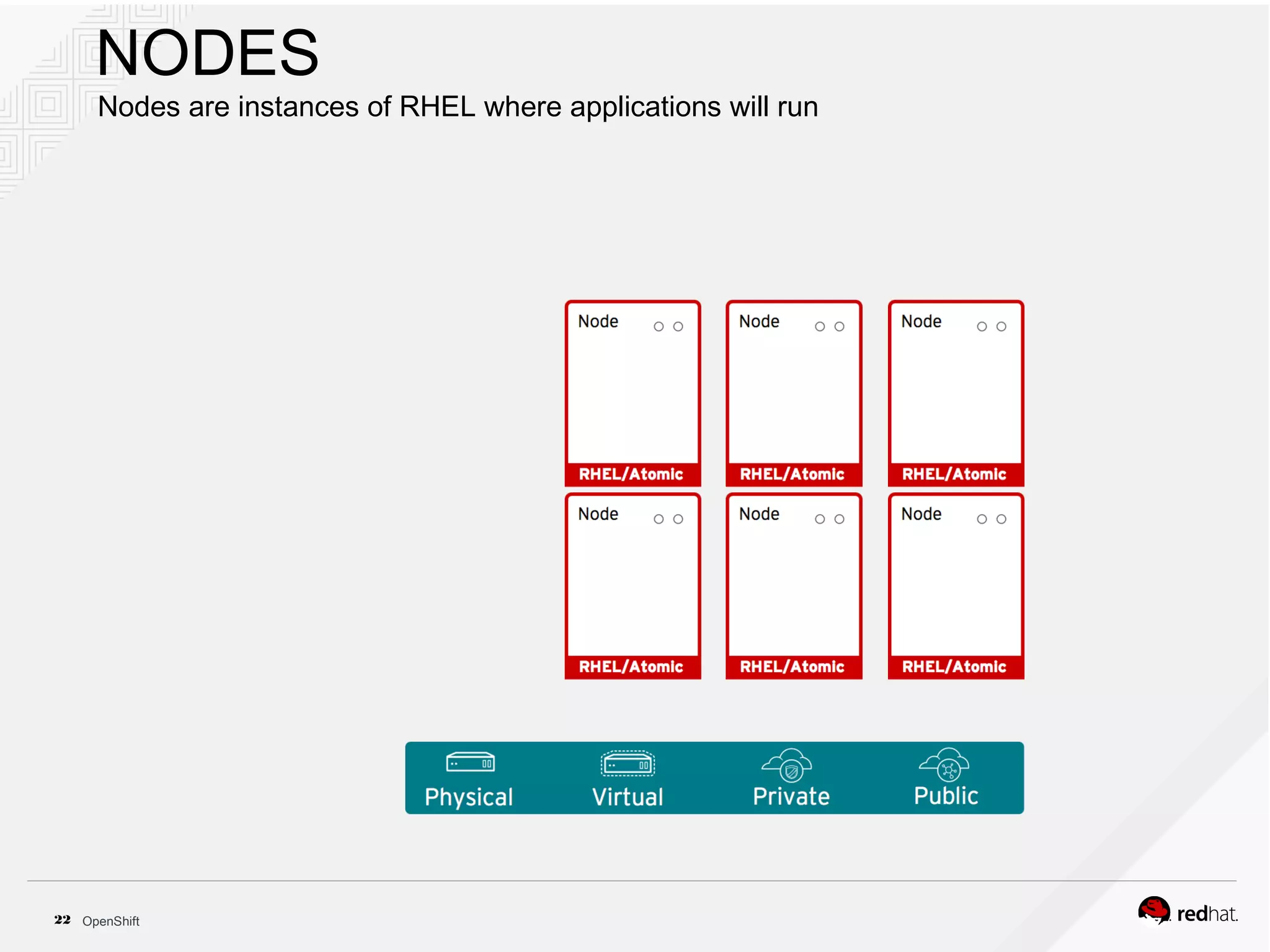
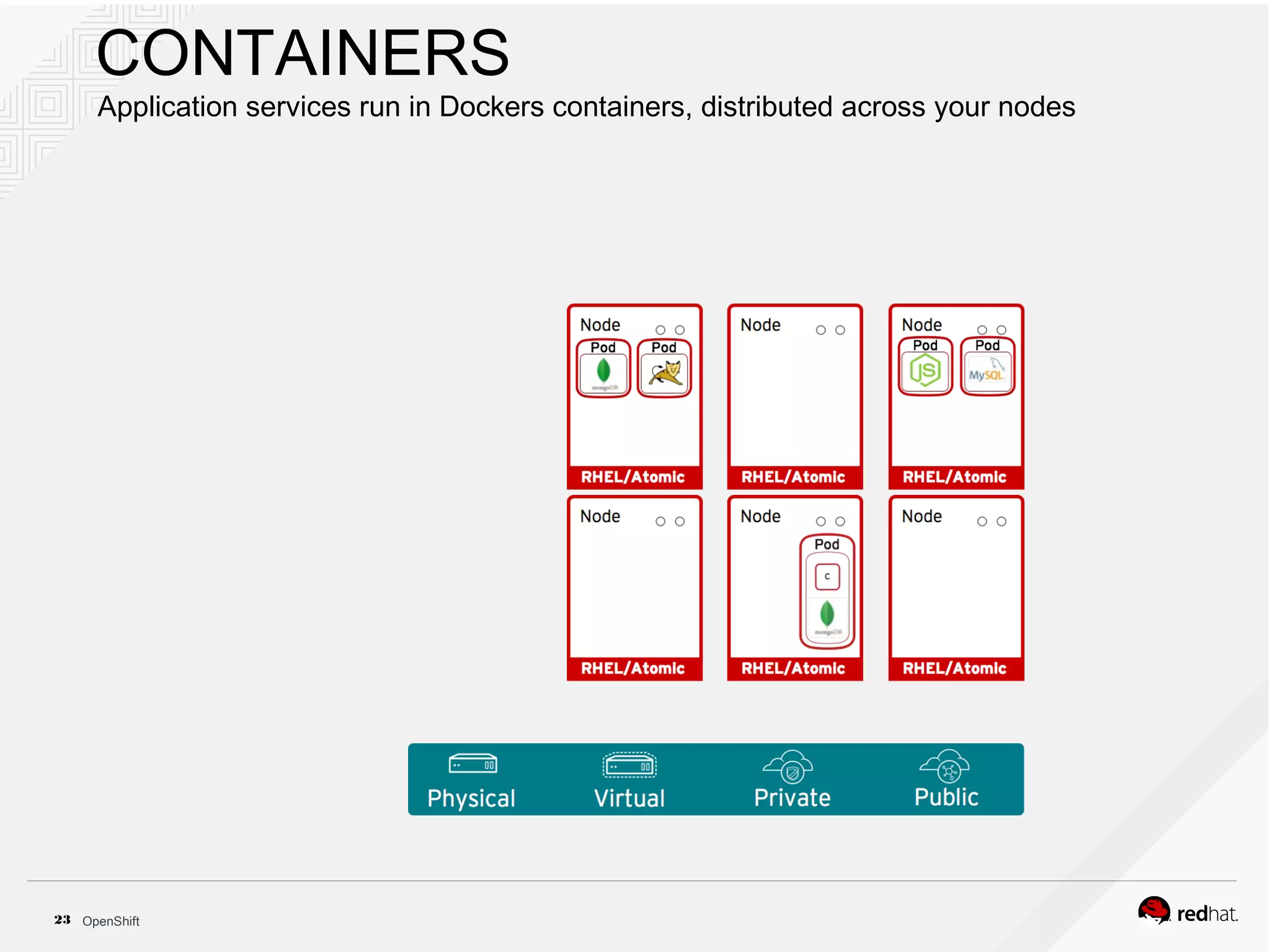
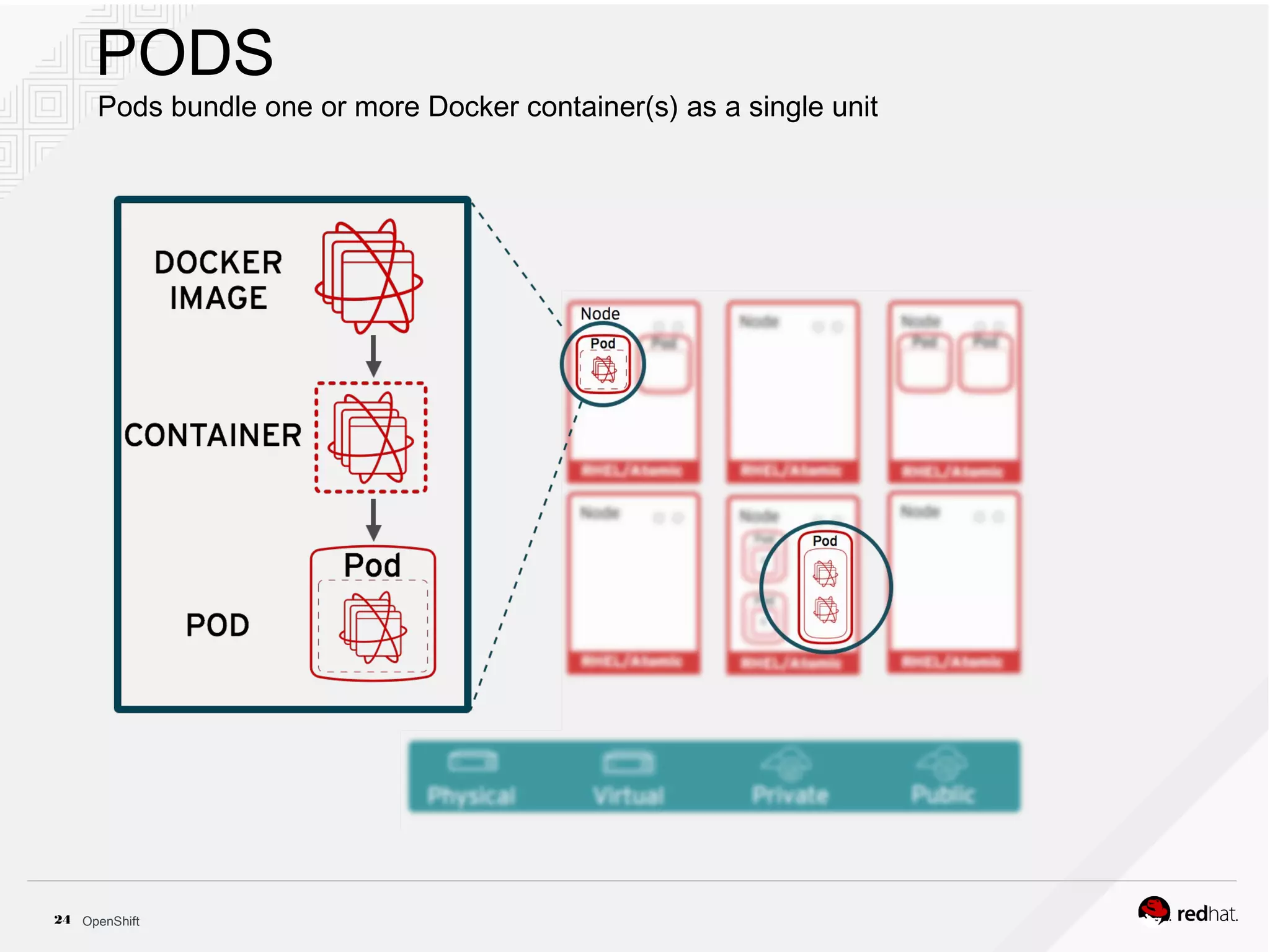
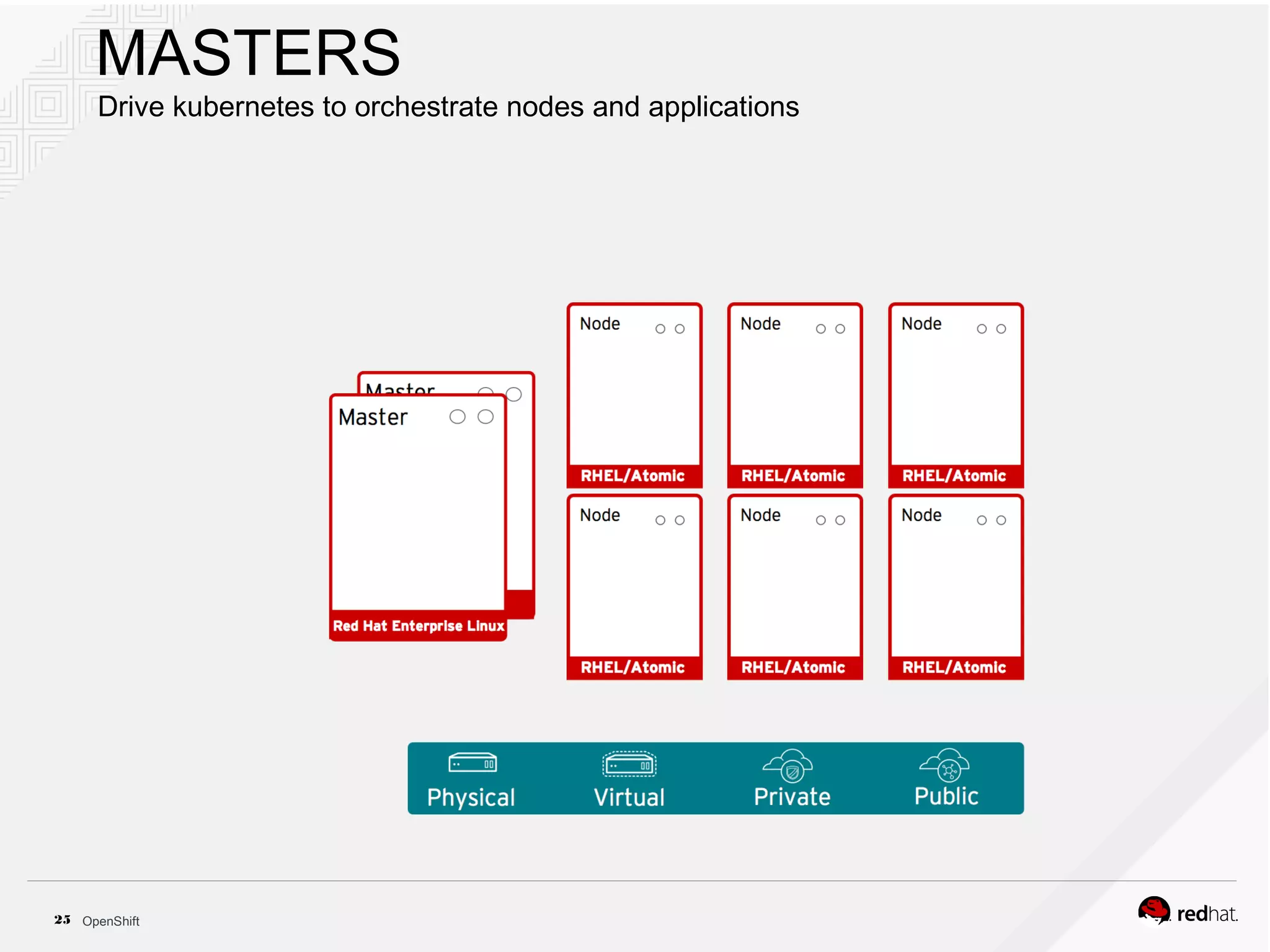
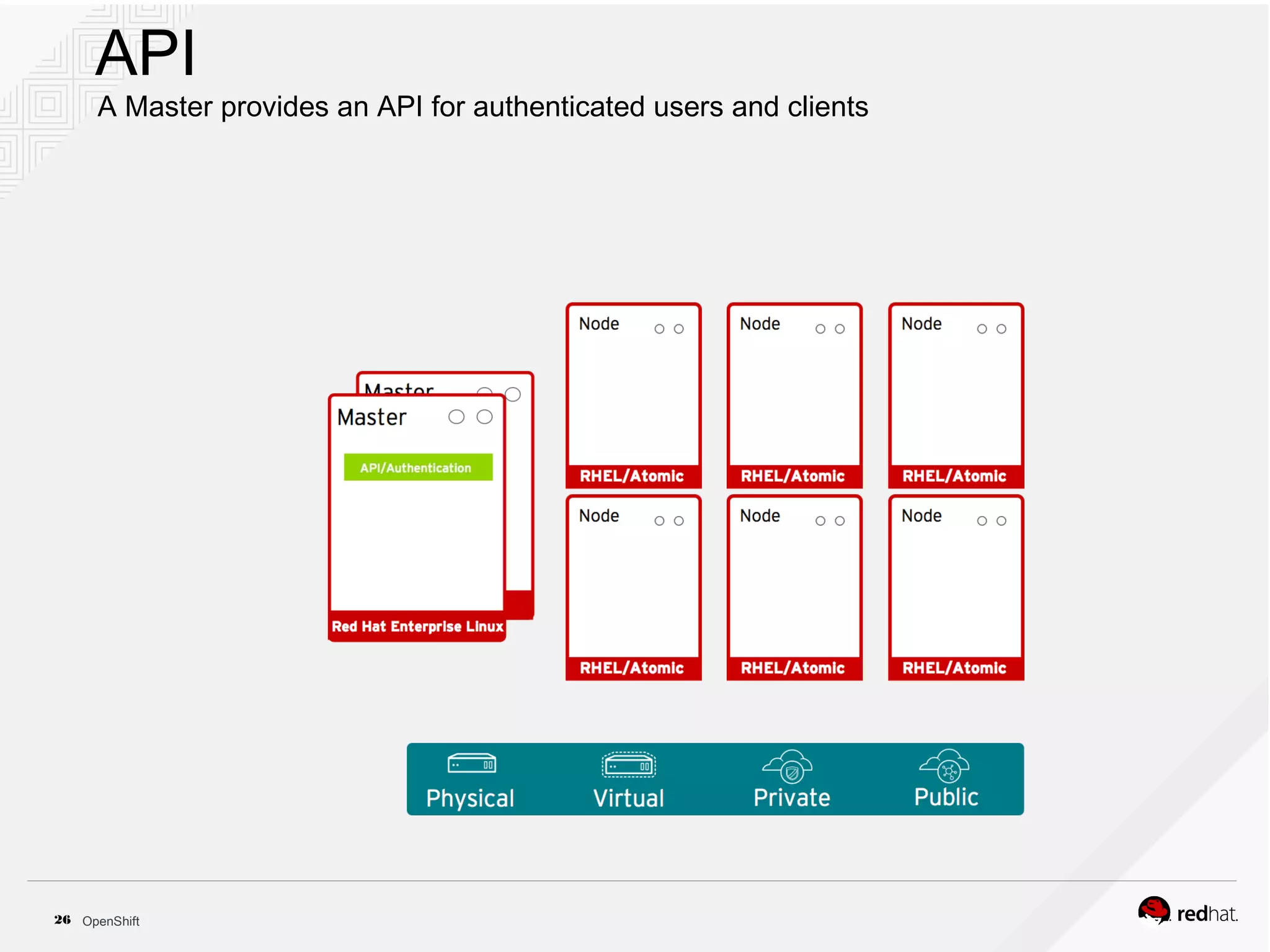
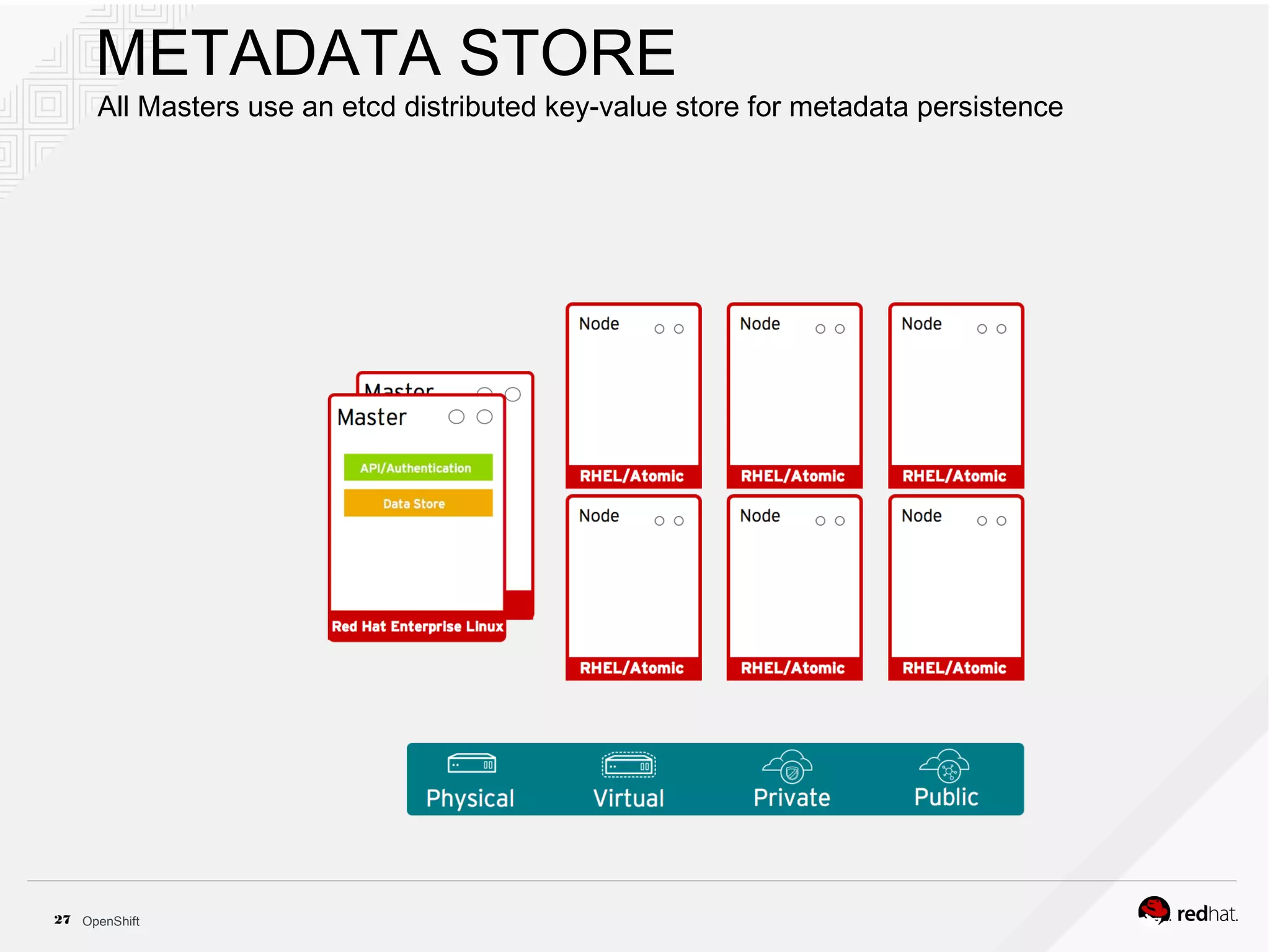
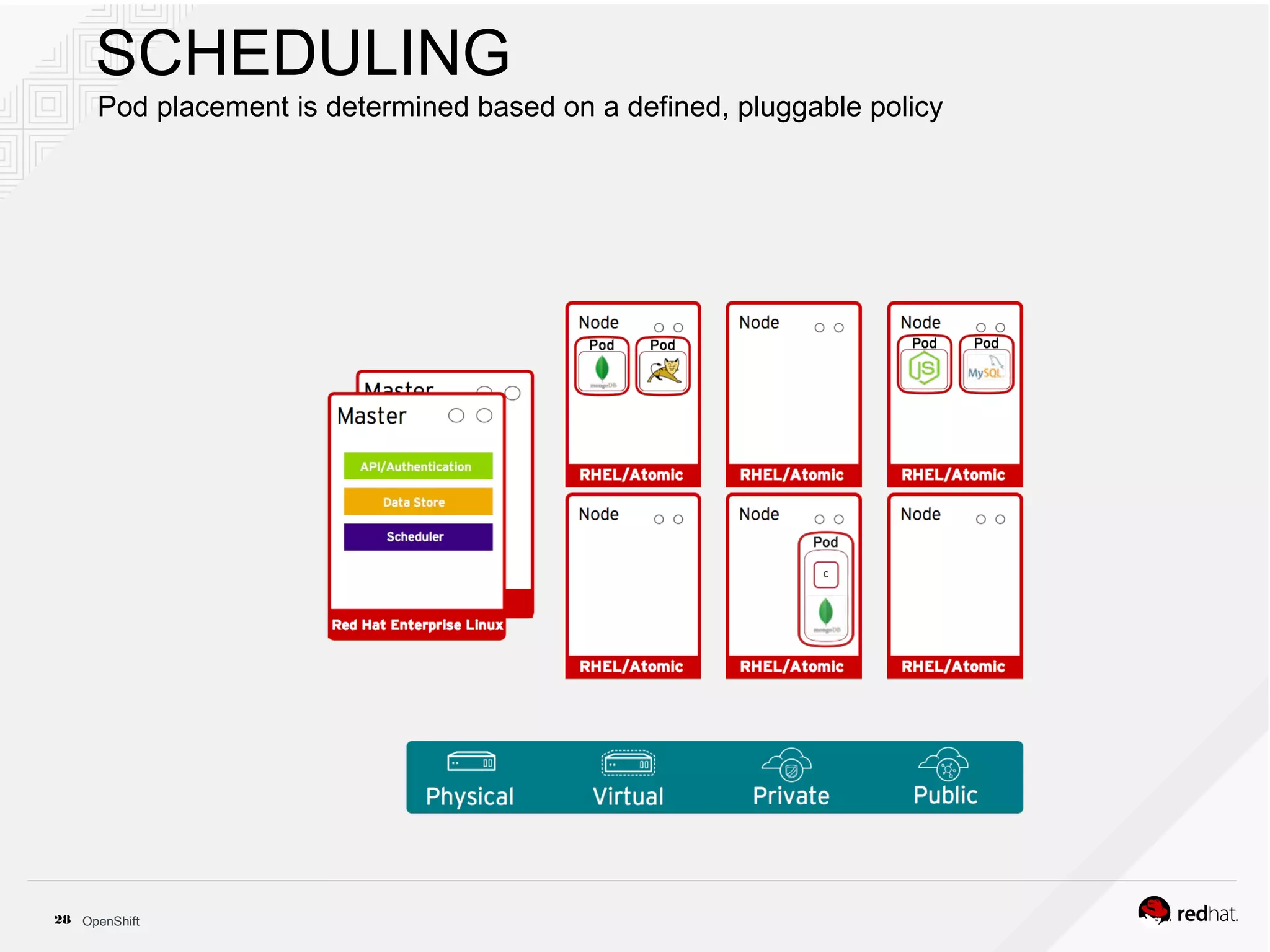
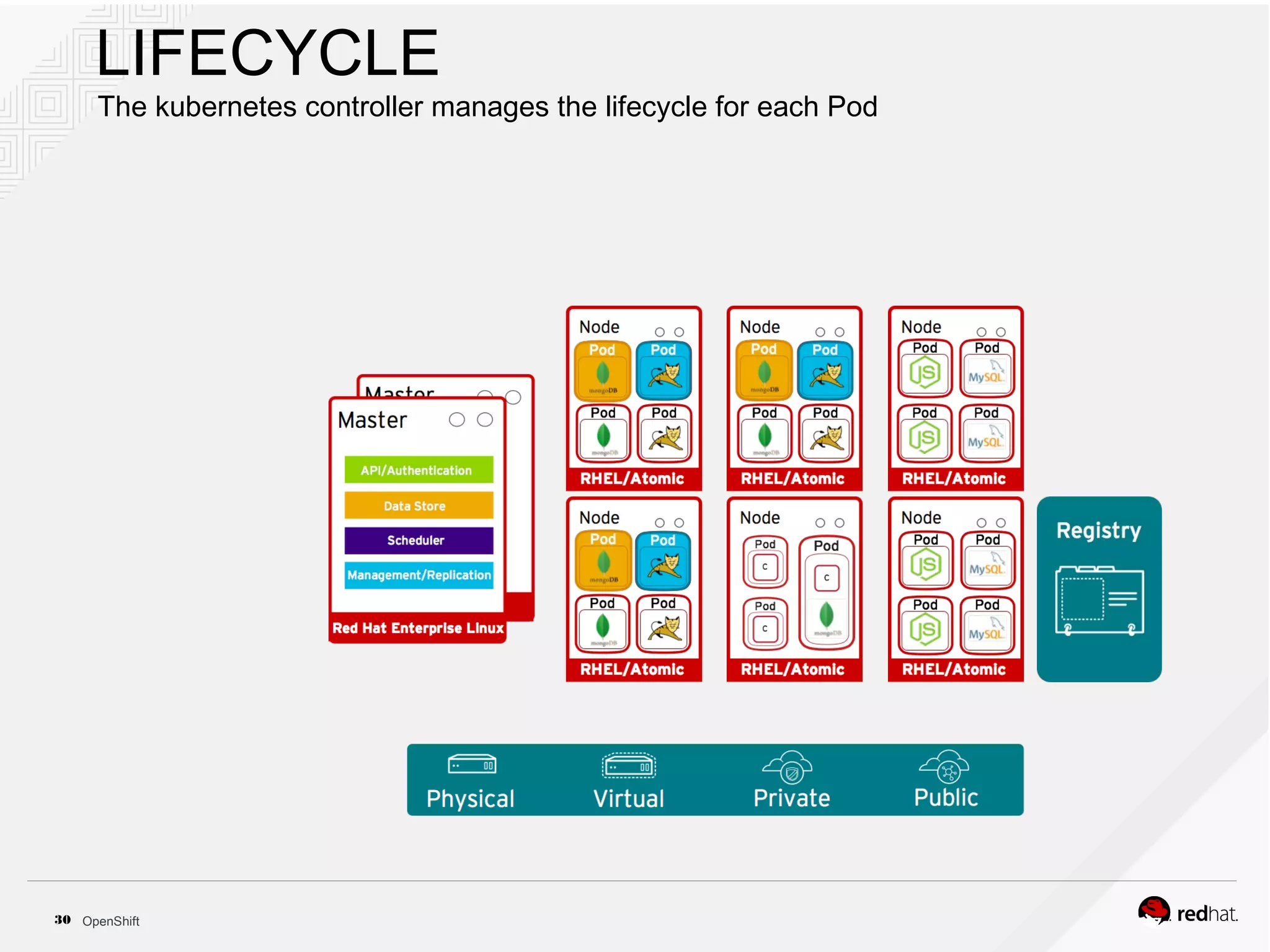
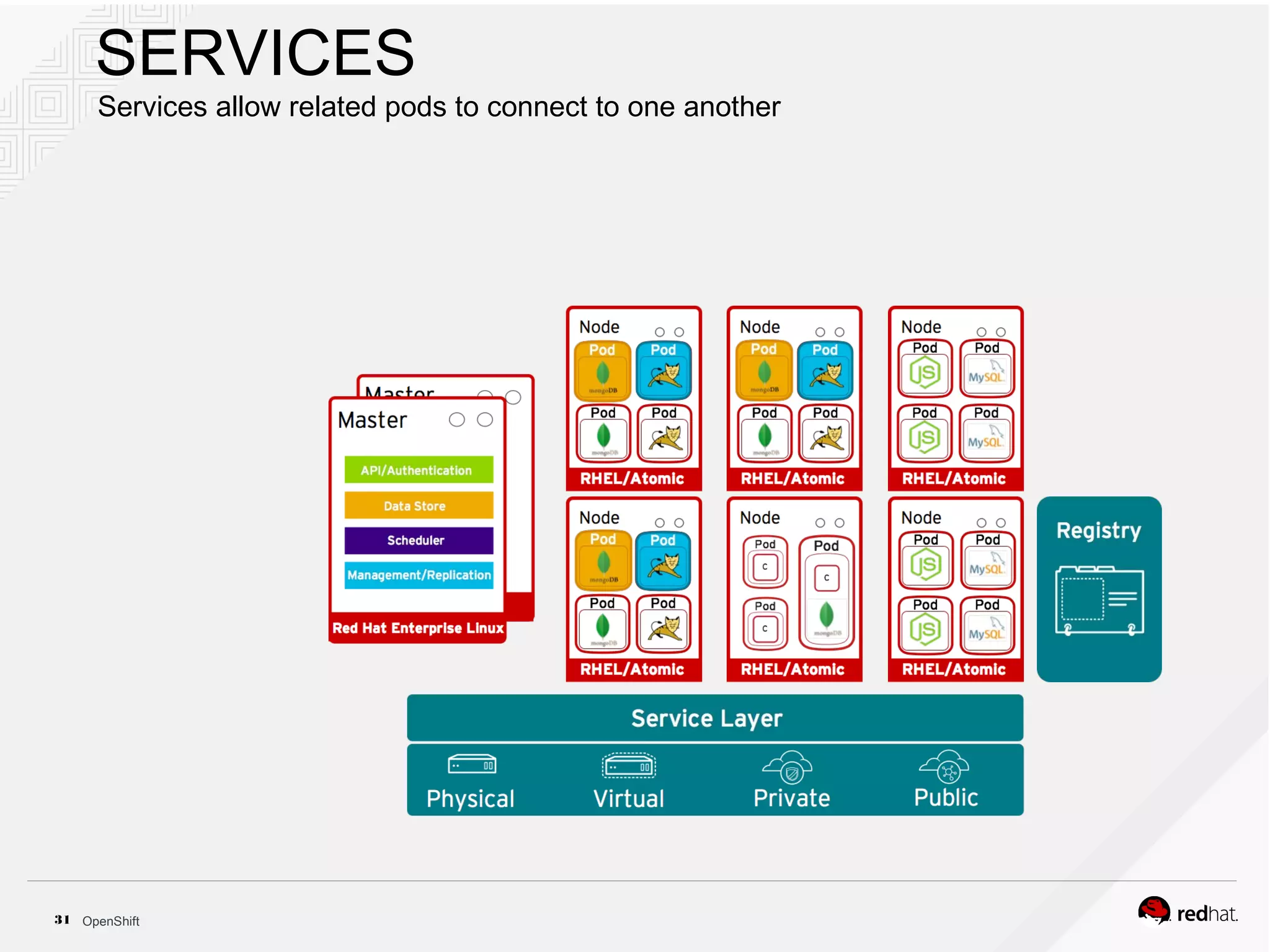
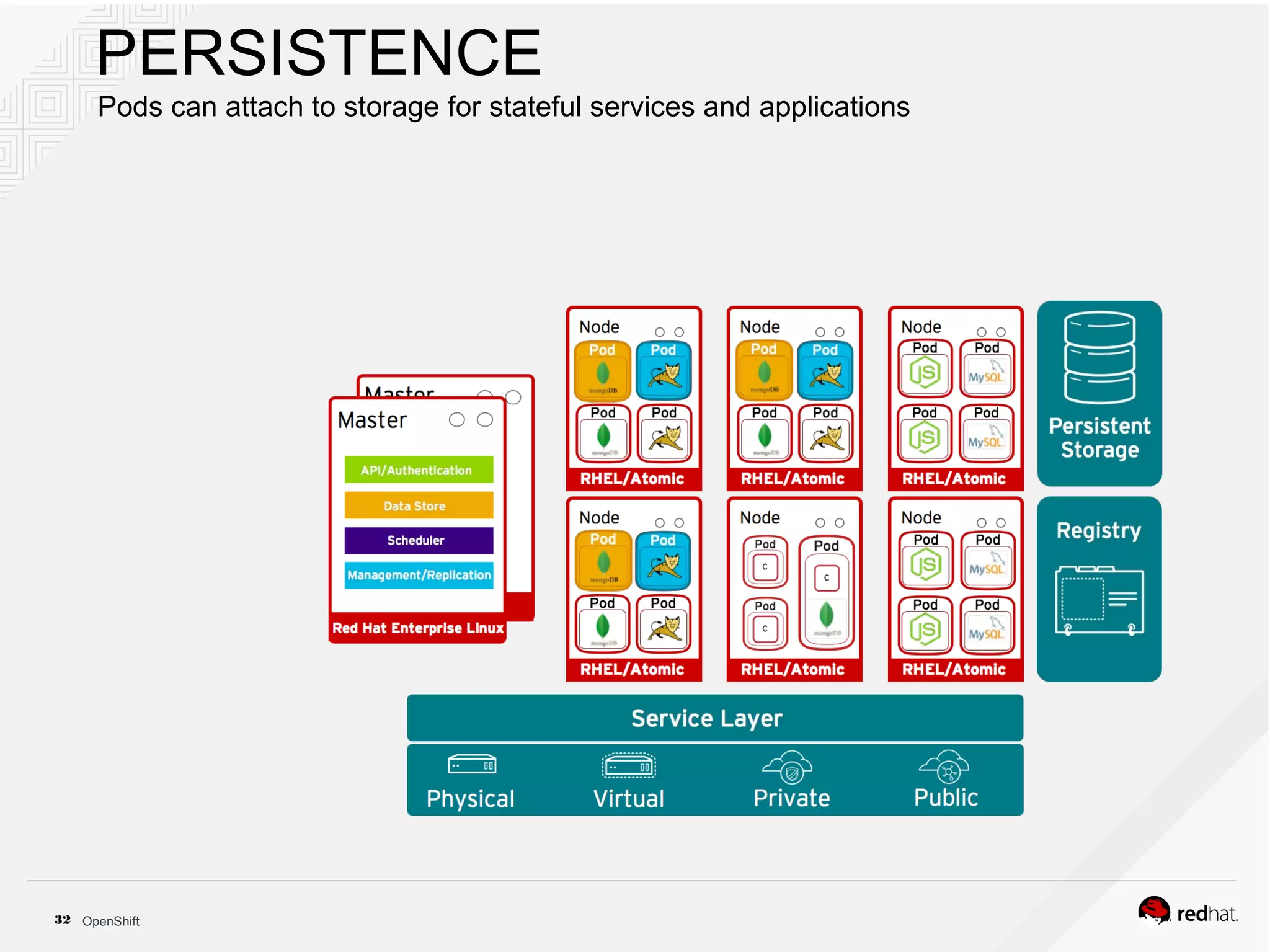
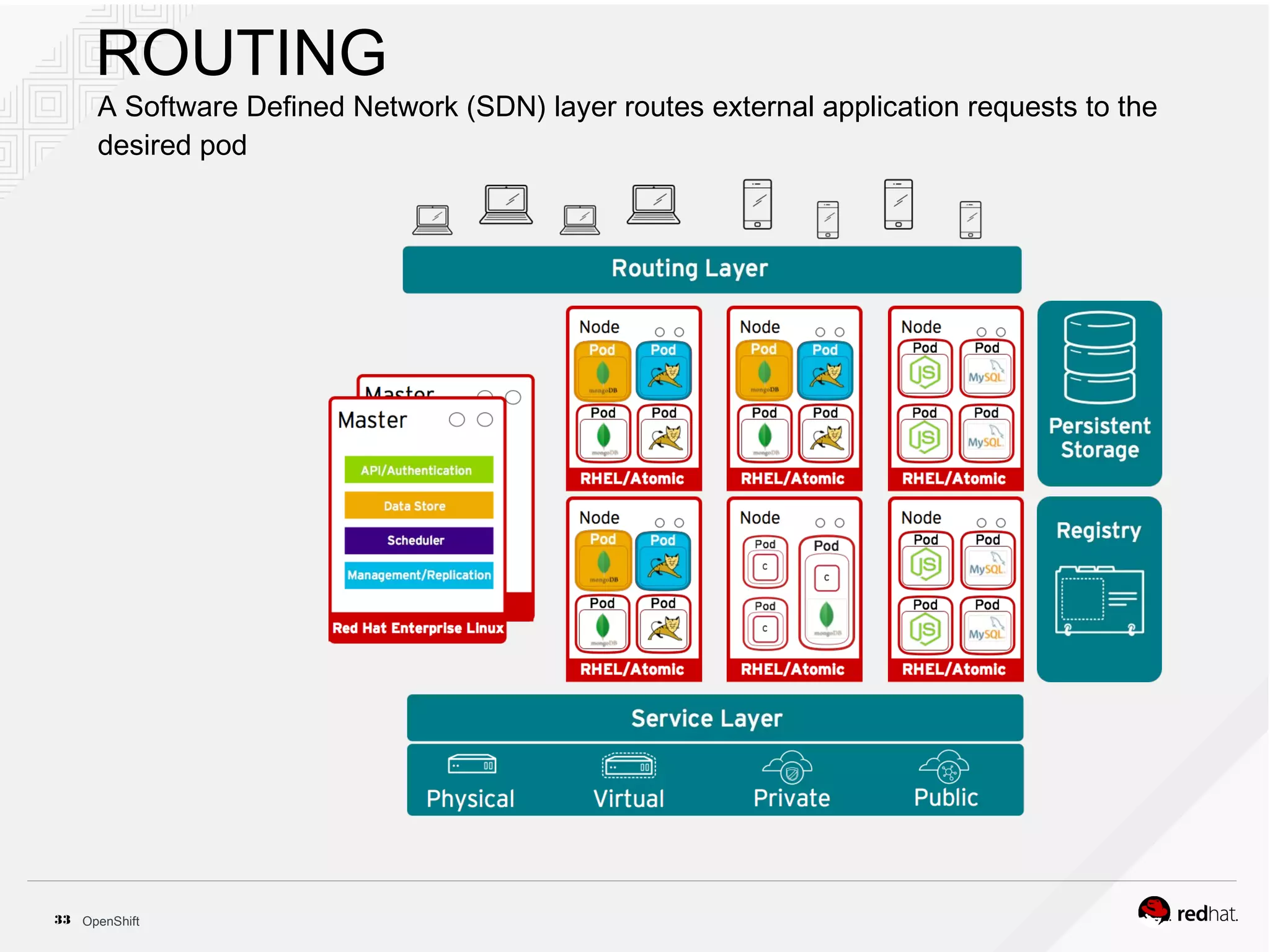
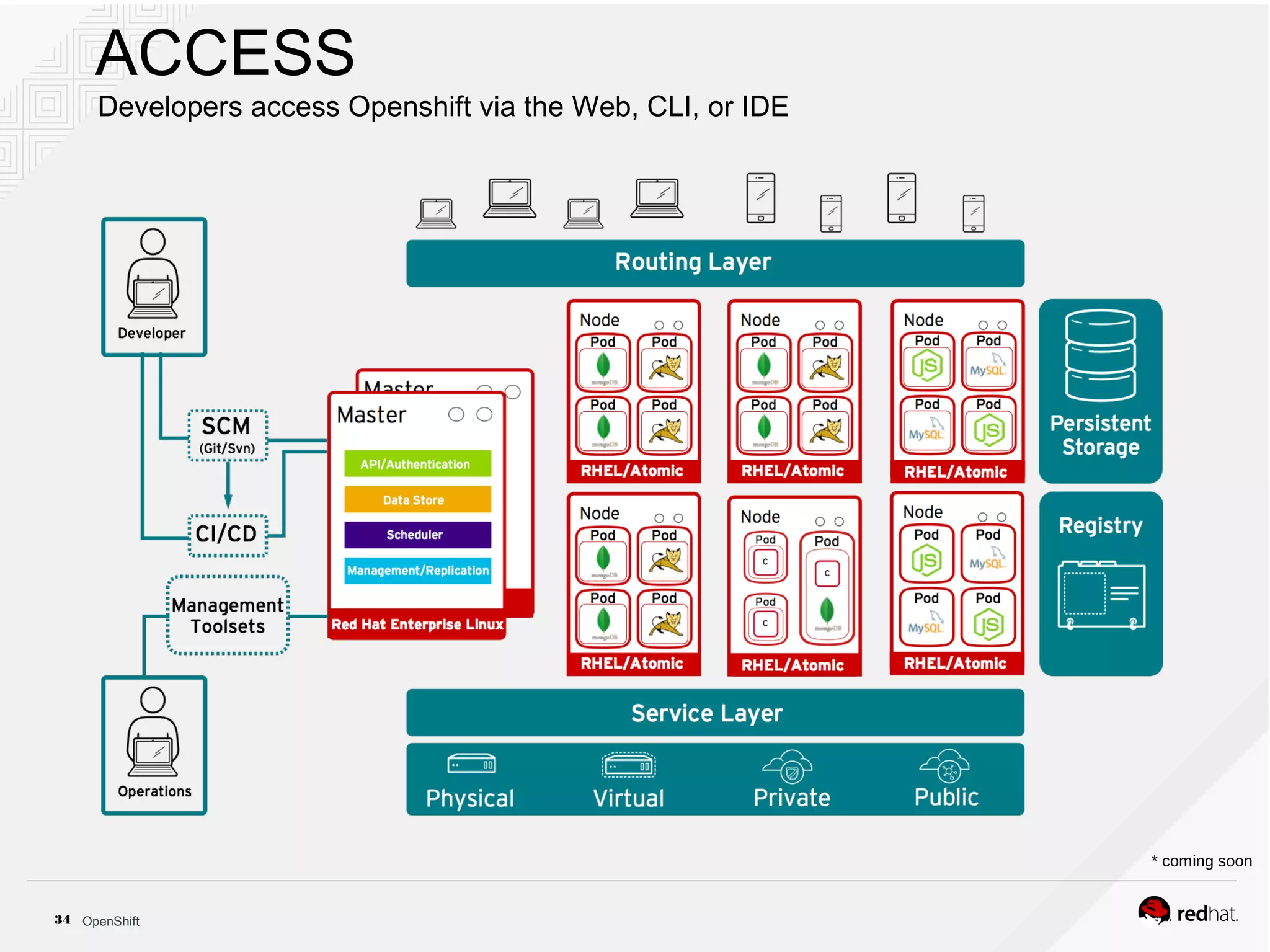
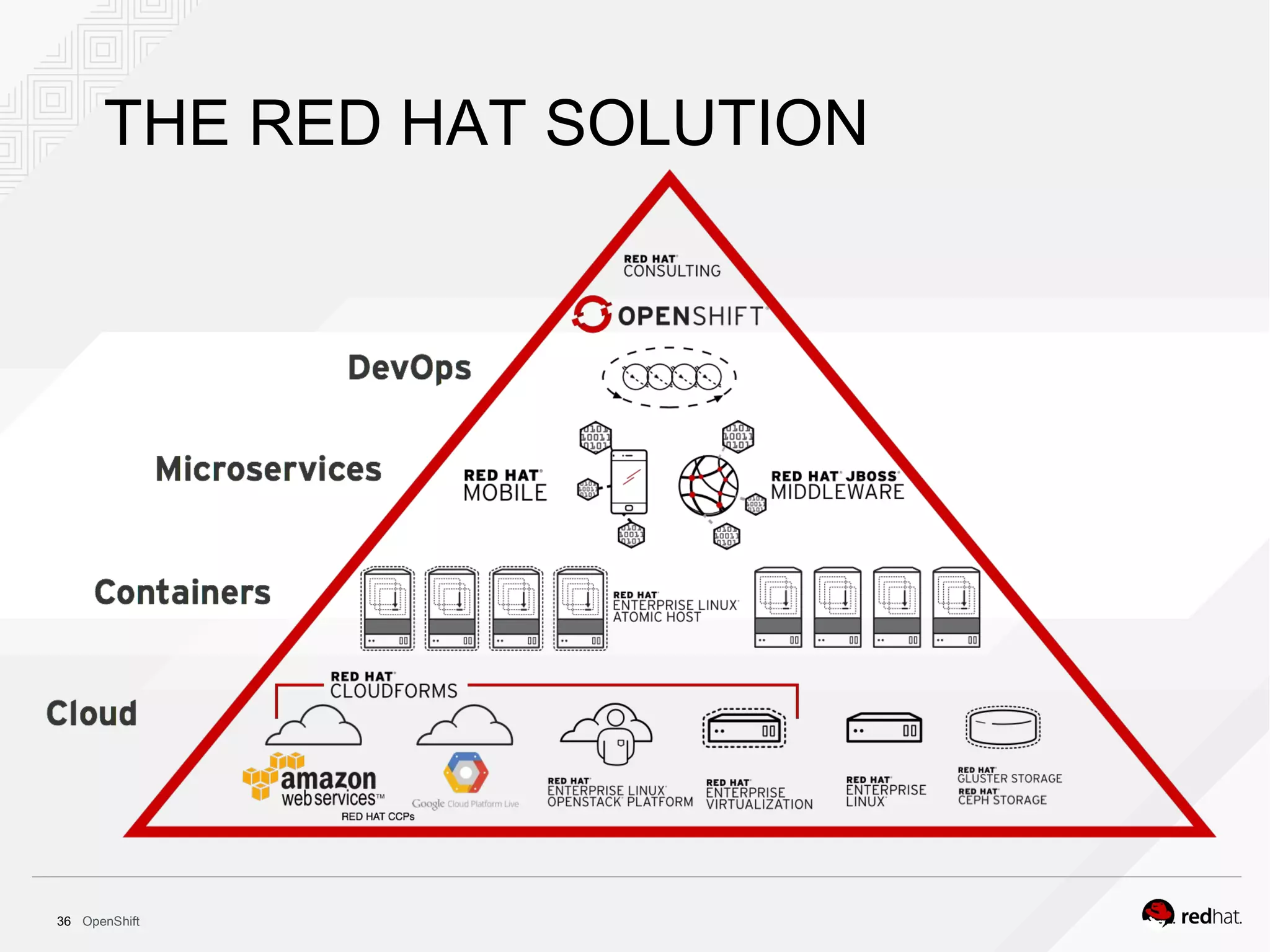
This document discusses OpenShift Container Platform, a platform as a service (PaaS) that provides a full development and deployment platform for applications. It allows developers to easily manage application dependencies and development environments across basic infrastructure, public clouds, and production servers. OpenShift provides container orchestration using Kubernetes along with developer tools and a user experience to support DevOps practices like continuous integration/delivery.