Downloaded 128 times
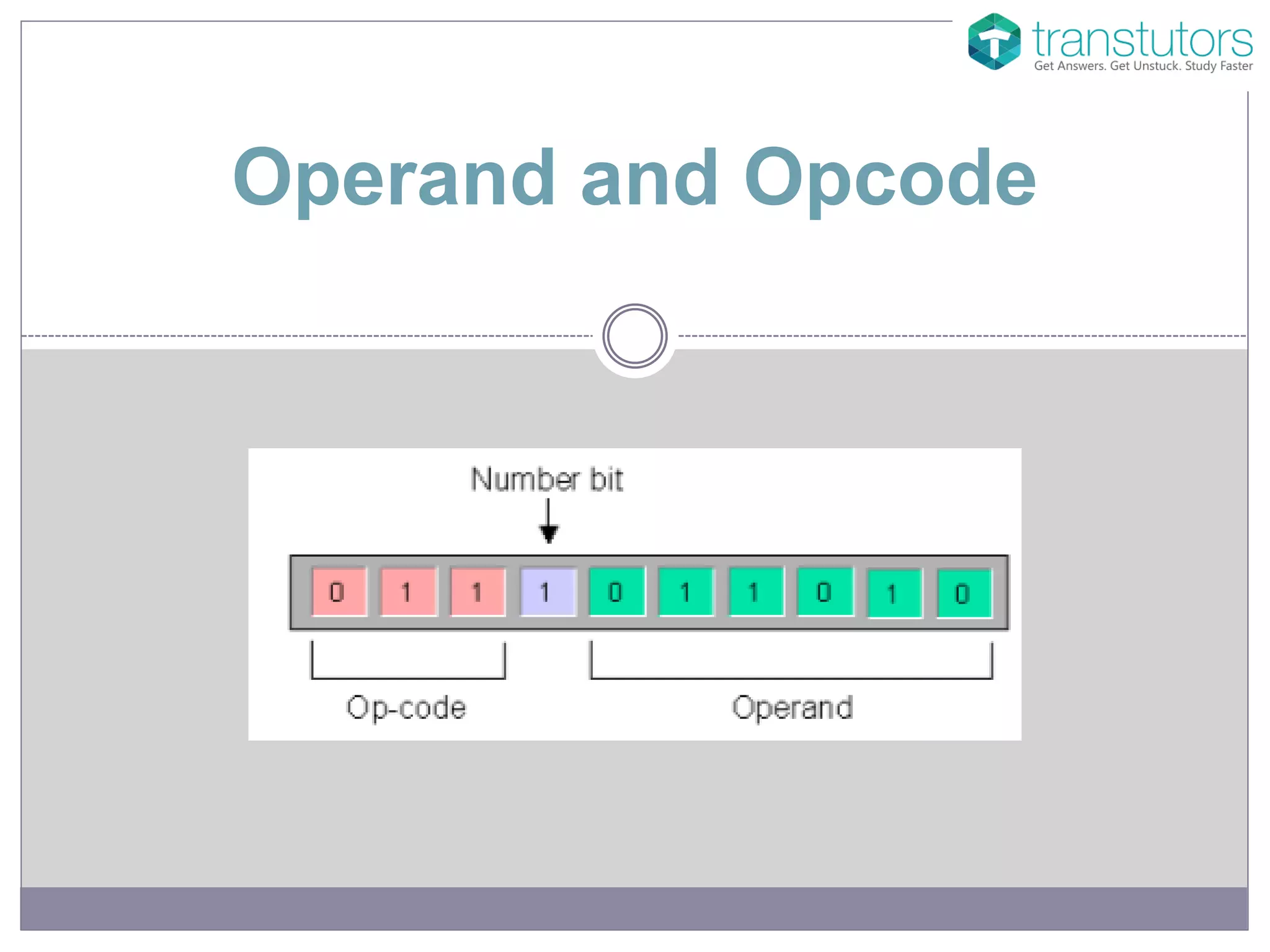
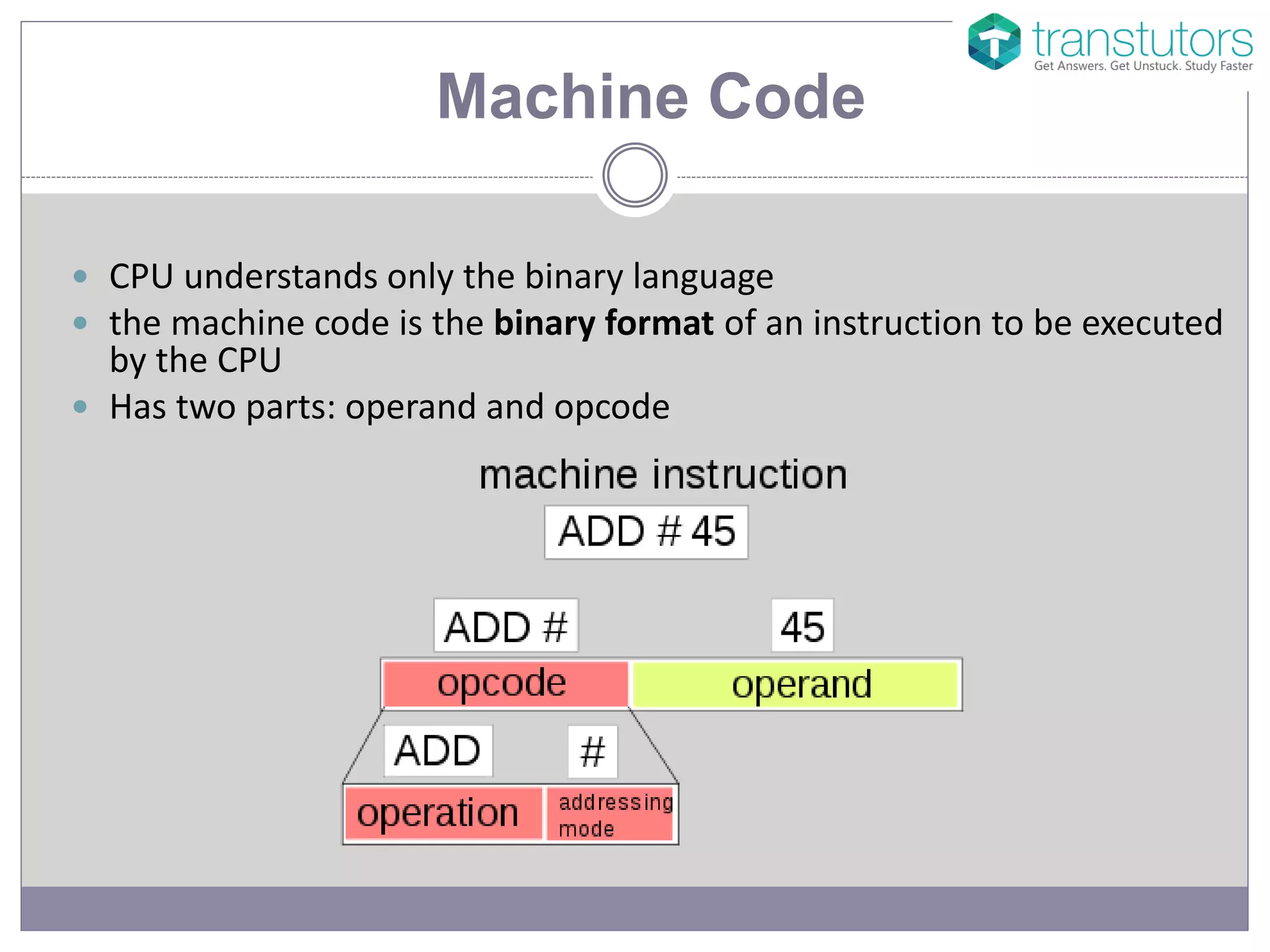
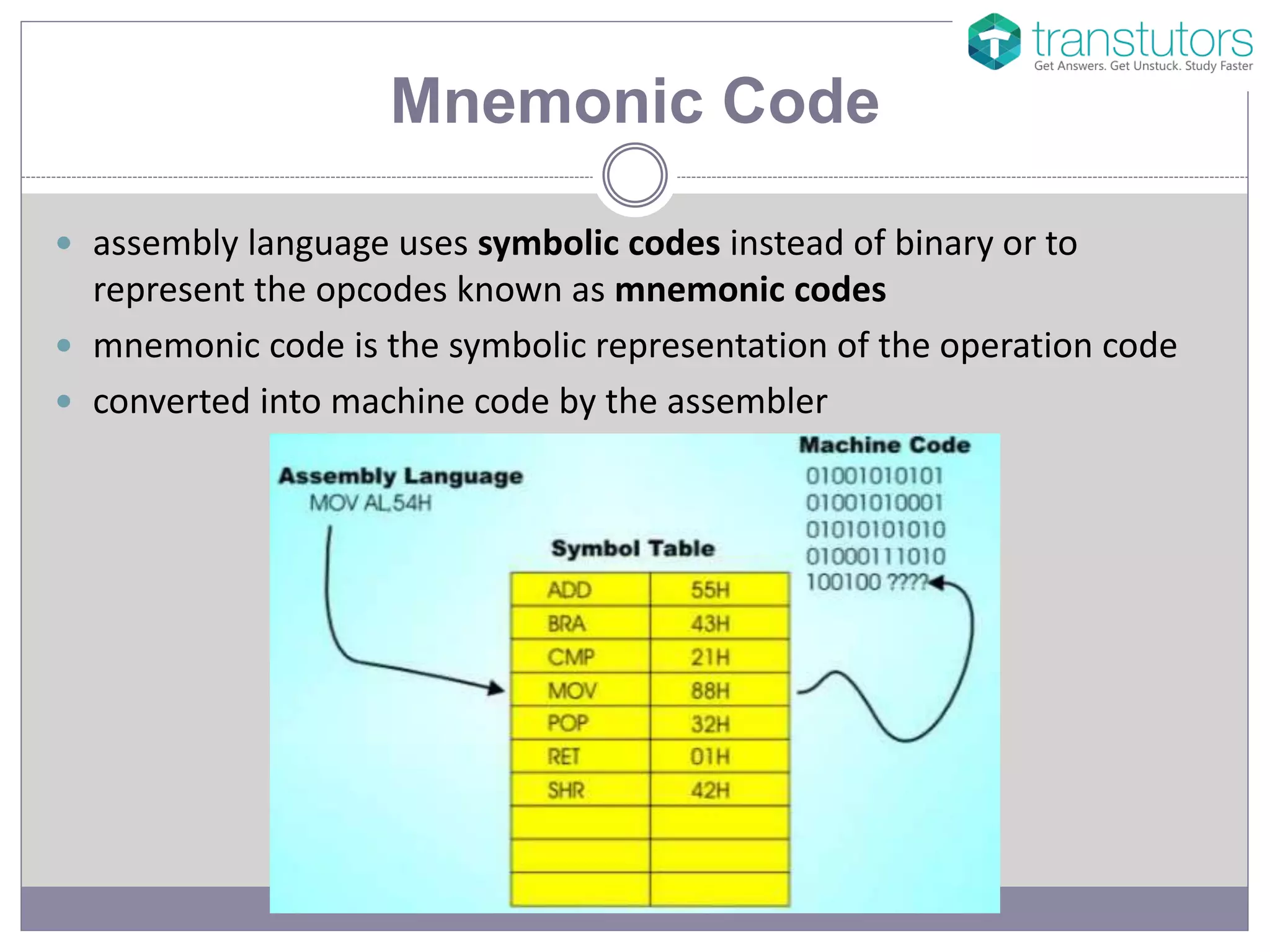
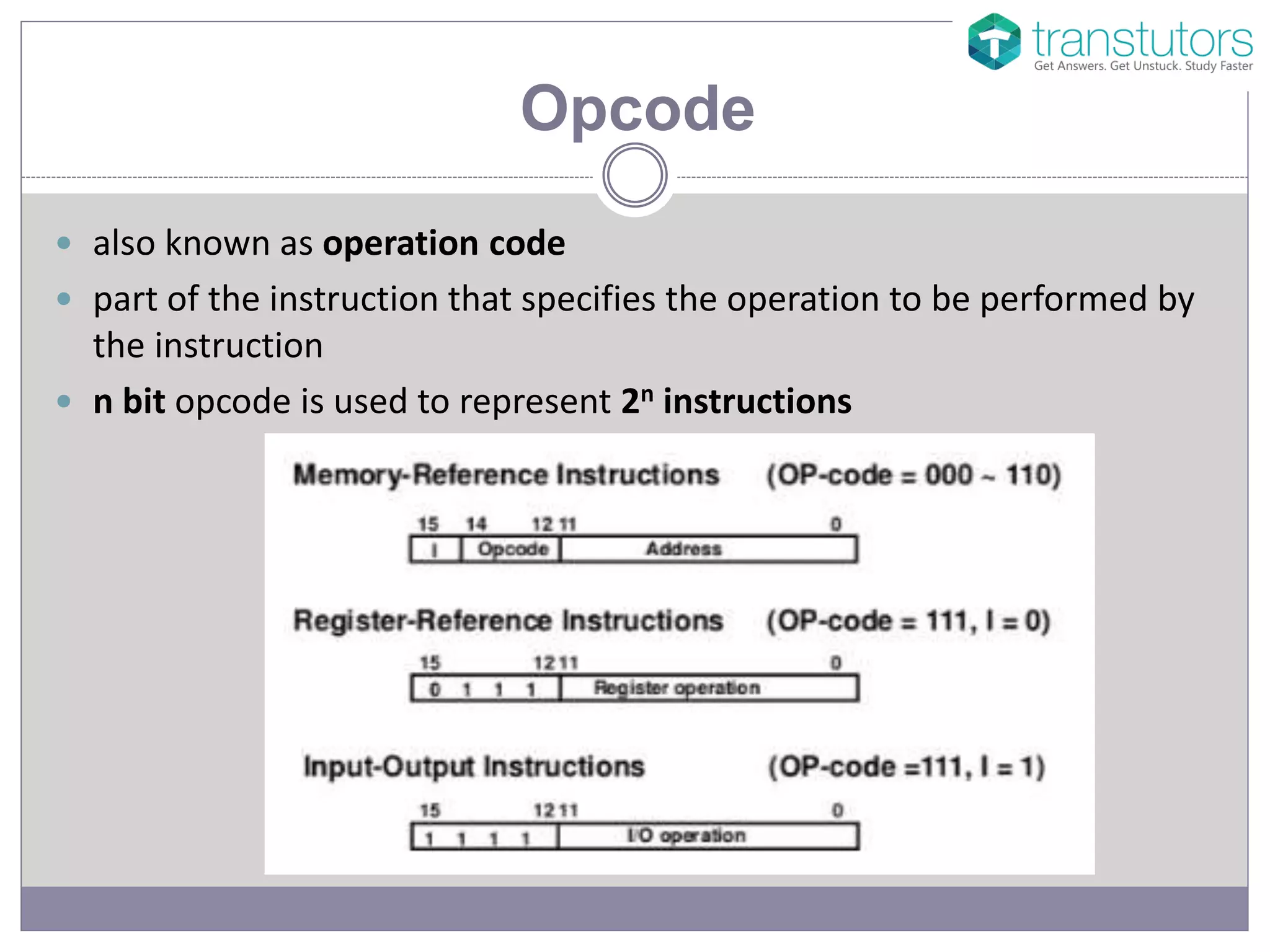
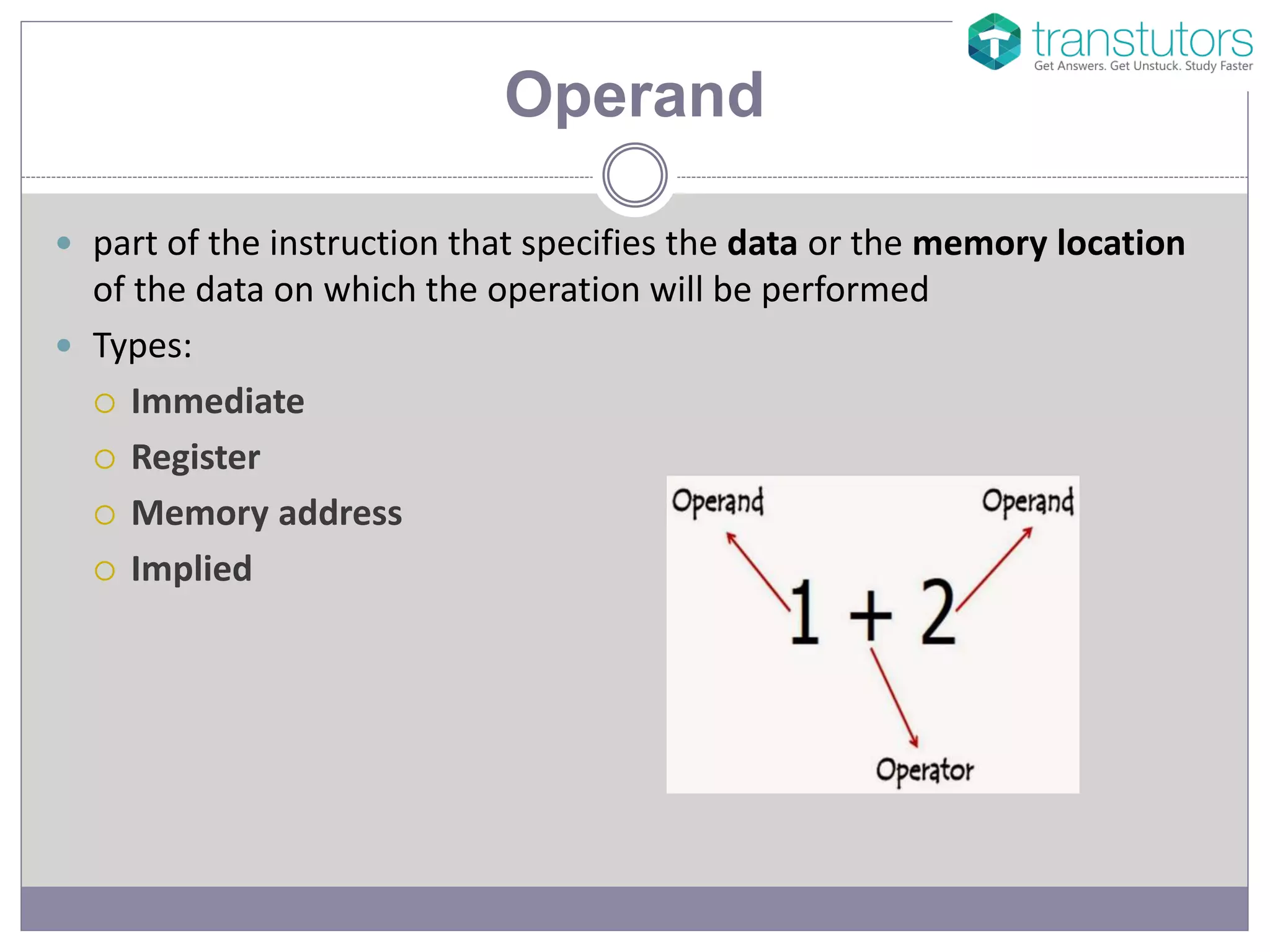
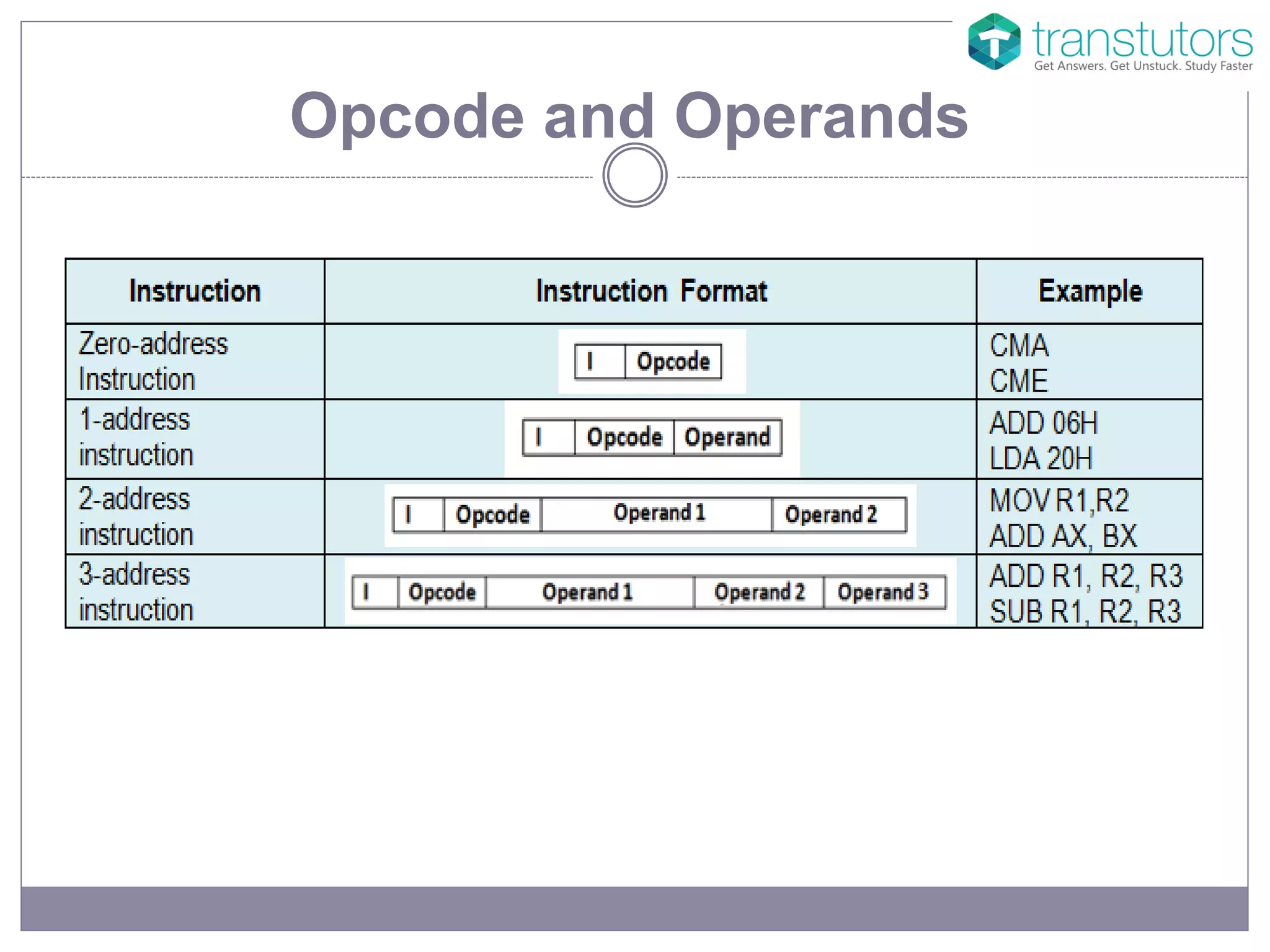


The document explains the components of machine code, specifically focusing on operand and opcode. It describes how machine code is in binary format, with opcodes representing operations and operands specifying the data. Additionally, it mentions that assembly language uses mnemonic codes to represent opcodes.






