Downloaded 110 times

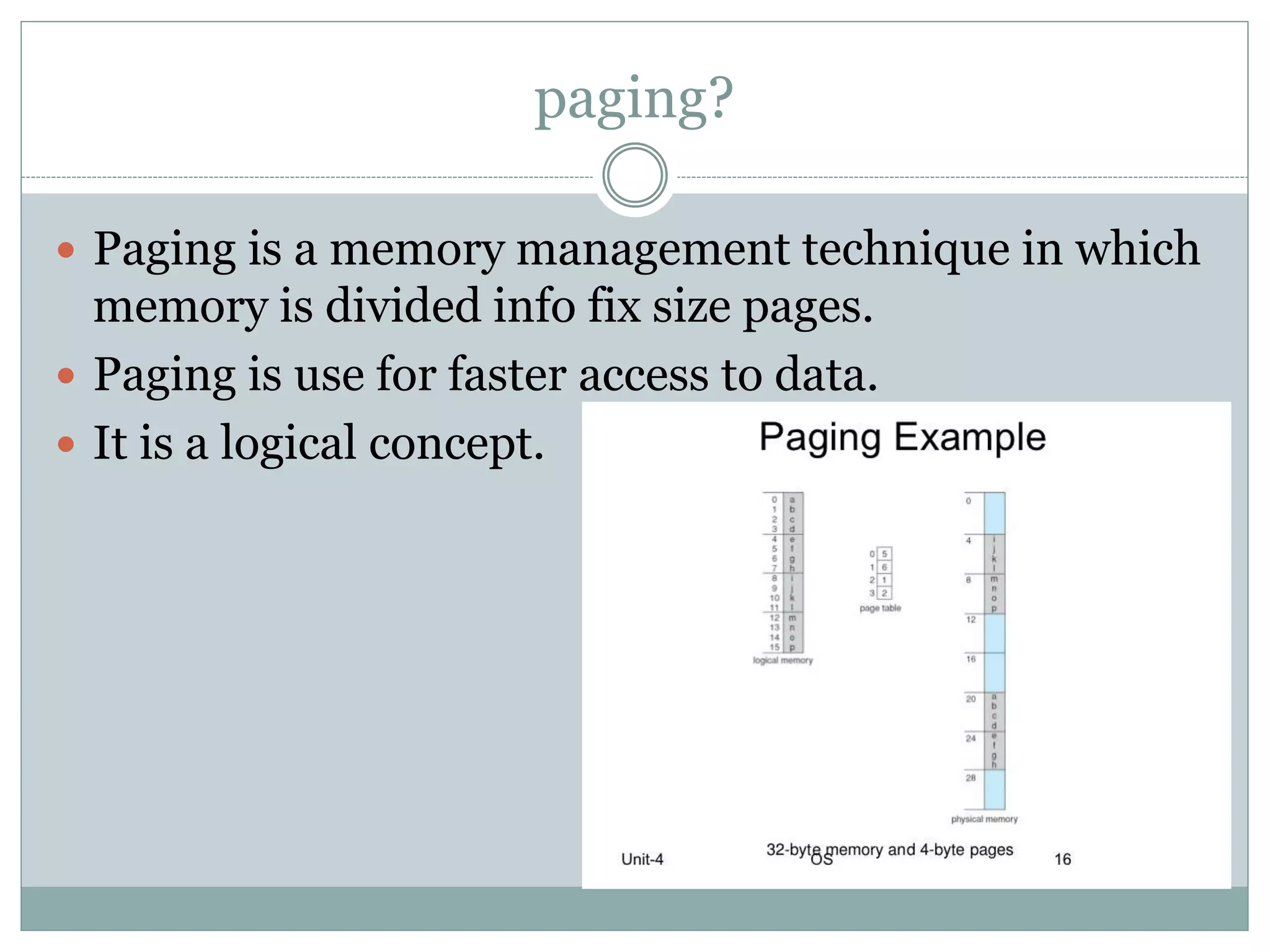

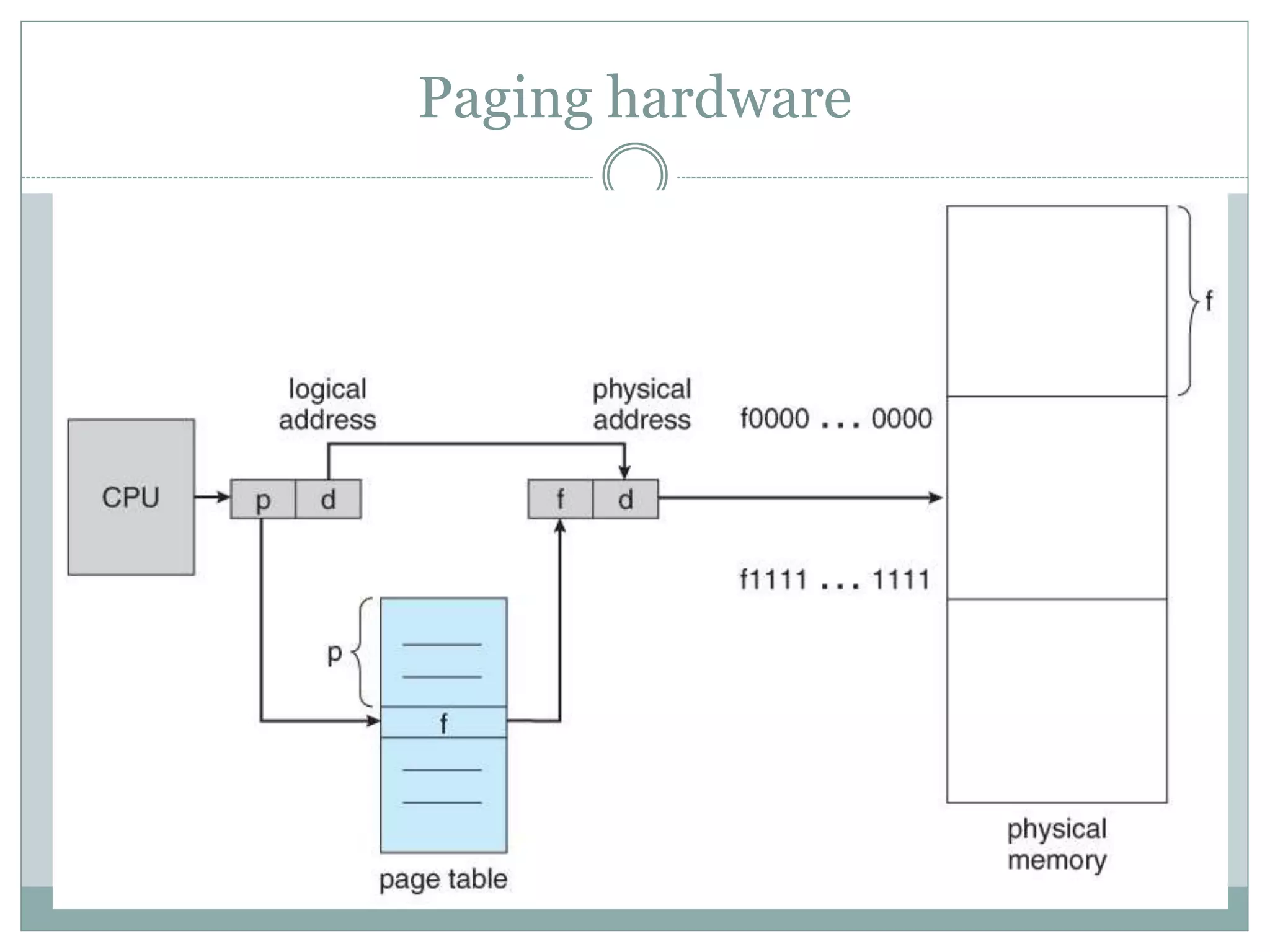
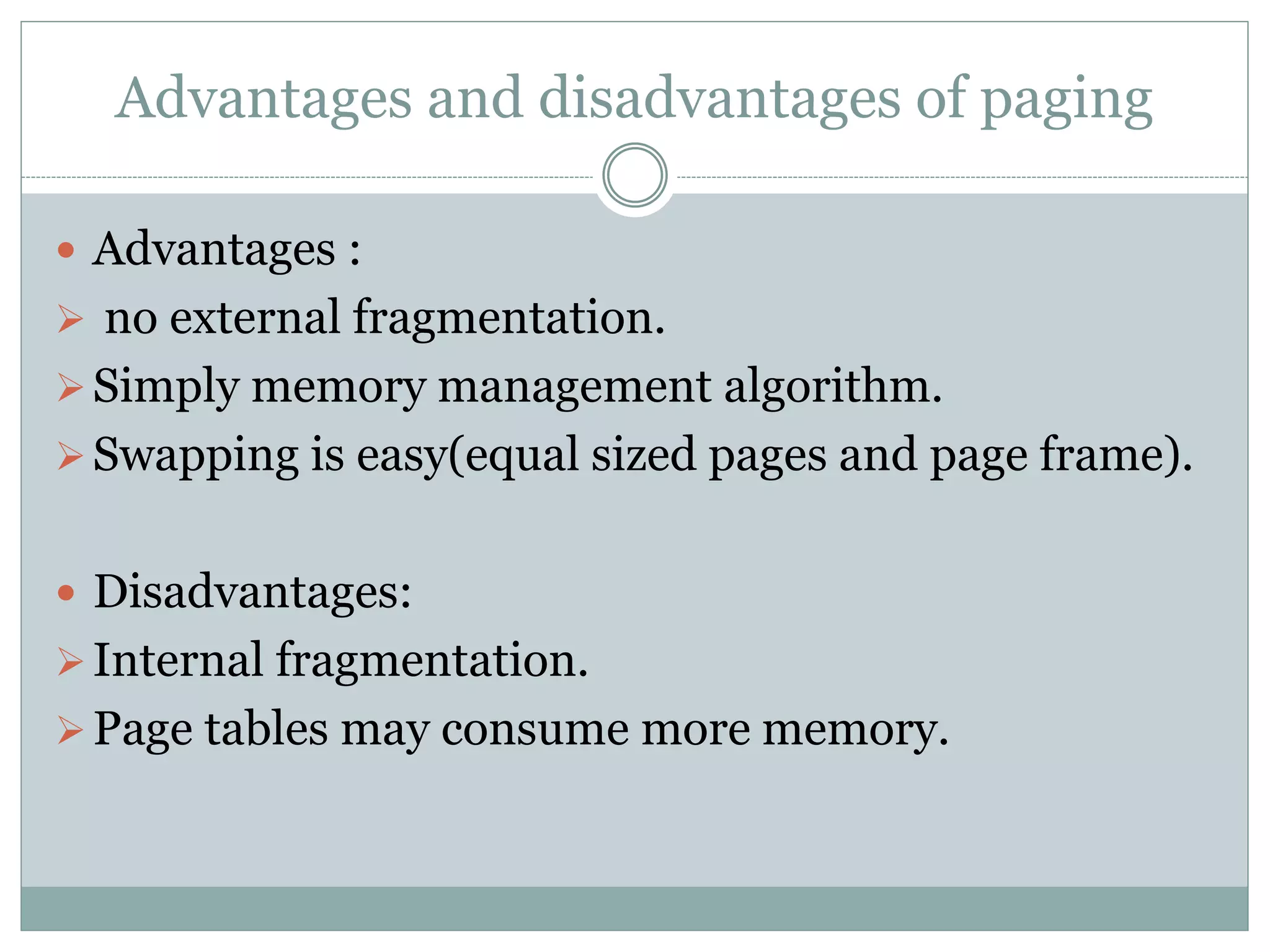
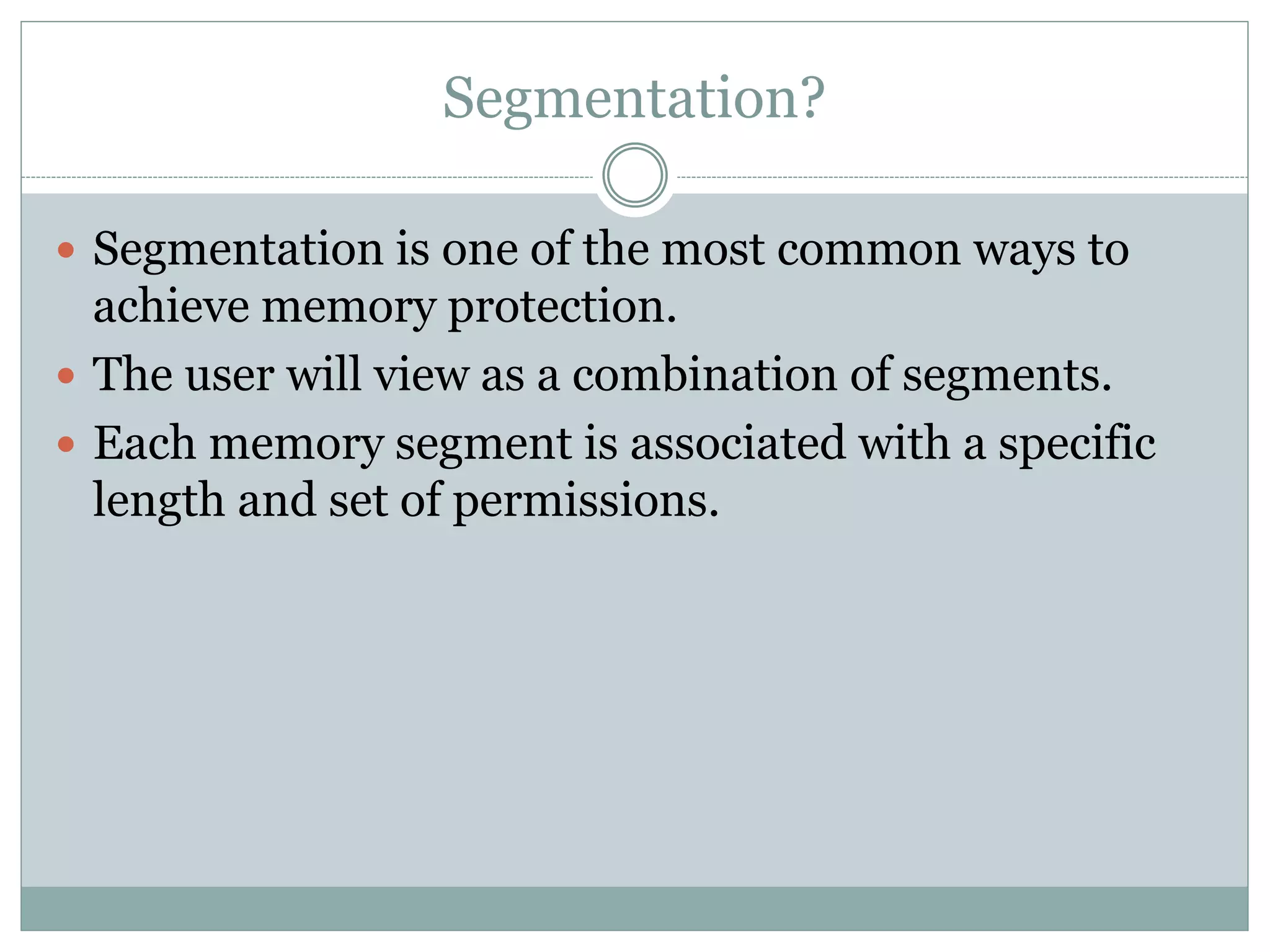
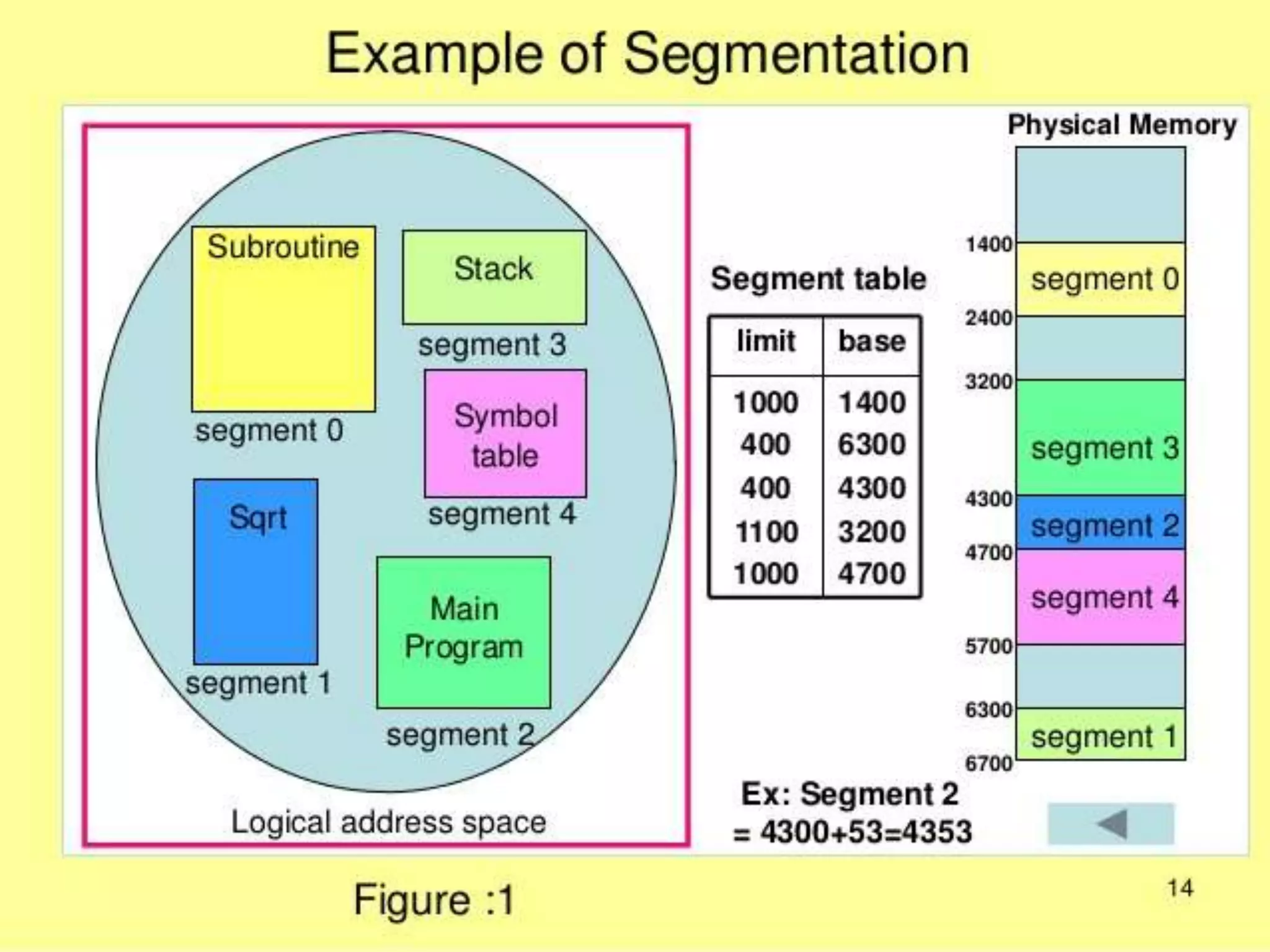
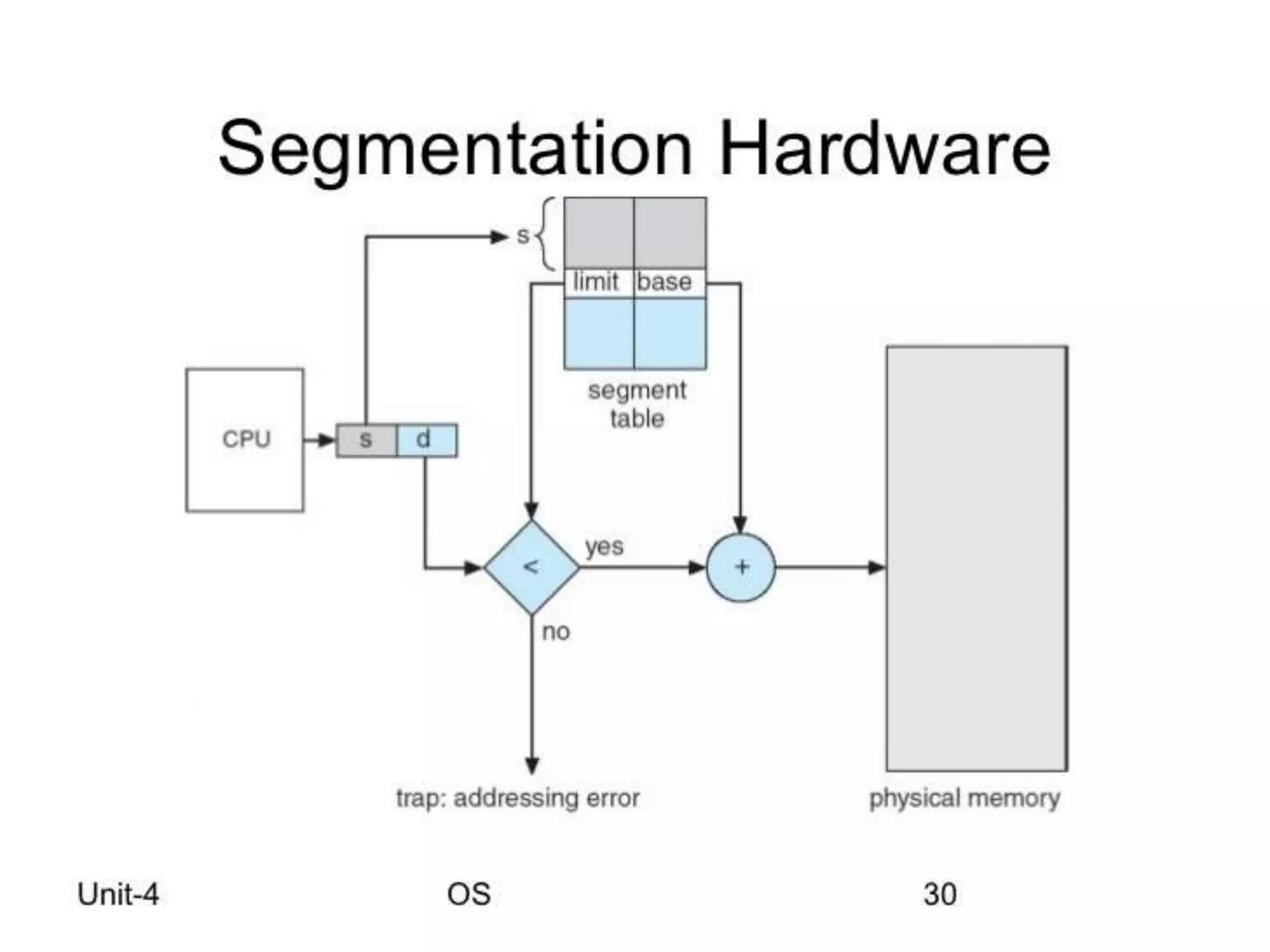
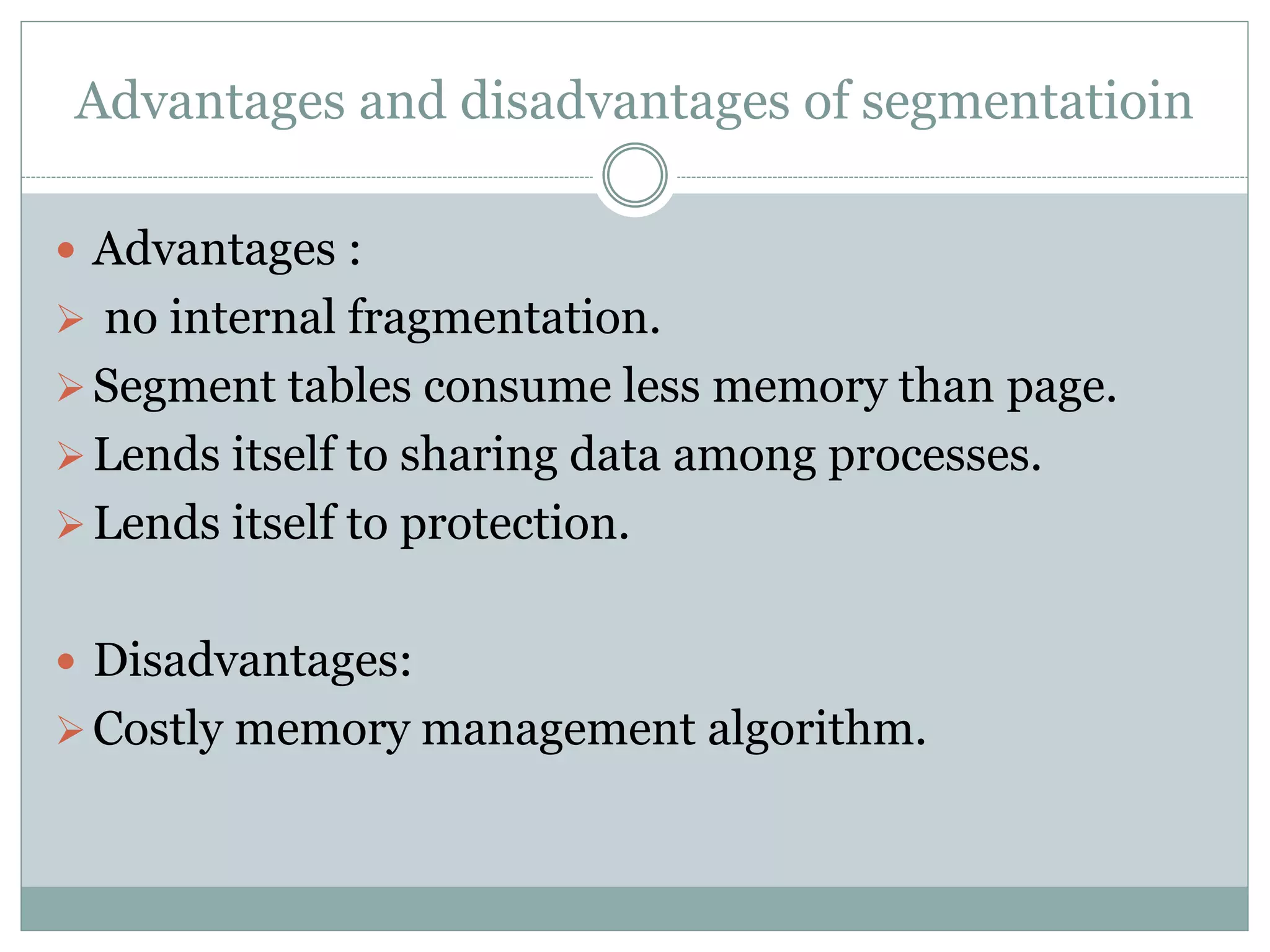
This document discusses paging and segmentation in operating systems. Paging divides memory into fixed-size pages for faster data access and allows physical addresses to be non-contiguous. It has advantages like no external fragmentation but disadvantages like internal fragmentation and consuming memory for page tables. Segmentation divides memory into segments of varying lengths and permissions for memory protection. It has advantages like no internal fragmentation and less memory used for segment tables, while lending itself to data sharing and protection but has the disadvantage of a more costly memory management algorithm.








