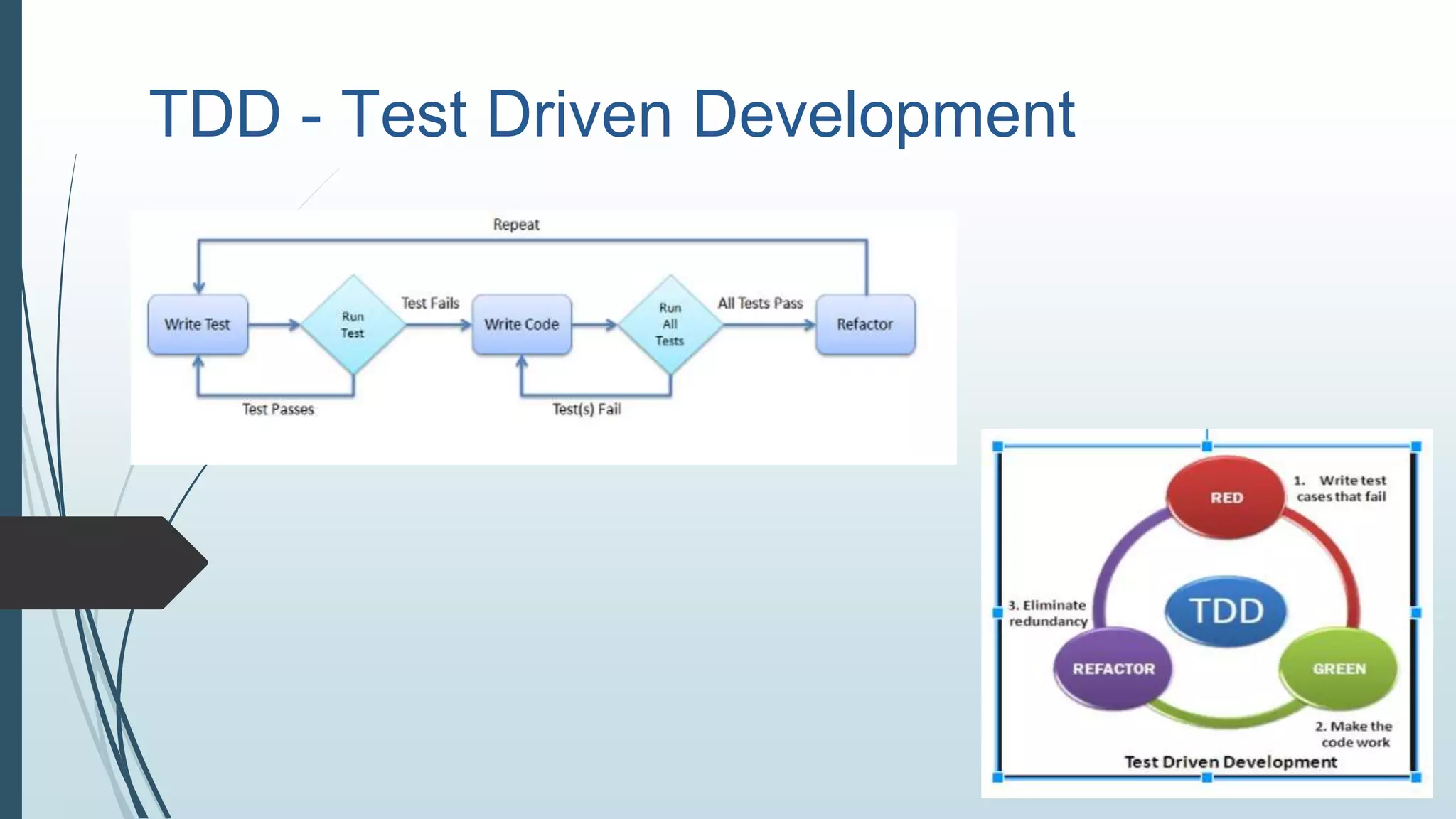
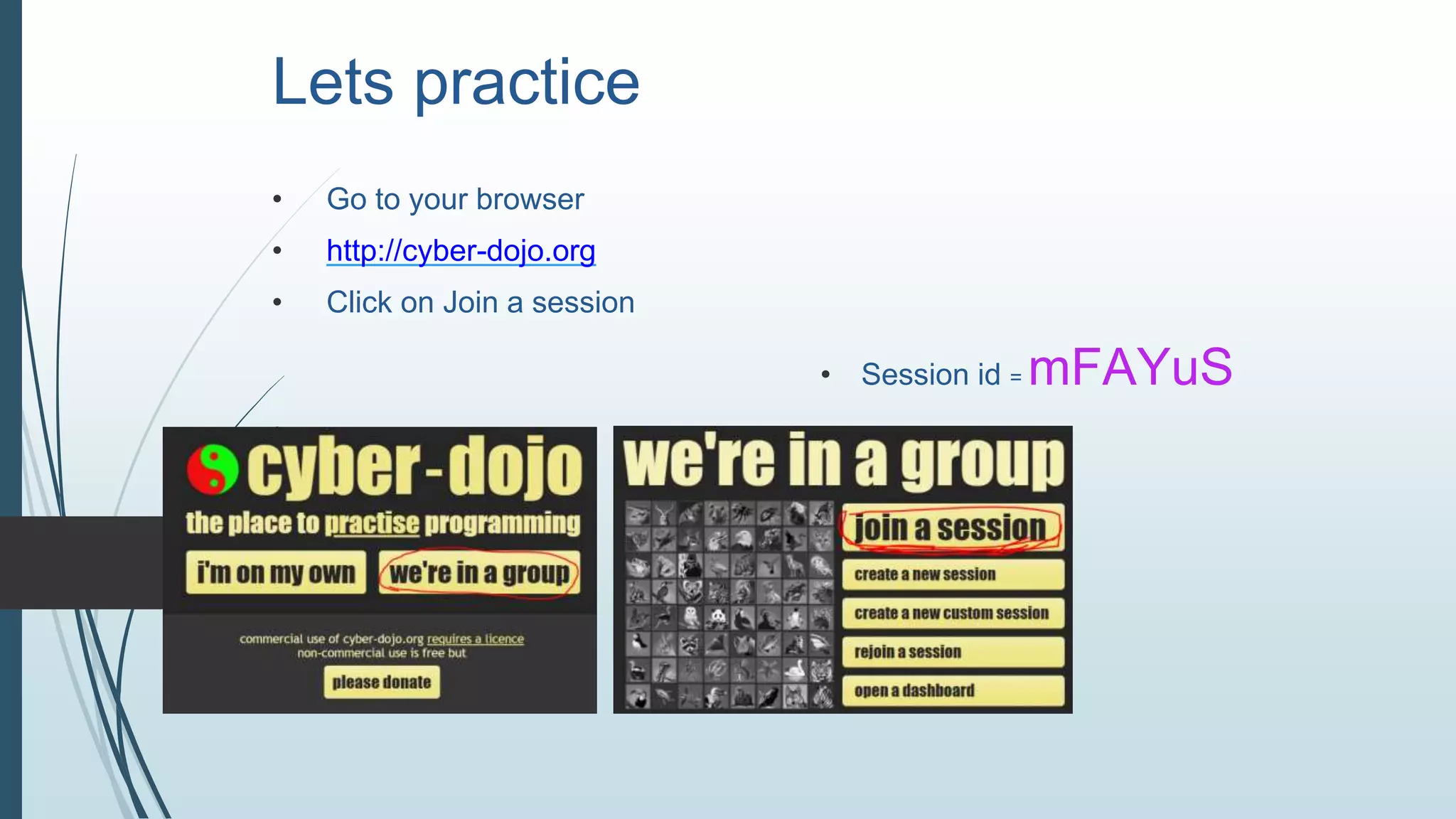
The document details a session agenda focused on paired programming and test-driven development (TDD). It outlines goals, preparation tips, and the TDD process, emphasizing collaboration, feedback, and the benefits of TDD in creating maintainable and flexible code. The document includes practical exercises and resources for further learning.