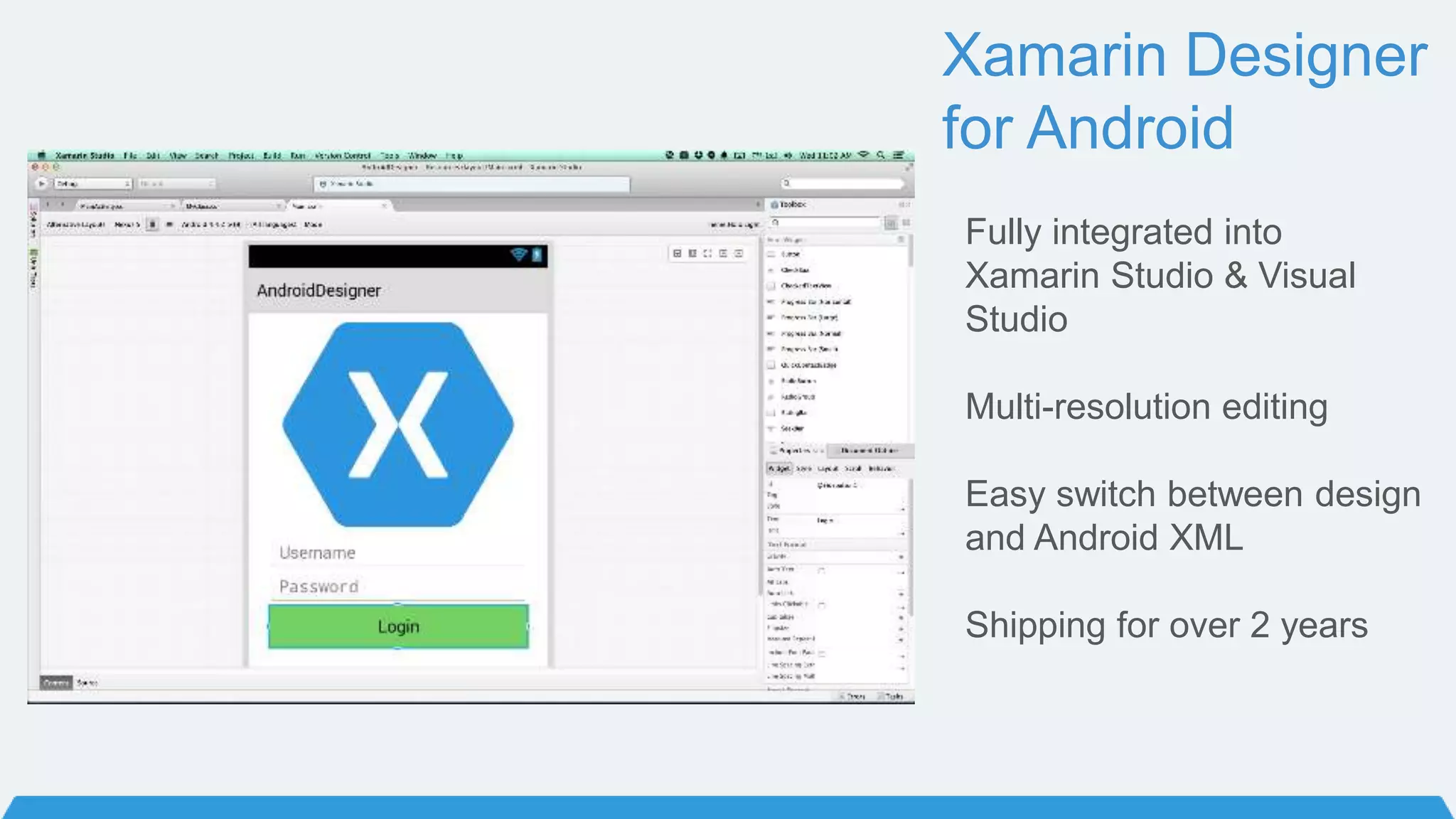
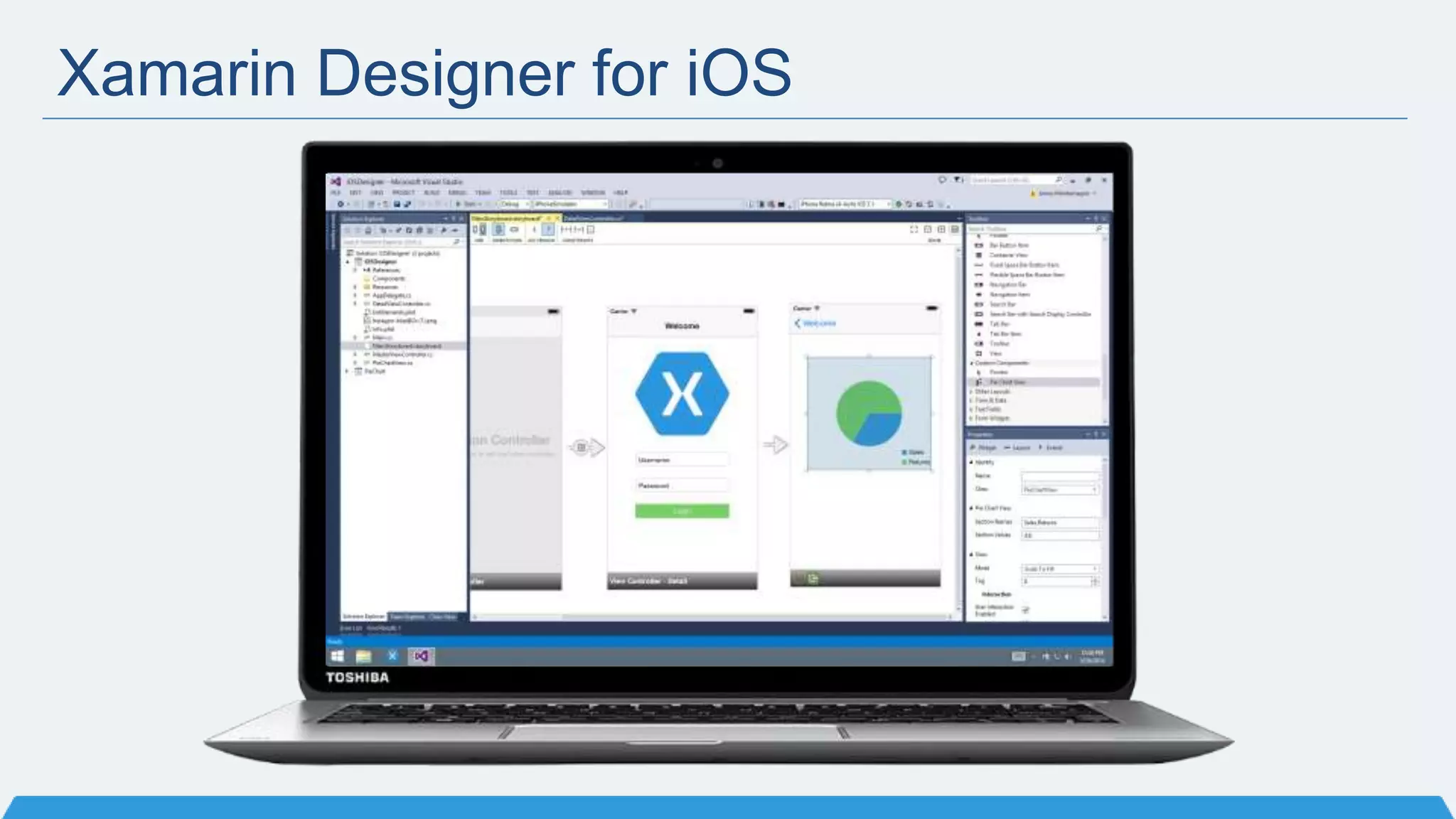
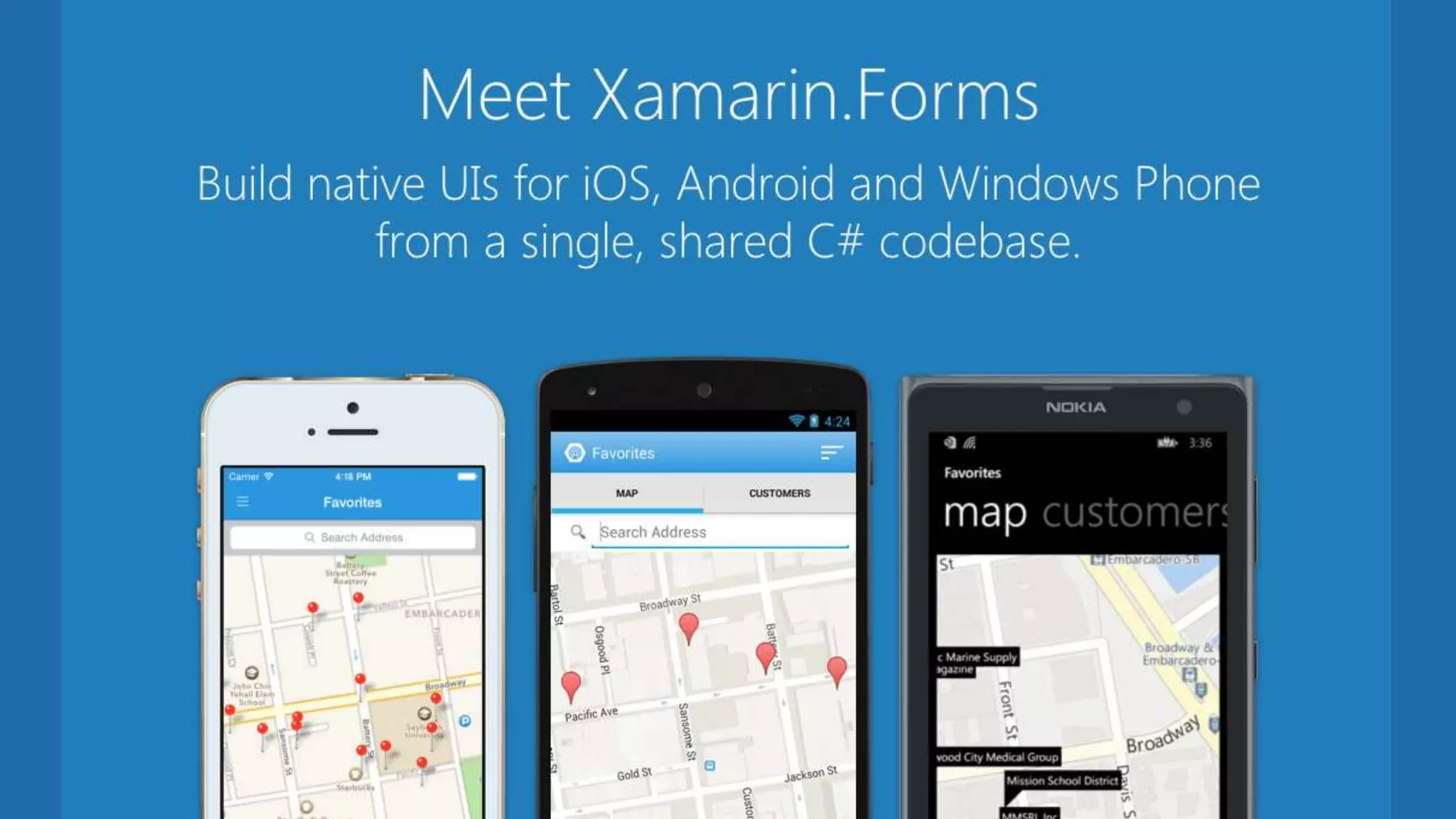
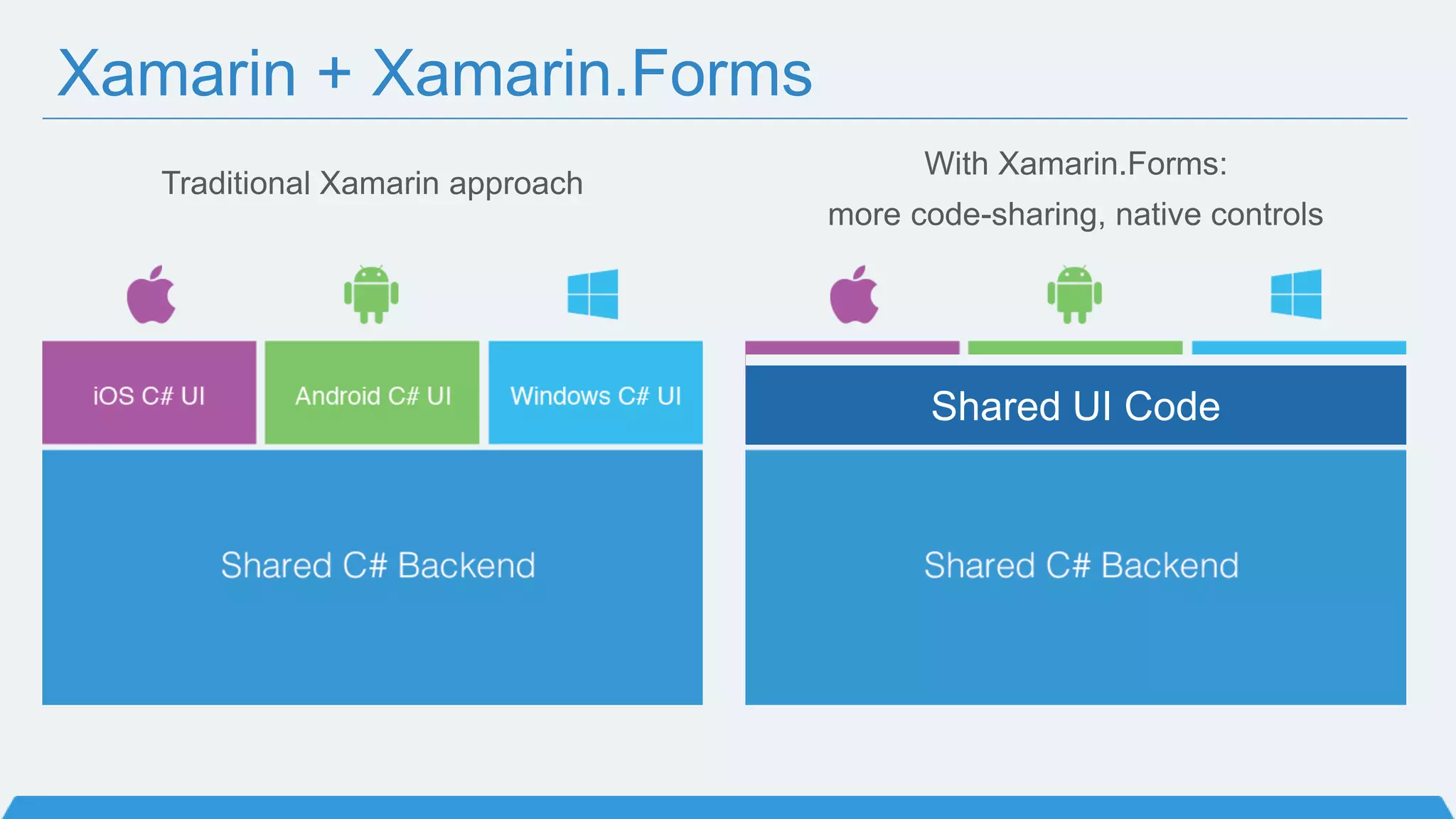
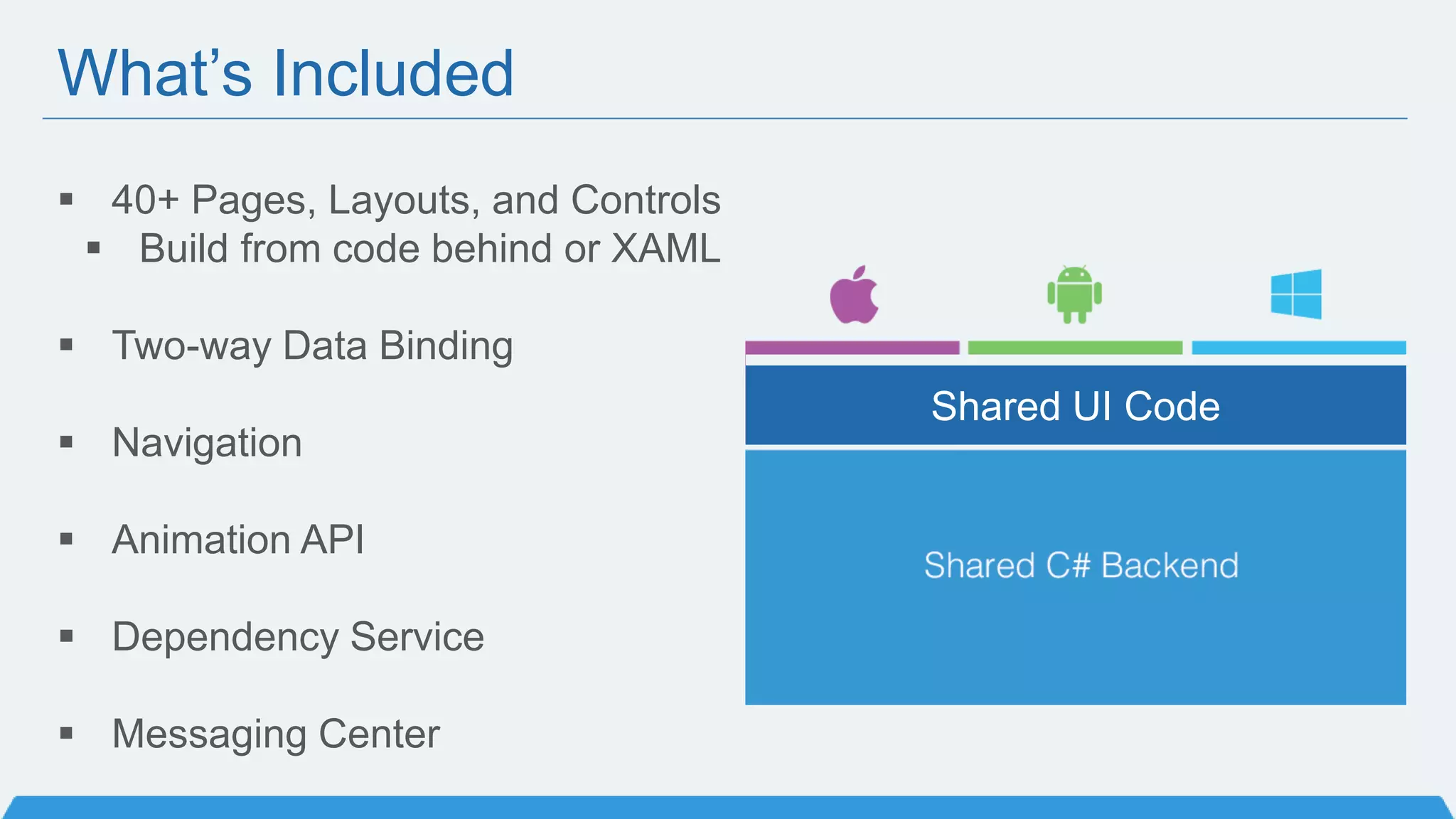
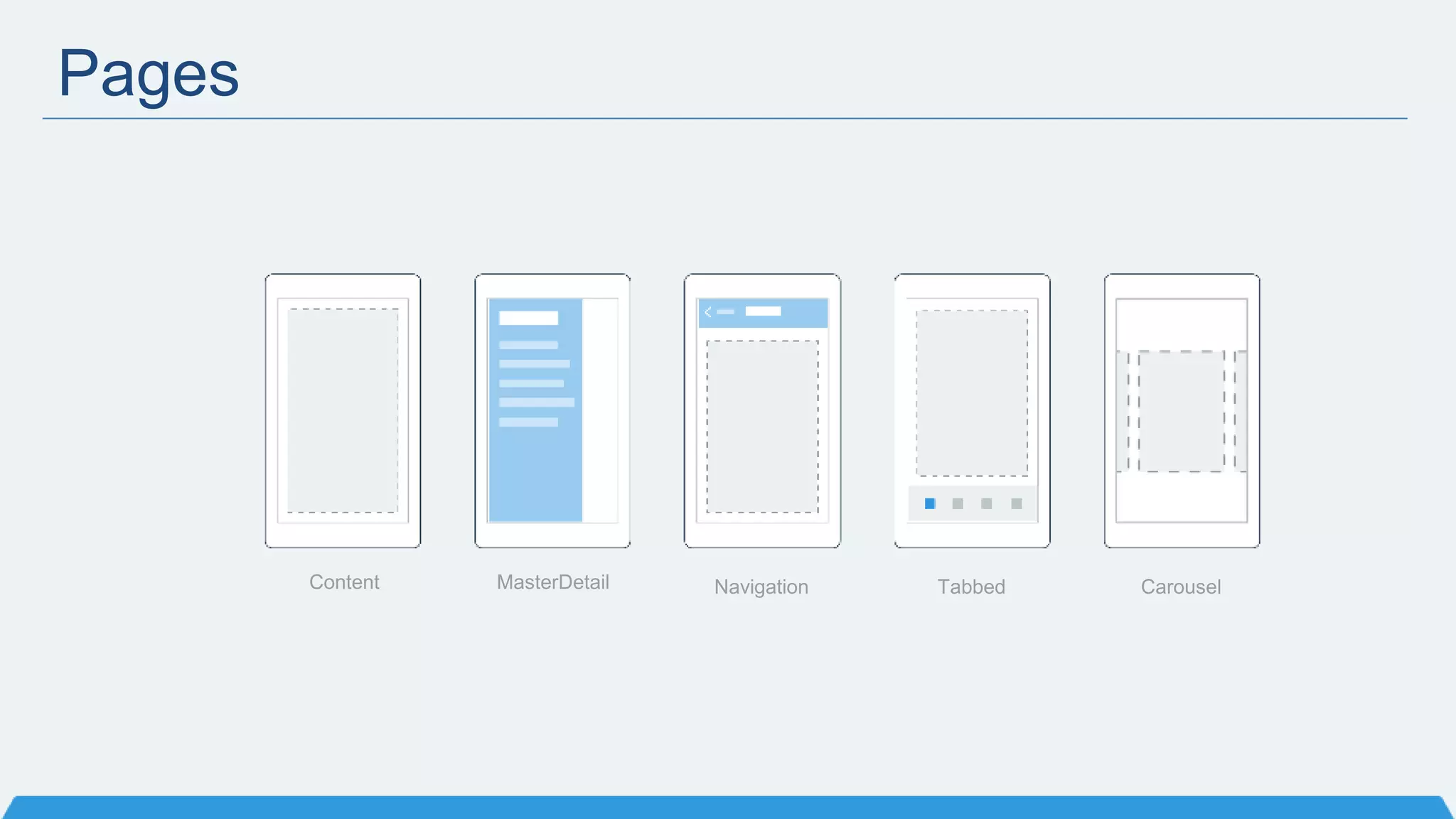
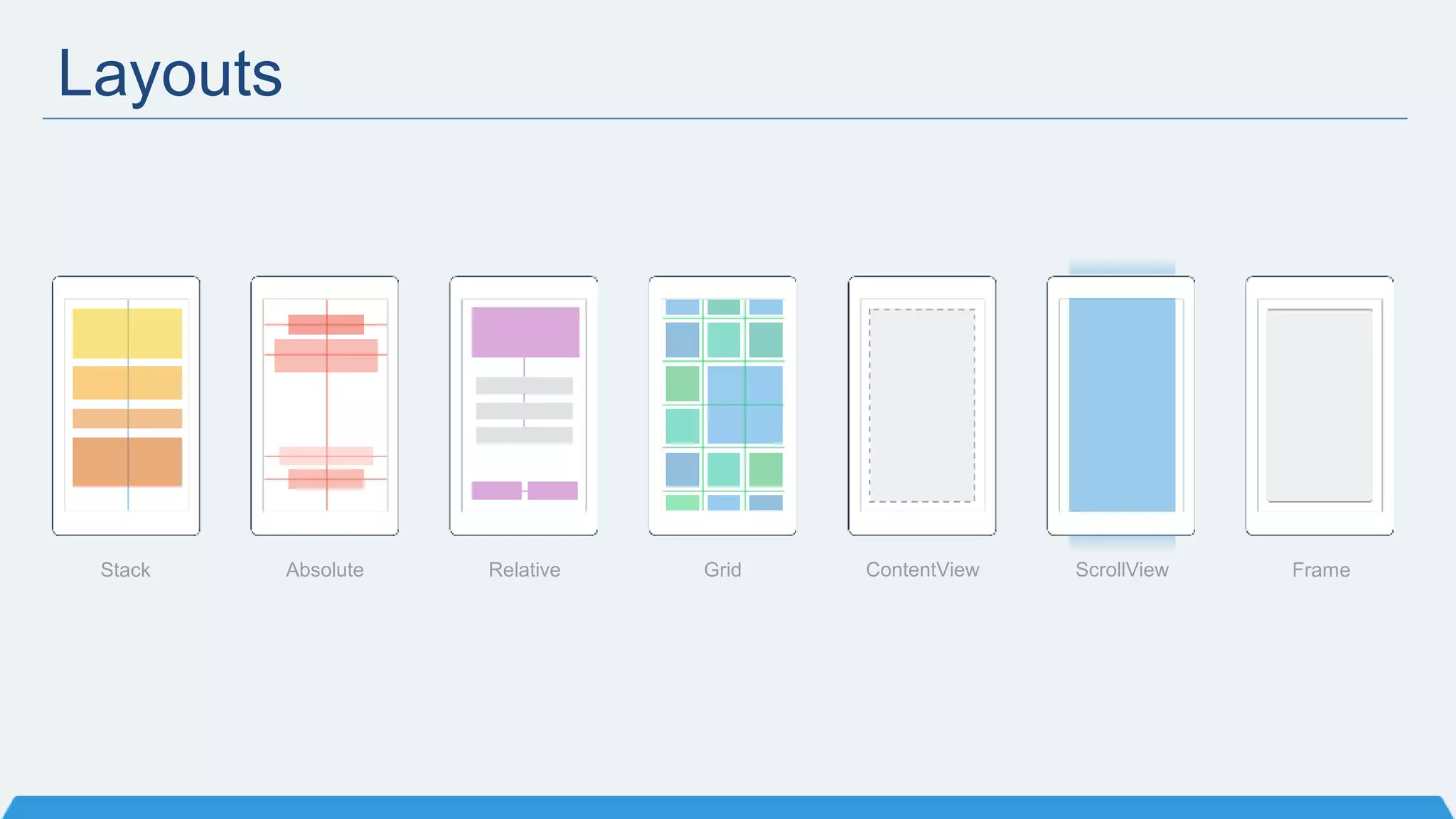
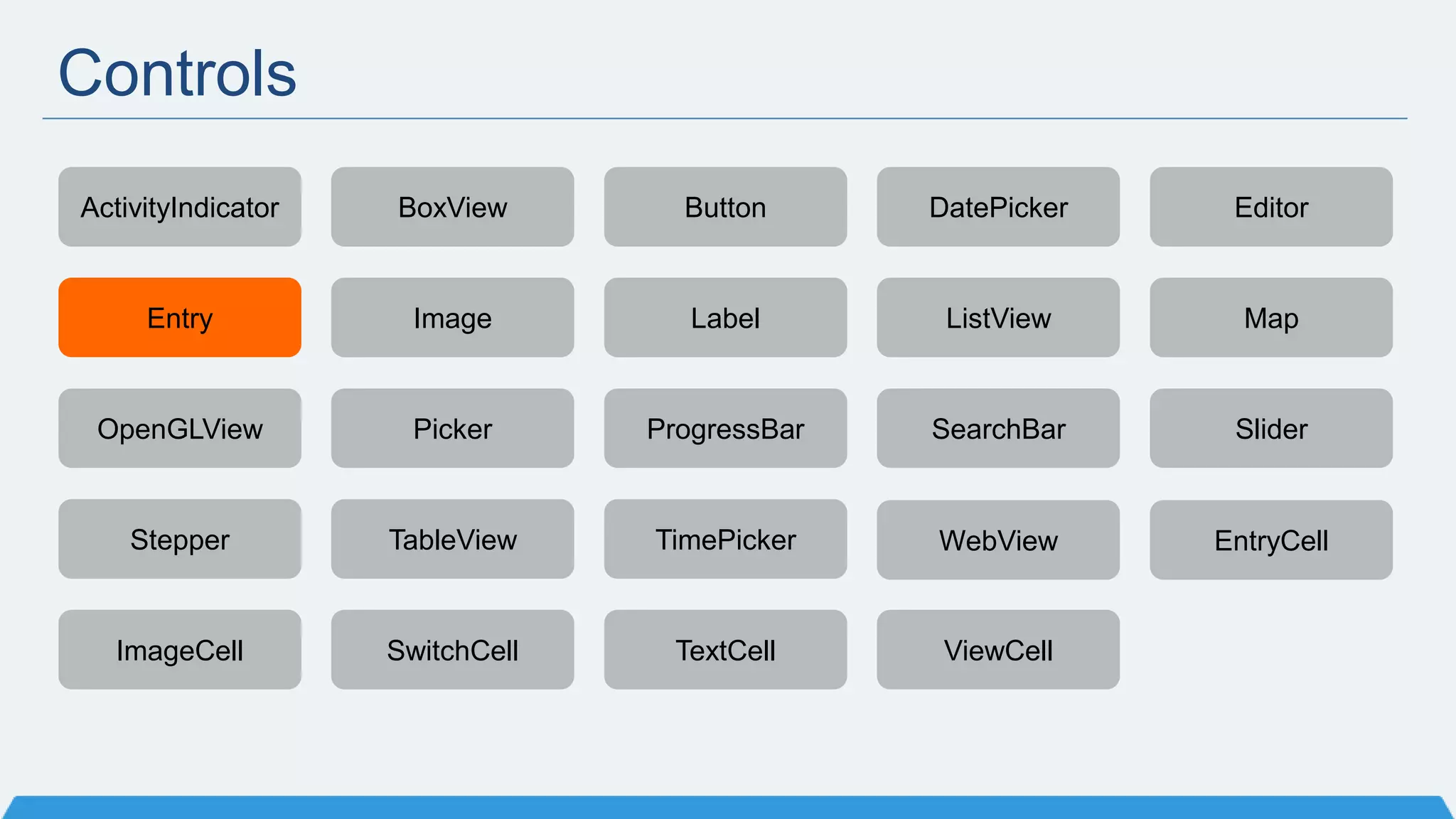
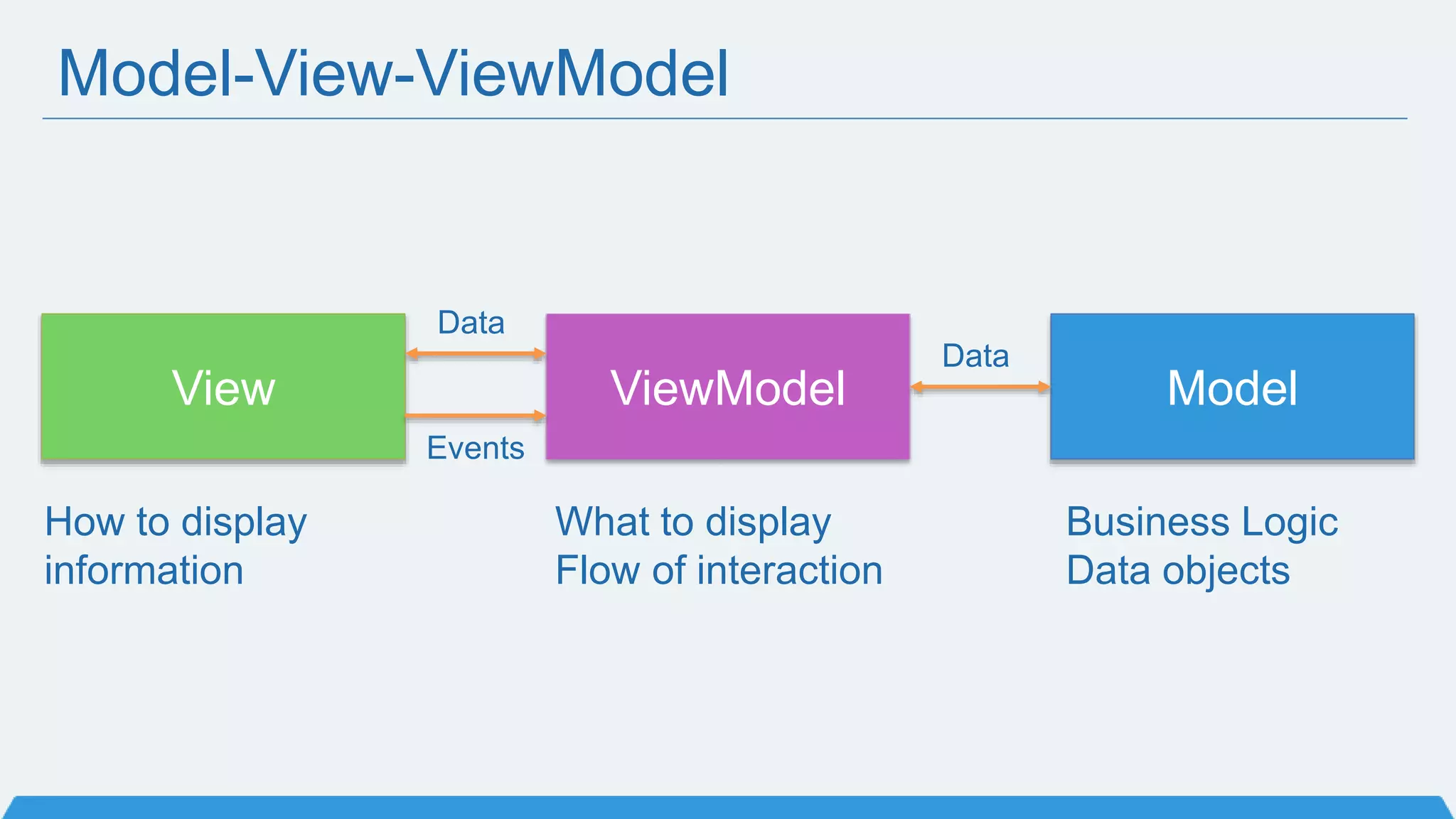
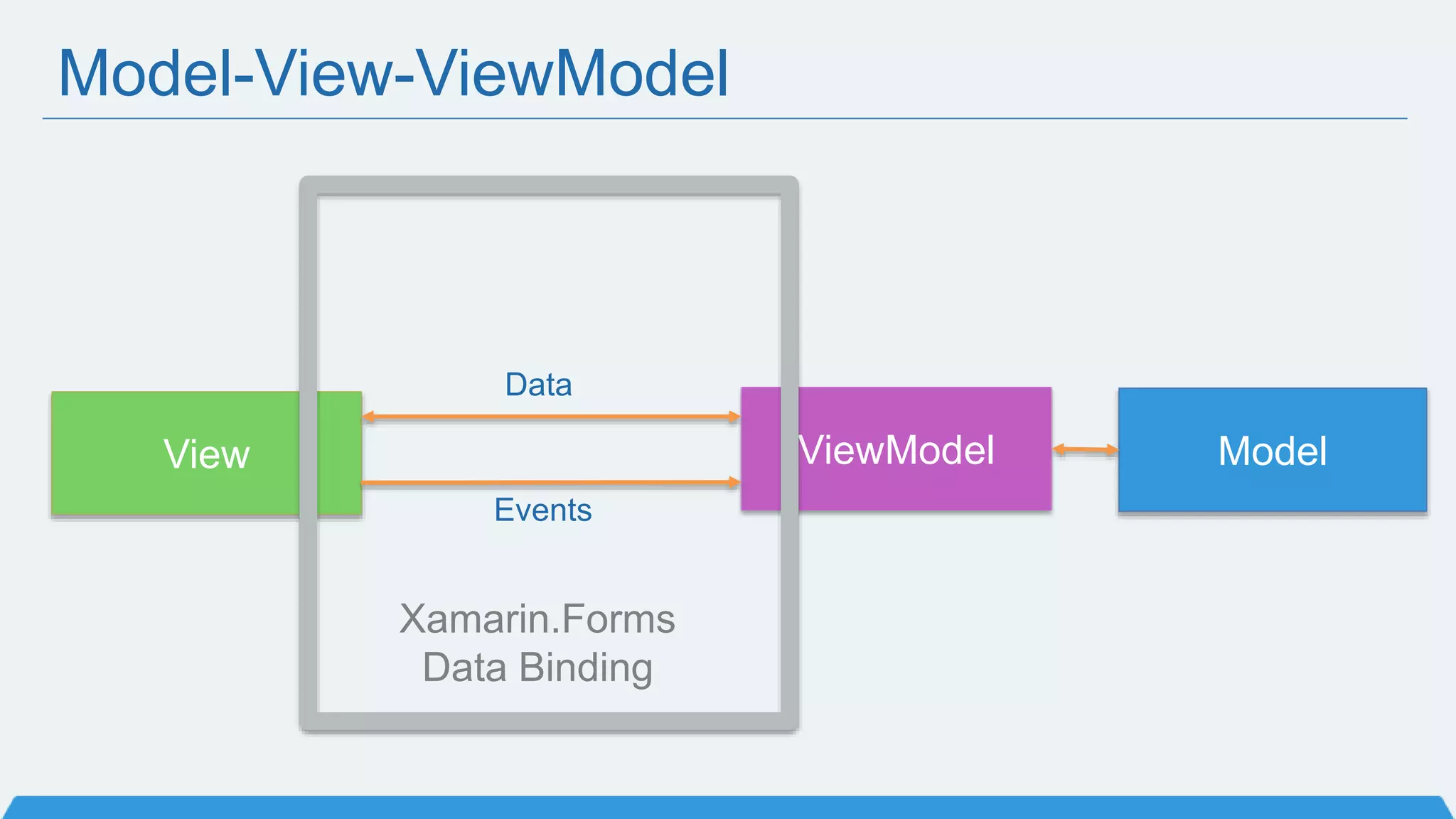
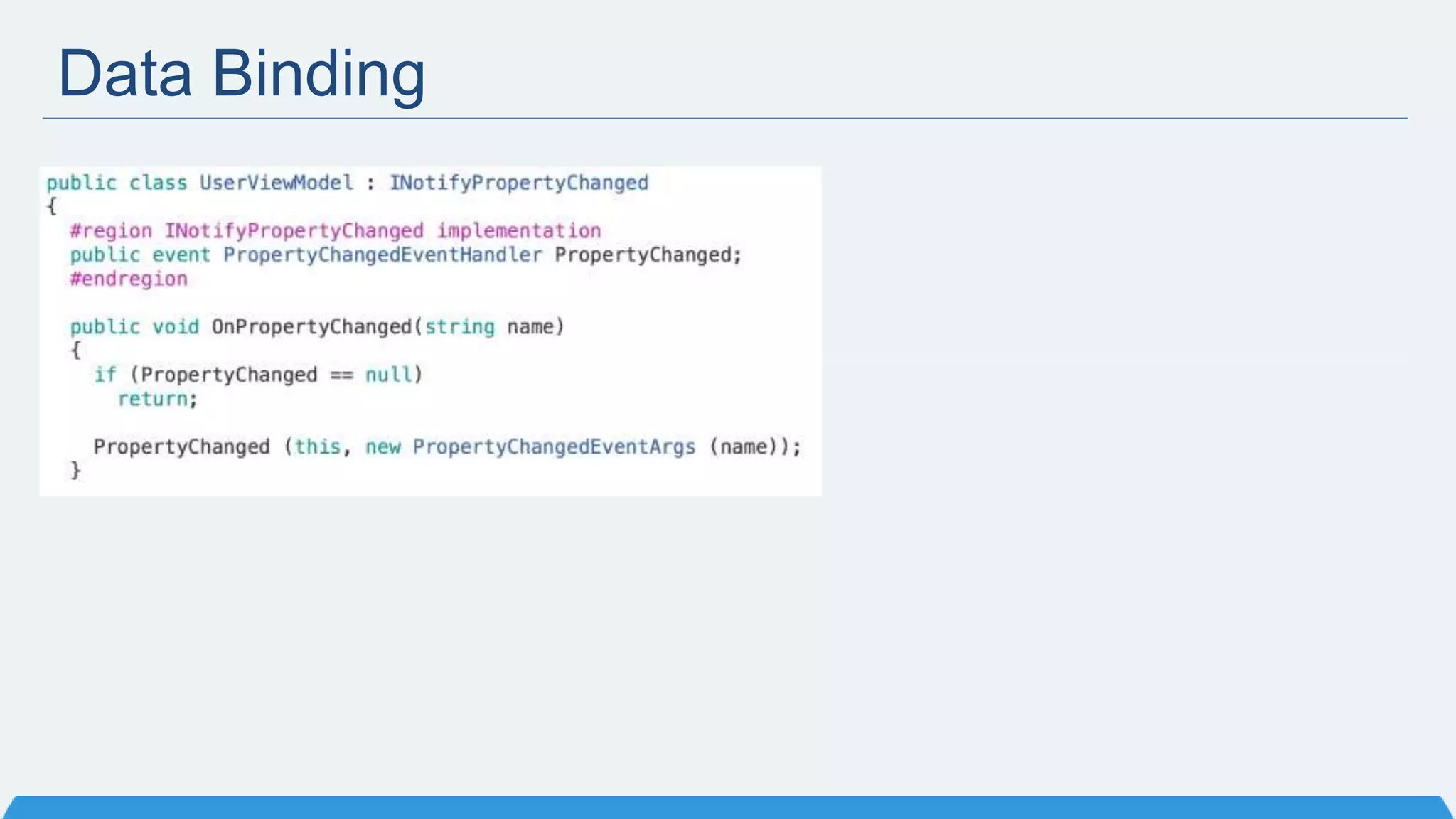
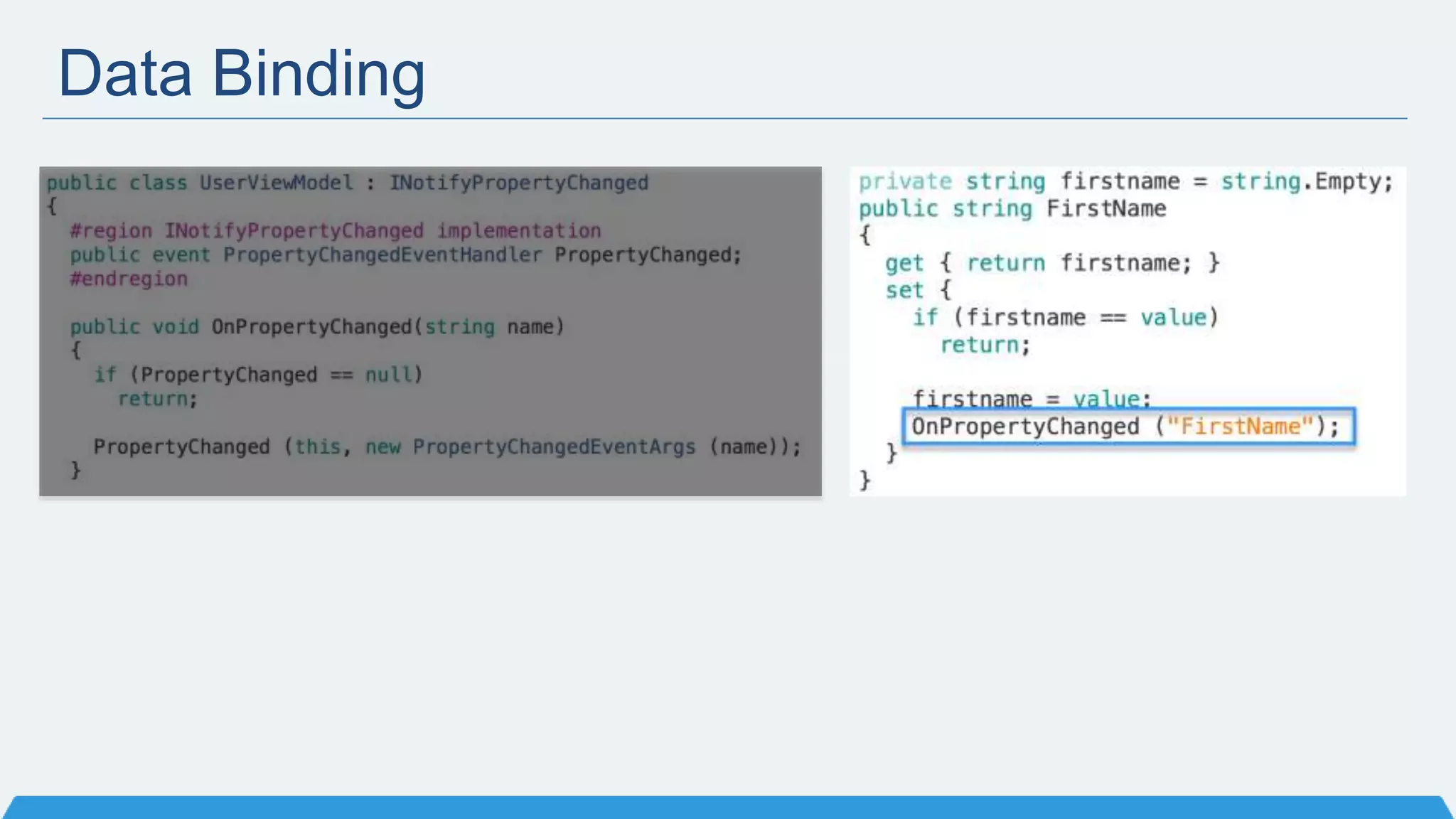
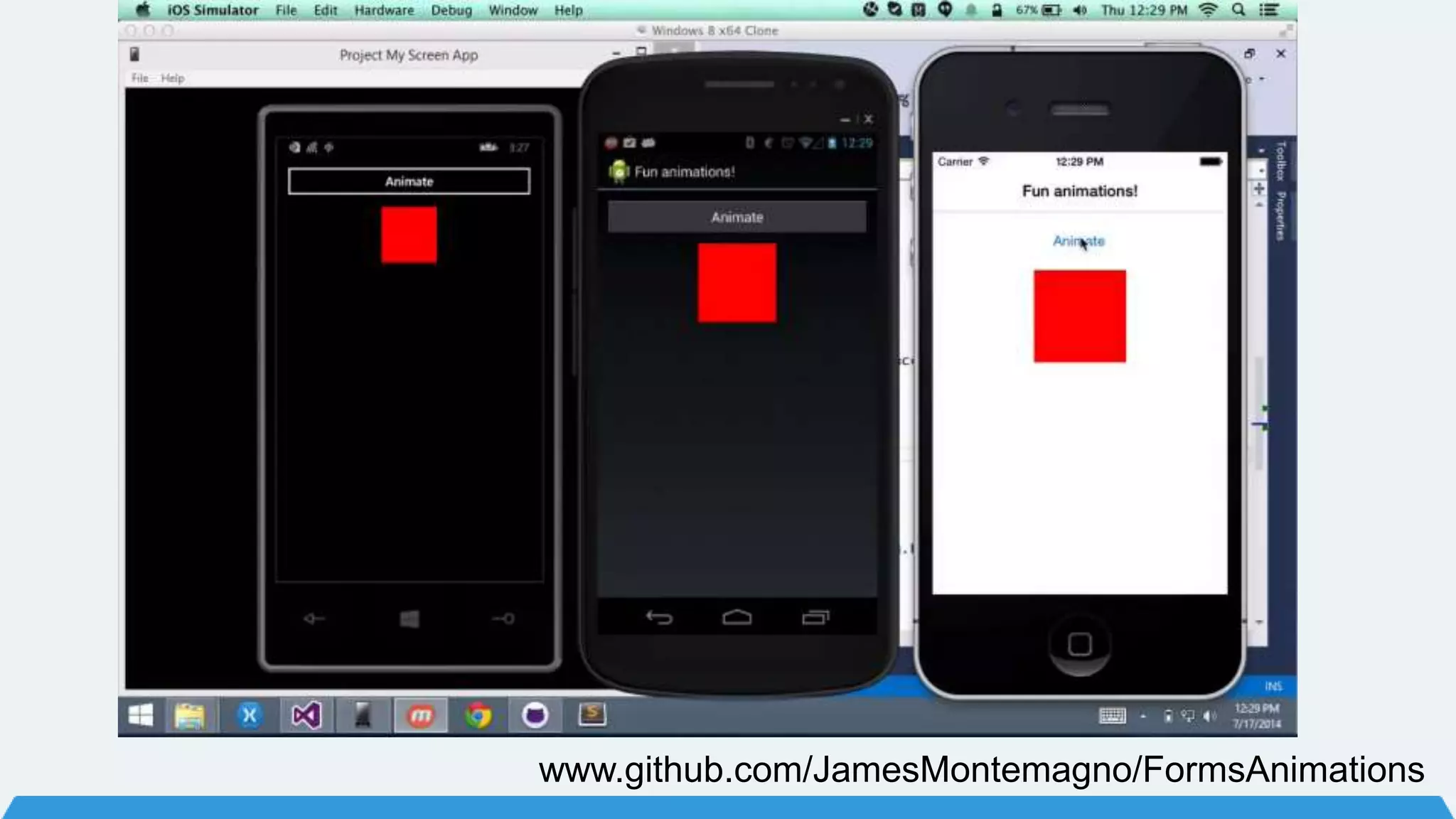
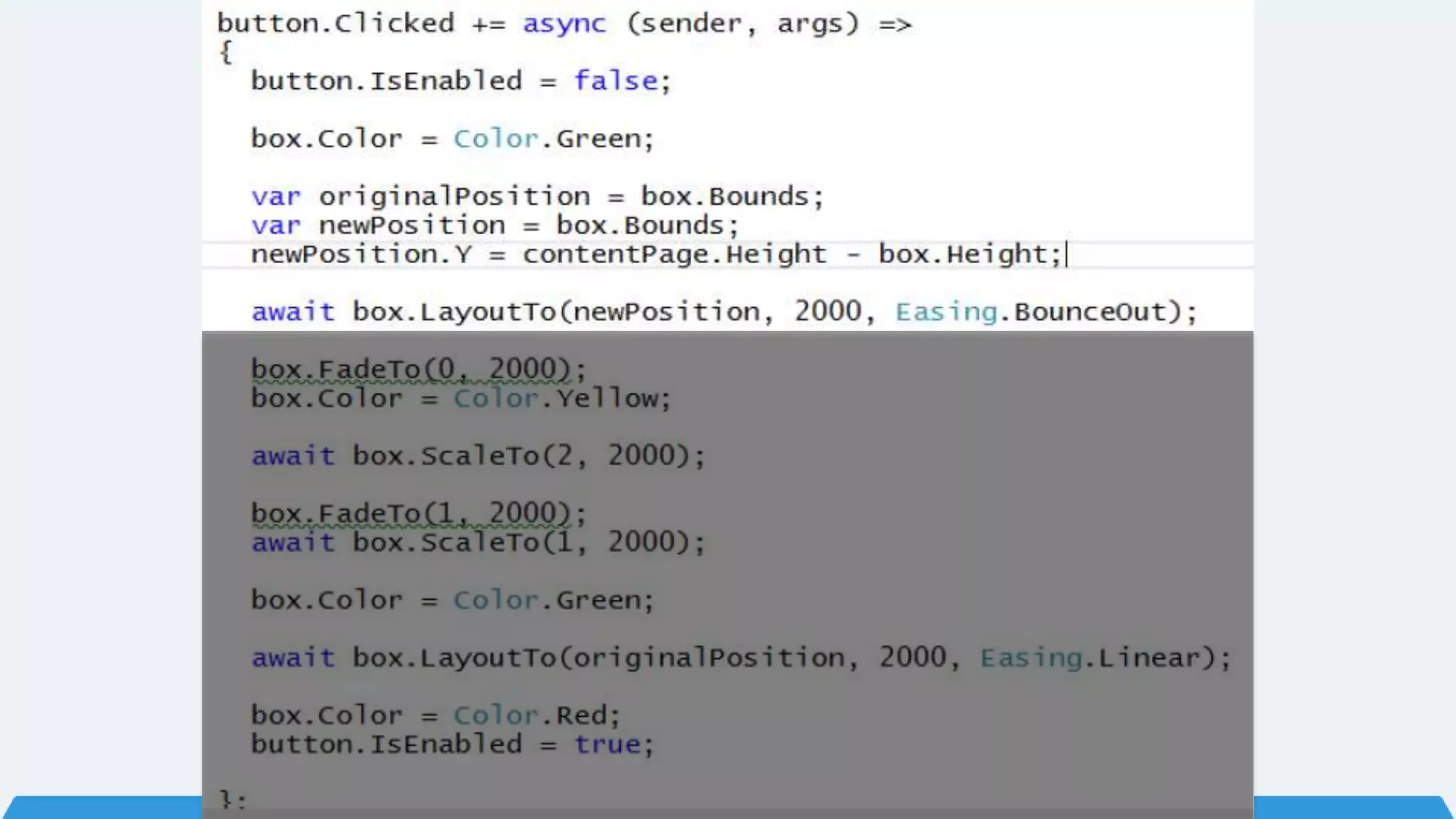
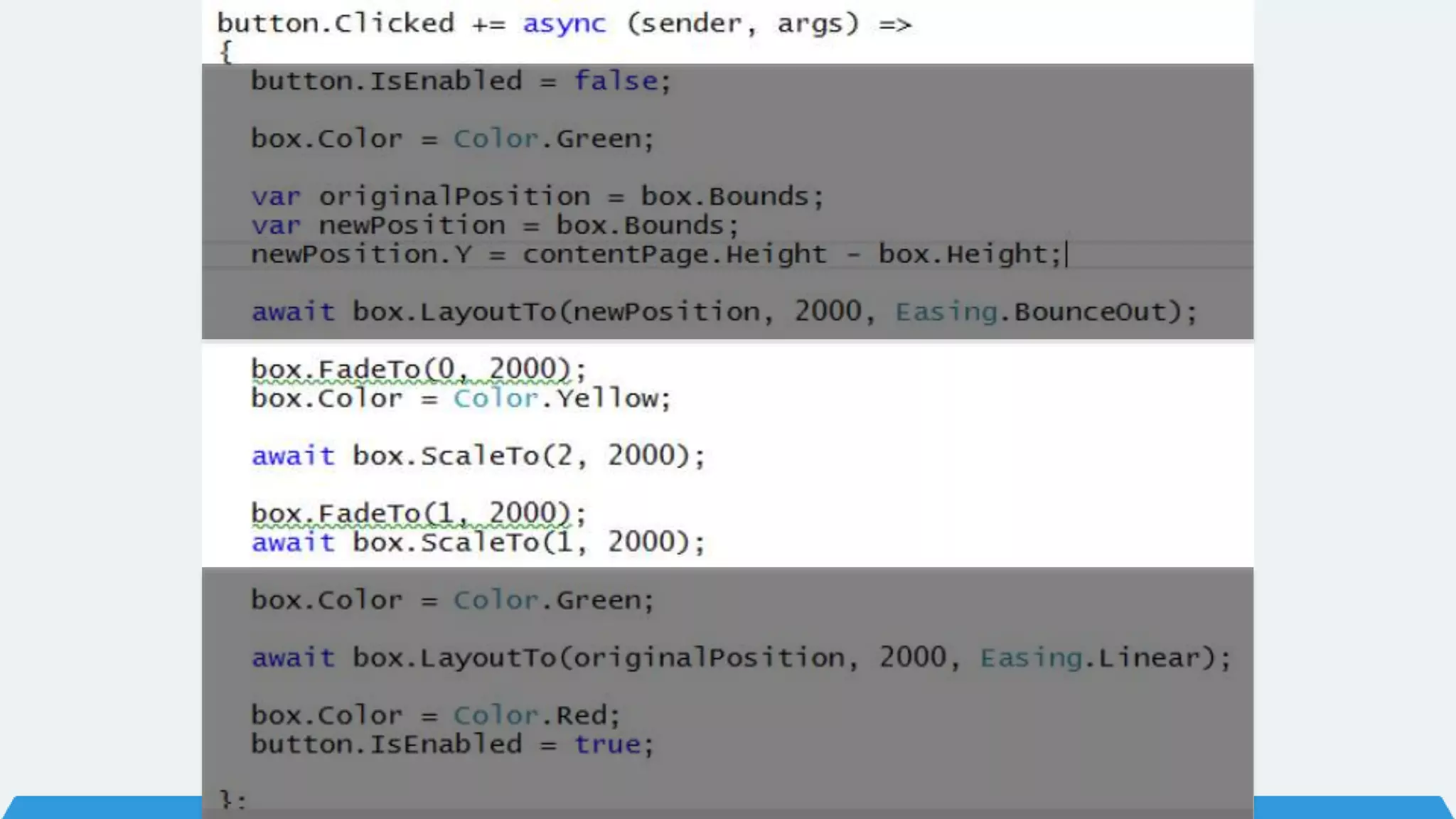
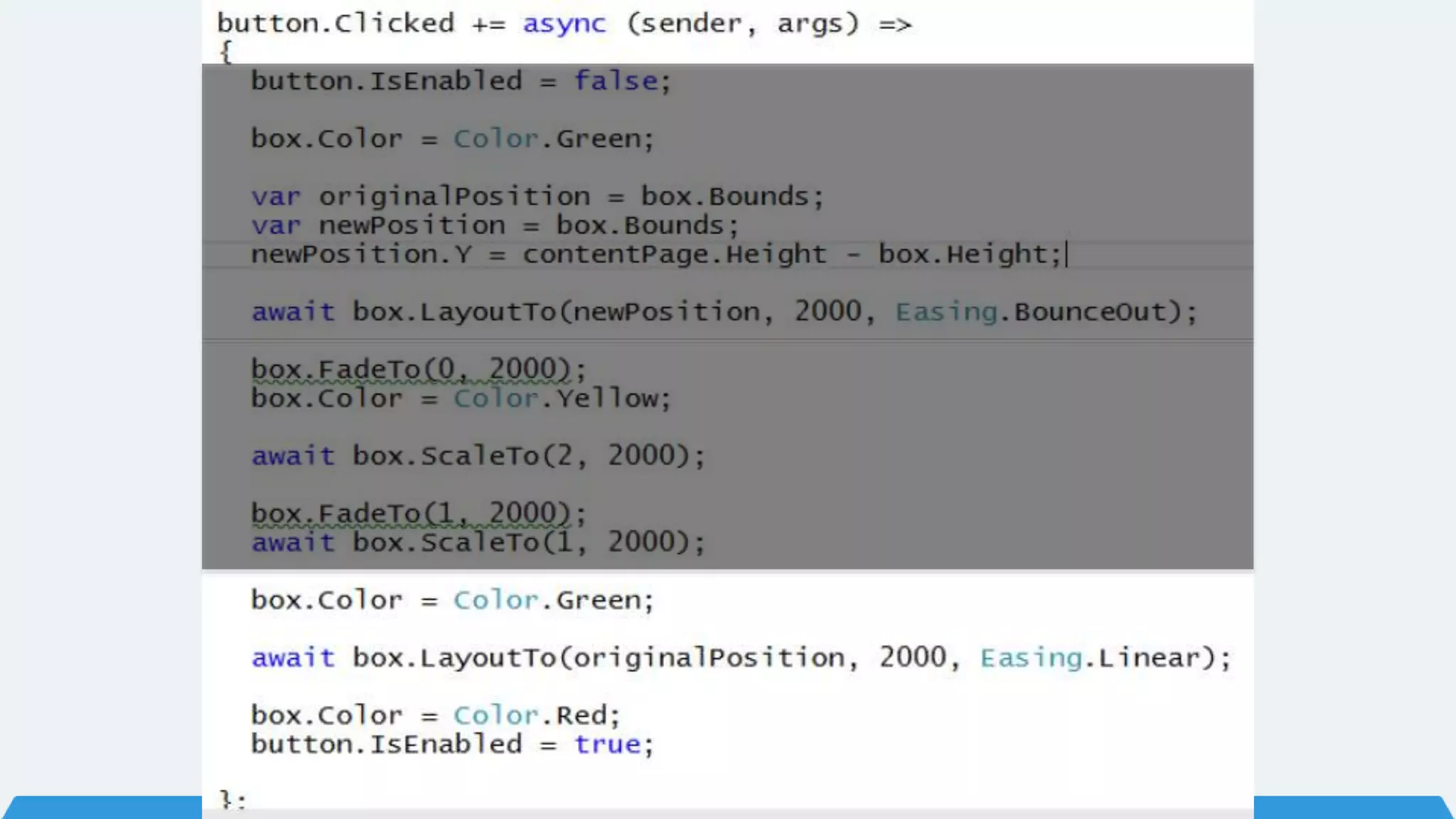
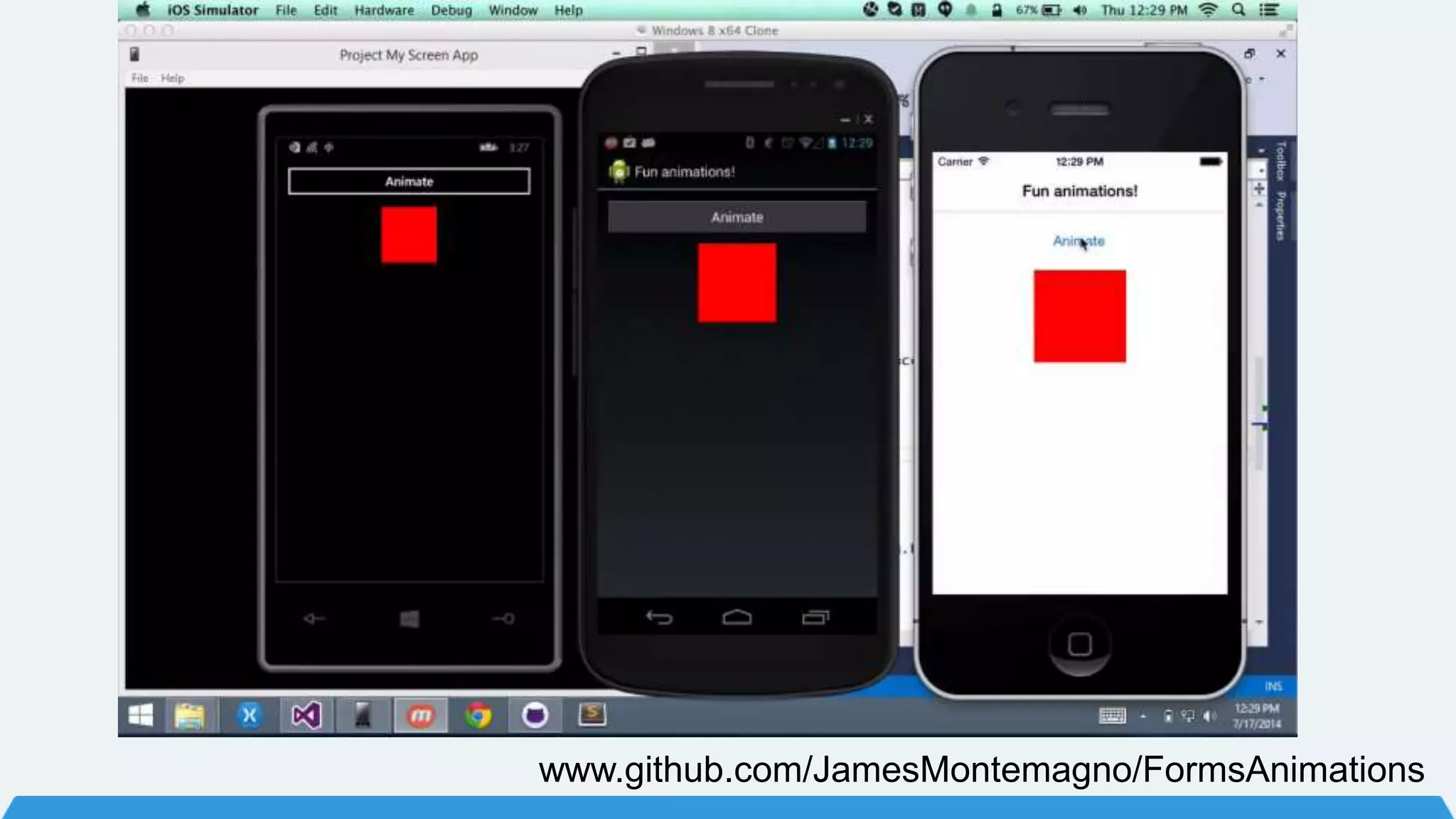
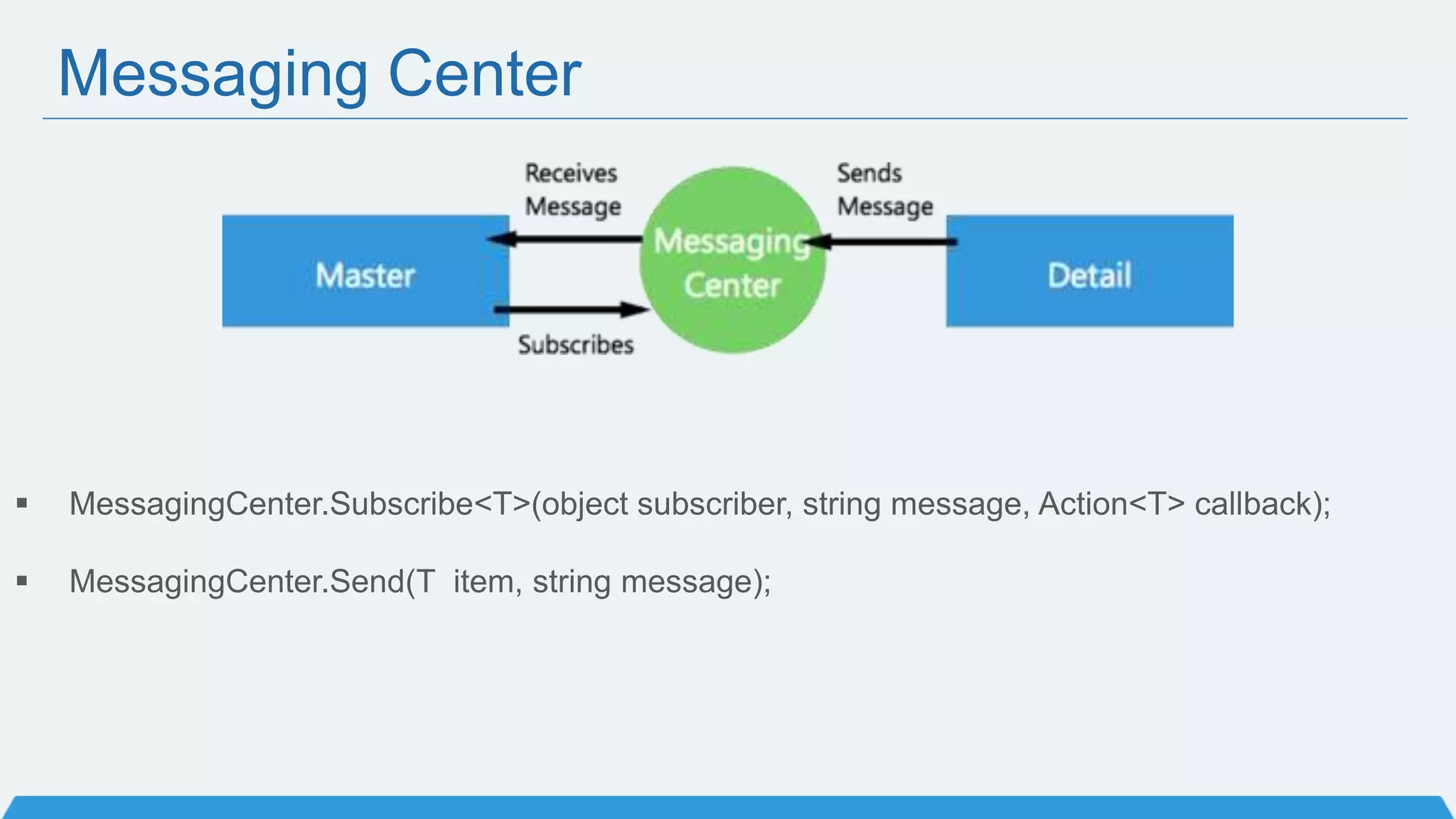
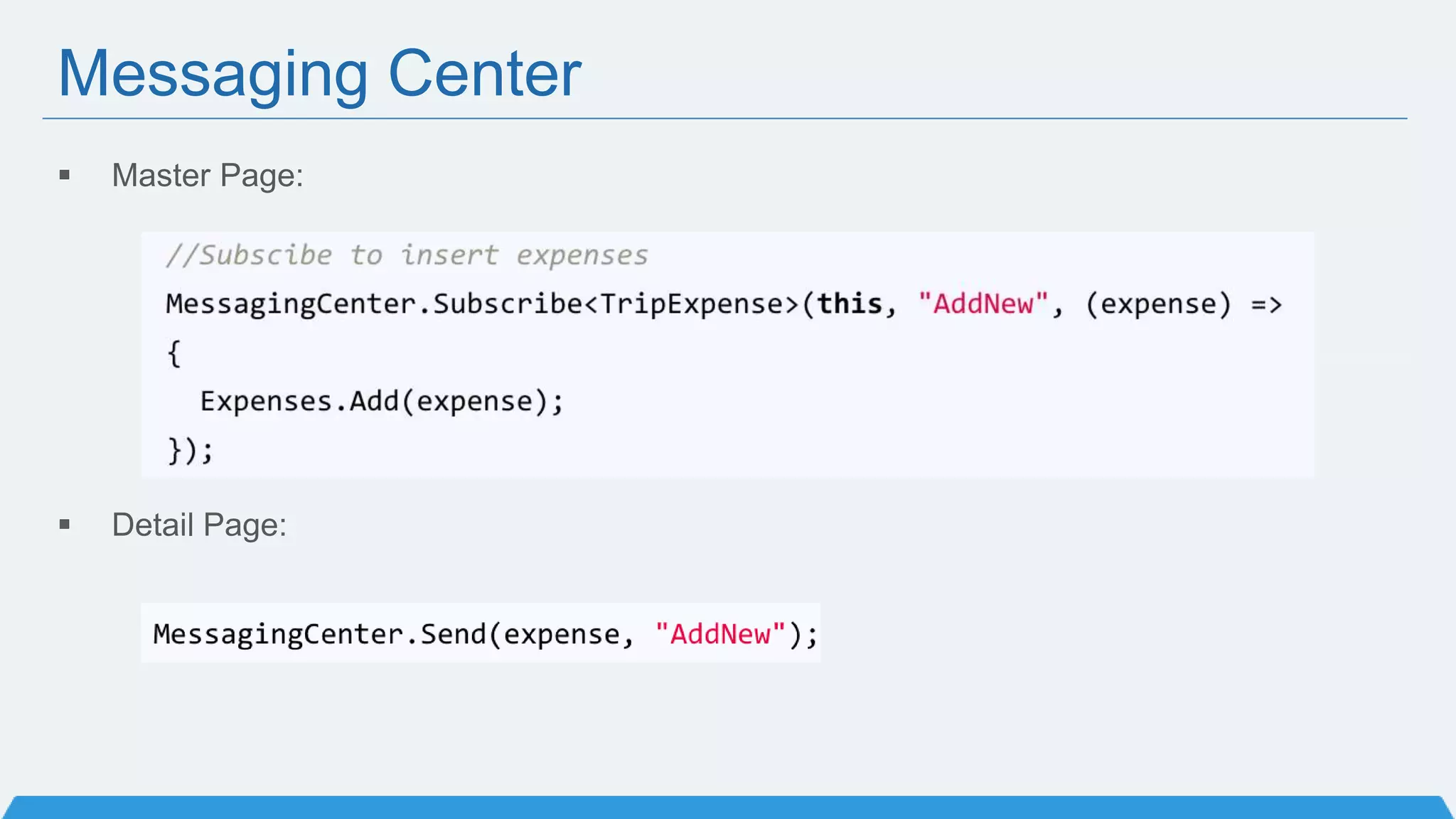
The document discusses Xamarin Forms, a framework that allows building cross-platform mobile apps for iOS, Android, and Windows using C# and XAML. It can create native UIs and allows code sharing via portable class libraries. Key features covered include pages and layouts, data binding, navigation, animations API, messaging center, and MVVM pattern support. Resources provided include documentation, XAML docs, and code samples.