Download to read offline
![History and Concepts of PERL
Author: [Your Name]
Date: July 2, 2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perlhistoryconceptsscalarsyntaxexample-240703003007-472ef11f/75/PERL_History_Concepts_Scalar_Syntax_Example-pptx-1-2048.jpg)


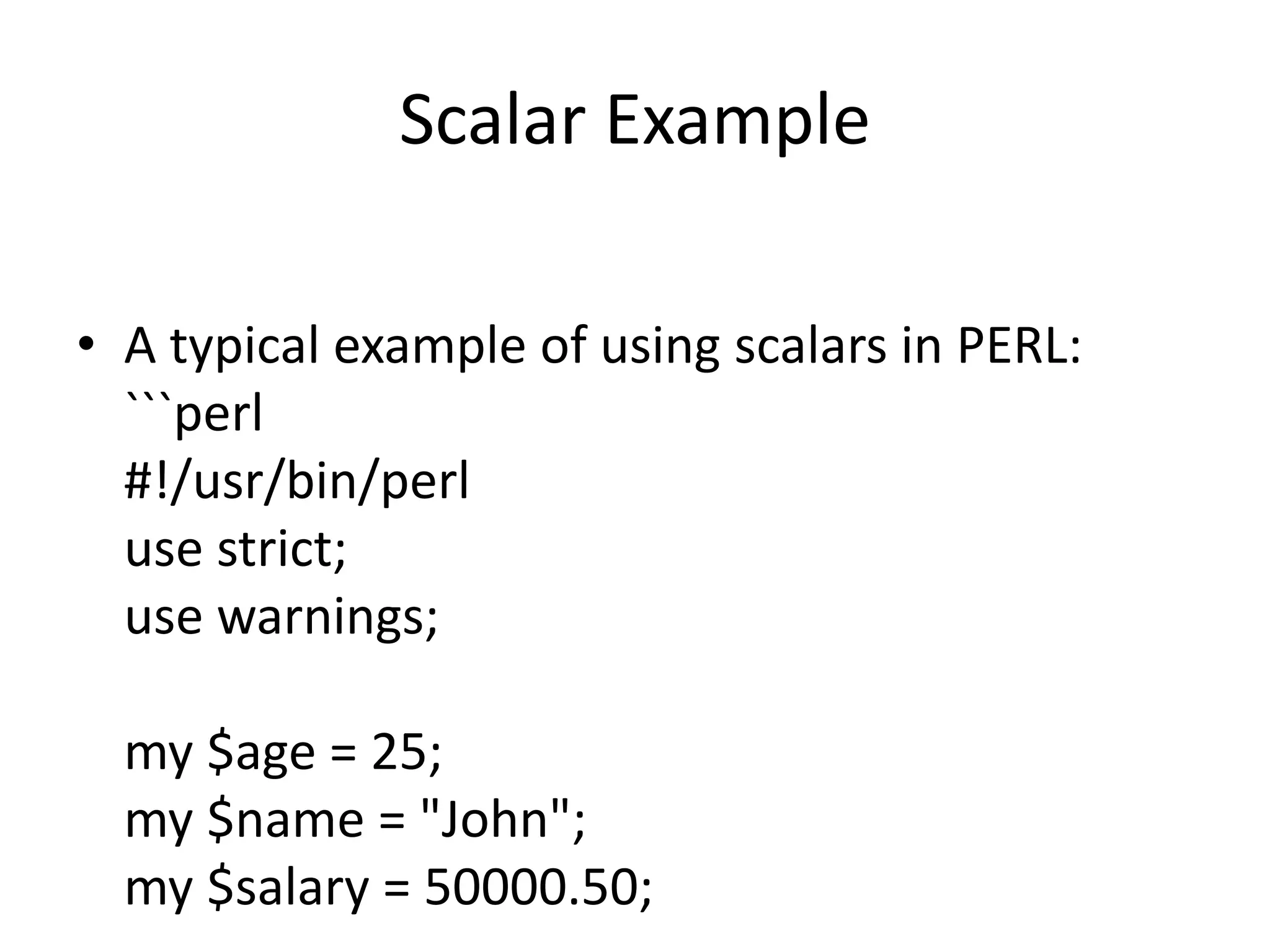
The document discusses the basics of scalar data in Perl, defining it as a representation of single values like numbers and strings. It outlines the syntax for declaring scalar variables using examples, including integer, string, and floating-point number types. Additionally, it emphasizes Perl's ability to automatically handle type conversion for smooth operations.
![History and Concepts of PERL
Author: [Your Name]
Date: July 2, 2024](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/perlhistoryconceptsscalarsyntaxexample-240703003007-472ef11f/75/PERL_History_Concepts_Scalar_Syntax_Example-pptx-1-2048.jpg)


