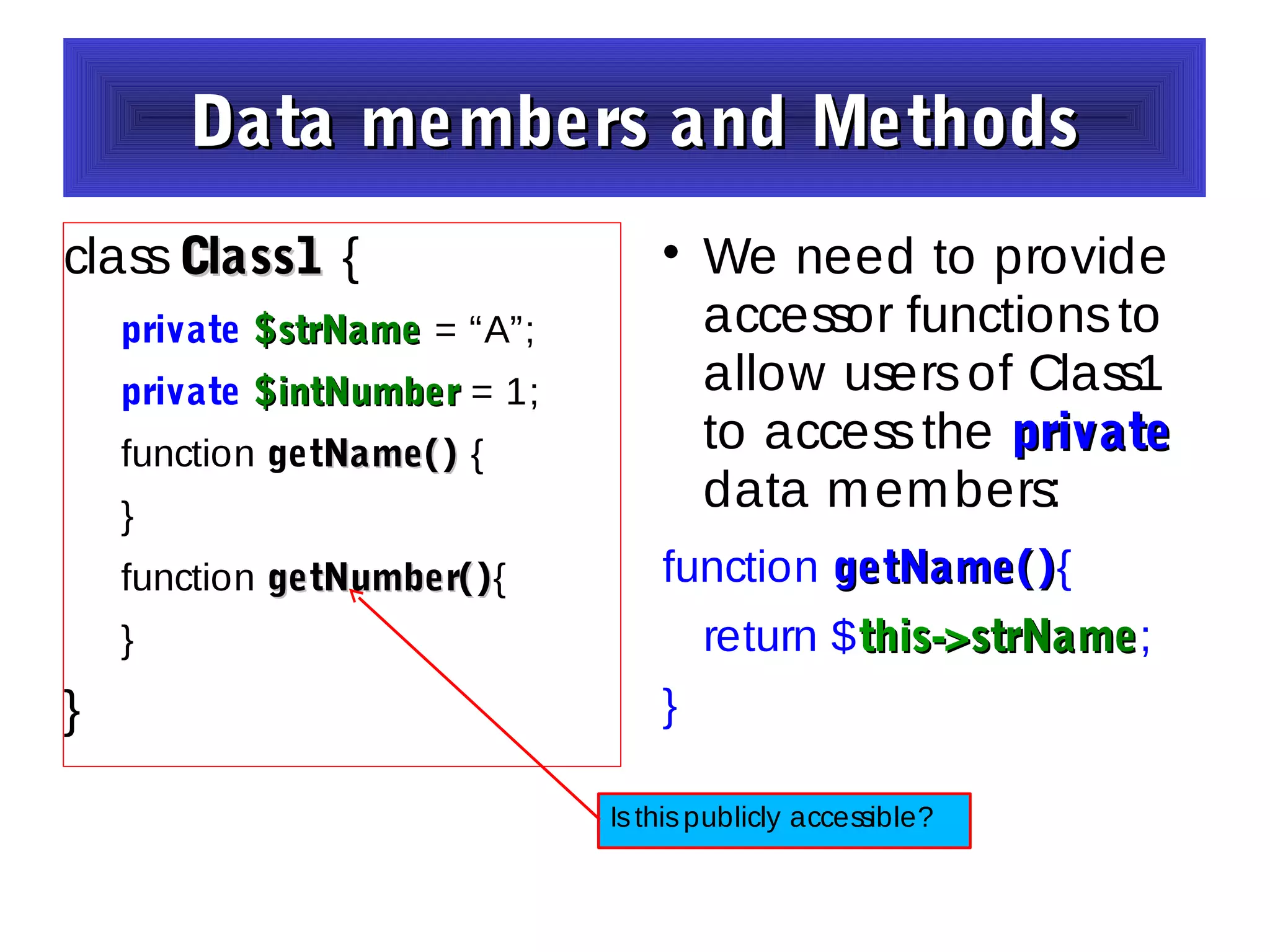
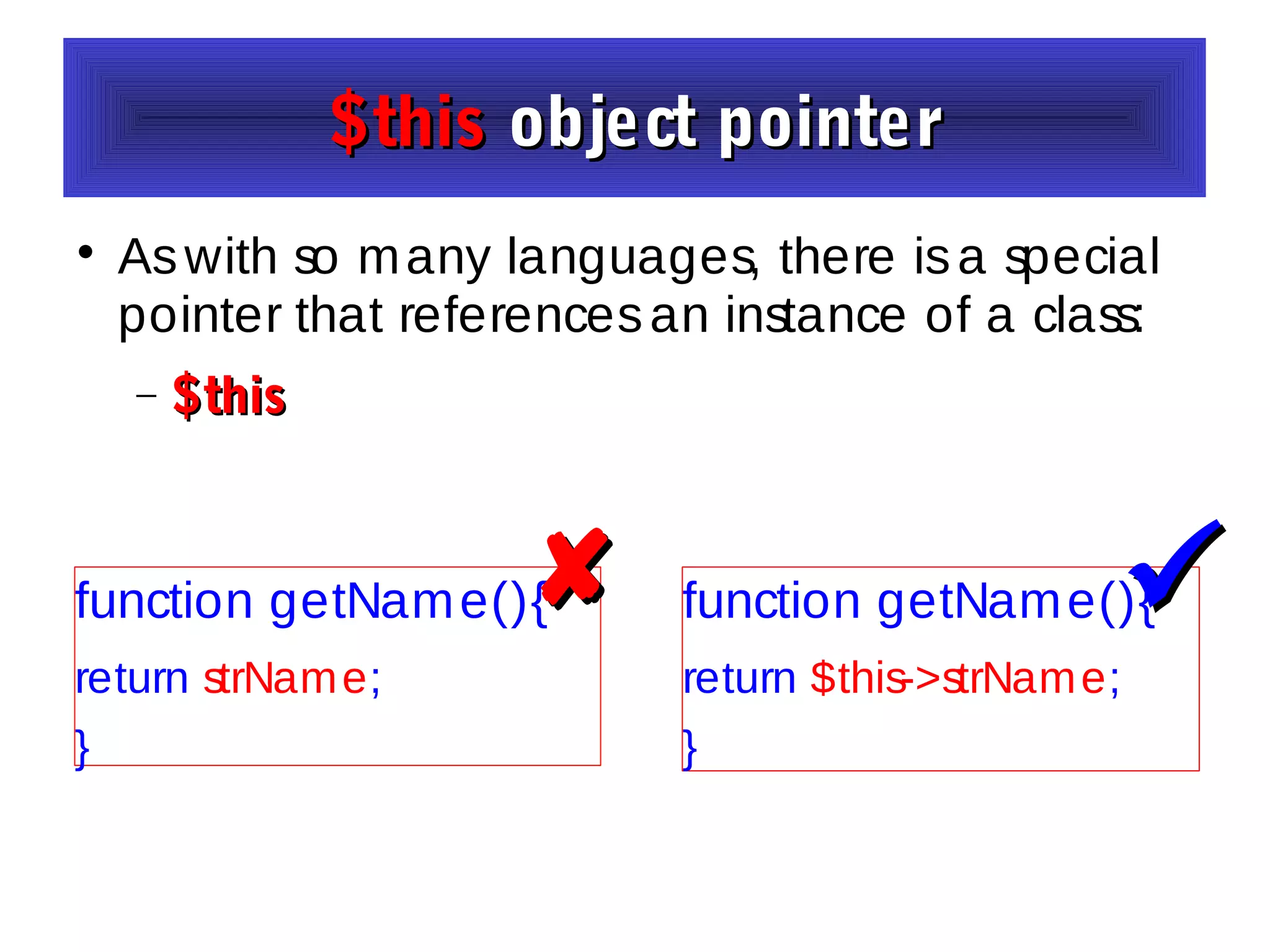
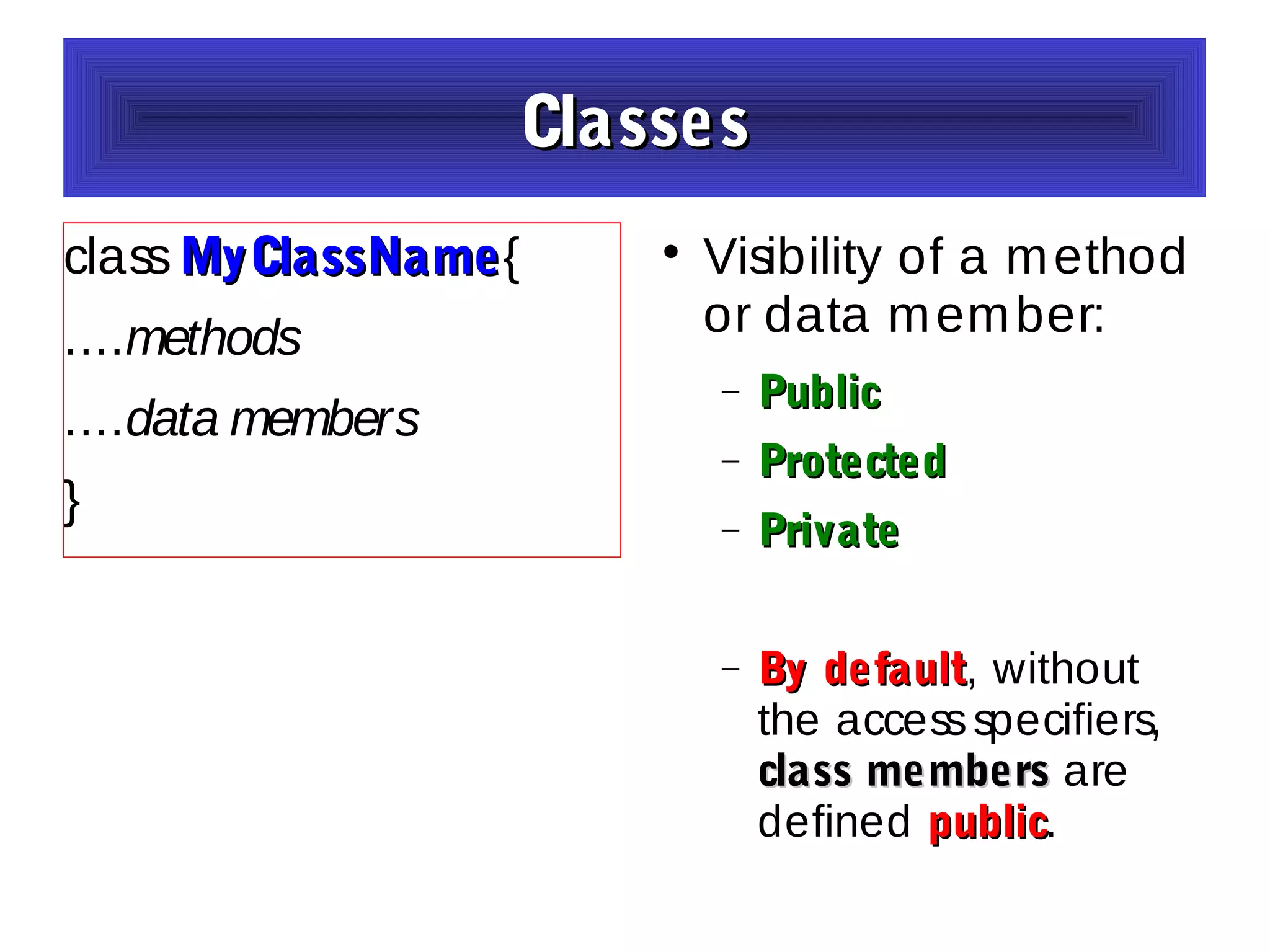
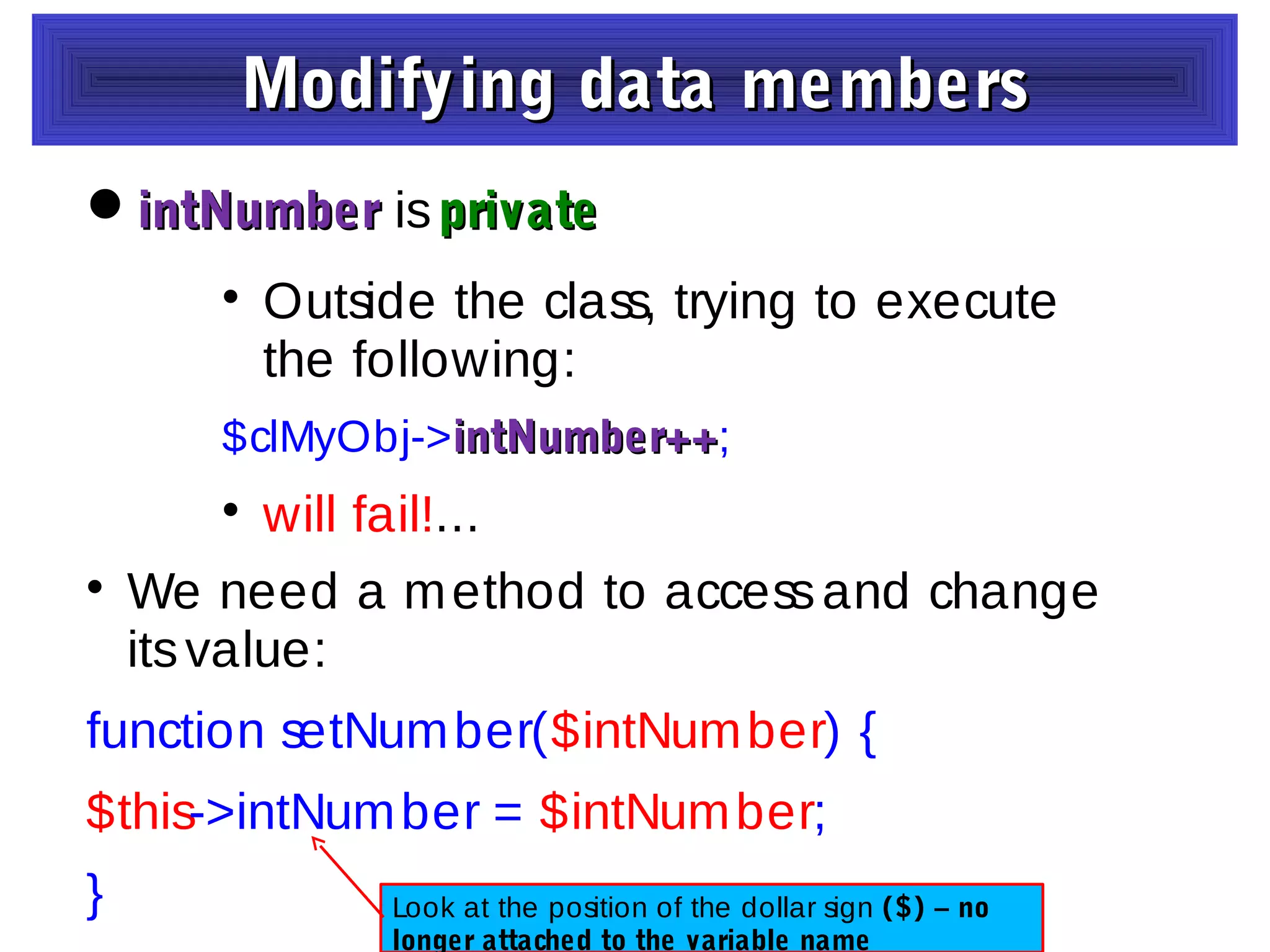
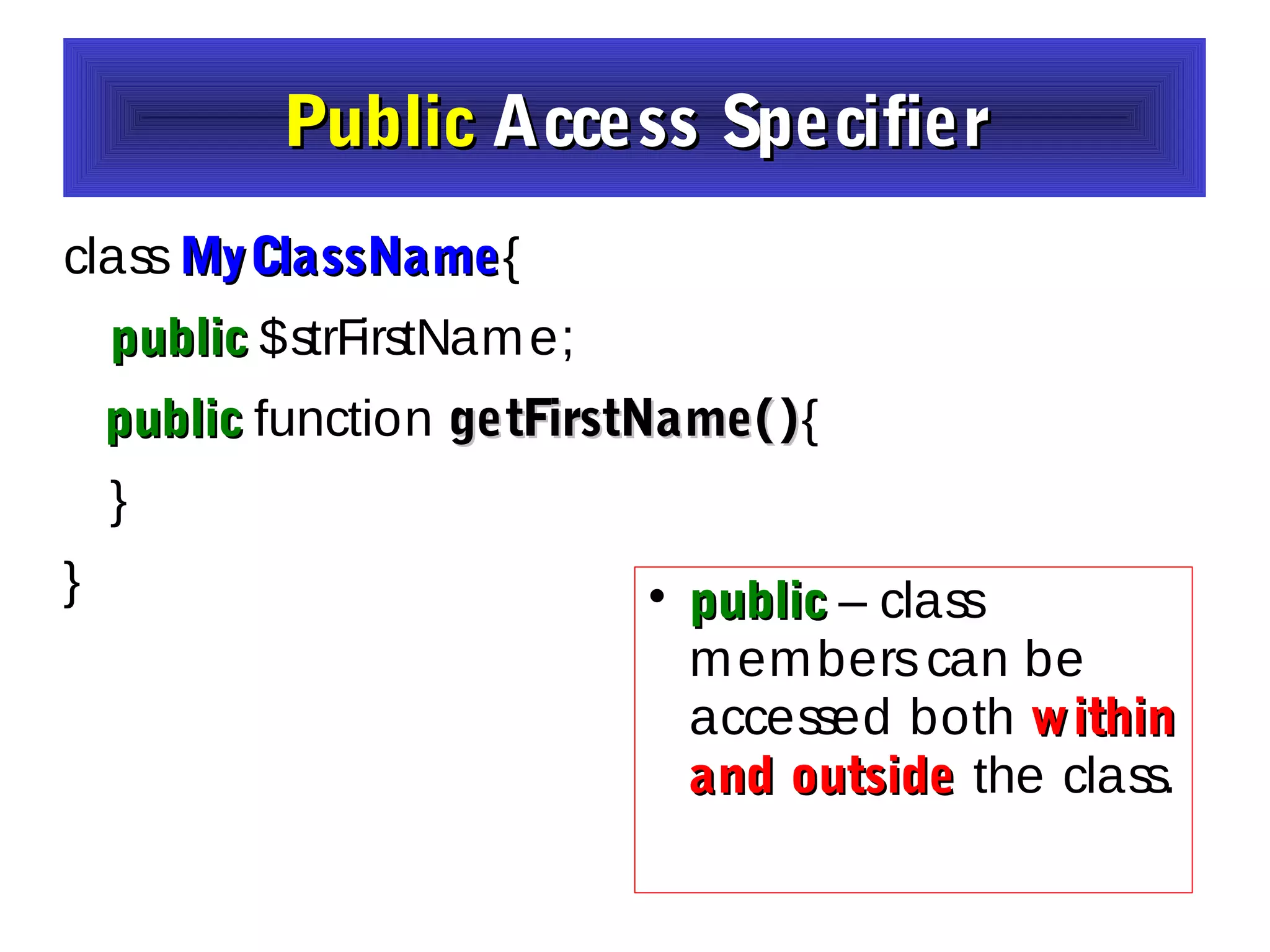
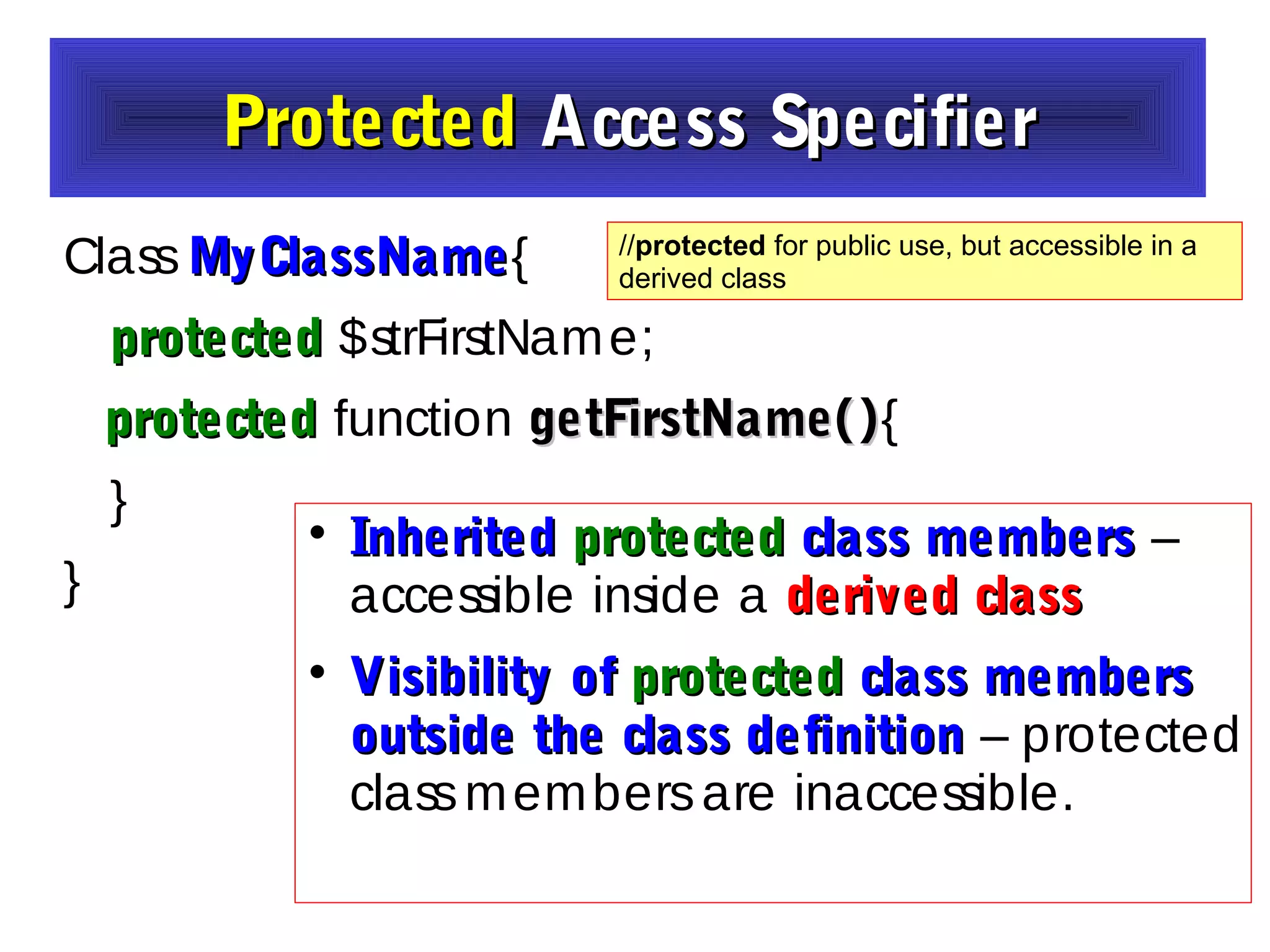
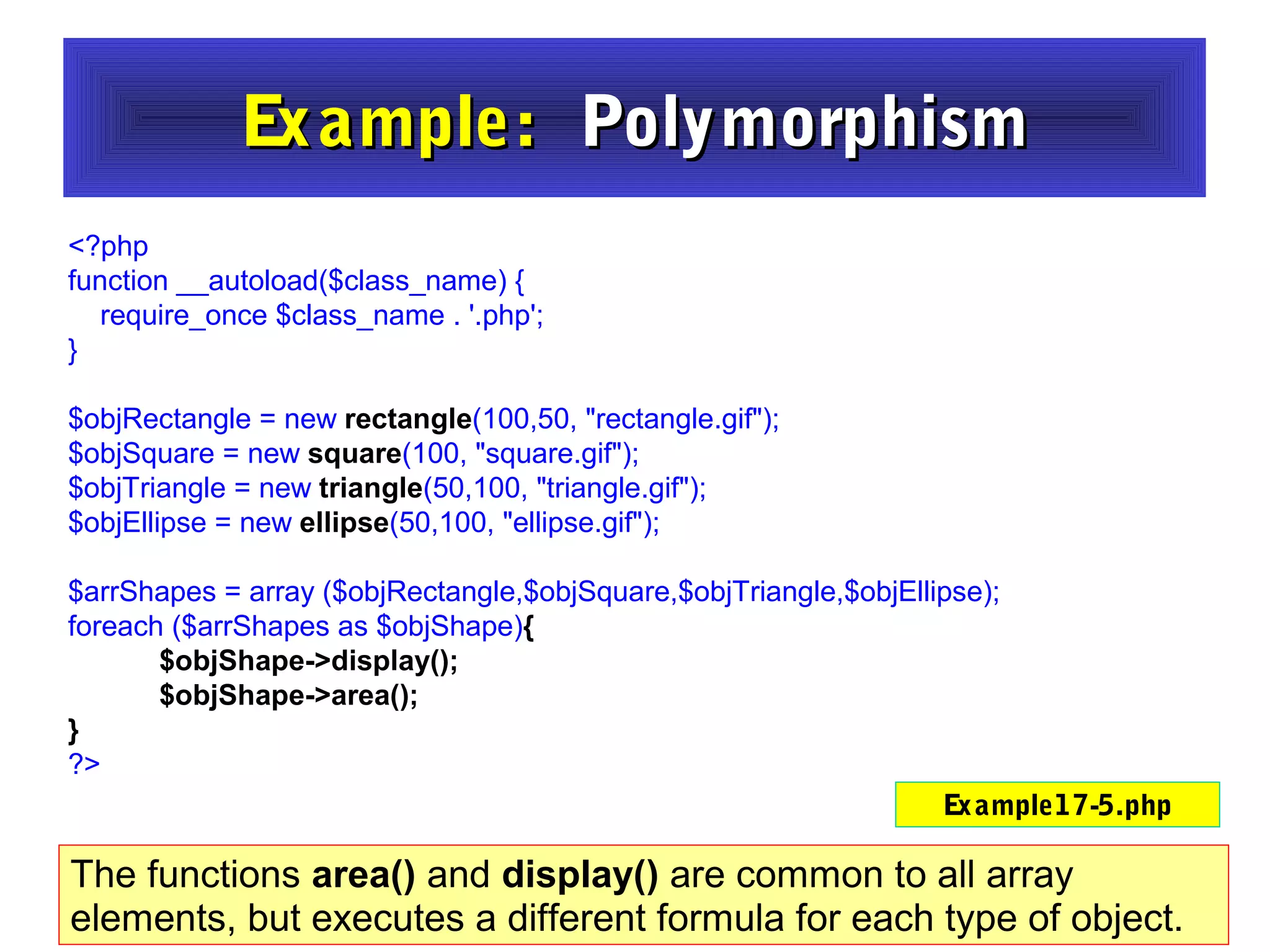
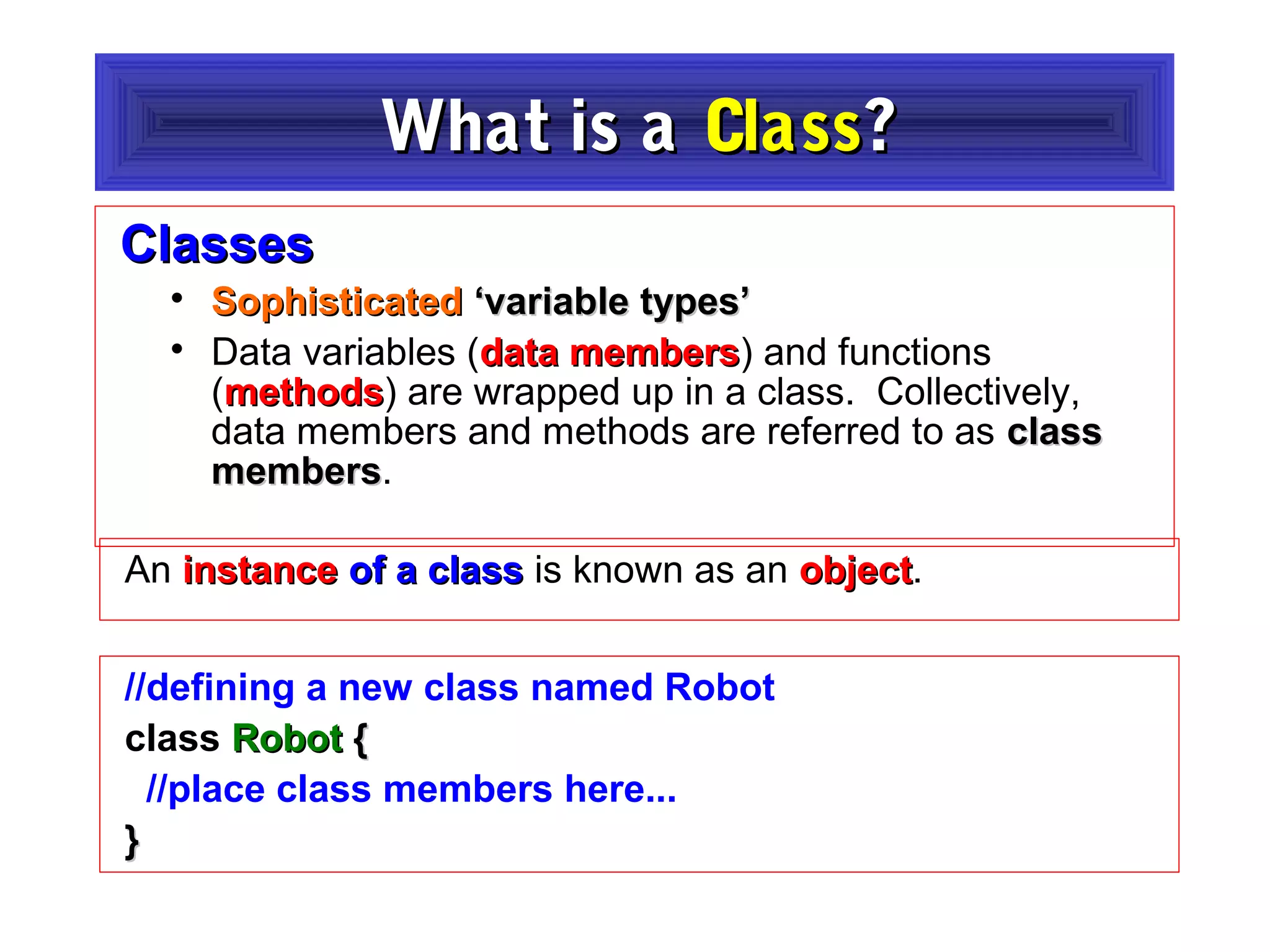
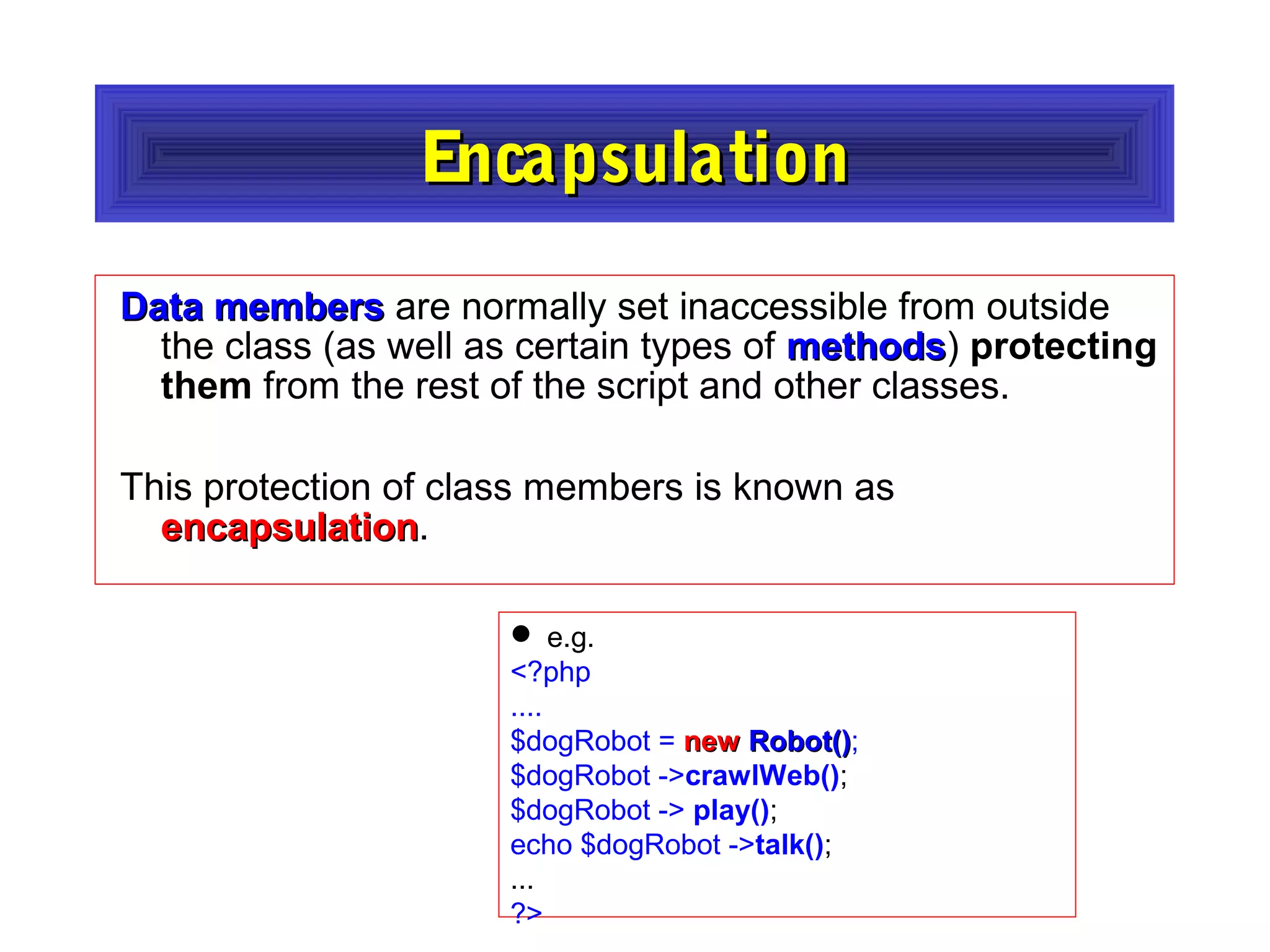
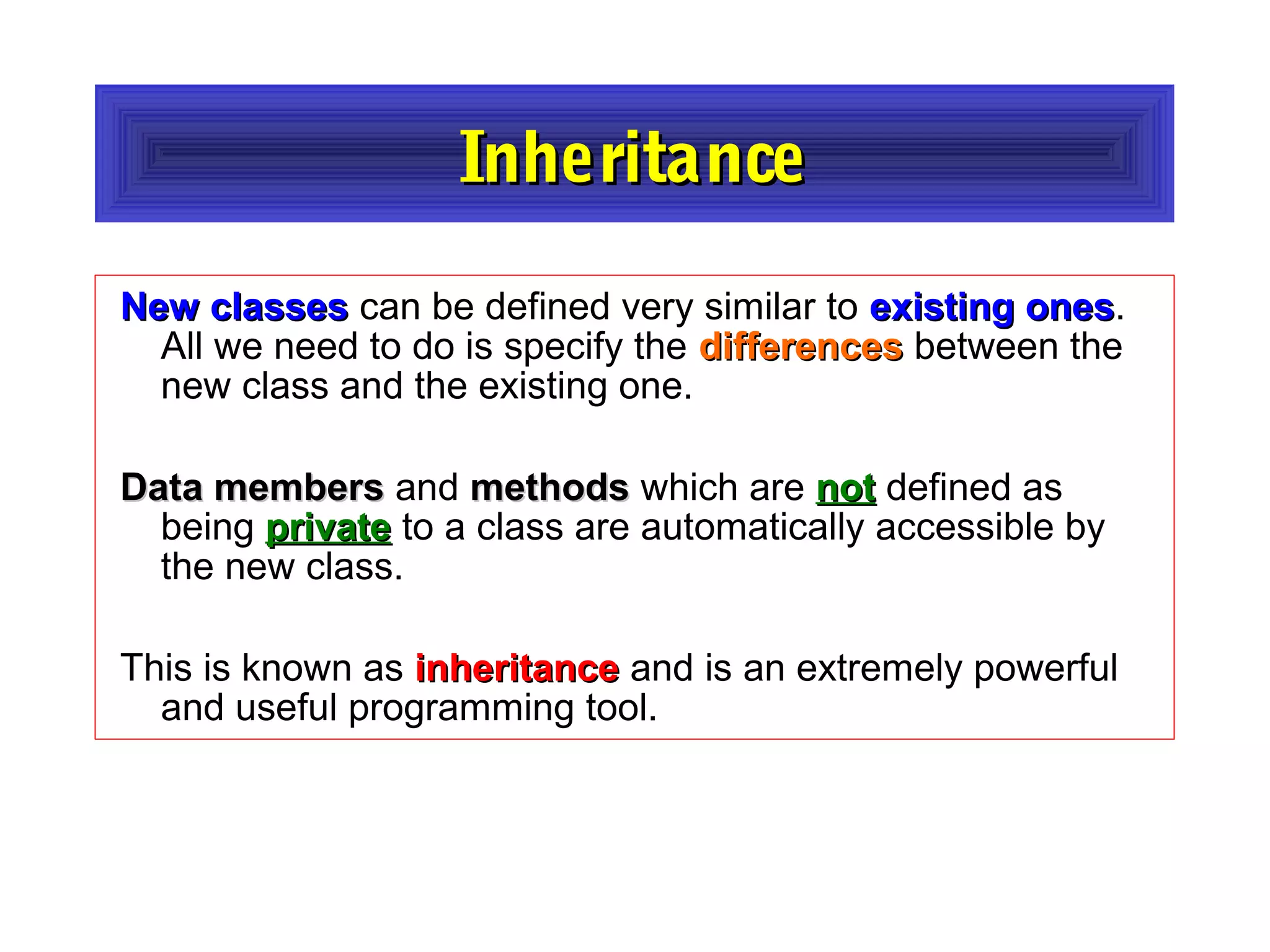
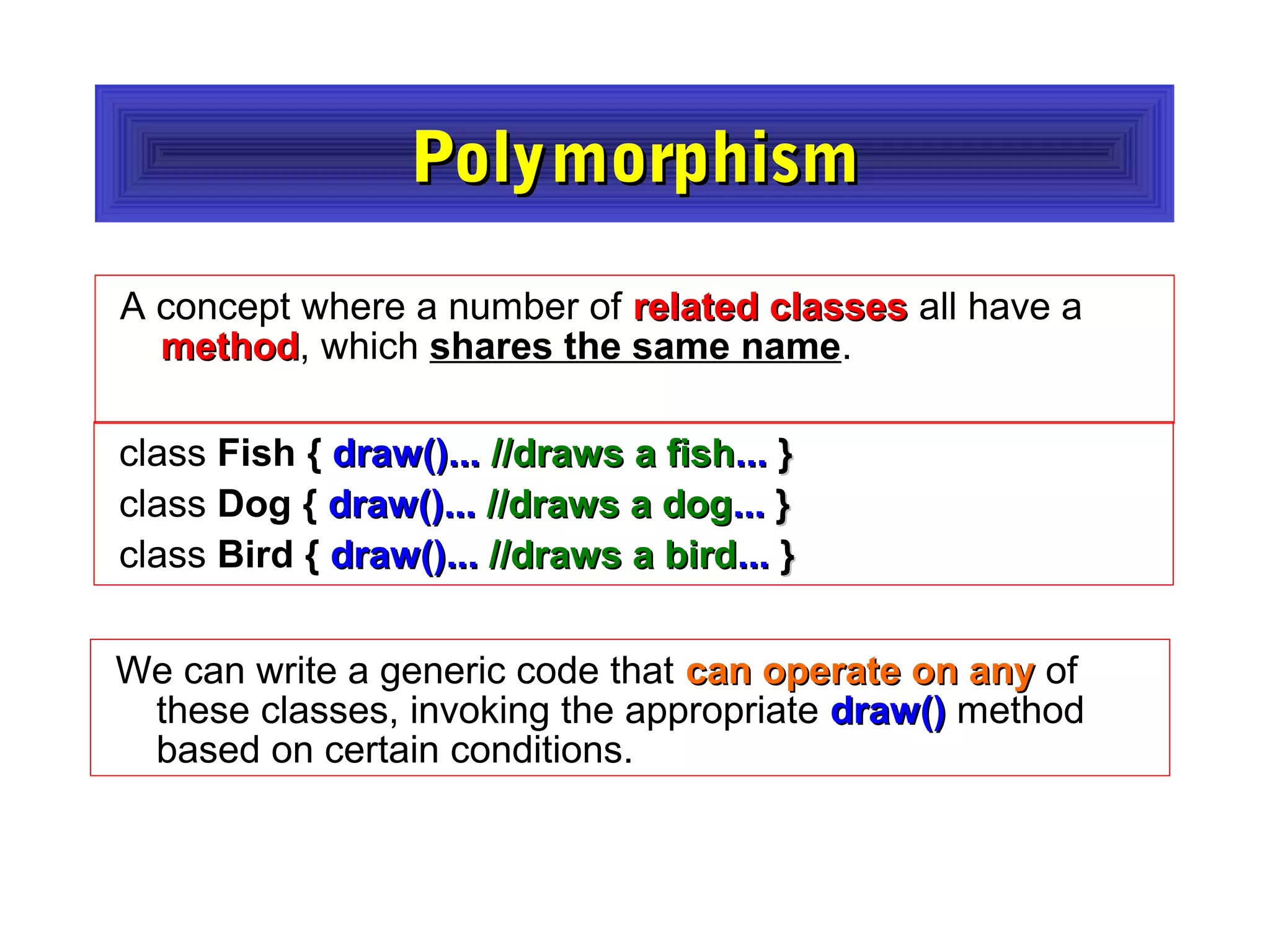
- The document discusses object-oriented programming concepts in PHP including classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
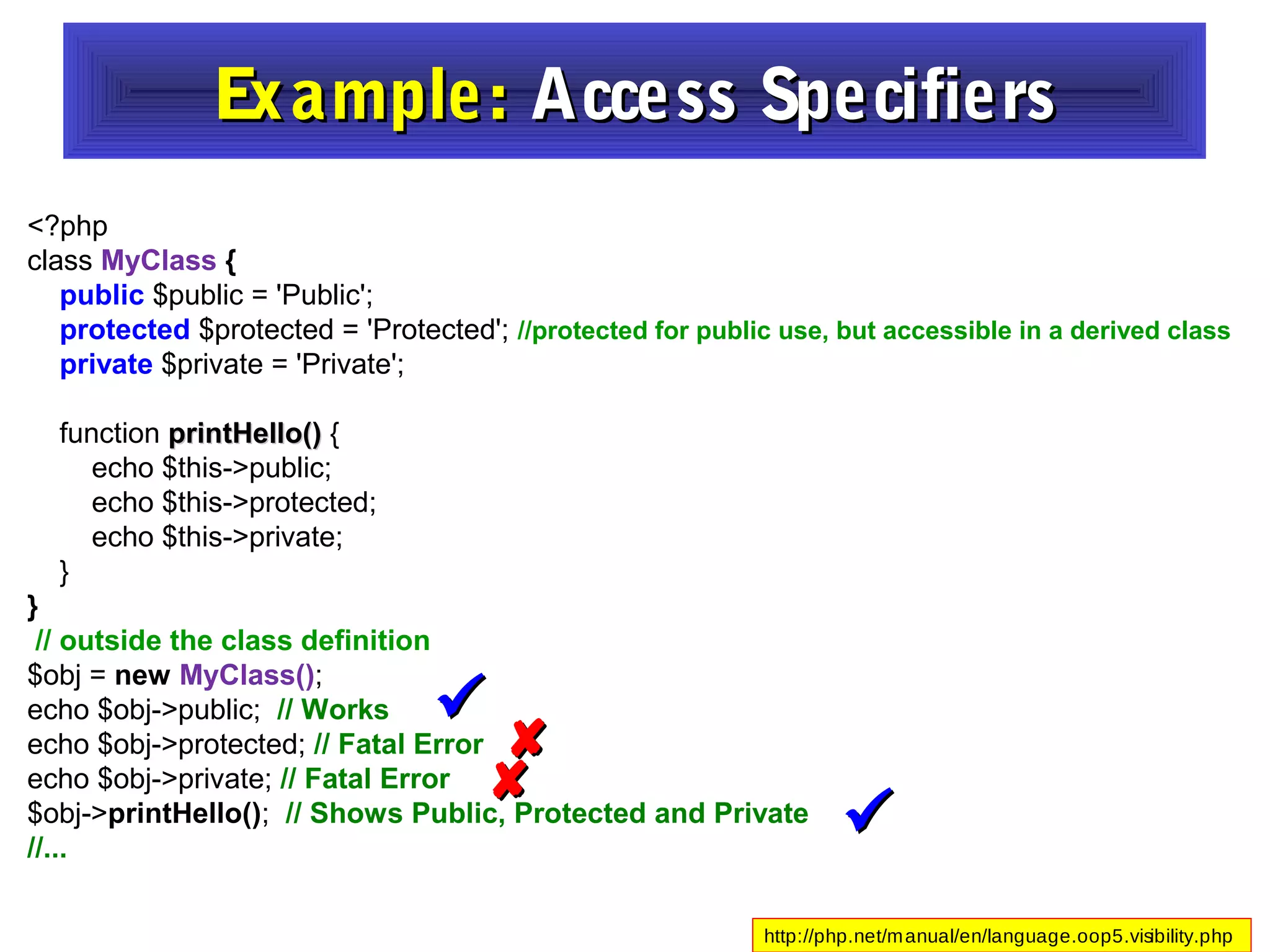
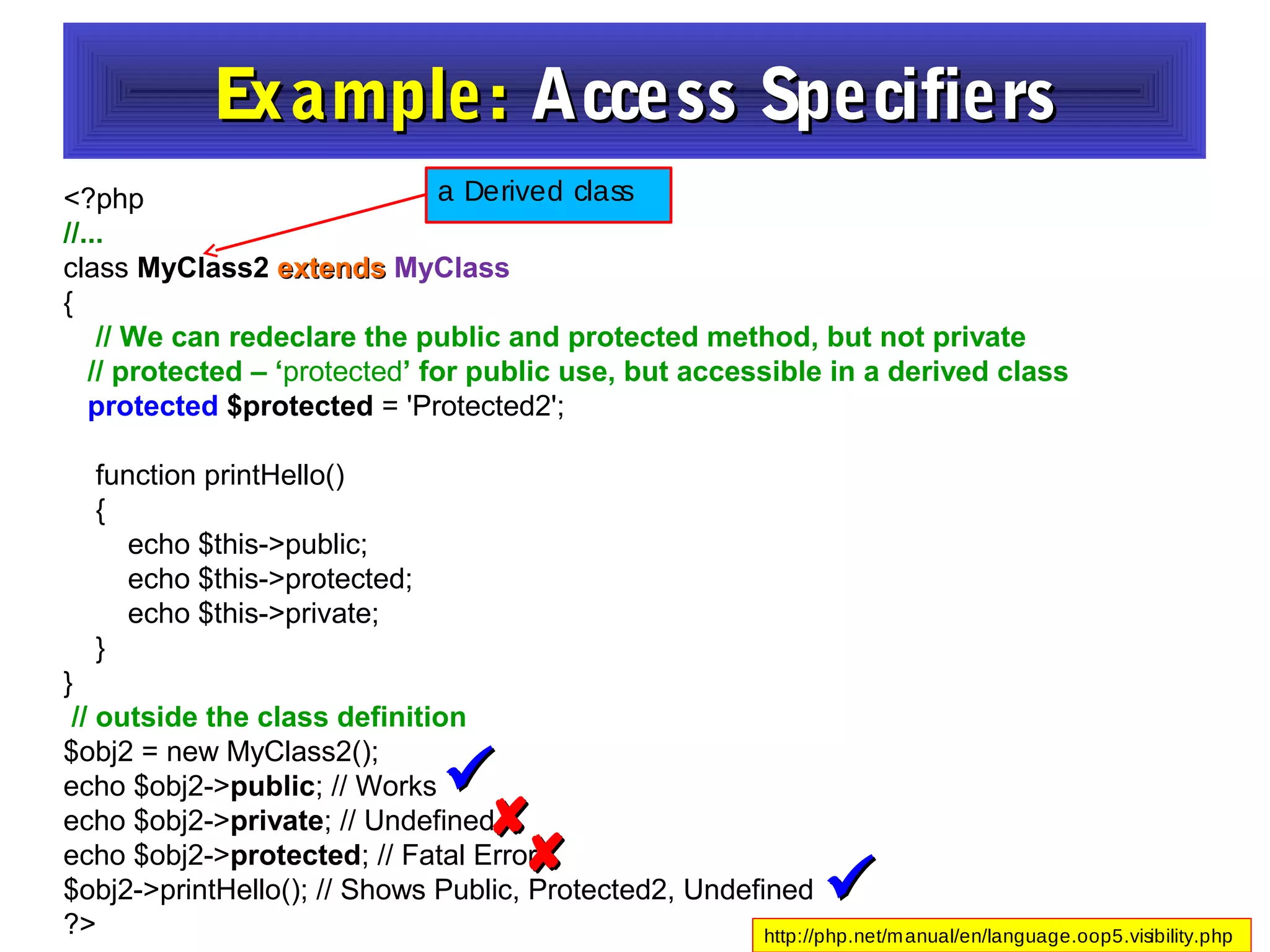
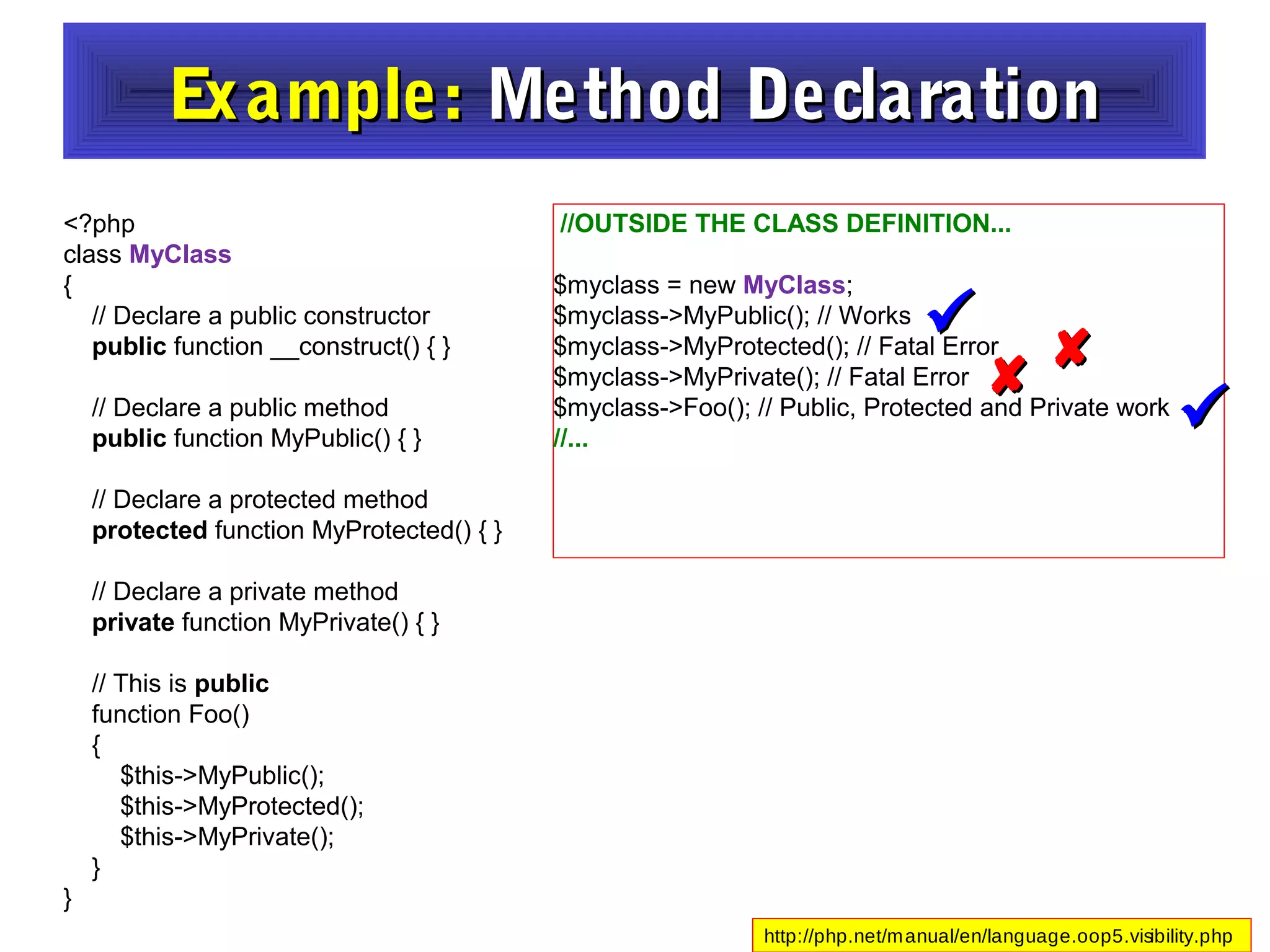
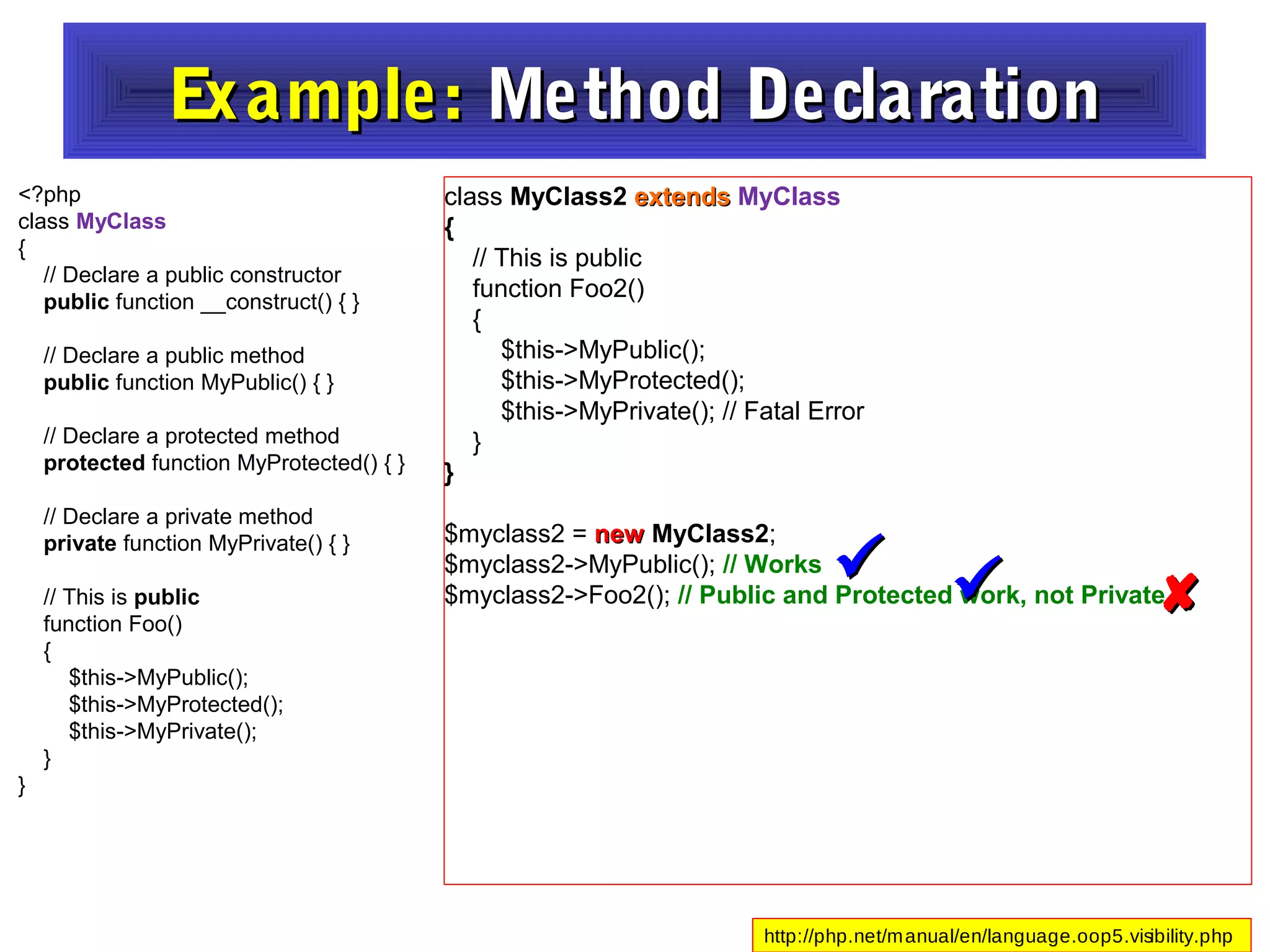
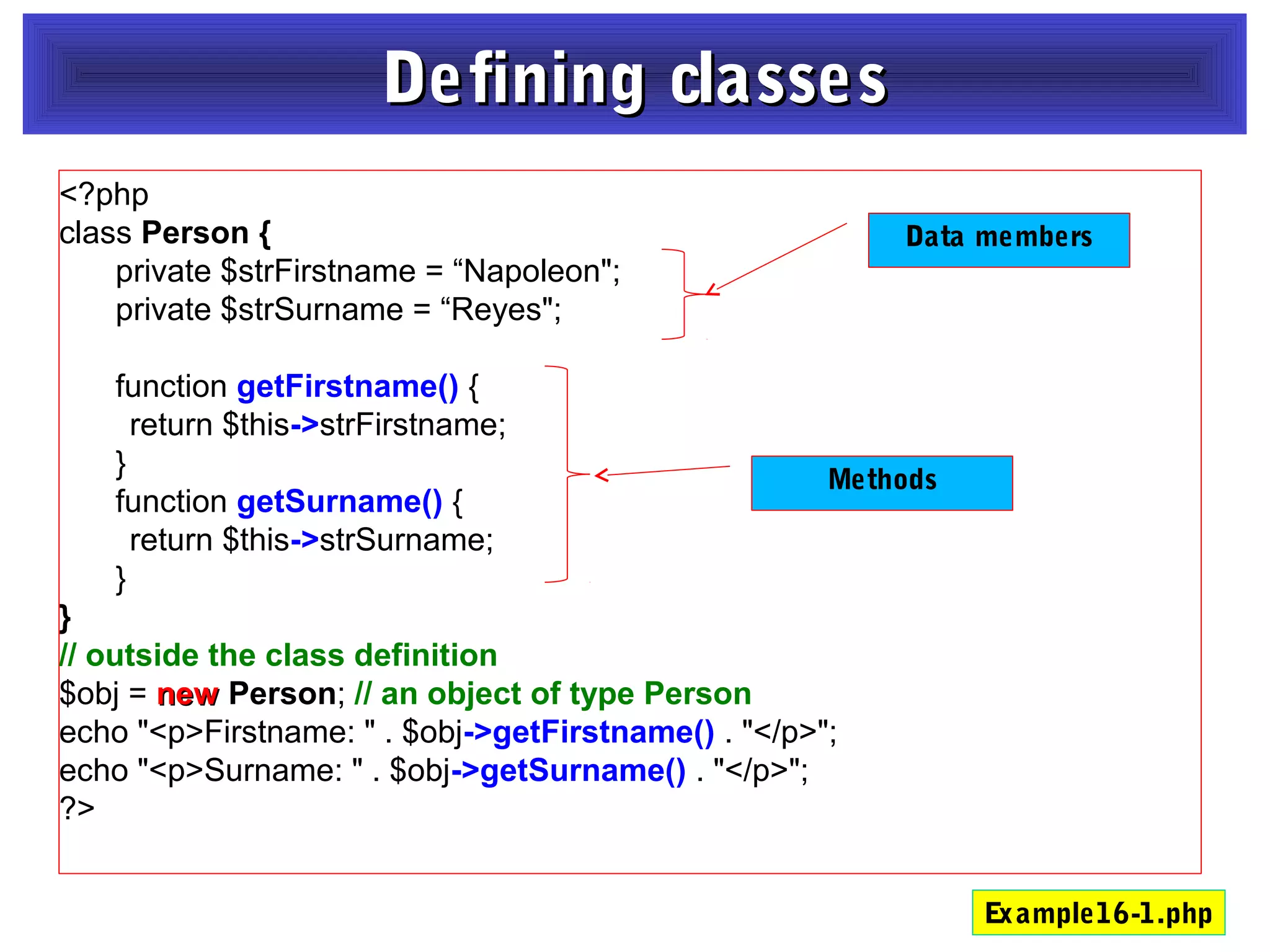
- It provides examples of defining classes with properties and methods, and using access specifiers like public, private, and protected.
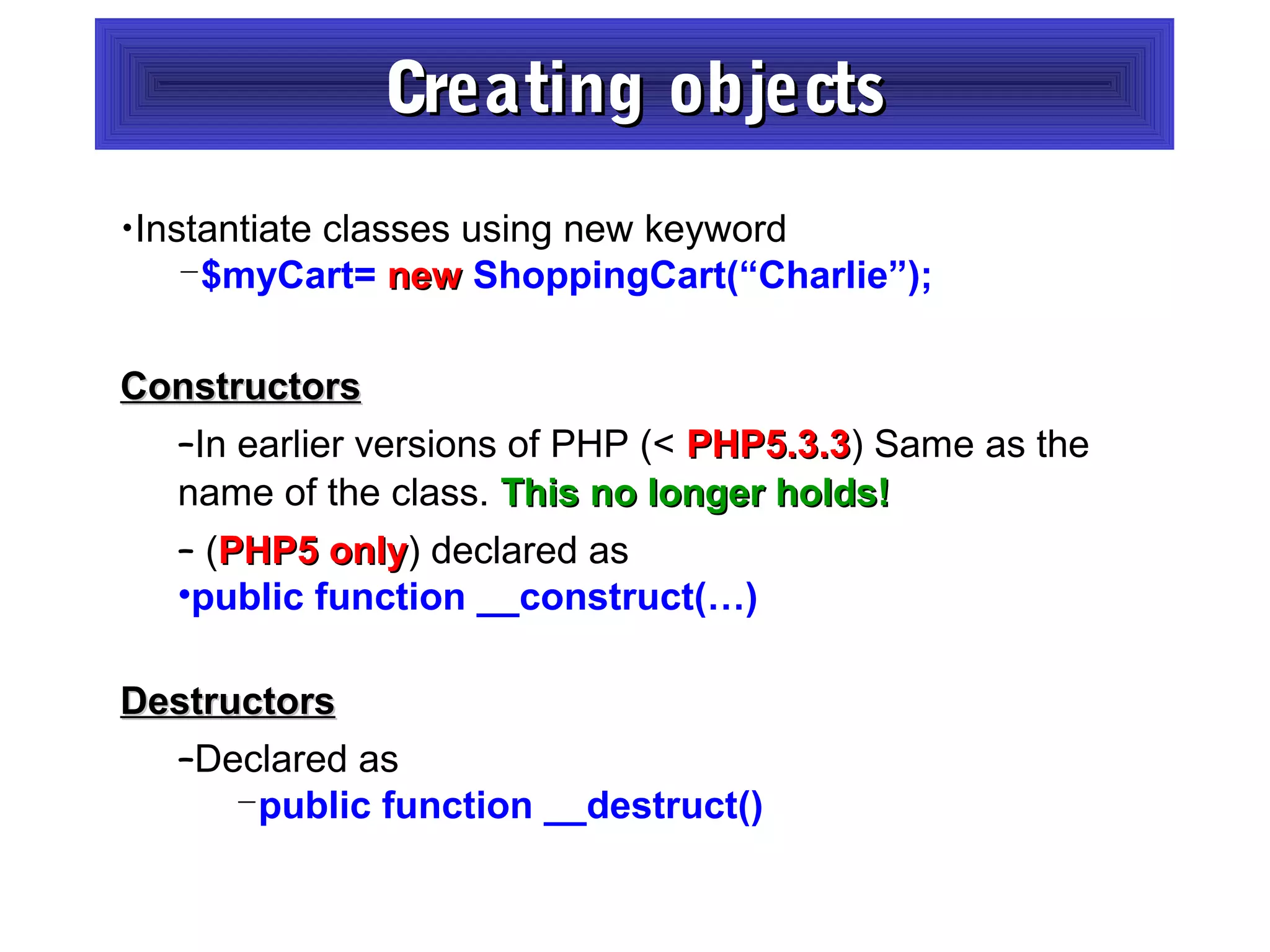
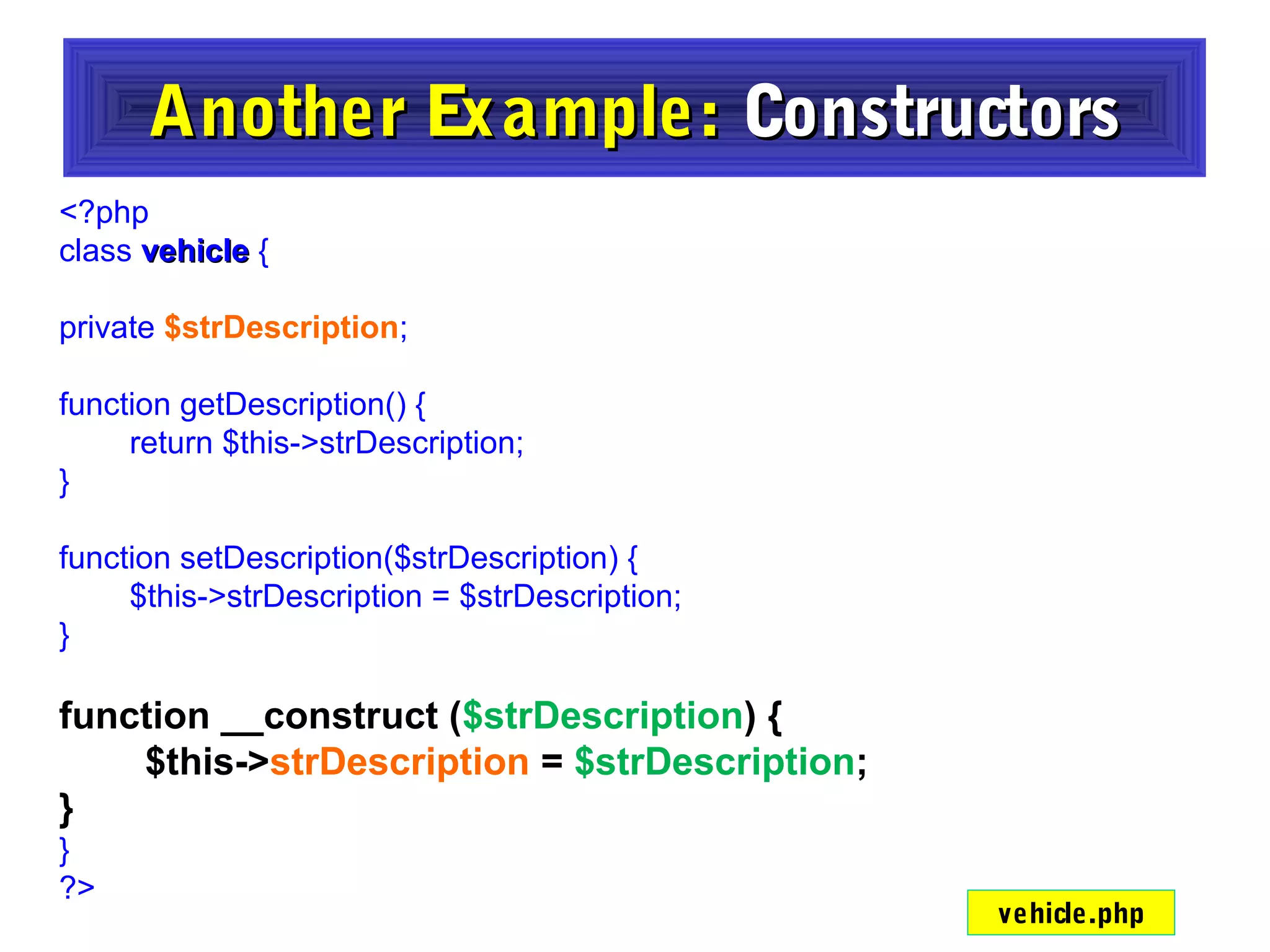
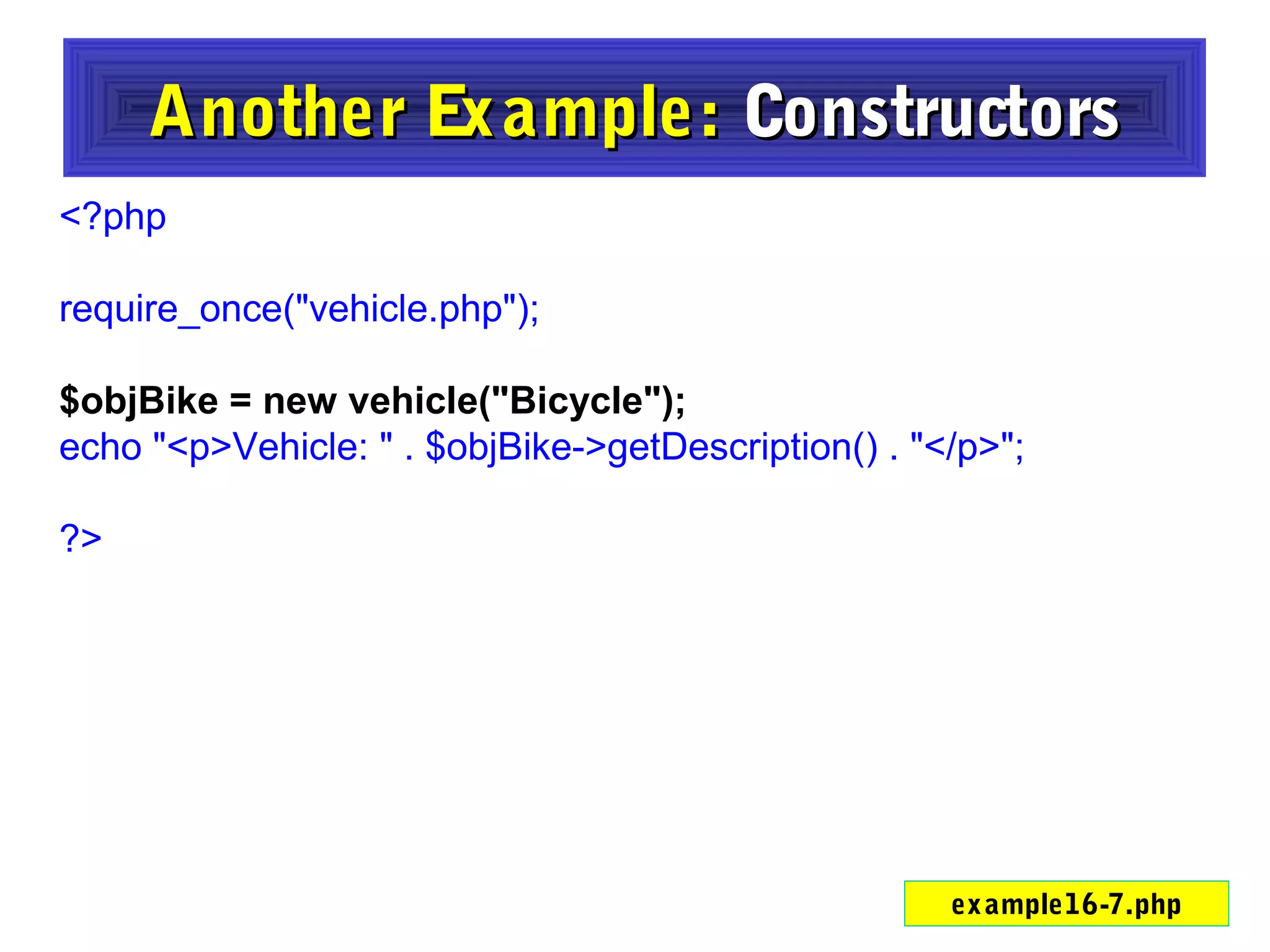
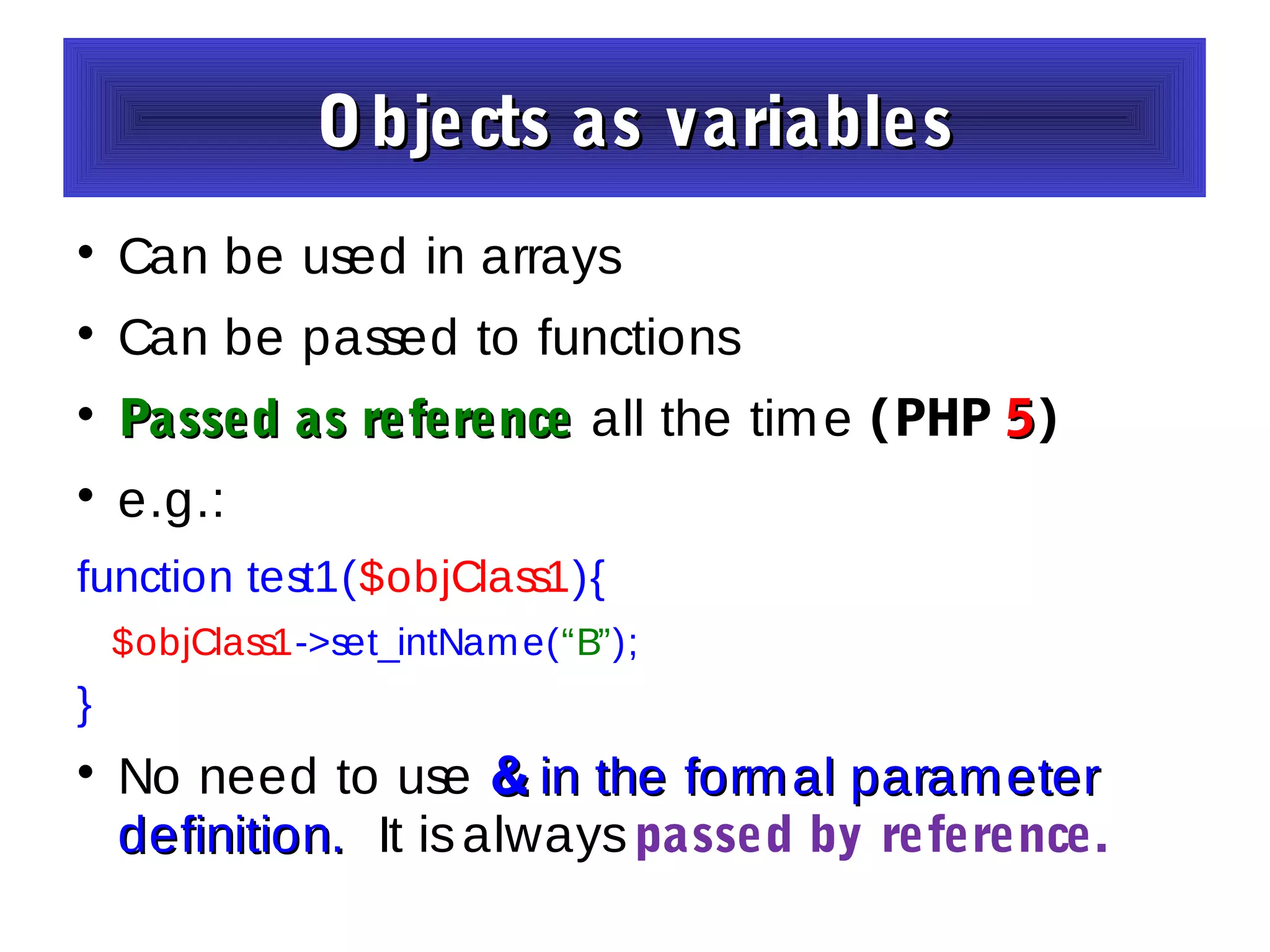
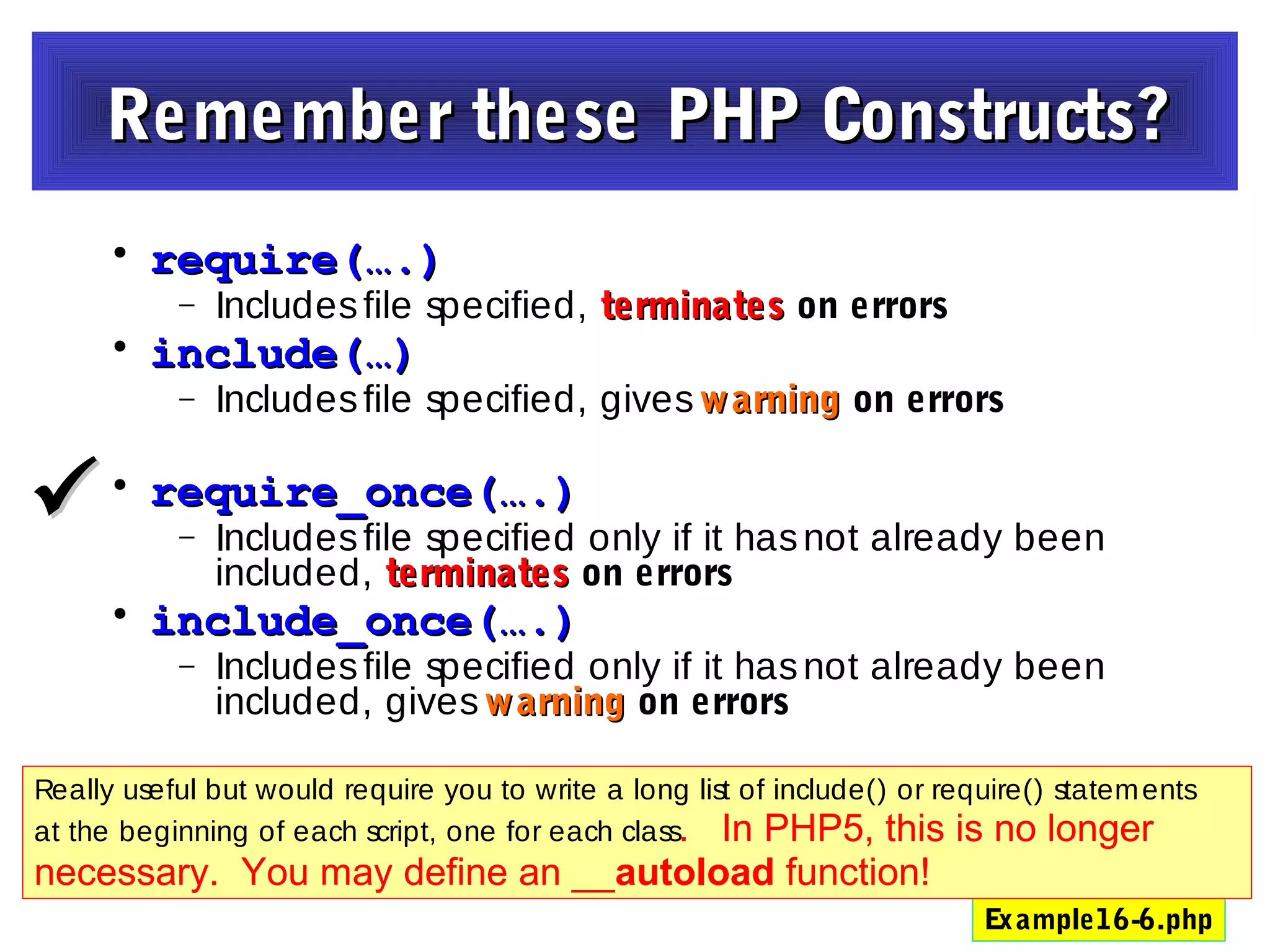
- Constructors and destructors are explained, as well as how to instantiate objects and use objects in arrays or pass them as references to functions.






![Example:Example: Defining classesDefining classes
class ShoppingCart {
private $name; // Name of shoppershopper
private $items; // Items in our shopping cartItems in our shopping cart
public function ShoppingCartShoppingCart($inputname) {
$this->name = $inputname;
}
// Add $num articles of $artnr to the cart
public function addItemaddItem($artnr, $num) {
$this->items[$artnr] += $num;
}
// Take $num articles of $artnr out of the cart
public function removeItemremoveItem($artnr, $num) {
if ($this->items[$artnr] > $num) {
$this->items[$artnr] -= $num;
return true;
} elseif ($this->items[$artnr] == $num) {
unset($this->items[$artnr]);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
Let’sexamine the syntax of defining a classnext...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php-objectorientationandclasses-130418120656-phpapp02/75/Php-object-orientation-and-classes-15-2048.jpg)