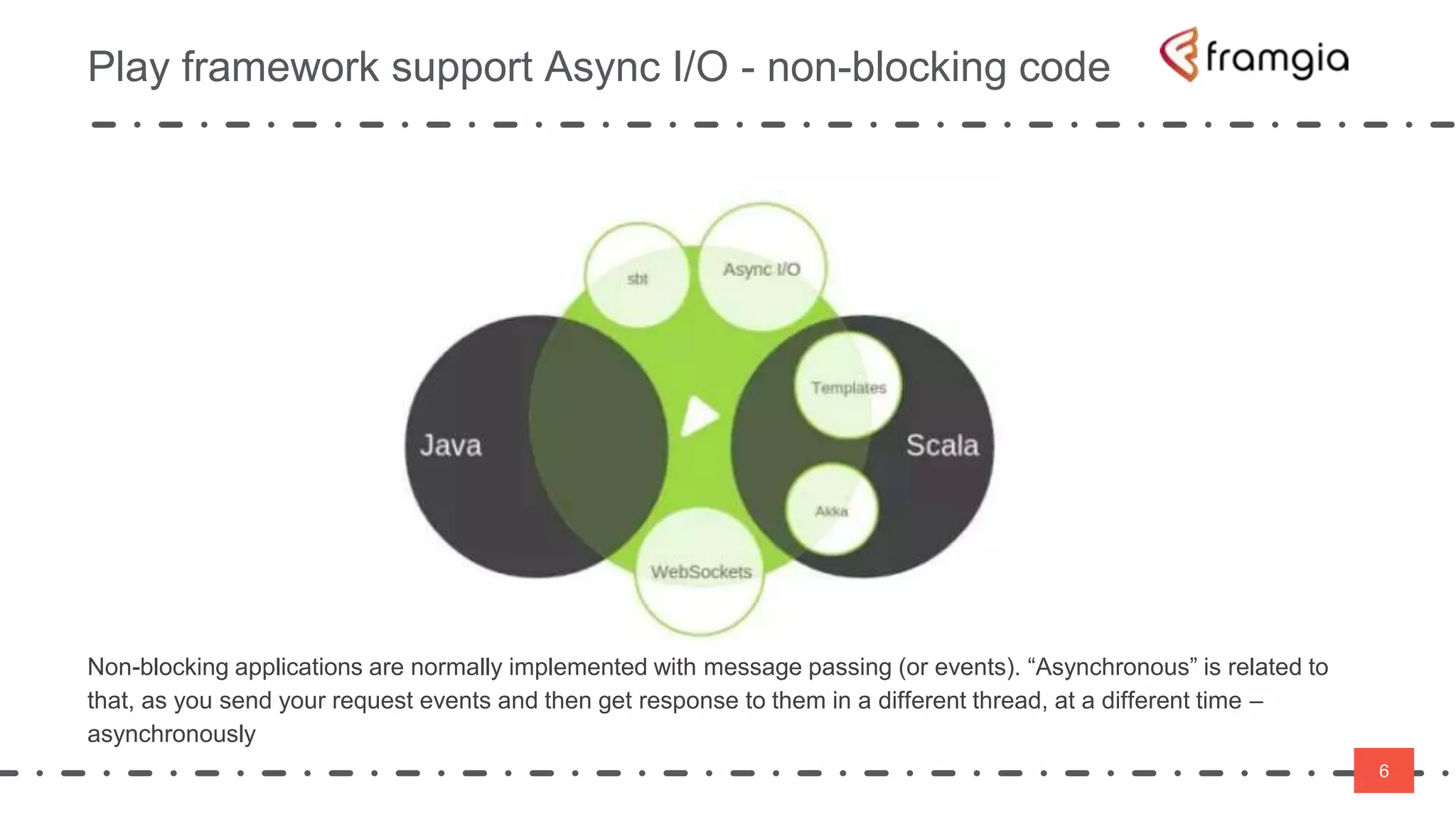
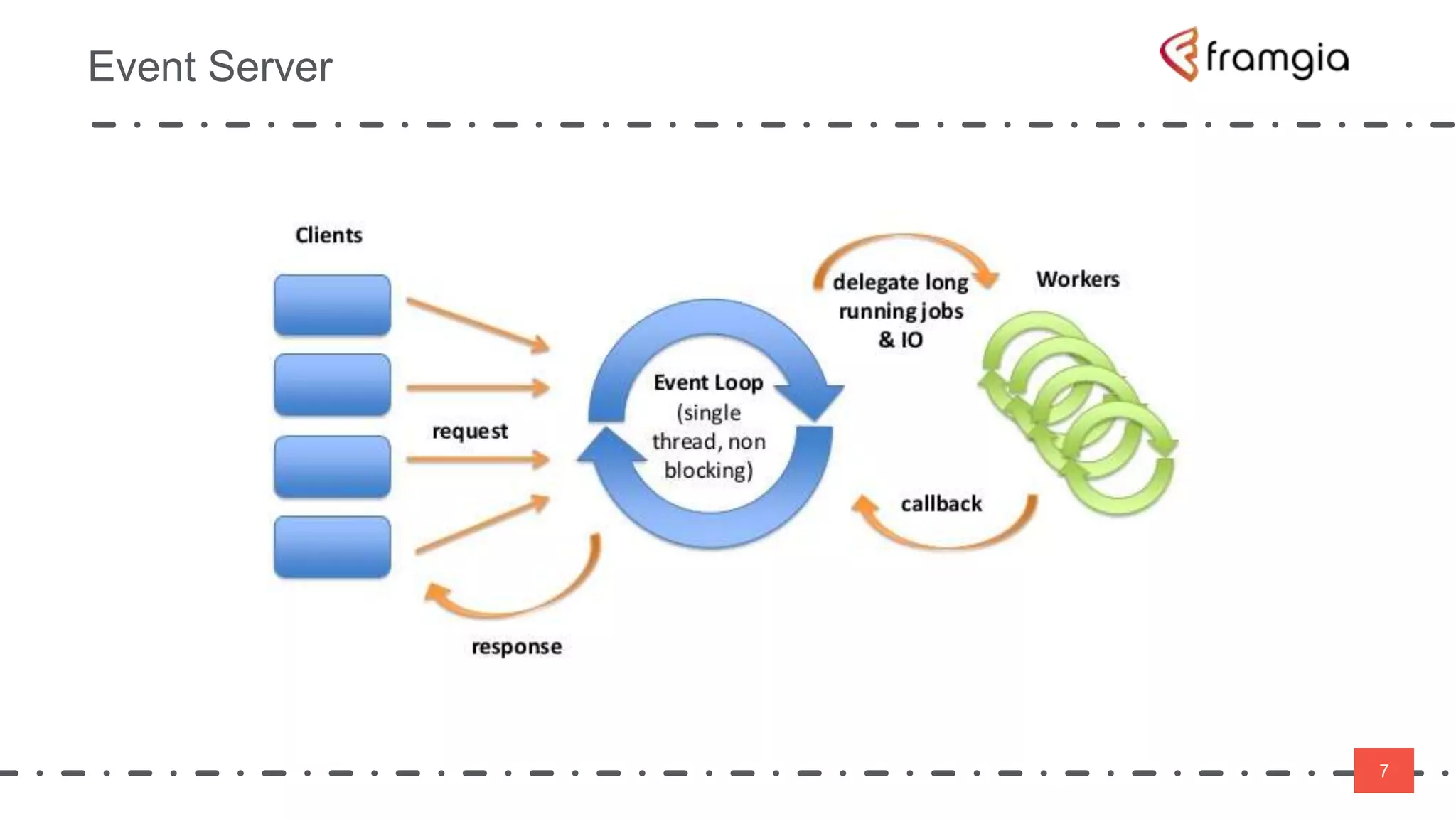
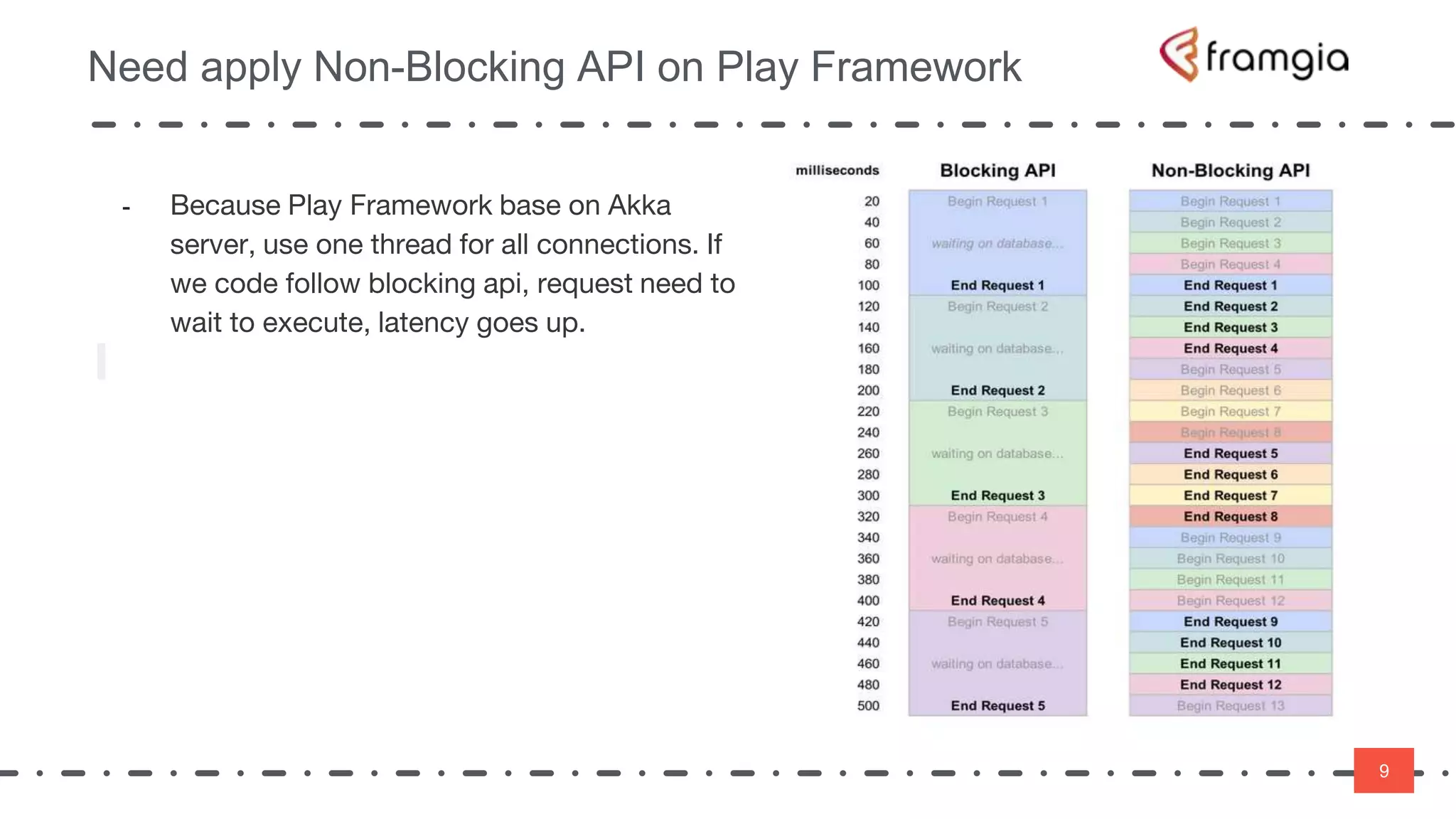
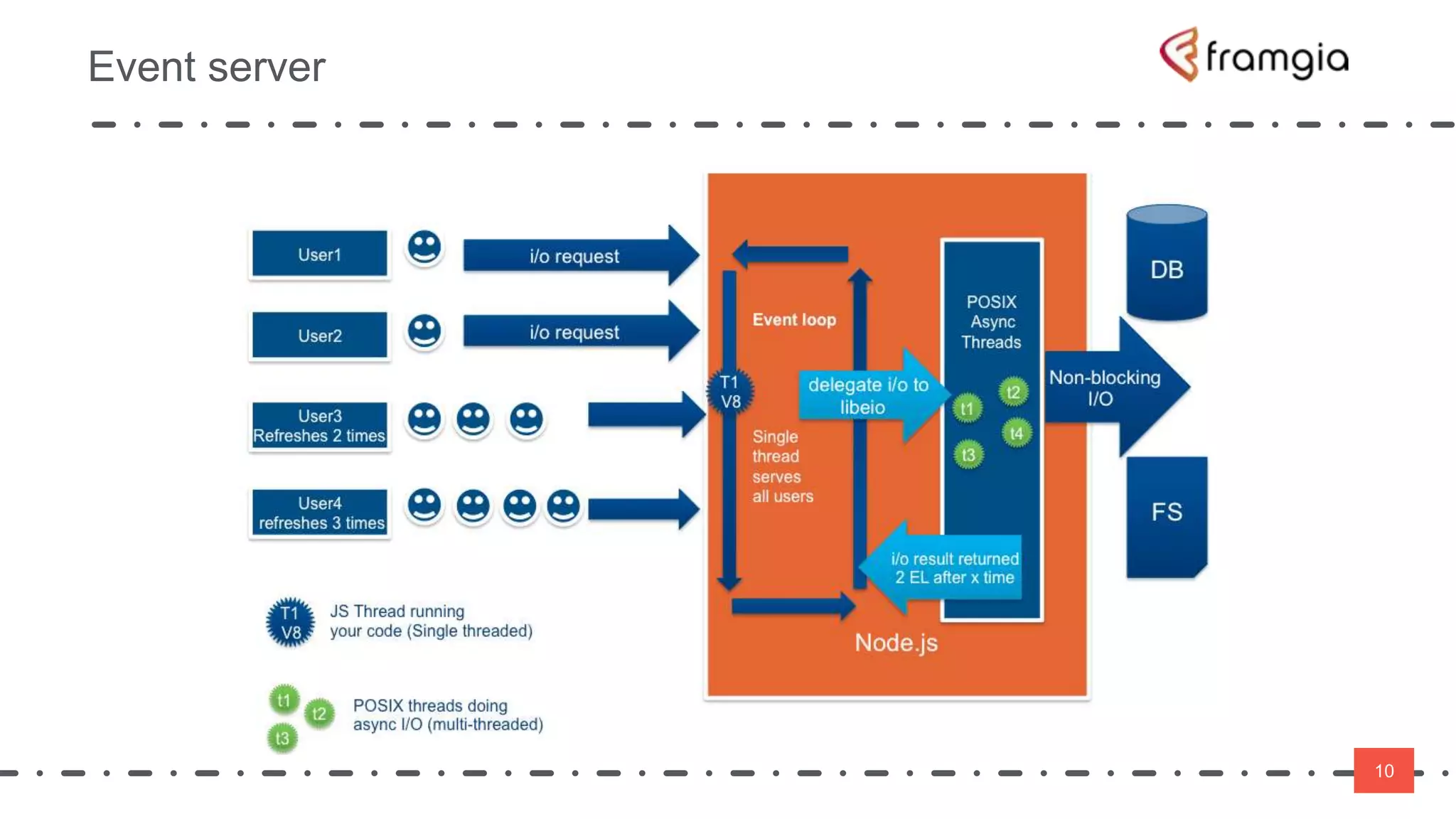
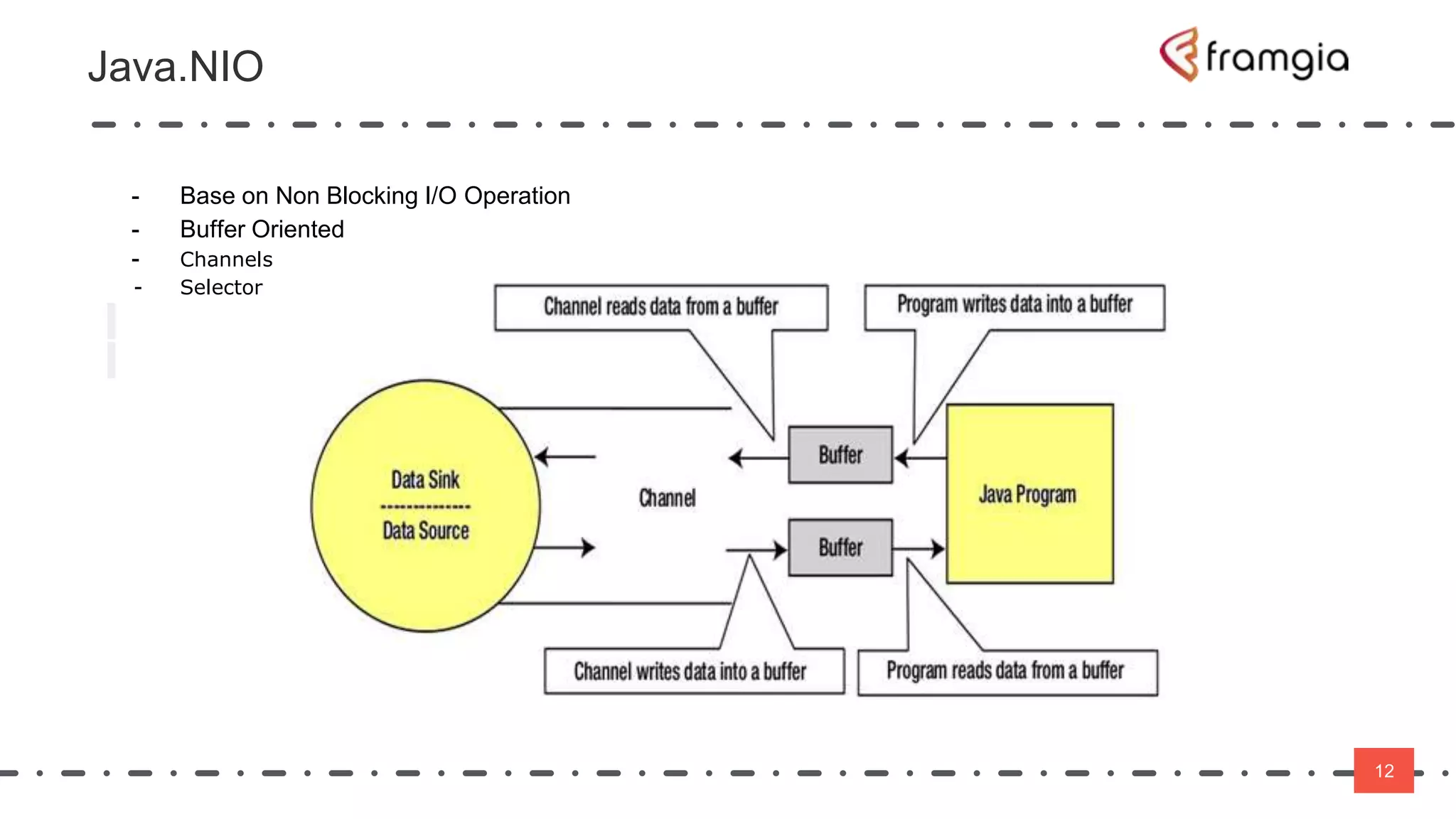
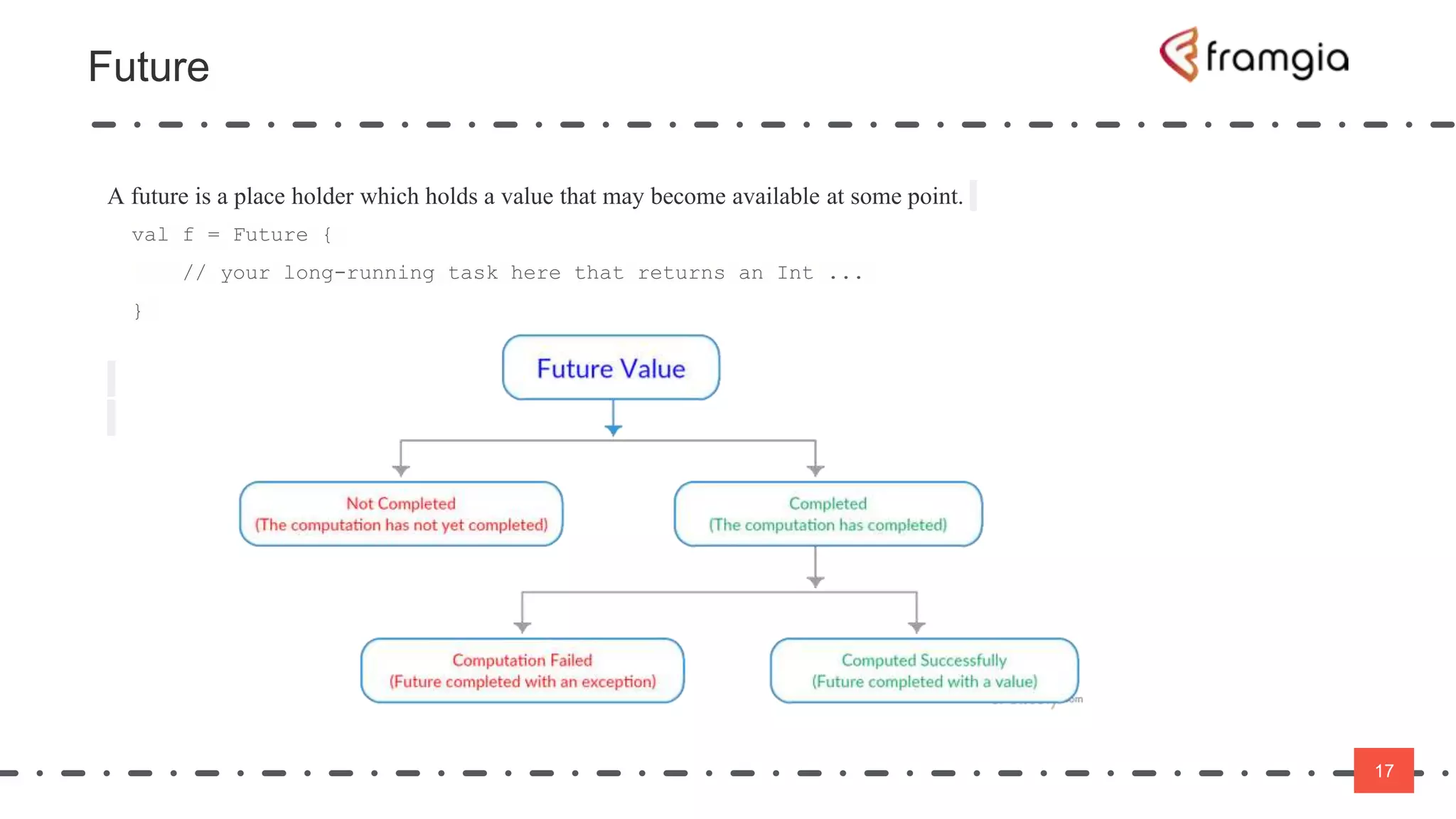
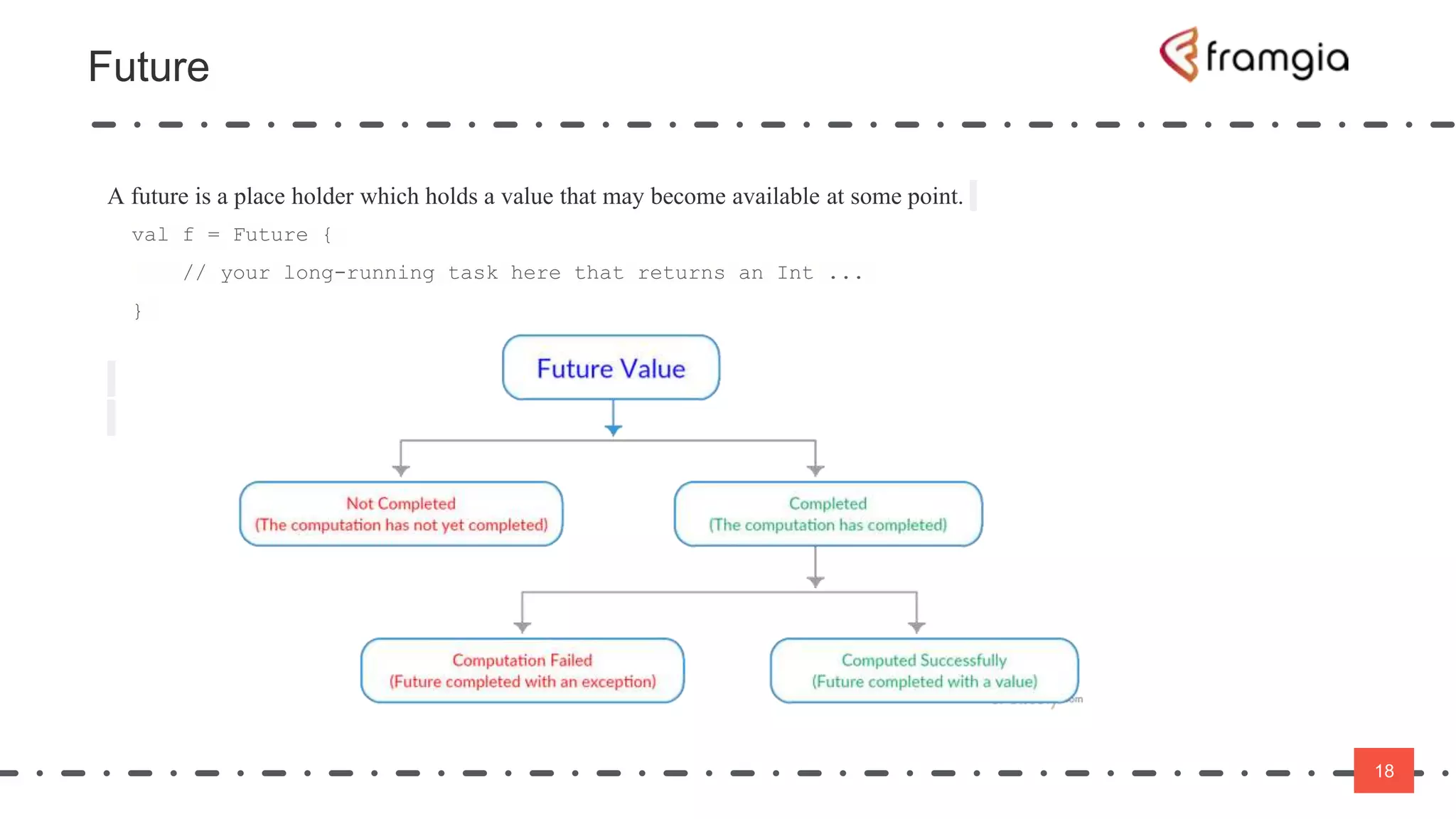
Play framework supports asynchronous and non-blocking code using Scala. Asynchronous applications use message passing and events to handle requests in a non-blocking way across threads. This improves performance by reducing thread switching and allowing many concurrent connections using fewer system resources. However, non-blocking code is more difficult to manage state and data. The Play framework uses Akka which handles requests asynchronously using a single thread per connection. To take advantage of this, code needs to be written using non-blocking APIs to avoid blocking the thread and reducing latency.






![13
Runnable & Callable
13
- java.lang.runnable
trait Runnable {
def run(): Unit
}
- java.util.concurrent.Callable
trait Callable[V] {
def call(): V
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalaasync-2-180626082833/75/play-framework-async-with-scala-13-2048.jpg)




![21
21
Can chain several of these together like this:
val first:Future[Int] = Future{
….
10 //return 10
}
val second:Future[Int] = Future{
….
100 //return 100
}
val addResult:Future[Int] = for{
one <- first //here one is of of type int
two <- second
} yield one + two //yield returns the Future of value computed by adding two integers
val finalVerifiedResult:Future[Int] = addResult.recover{case ex:Exception => -1}
Combinators](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalaasync-2-180626082833/75/play-framework-async-with-scala-21-2048.jpg)
![22
The async / await language extension like C#
22
We can use scala-async library to write code more readable like this:
val combined: Future[Int] = async {
await(first) + await(second)
}
https://github.com/scala/scala-async](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalaasync-2-180626082833/75/play-framework-async-with-scala-22-2048.jpg)