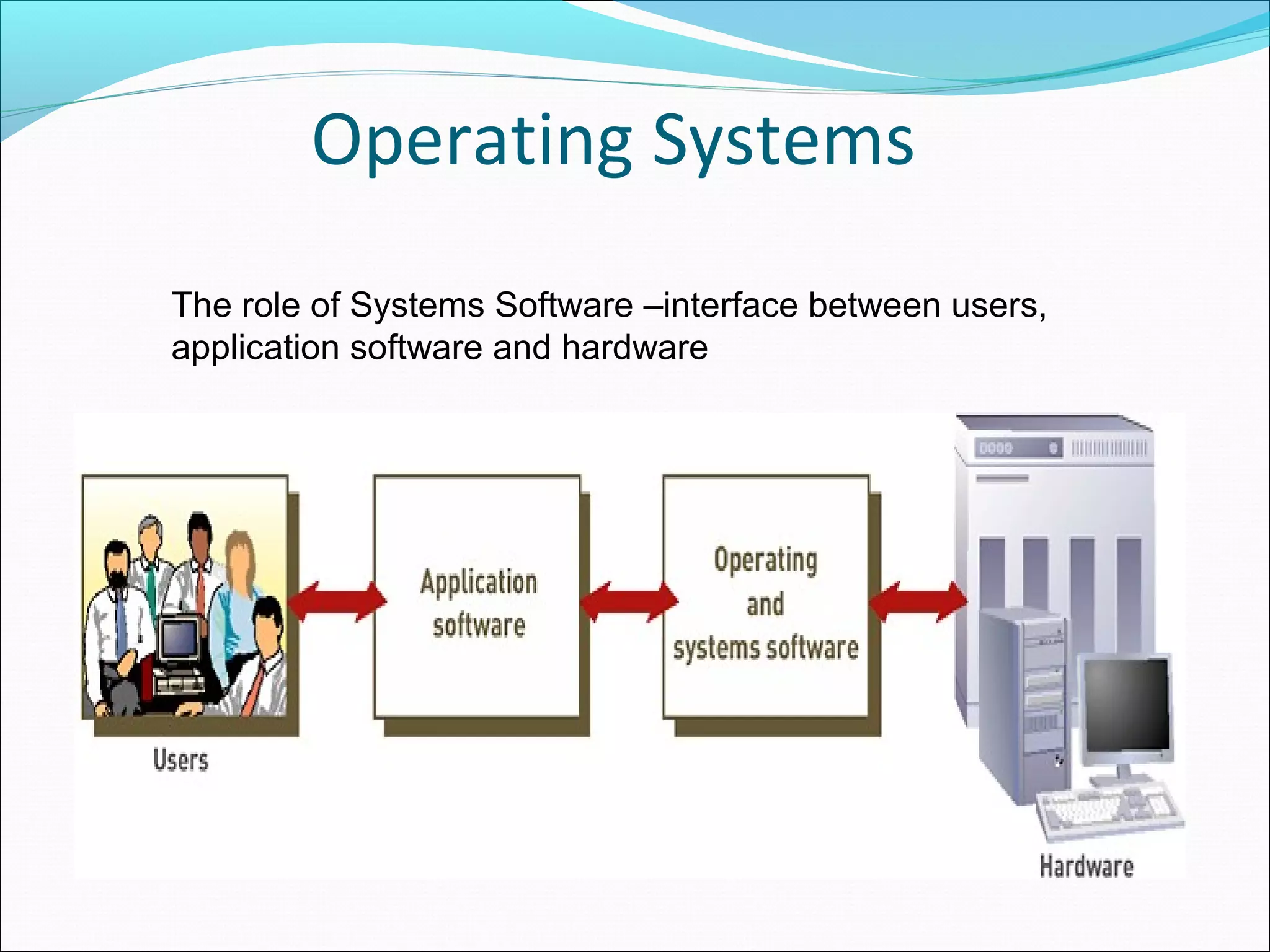
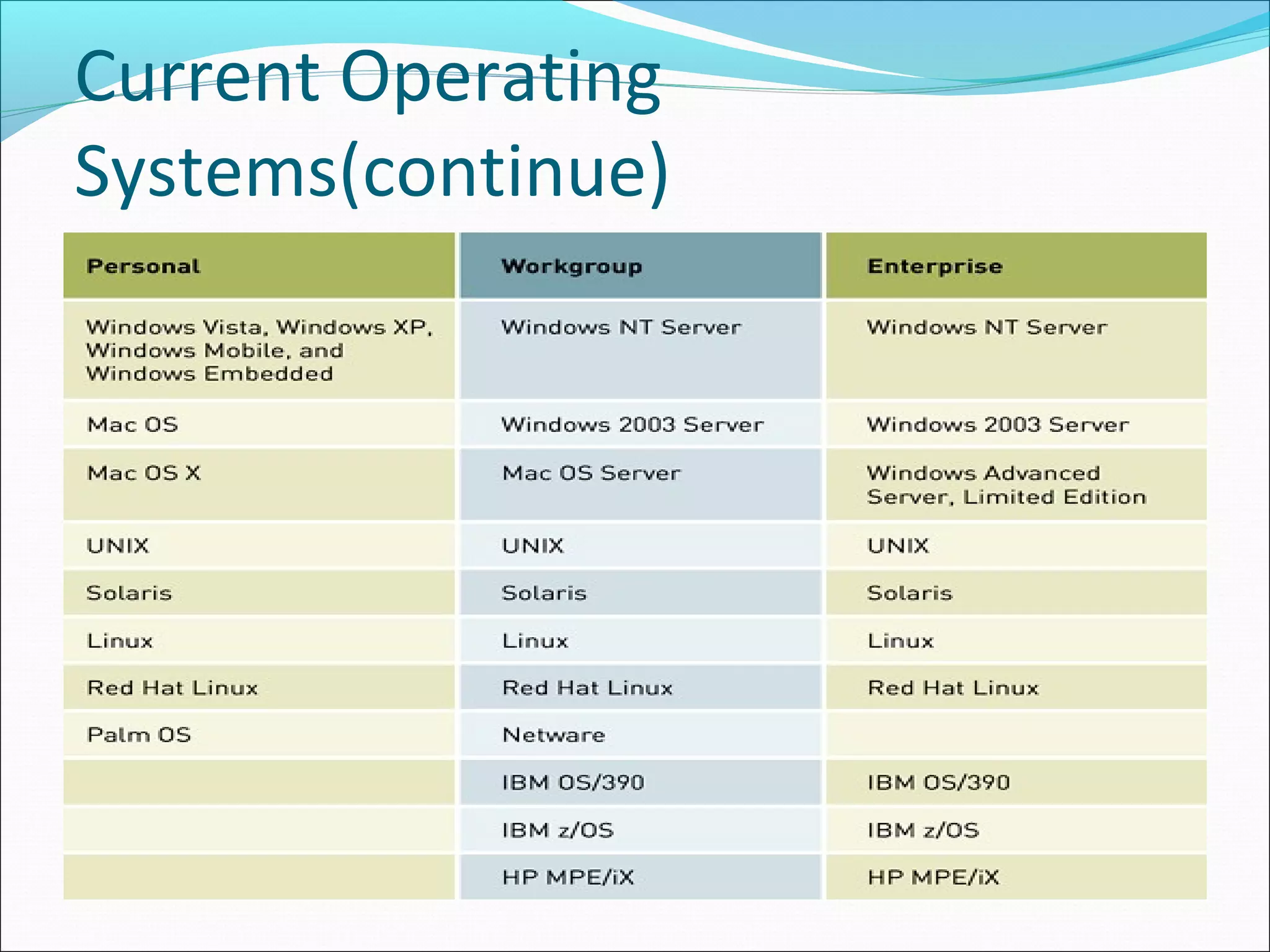
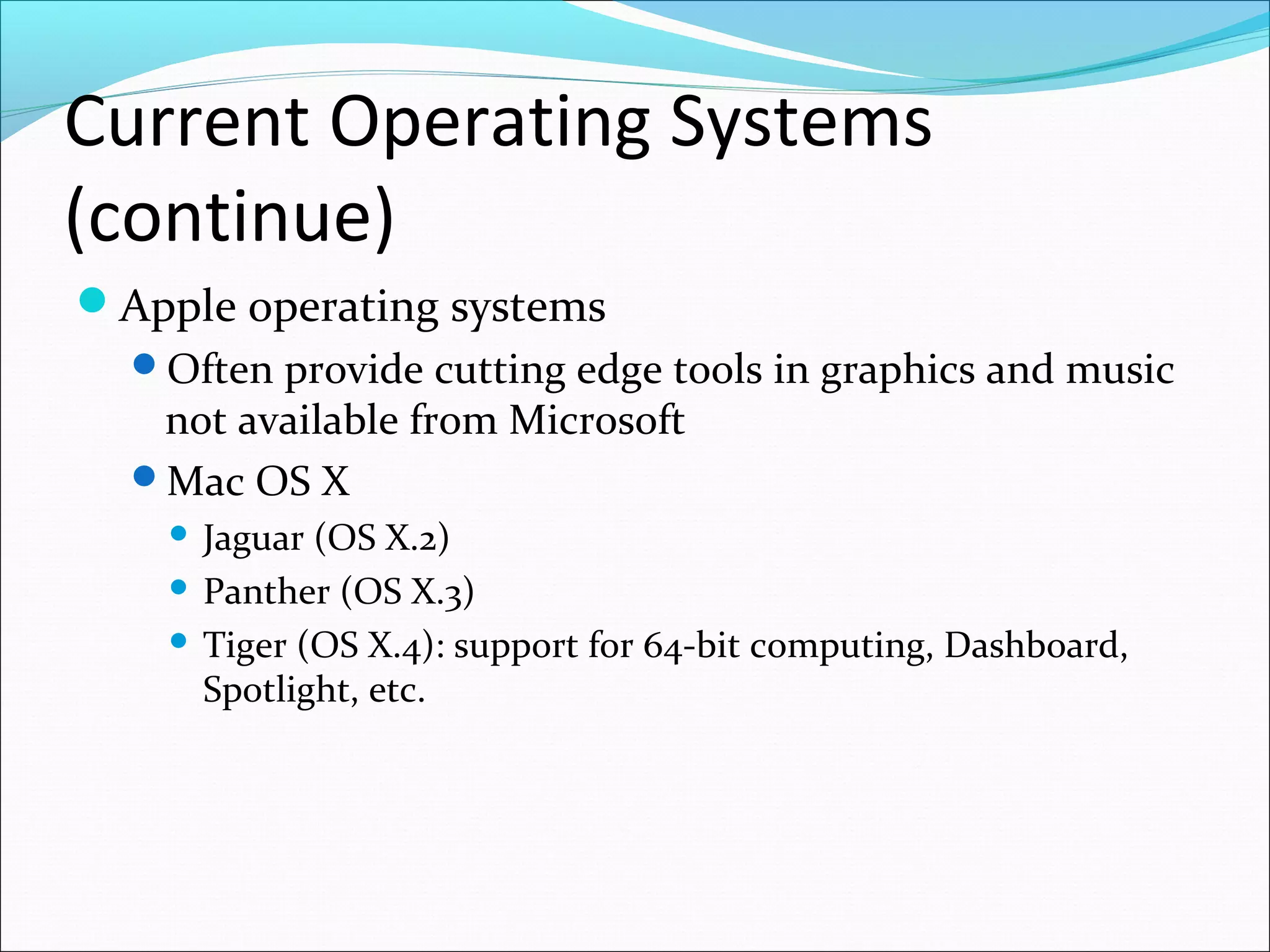
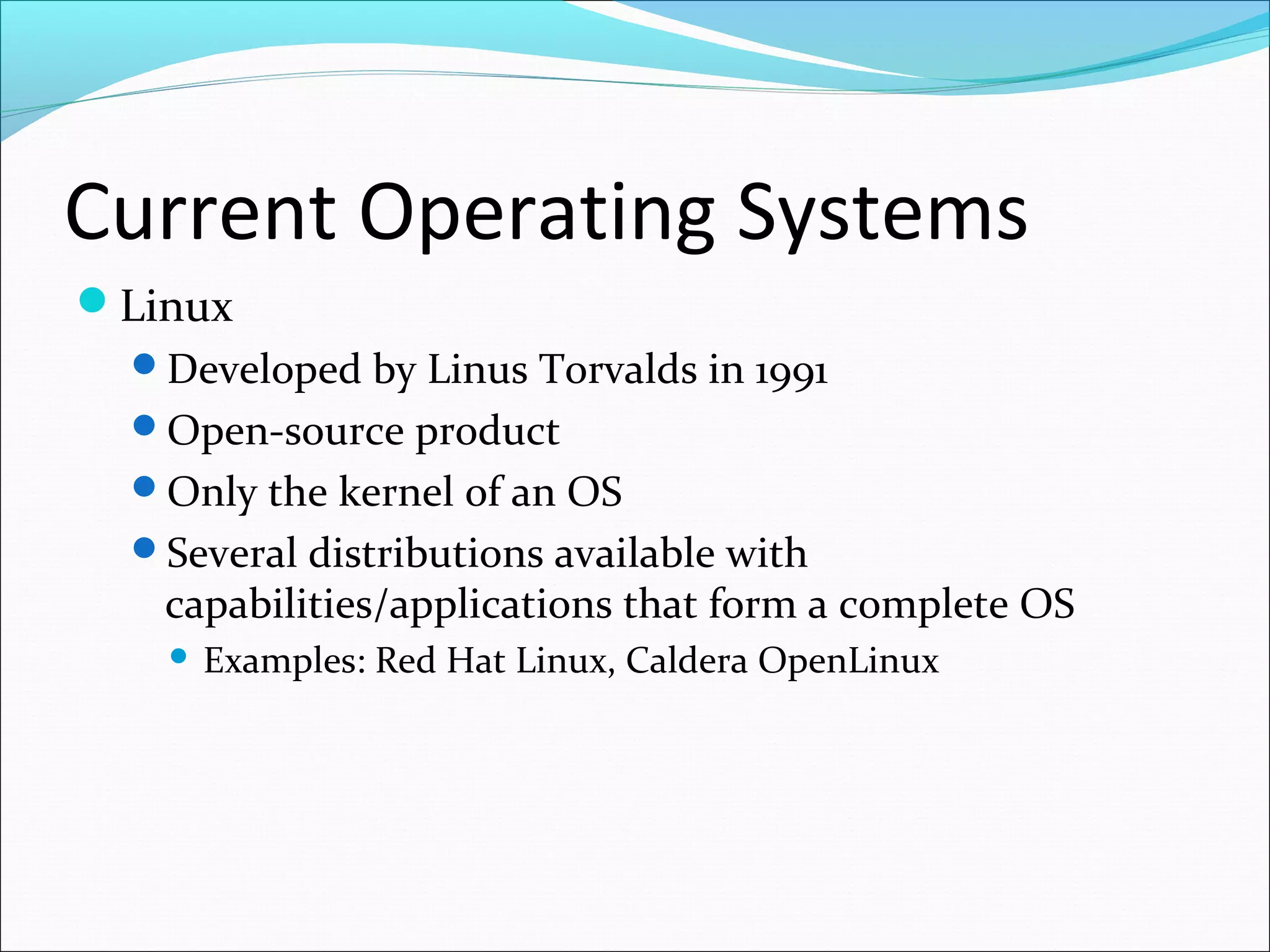
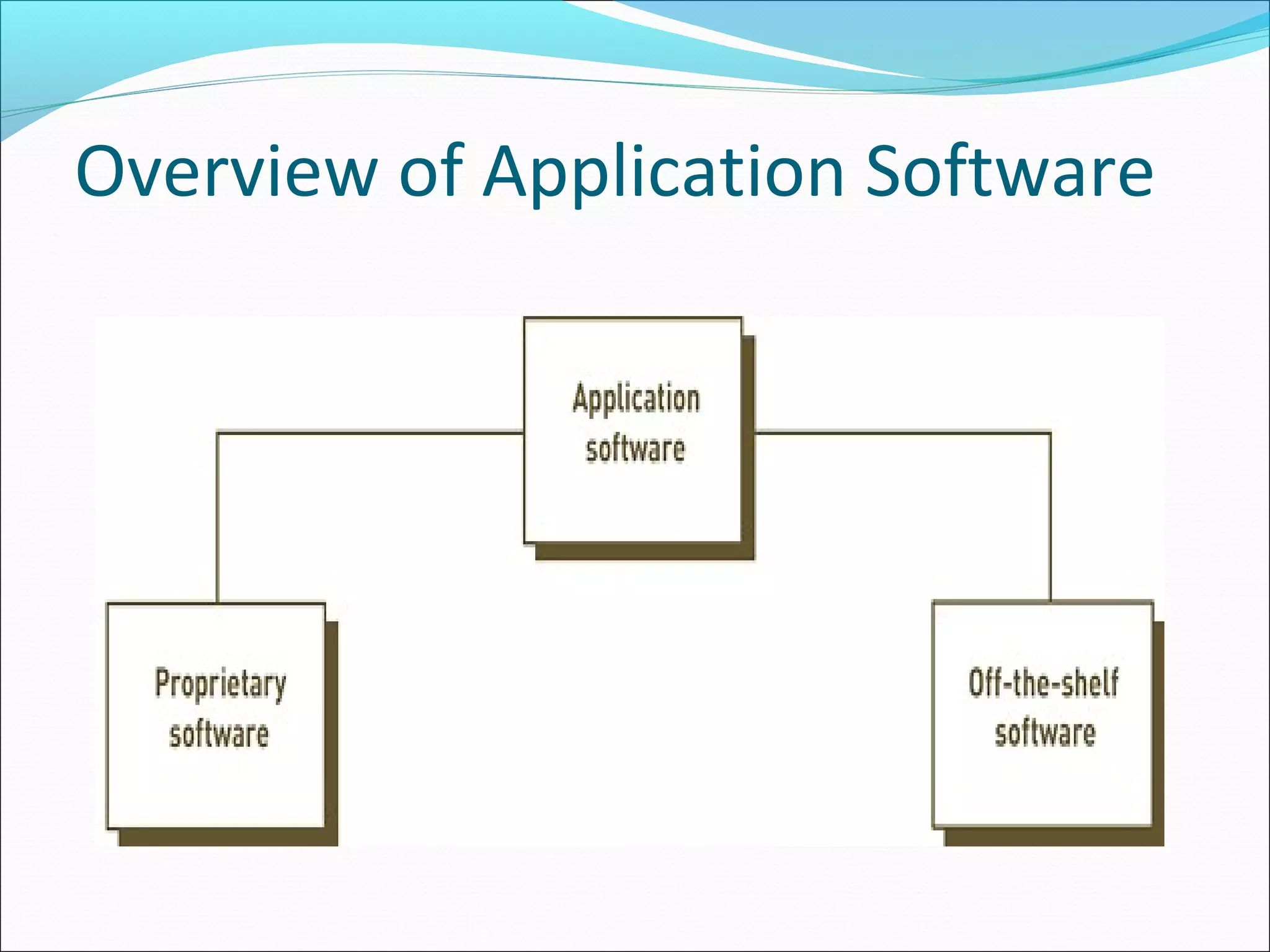
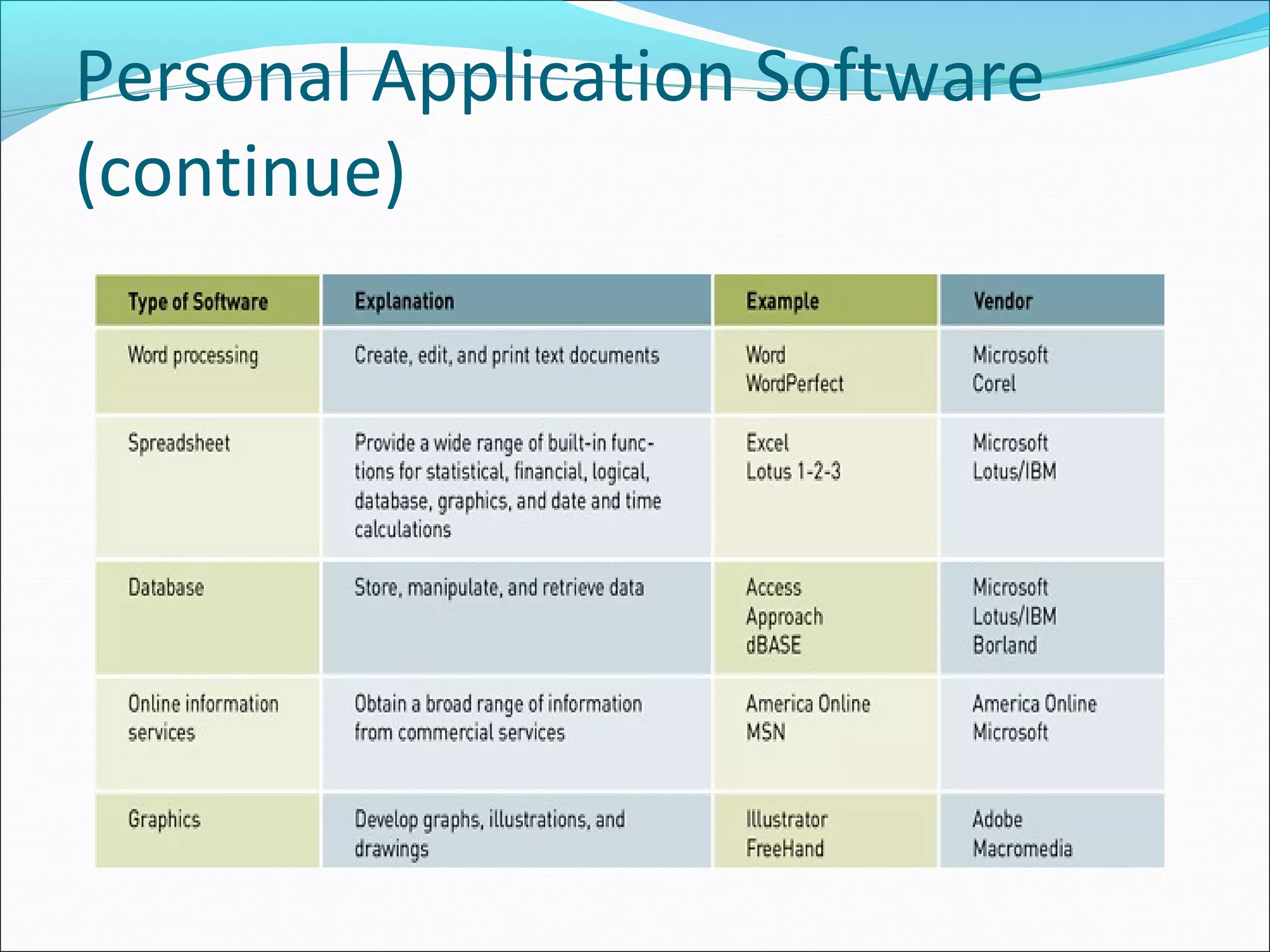
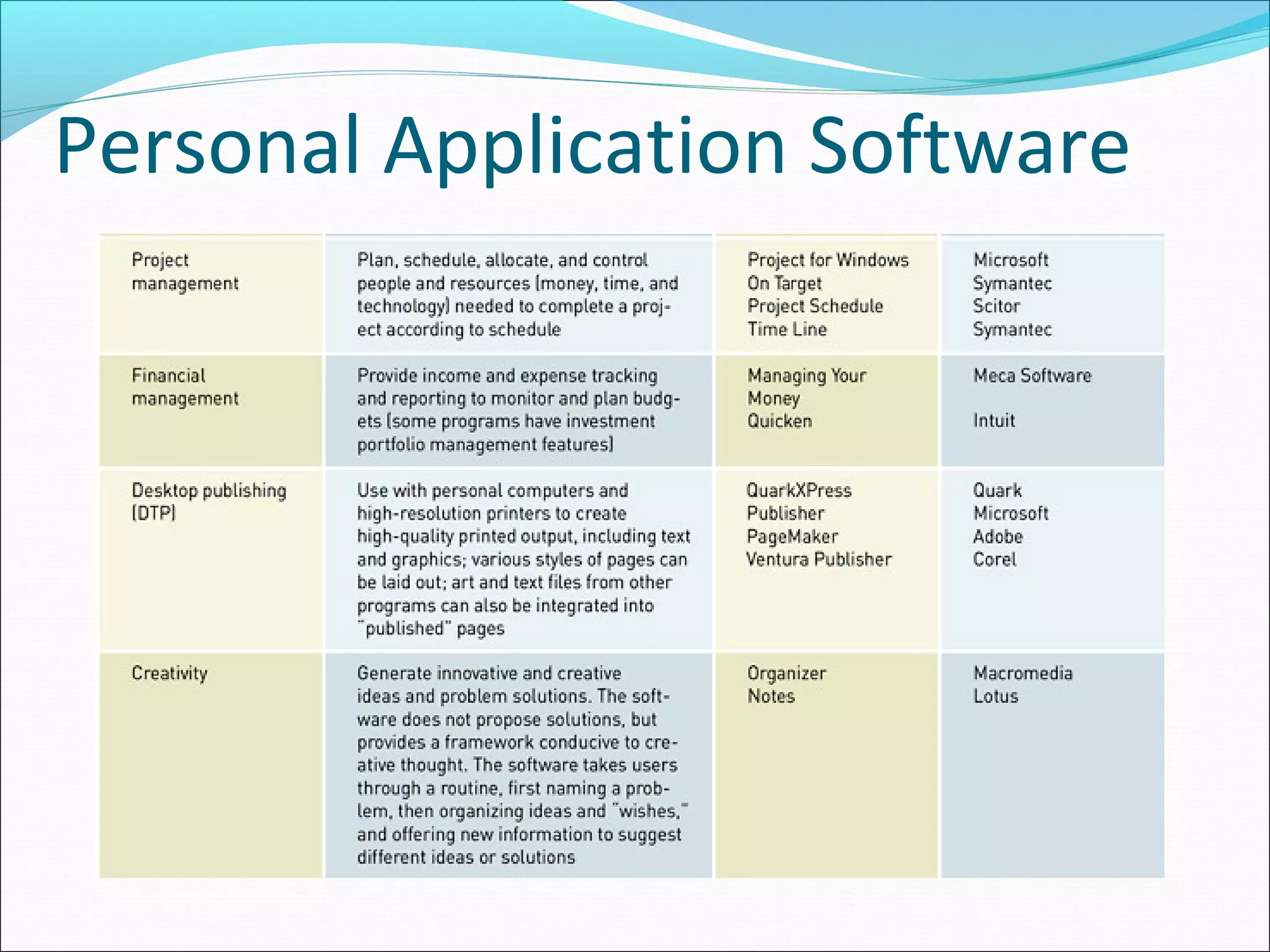
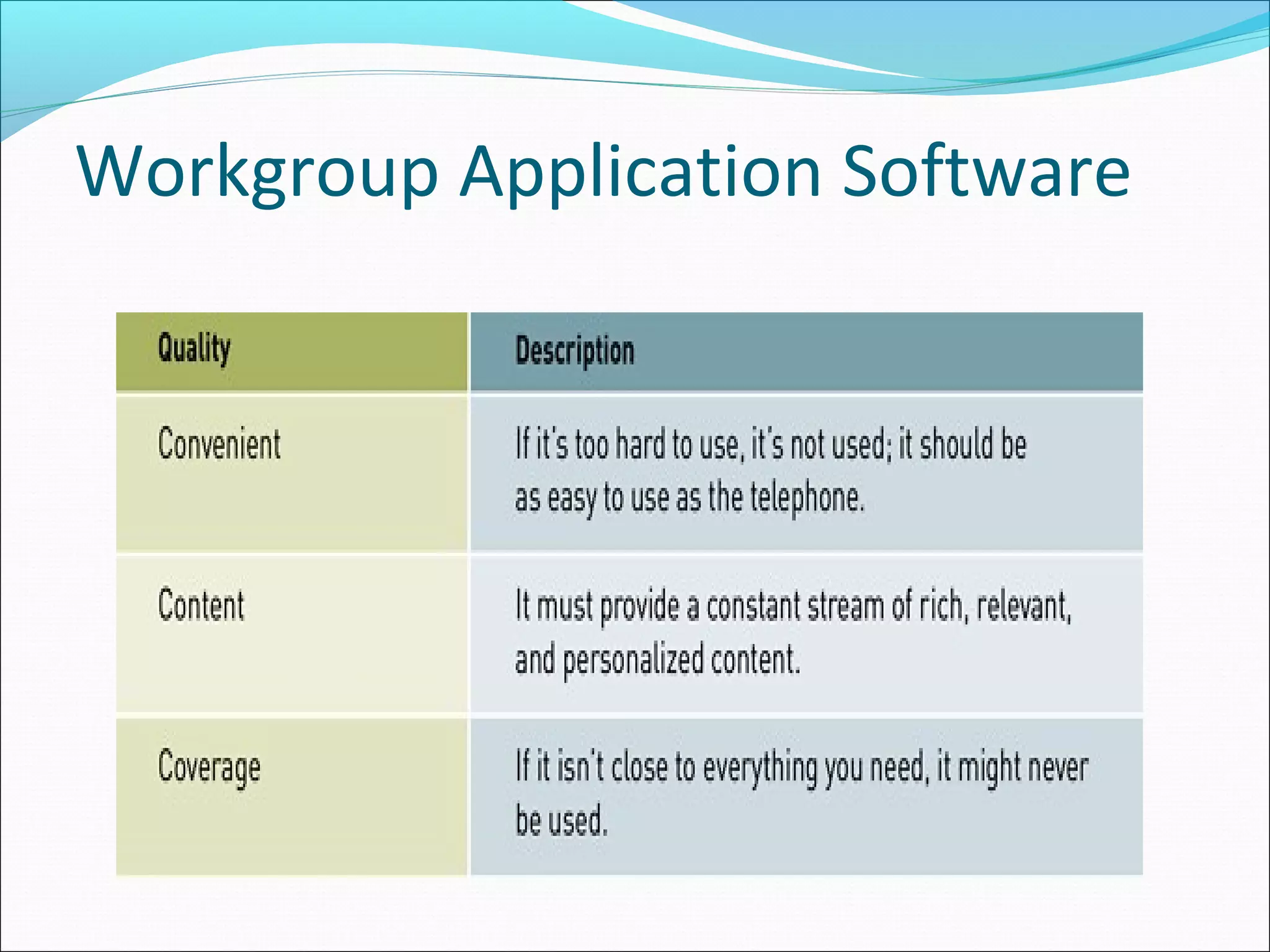
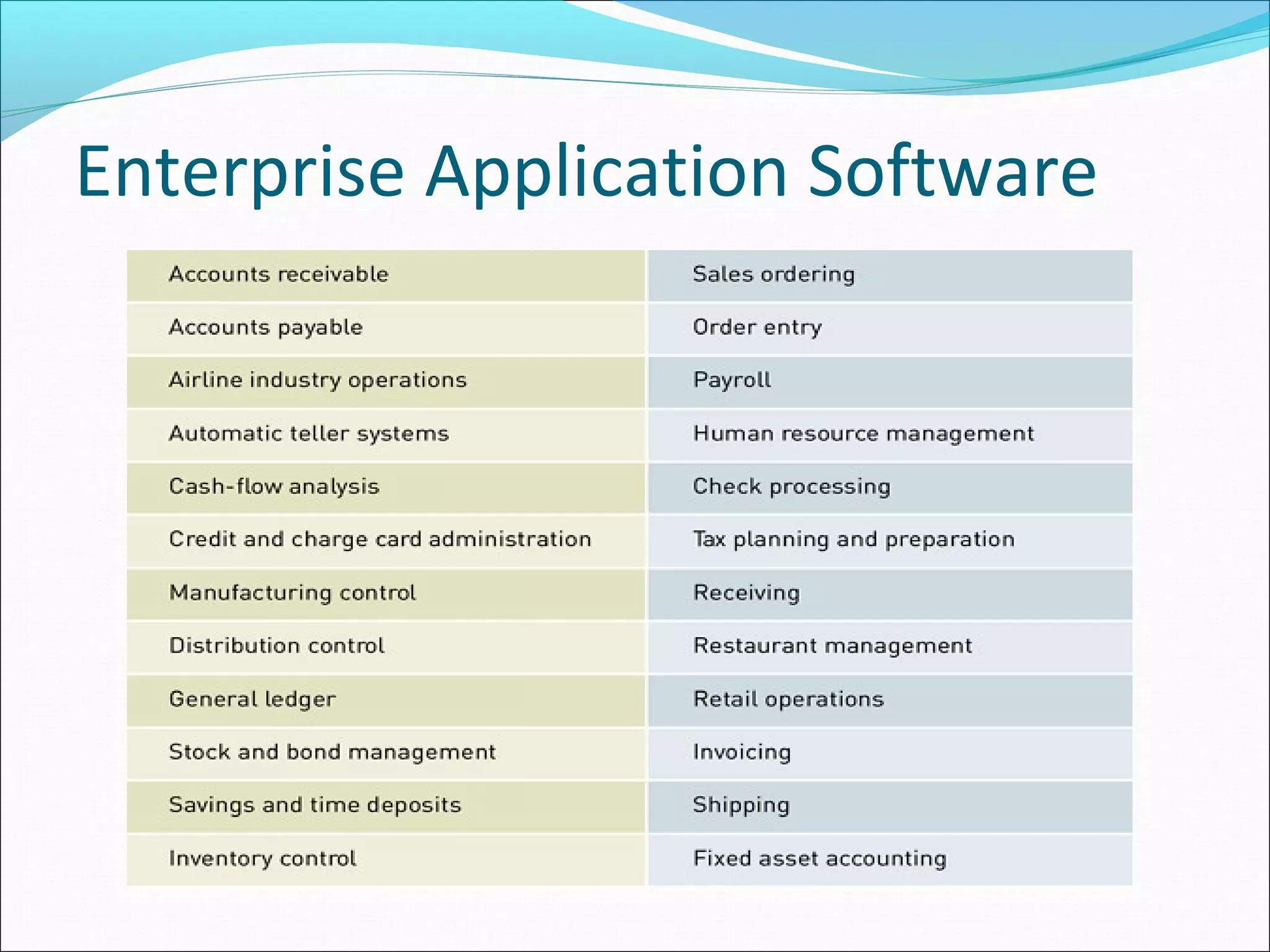
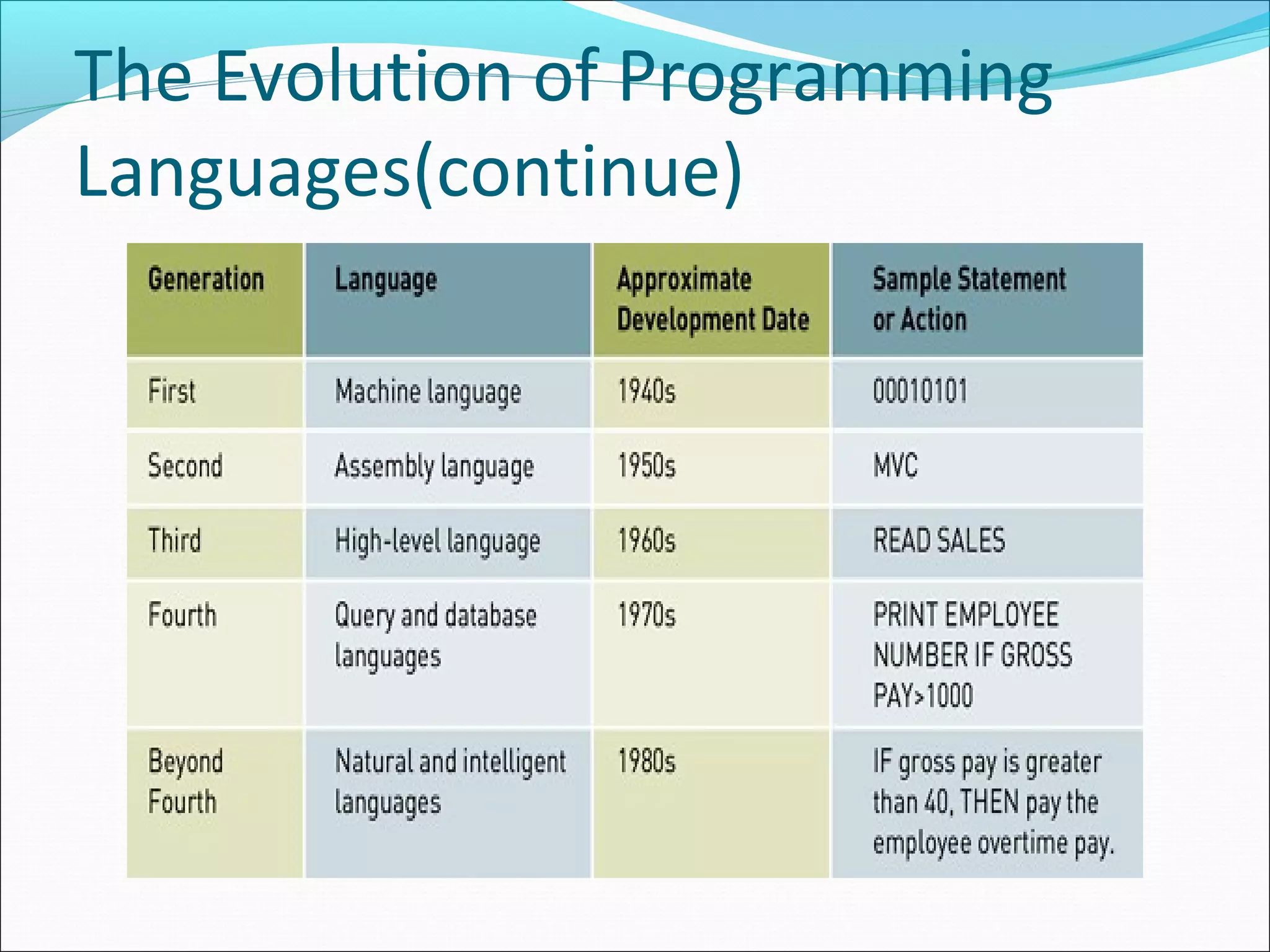
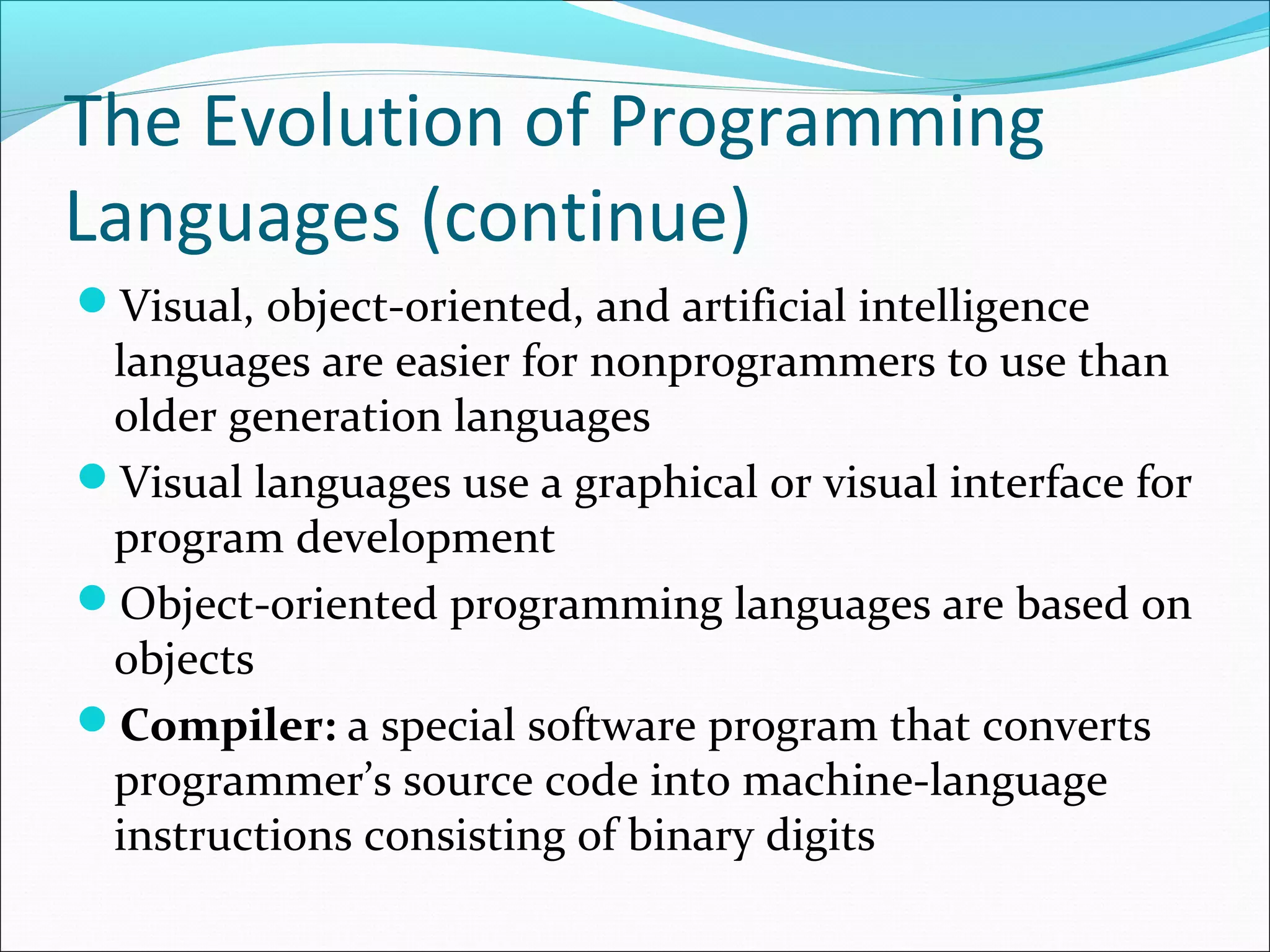
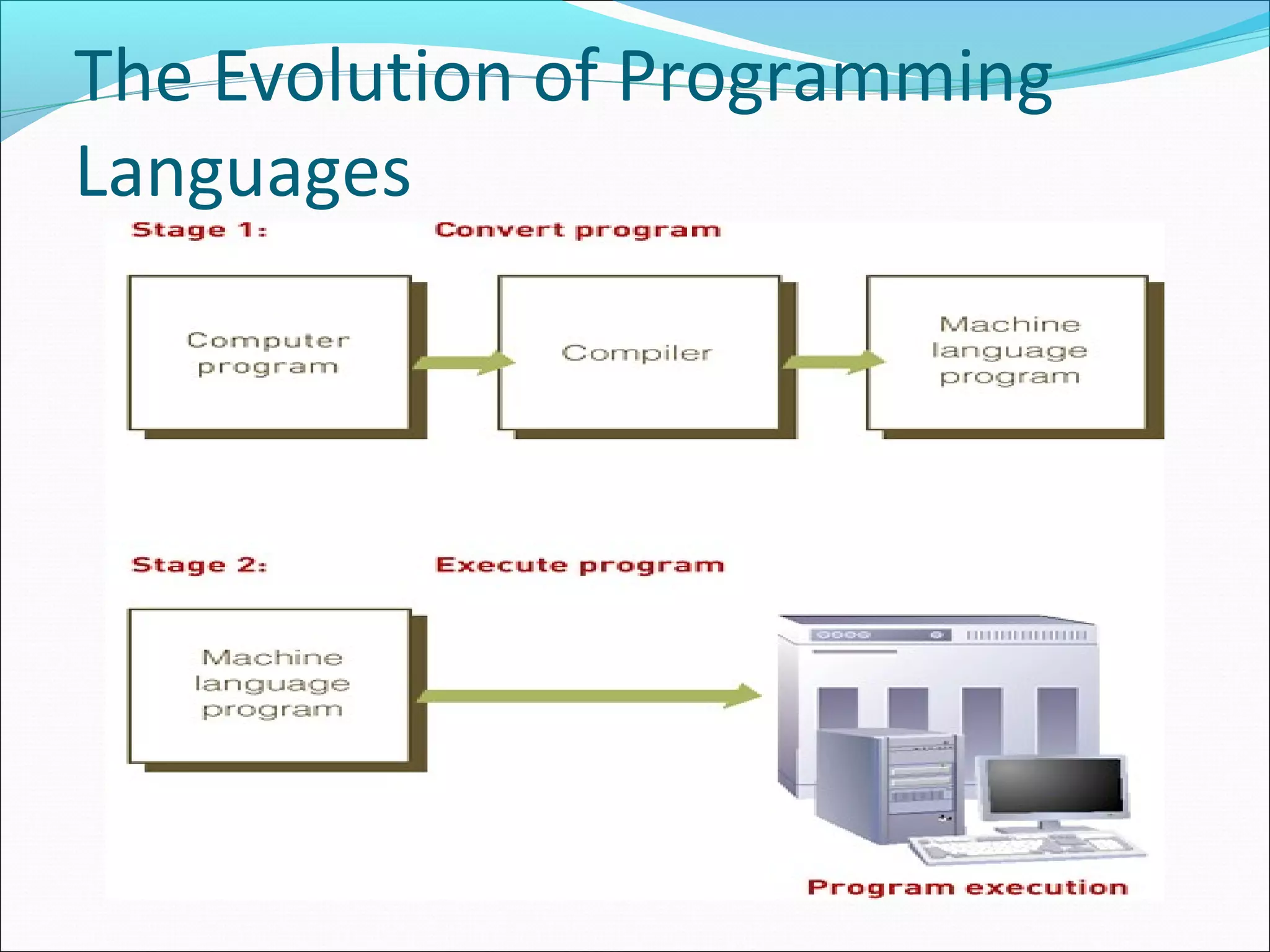
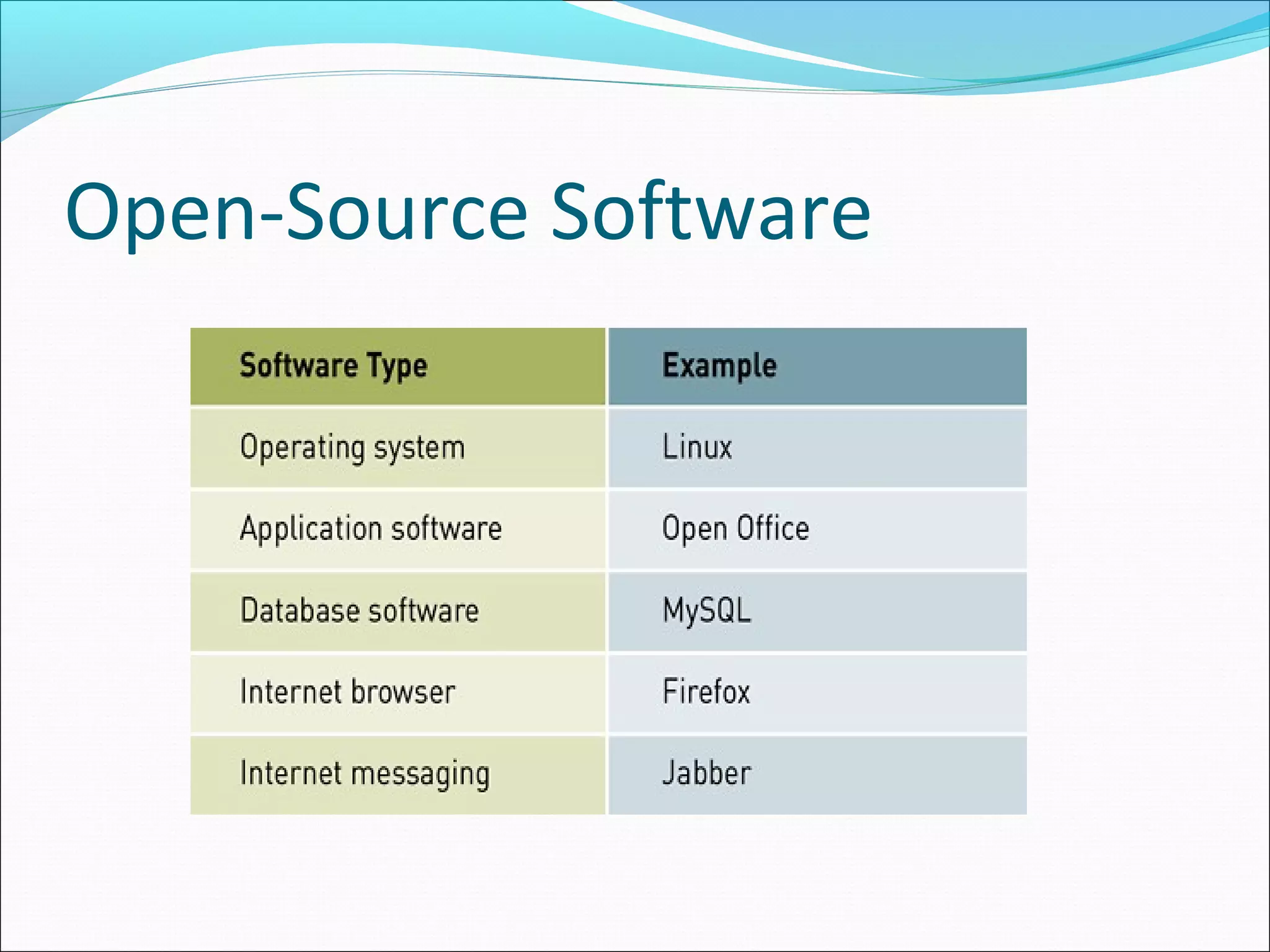
The document discusses various types of computer software. It defines systems software as software that coordinates hardware and programs, with operating systems being a key type of systems software. It outlines popular operating systems like Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. It also defines application software as software that helps users solve problems, and discusses personal, workgroup, and enterprise application software. The document outlines the evolution of programming languages from early to modern visual and object-oriented languages. It discusses issues like software bugs, copyrights, open-source software, and software upgrades.