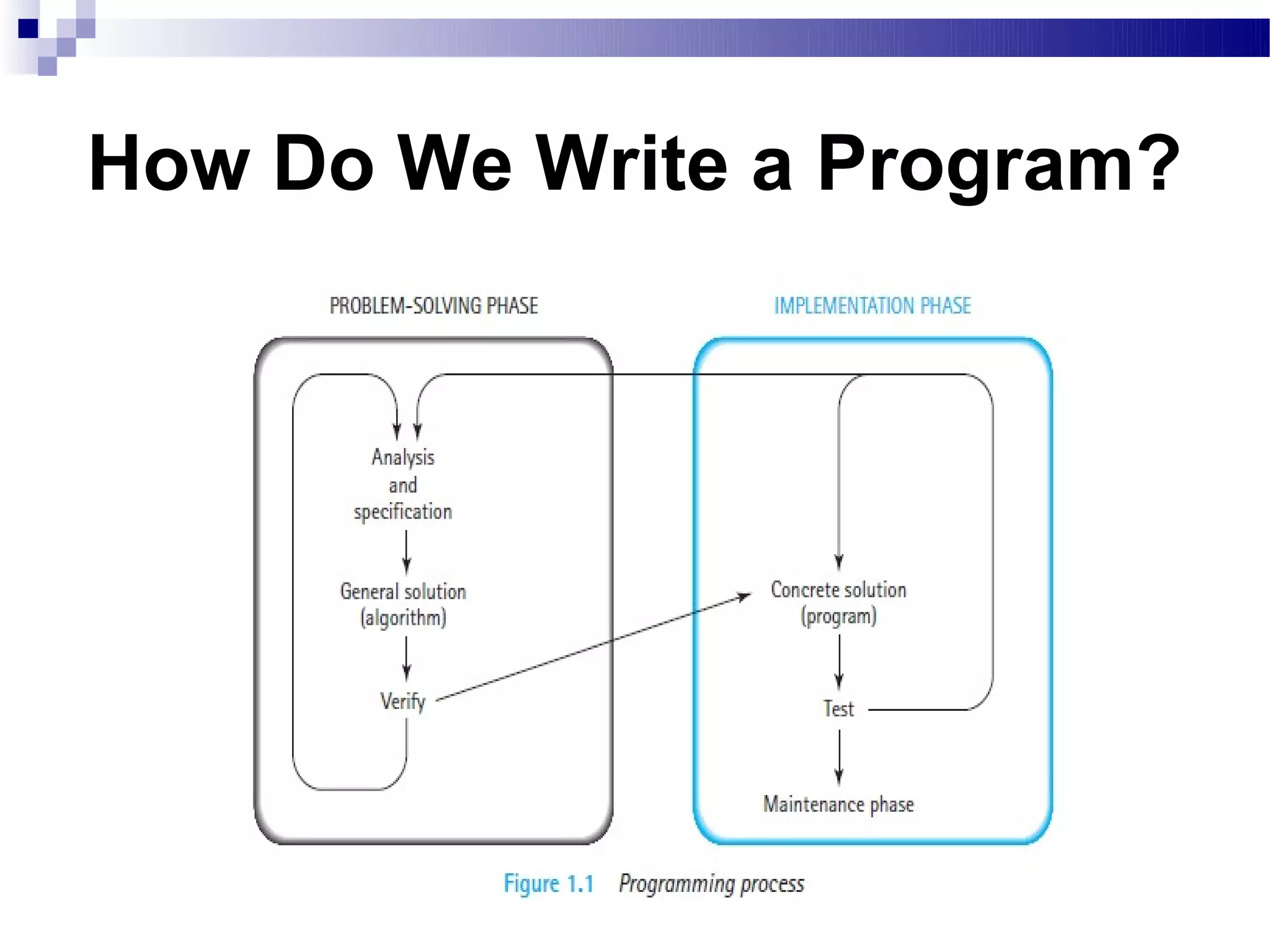
The document discusses the process of writing a computer program. It explains that programming involves breaking a problem down into a logical sequence of steps. There are two main phases: the problem-solving phase where the problem is analyzed and an algorithm is developed, and the implementation phase where the algorithm is translated into a programming language and tested. The process also includes a maintenance phase to modify the program as needed over time.