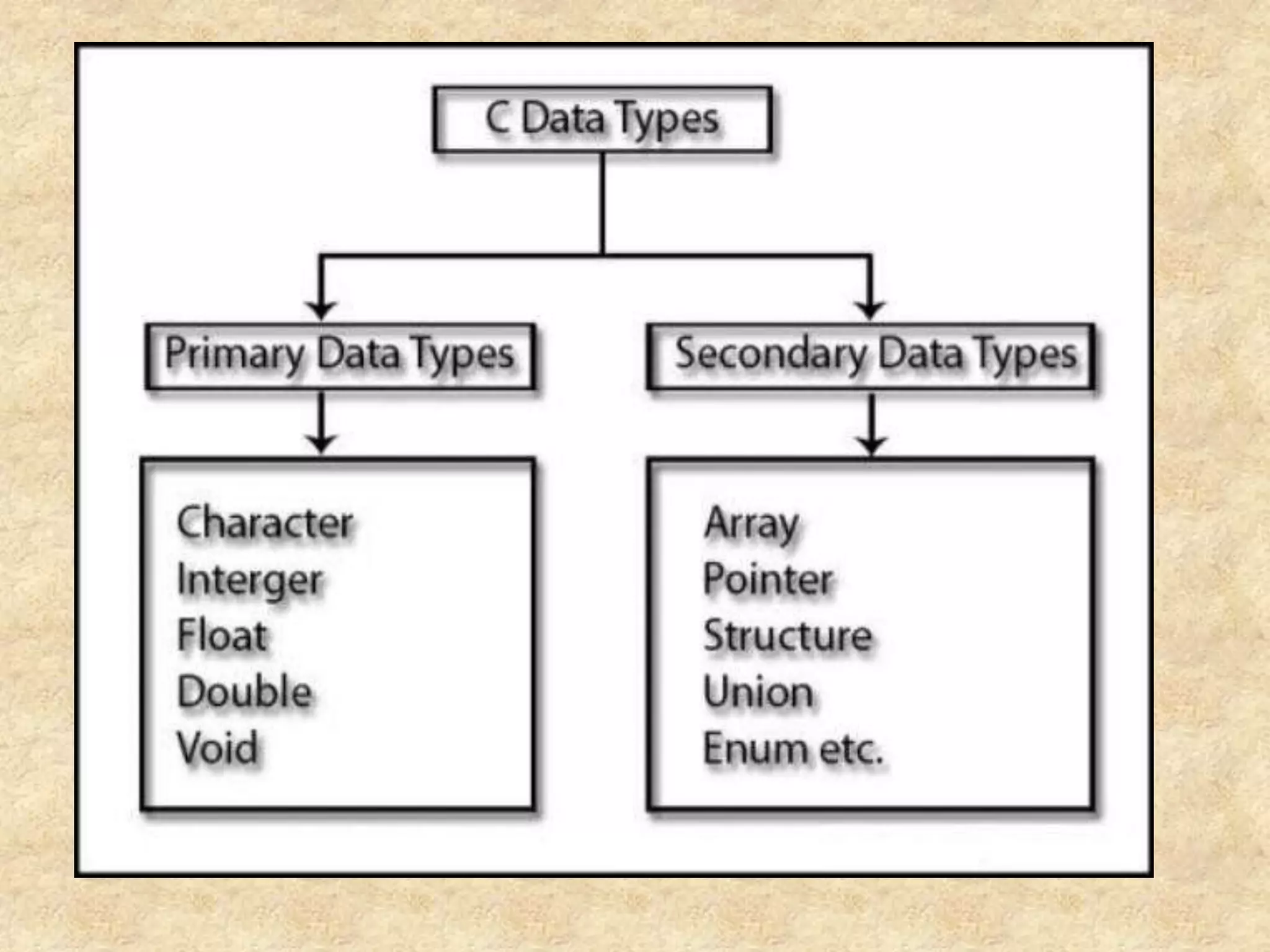
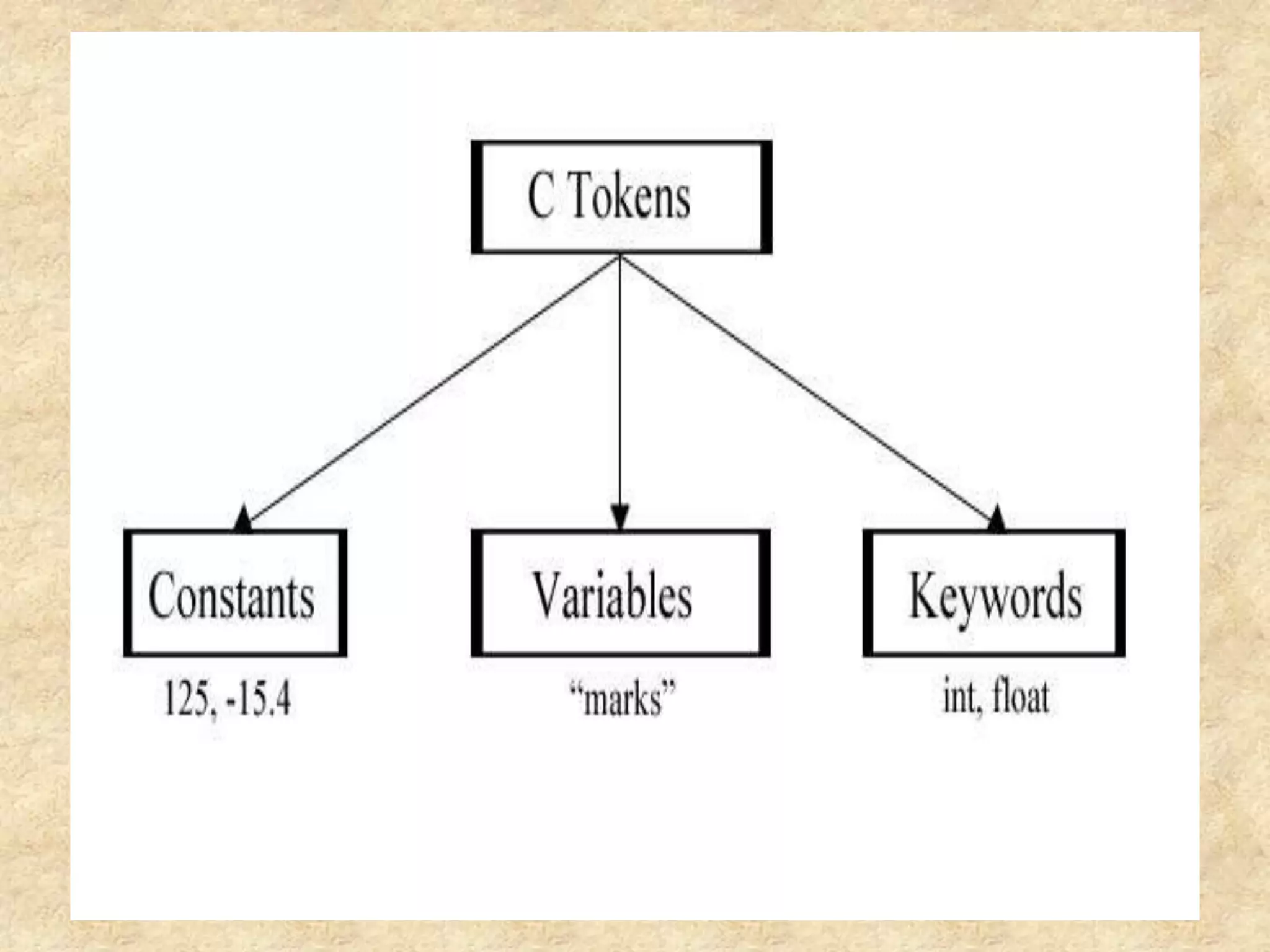
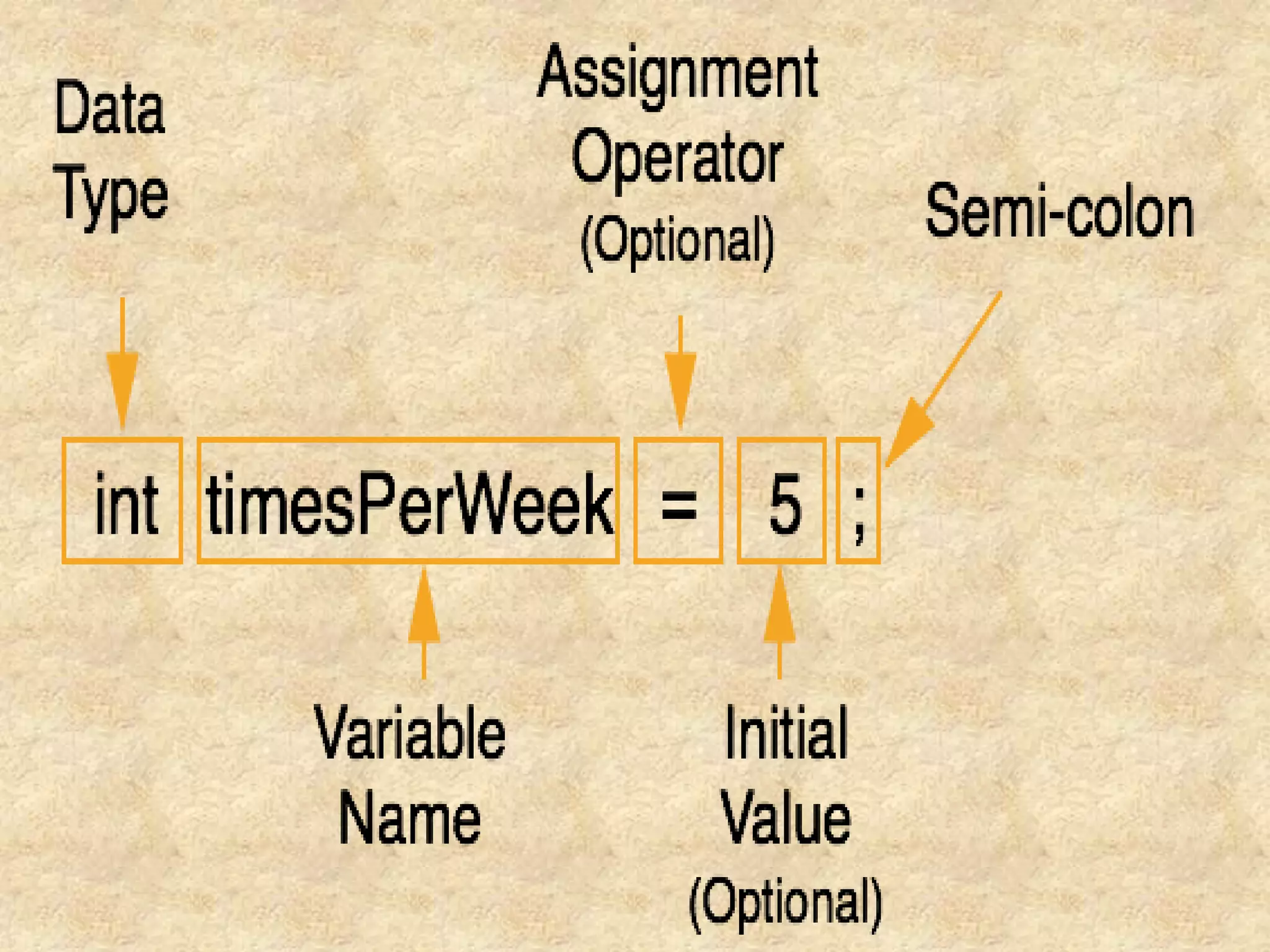
The document discusses various programming languages and their uses. It provides descriptions of several popular languages including C, C++, Visual Basic, Java, C#, PHP, Assembly, and Python. For each language, it briefly outlines characteristics like performance, ease of use, common applications, and portability. It also provides a high-level history of early programming languages.