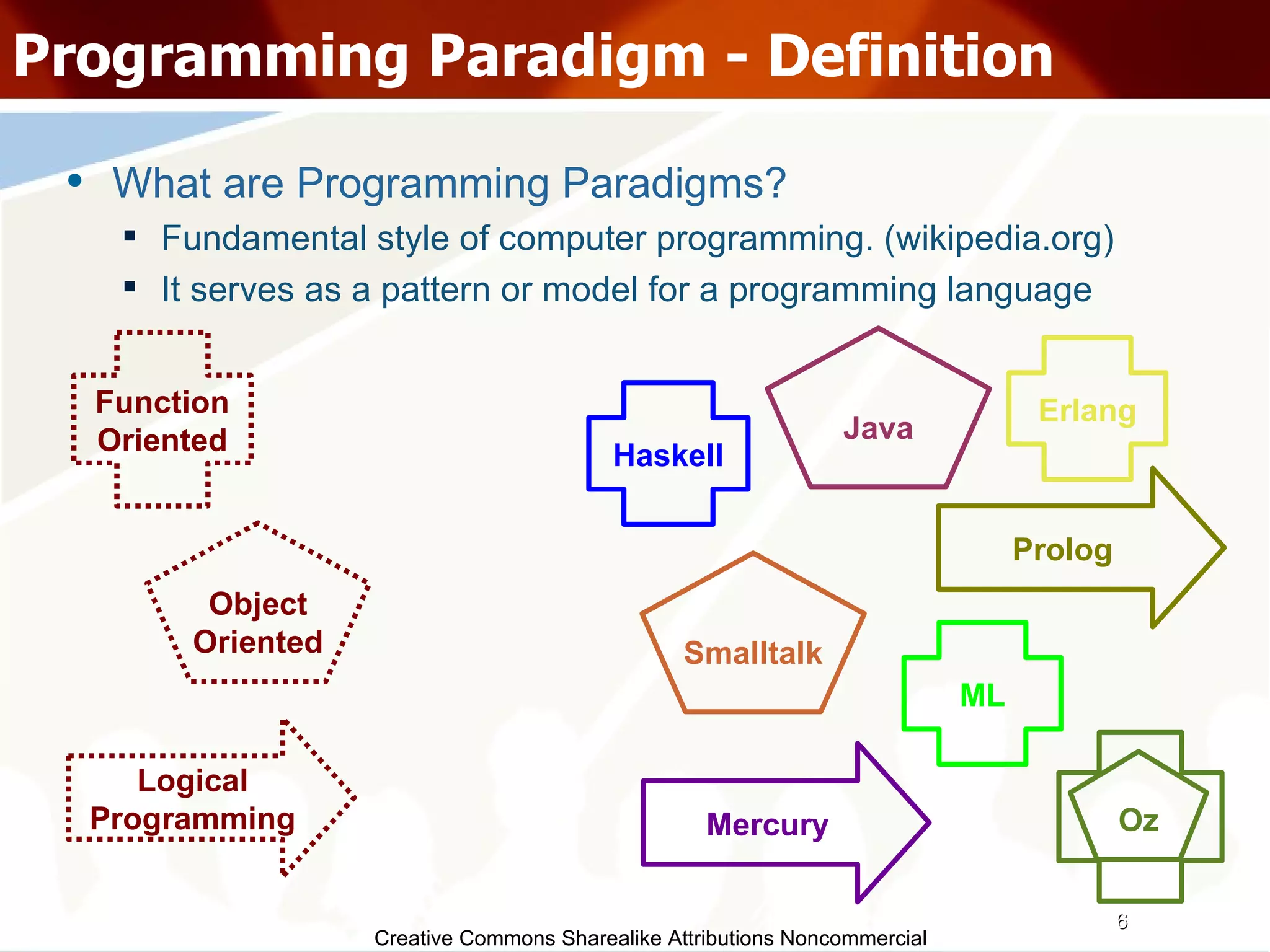
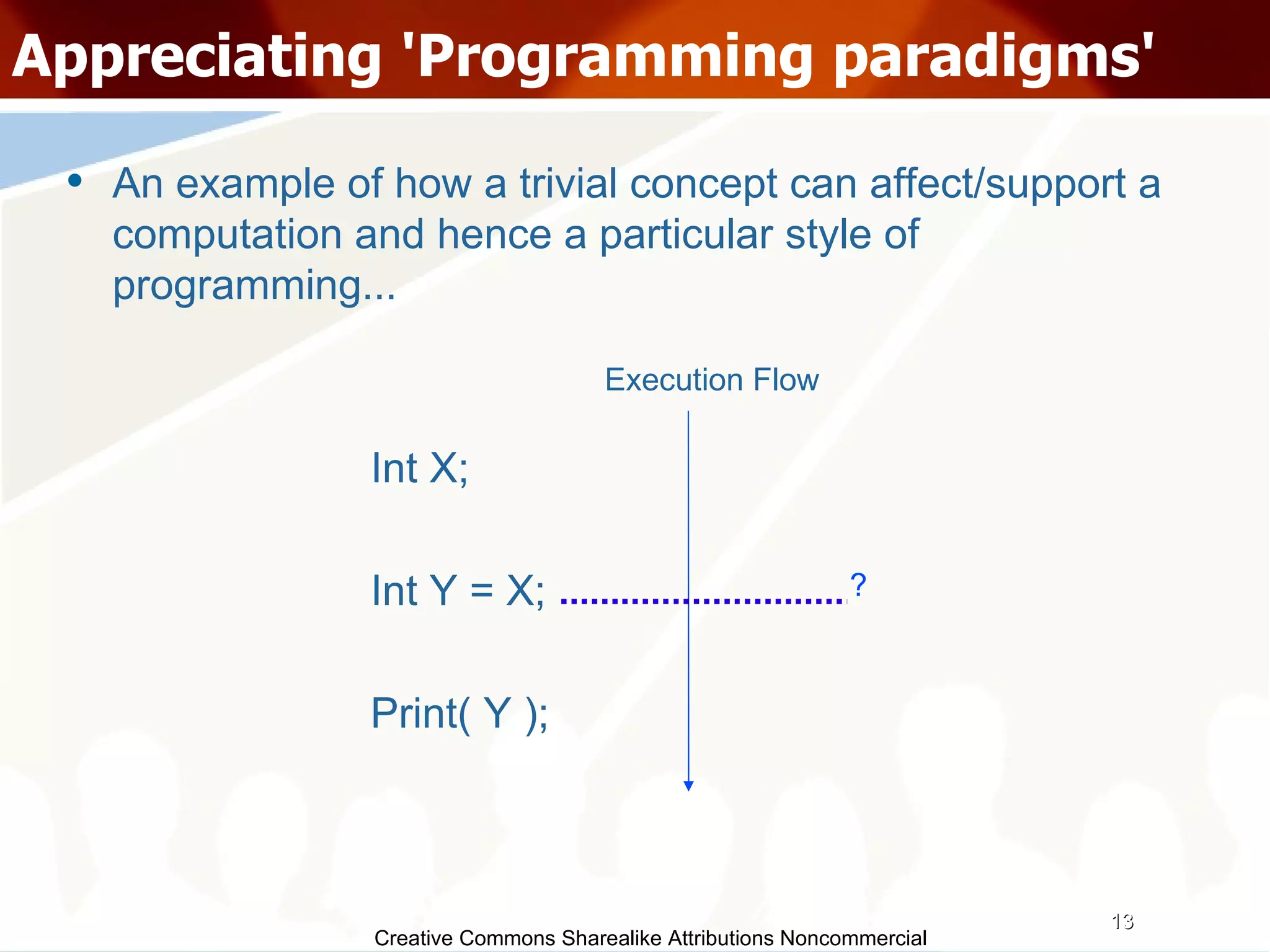
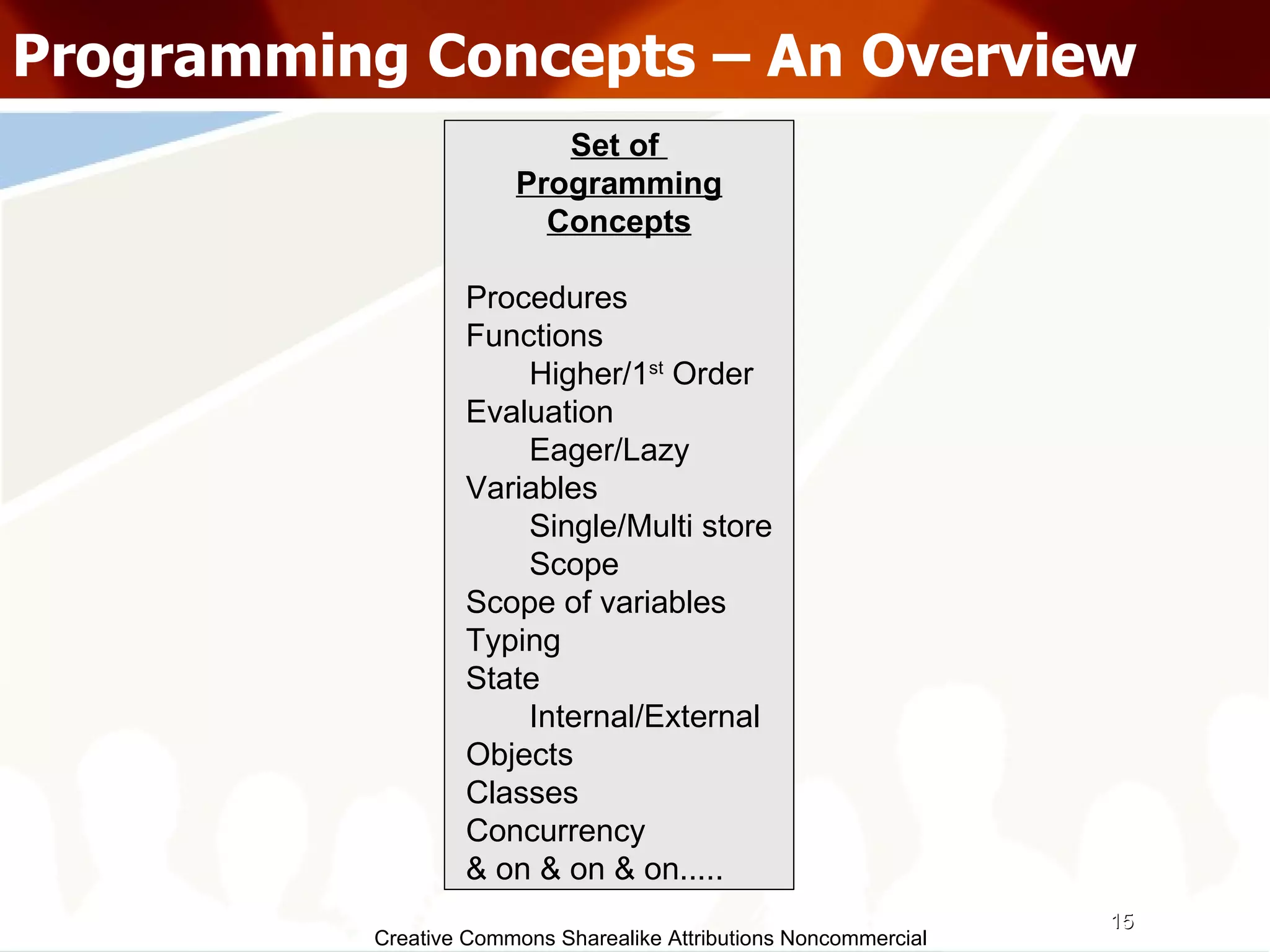
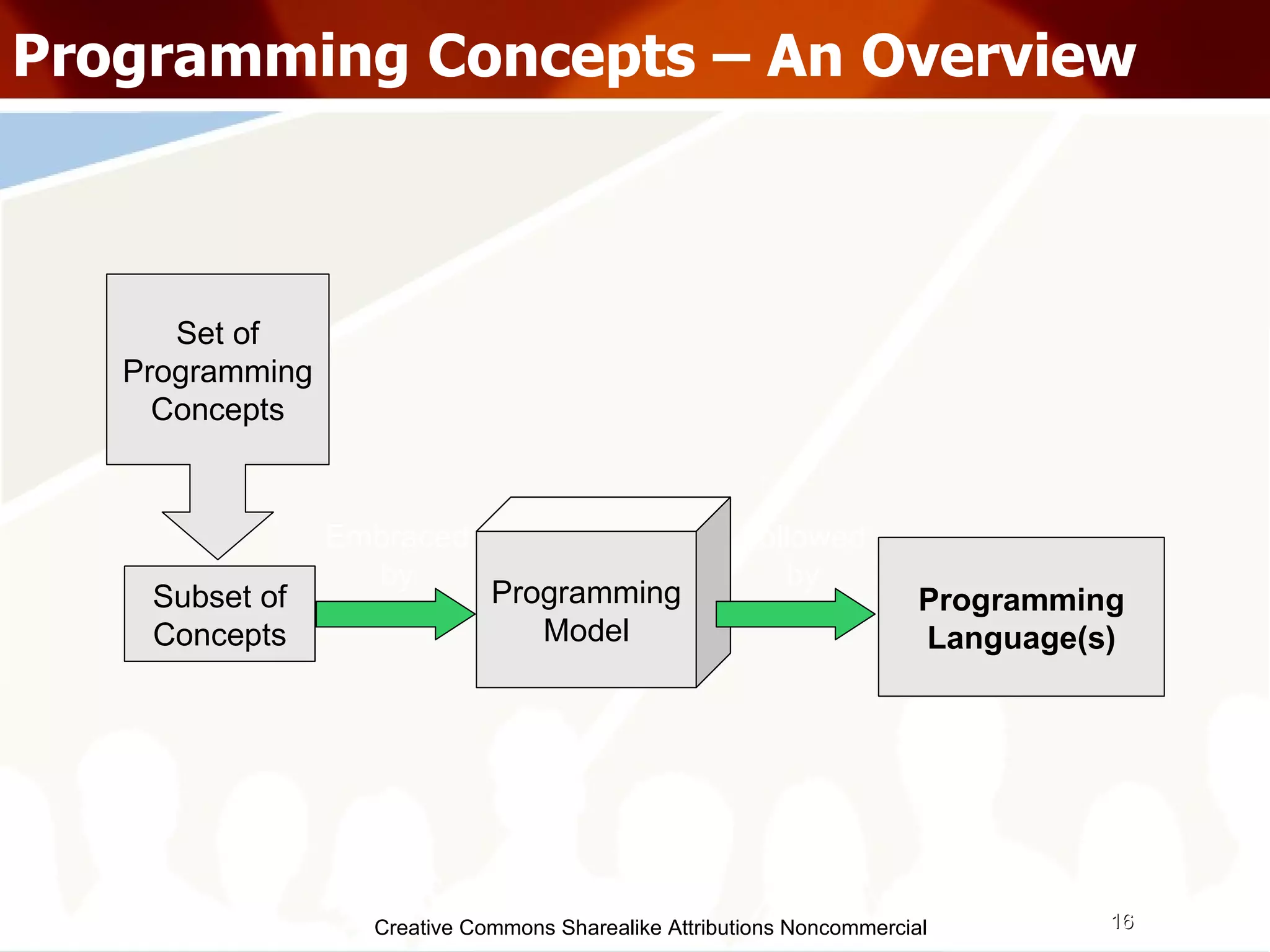
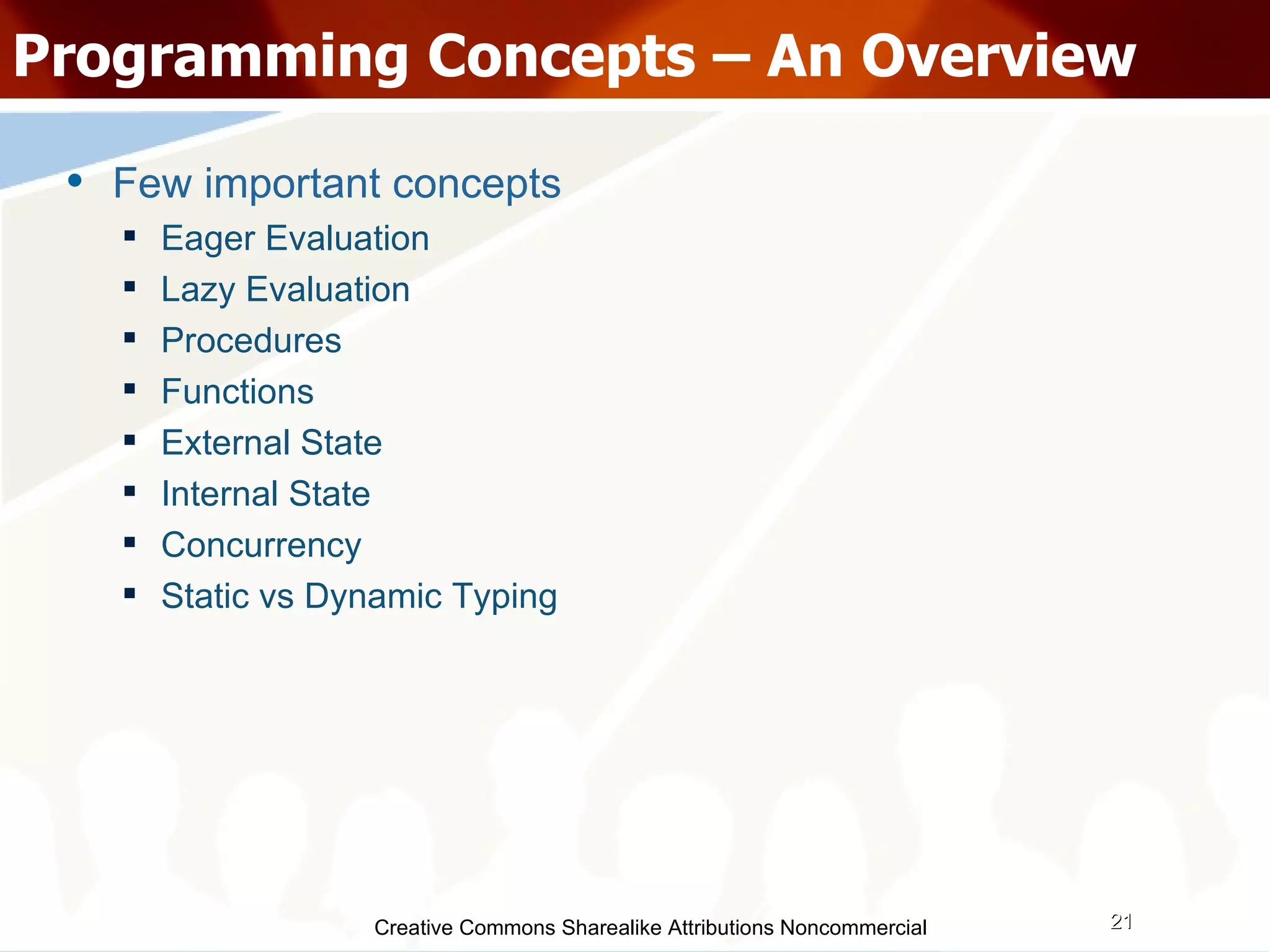
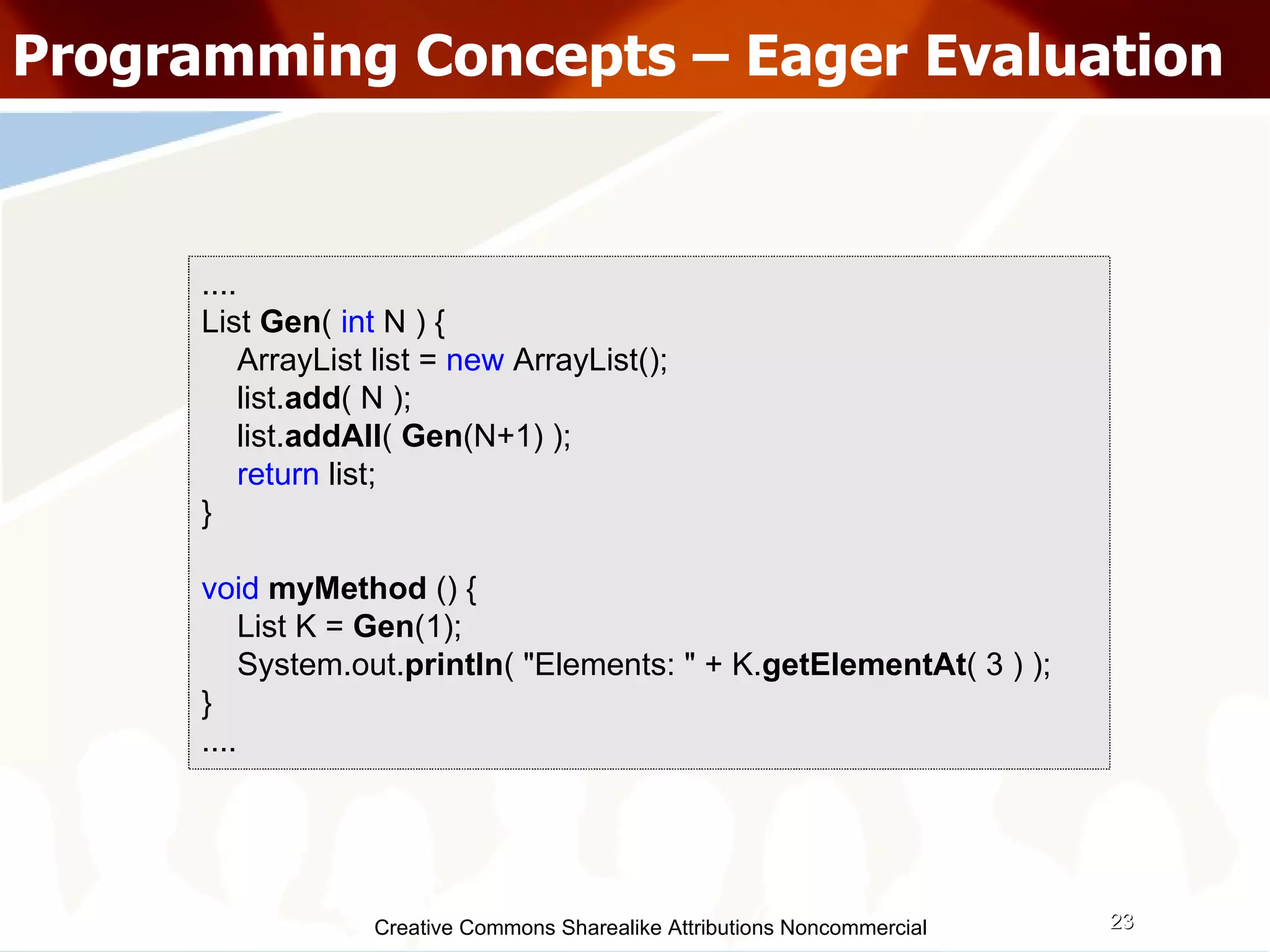
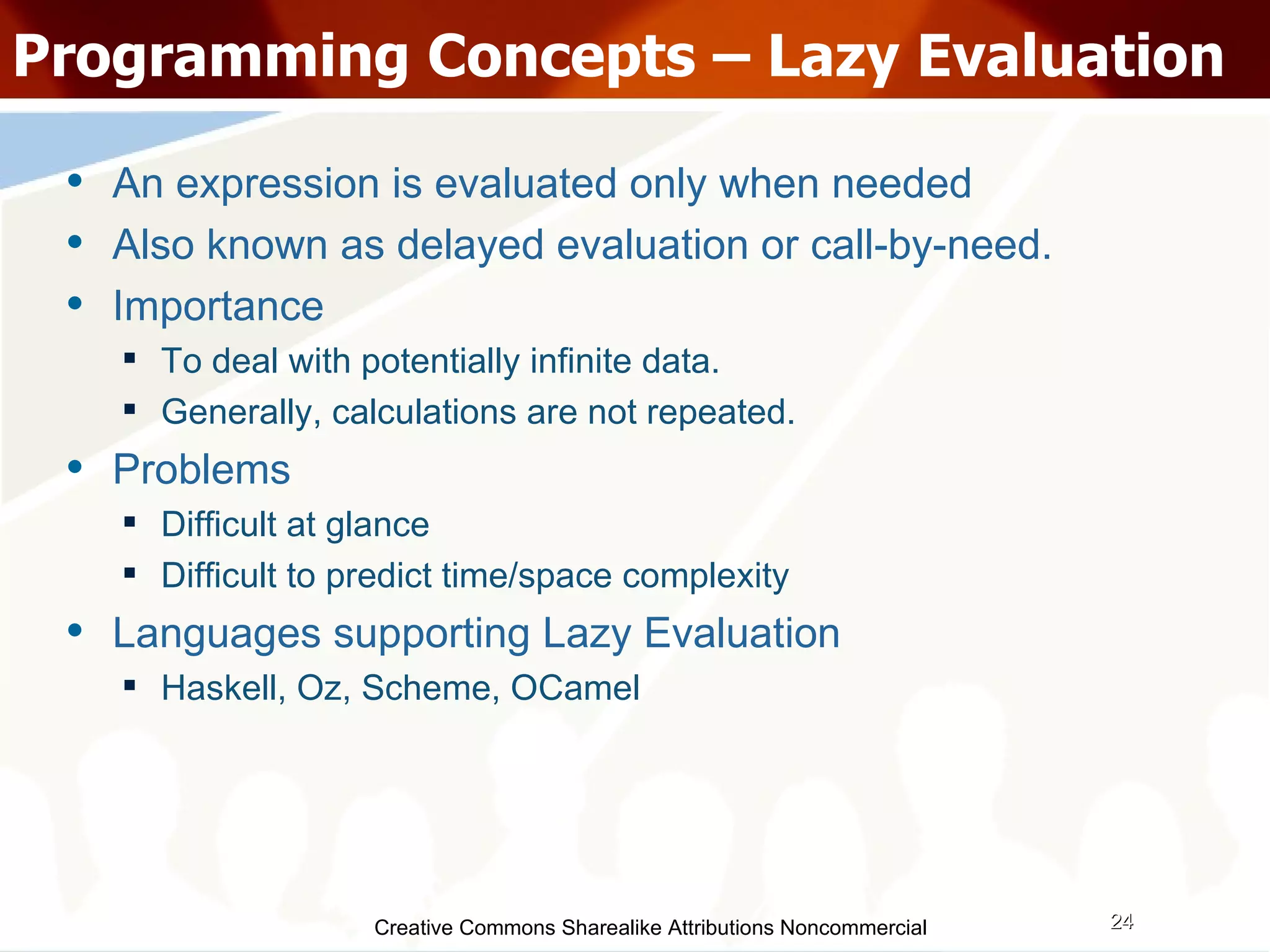
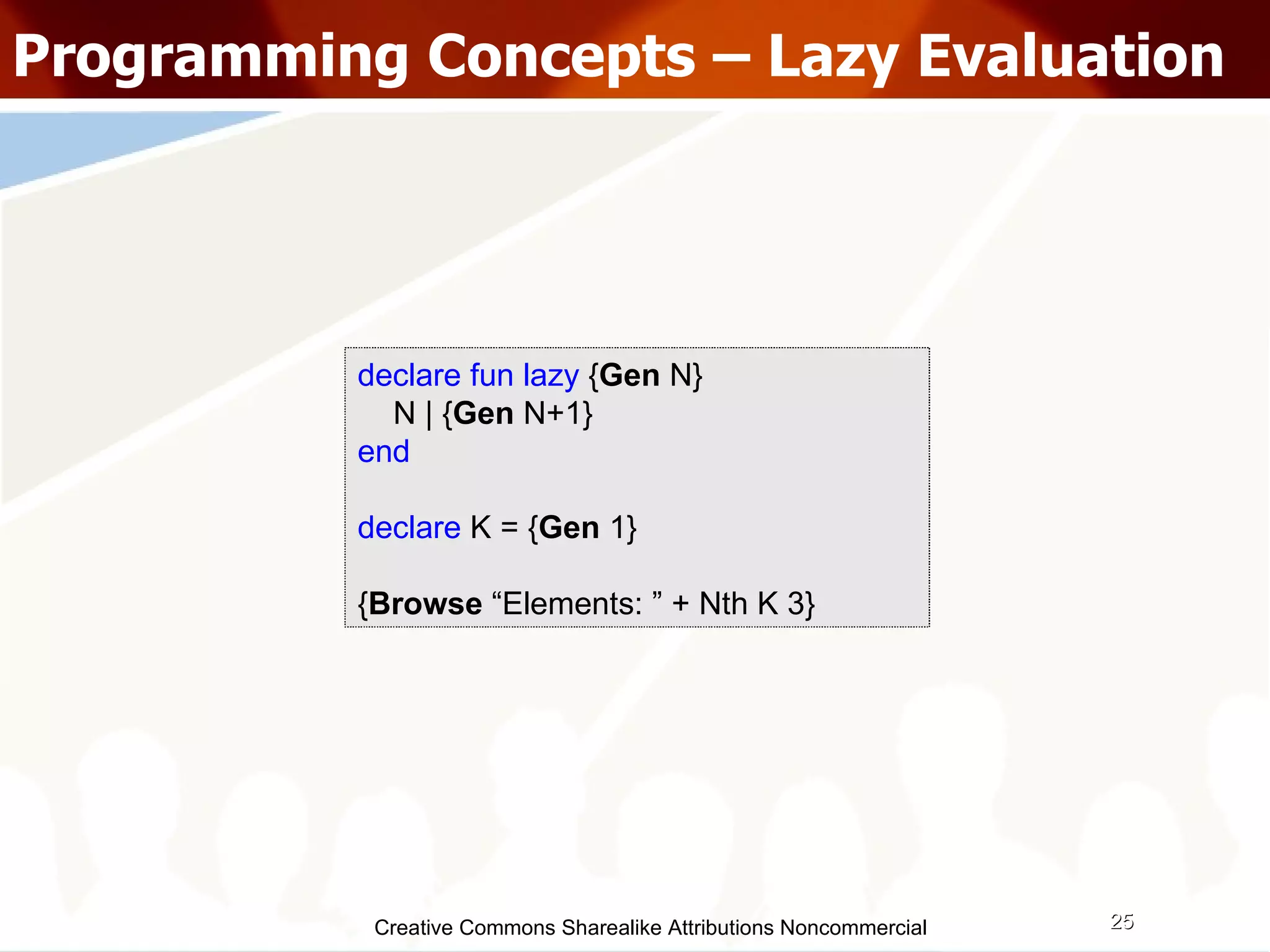
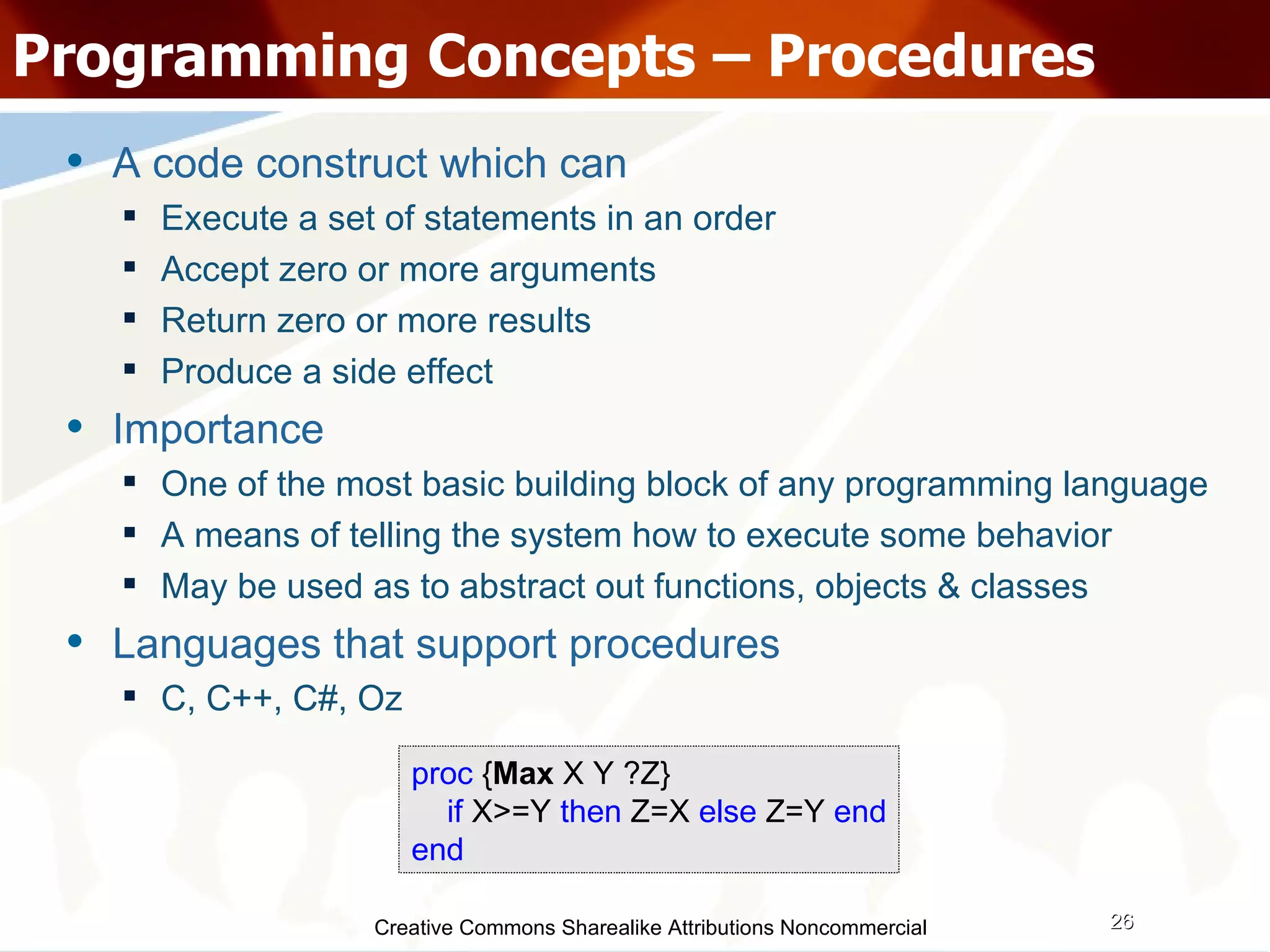
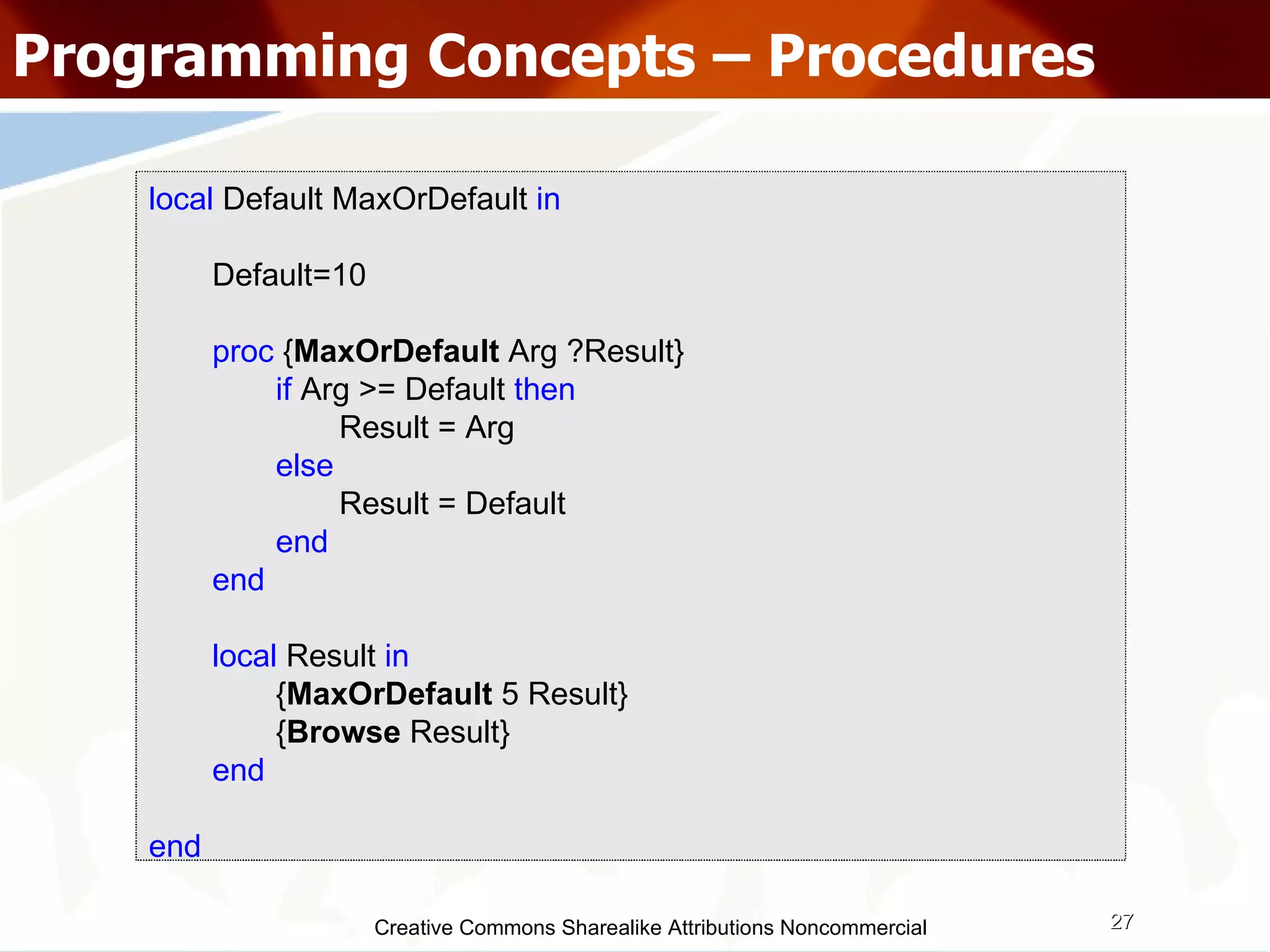
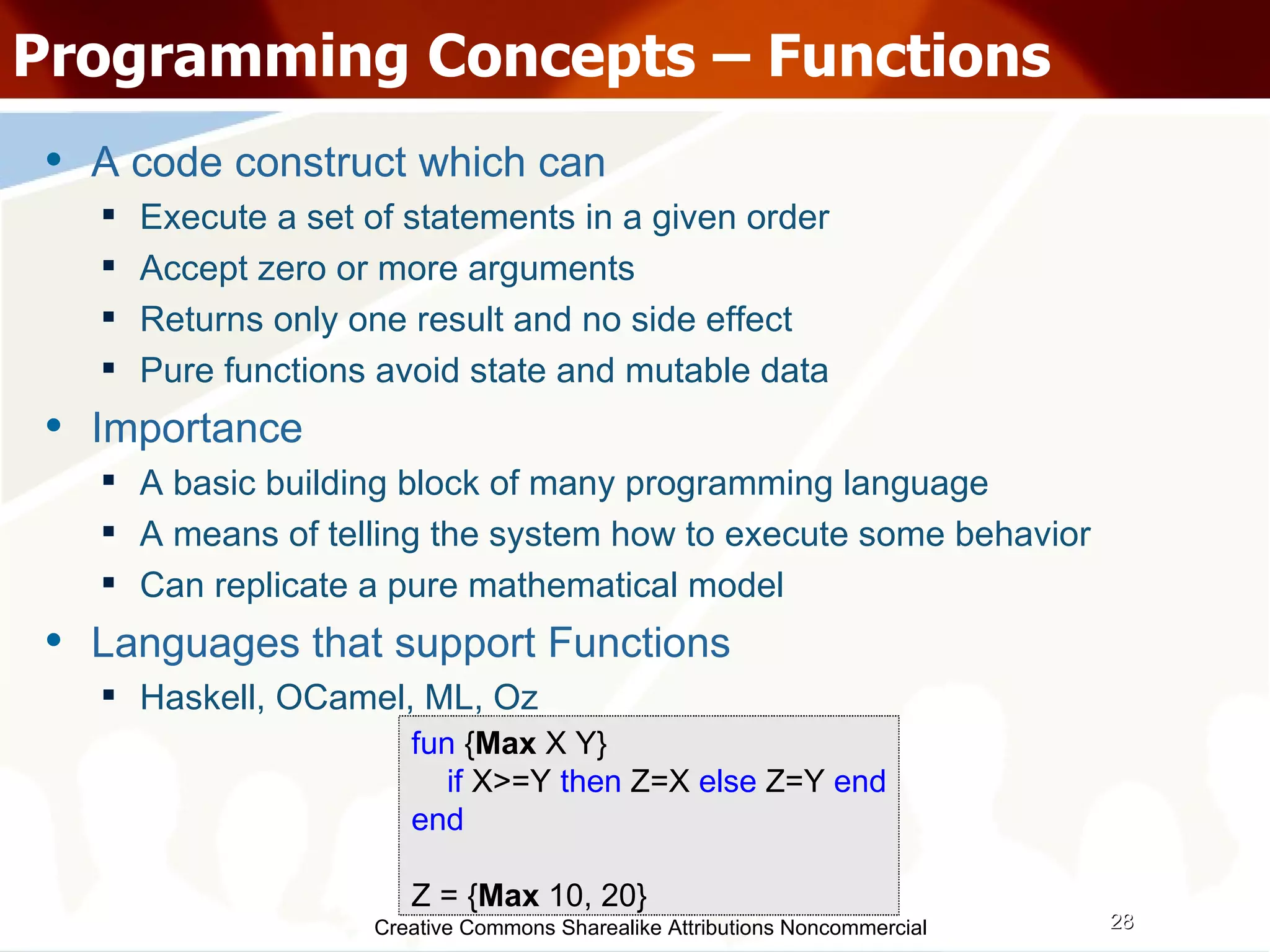
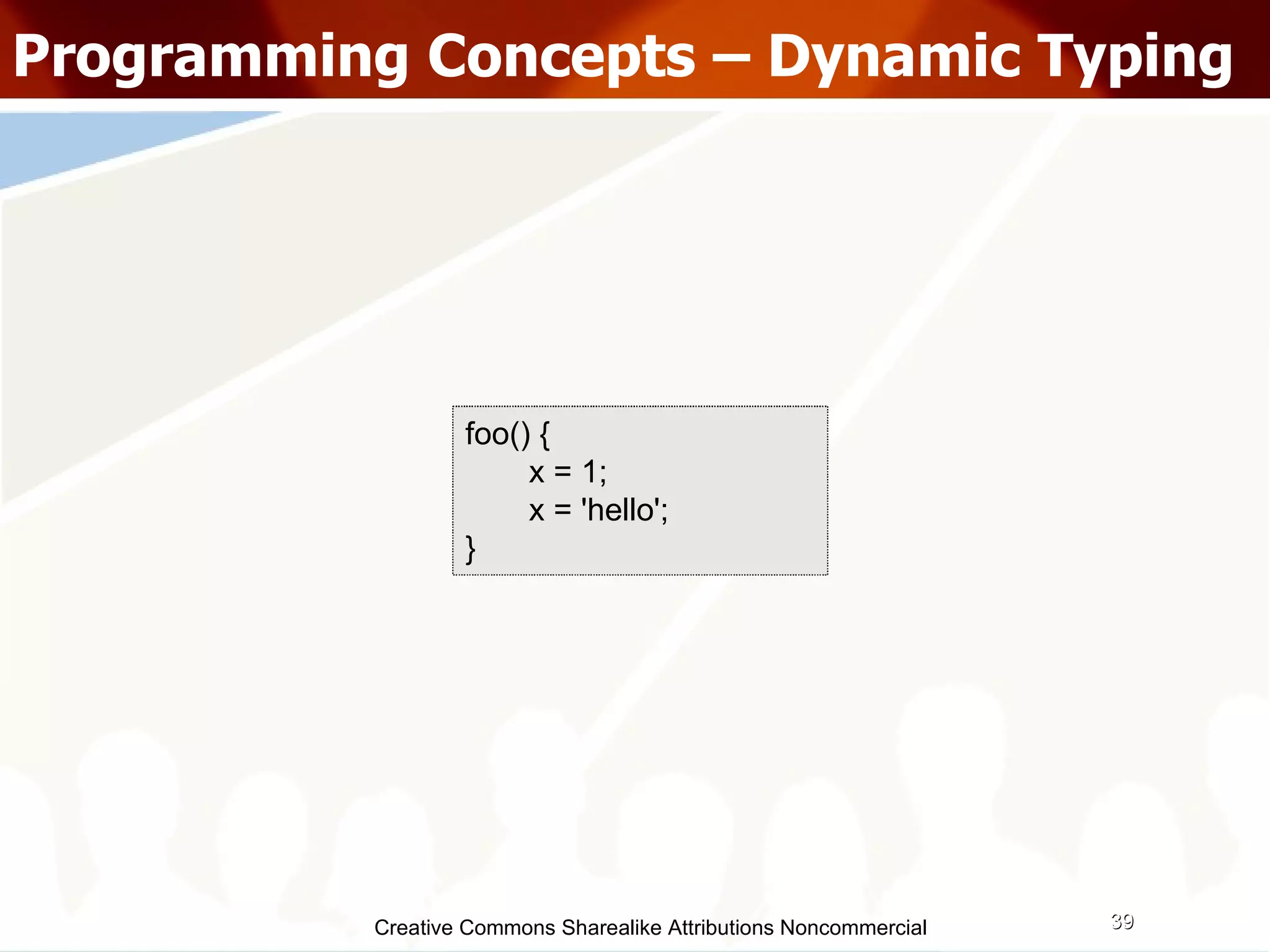
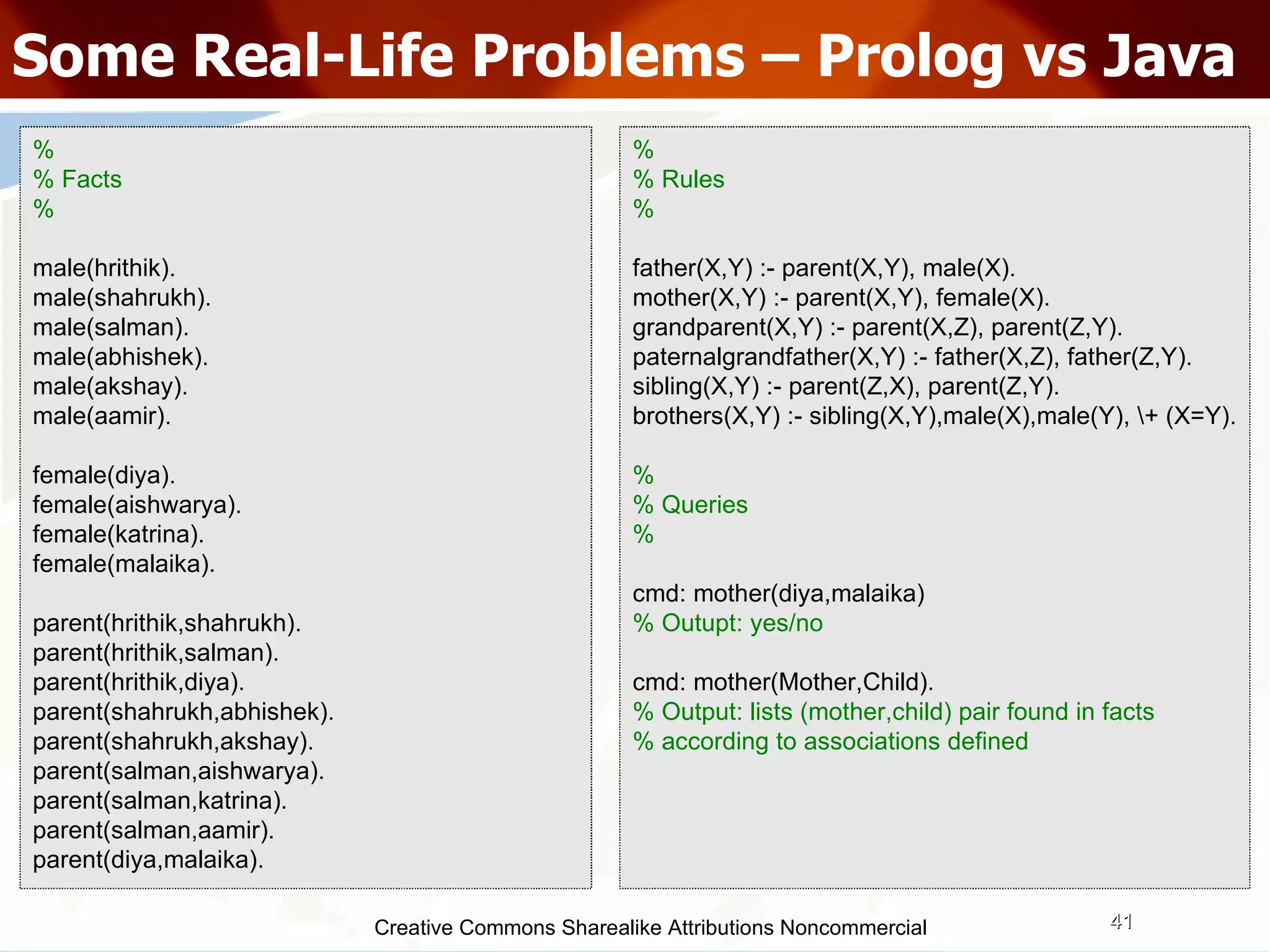
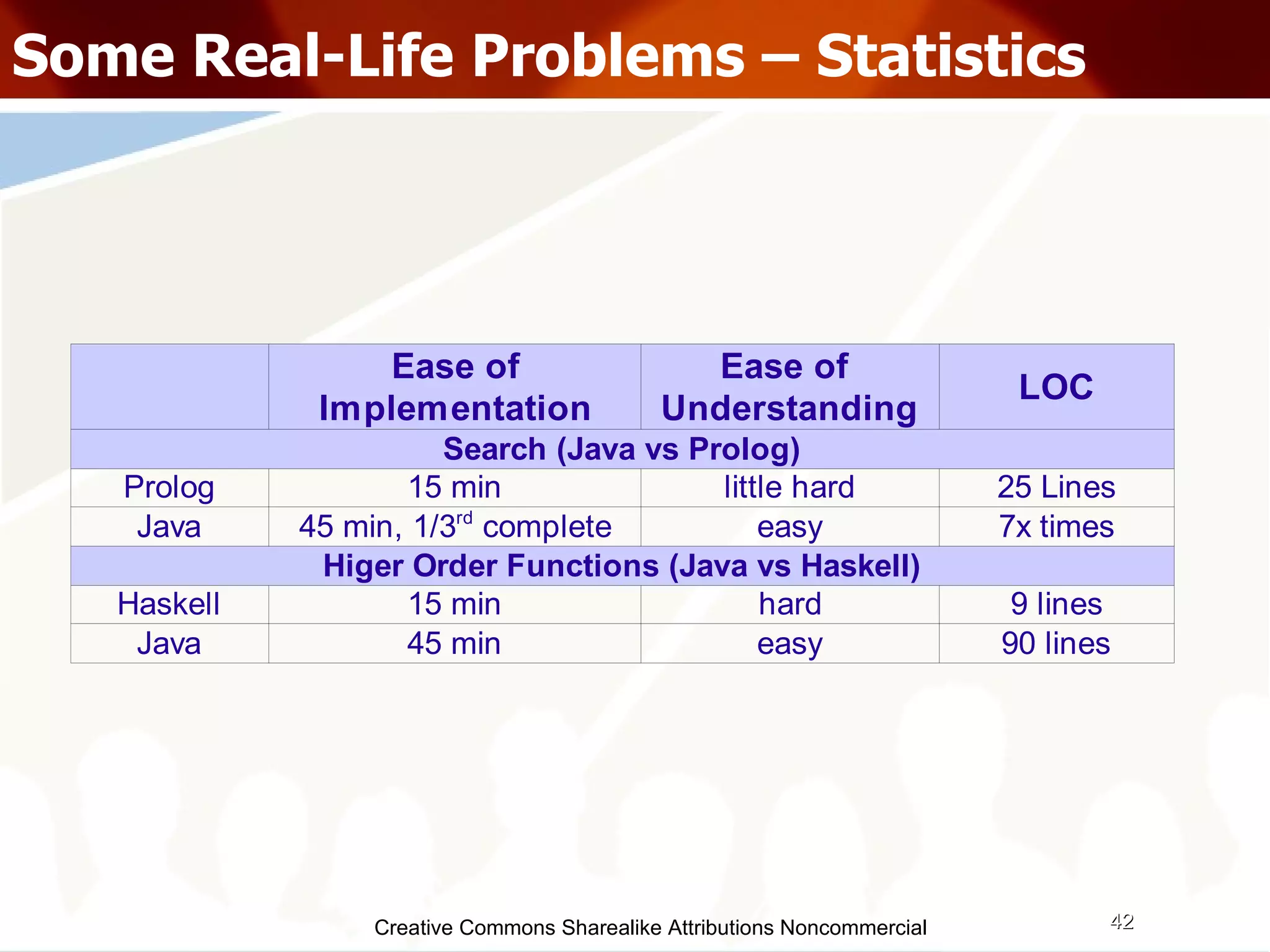
The document serves as an introduction to various programming paradigms, detailing their definitions, importance, and examples, such as functional, object-oriented, and logical programming. It discusses programming concepts including evaluation strategies, procedures, functions, concurrency, and typing models, illustrating how these concepts impact real-world problem-solving. The session encourages exploring different languages and experimentation with paradigms to enhance programming skills.
![Programming Paradigms ( http://www.directi.com | http://wiki.directi.com | http://careers.directi.com ) Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Sharealike Noncommercial By, Janeve George [email_address] & Nilesh Mevada [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-1-2048.jpg)











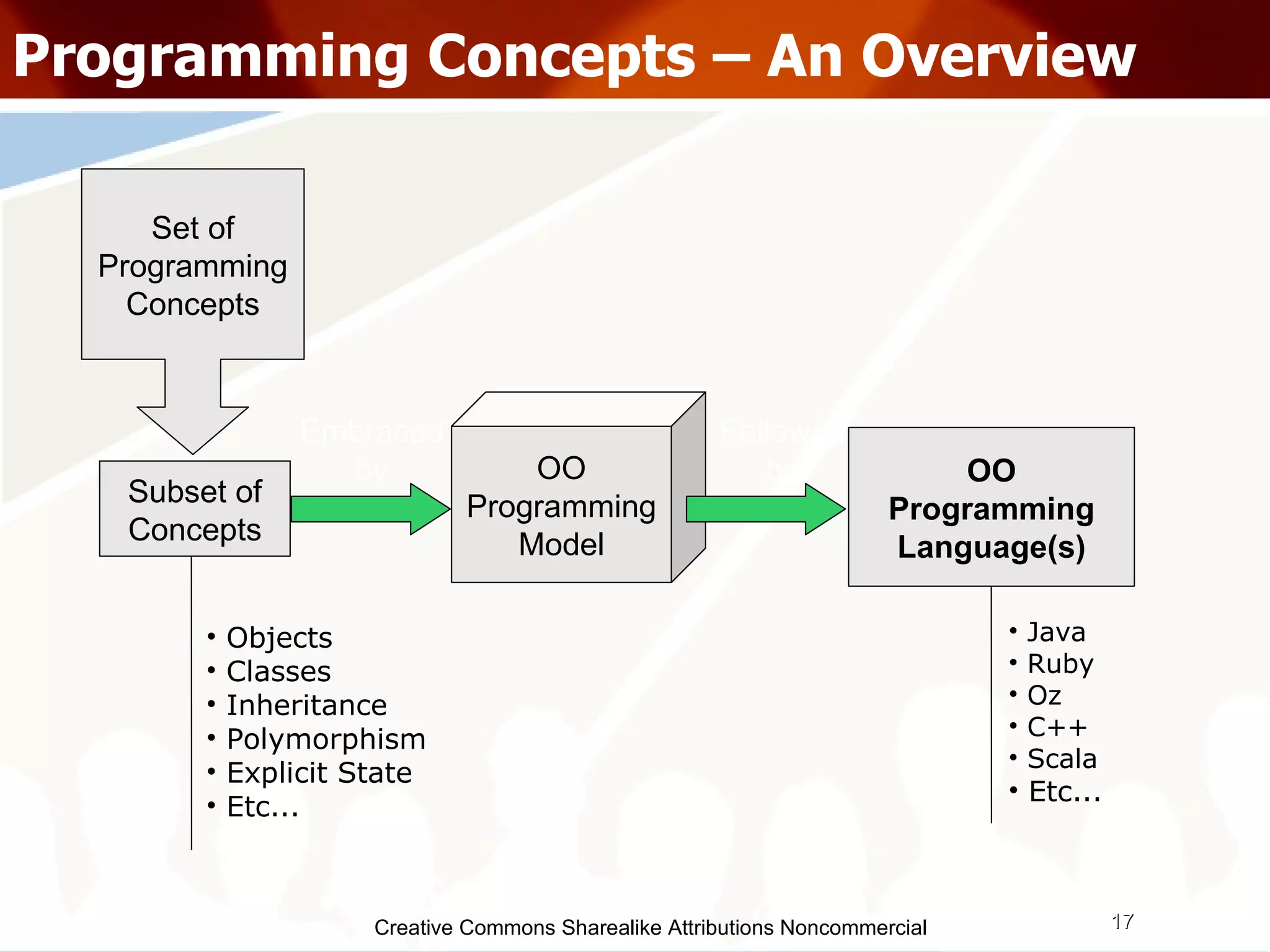
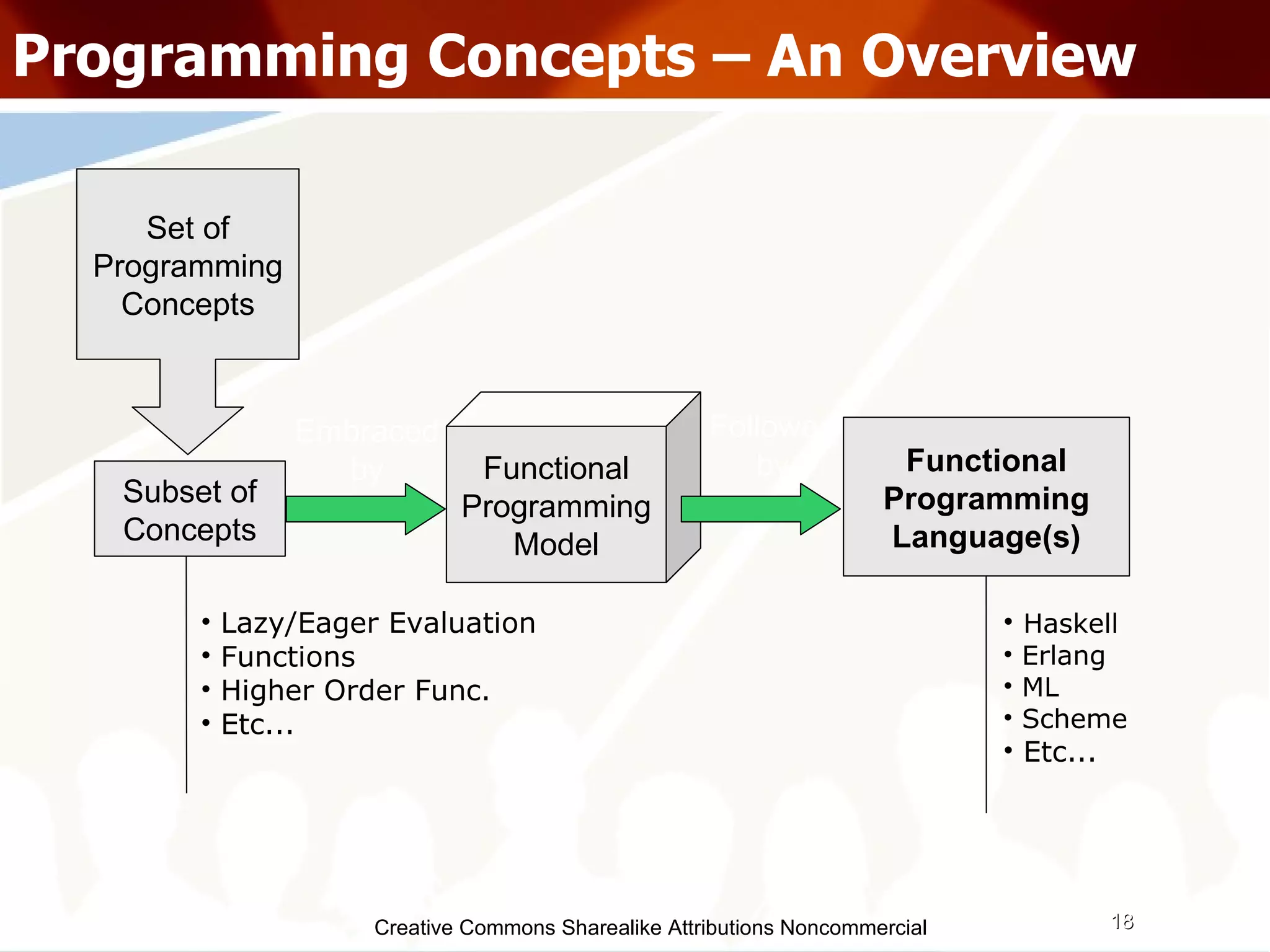
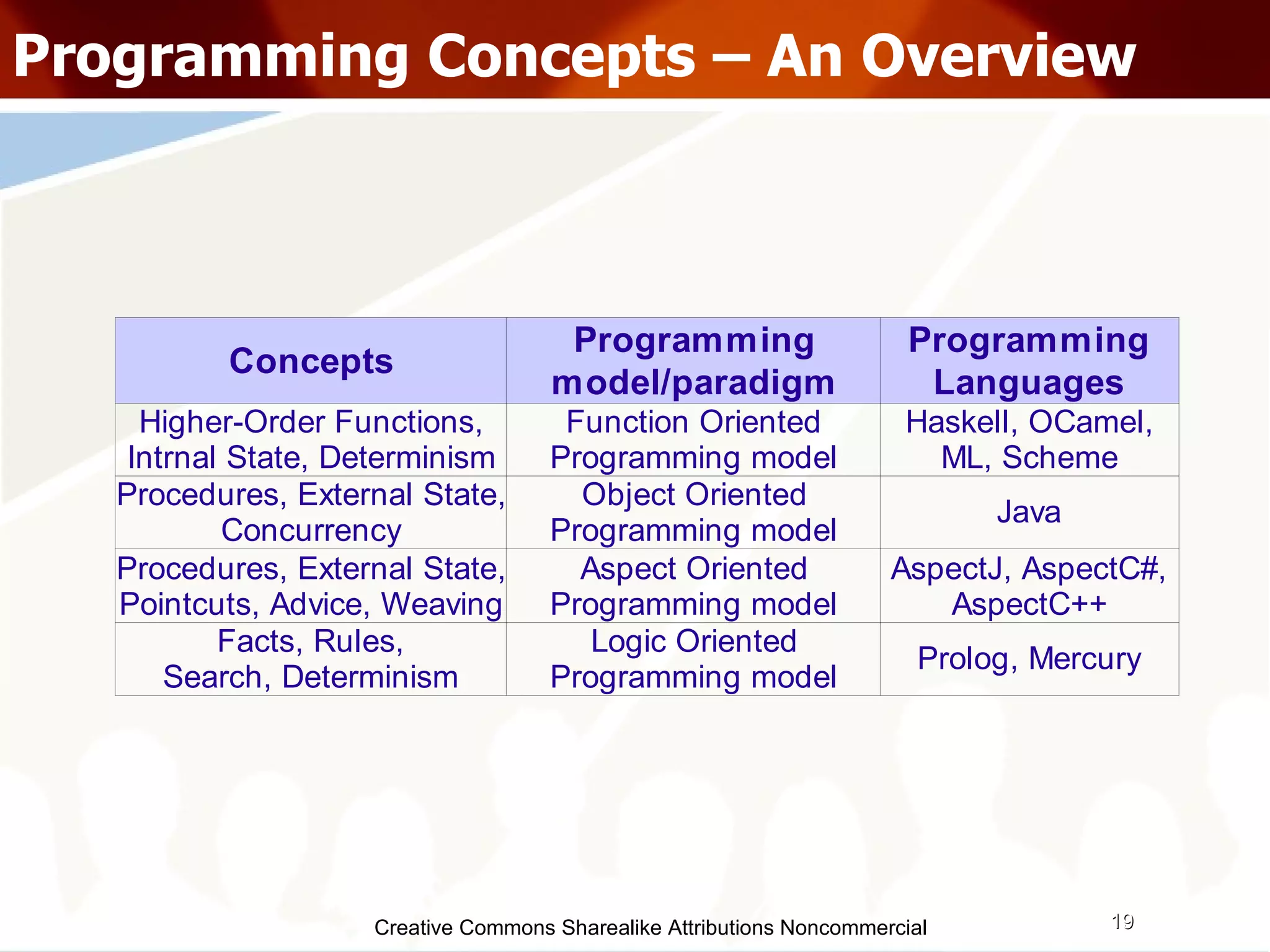
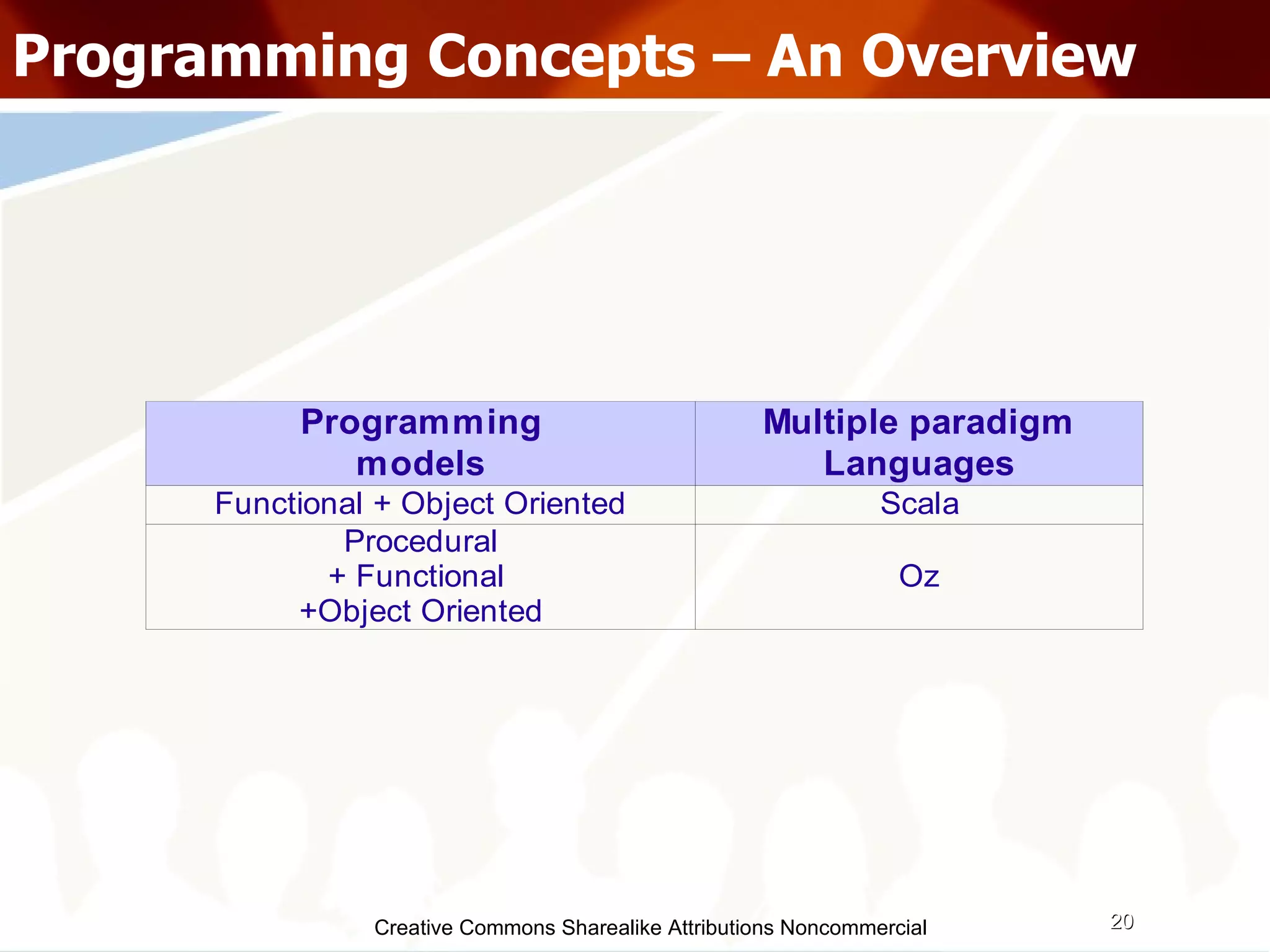

![Creative Commons Sharealike Attributions Noncommercial Programming Concepts – Functions (Higher Order) Higher Order Functions Accepts functions as arguments along with other types Can return a function as result Ordering means... 1st order :- having no functions as args 2nd order :- can have 1st order functions as args nth order :- can have n-1th order functions as args We can build abstraction using Higher Order Functions map f [] = [] map f (x:xs) = f x : map f xs numbers = [ 7,9,13 ] inc x = x + 1 more_numbers = map inc numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-29-2048.jpg)
![Creative Commons Sharealike Attributions Noncommercial Programming Concepts – Functions (Higher Order) listsum [] = 0 listsum (x:xs) = x + listsum xs listprod [] = 1 listprod (x:xs) = x * listprod xs fold op init [] = init fold op init (x:xs) = x `op` fold op init xs listsum = fold (+) 0 listprod = fold (*) 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-30-2048.jpg)

![Creative Commons Sharealike Attributions Noncommercial Programming Concepts – External and Internal State fun { Sum Numbers} Result = { NewCell 0} Input = { NewCell Numbers} proc { Sum } case @Input of nil then skip [] X | Y then Result := @Result + X Input := Y { Sum } end end in { Sum } @Result end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-32-2048.jpg)
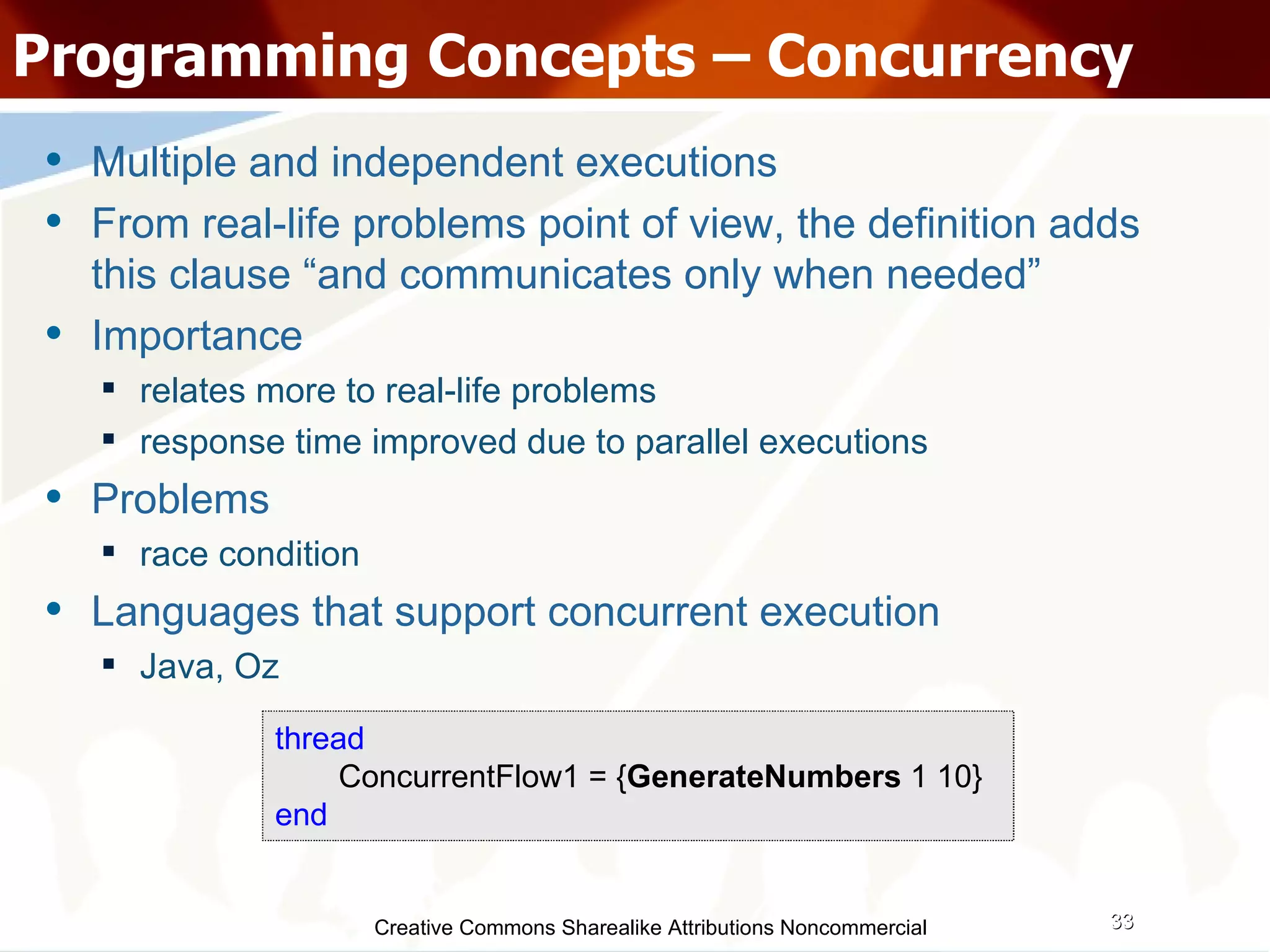
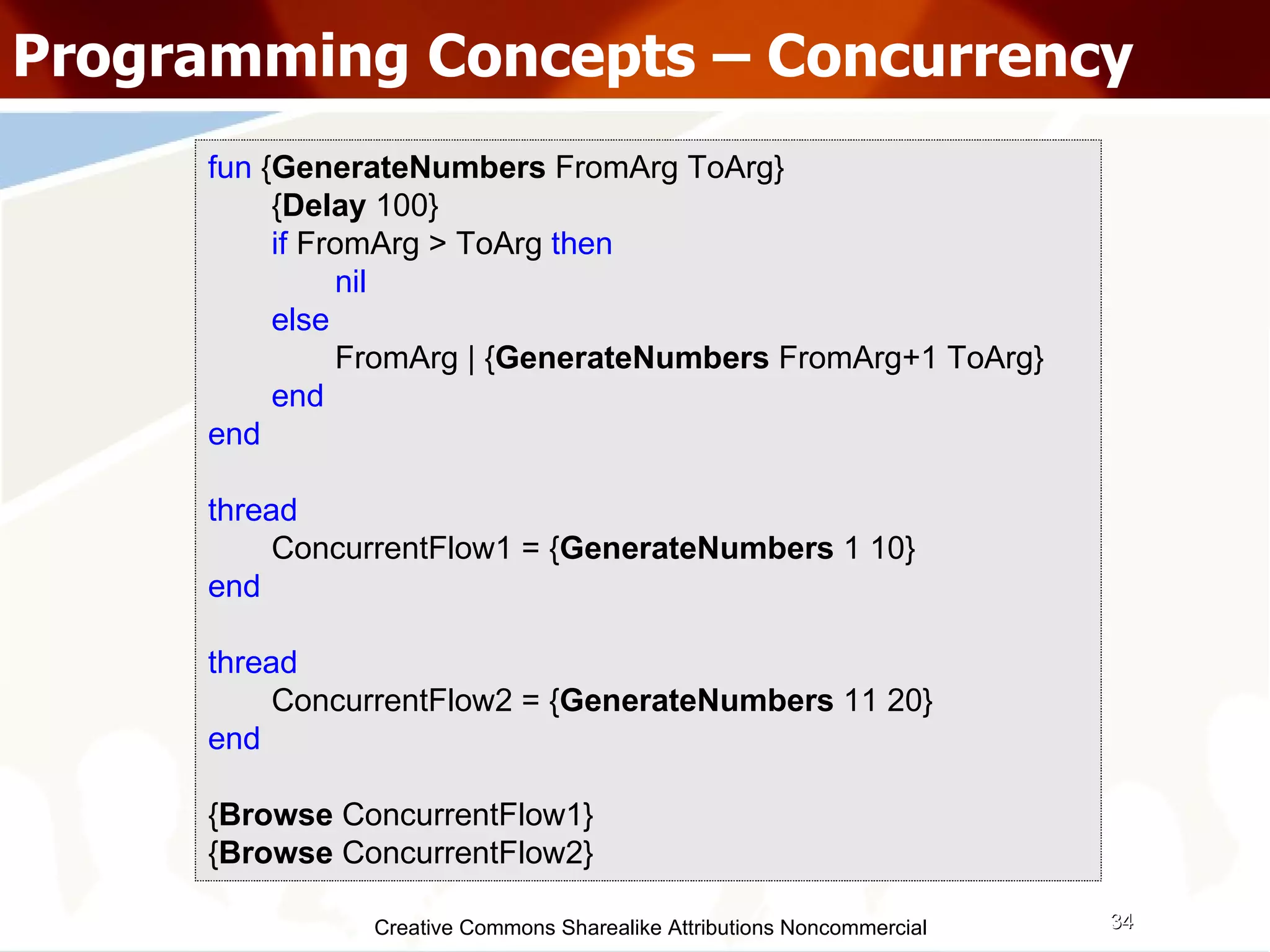
![Creative Commons Sharealike Attributions Noncommercial Programming Concepts – Concurrency .... public void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Temp temp = new Temp(); createAConcurrentFlow(1, 10); createAConcurrentFlow(11, 20); } .... private void createAConcurrentFlow( int FromArg, int ToArg) { new Runnable() { public void run() { try { new Temp().GenerateNumbers(FromArg, ToArg); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }; } ....](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-35-2048.jpg)
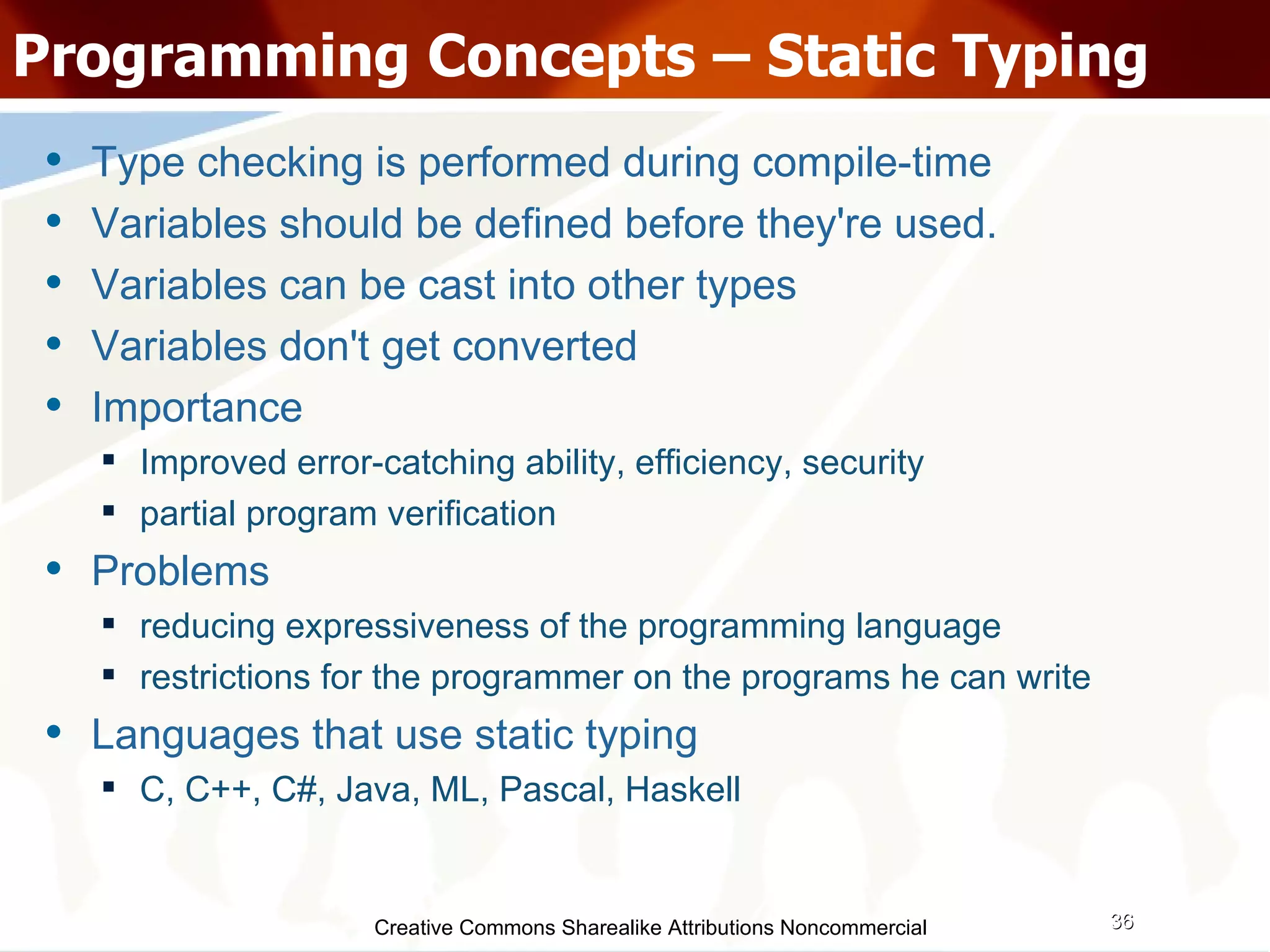
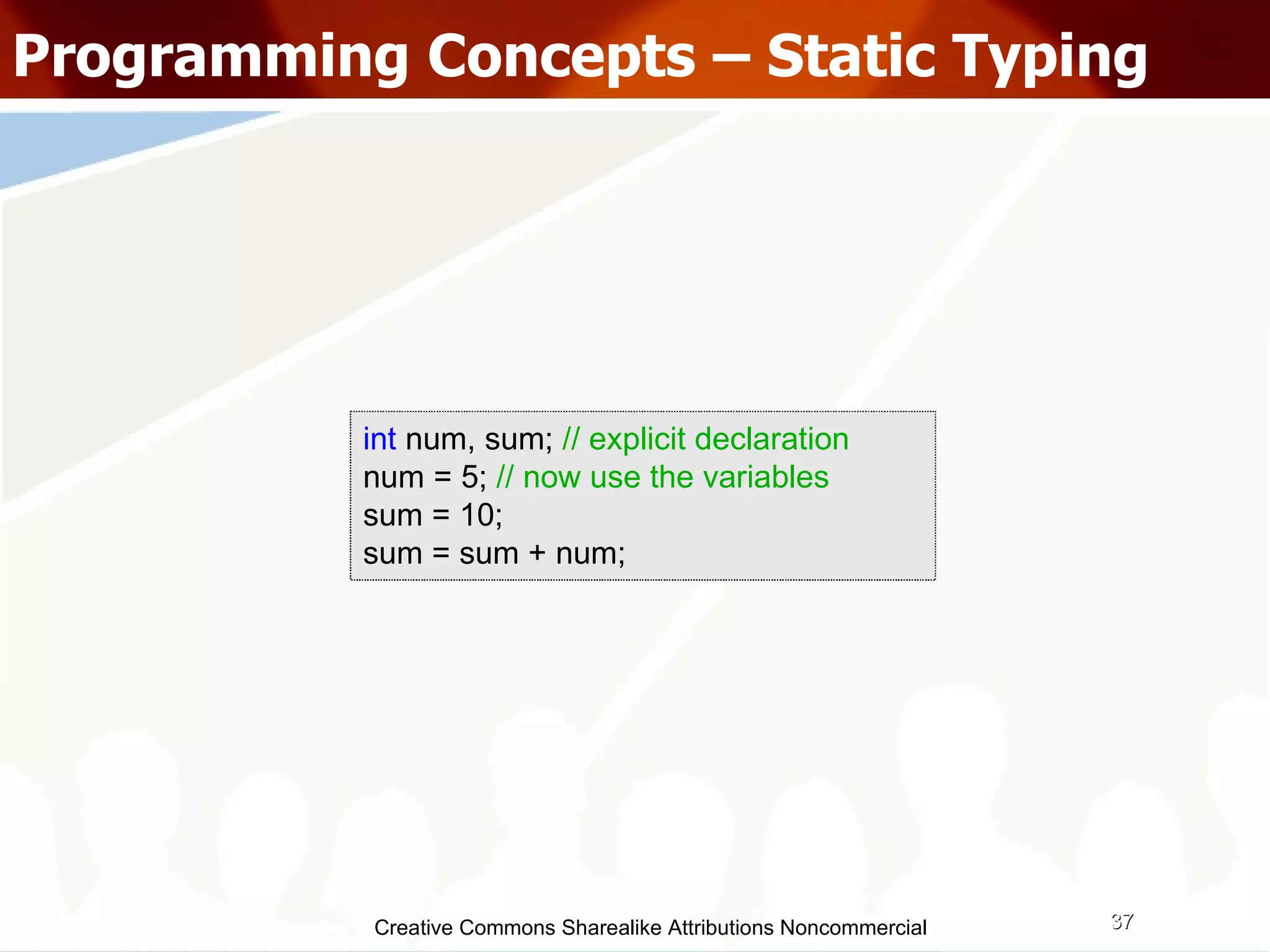
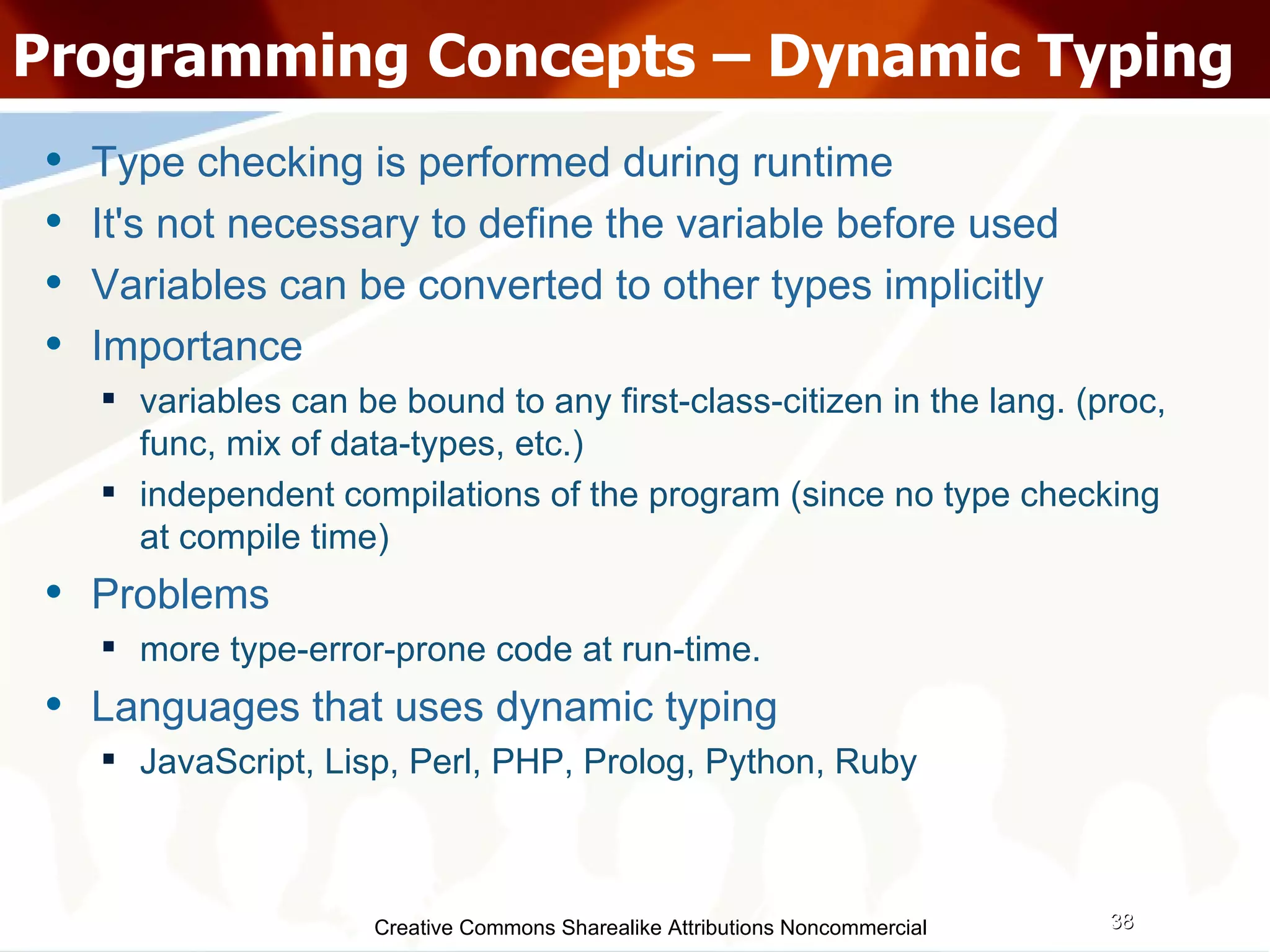




![Questions??? [email_address] & [email_address] http://directi.com http://careers.directi.com Download slides: http://wiki.directi.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-46-2048.jpg)
![Retrospective!!! [email_address] & [email_address] http://directi.com http://careers.directi.com Download slides: http://wiki.directi.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programmingparadigmsiitfest-1233069847346290-1/75/Programming-Paradigms-47-2048.jpg)