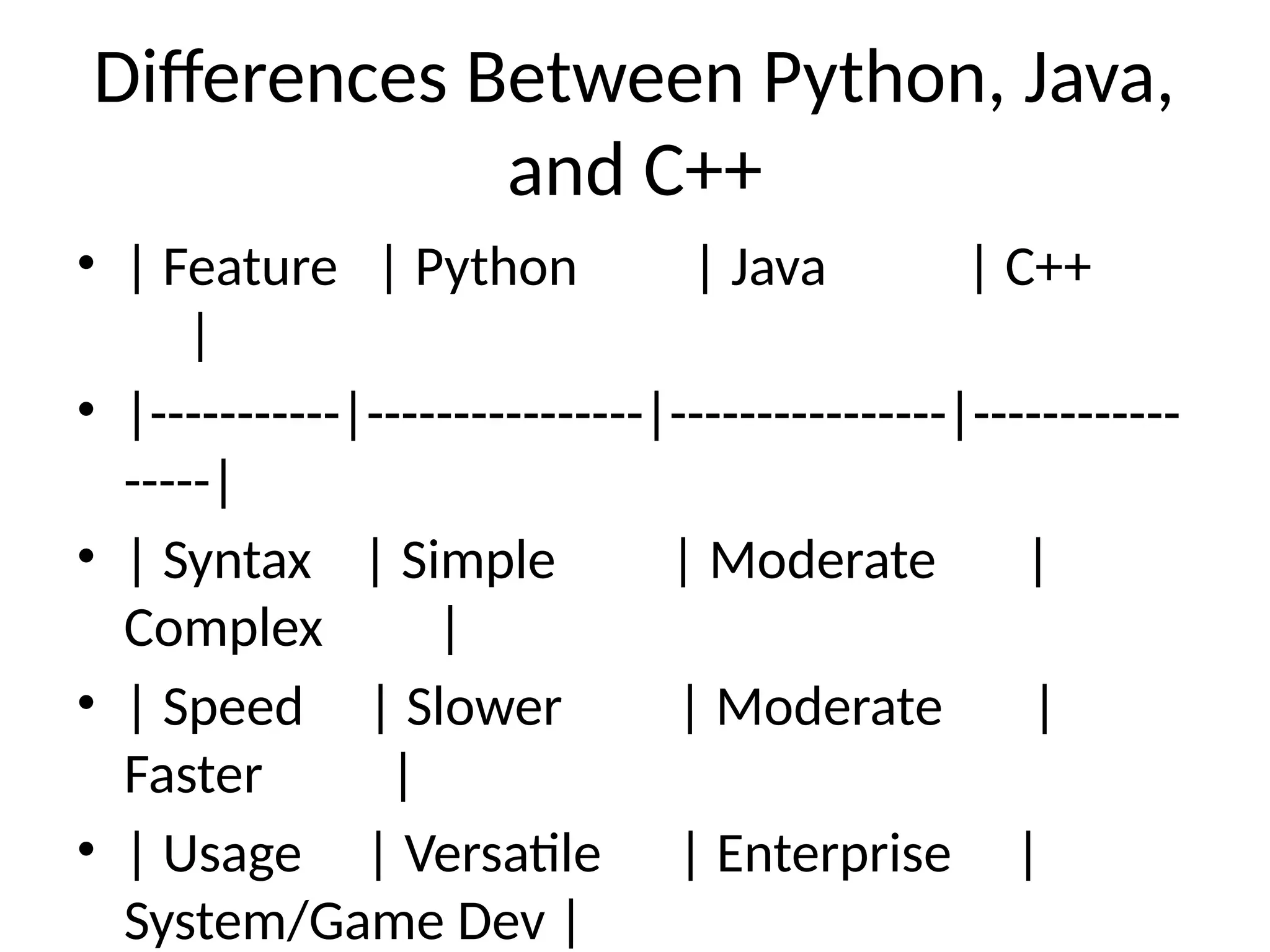
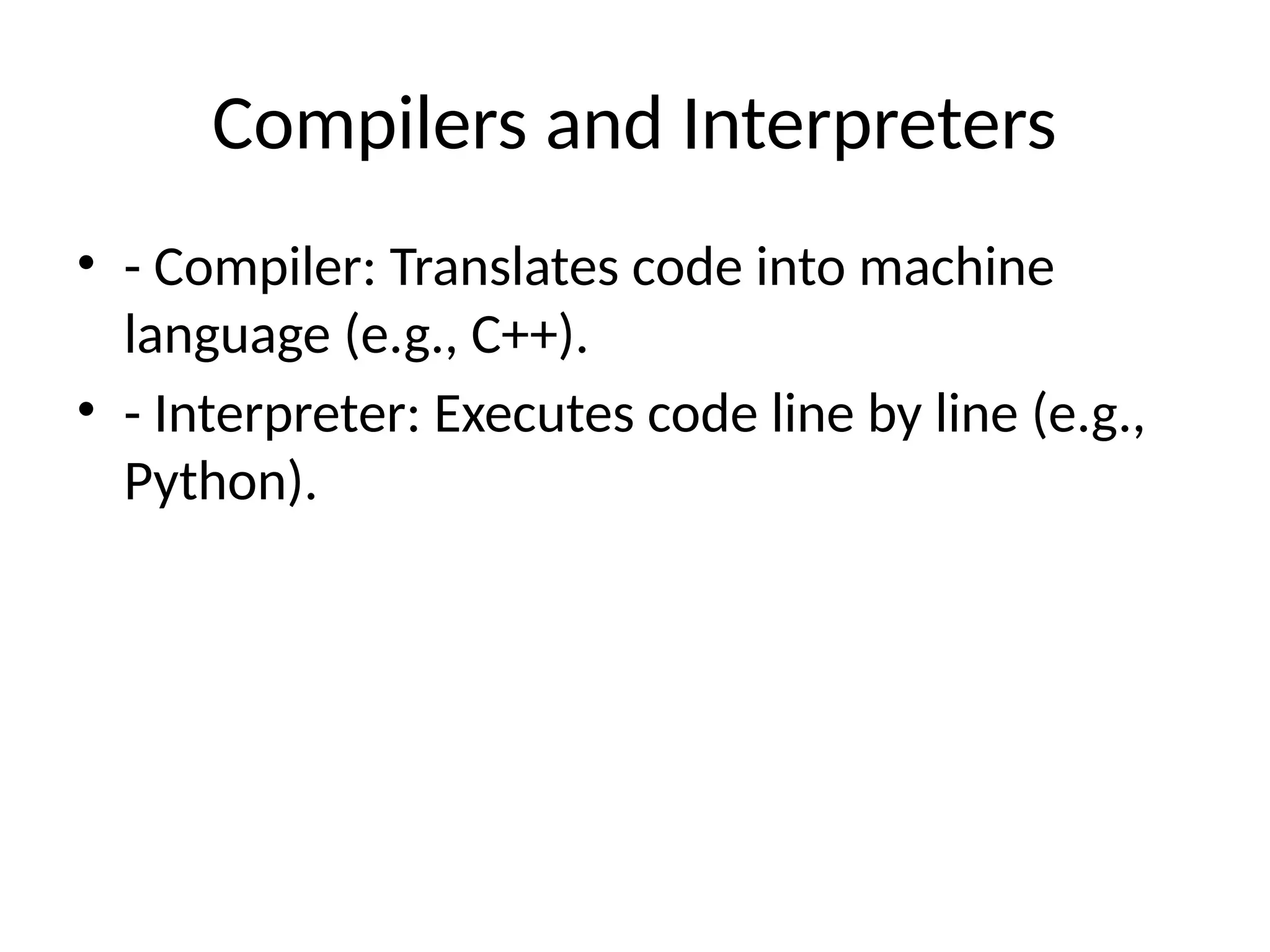
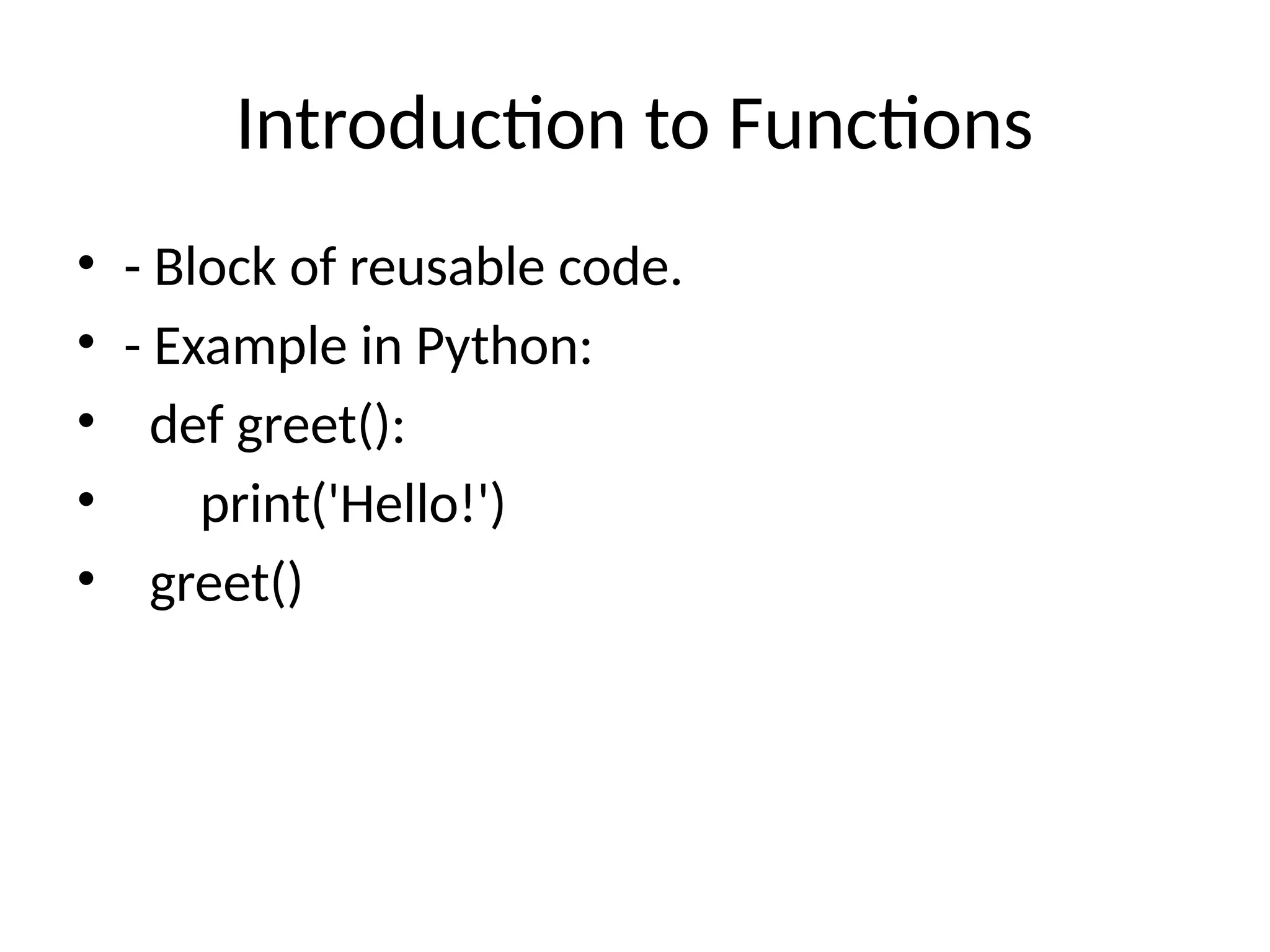
The document provides an overview of programming languages, defining them as a set of instructions for computers, and categorizing them into low-level and high-level types. It highlights several popular languages, including Python, Java, and C++, along with their key features, use cases, and differences. Additionally, it discusses concepts like syntax, compilers vs interpreters, and the significance of learning programming for problem-solving and career opportunities.
![Introduction to Programming
Languages
Group Members:
- Abdillahi Mohamed Abdillahi
(Registration No: 16527)
- [Other Group Members]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programminglanguagespresentation-241224093809-da60bf36/75/Programming_Languages_Presentation-pptx-1-2048.jpg)