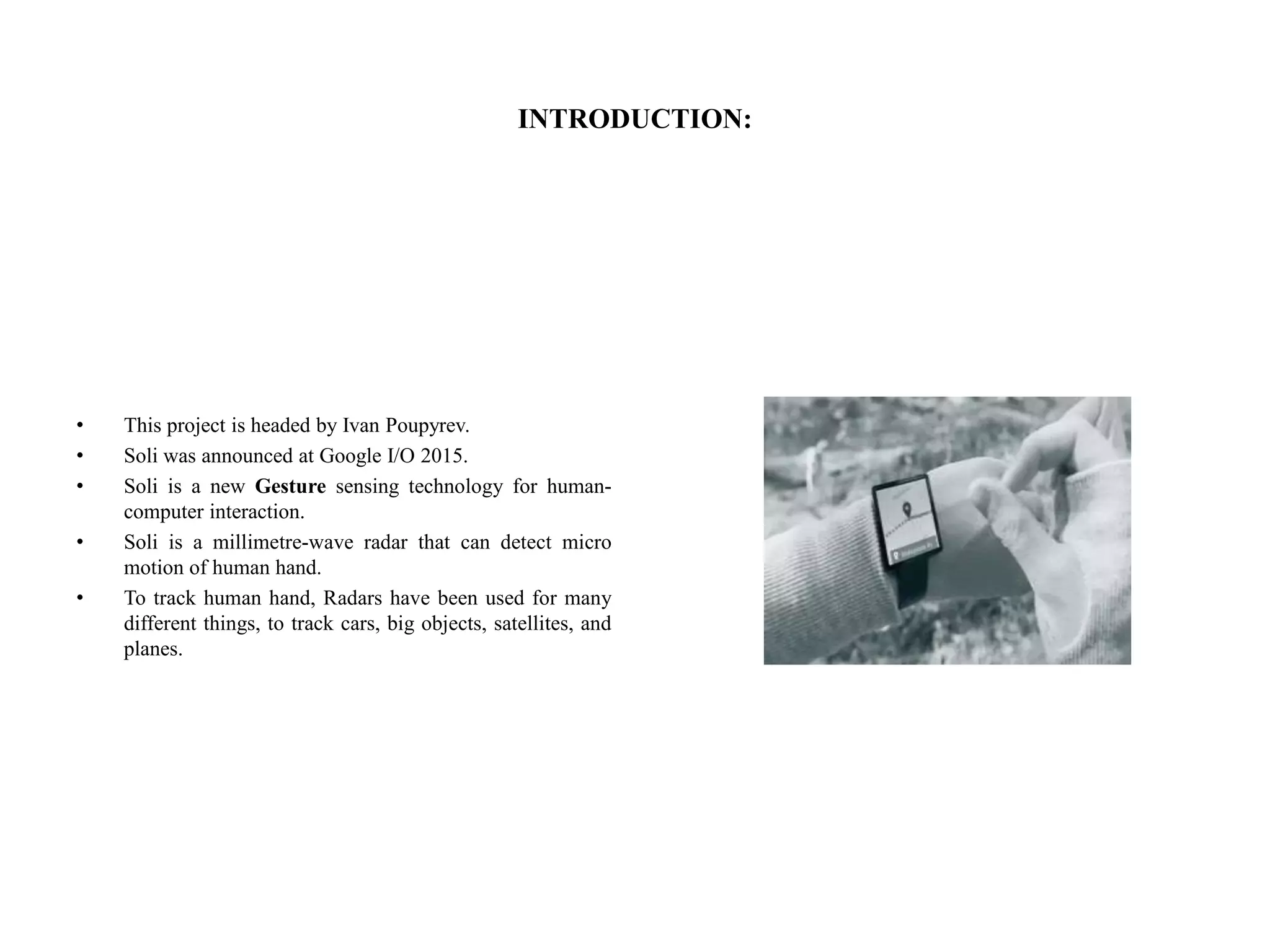
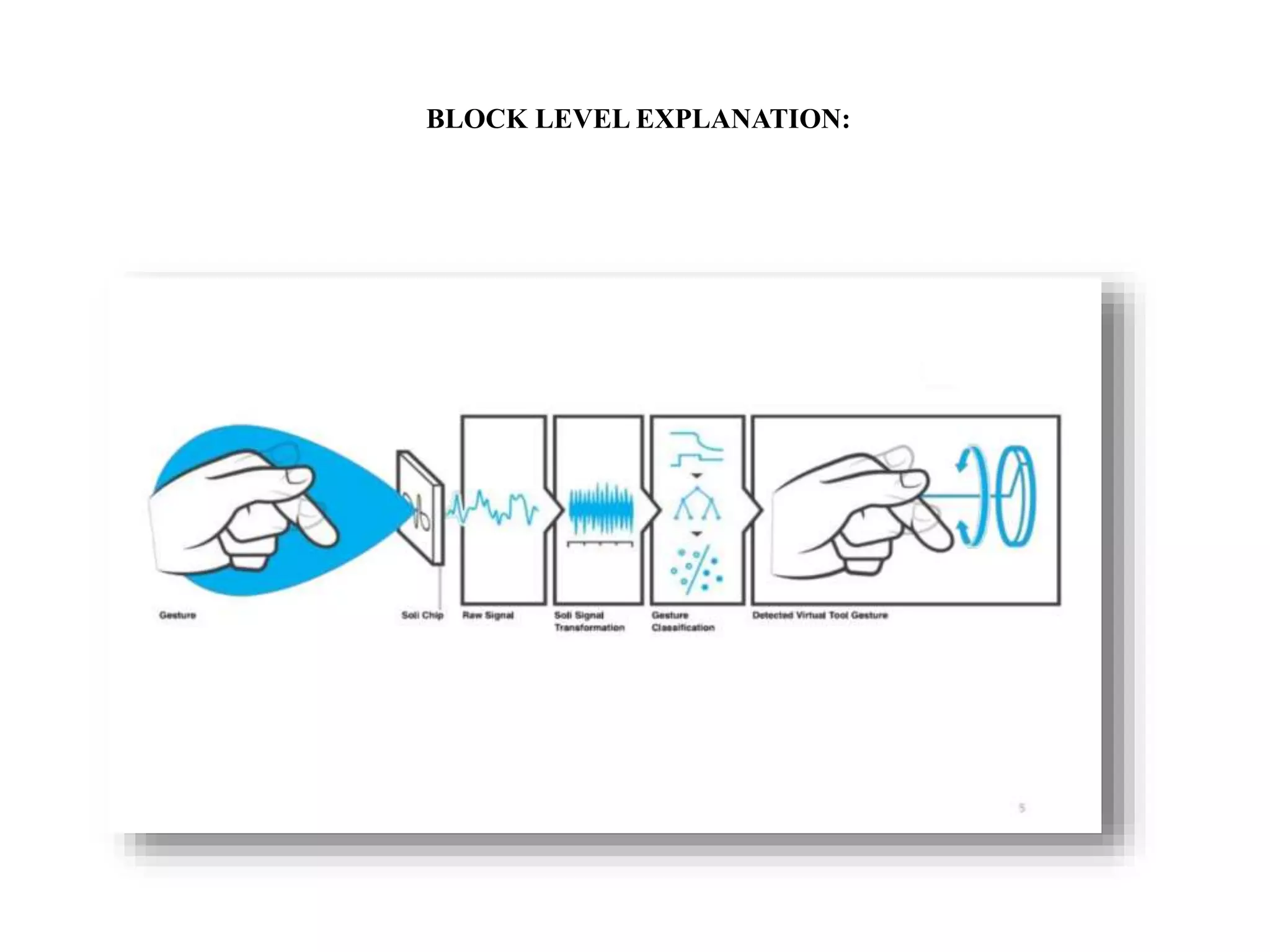
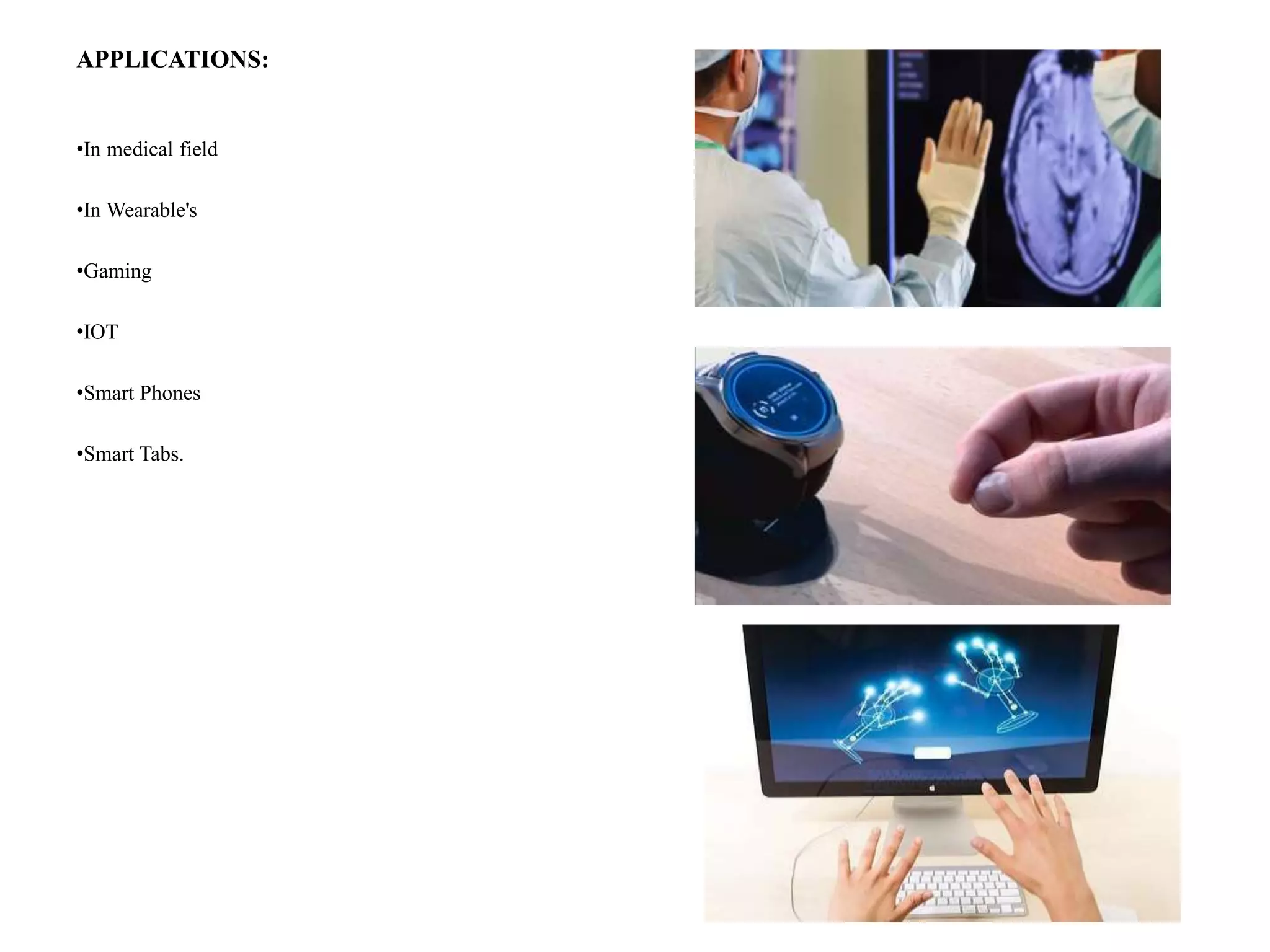
Project Soli, developed by Google's ATAP team, utilizes advanced radar technology to enable touchless human-computer interactions through gesture recognition. While it offers high-accuracy motion tracking and the potential for applications in fields like healthcare and gaming, challenges include limited radar range, predefined gestures, and high costs. The system captures micro-movements at rapid speeds, but currently lacks intuitive control for device inputs.



![LITERATURE SURVEY:
• Erol, A., G. Bebis, M. Nicolescu, R. D. Boyle, and X. Twombly. Vision-based hand pose estimation: A review. Comput.
Vision Image Understanding 108, 1-2 (Oct. 2007), 52–73.
A number of camera based solutions exist, with early work focusing on 2D RGB cameras.
• Kim, D., O. Hilliges, S. Izadi, A. D. Butler, J. Chen, I. Oikonomidis, and P. Olivier. Digits: Freehand 3D interactions
anywhere using a wrist-worn gloveless sensor. In Proc. ACM UIST, 2012, 167.
In-air gestures in onthe-go scenarios have been shown using either wrist-worn cameras [20]
• Chen, K.-Y., K. Lyons, S. White, and S. Patel. uTrack: 3D input using two magnetic sensors. In Proc. ACM UIST, Oct.
2013, 237–244.
More recent methods have enabled fine-grained 3D hand-pose estimation in real-time from depth-images.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectsoli-180318203658/75/Project-soli-5-2048.jpg)


![REFERENCES:
[1]. Project Soli information document.
[2]. Soli: Ubiquitous Gesture Sensing with Millimeter Wave Radar. Jaime Lien , Nicholas Gillian, M. Emre Karagozler,
Patrick Amihood, Carsten Schwesig, Erik Olson, Hakim Raja, Ivan Poupyrev Google ATAP.
[3]. Interacting with Soli: Exploring Fine-Grained Dynamic Gesture Recognition in the Radio-Frequency Spectrum.
Saiwen Wang , Jie Song , Jaime Lien , Ivan Poupyrev , Otmar Hilliges ETH Zurich, Google ATAP.
{jsong|otmar.hilliges}@inf.ethz.ch, sawang@student.ethz.ch, {jaimelien|ipoupyrev}@google.com.
[4]. Erol, A., G. Bebis, M. Nicolescu, R. D. Boyle, and X. Twombly. Vision-based hand pose estimation: A review. Comput.
Vision Image Understanding 108, 1-2 (Oct. 2007).
[5]. Chen, K.-Y., K. Lyons, S. White, and S. Patel. uTrack: 3D input using two magnetic sensors. In Proc. ACM UIST, Oct.
2013.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectsoli-180318203658/75/Project-soli-11-2048.jpg)