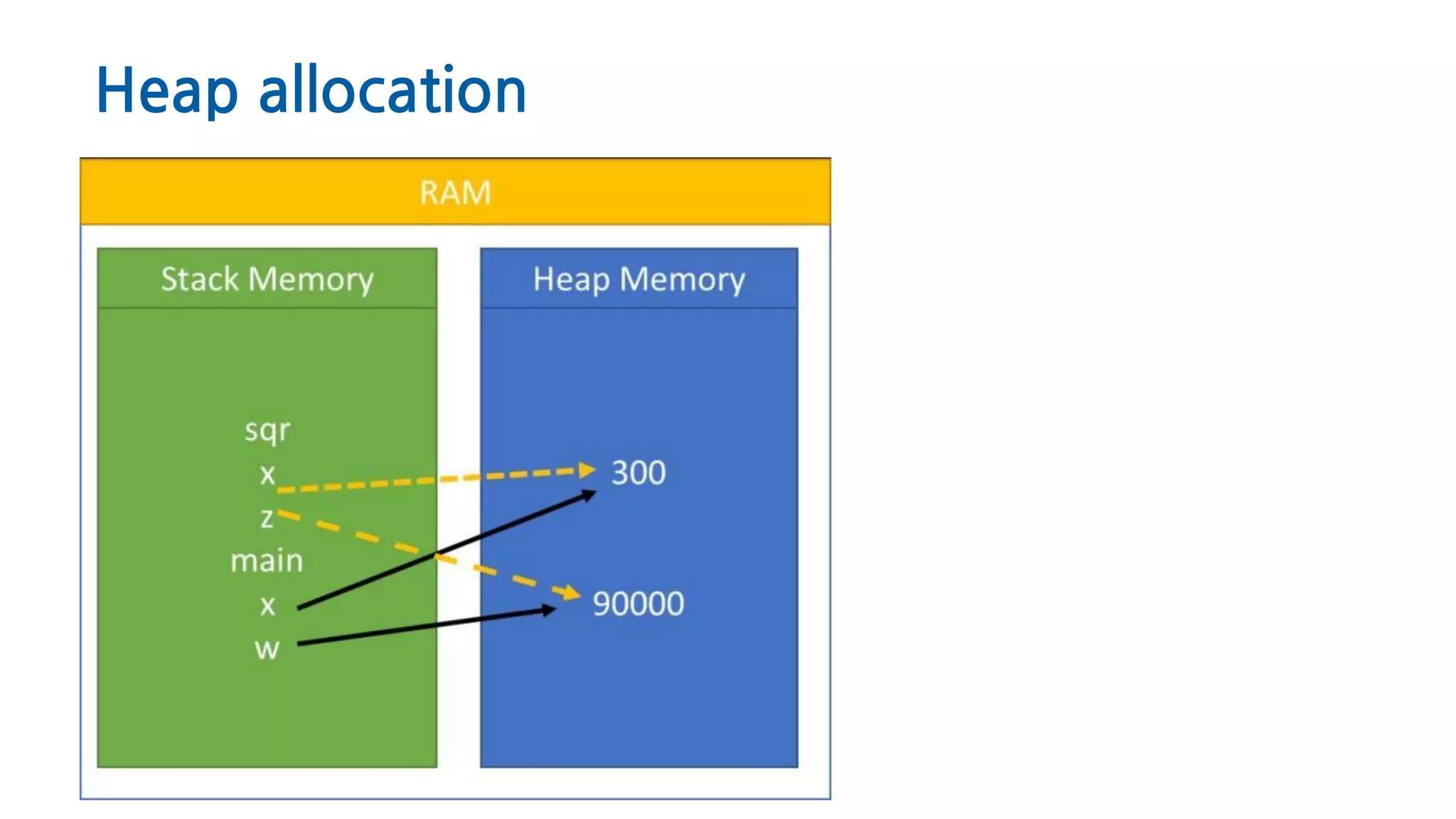
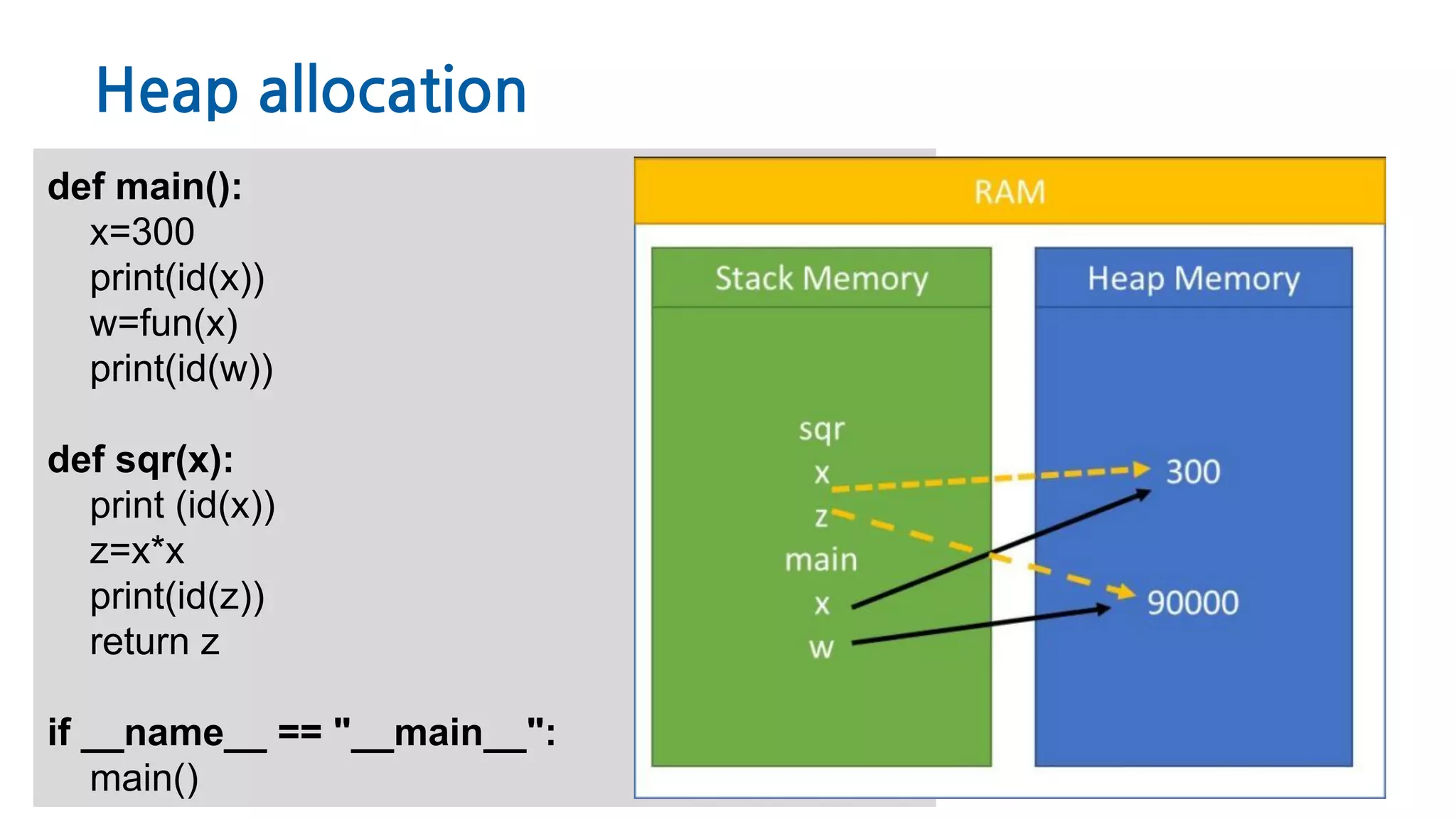
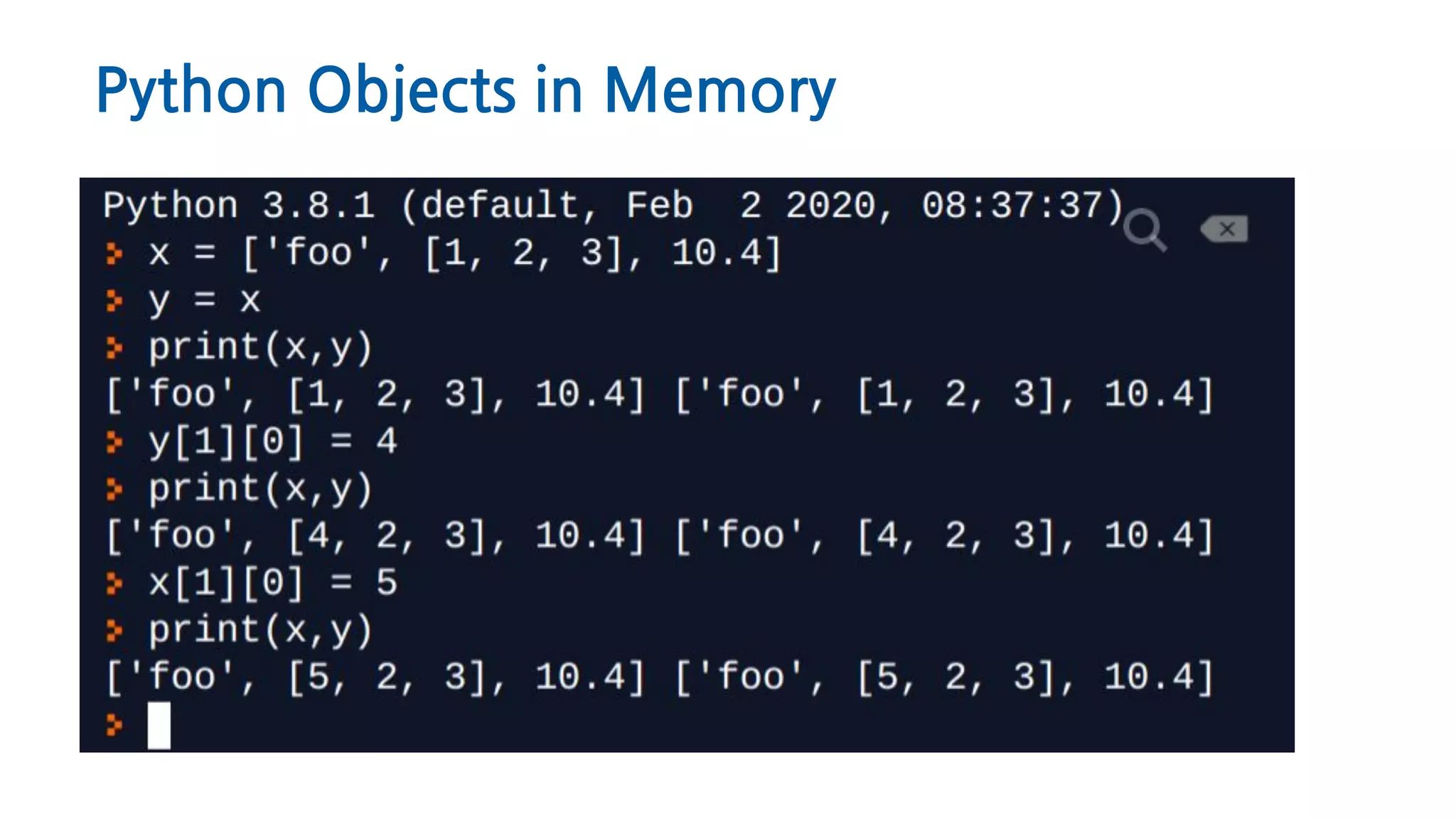
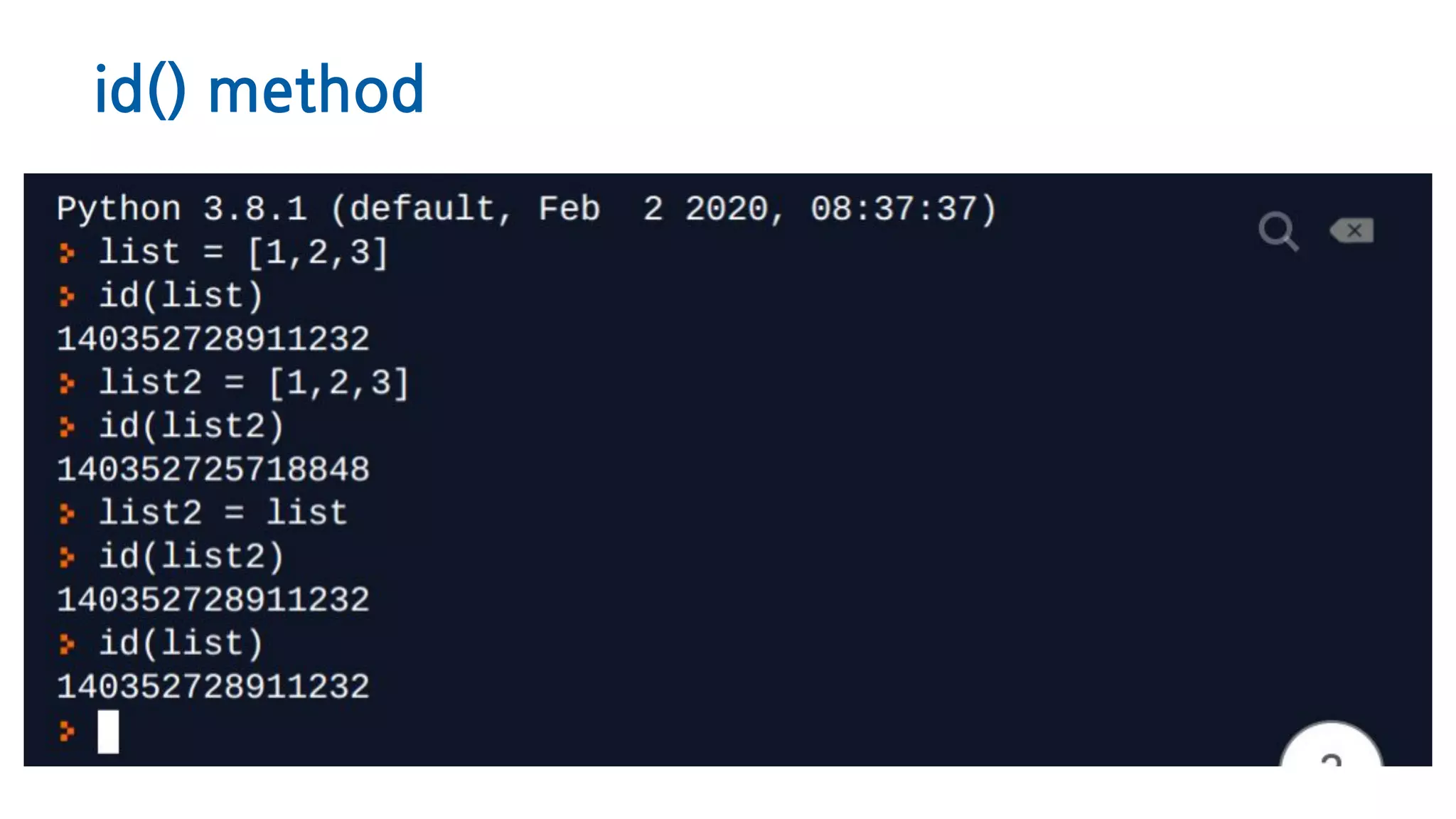
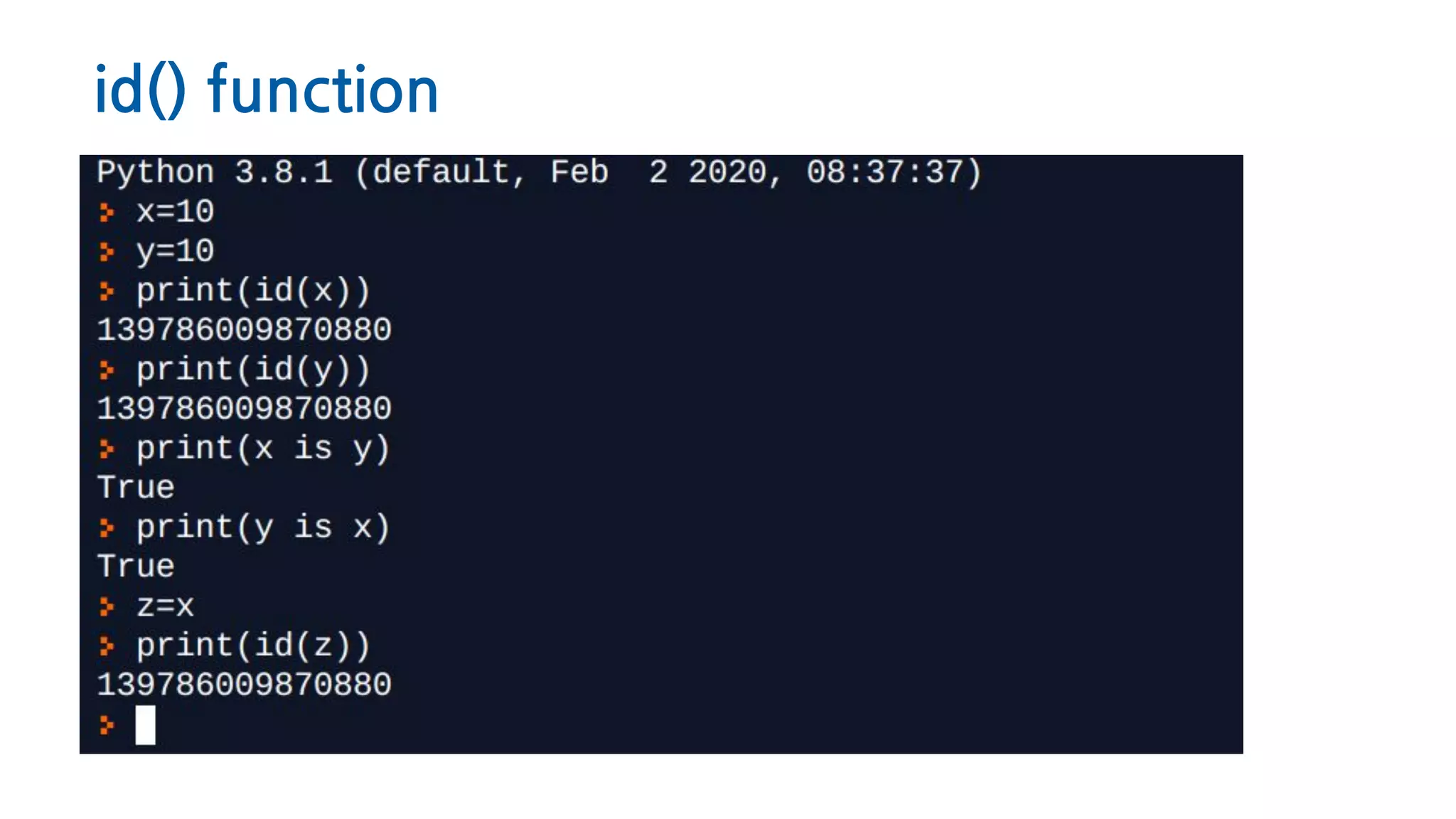
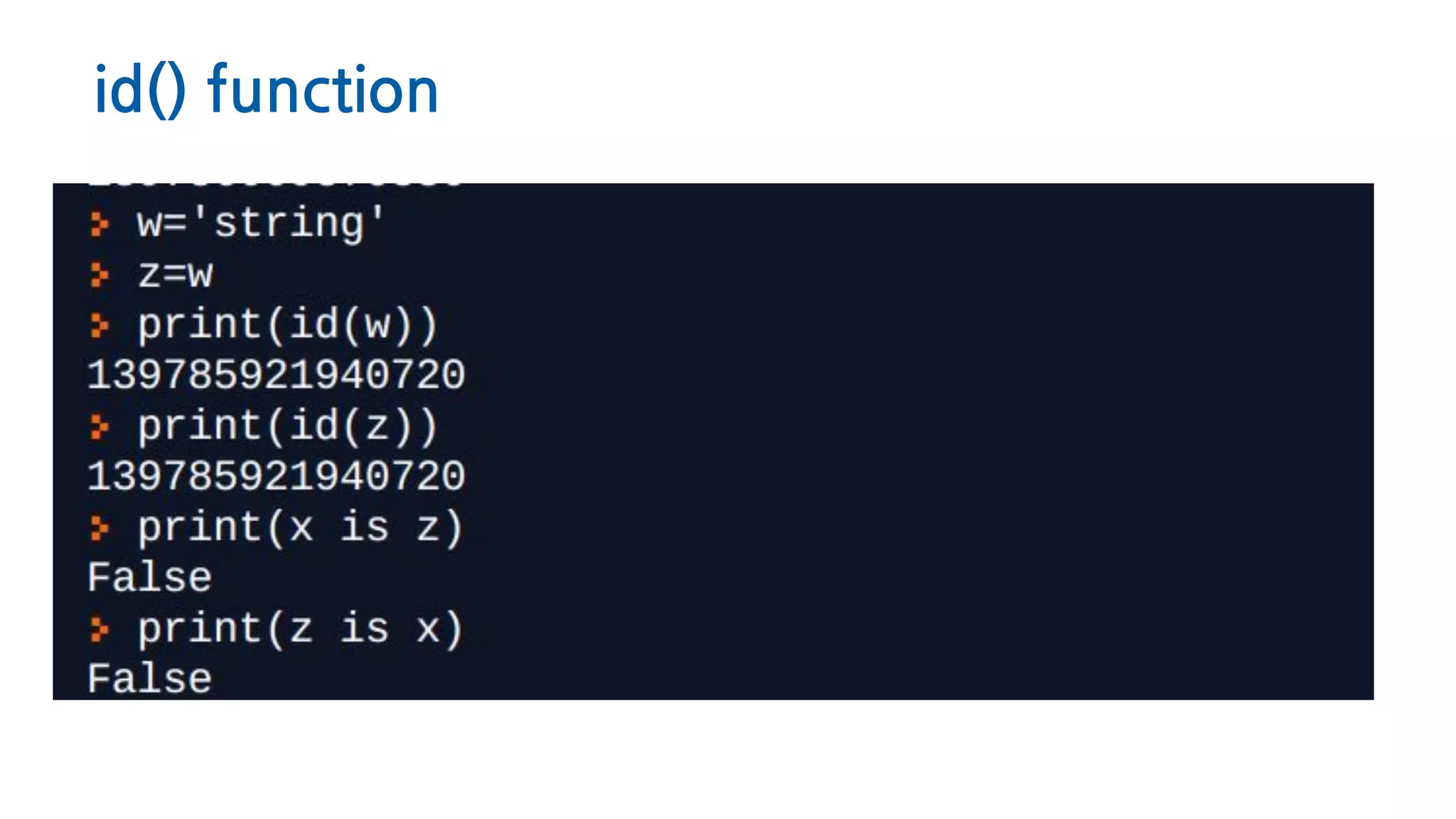
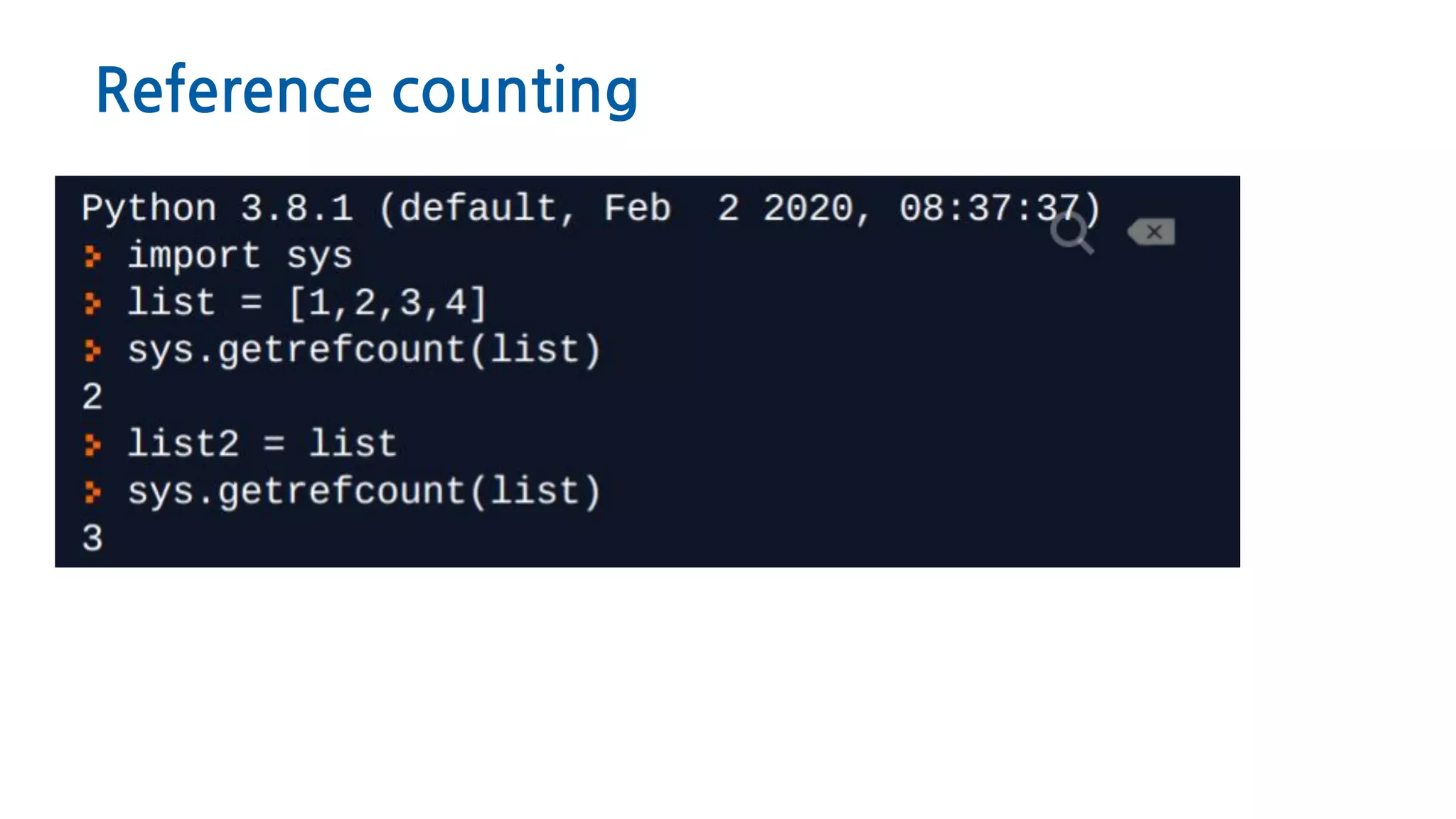
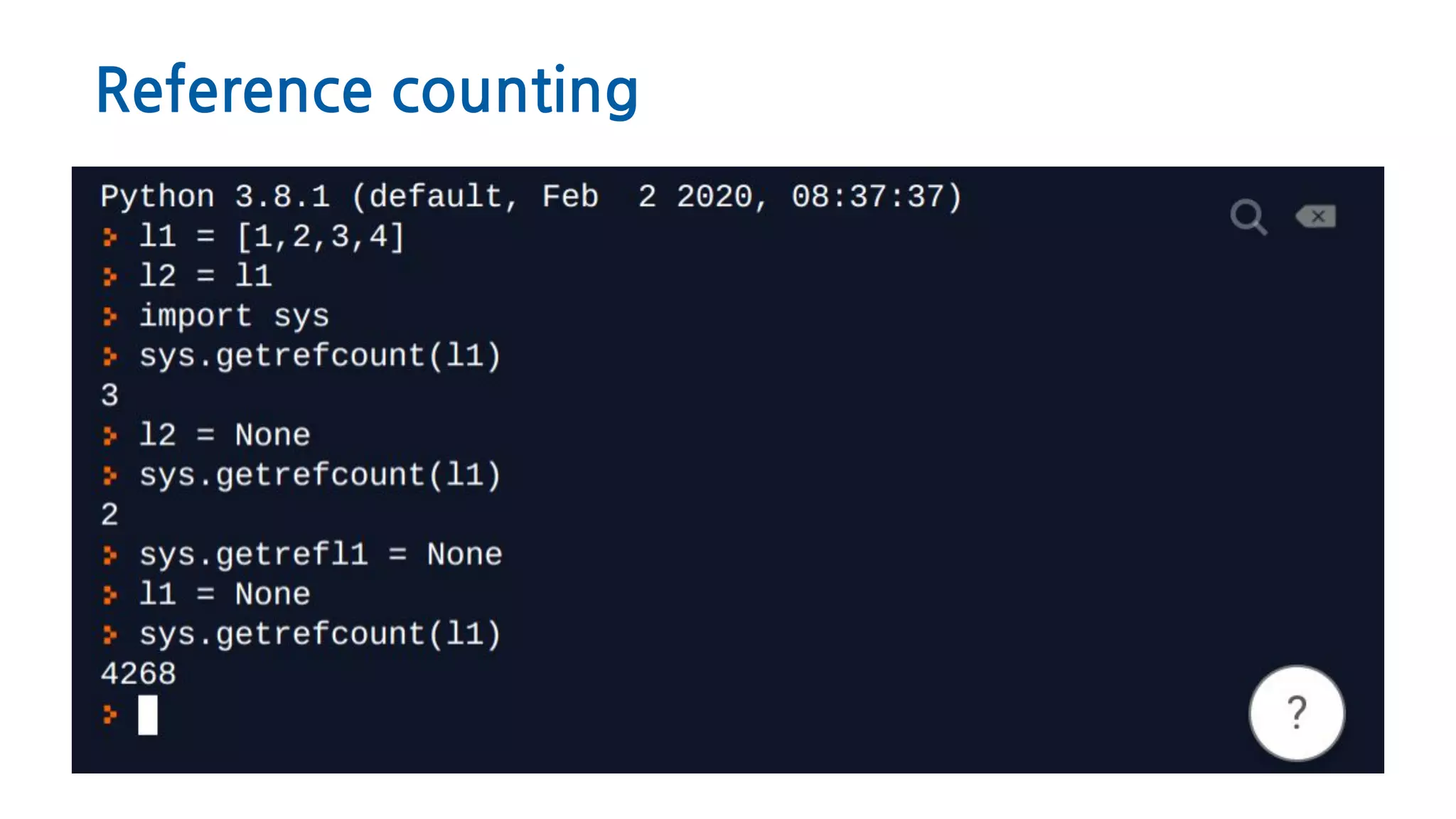
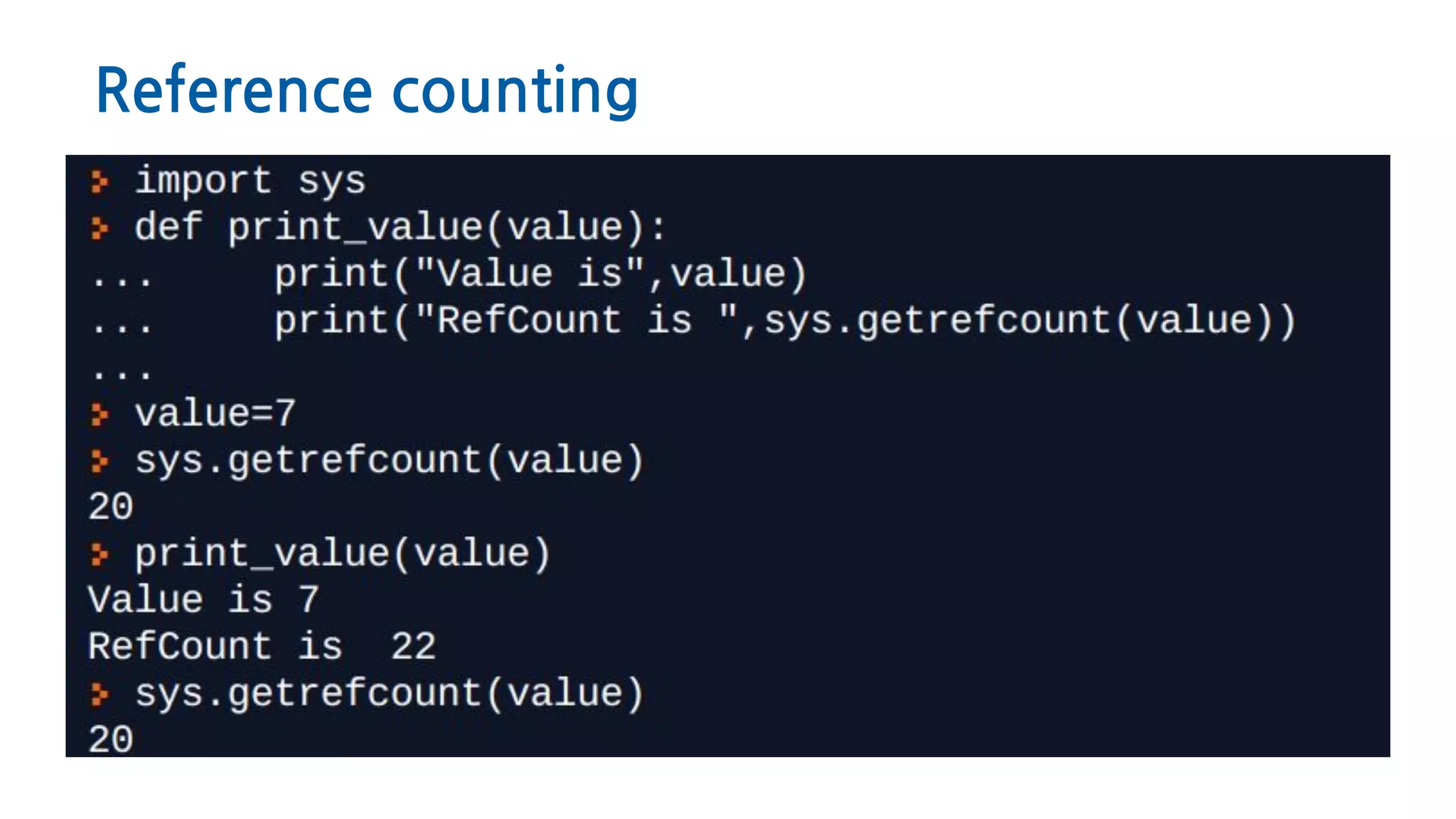
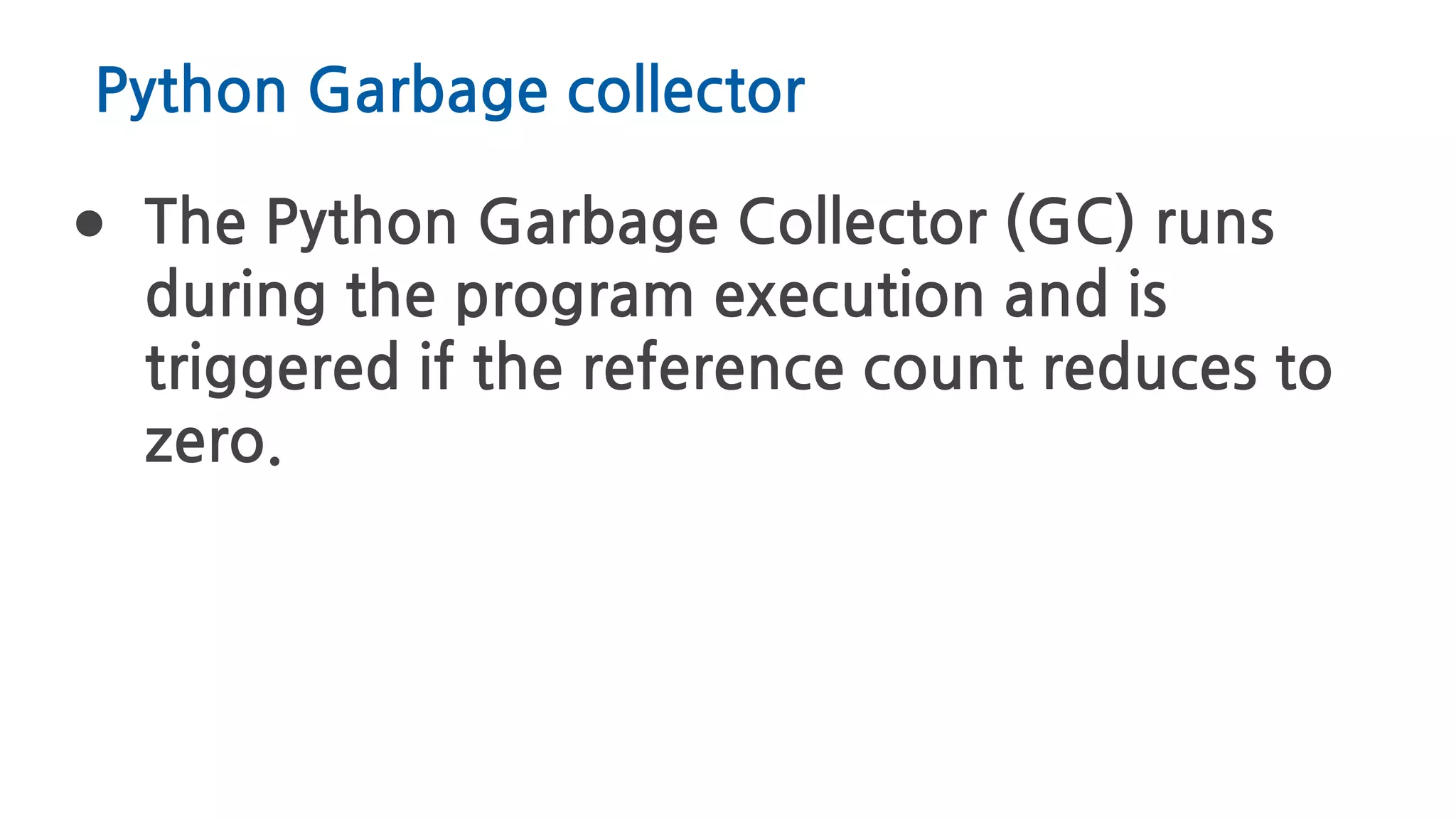
The document discusses Python memory management, focusing on garbage collection and reference counting. It explains how Python allocates and de-allocates memory, illustrates the role of the garbage collector, and provides best practices for effective memory management in Python applications. It also includes coding examples and references for further reading.














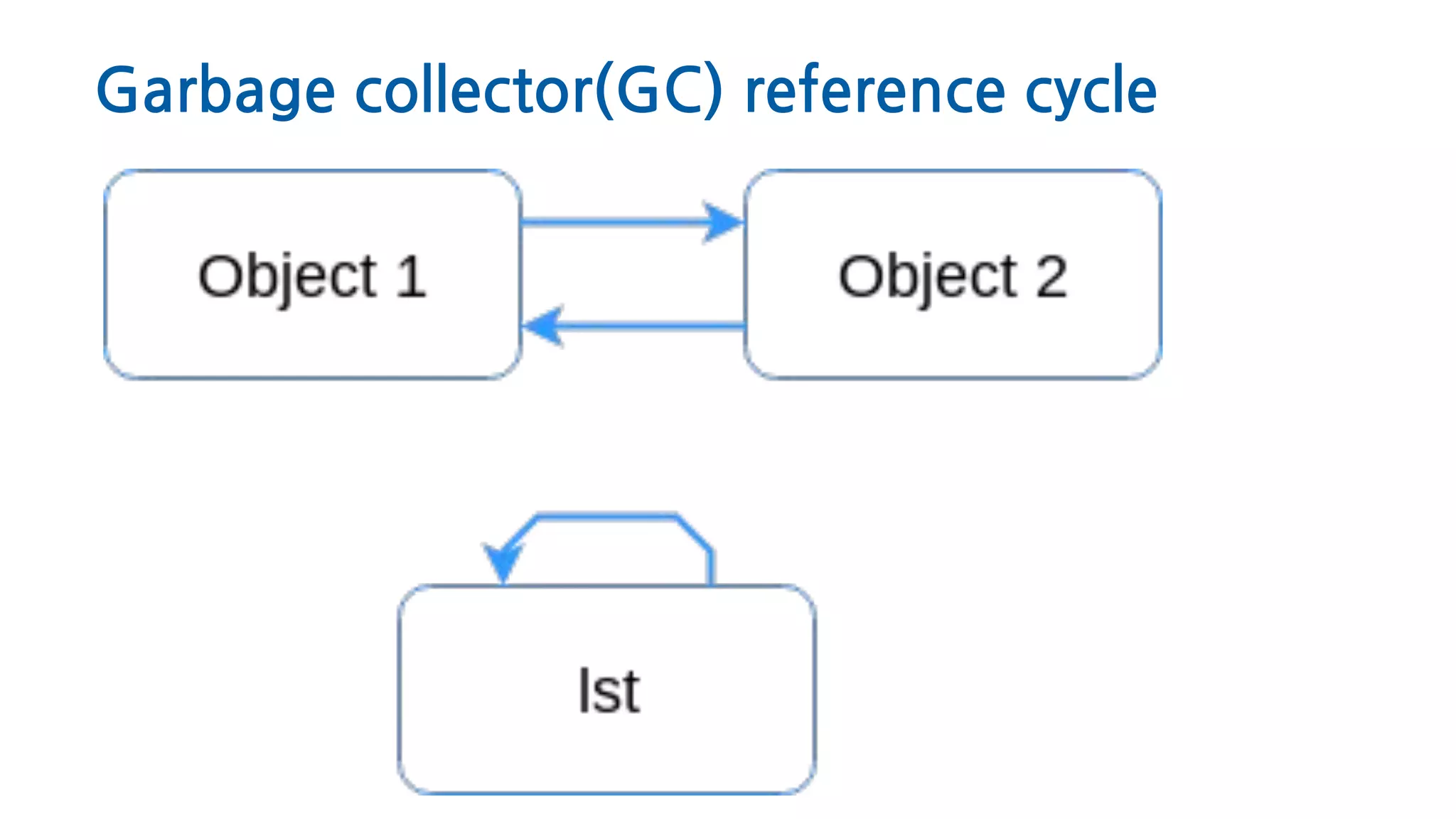
![Garbage collector(GC) reference cycle
>>> def ref_cycle():
... list = [1, 2, 3, 4]
... list.append(list)
... return list](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonmemorymanagment-200509170620/75/Python-memory-managment-Deeping-in-Garbage-collector-29-2048.jpg)


![Python Object Graphs
https://mg.pov.lt/objgraph/
>>> x = []
>>> list = [x, [x], dict(x=x)]
>>> import objgraph
>>> objgraph.show_refs([y],
filename='sample-graph.png')](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonmemorymanagment-200509170620/75/Python-memory-managment-Deeping-in-Garbage-collector-32-2048.jpg)


![Best practices for memory managment
● Avoid List Slicing with [:]
list= [1,2,3,4]
list[1:3]
list[slice(1,3)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonmemorymanagment-200509170620/75/Python-memory-managment-Deeping-in-Garbage-collector-35-2048.jpg)