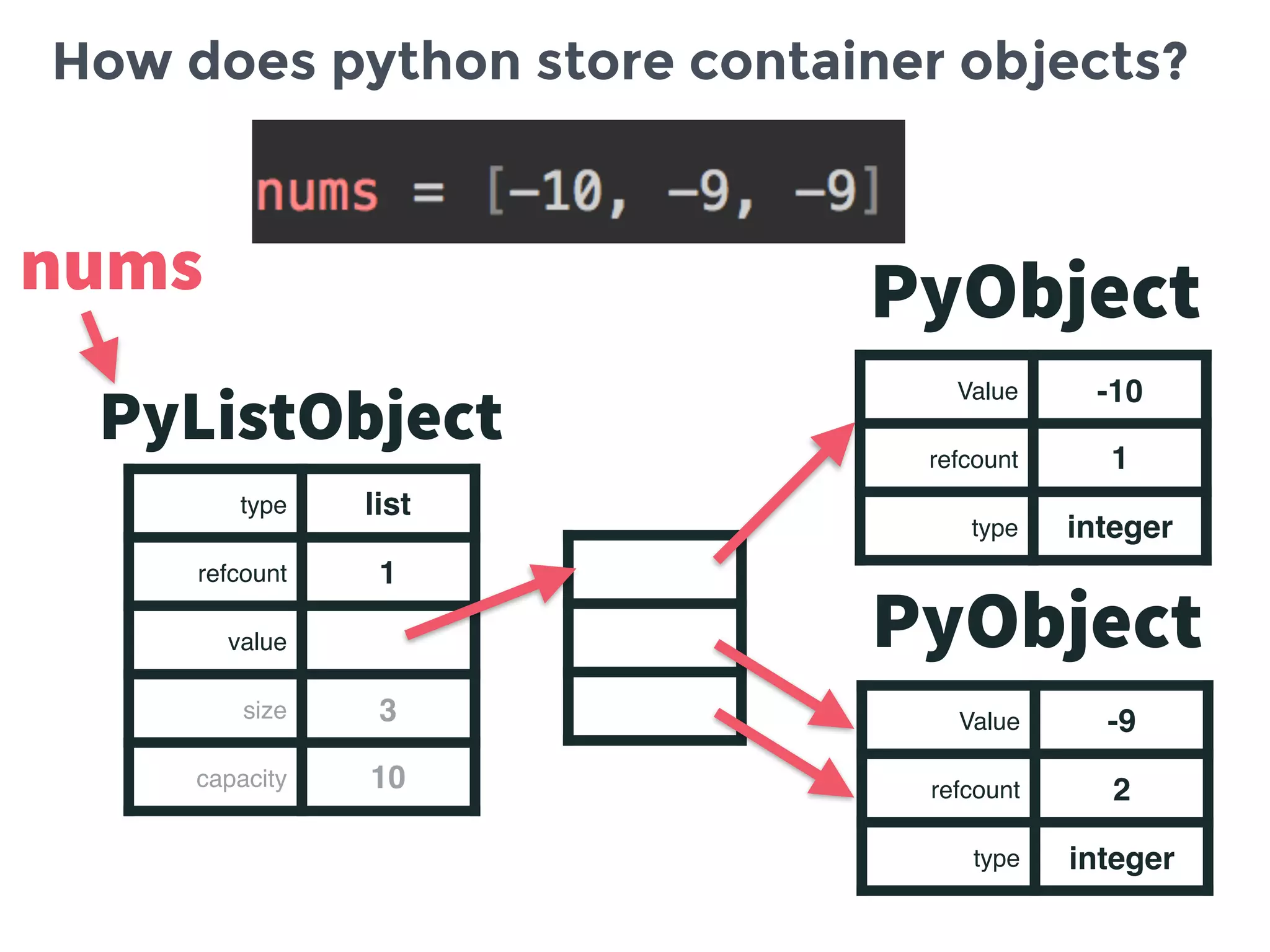
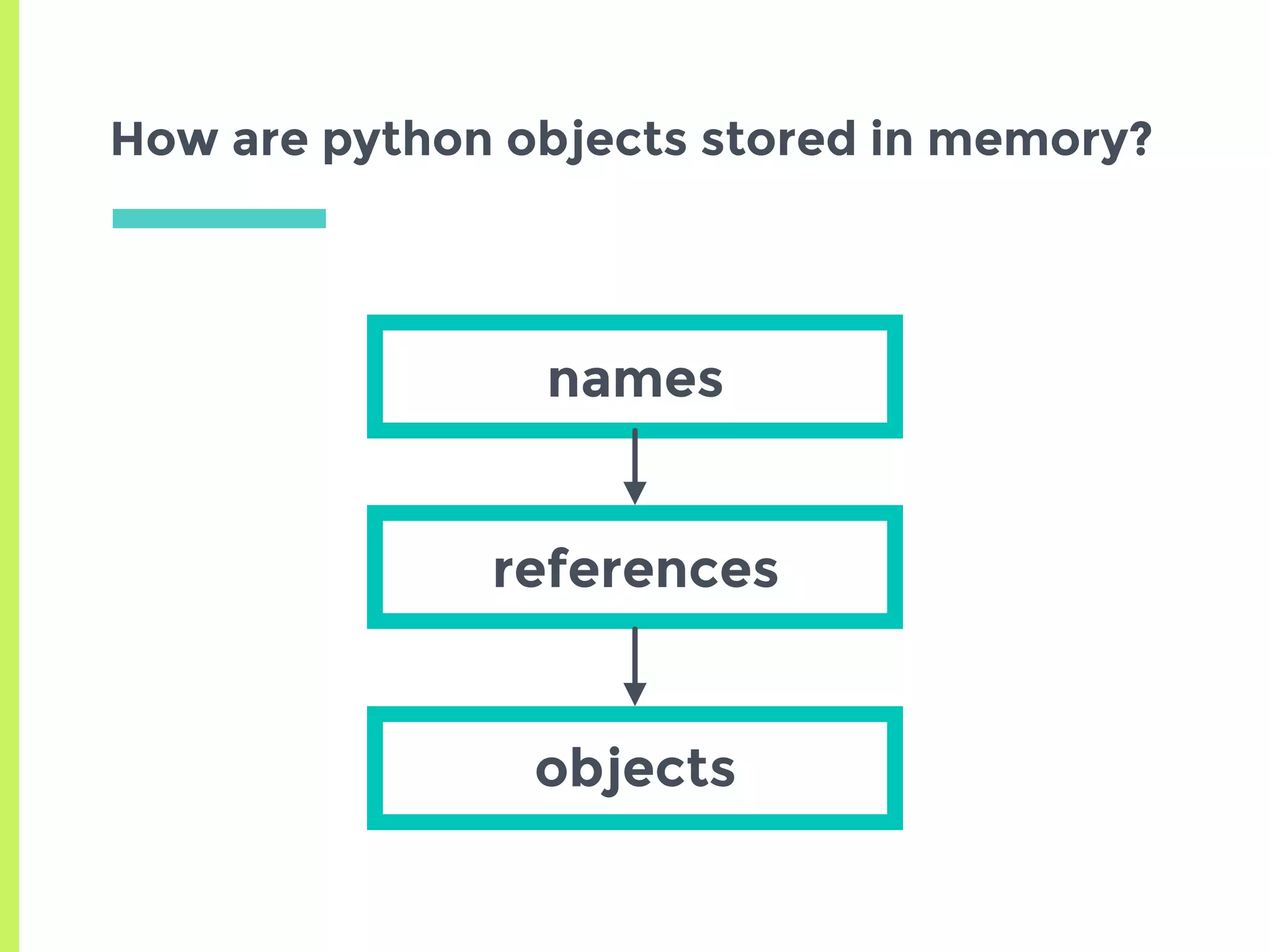
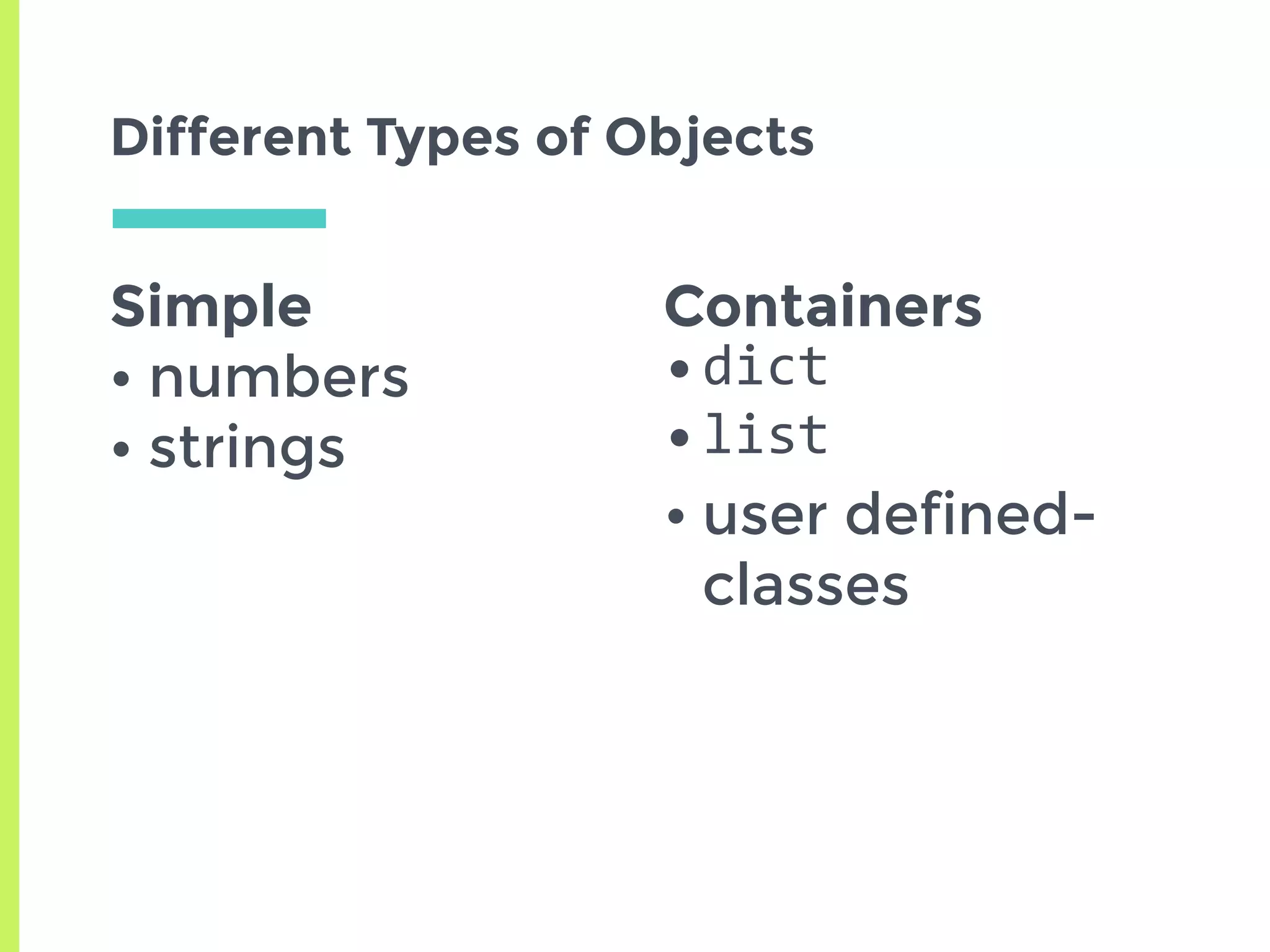
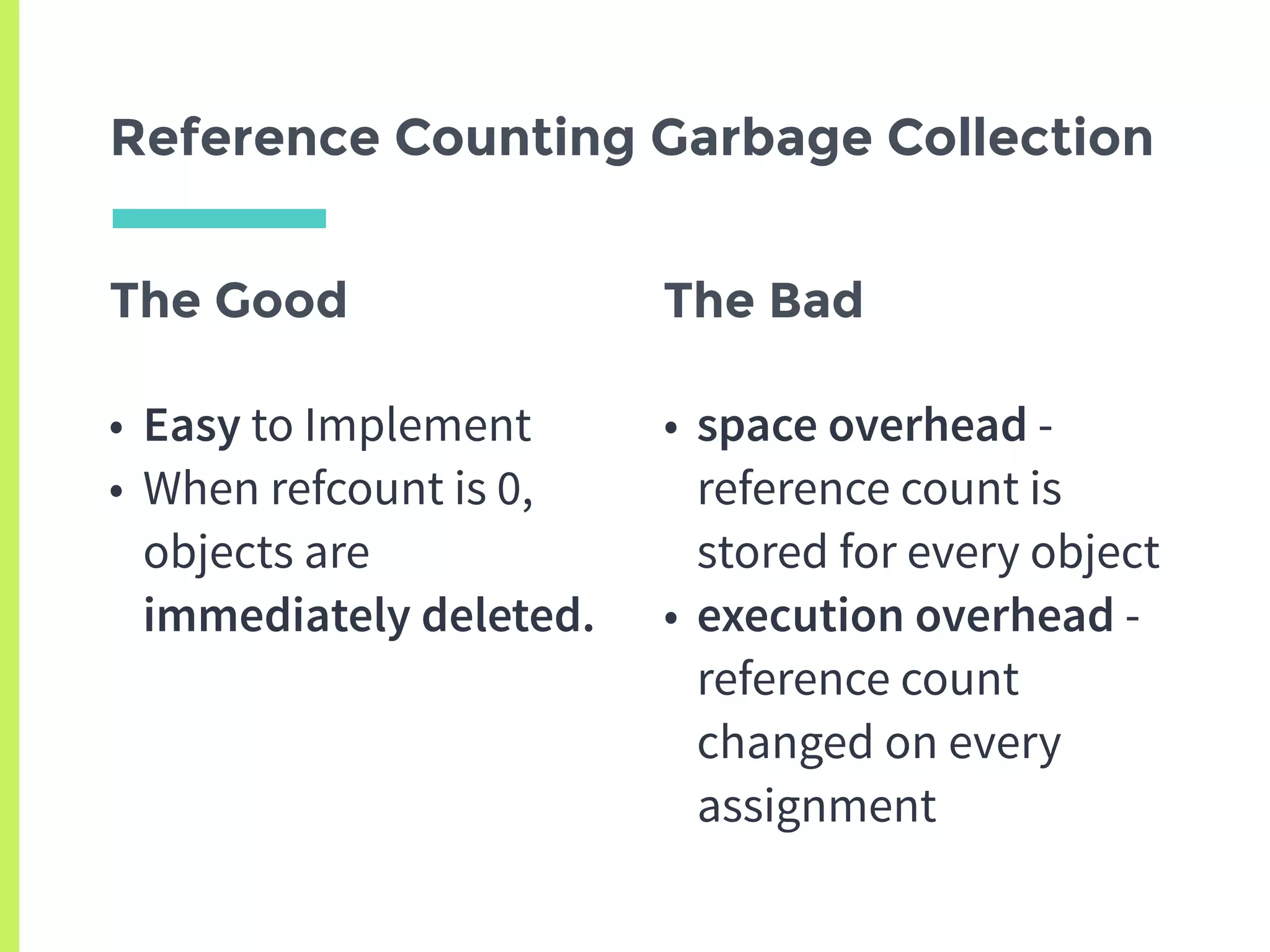
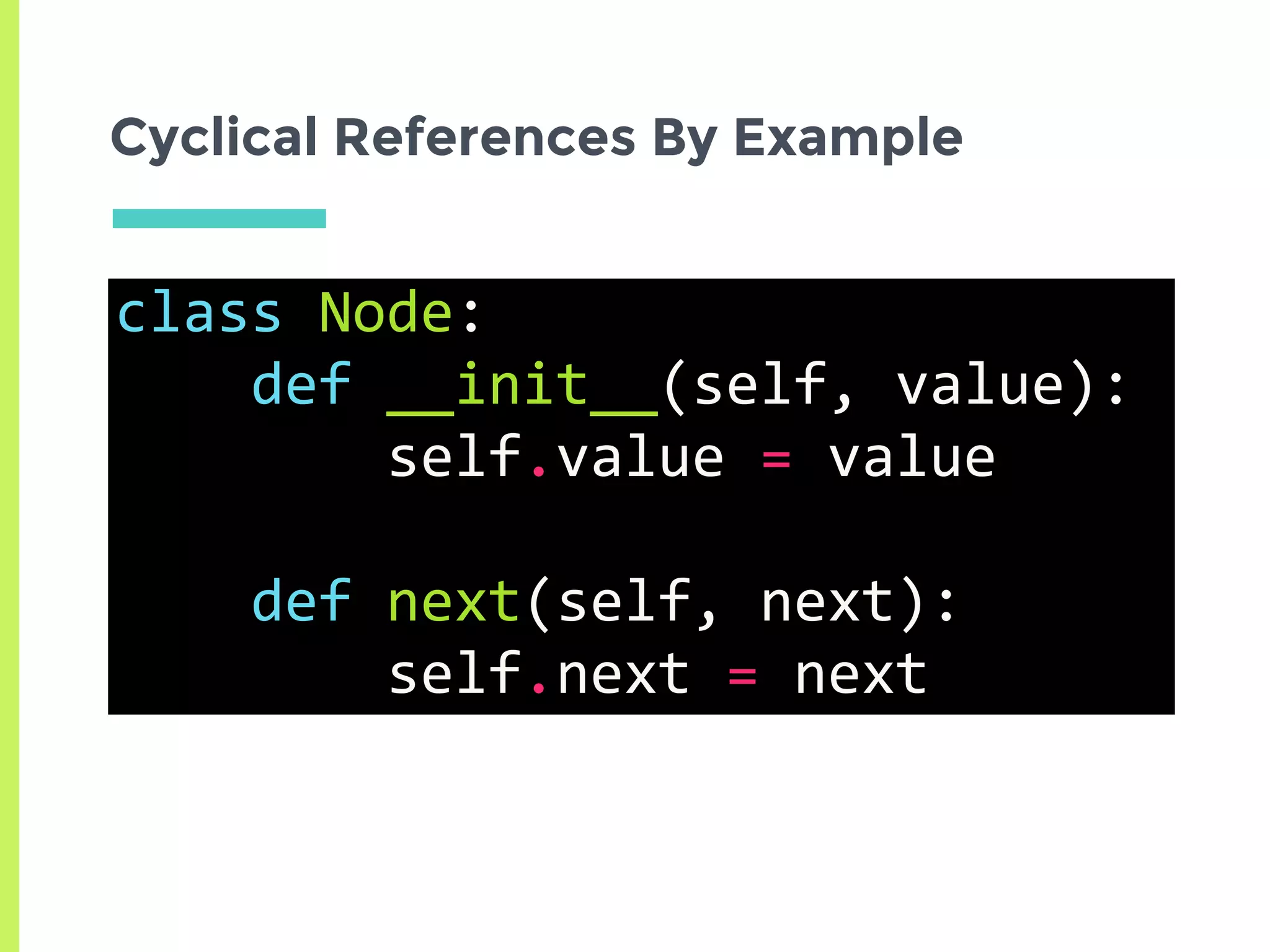
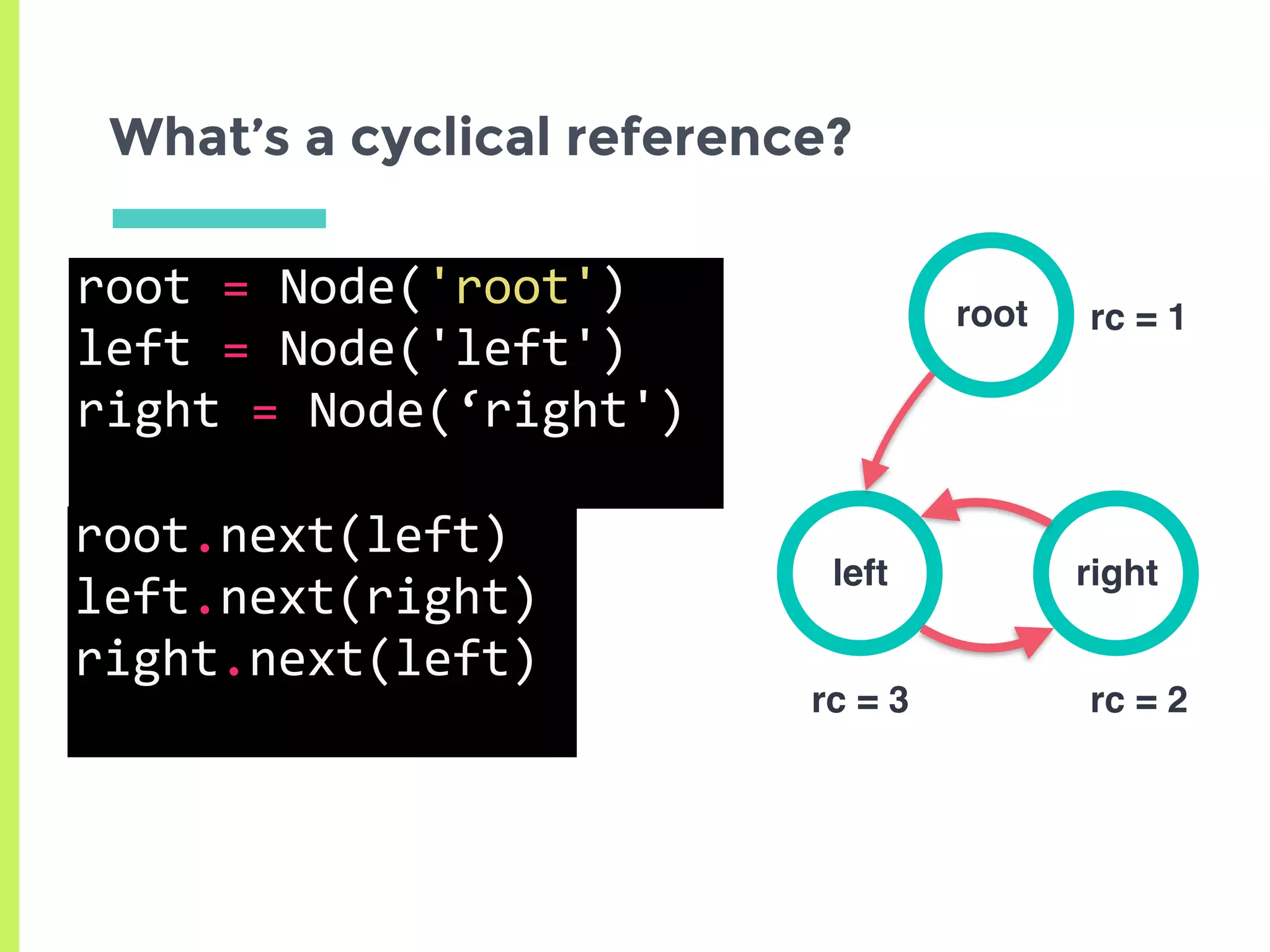
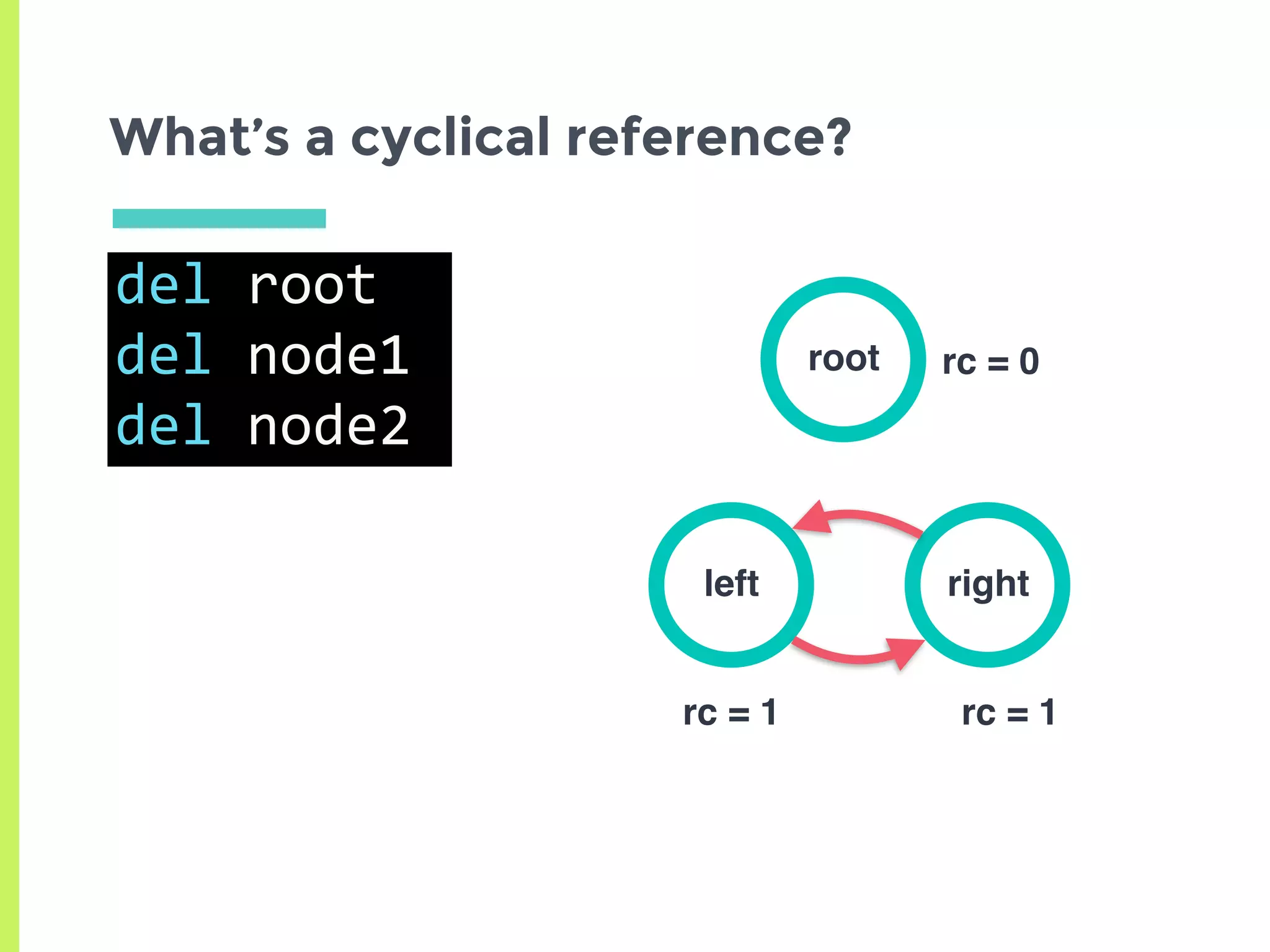
This document summarizes the basics of memory management in Python. It discusses key concepts like variables, objects, references, and reference counting. It explains how Python uses reference counting with generational garbage collection to manage memory and clean up unused objects. The document also covers potential issues with reference counting like cyclic references and threads, and how the global interpreter lock impacts multi-threading in Python.





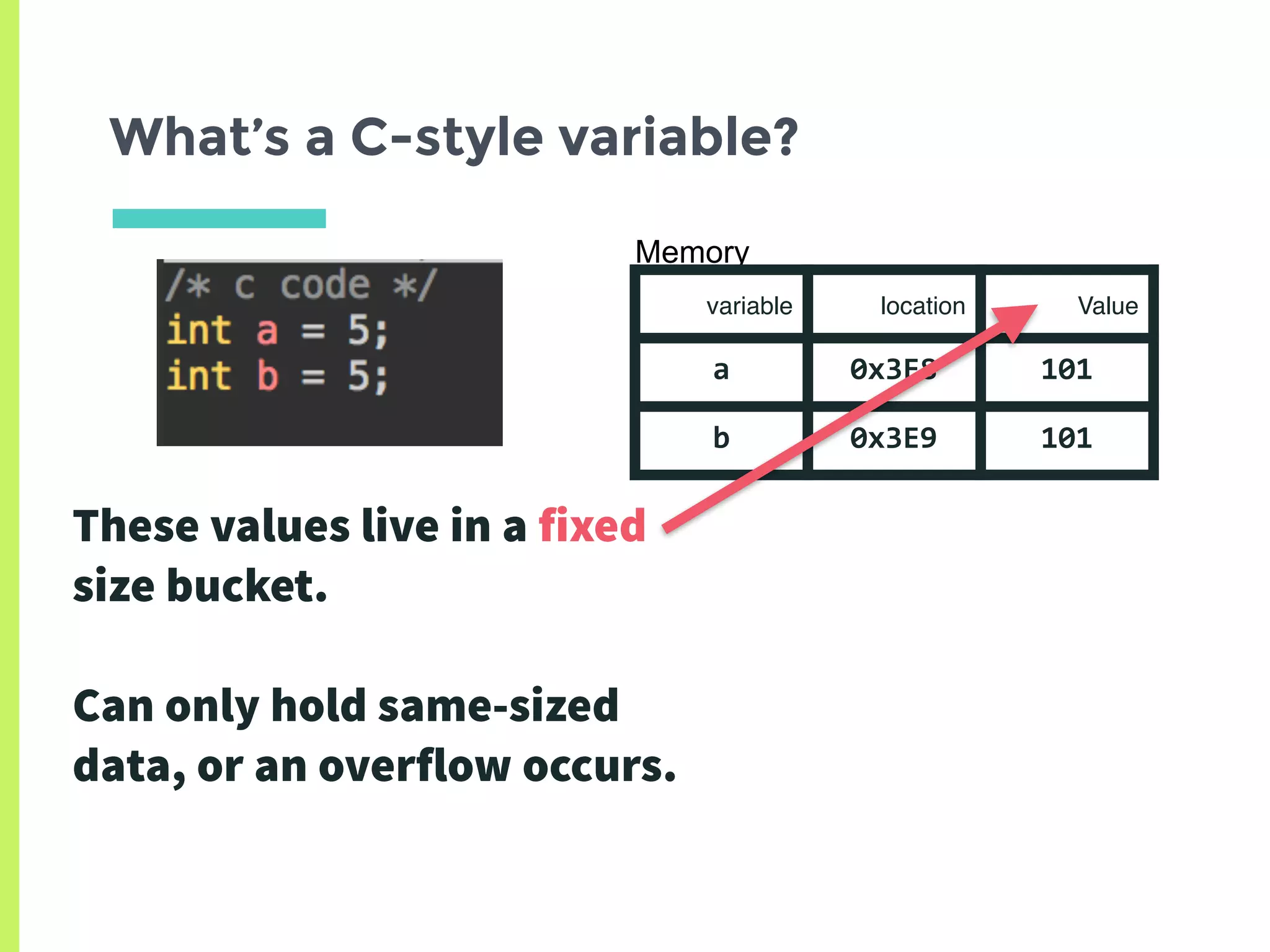
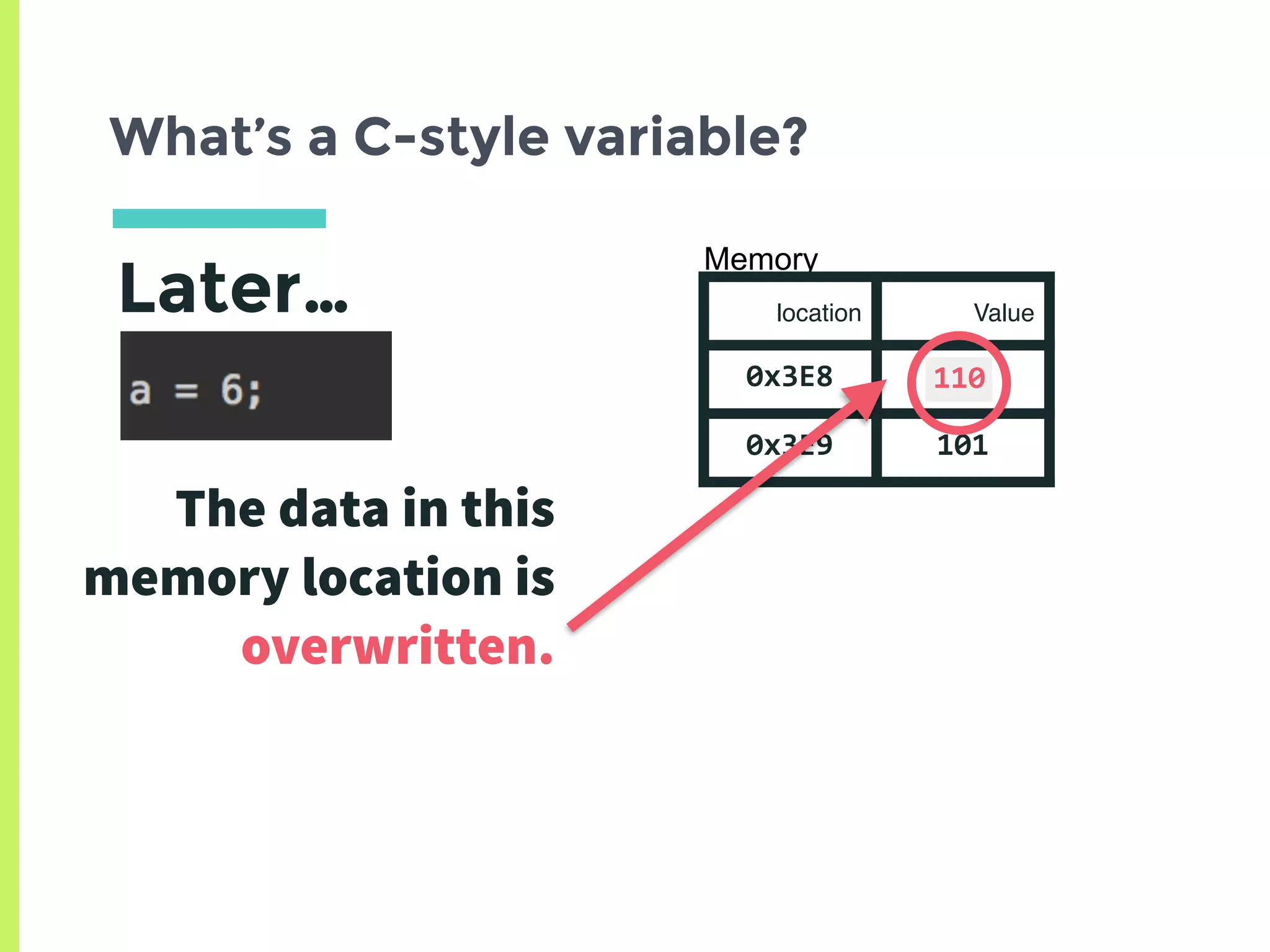




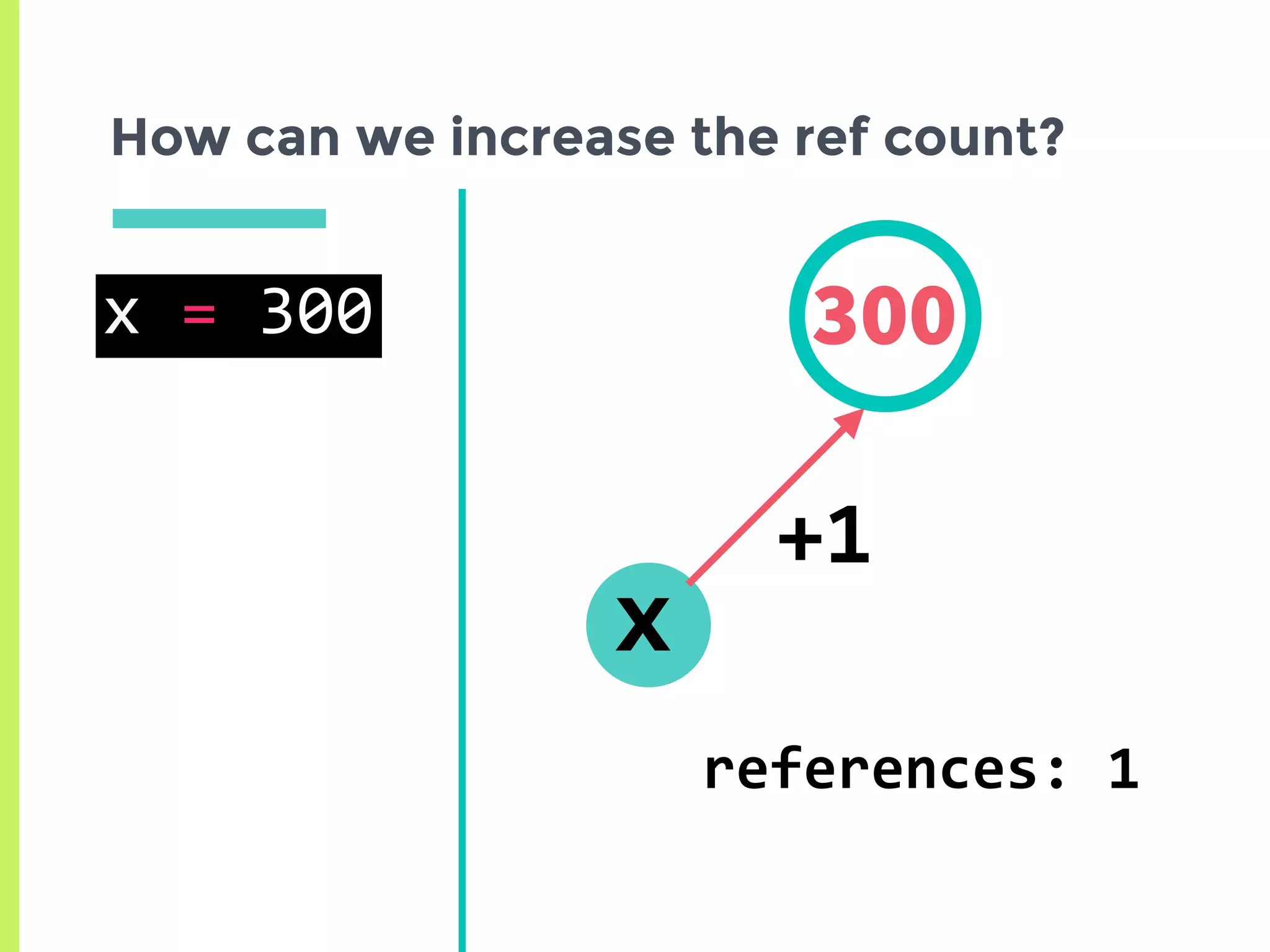
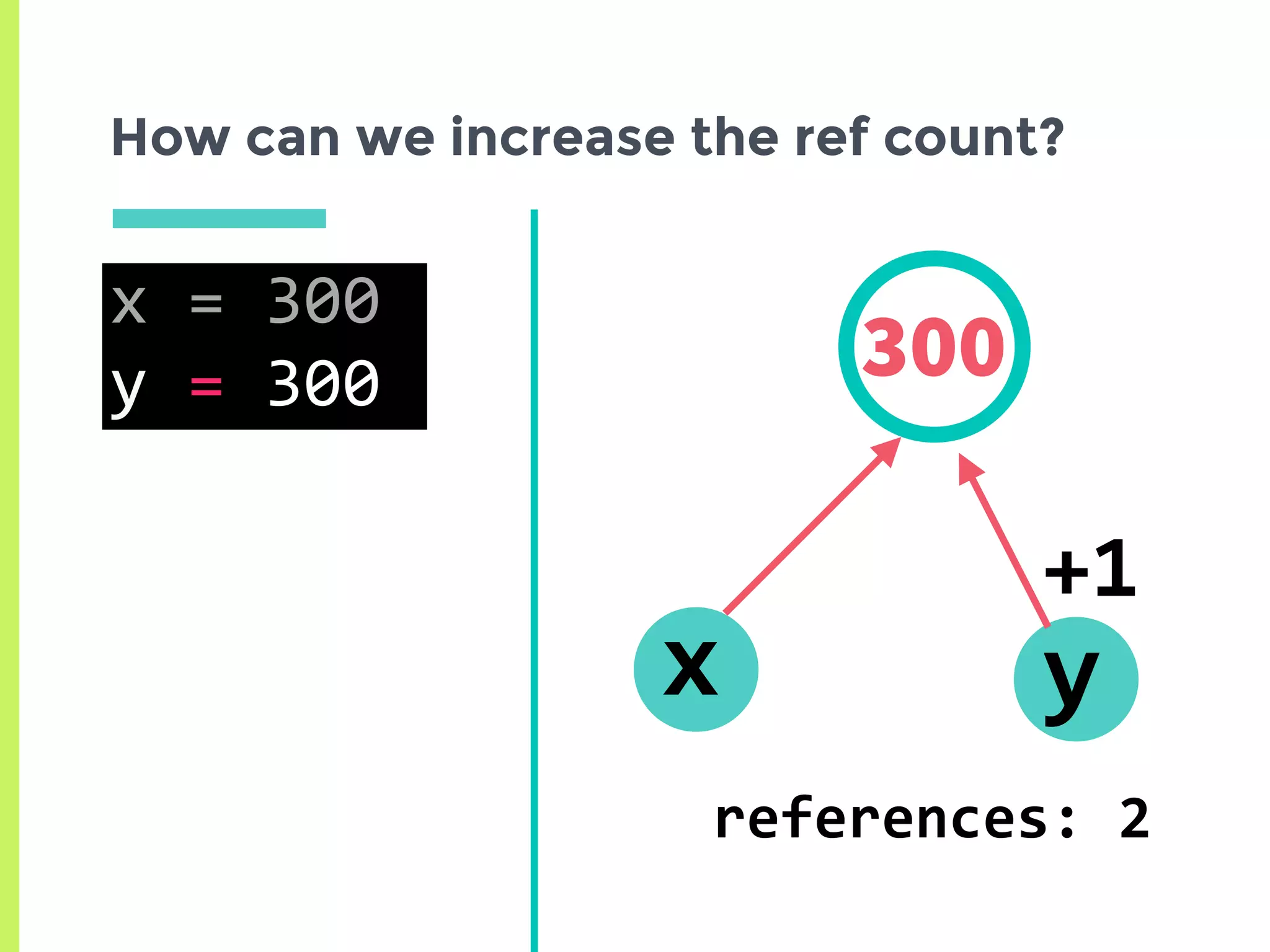
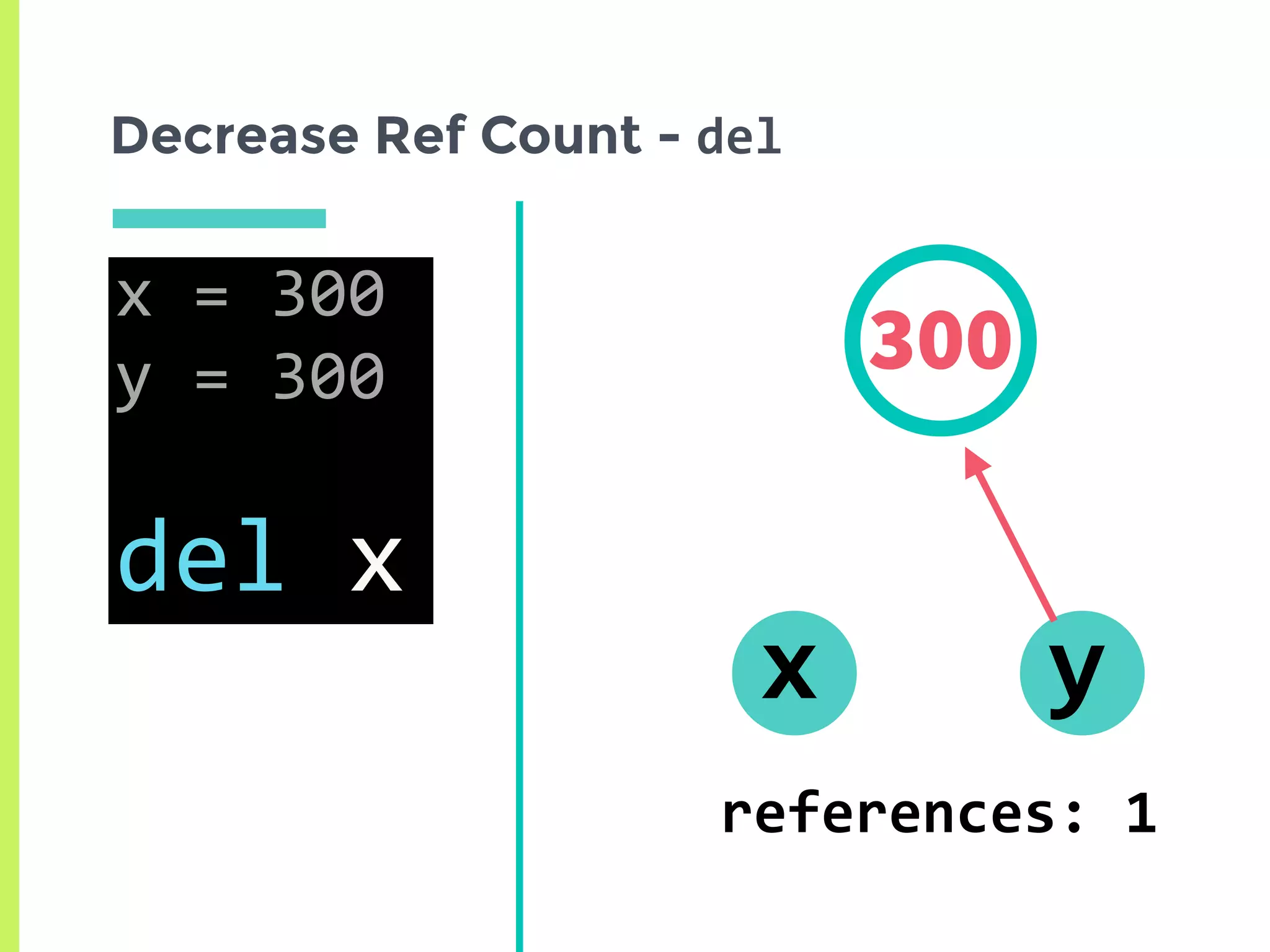
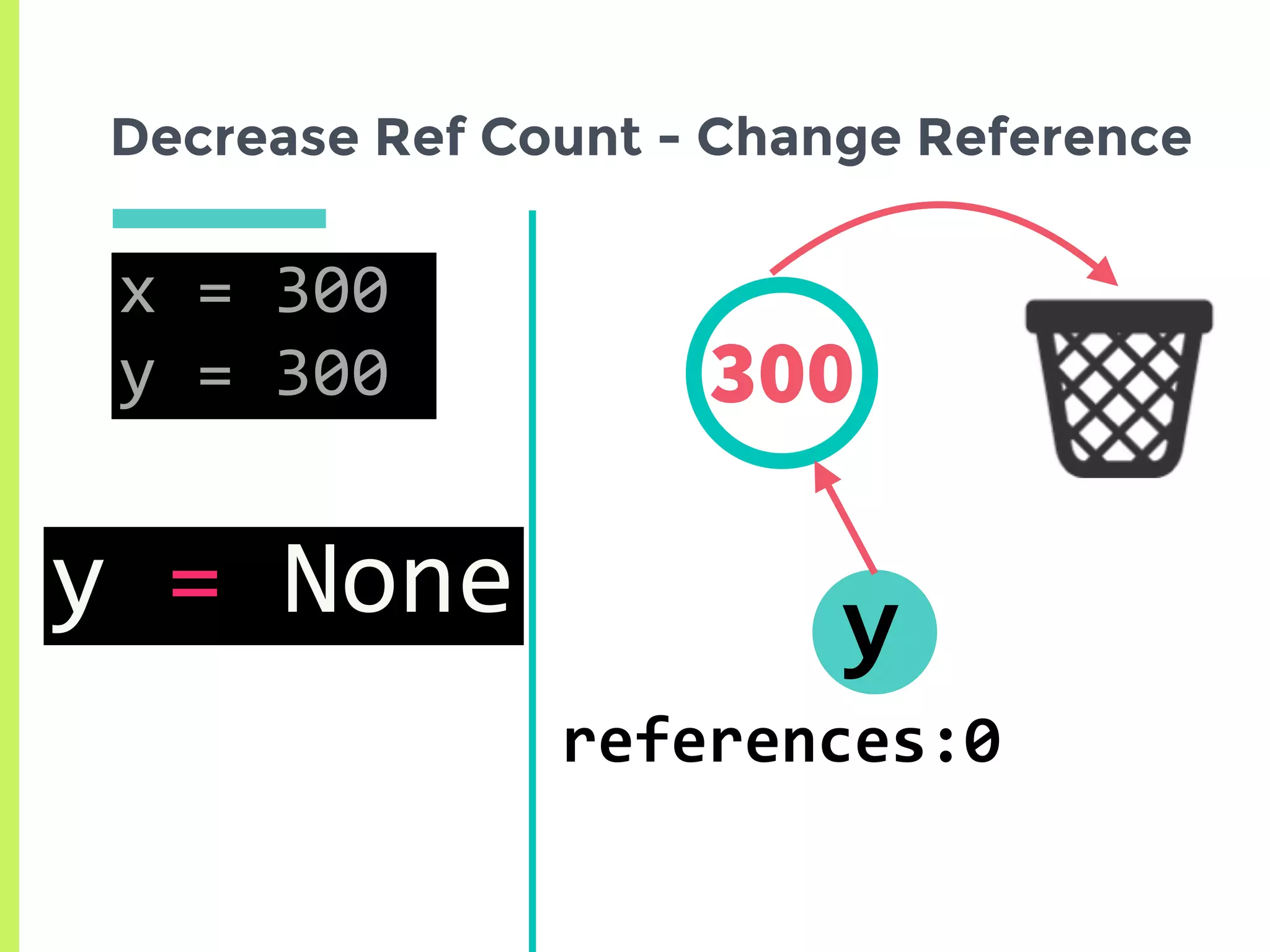
![How can we increase the ref count?
300
z = [300, 300]
x
references: 4
y](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-160530215919/75/Memory-Management-In-Python-The-Basics-16-2048.jpg)



































![Thanks!
@nnja
nina.writes.code@gmail.com
[TODO SLIDESHARE LINK]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/upload-160530215919/75/Memory-Management-In-Python-The-Basics-69-2048.jpg)