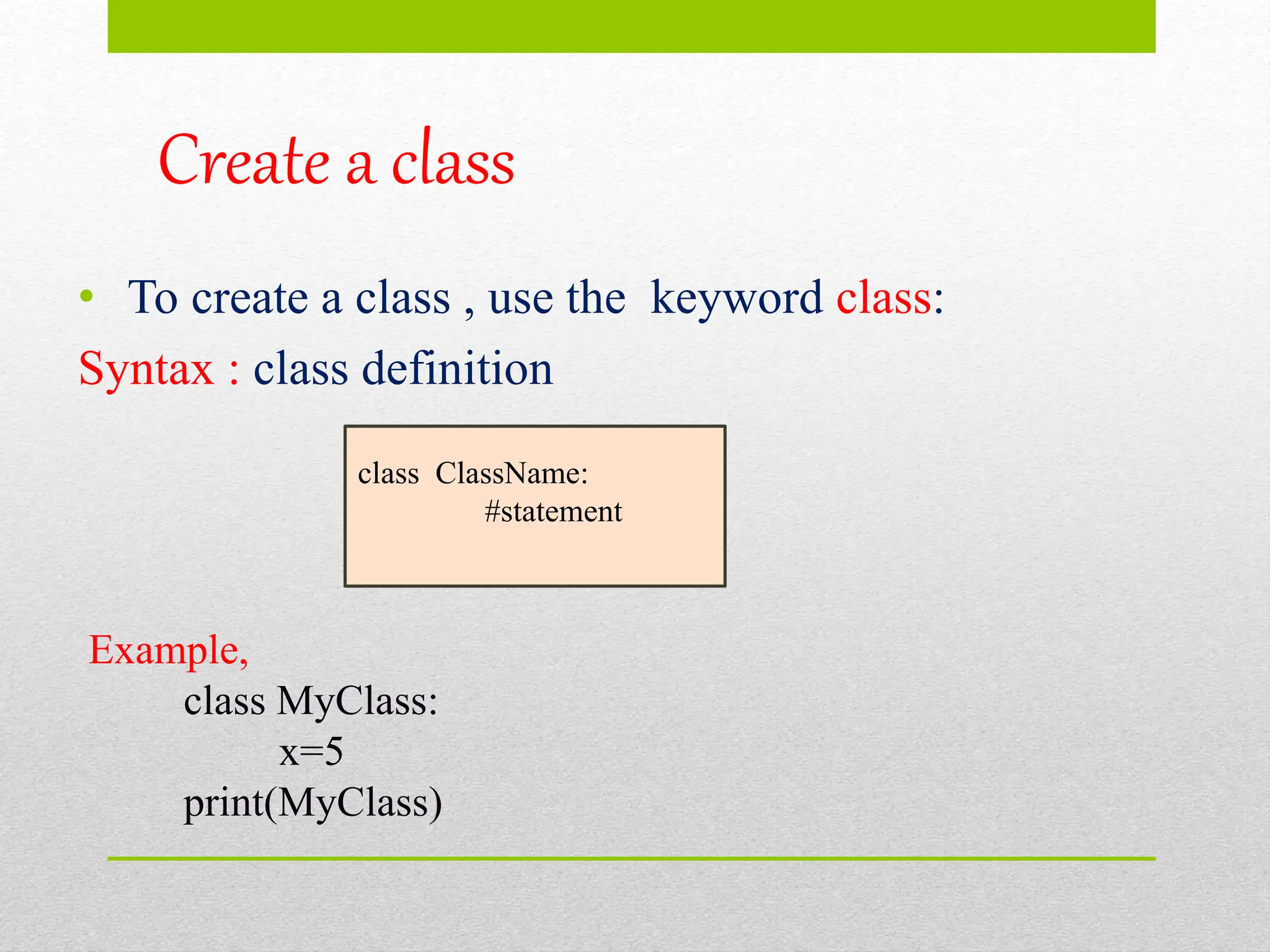
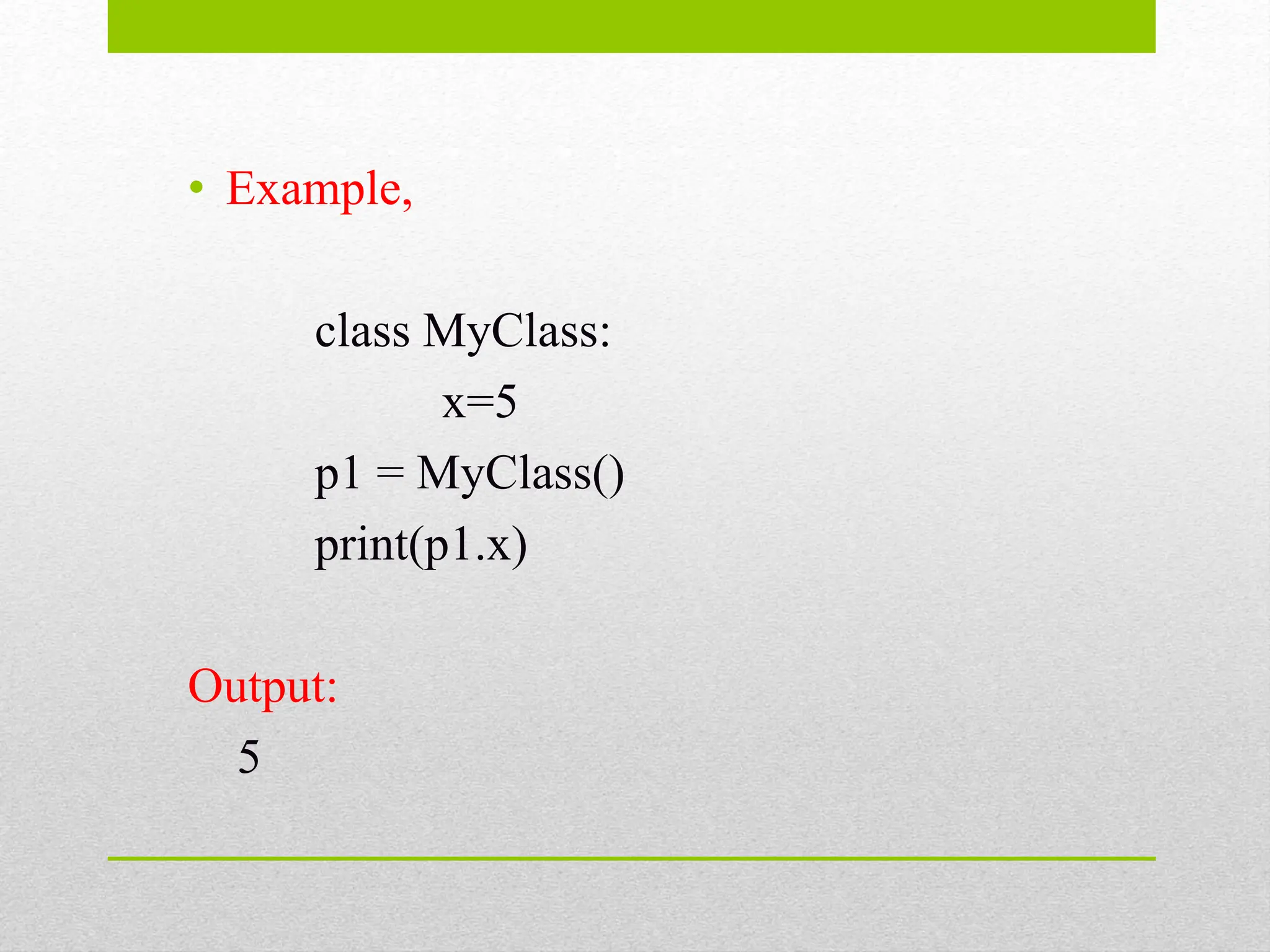
Object oriented programming involves concepts like polymorphism, encapsulation, inheritance, abstraction, and classes & objects. A class defines the properties and behaviors of an object using variables and functions. Classes are created using the class keyword, and objects are instances of classes that are initialized using the class name followed by parentheses. The __init__() function initializes object properties during instantiation, while __str__() controls object string representation. The self parameter refers to the current class instance and is used to access class variables and methods.