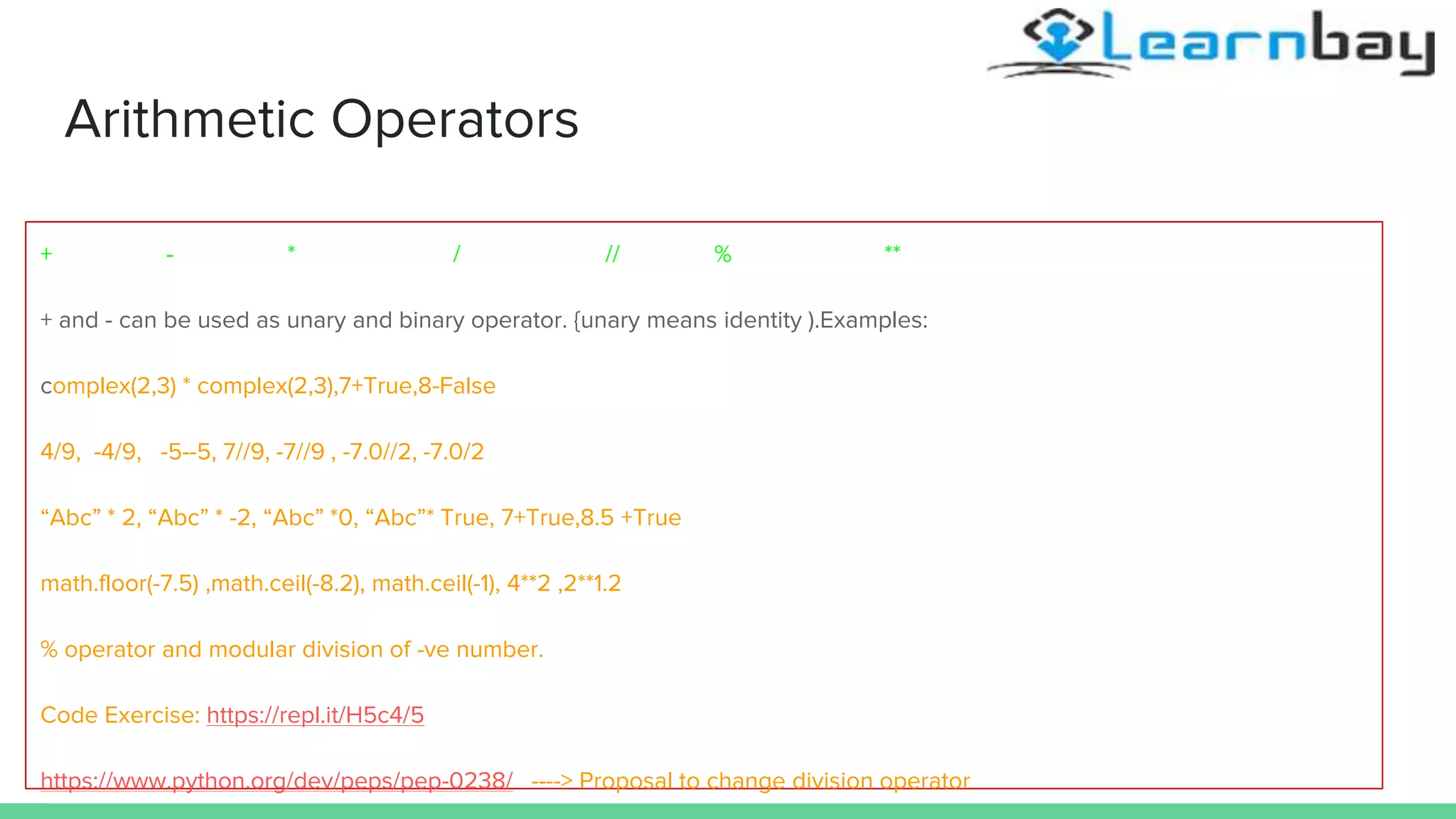
The document provides an overview of operators in Python, detailing arithmetic, relational, logical, and bitwise operators, along with their usage and examples. It explains how these operators interact with different data types, including complex numbers, and discusses control flow statements like if-else. Additionally, coding exercises are included to practice these concepts.