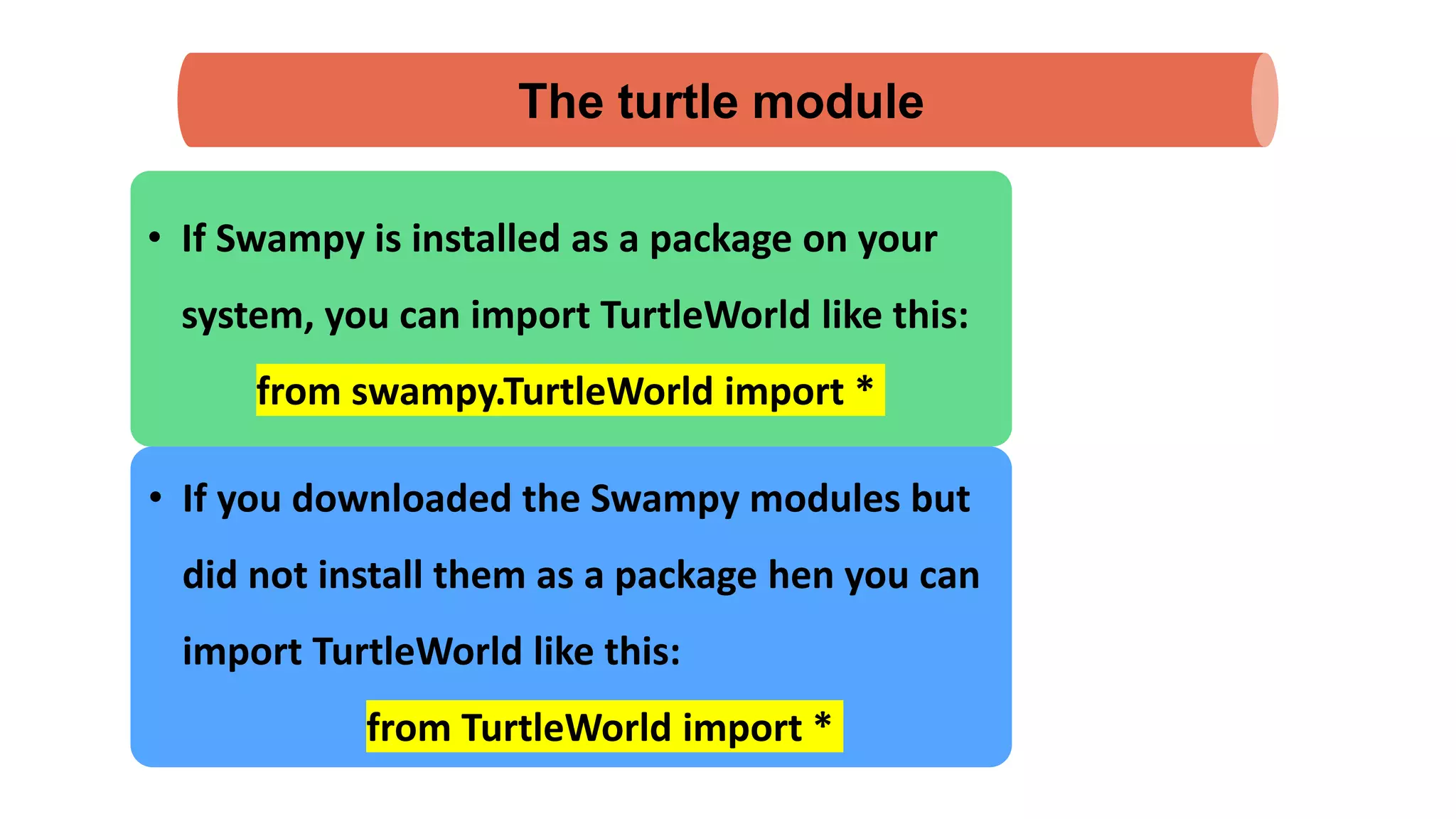
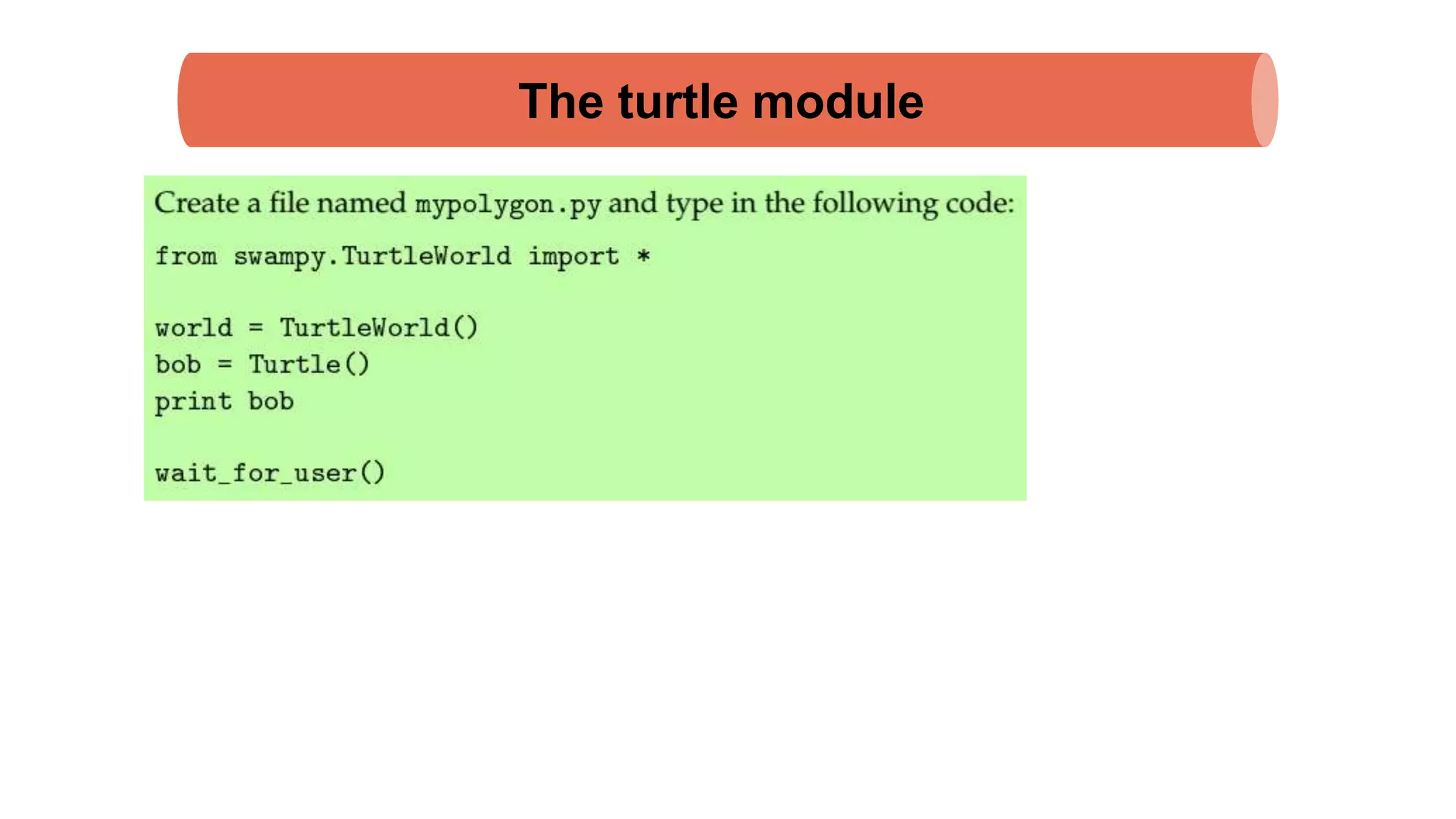
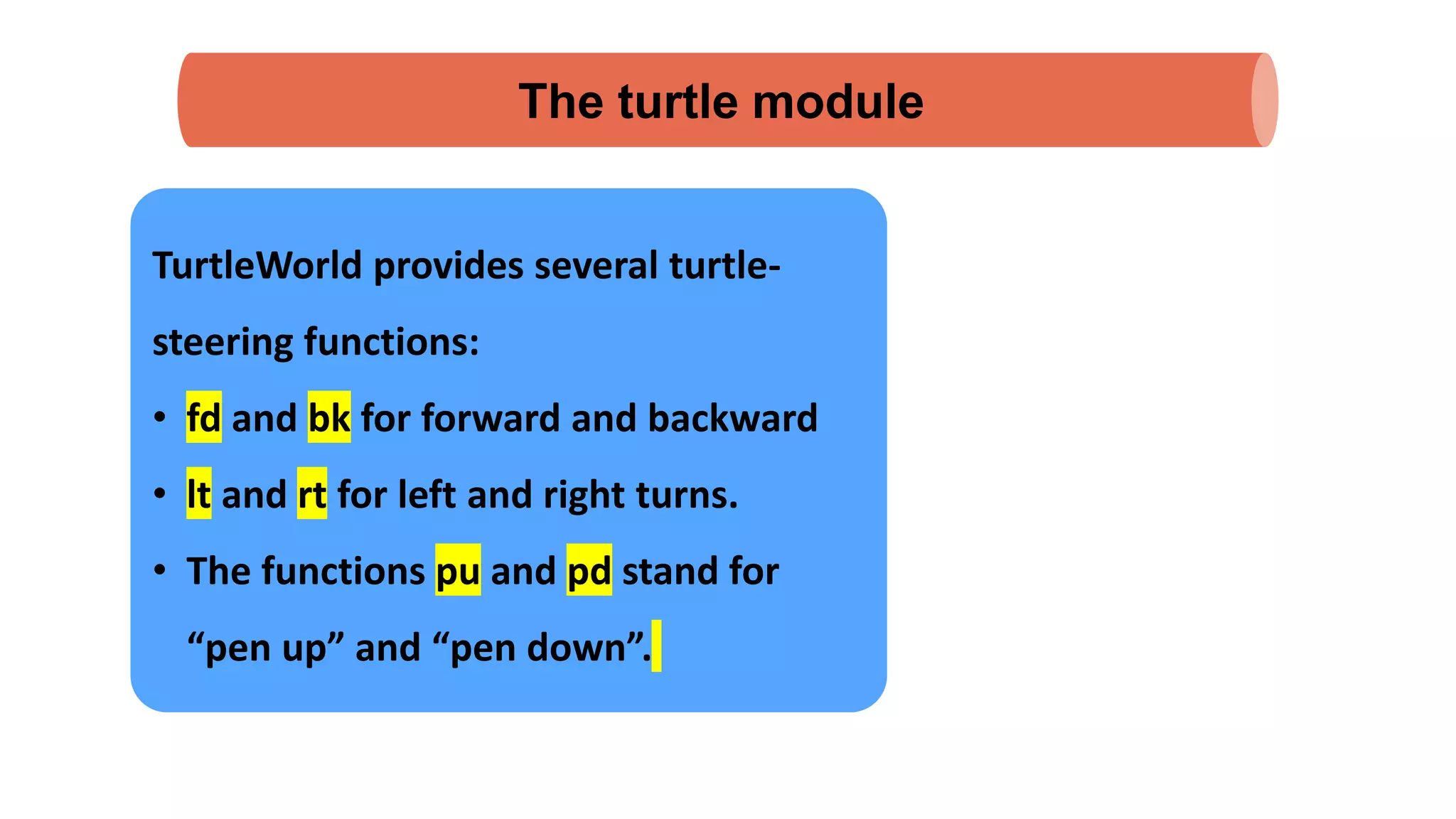
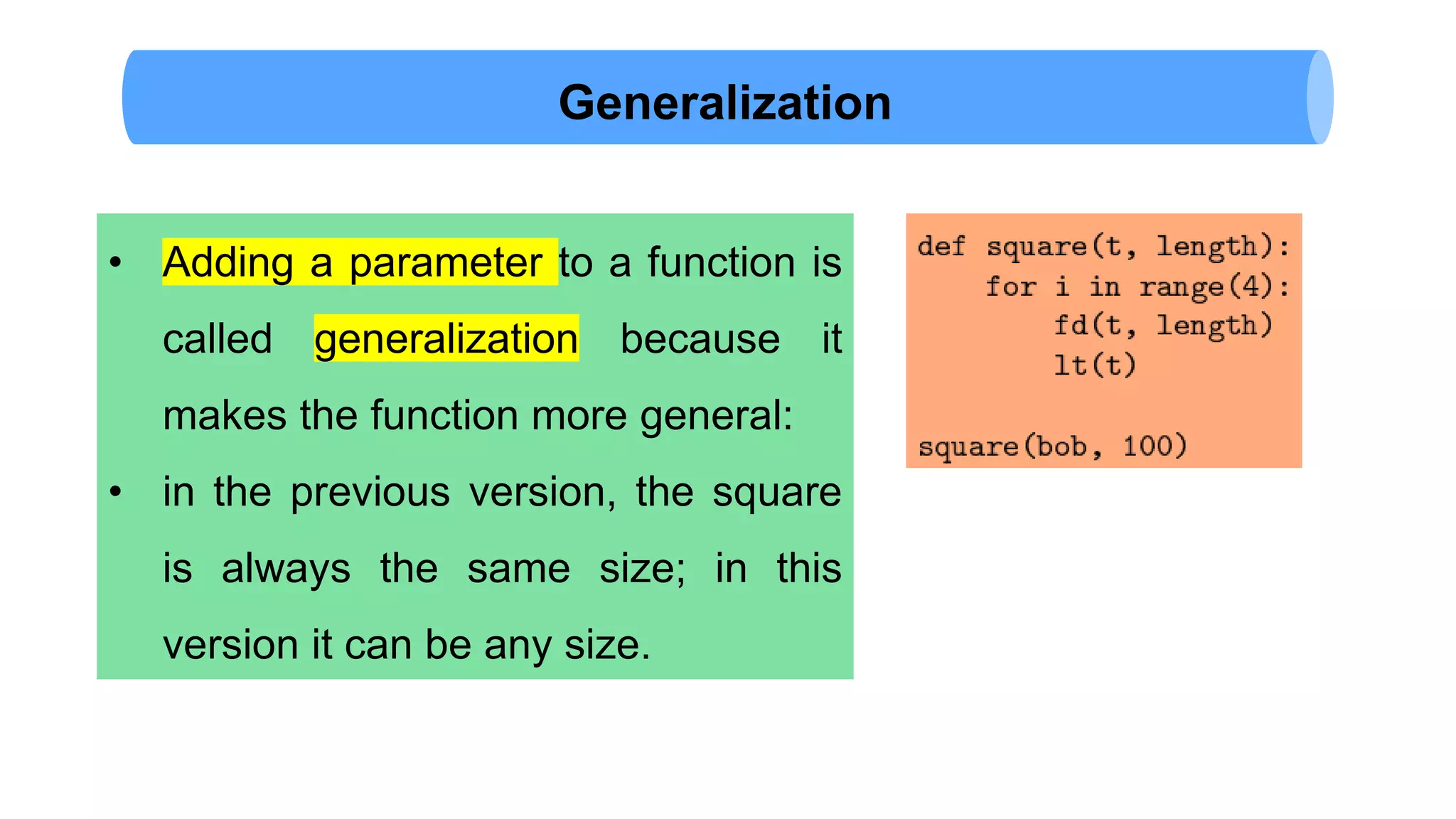
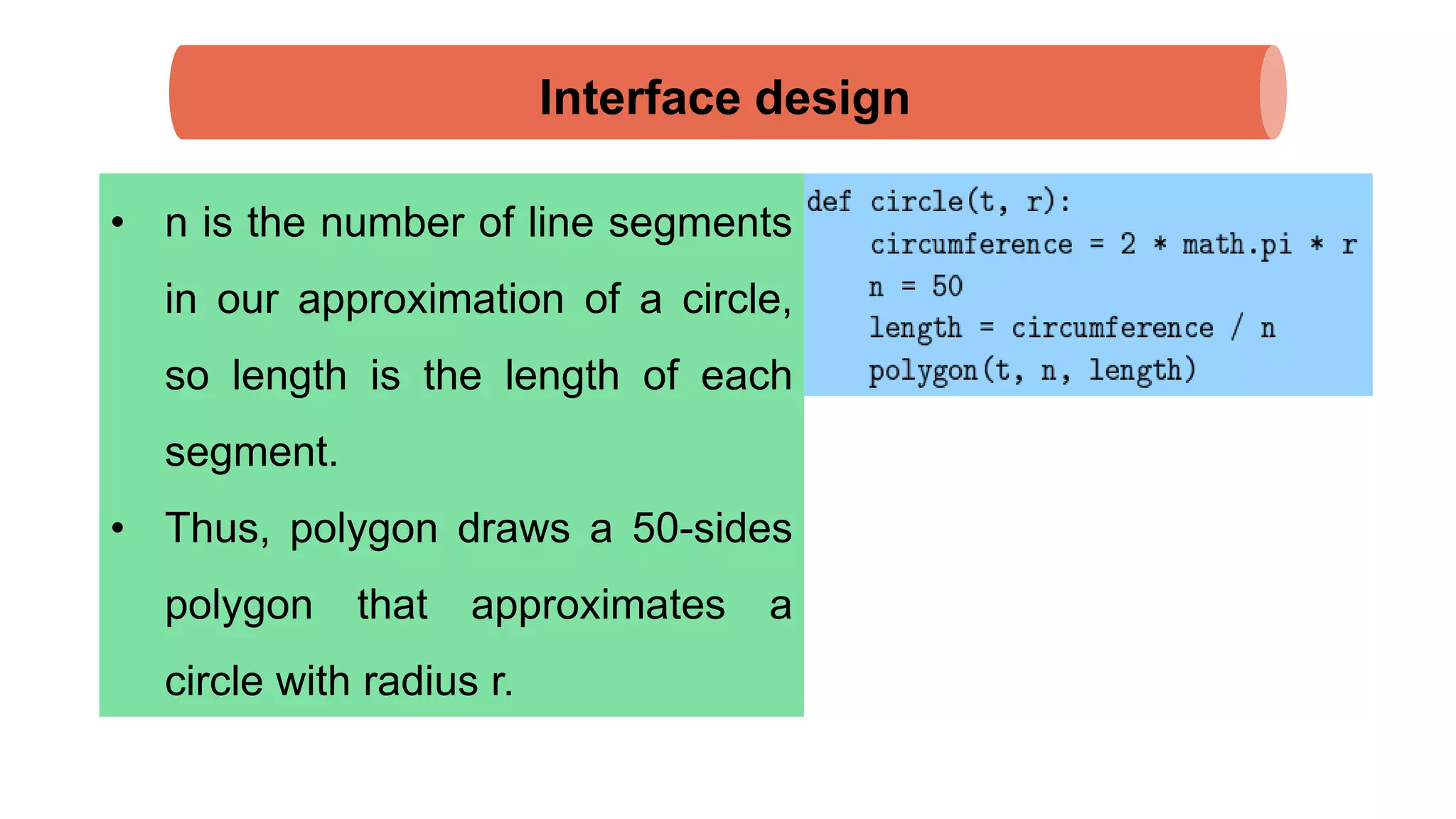
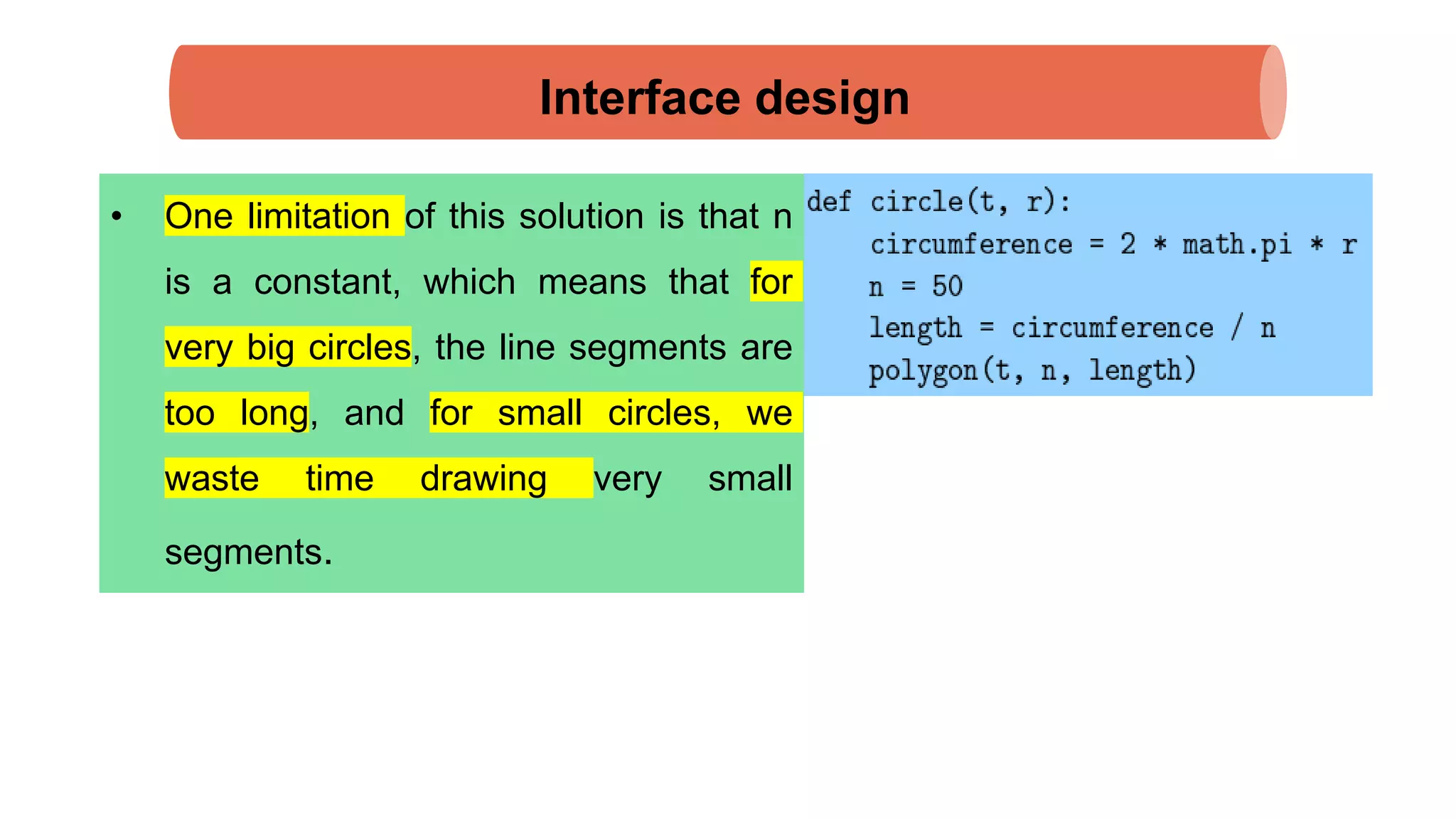
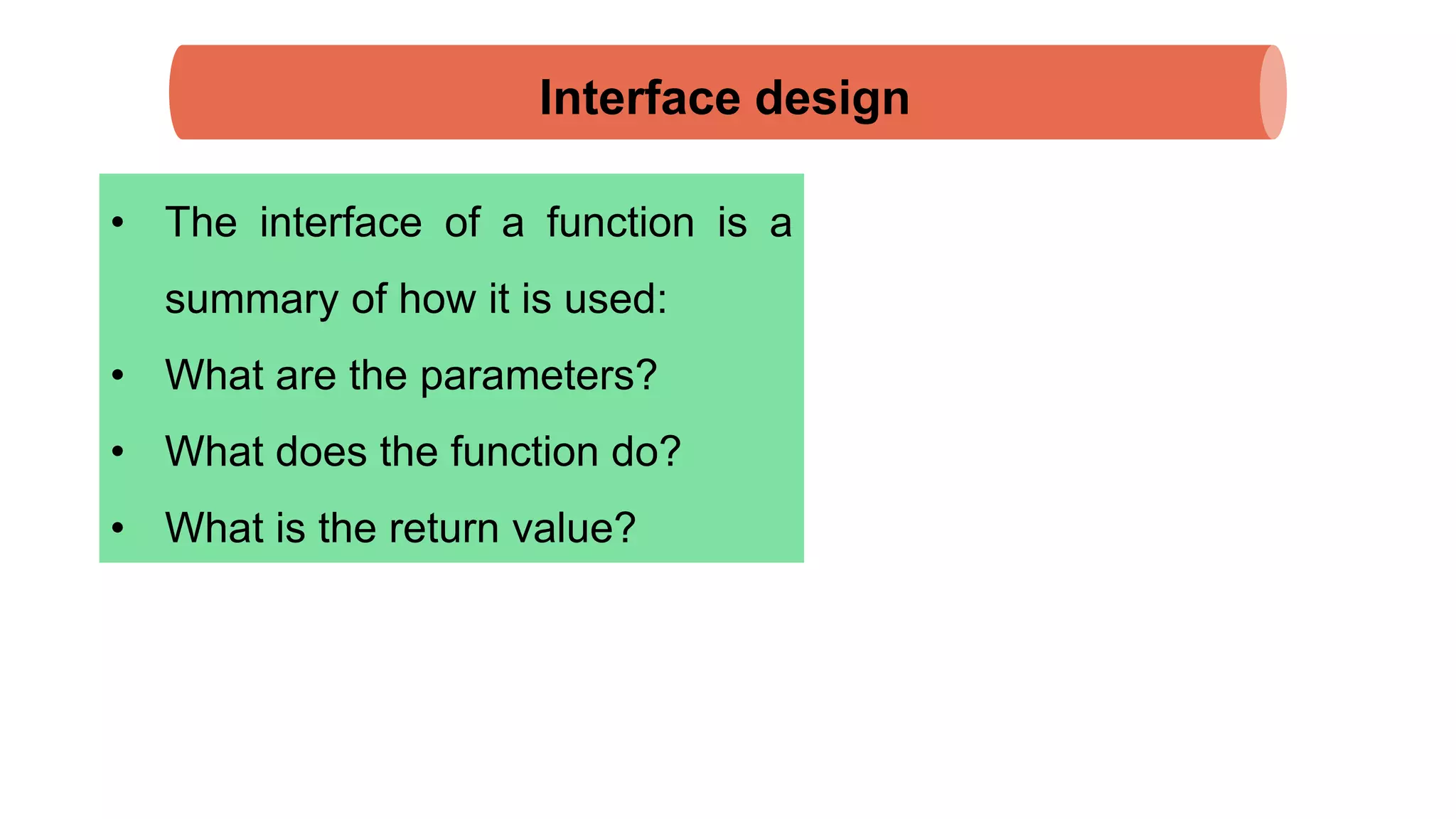
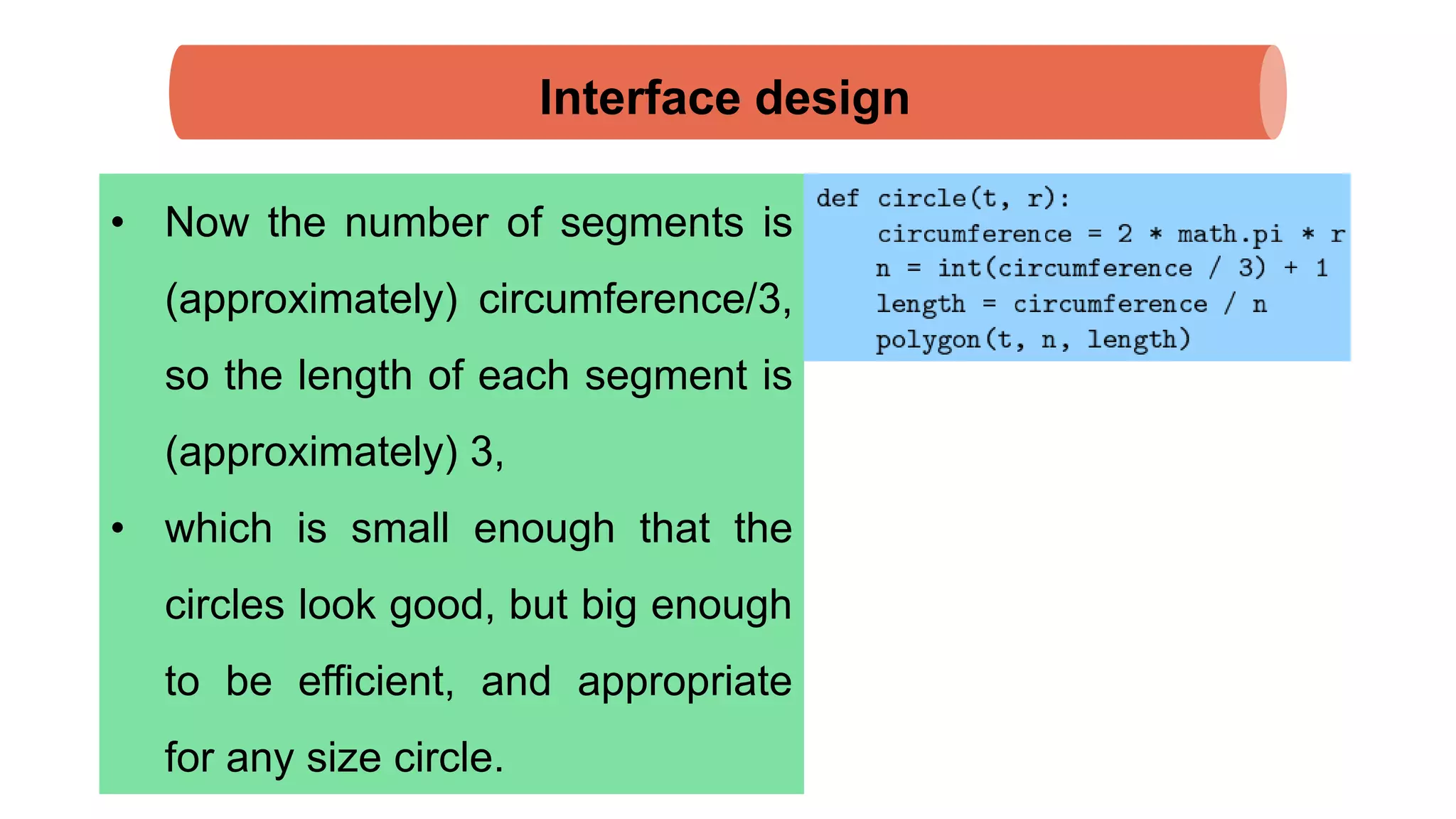
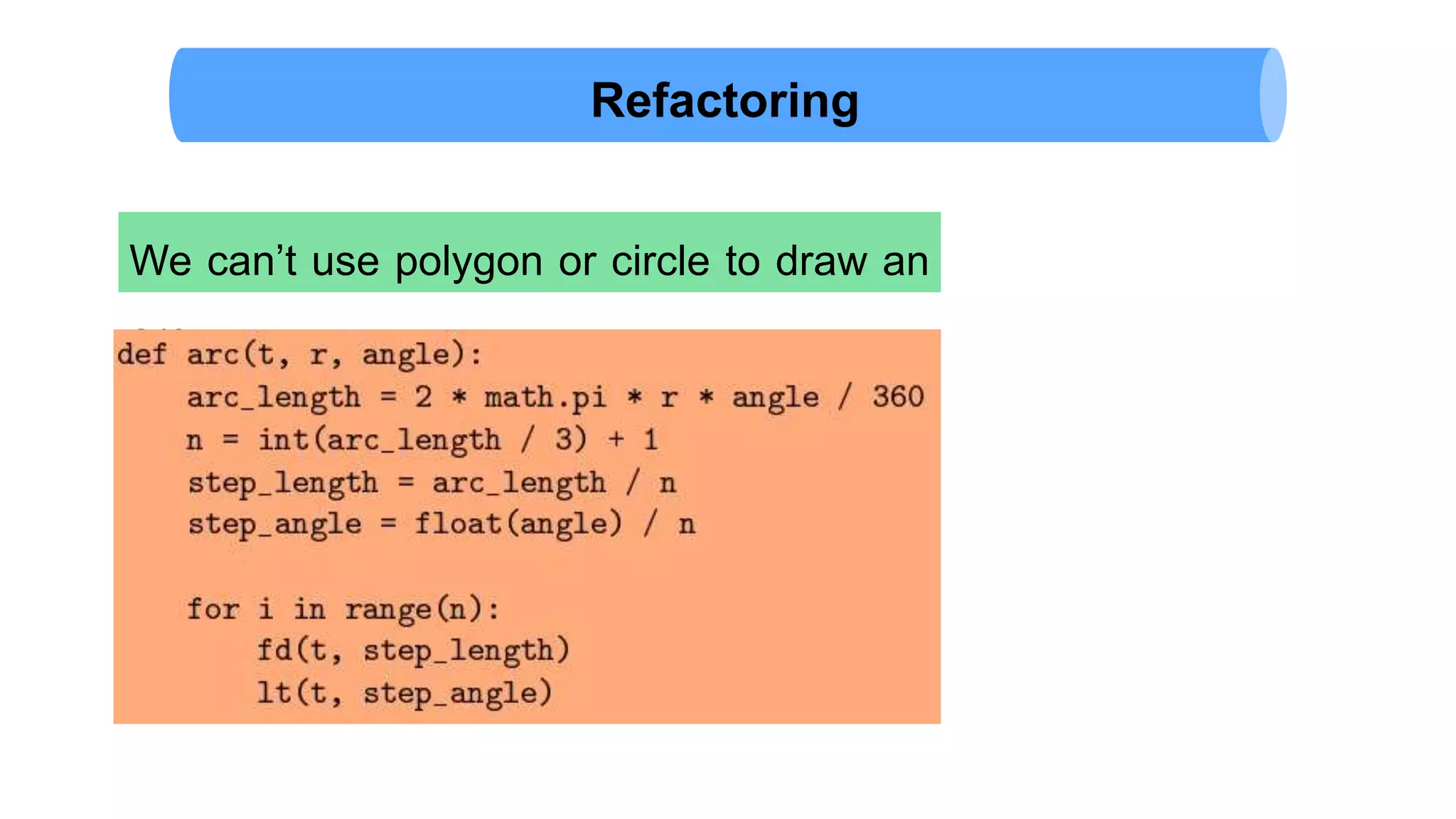
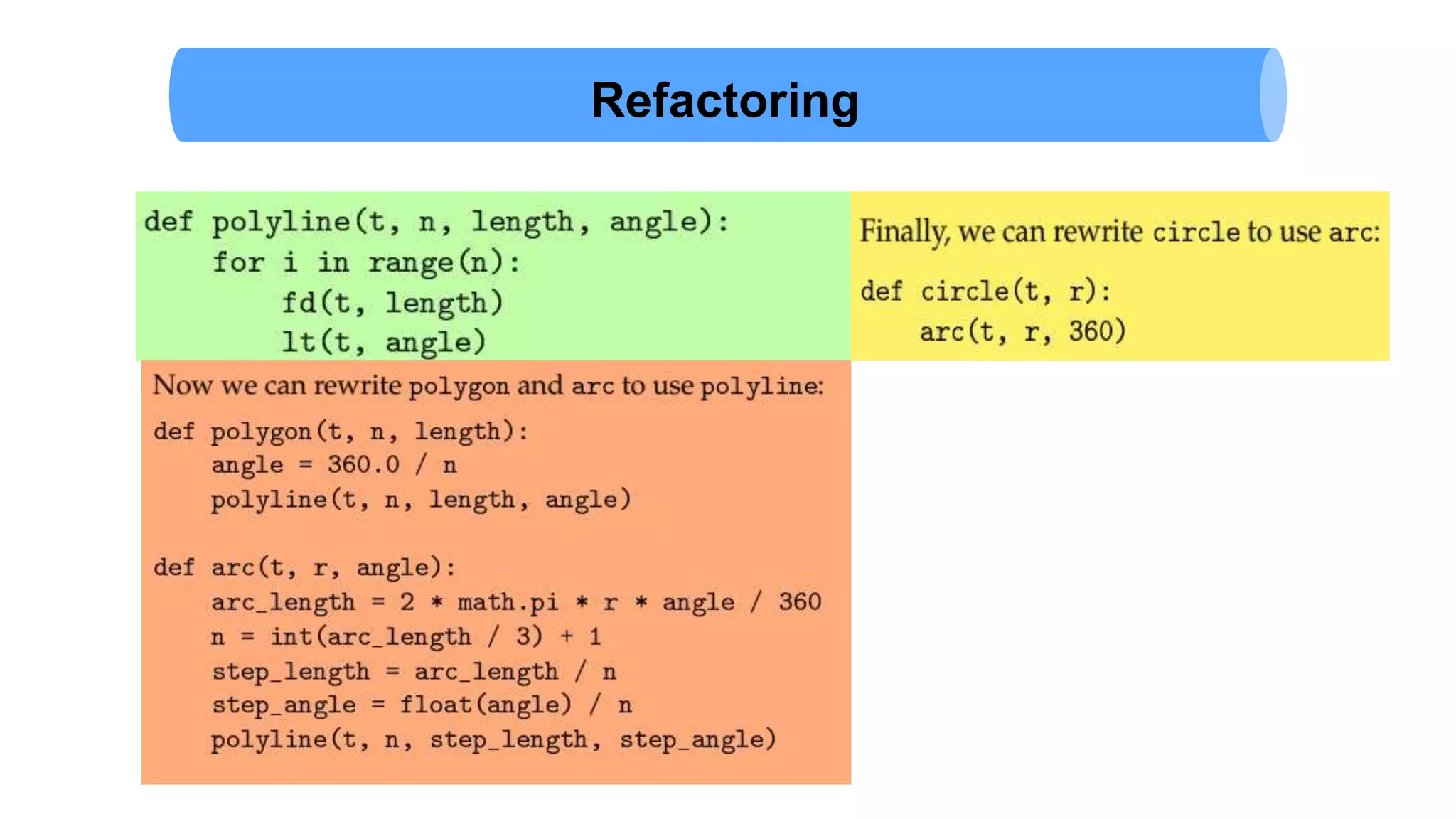
The document discusses Python's turtle module which allows drawing lines by steering turtles around the screen. It can be imported from the Swampy package. The turtle module provides functions like fd, bk, lt, rt for moving the turtle forward, backward, left, right. Simple repetition and encapsulation techniques are demonstrated. Generalization is discussed by adding parameters to functions. Interface design principles around parameters and return values are covered. Refactoring existing code and adding docstrings for documentation are also mentioned.