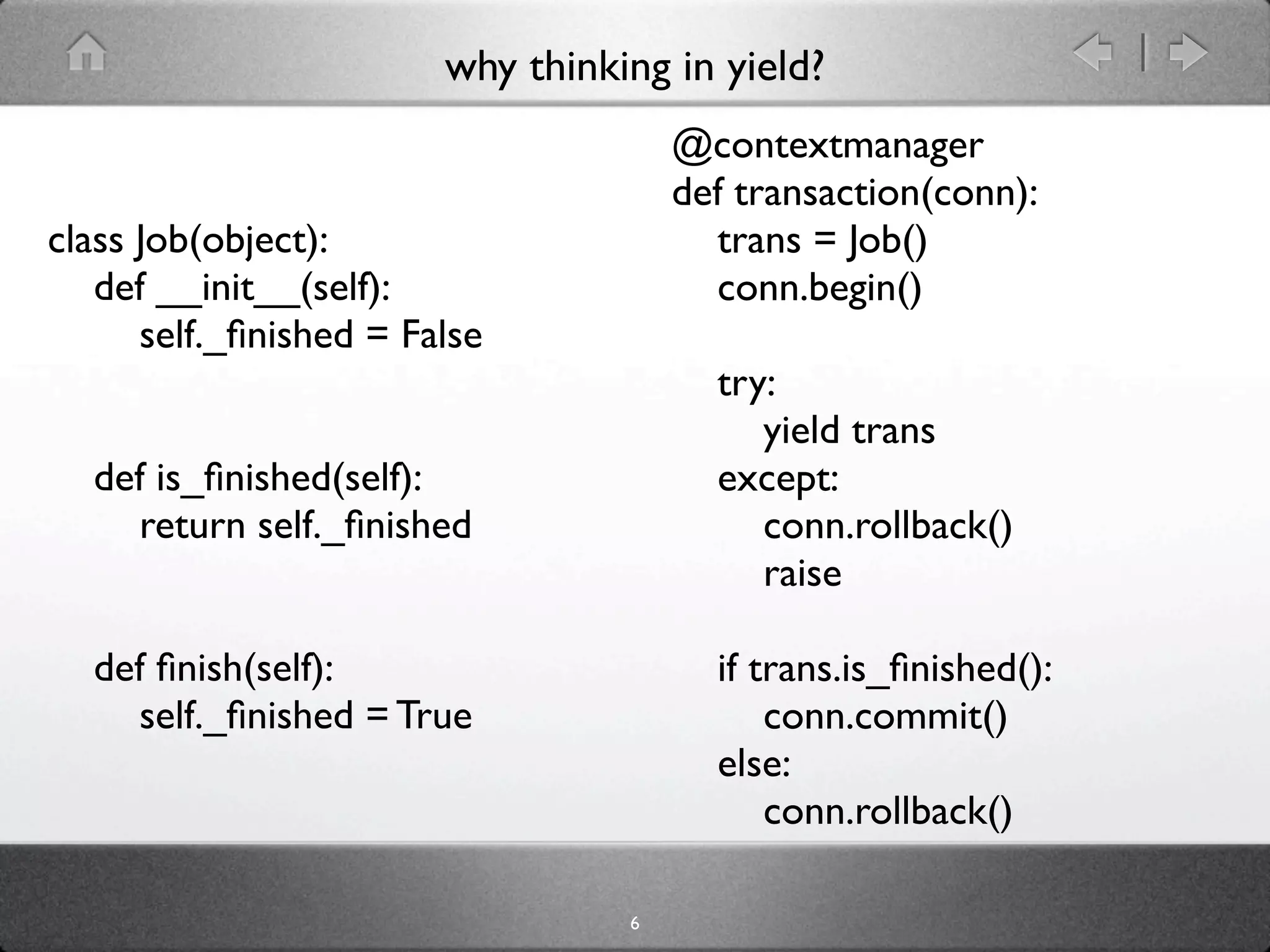
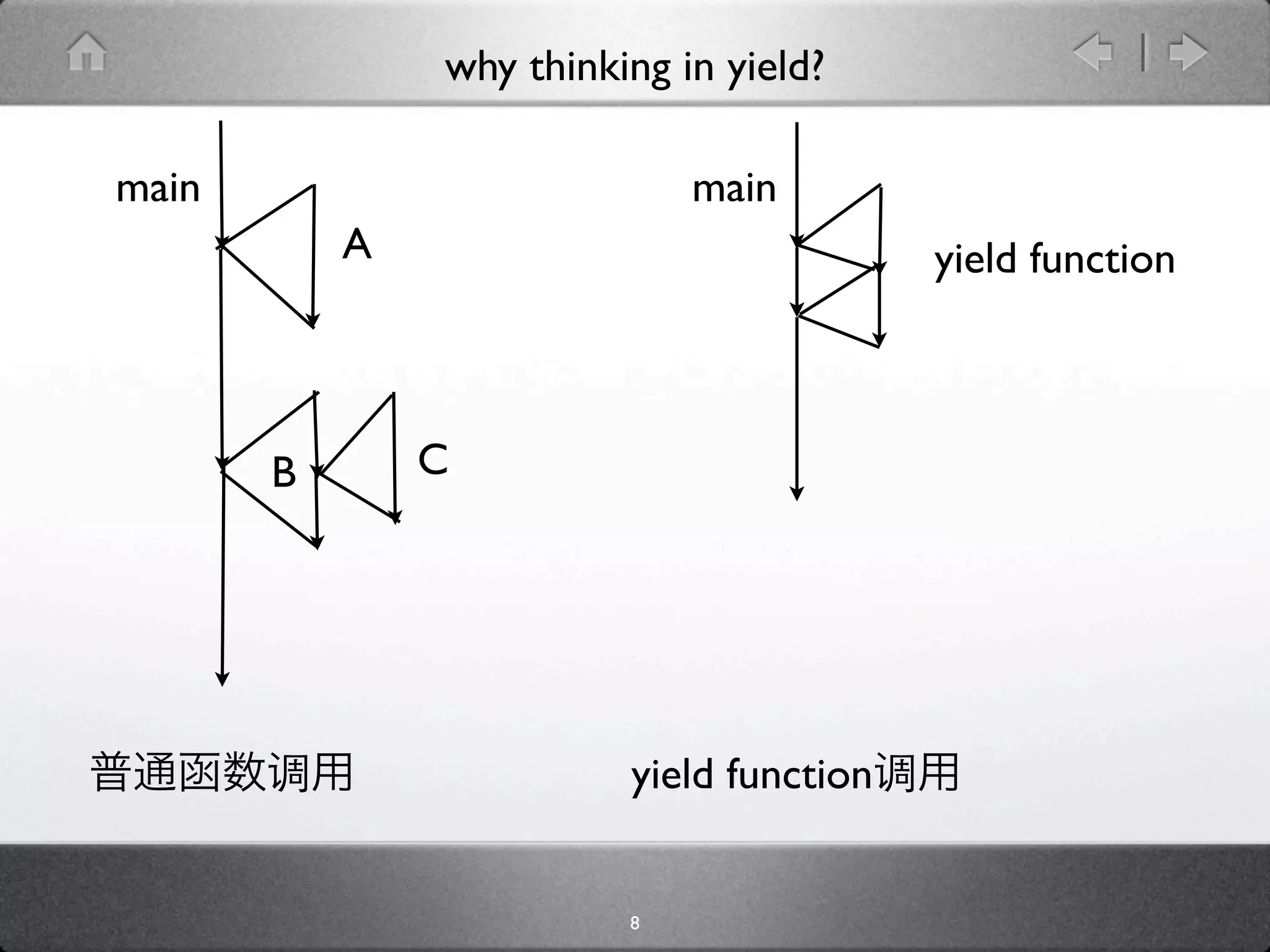
The document discusses yield in Python and how it allows functions to act as generators by using the yield keyword instead of return, enabling generator functions to control execution by yielding values and resuming at the point after each yield. It explains how generators are created and how yield allows suspending and resuming execution of generator functions to implement features like coroutines, trampolines to avoid recursion limits, and the with statement in Python.


















![yield
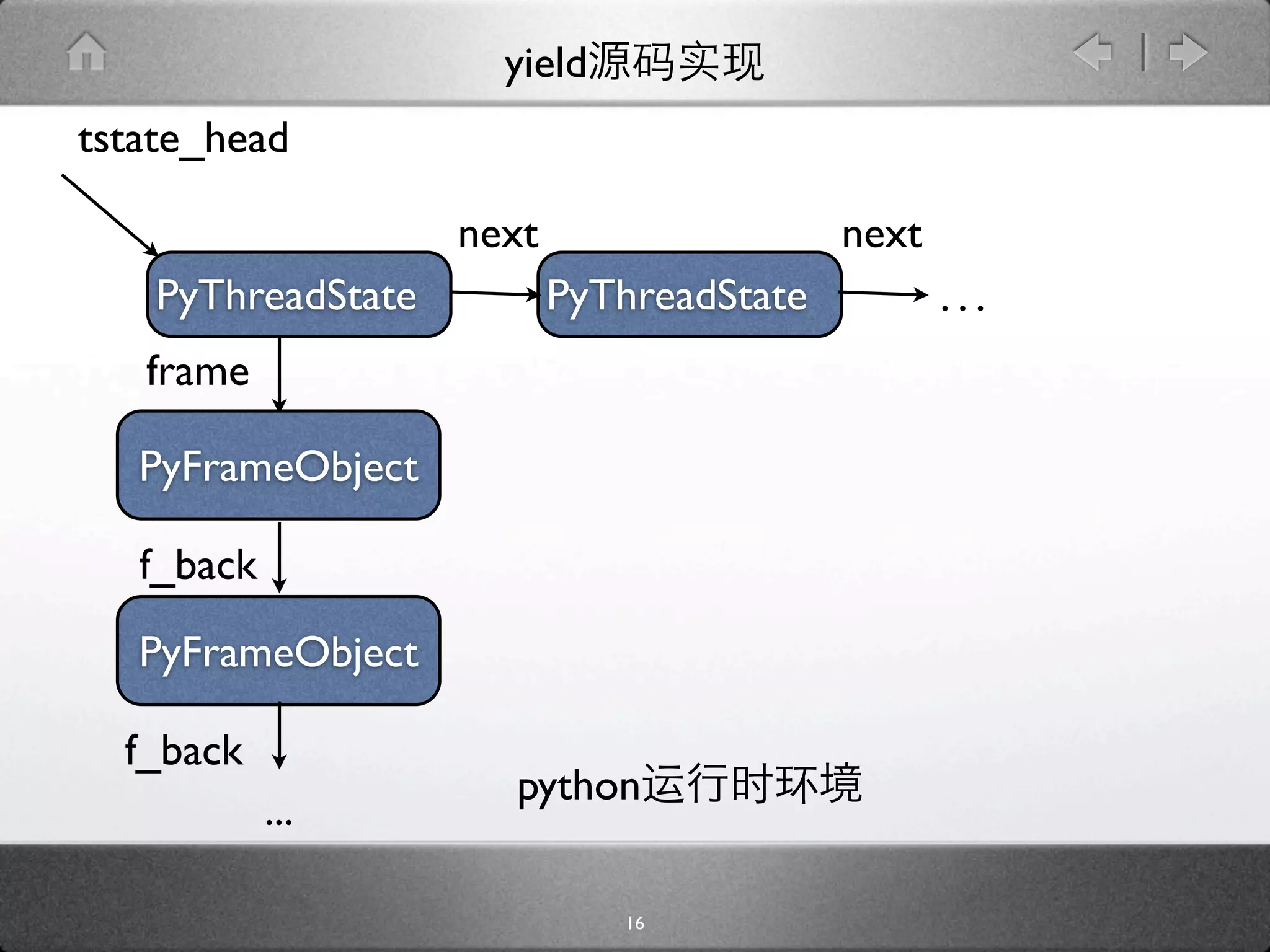
[frameobject.c]
typedef struct {
...
struct _frame *f_back;
PyCodeObject *f_code;
PyObject *f_builtins;
PyObject *f_globals;
PyObject *f_locals;
PyObject *f_valuestack;
PyObject *f_stacktop;
...
int f_lasti;
...
} PyFrameObject;
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-23-2048.jpg)
![yield
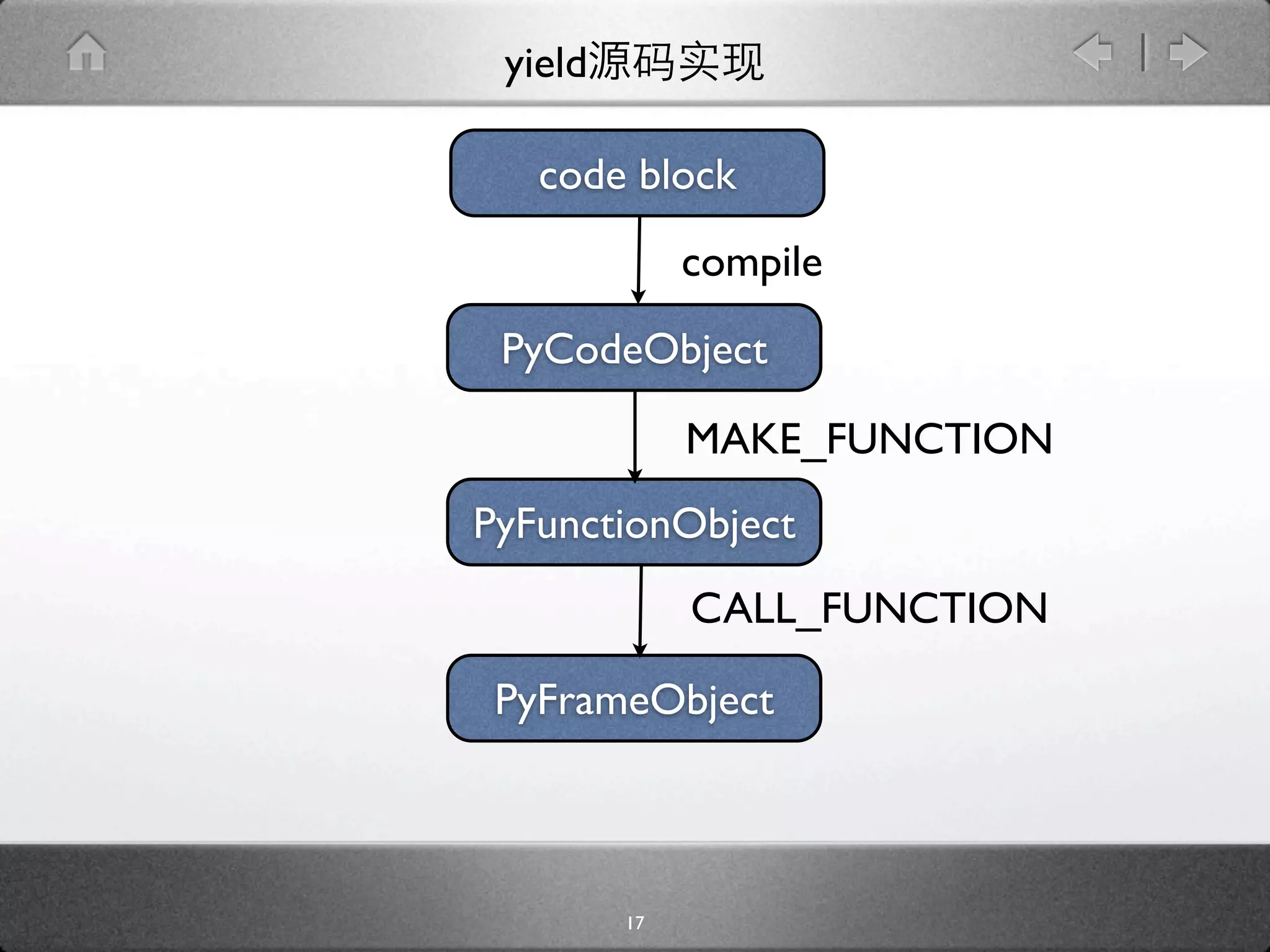
[codeobject.c]
typedef struct {
...
int co_flags;
...
PyObject *co_code;
PyObject *co_consts;
PyObject *co_names;
...
} PyCodeObject;
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-24-2048.jpg)
![yield
[a.py] [b.py]
def f(): def f():
return “hello world” yield “hello world”
f() f()
PyCodeObject <==> code block
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-25-2048.jpg)



![yield
[ceval.c] CALL_FUNCTION
f = PyFrame_New(tstate, co, globals, locals);
...
if (co->co_flags & CO_GENERATOR) {
...
f->f_back = NULL;
...
return PyGen_New(f);
}
retval = PyEval_EvalFrameEx(f,0);
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-29-2048.jpg)
![yield
[frameobject.c]
PyFrame_New(PyThreadState *tstate,
PyCodeObject *code, PyObject *globals, PyObject *locals){
...
PyFrameObject *back = tstate->frame;
PyFrameObject *f;
f = PyObject_GC_Resize(PyFrameObject, f, extras);
...
f->f_code = code;
...
f->f_back = back;
f->f_tstate = tstate;
return f;
}
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-30-2048.jpg)
![yield
[ceval.c]
PyObject *PyEval_EvalFrameEx(PyFrameObject *f,
int throwflag){
...
PyThreadState *tstate = PyThreadState_GET();
tstate->frame = f;
...
// exec opcode
...
tstate->frame = f->f_back;
return retval;
}
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-31-2048.jpg)
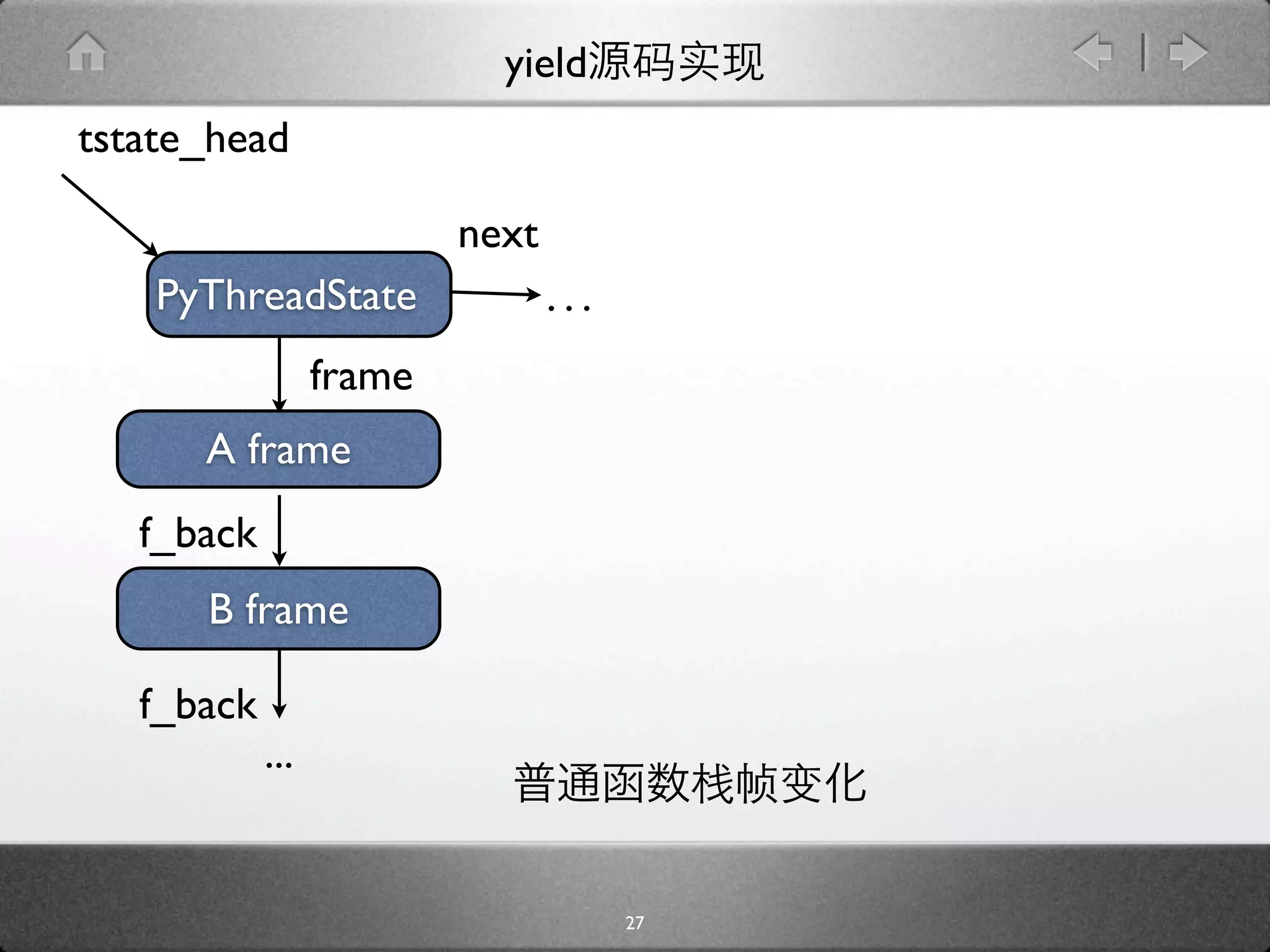
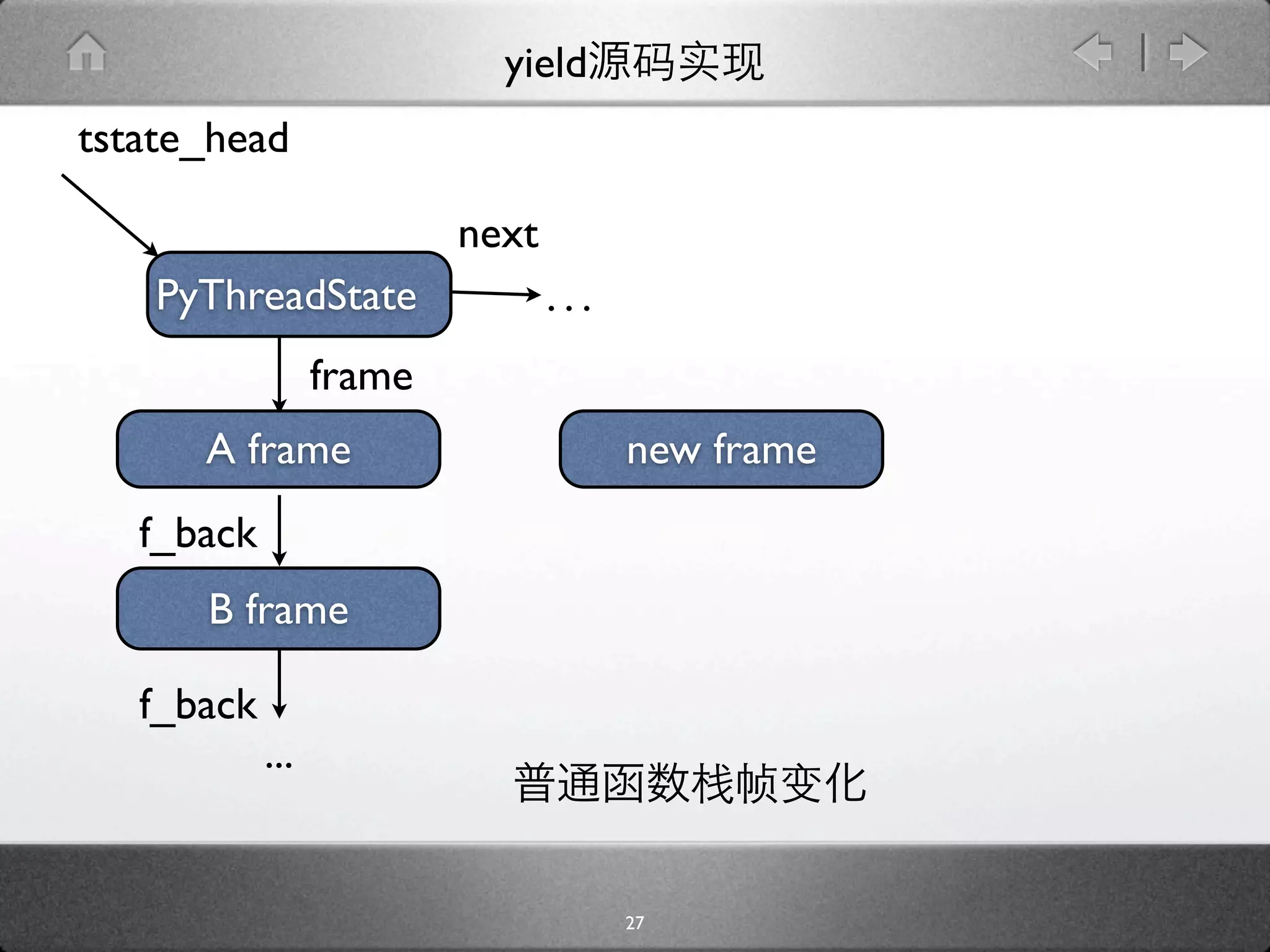
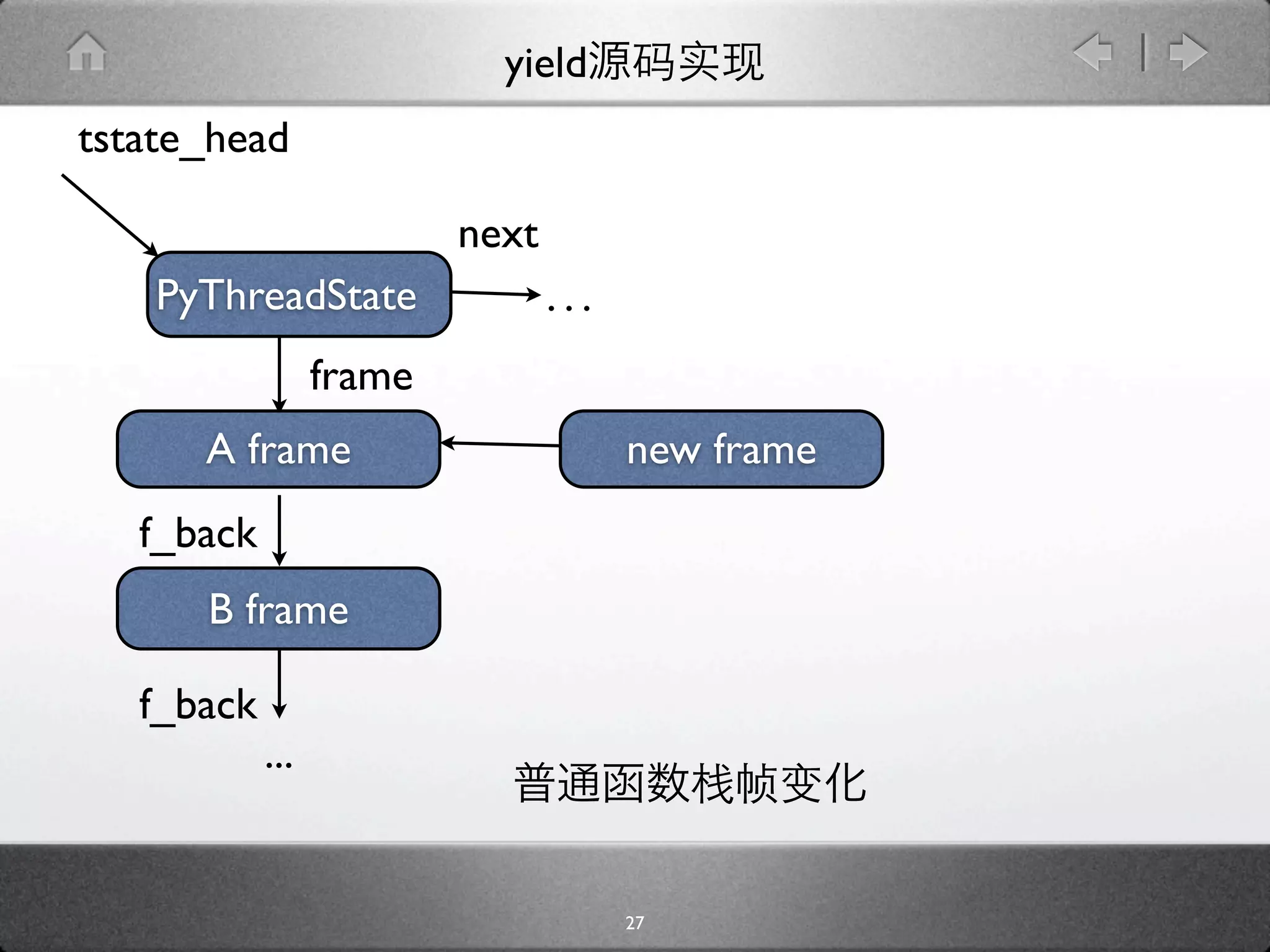
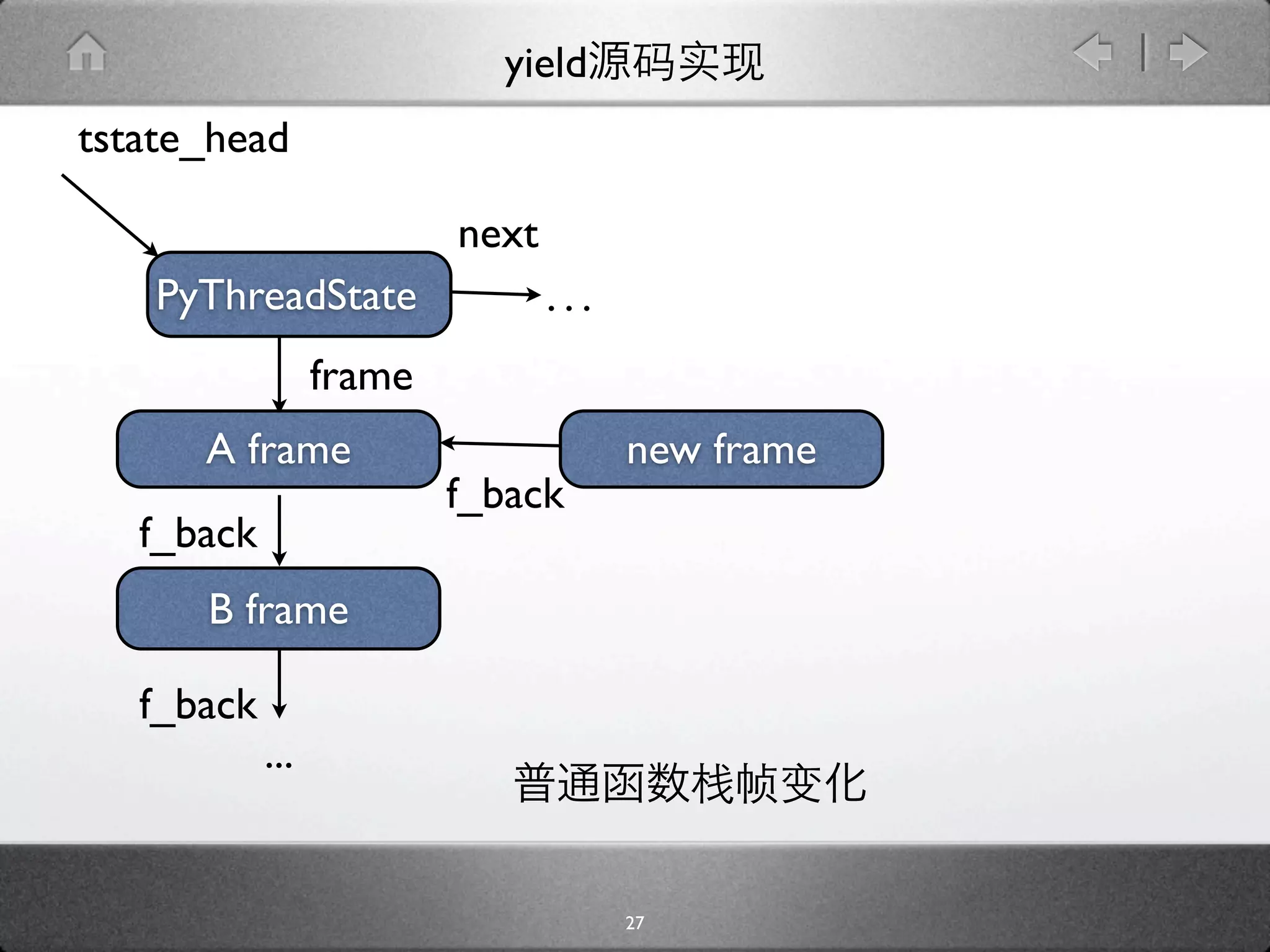
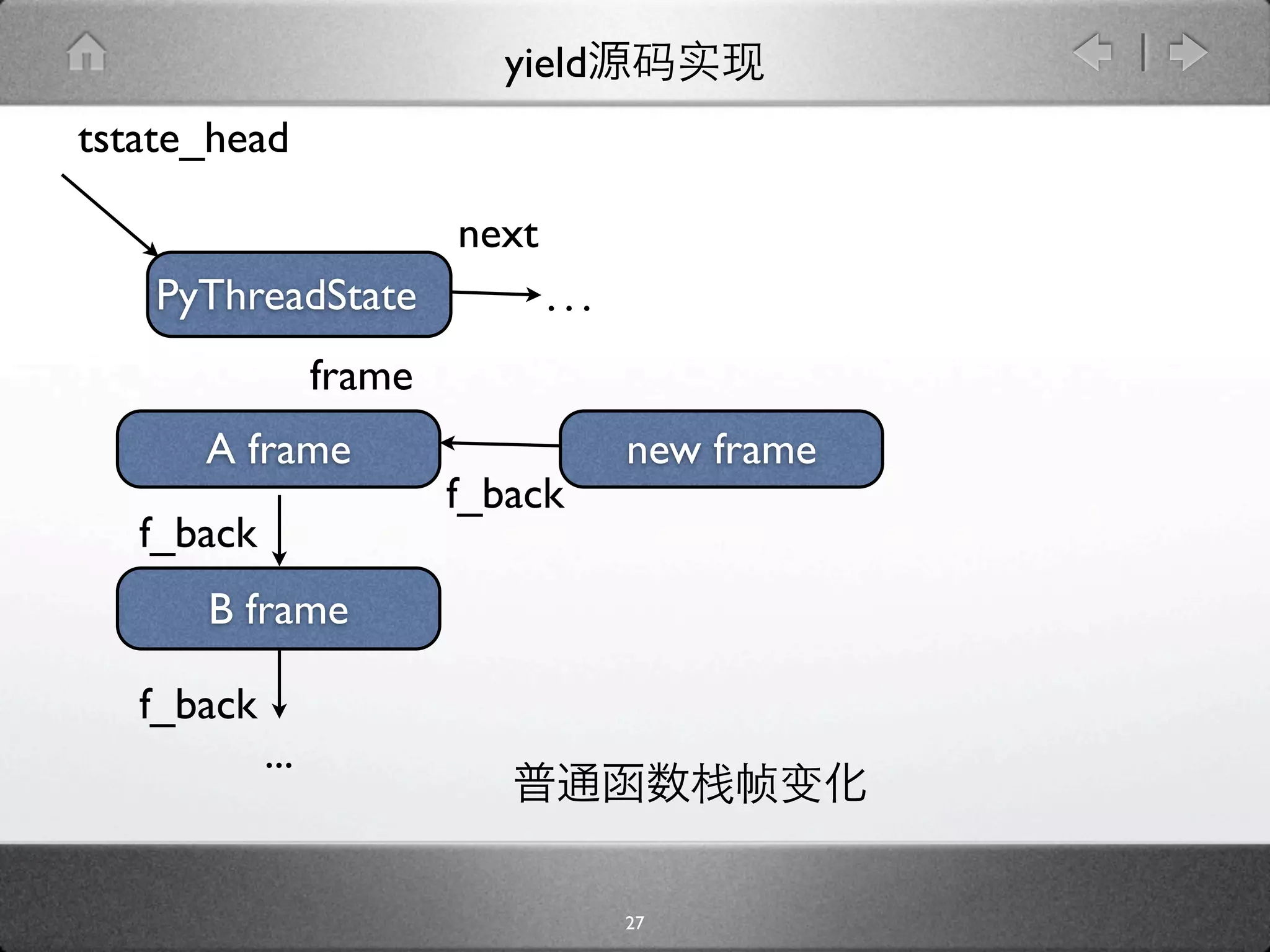
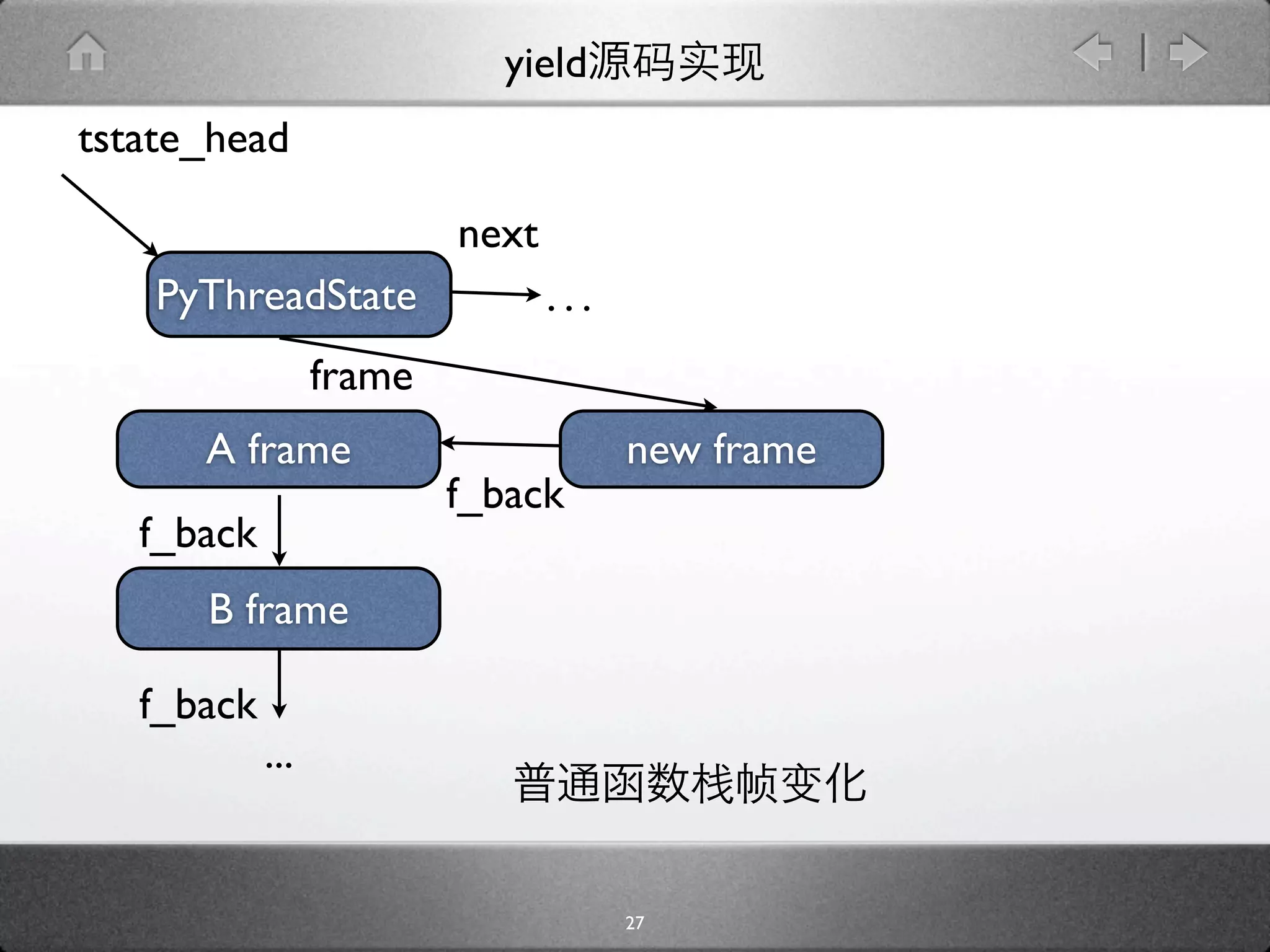
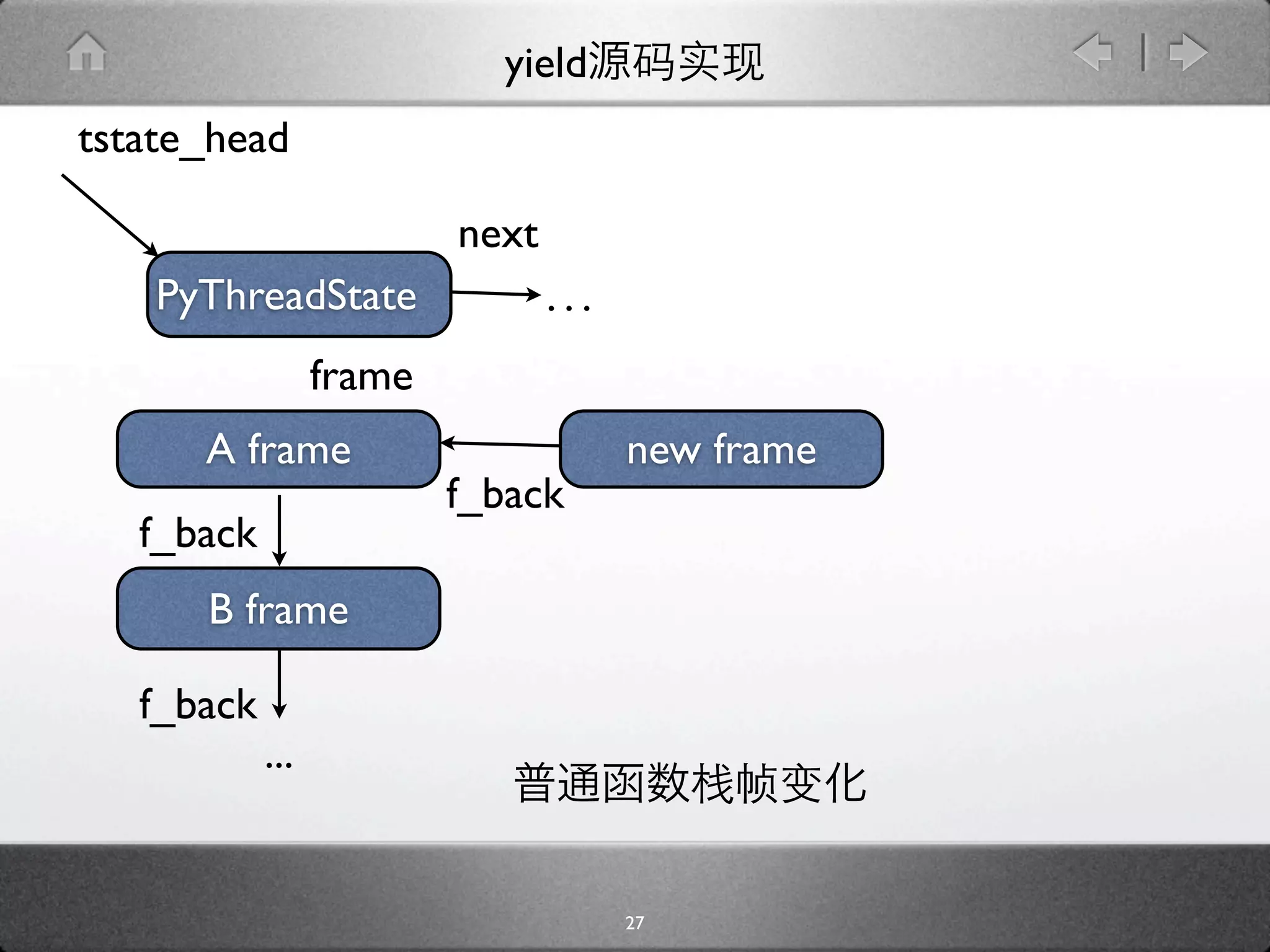
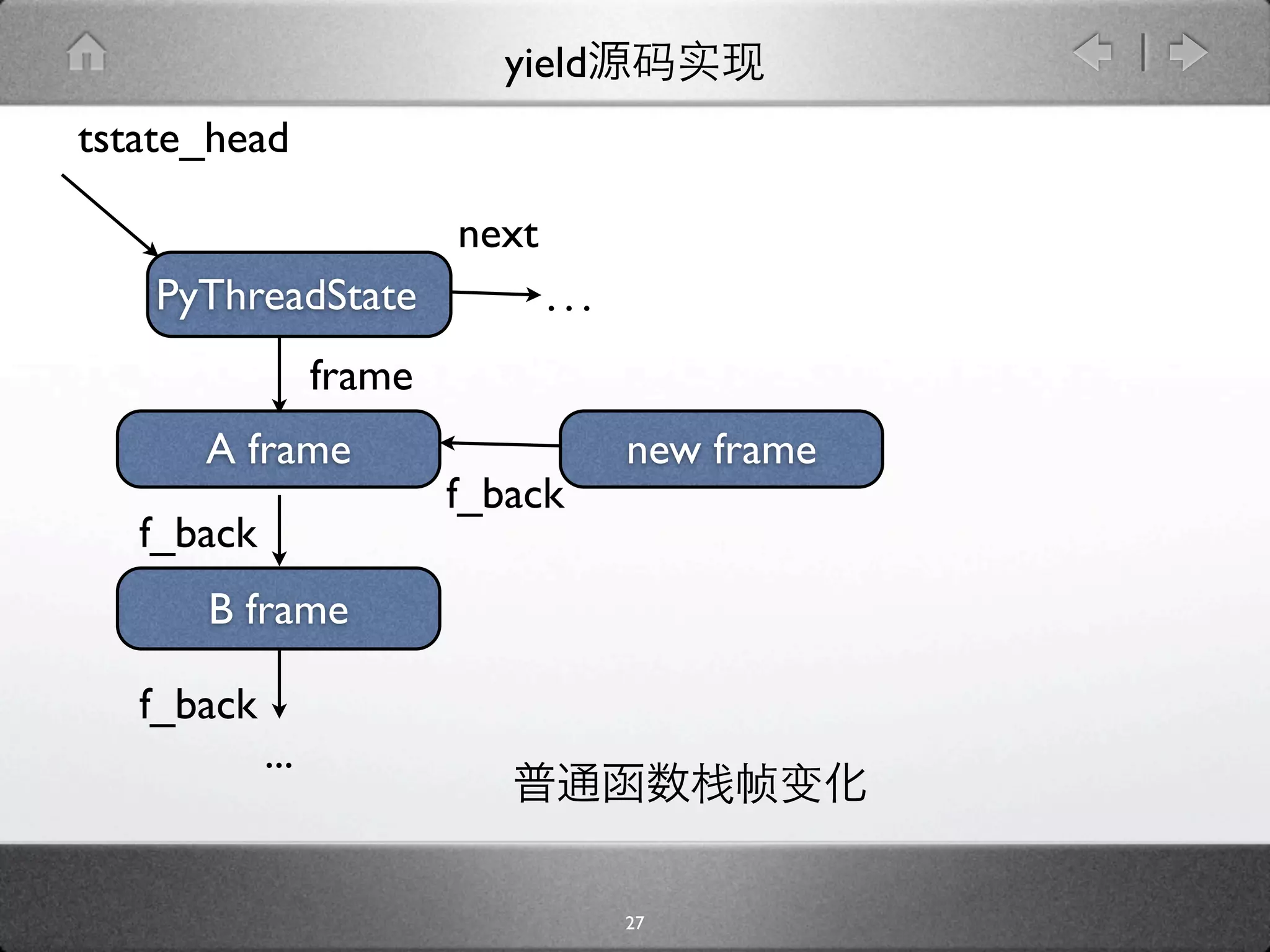
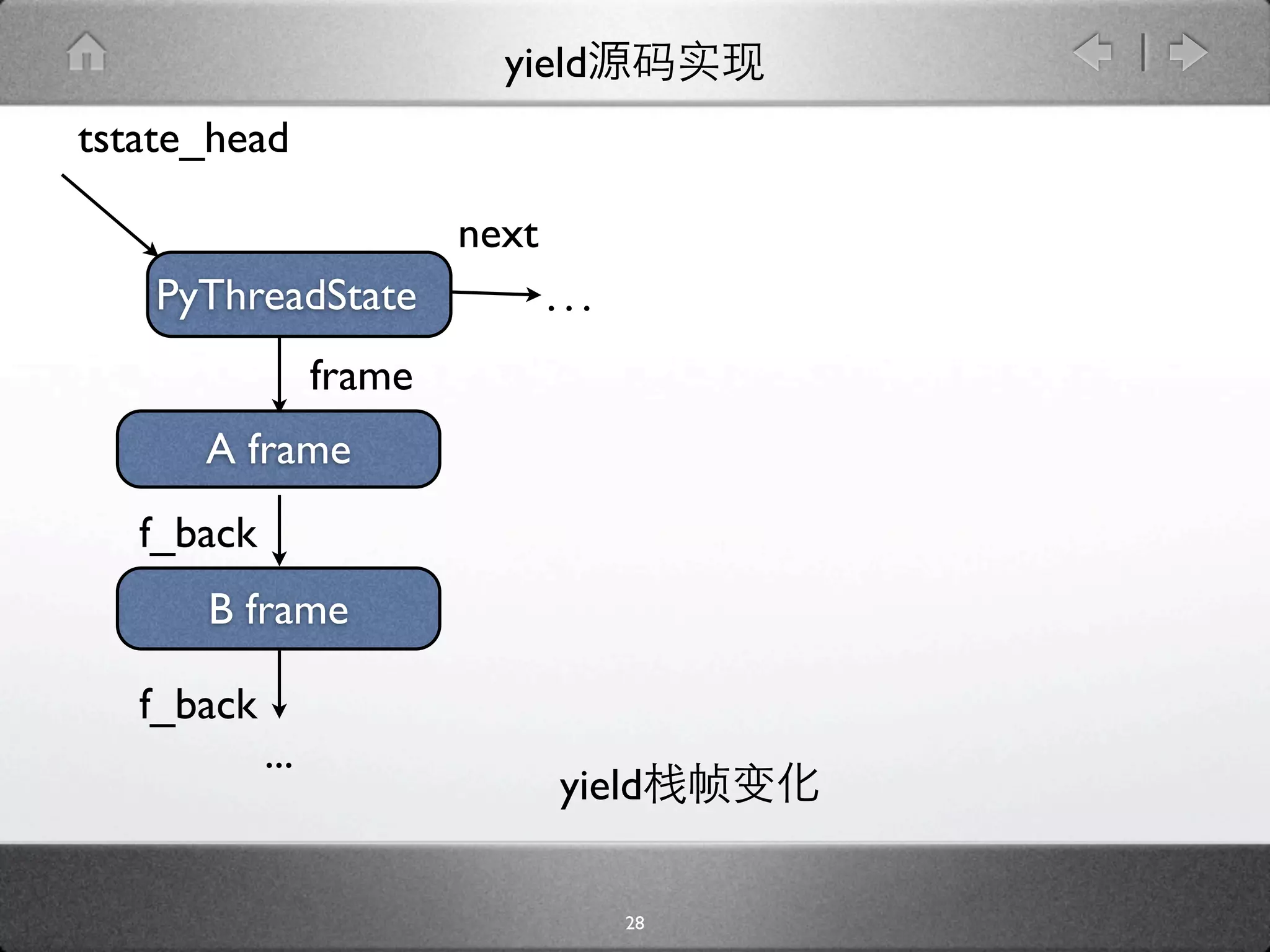
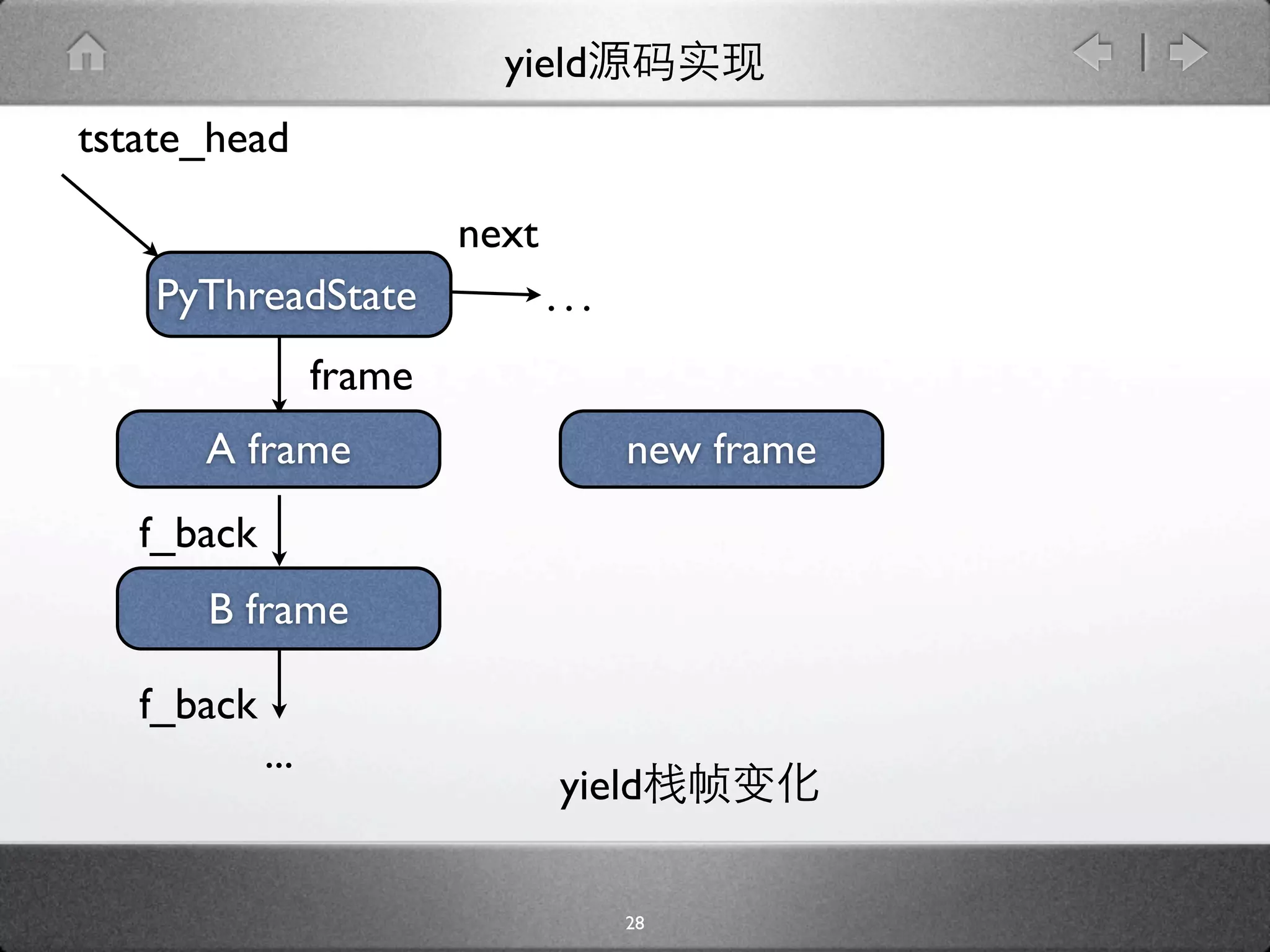
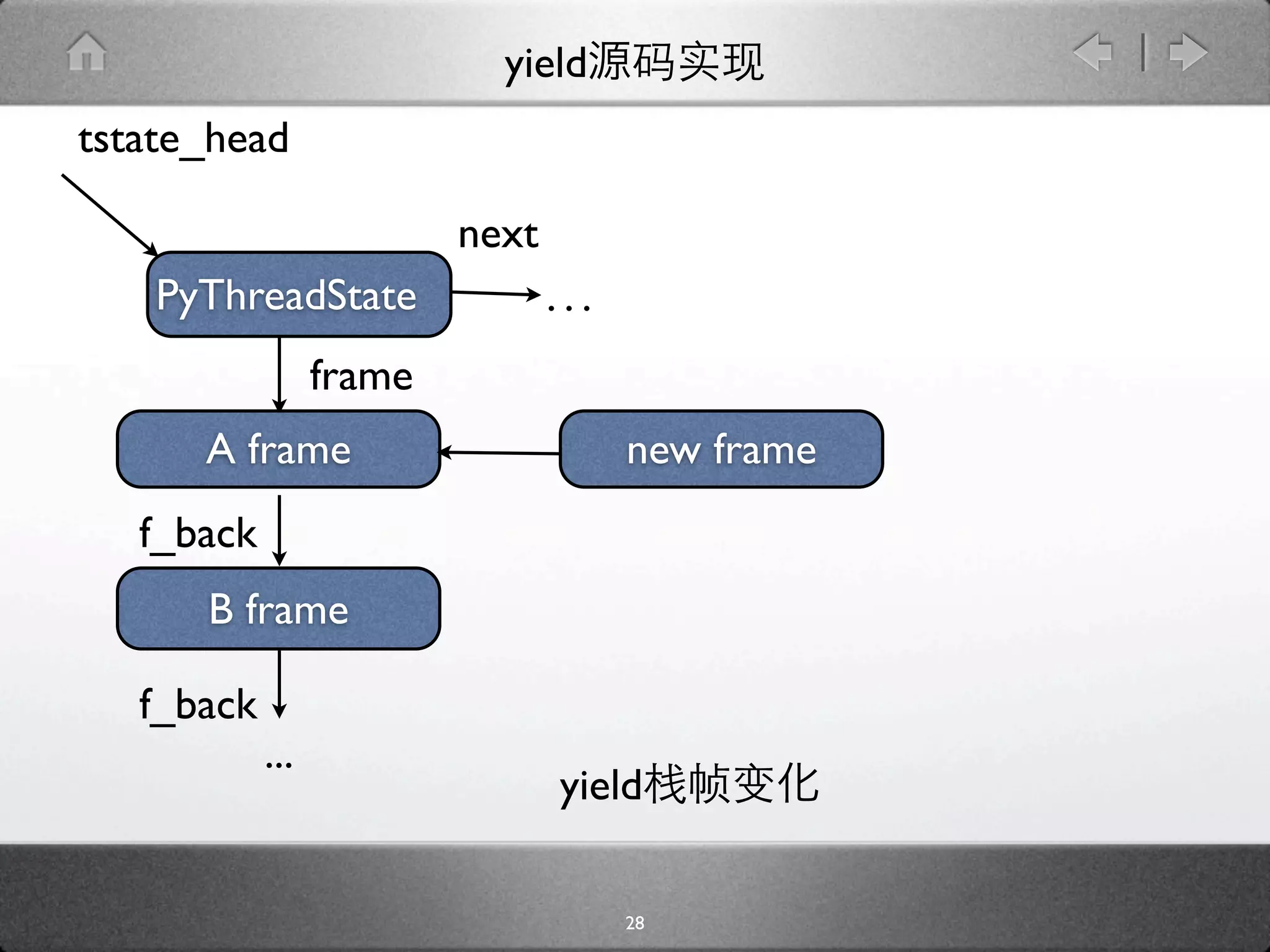
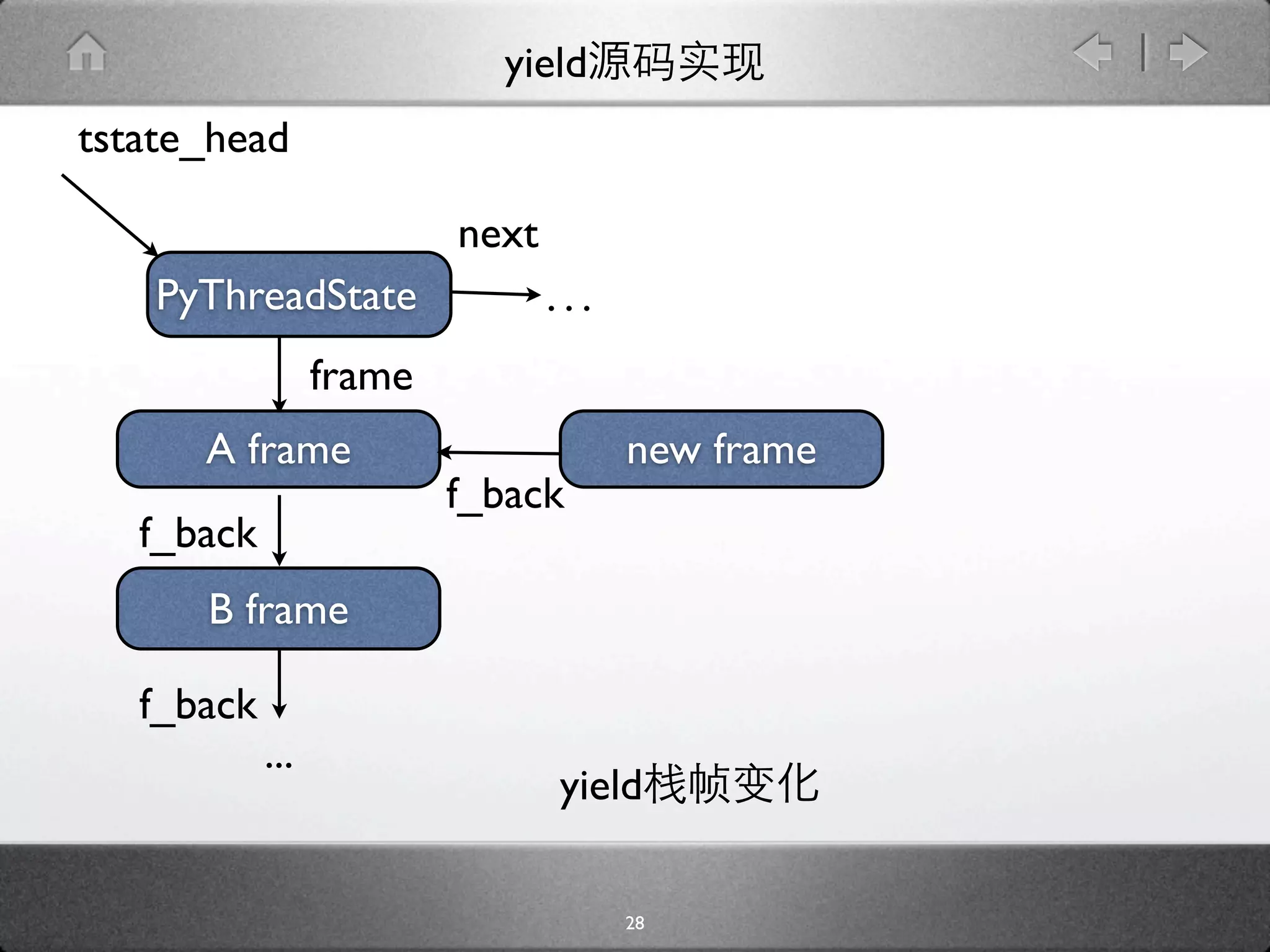
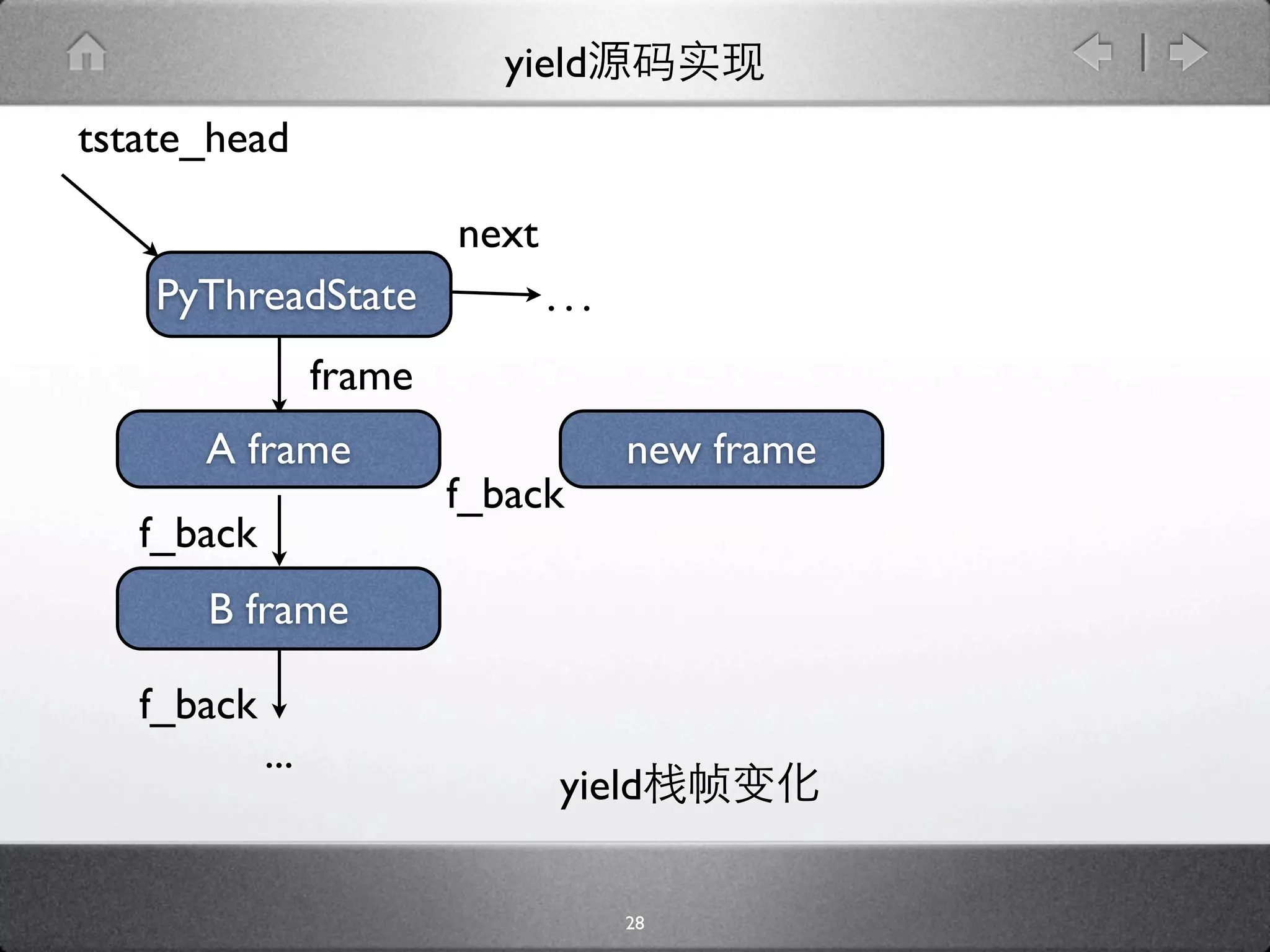
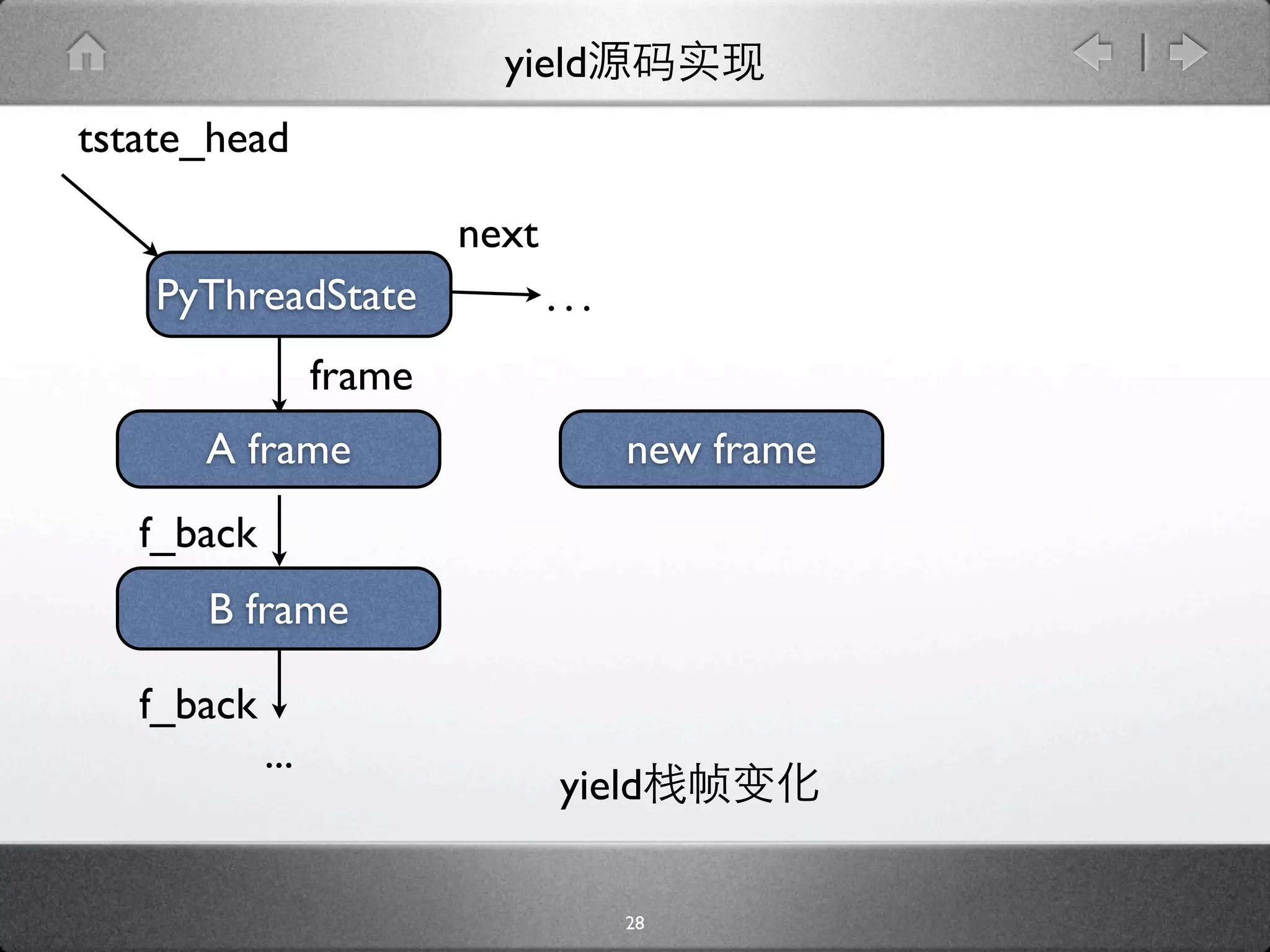
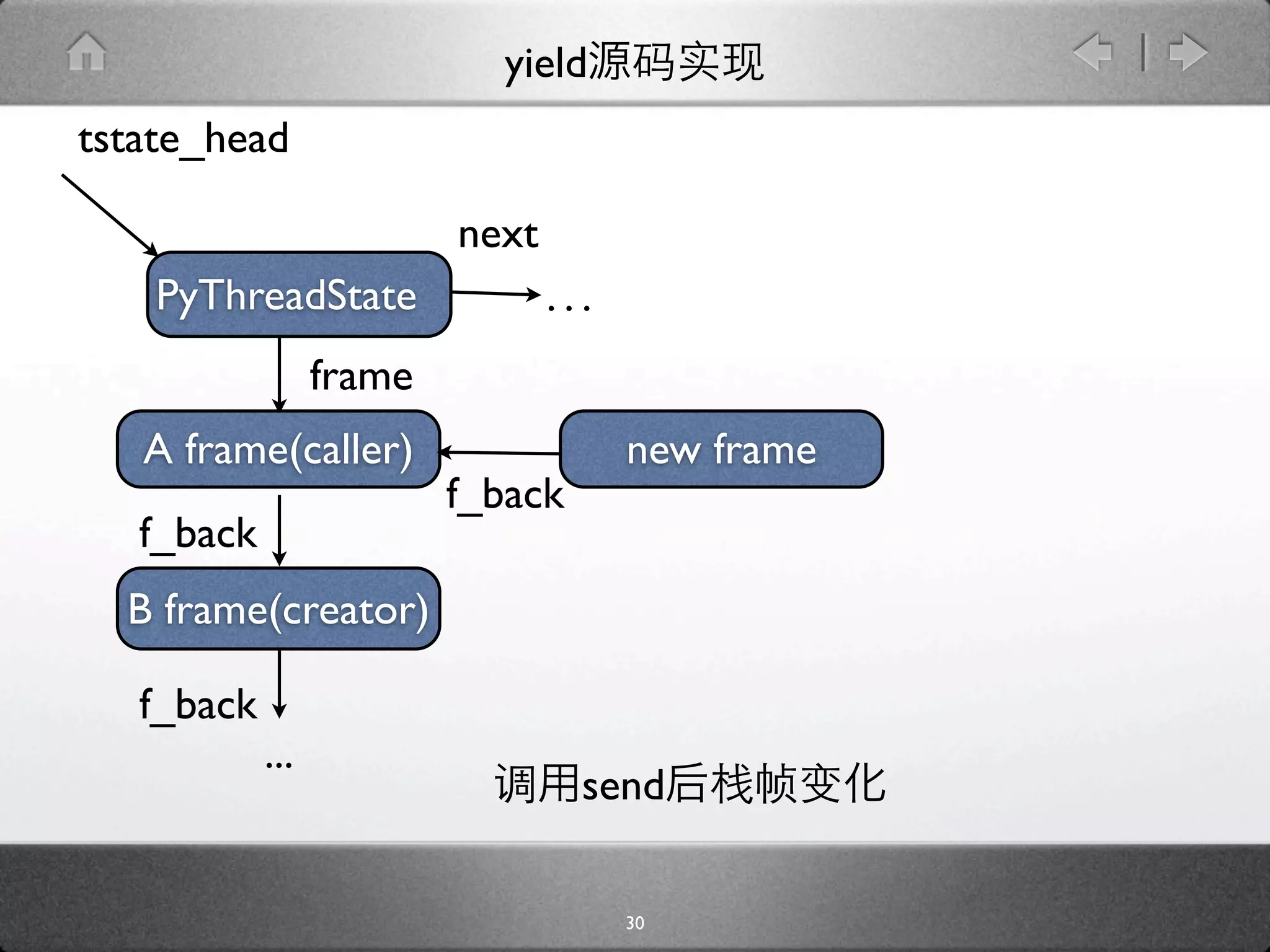
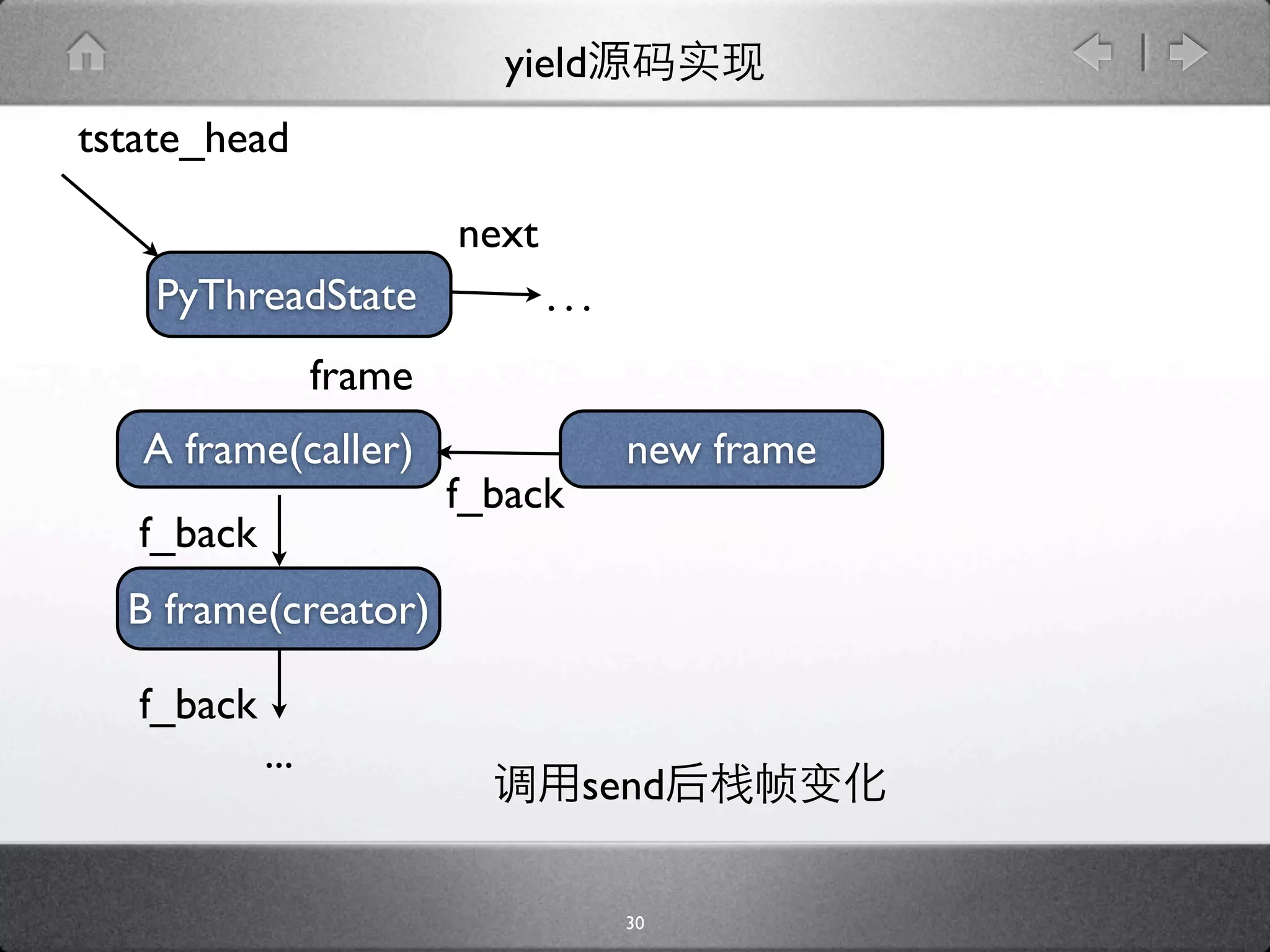
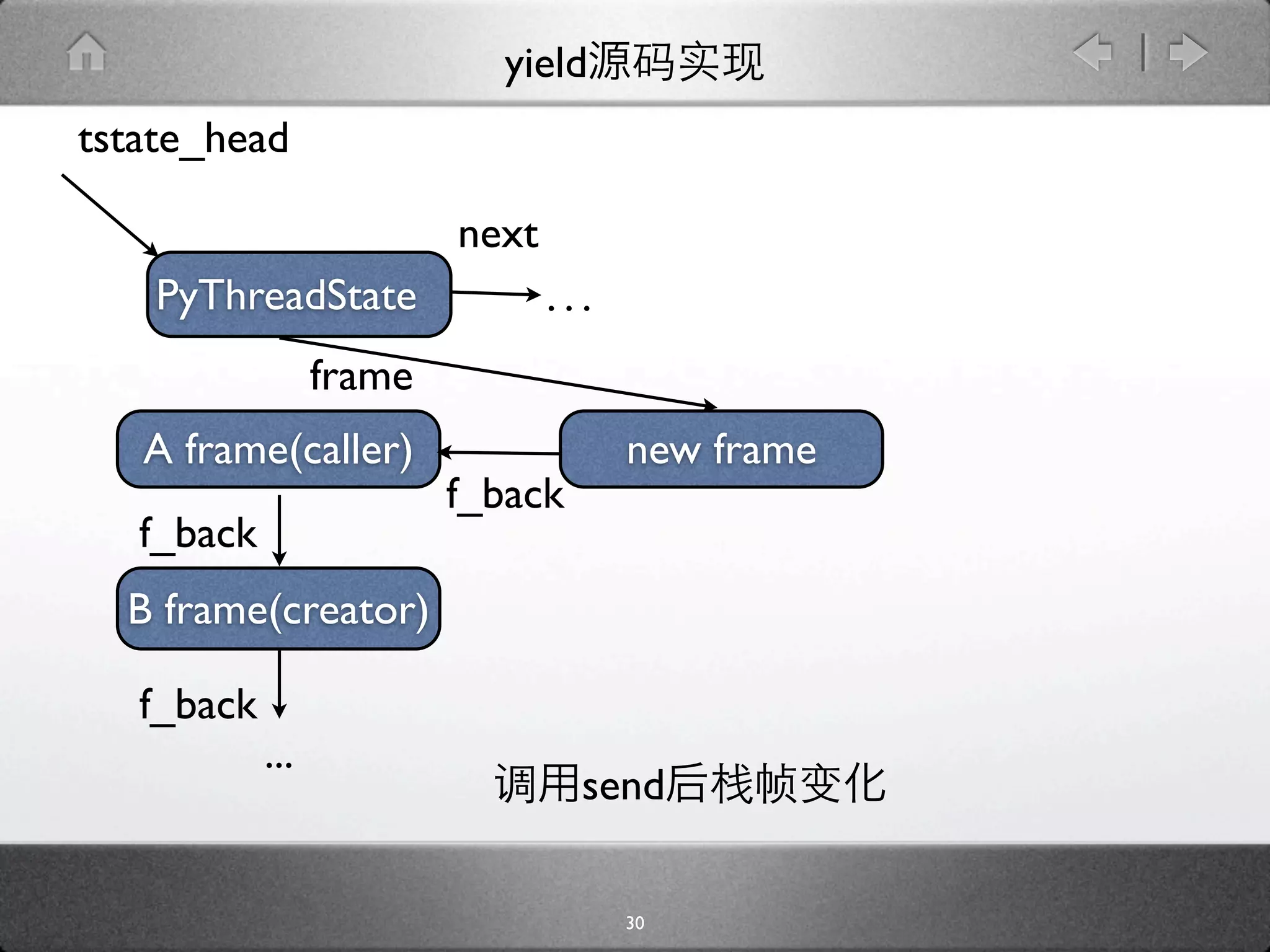
![yield
[genobject.c]
static PyObject * gen_send_ex(PyGenObject *gen, PyObject *arg, int
exc) {
PyFrameObject *f = gen->gi_frame;
f->f_back = tstate->frame;
...
if (f->f_lasti == -1) {
....
} else {
result = arg ? arg : Py_None;
Py_INCREF(result);
*(f->f_stacktop++) = result;
}
...
result = PyEval_EvalFrameEx(f, exc);
}
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-46-2048.jpg)
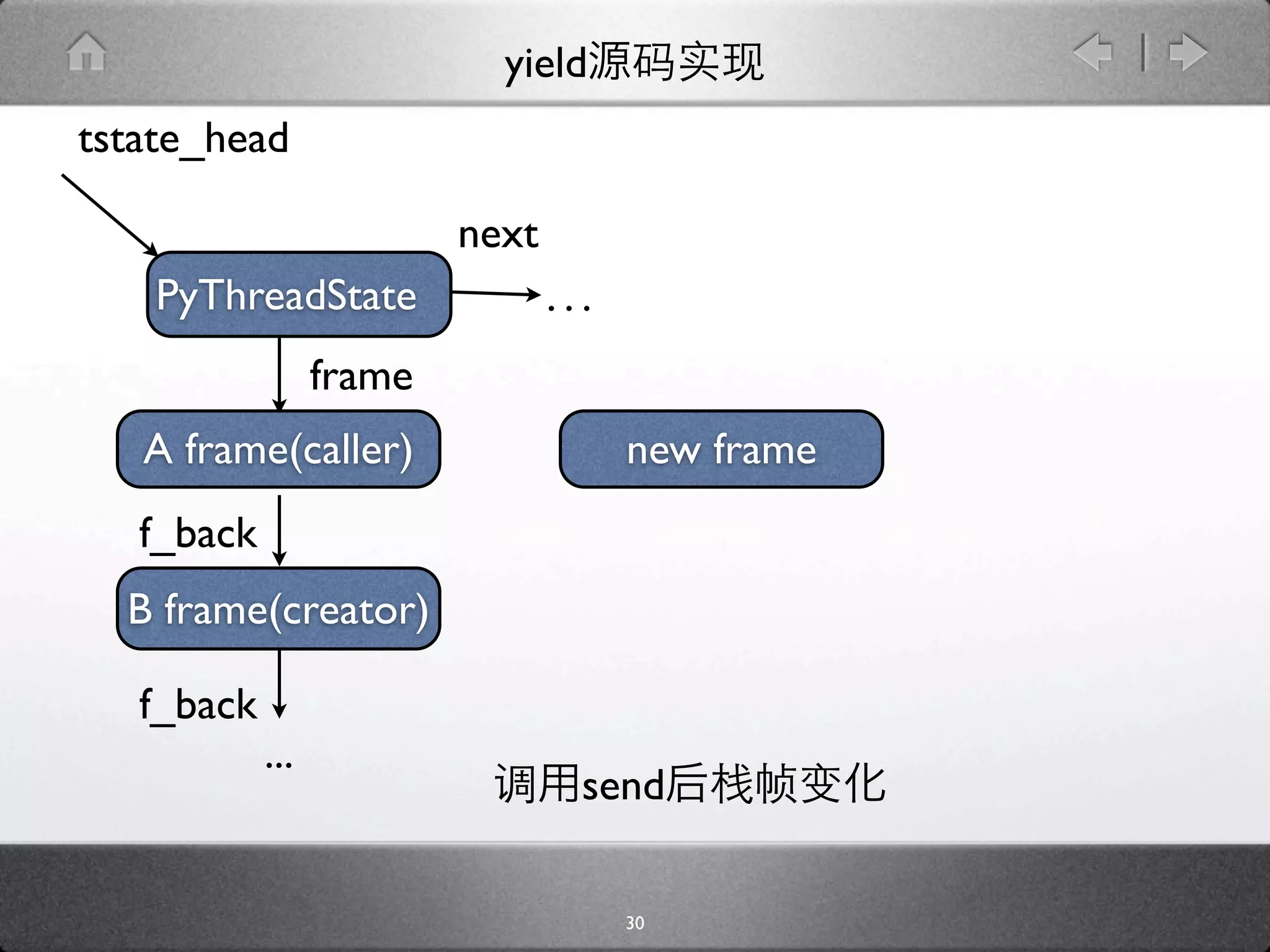
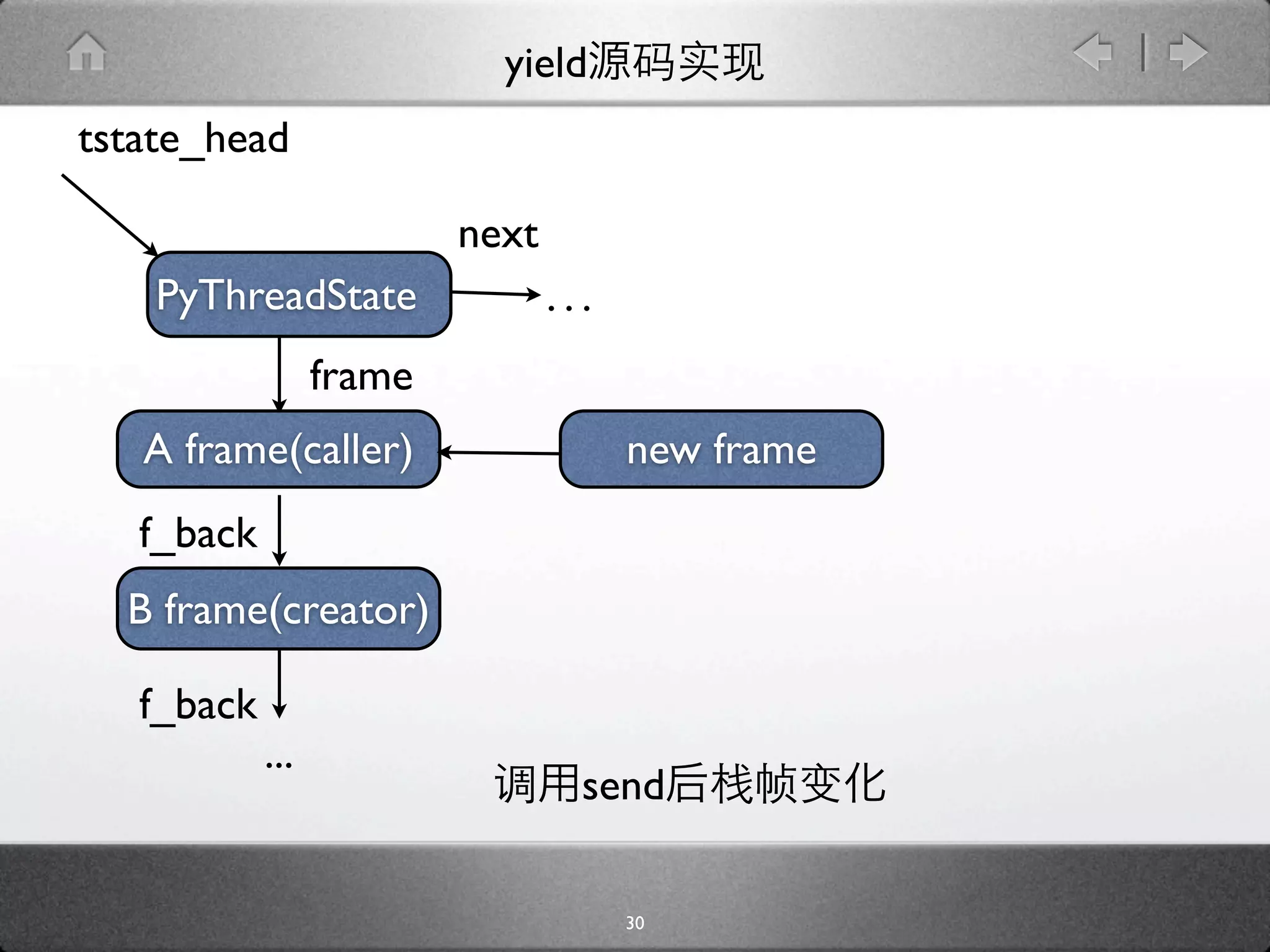

![yield
[ceval.c]
PyObject *PyEval_EvalFrameEx(PyFrameObject *f,
int throwflag){
...
next_instr = first_instr + f->f_lasti + 1;
stack_pointer = f->f_stacktop;
assert(stack_pointer != NULL);
f->f_stacktop = NULL;
...
case YIELD_VALUE:
retval = POP();
f->f_stacktop = stack_pointer;
why = WHY_YIELD;
goto fast_yield;
}
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-53-2048.jpg)
![yield
[genobject.c]
static PyObject *gen_throw(PyGenObject *gen,
PyObject *args){
...
PyErr_Restore(typ, val, tb);
return gen_send_ex(gen, Py_None, 1);
}
throw
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-54-2048.jpg)




![xrange
[rangeobject.c]
static PyObject *
rangeiter_next(rangeiterobject *r)
{
if (r->index < r->len)
return PyInt_FromLong(r->start + (r->index++) * r-
>step);
return NULL;
}
xrange
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-59-2048.jpg)

![xrange
l = [x for x in xrange(10)]
g = (x * x for x in xrange(10))
list generator
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-61-2048.jpg)
![xrange
l = [x for x in xrange(10)]
g = (x * x for x in xrange(10))
list generator
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-62-2048.jpg)
![xrange
l = [x for x in xrange(10)]
g = (x * x for x in xrange(10))
list generator
def f():
for x in xrange(10):
yield x * x
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-63-2048.jpg)












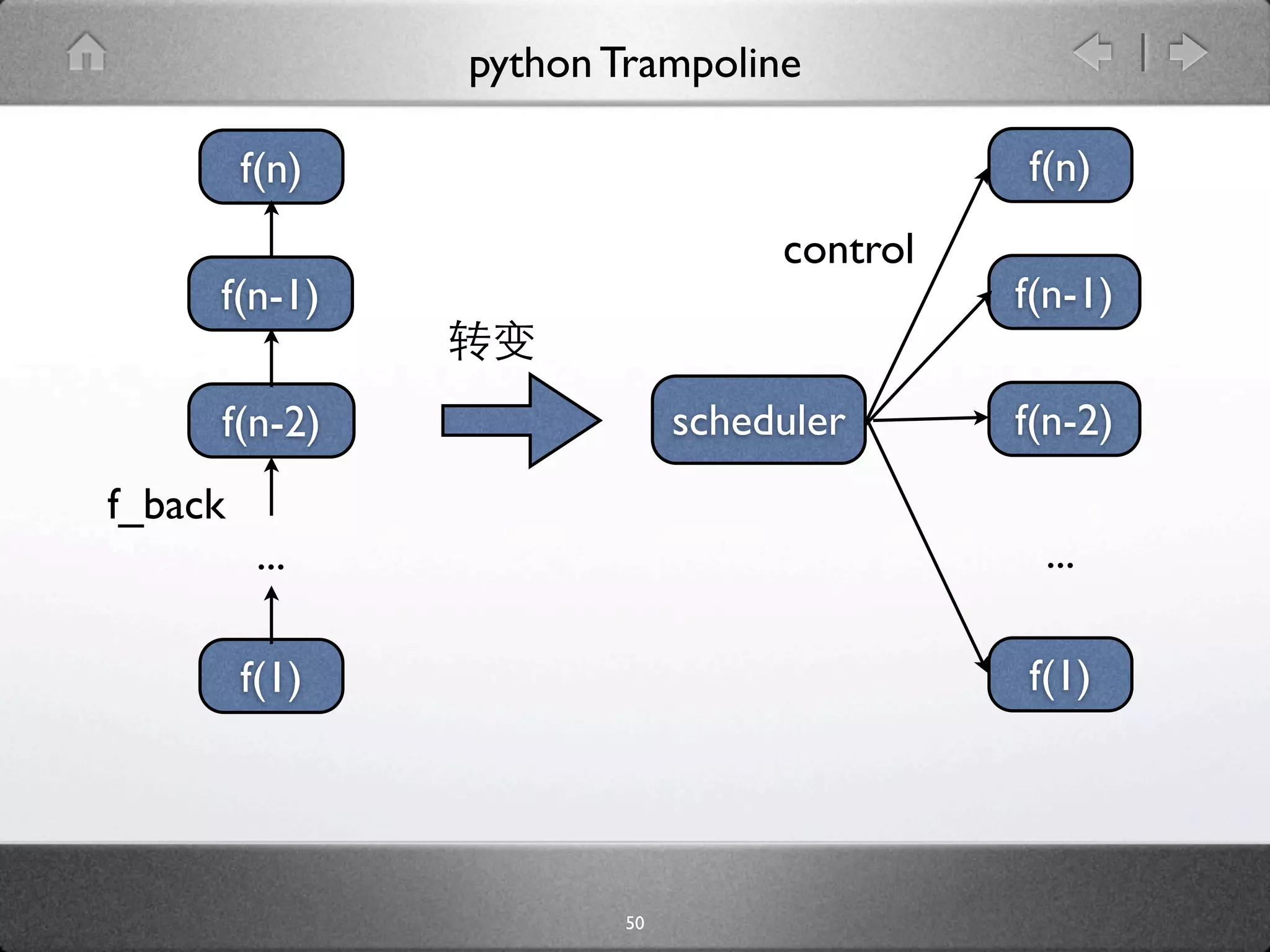


![python Trampoline
def trampoline(main):
stack = []
value = main
while True:
if type(value) is types.GeneratorType:
stack.append(value)
value = stack[-1].next()
else:
stack.pop()
if stack:
value = stack[-1].send(value)
else:
return value
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/yield-110701043704-phpapp01/75/Python-Yield-79-2048.jpg)








