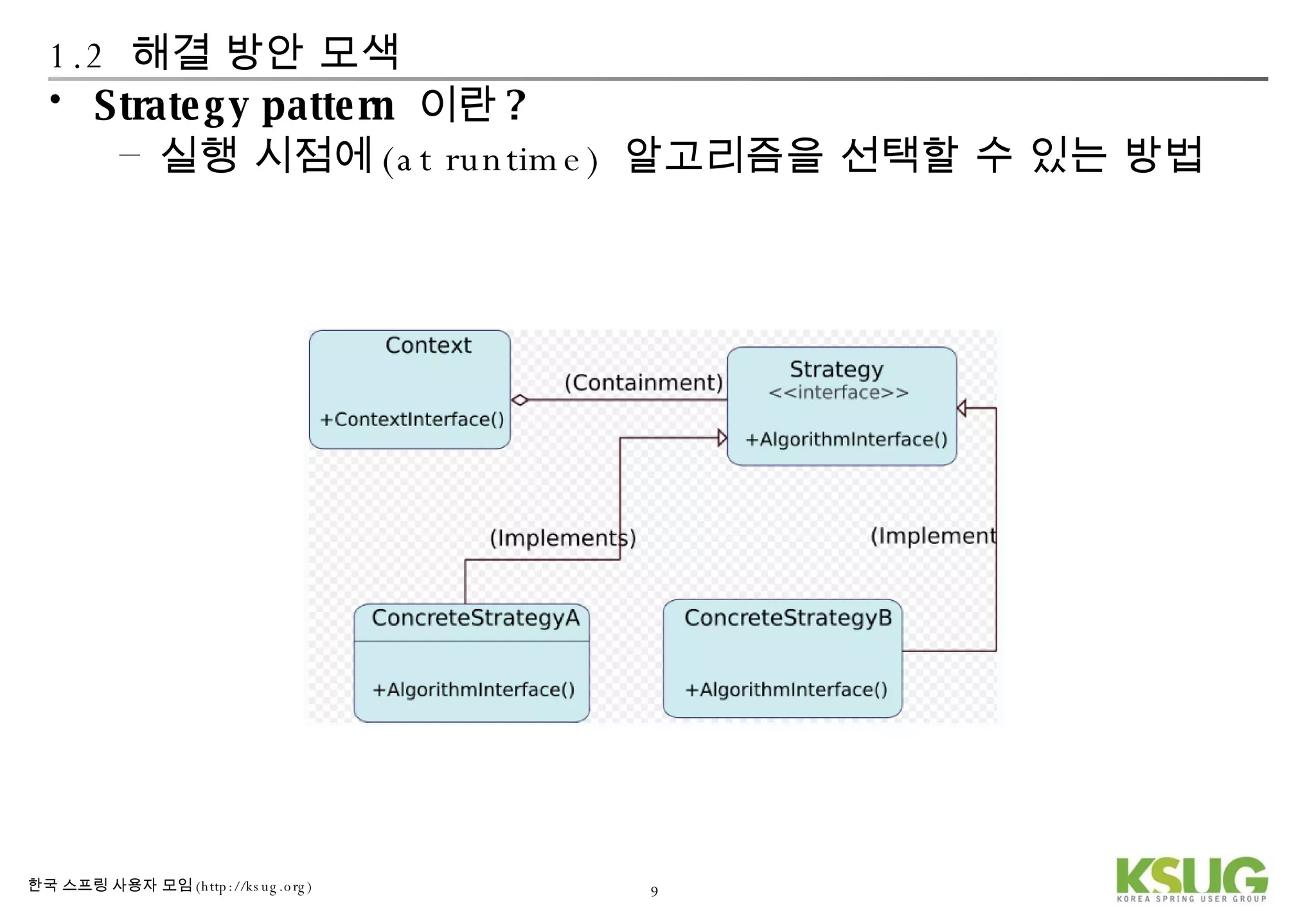
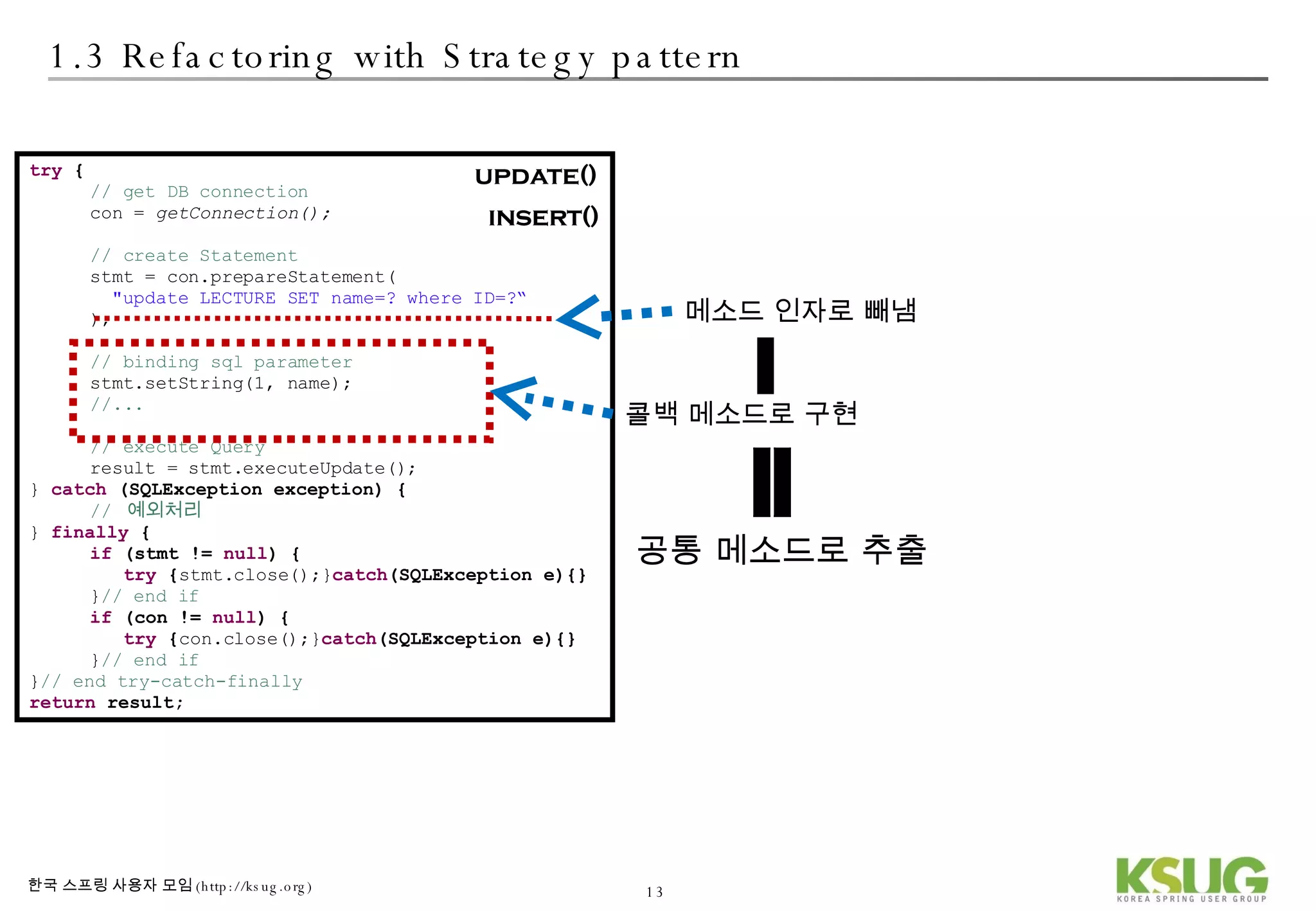
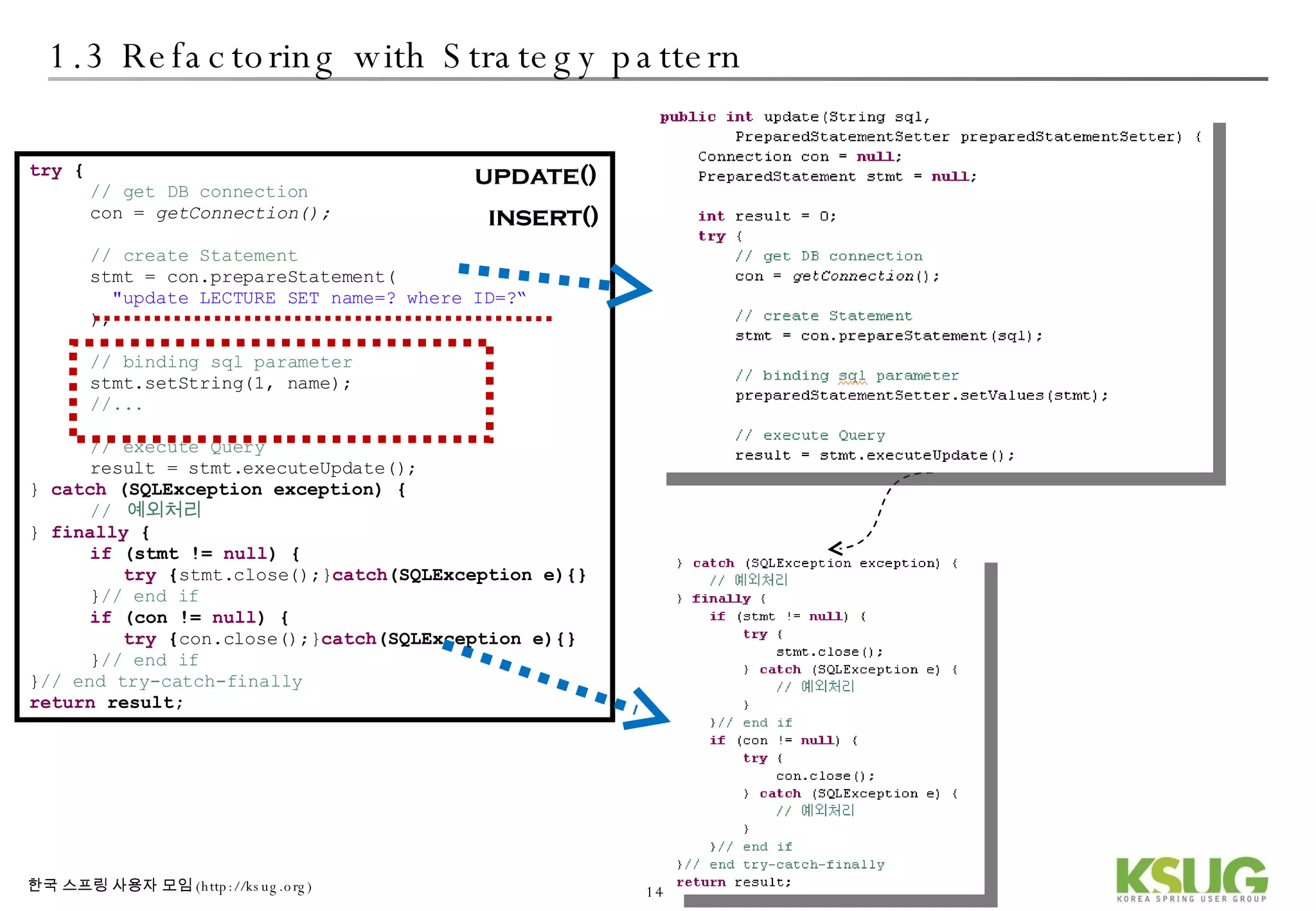
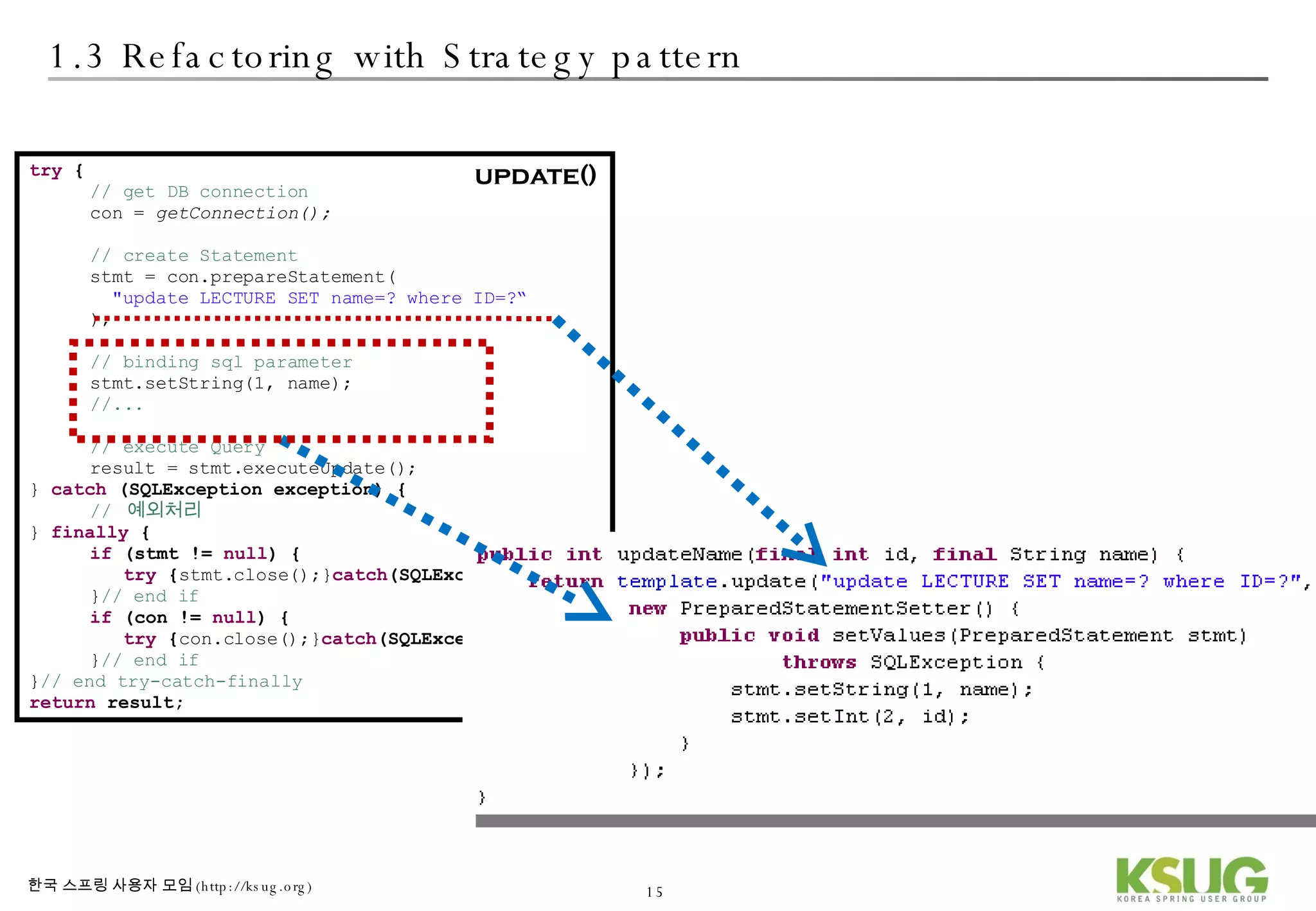
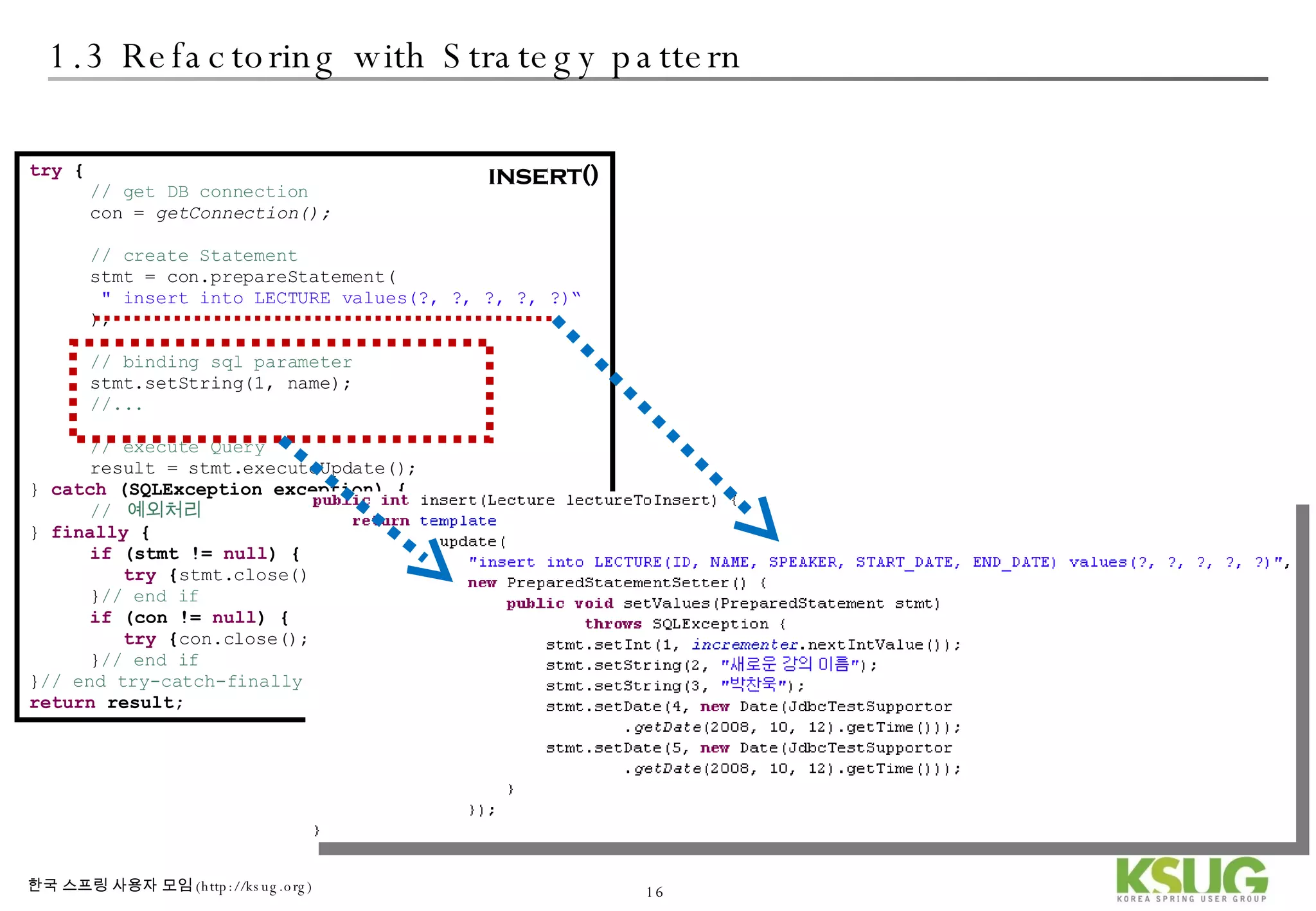
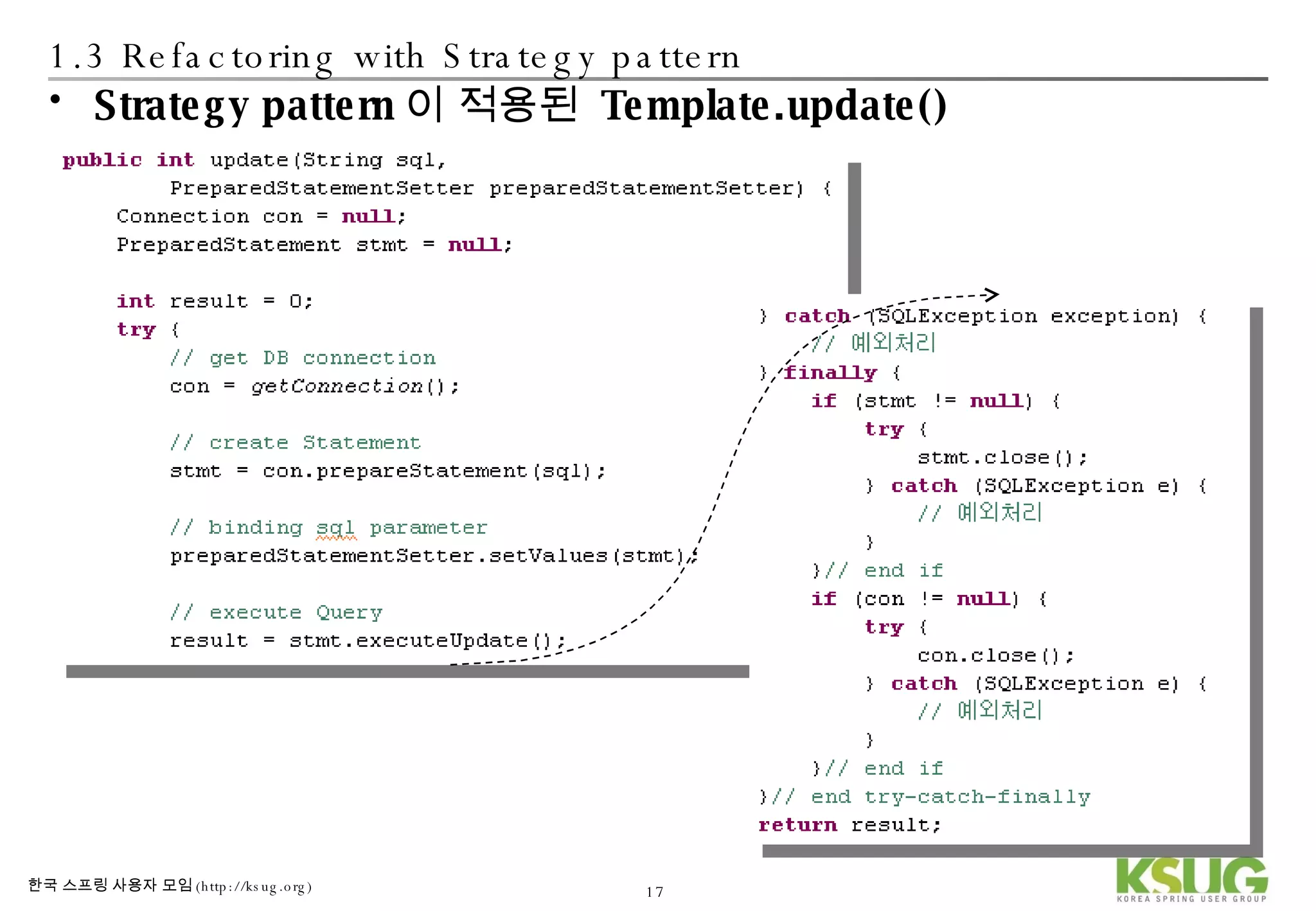
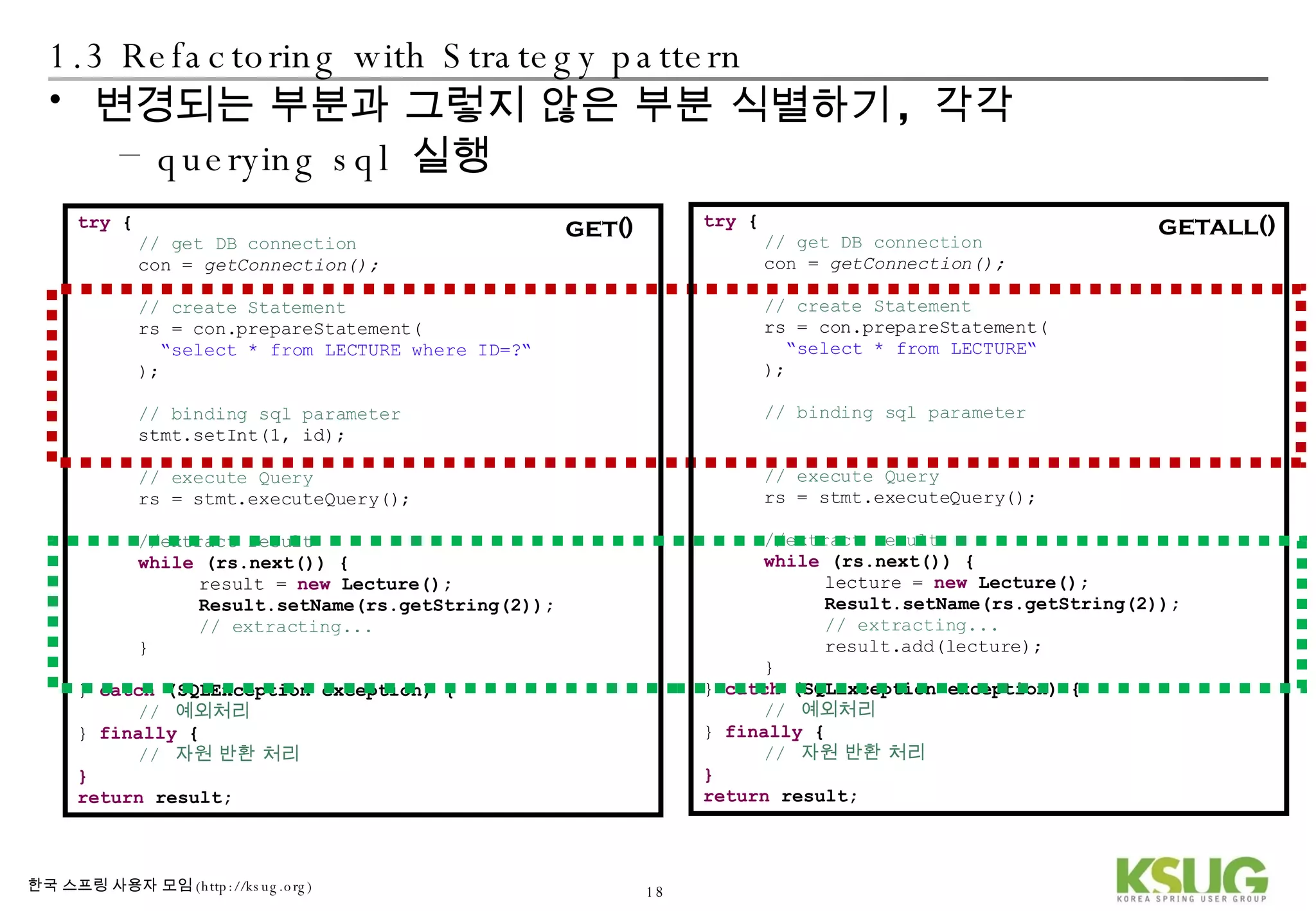
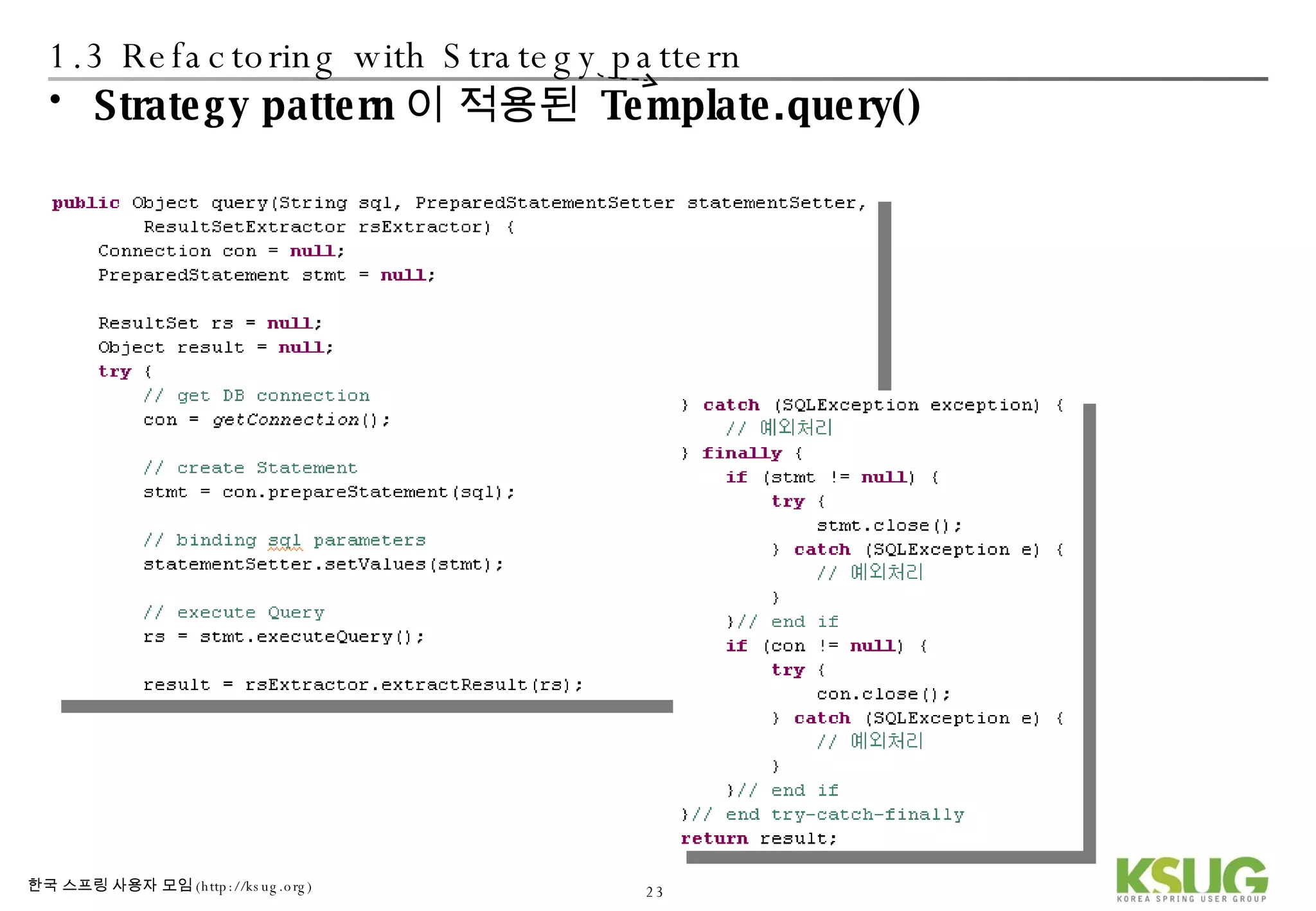
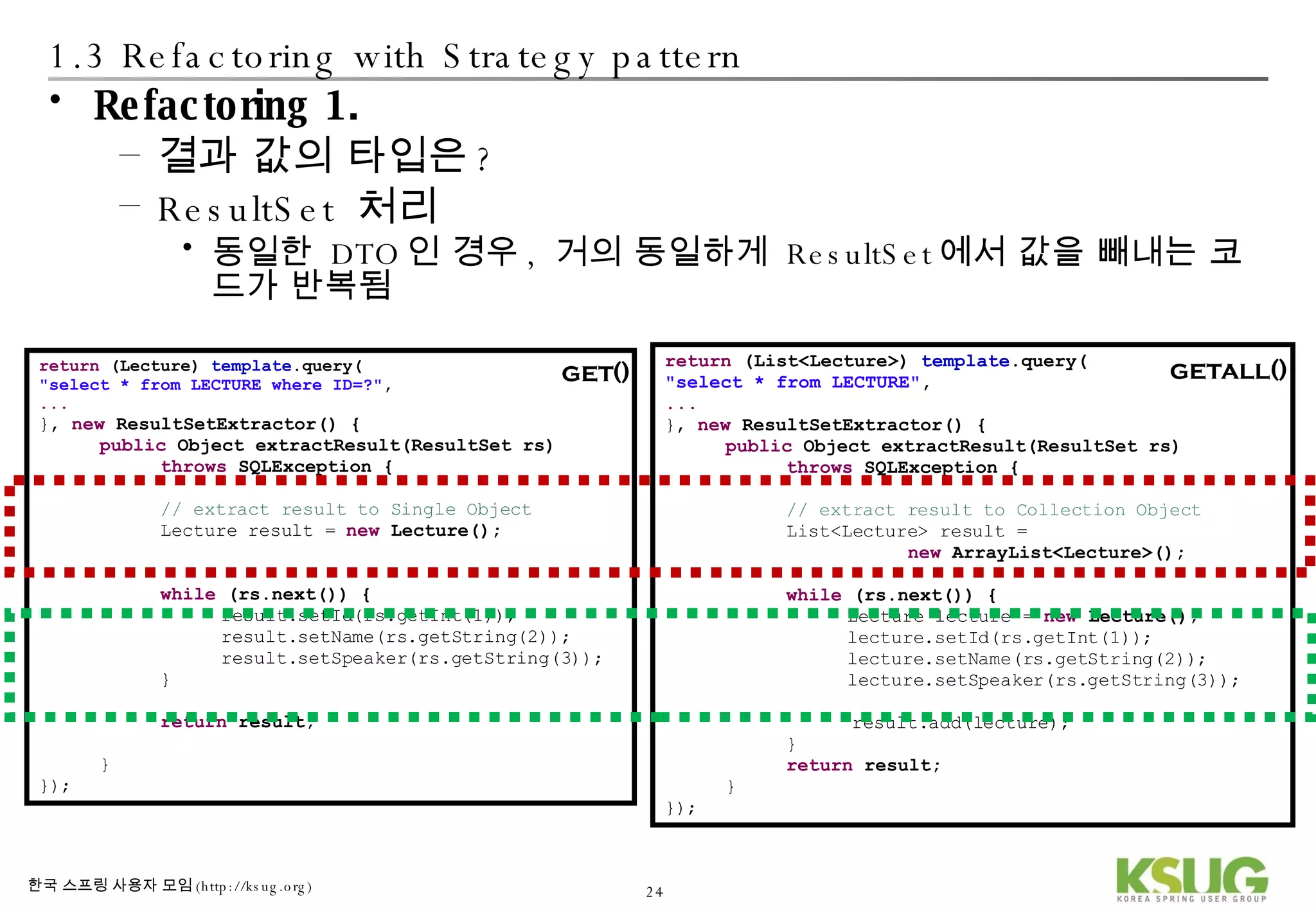
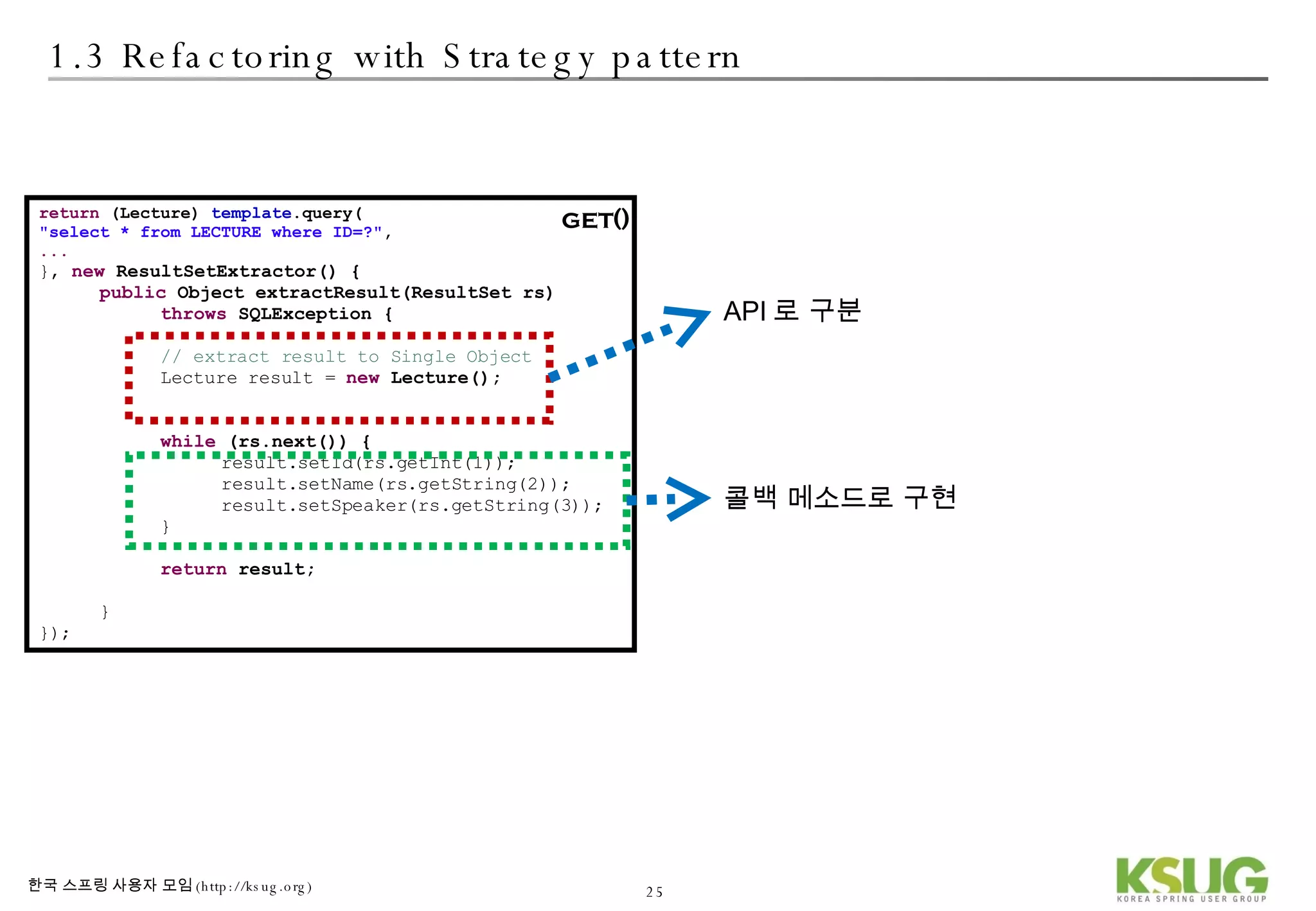
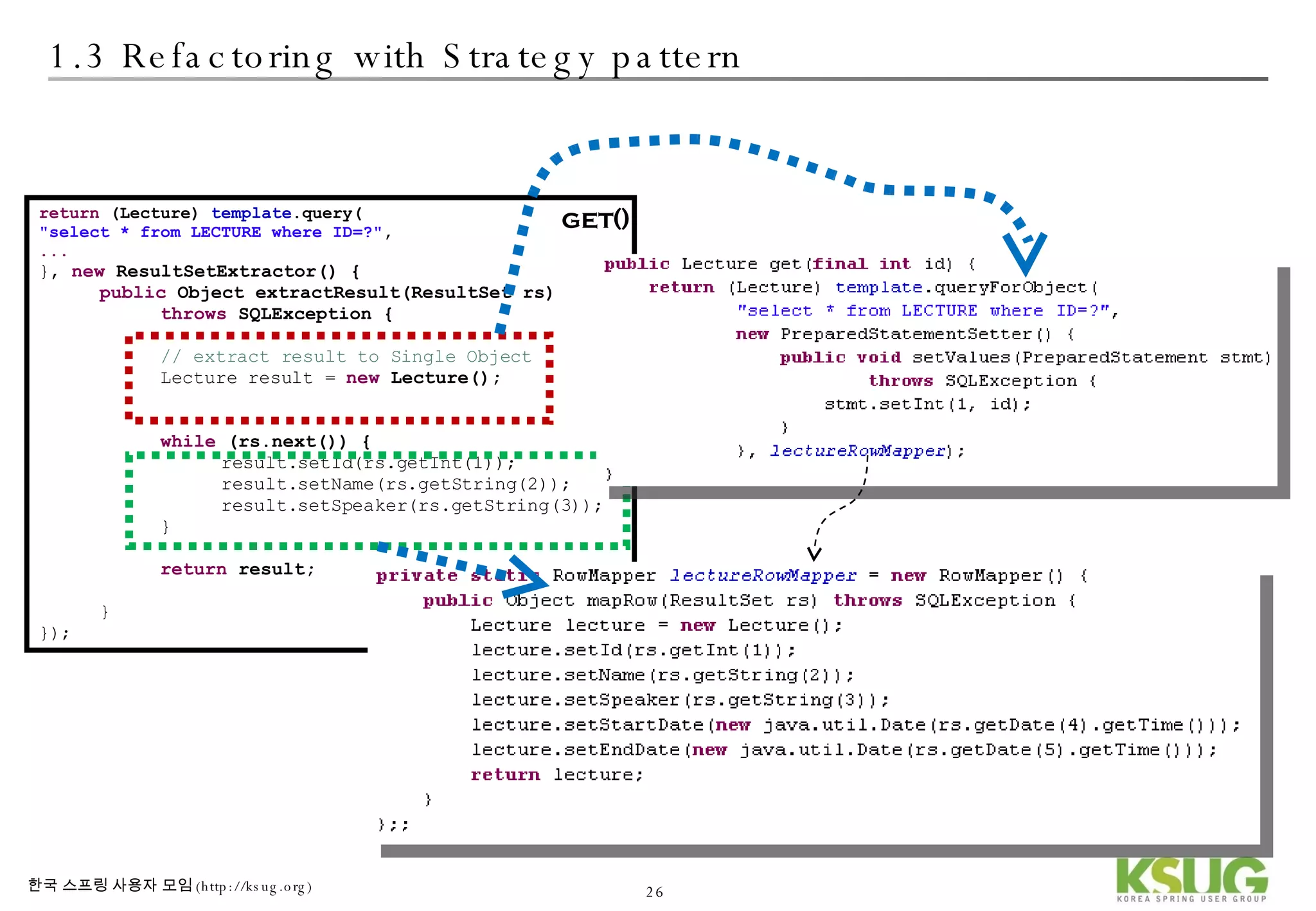
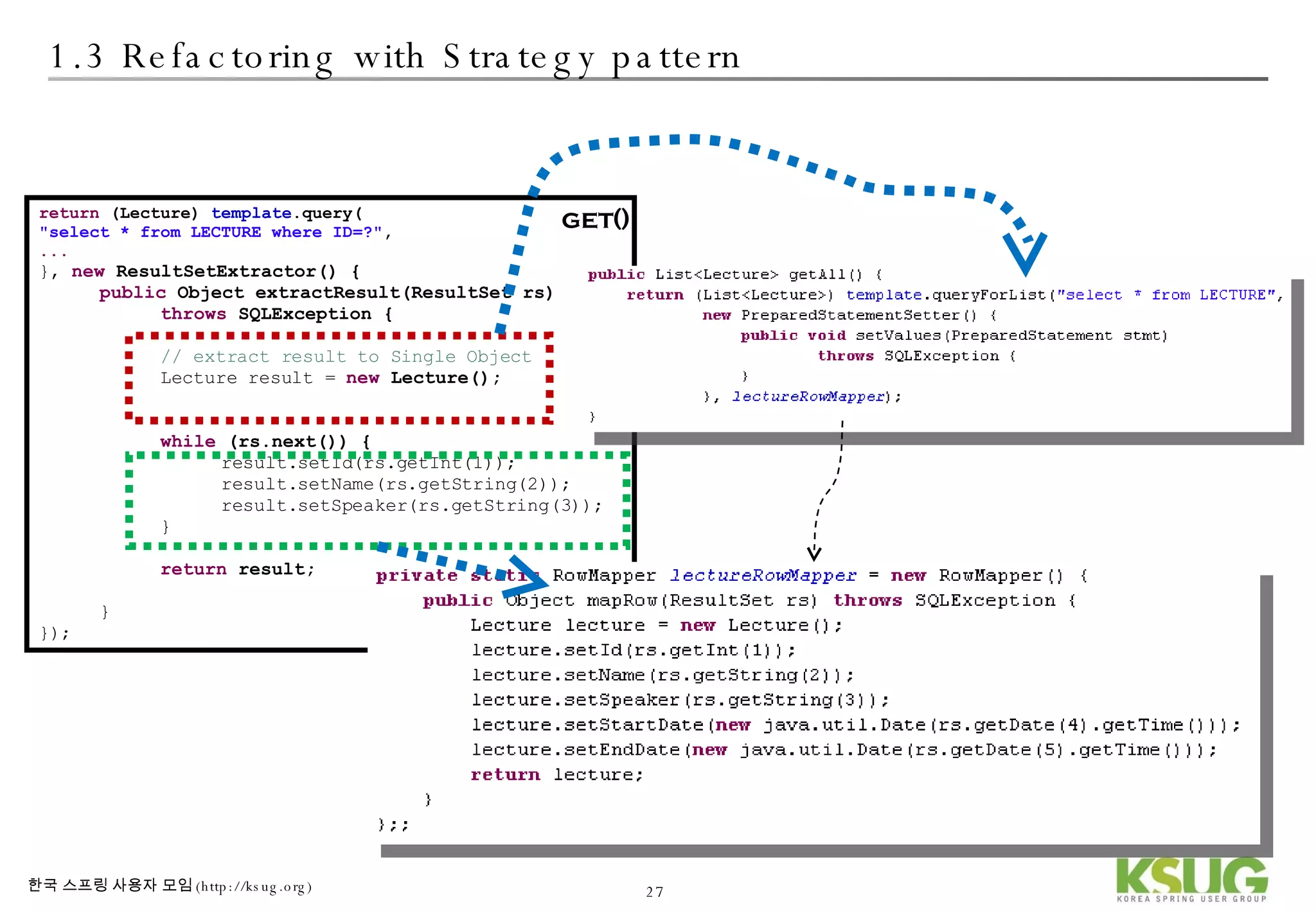
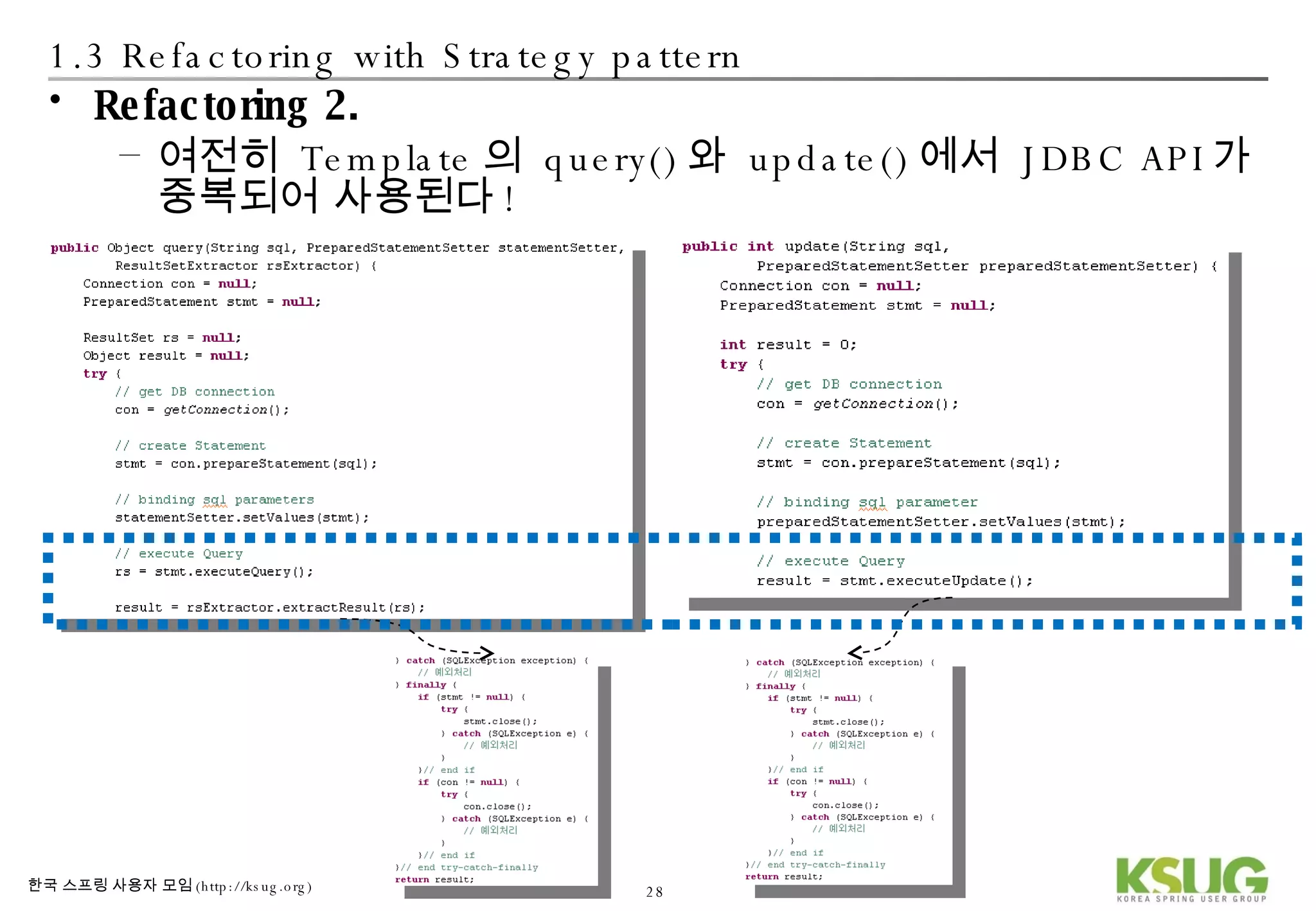
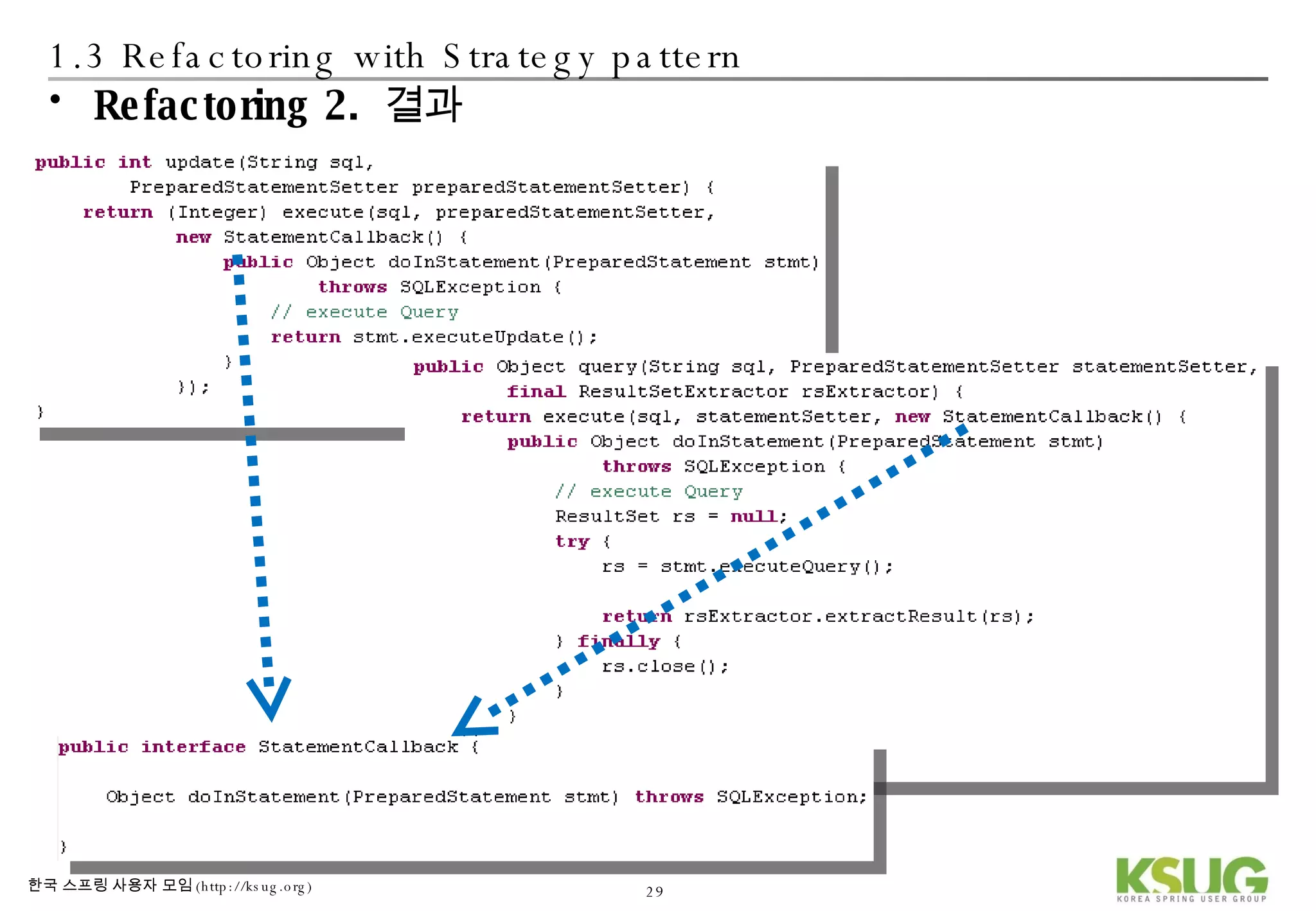
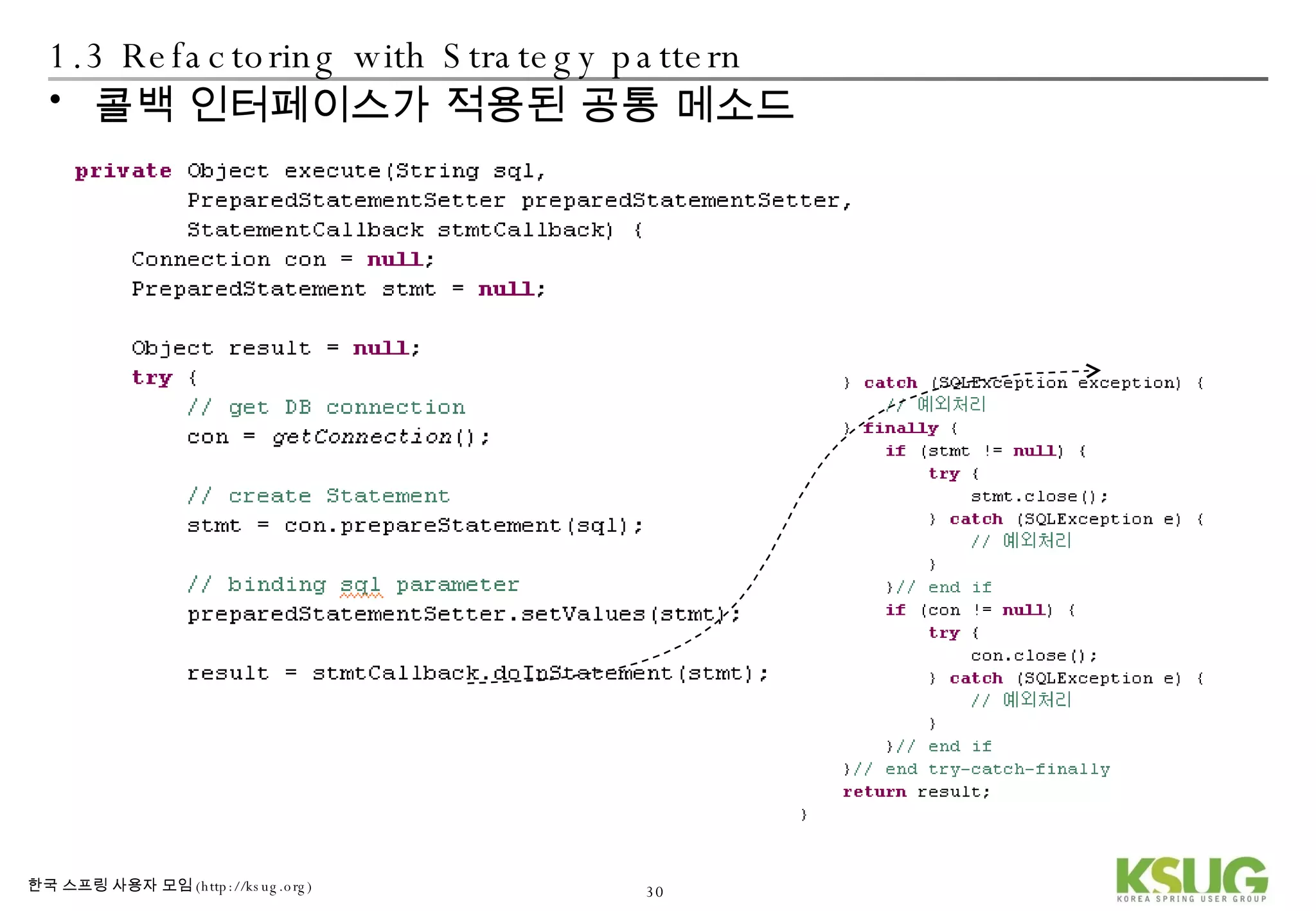
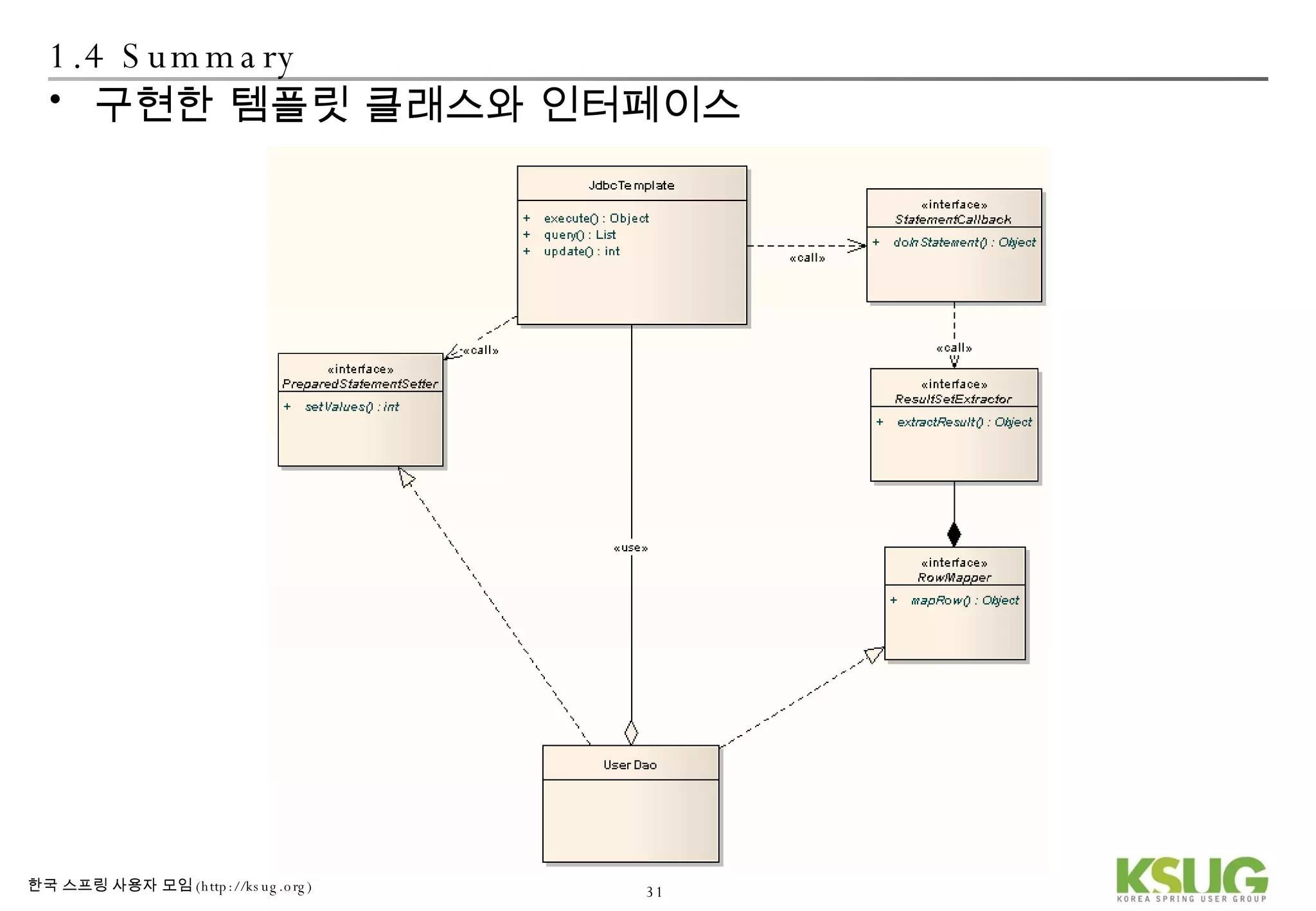
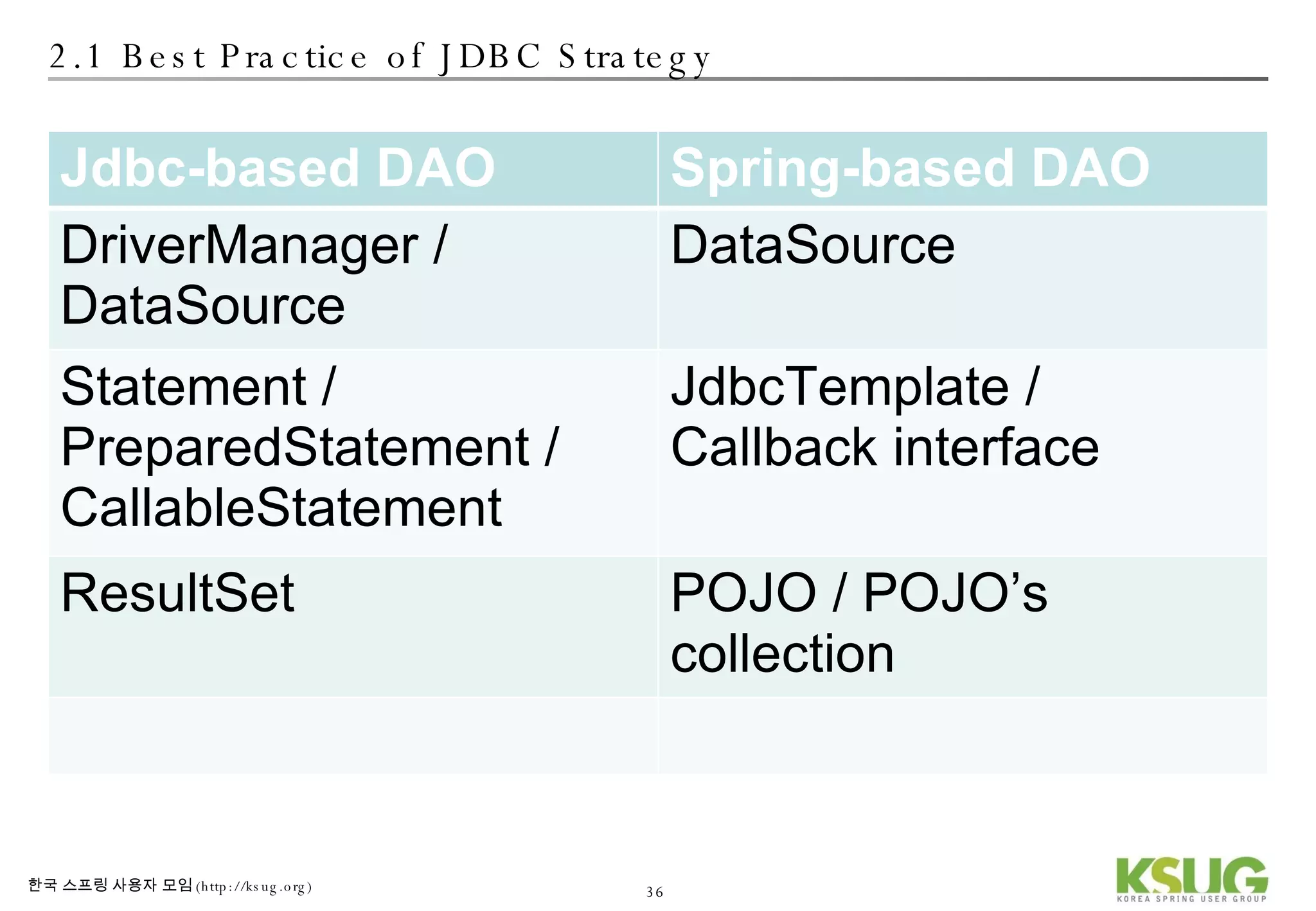
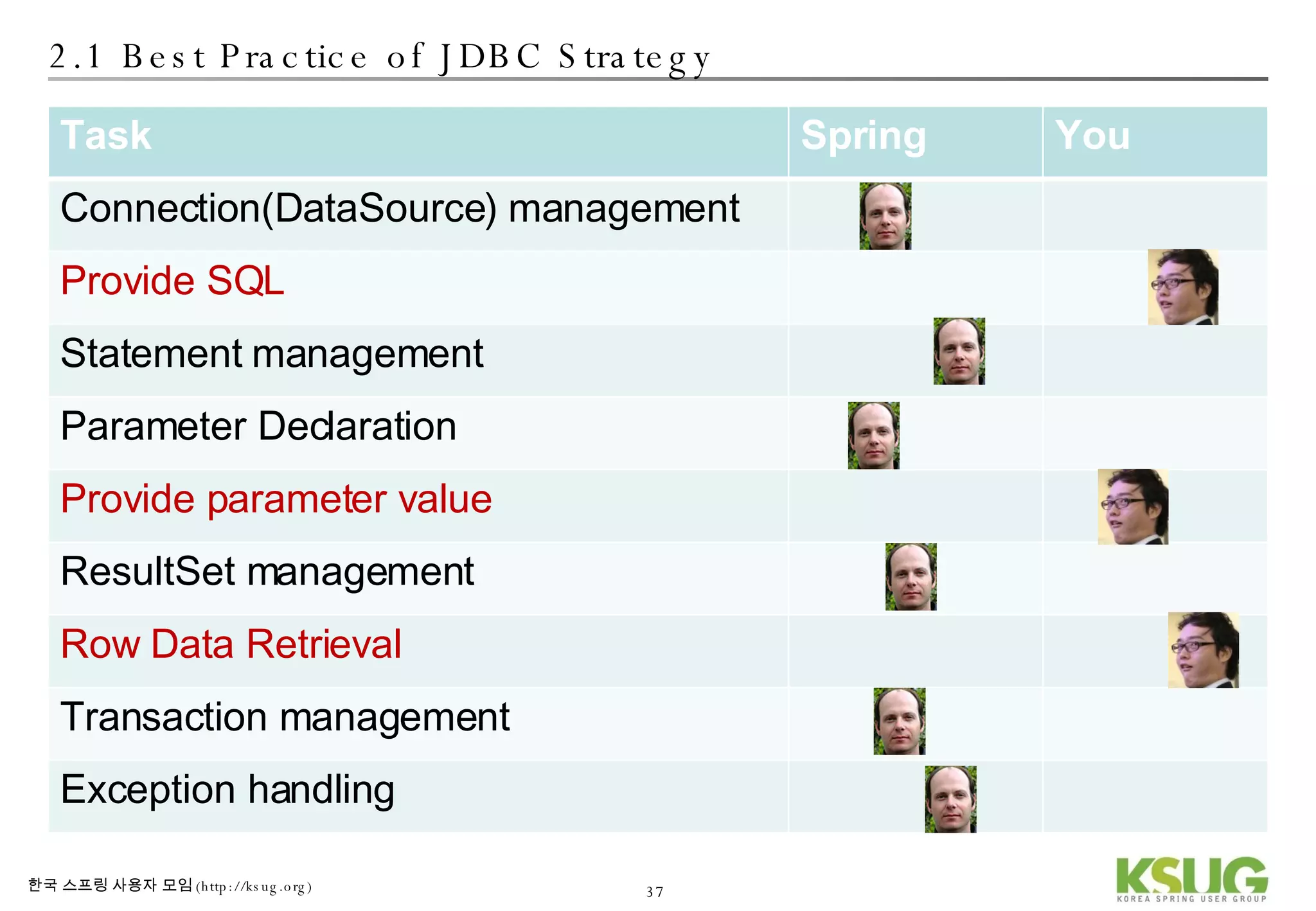
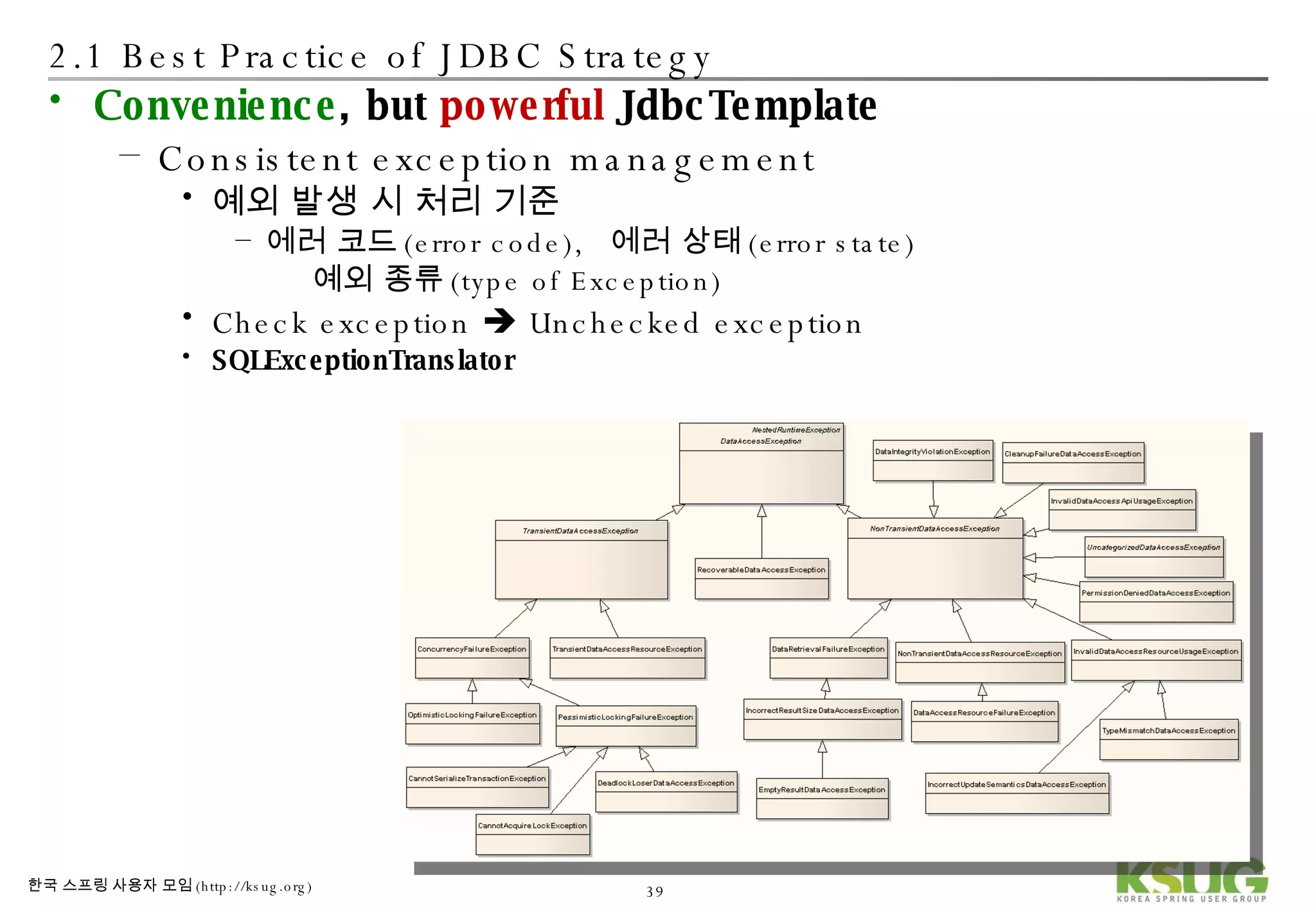
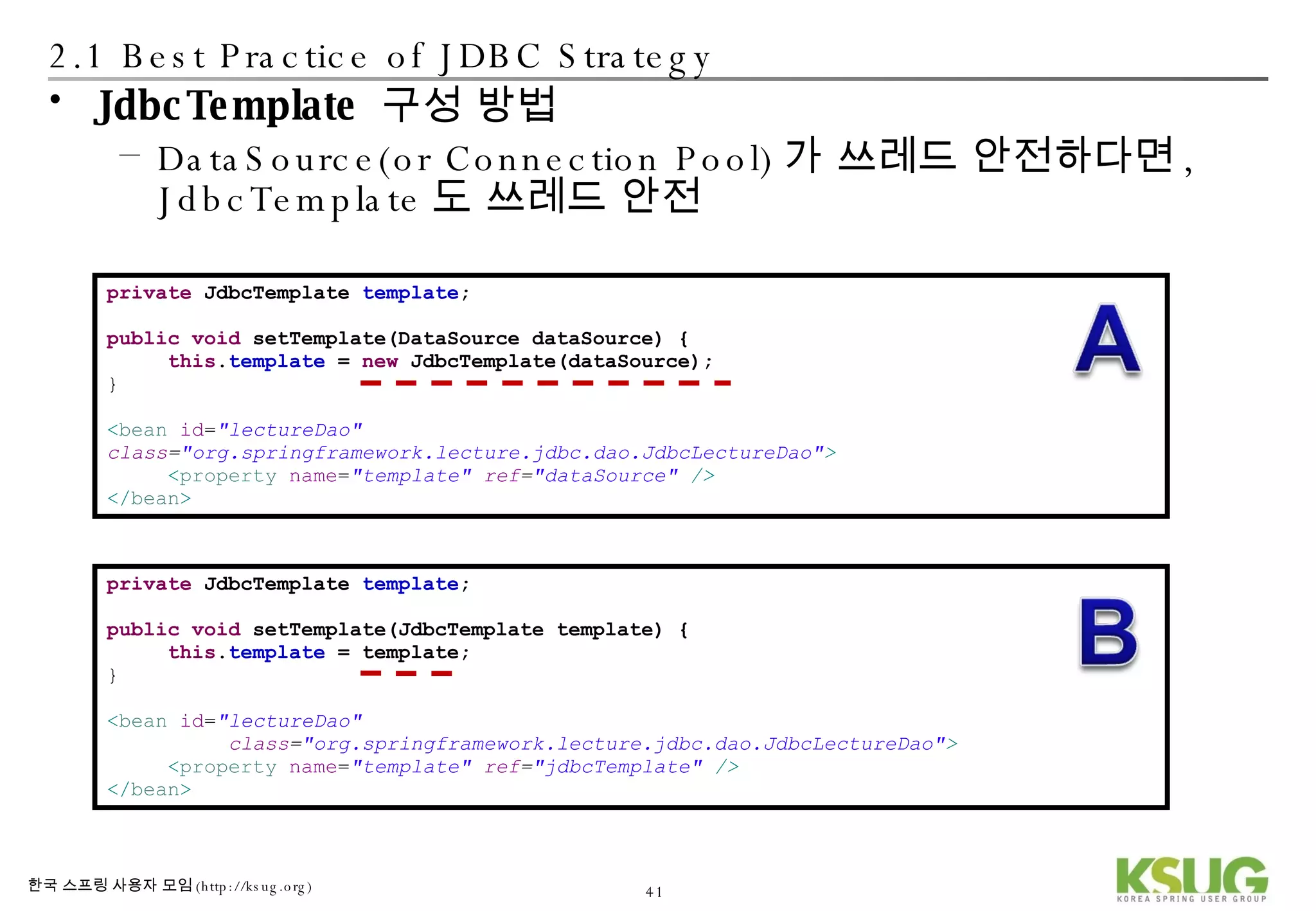
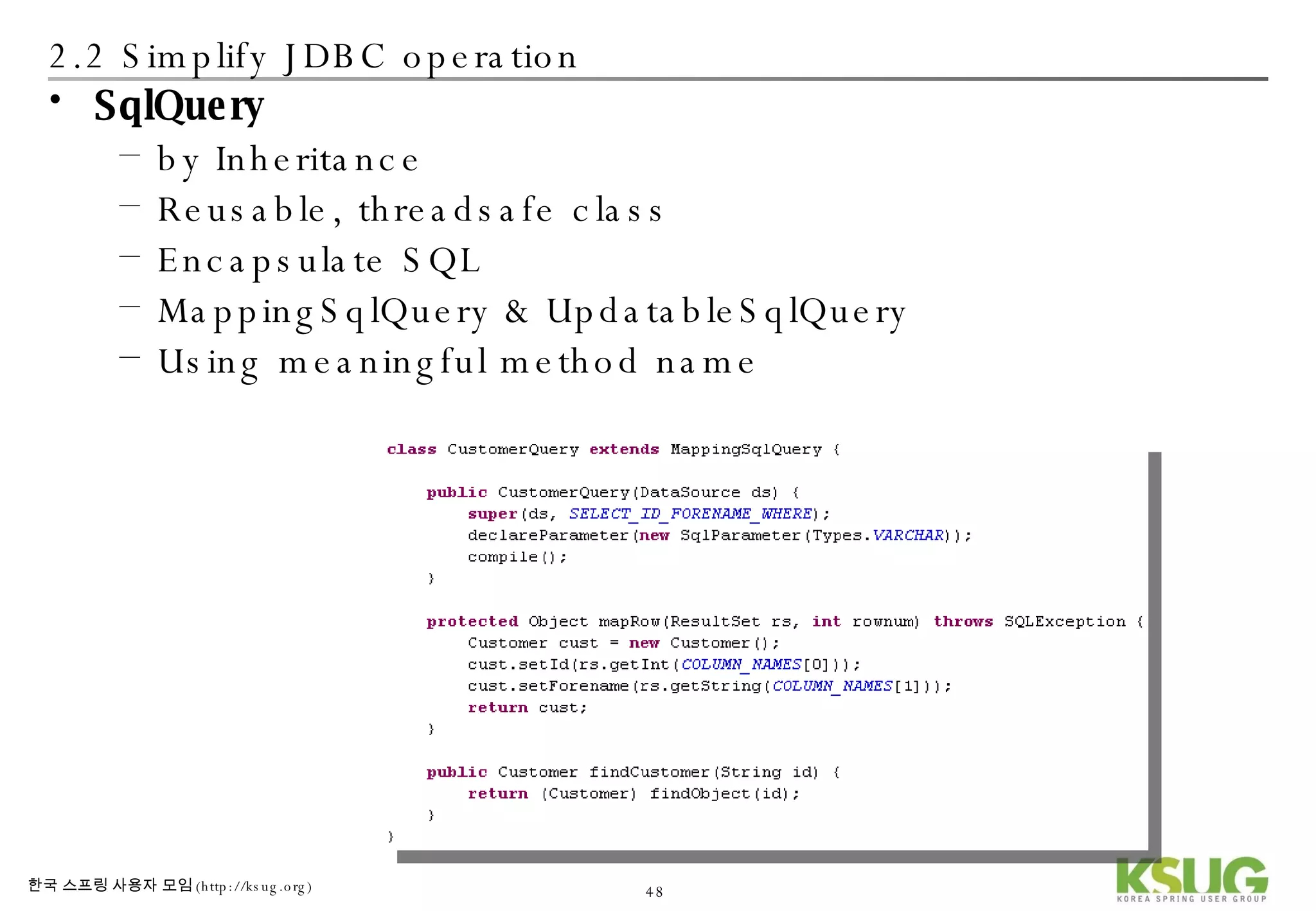
The document discusses refactoring JDBC code using the Strategy pattern and Spring JdbcTemplate. It describes identifying variable and constant parts of JDBC code and extracting them. Template methods are created using callback interfaces to encapsulate common JDBC operations like querying and updating. This improves code reuse and reduces duplication. Spring JdbcTemplate is also introduced as it implements the Strategy pattern and provides convenience for common data access tasks while maintaining flexibility.








![2.1 Best Practice of JDBC Strategy Strategy pattern 참조 : wiki[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springdao-1225333431138289-8/75/Refactoring-Jdbc-Programming-11-2048.jpg)

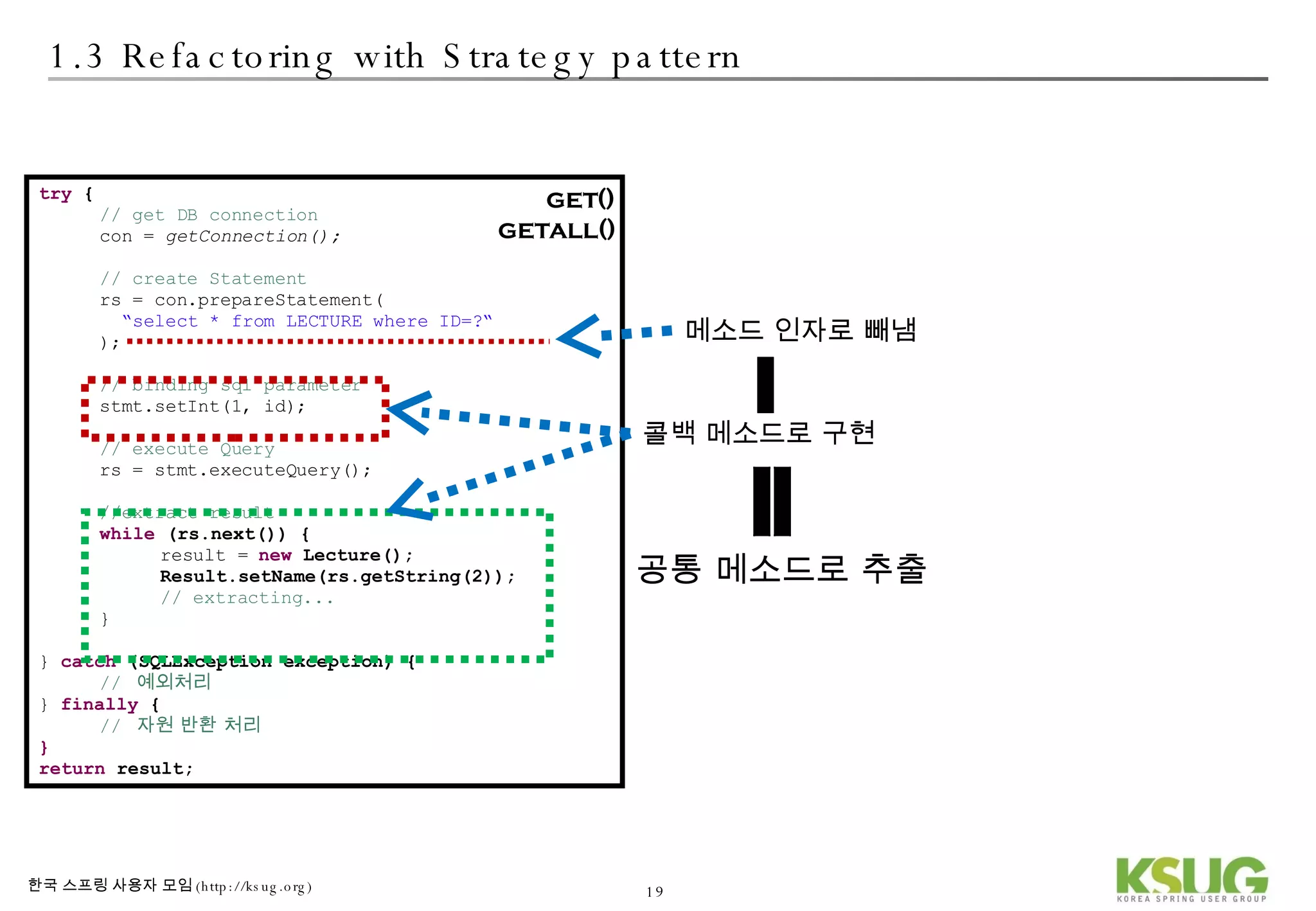
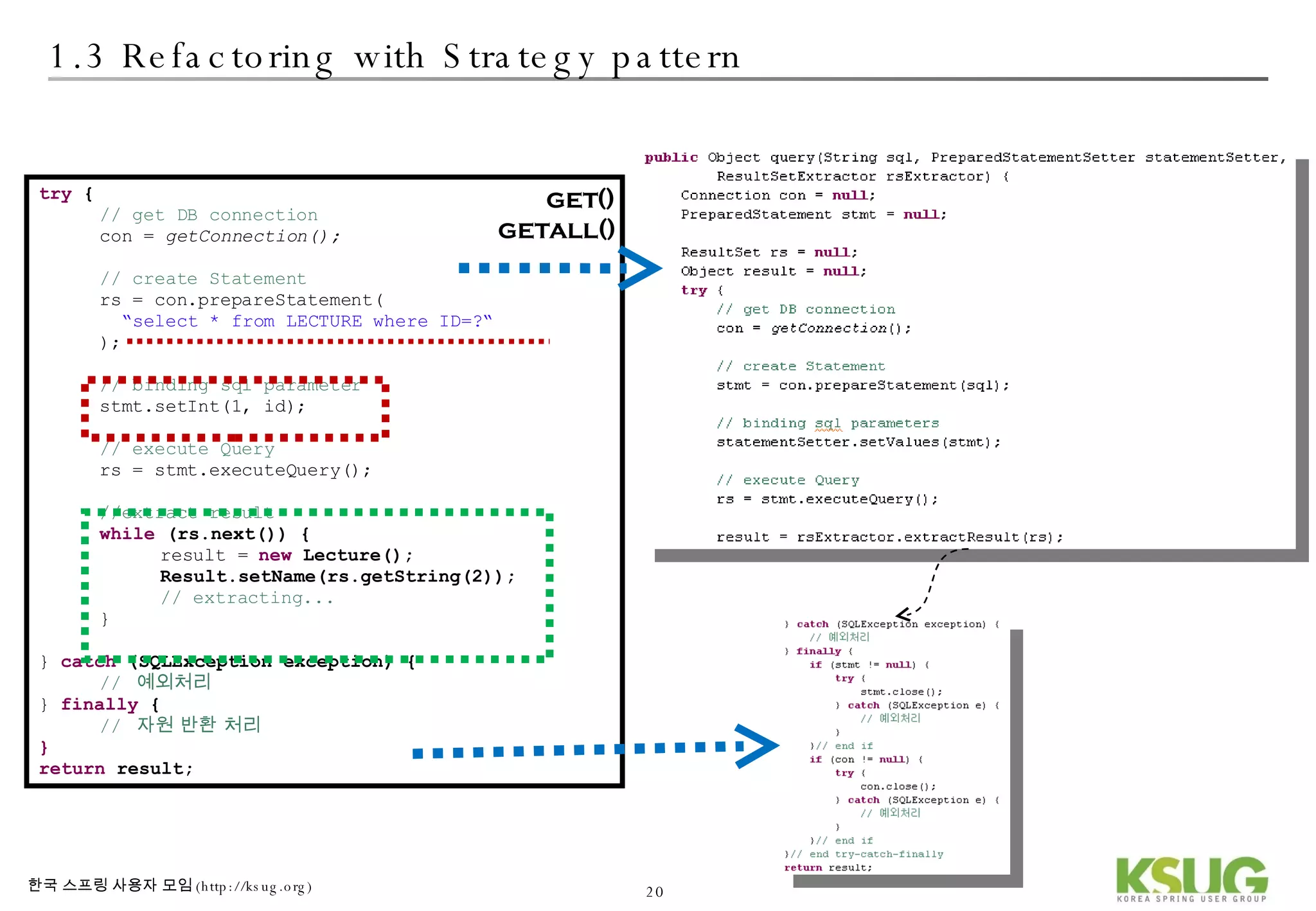
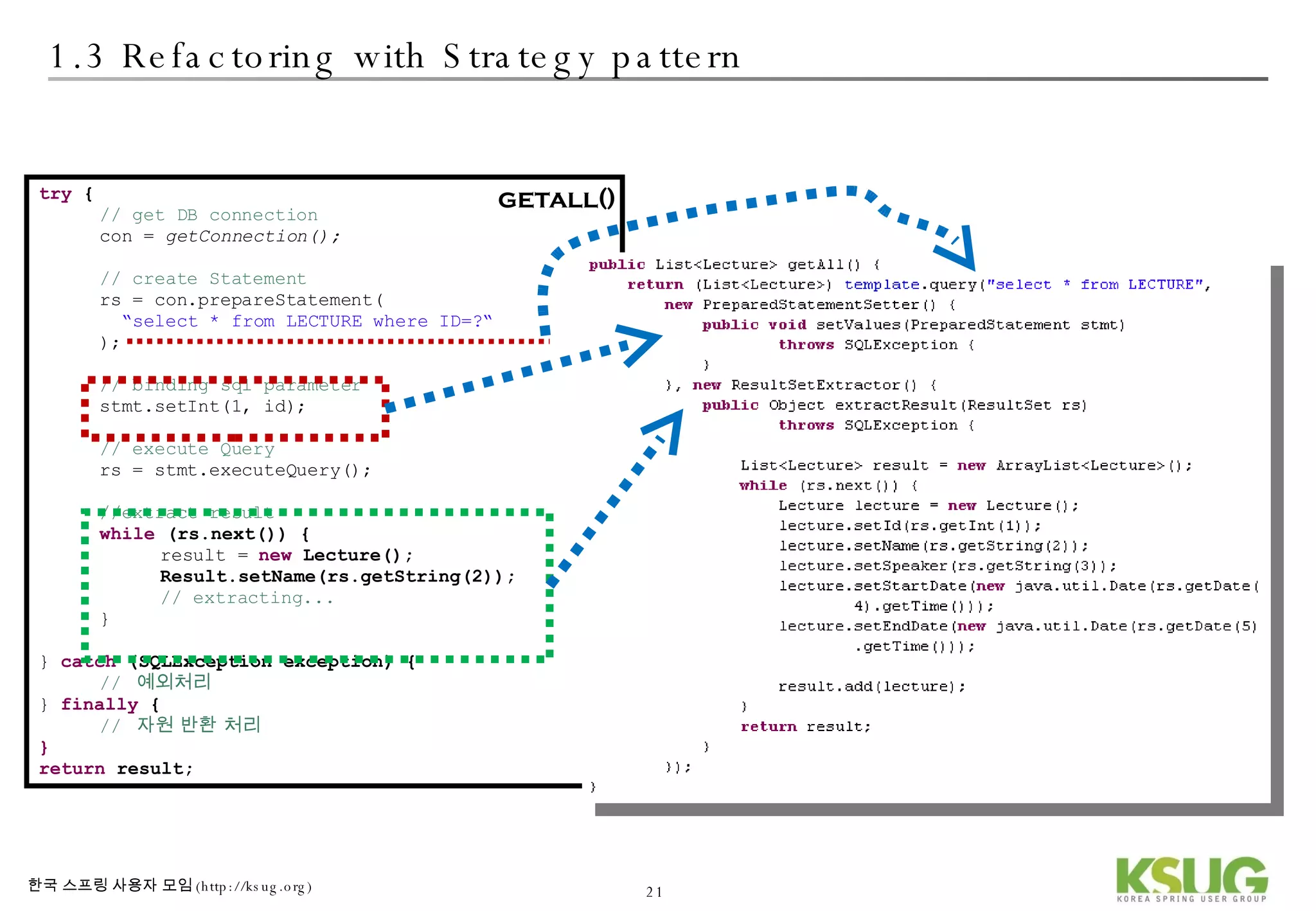
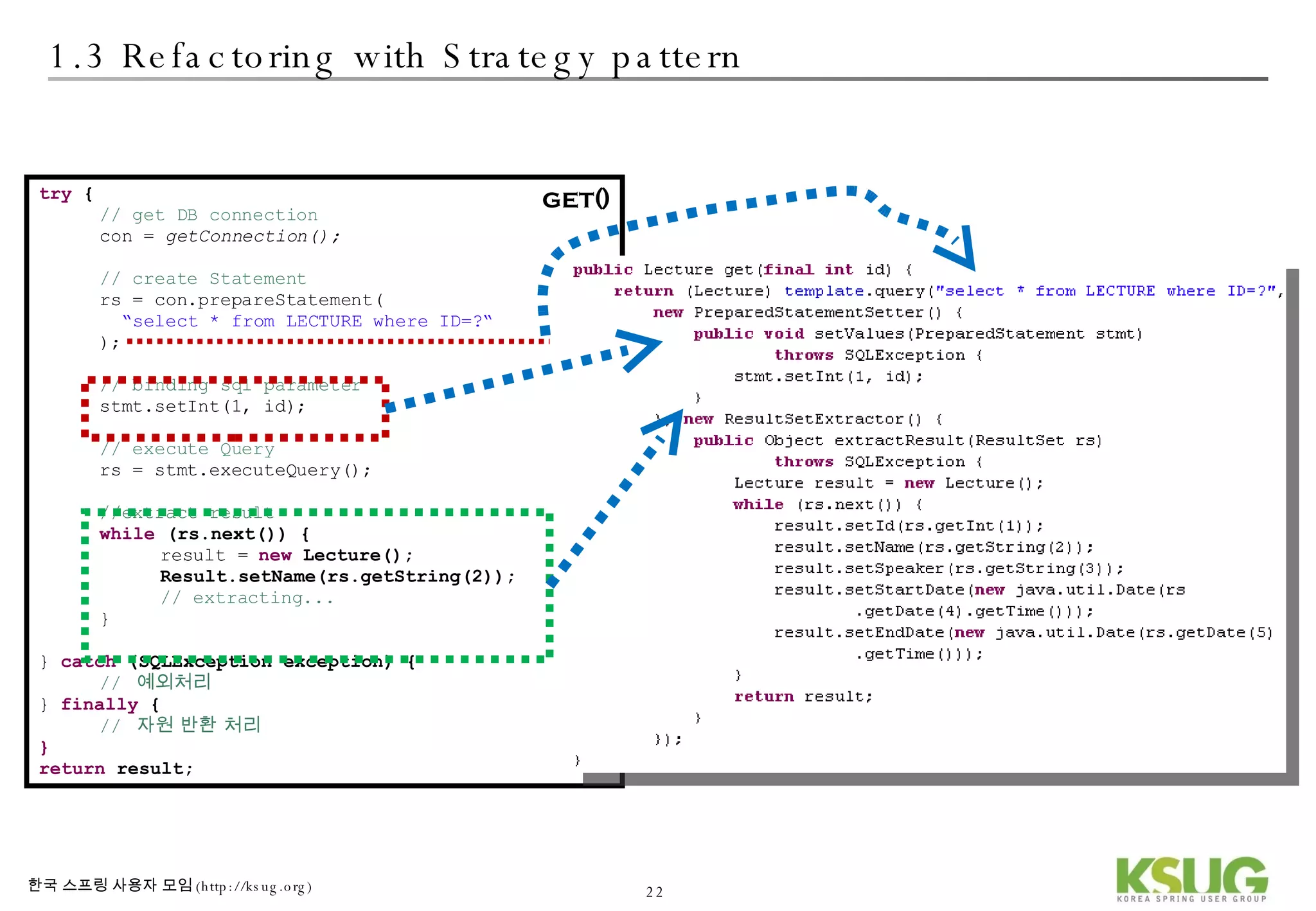



![2.1 Best Practice of JDBC Strategy JdbcTemplate with Strategy pattern DAO Template Callback Interface implementation 참조 : wiki[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springdao-1225333431138289-8/75/Refactoring-Jdbc-Programming-35-2048.jpg)








![Reference wiki[1]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Strategy_Pattern_Diagram_ZP.svg wiki[2]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Strategy_pattern_in_LePUS3.gif Tomas[1]: JDBC Development with the Spring Framework Spring reference Spring API J2EE Design and Development J2EE without EJB](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springdao-1225333431138289-8/75/Refactoring-Jdbc-Programming-51-2048.jpg)
