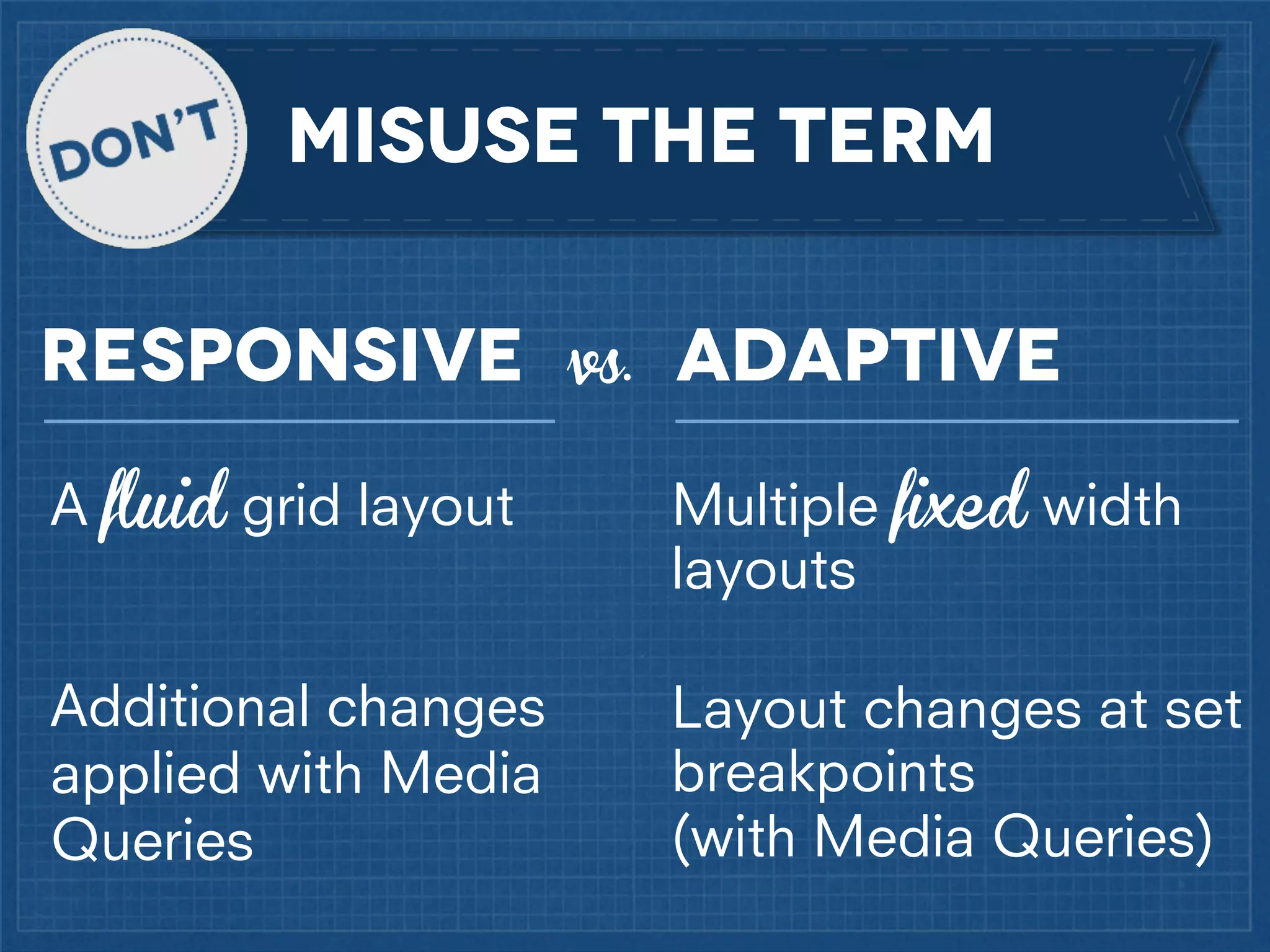
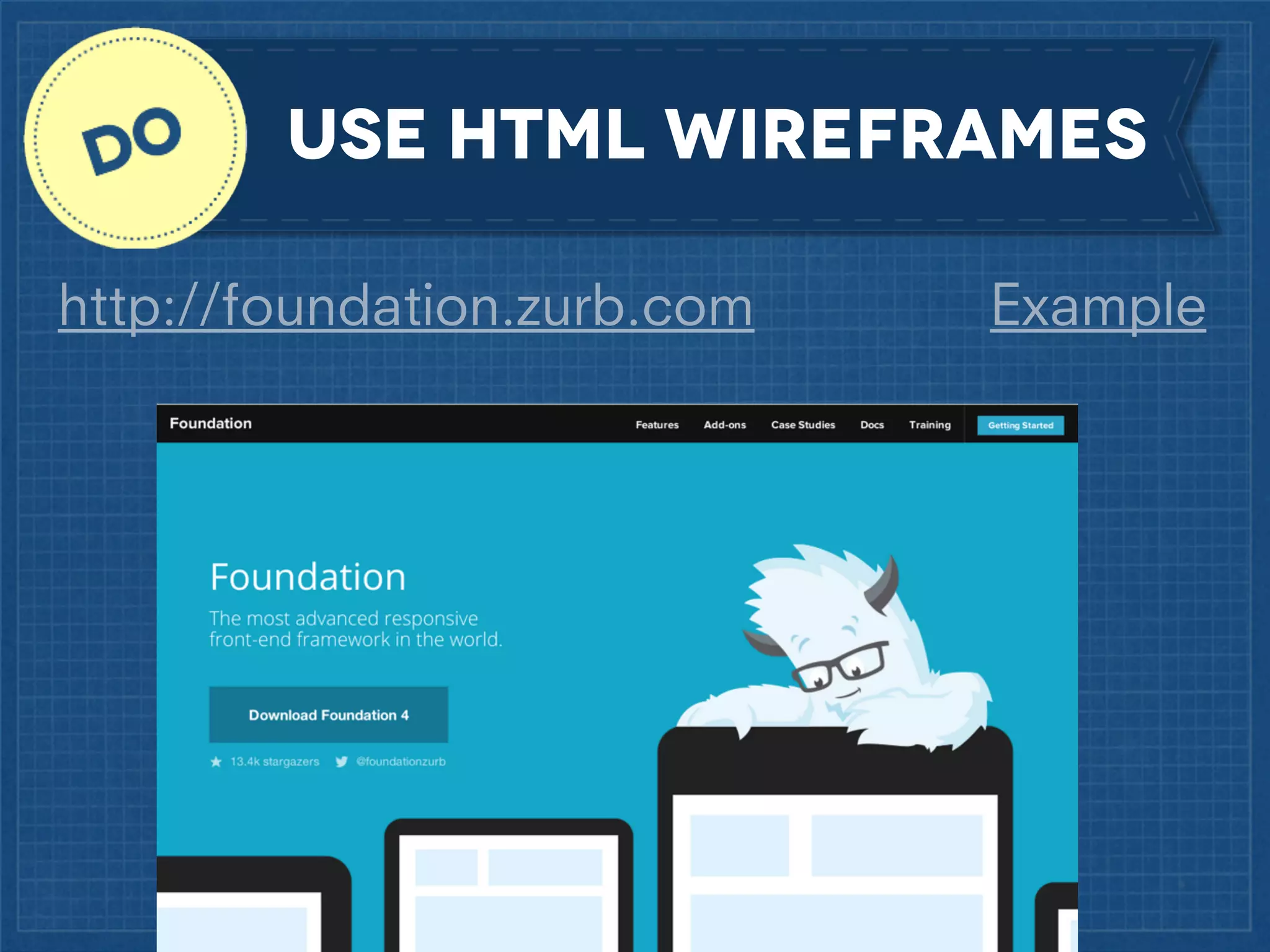
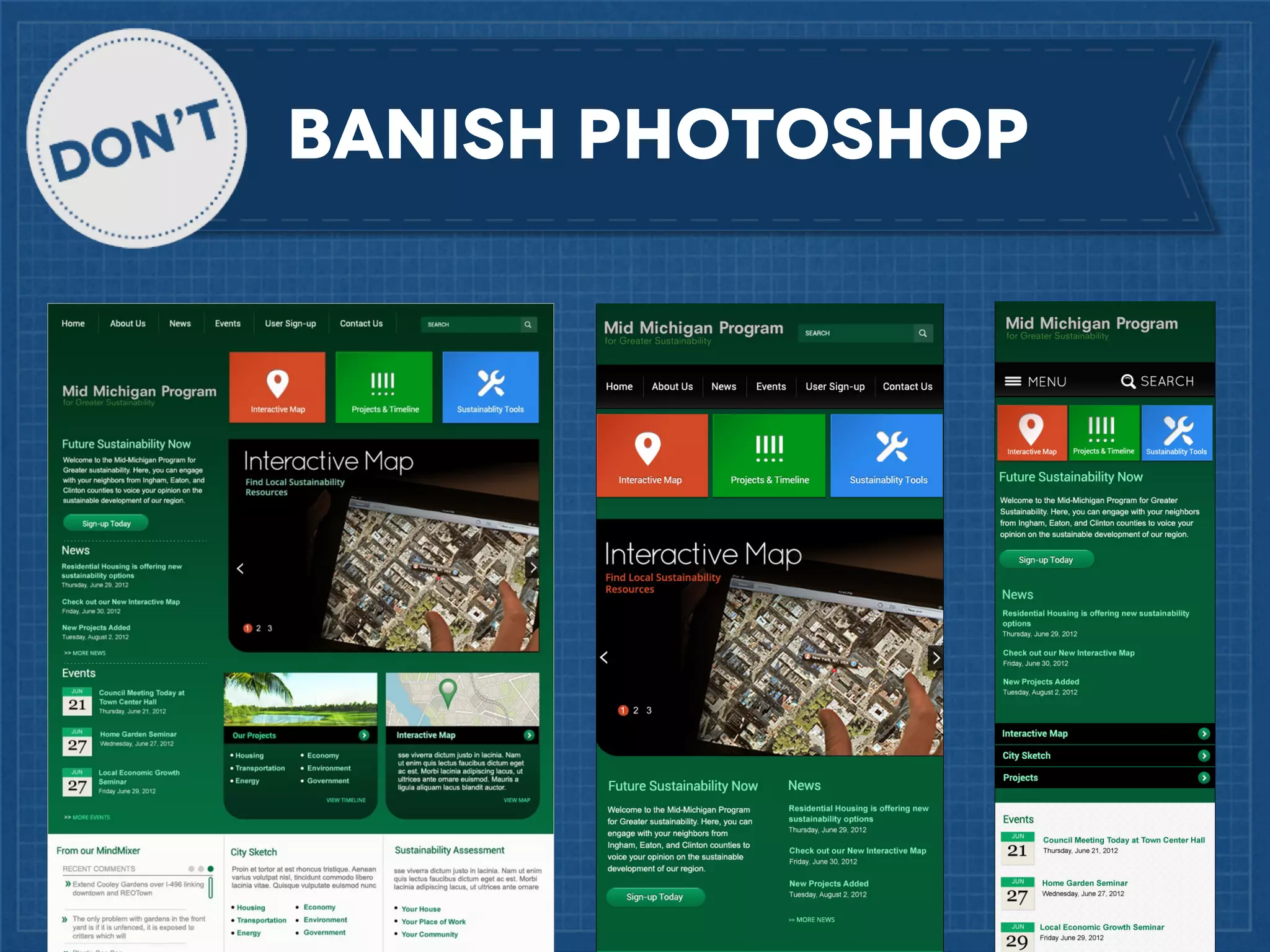
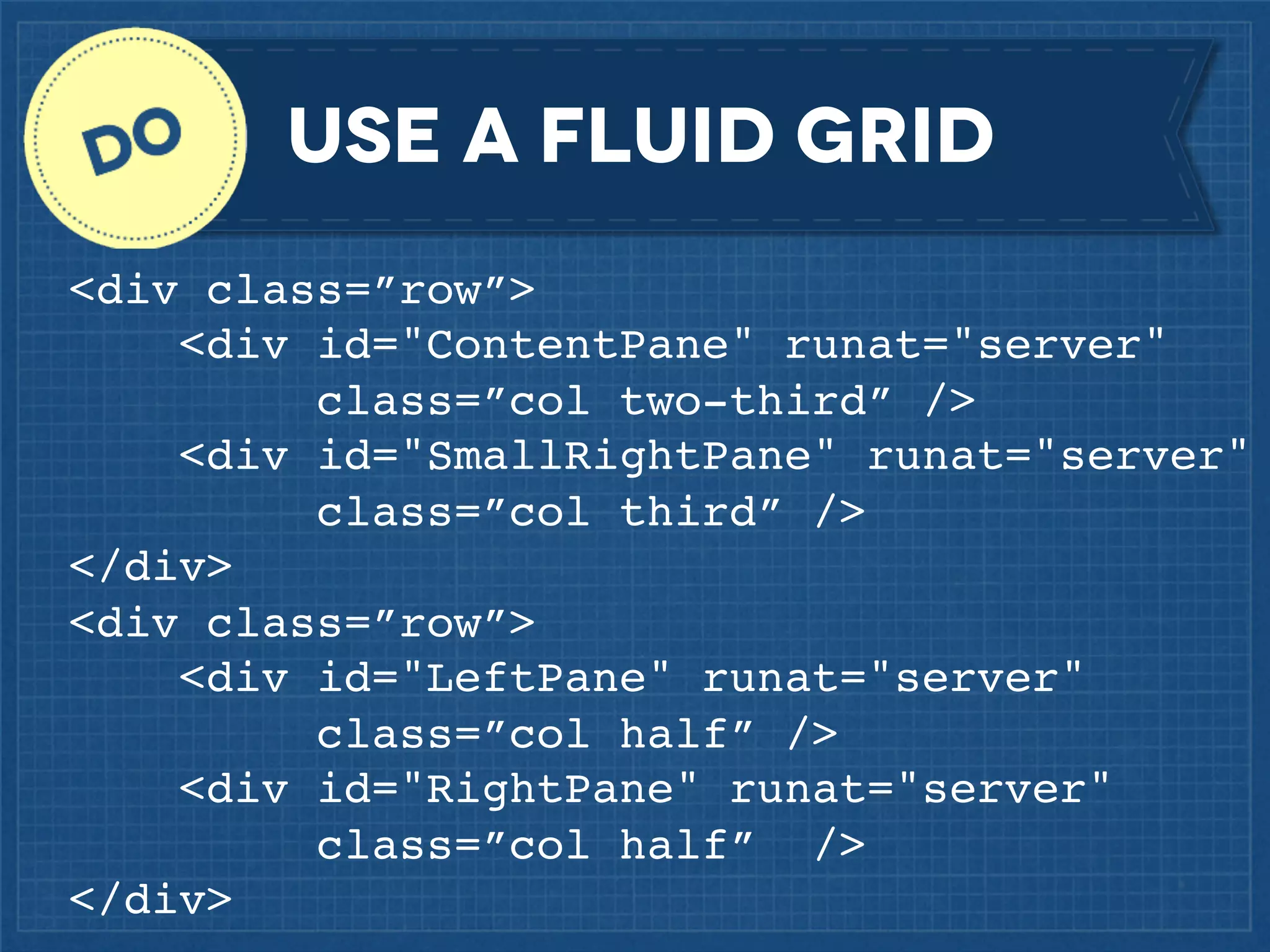
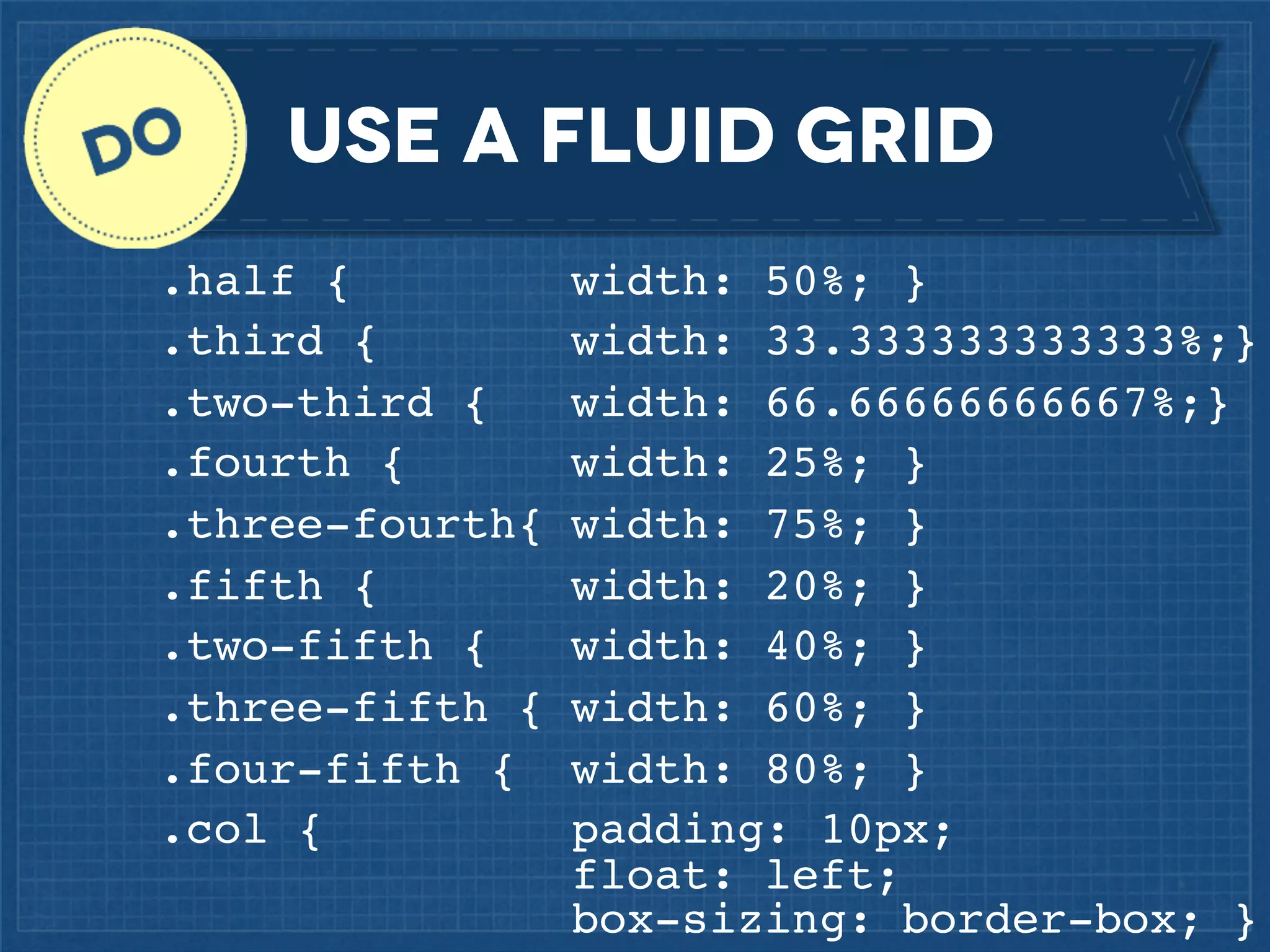
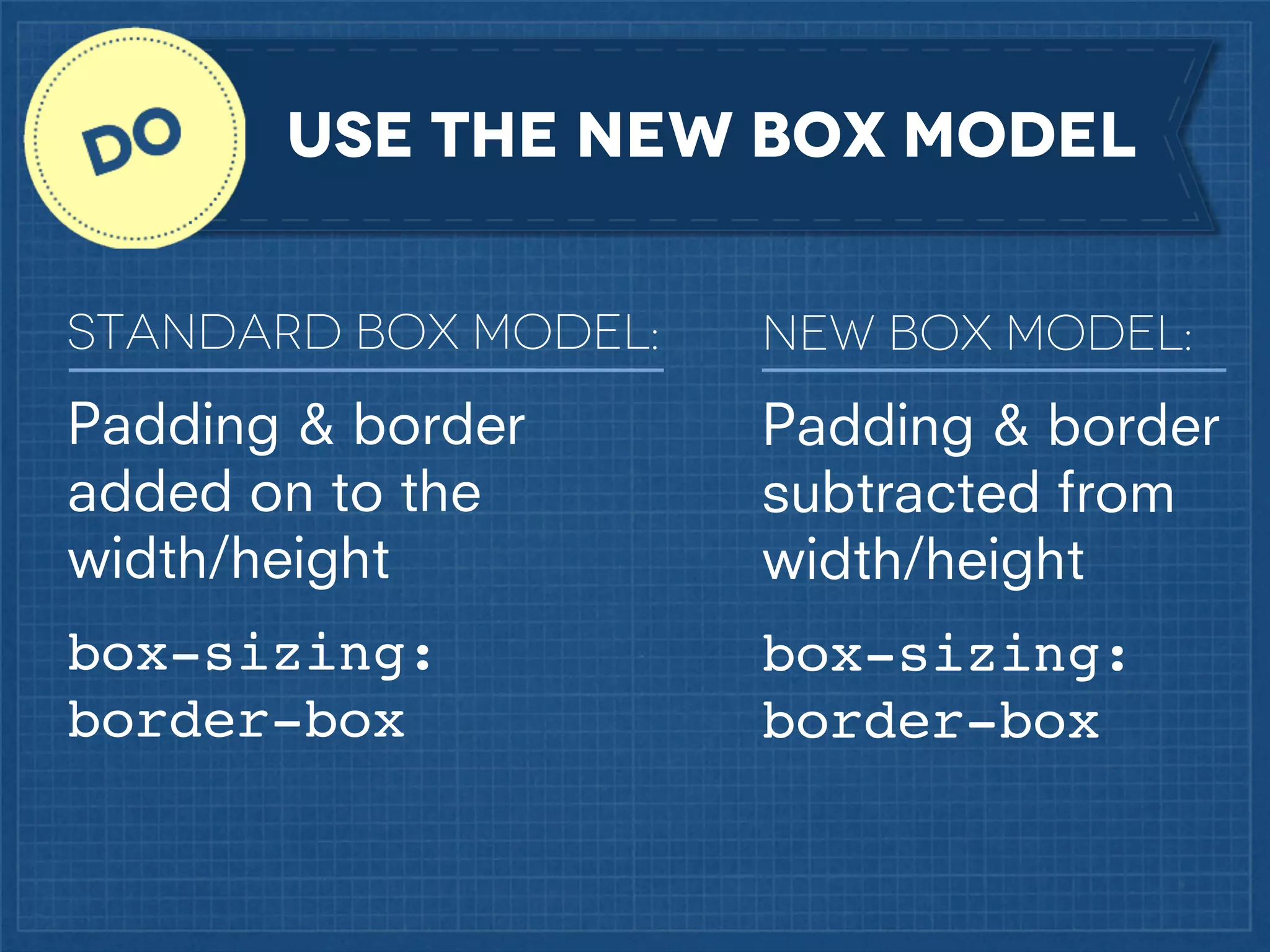
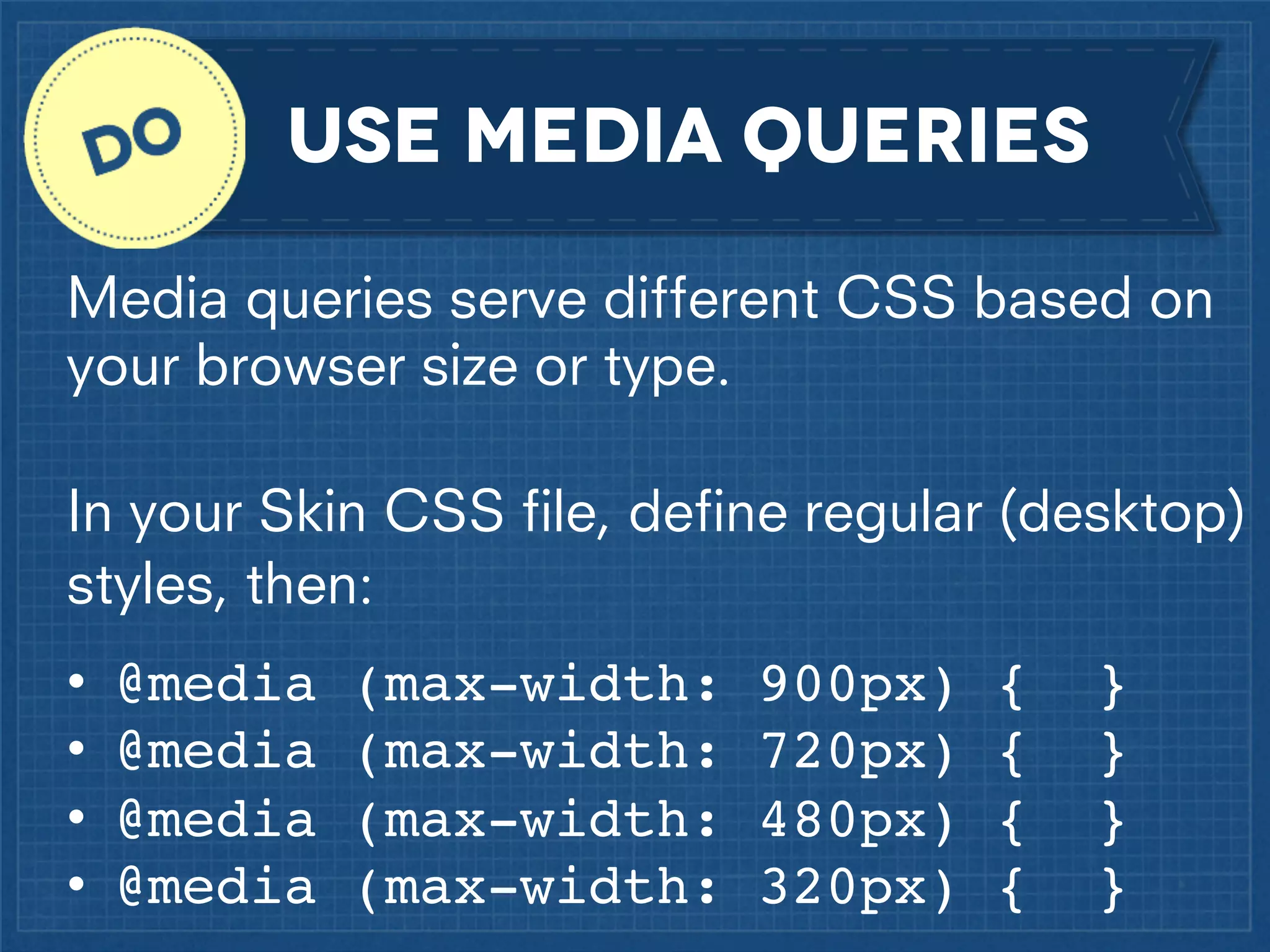
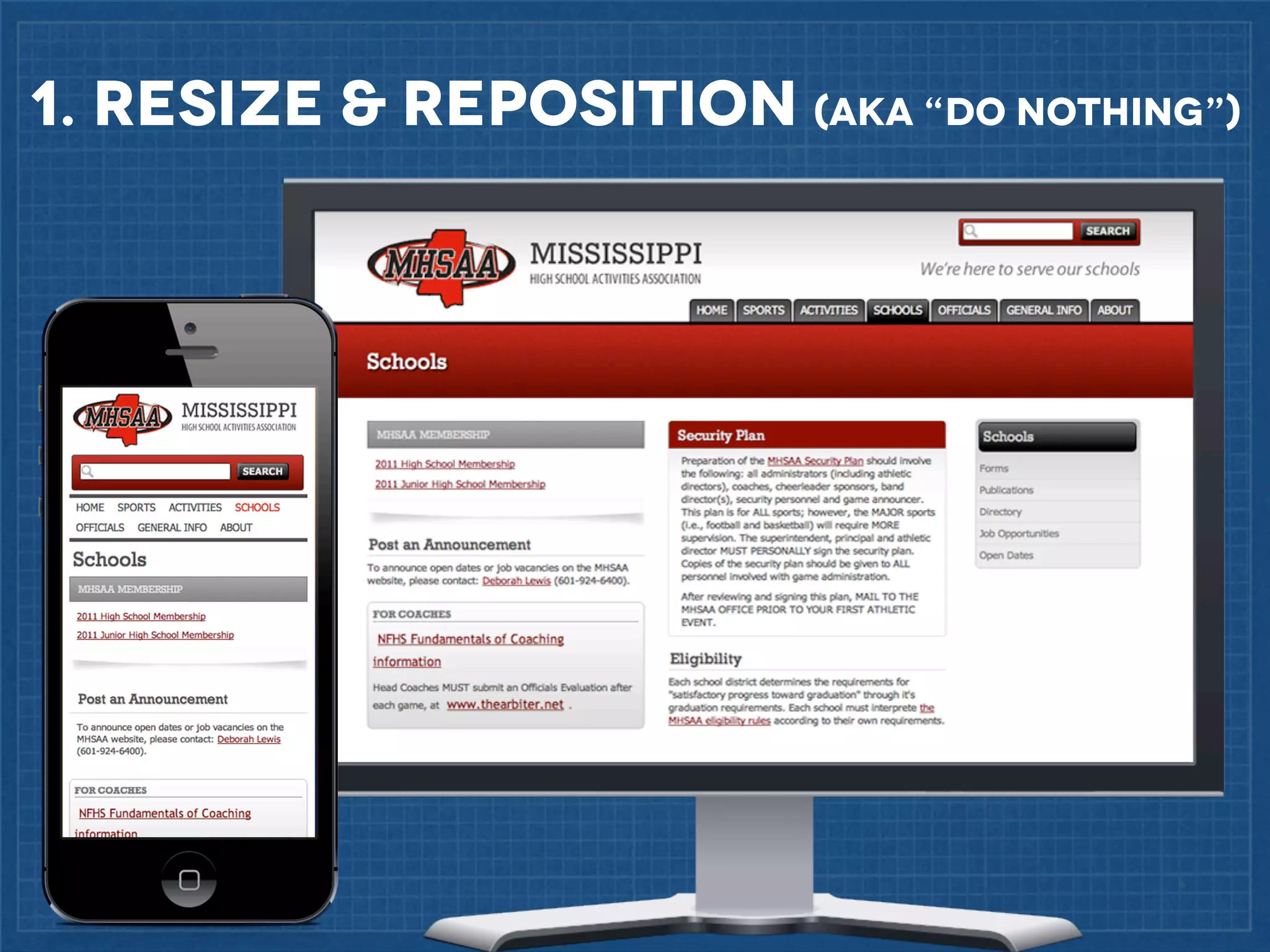
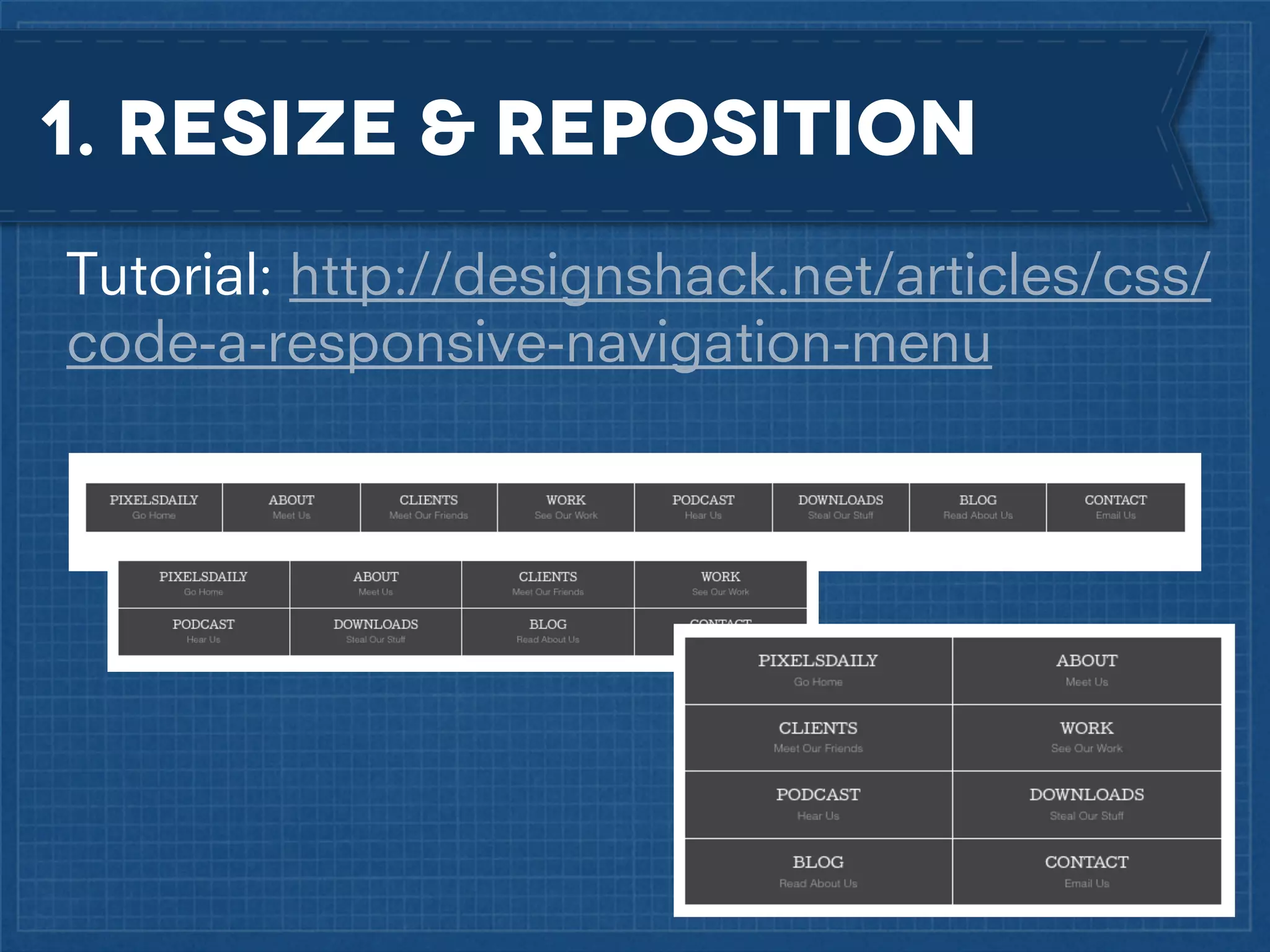
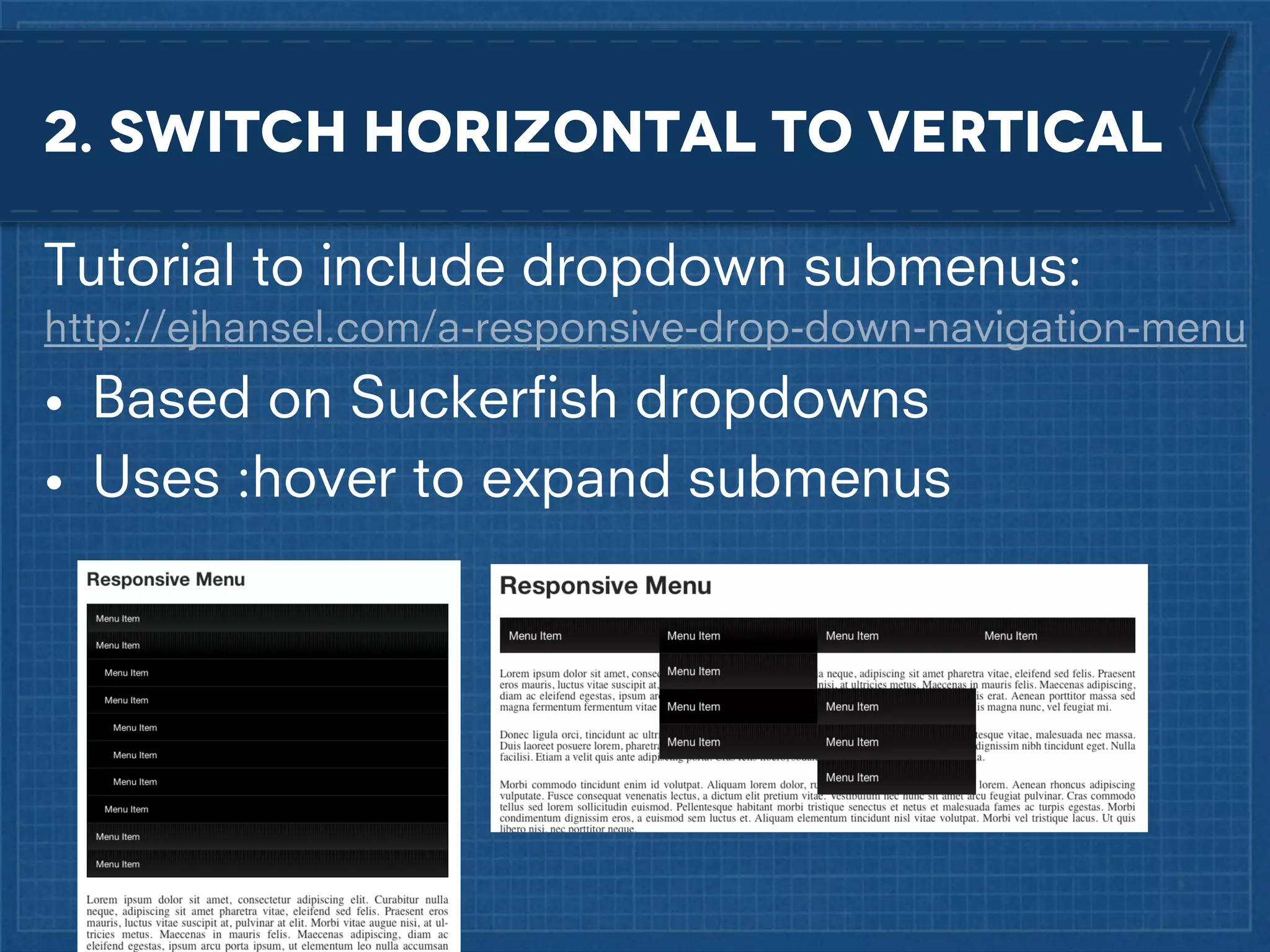
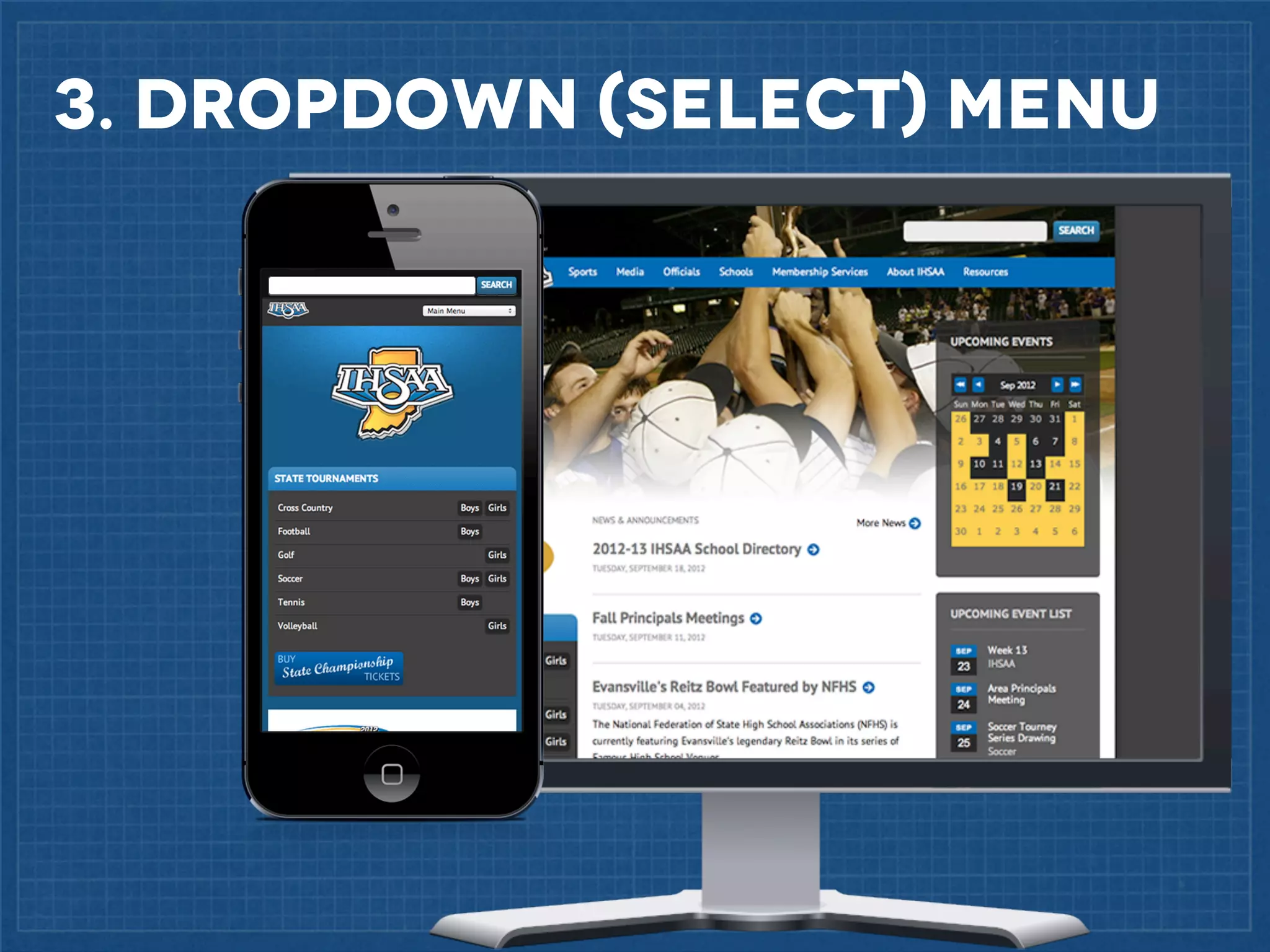
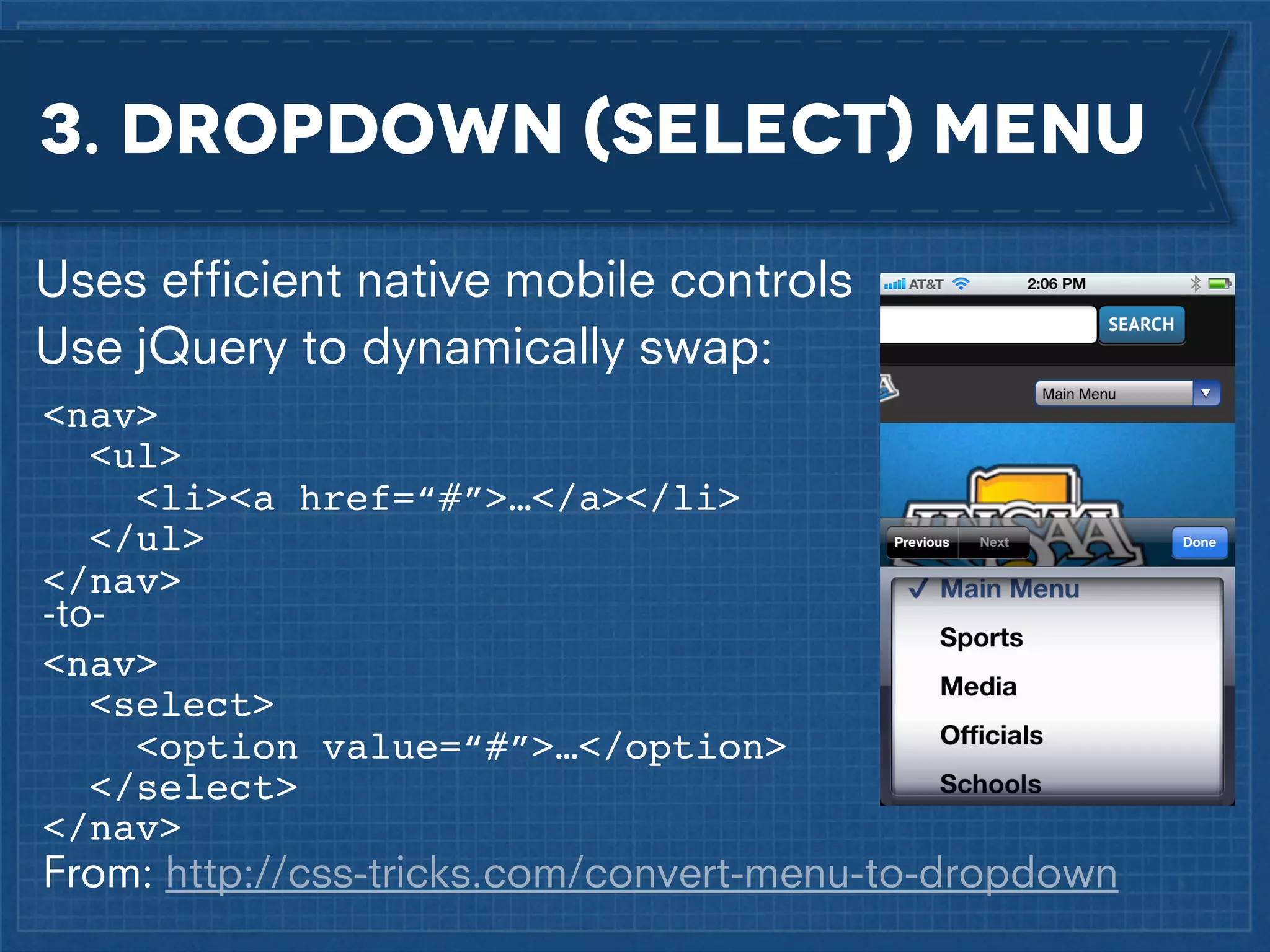
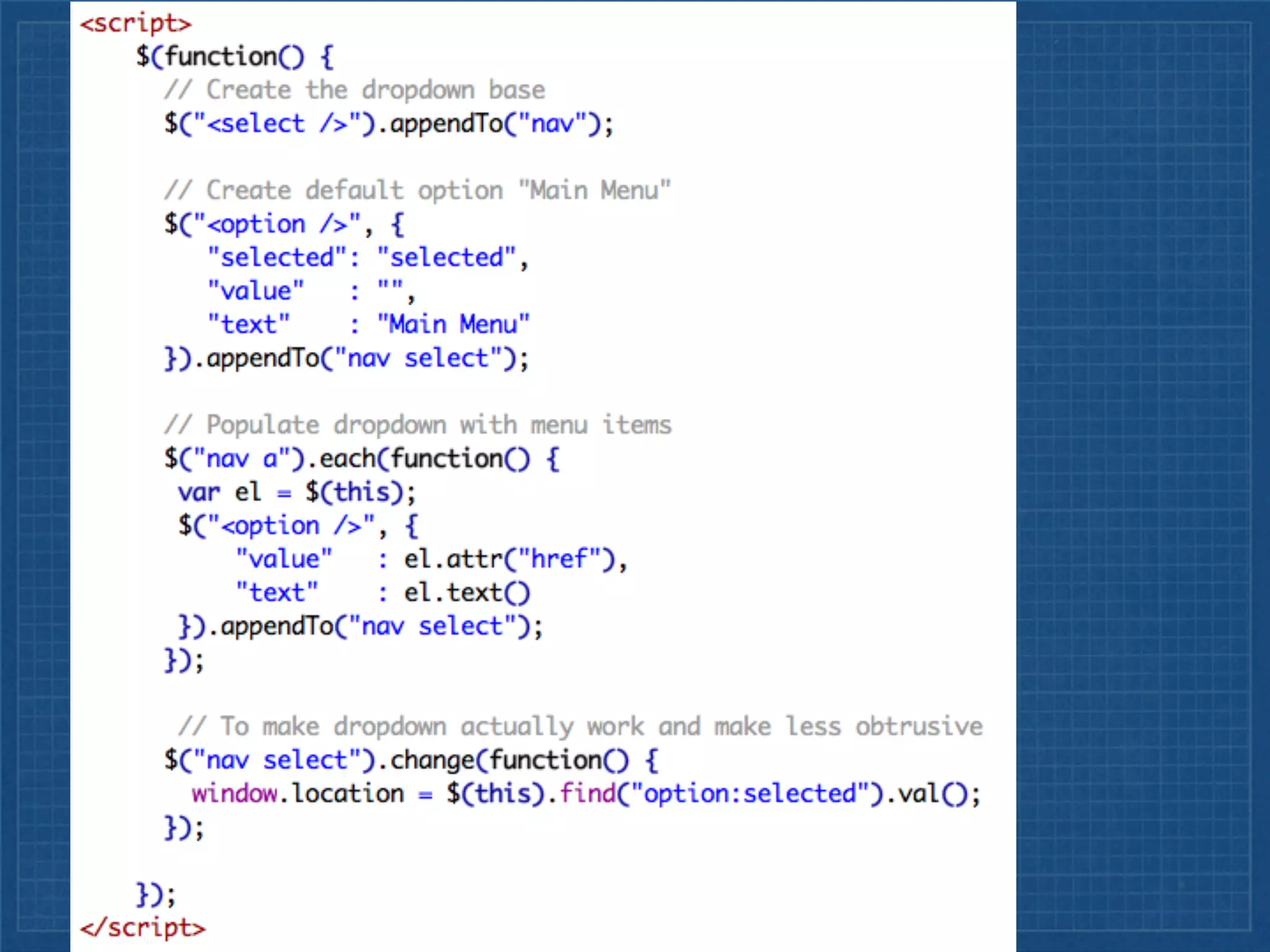
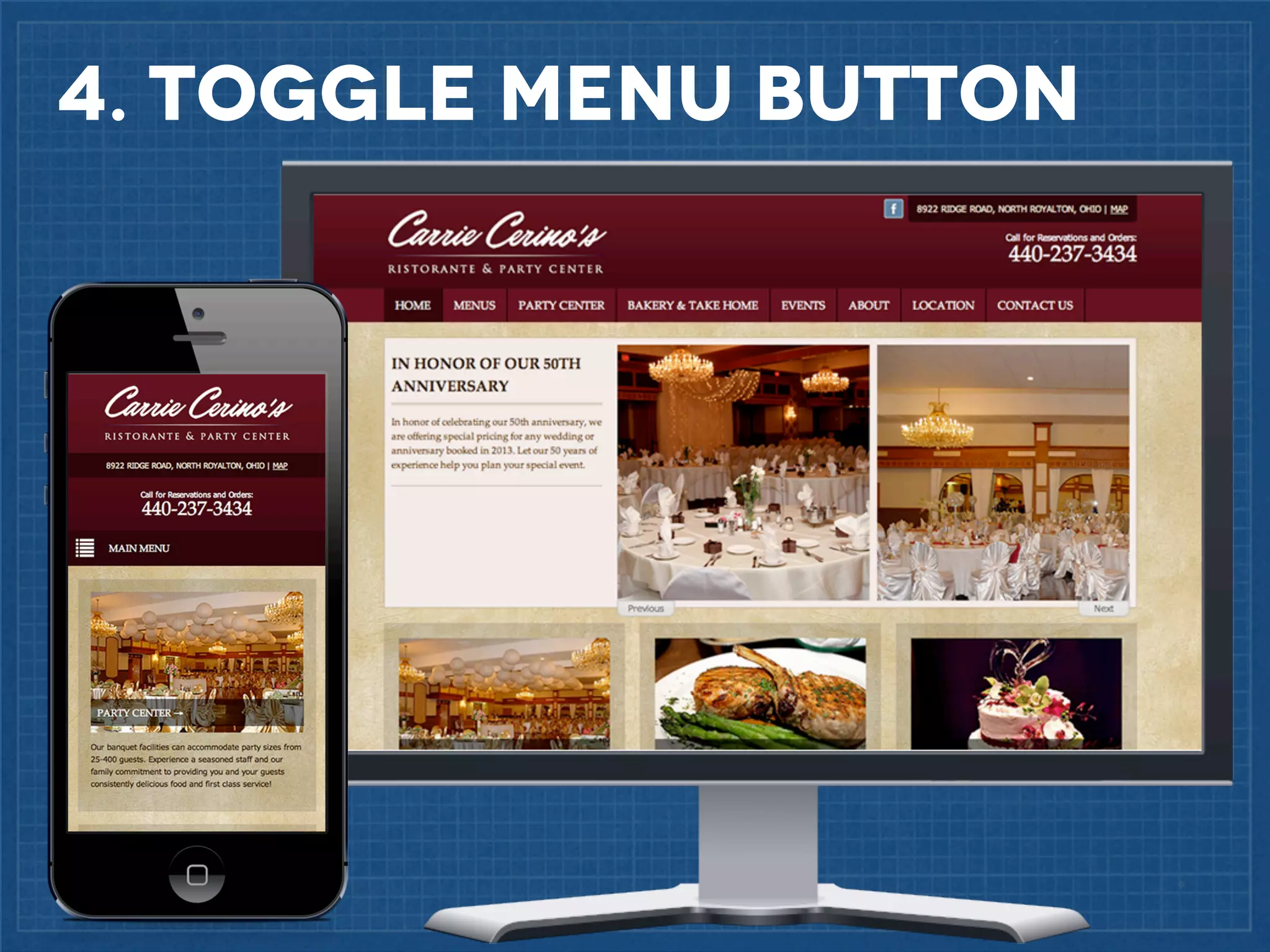
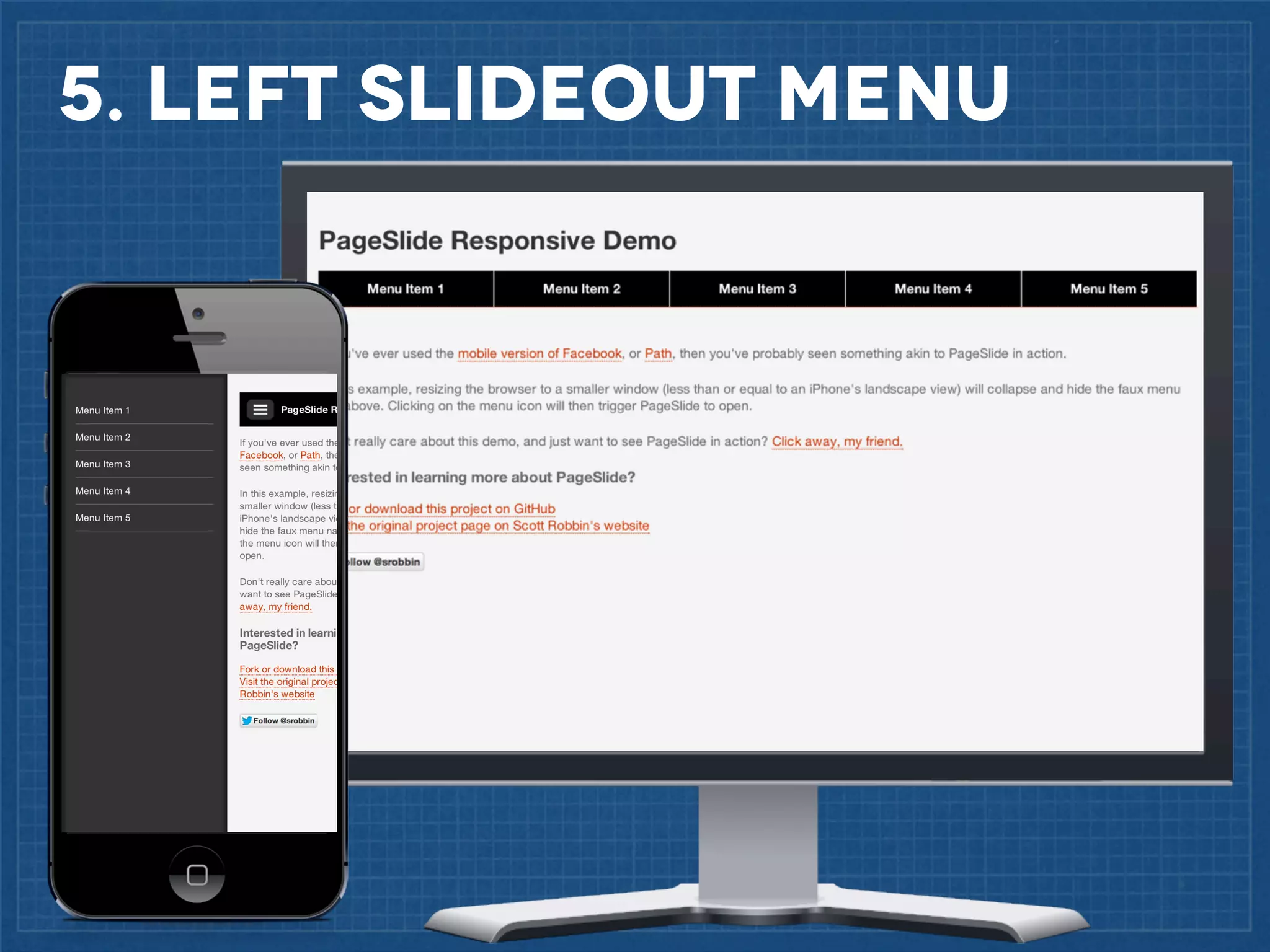
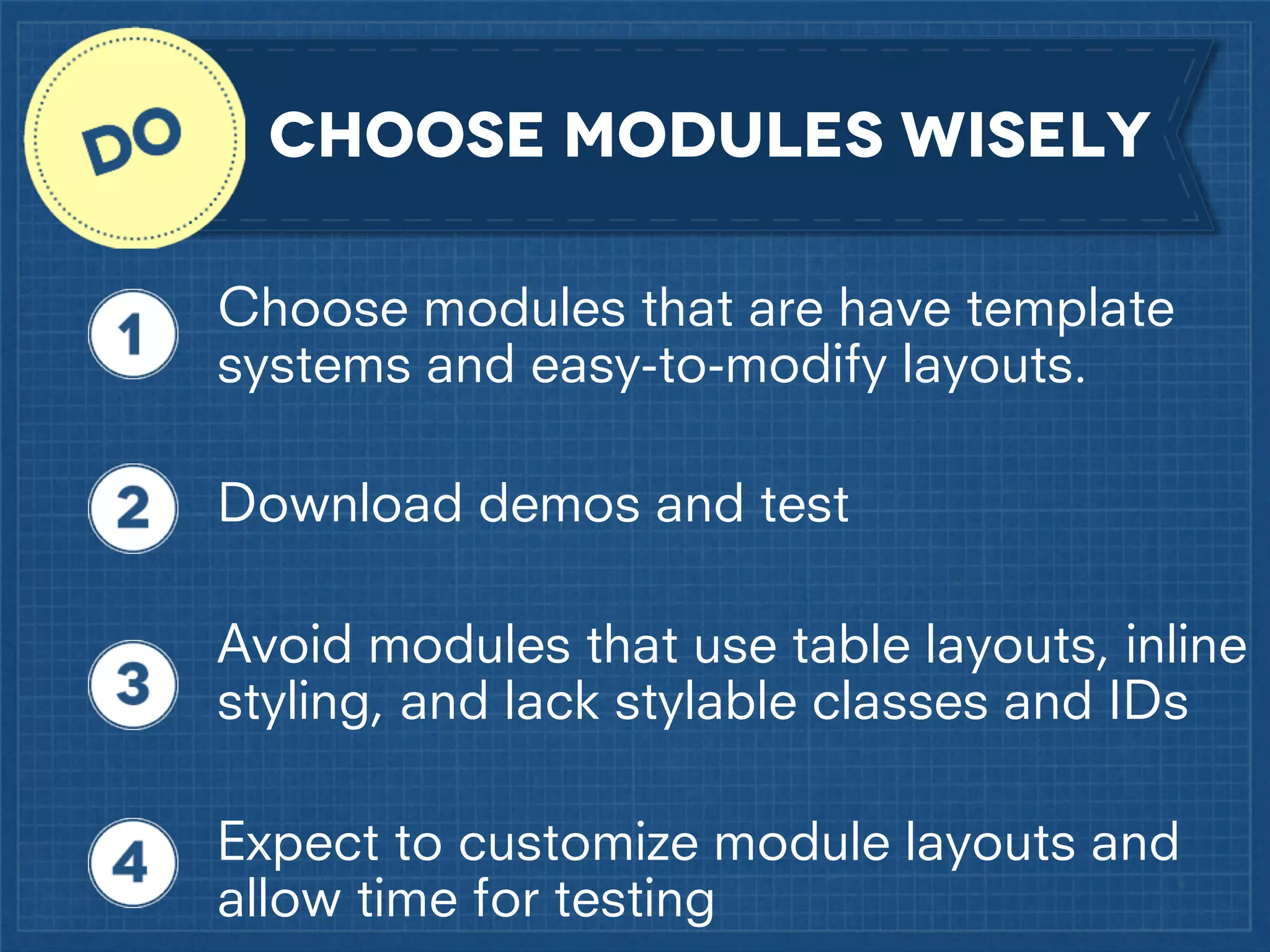
The document outlines best practices for implementing responsive web design with a focus on fluid layouts, media queries, and mobile-first priorities. It emphasizes the importance of content prioritization, using HTML wireframes, and creating a style guide for efficient development. Various strategies for creating responsive navigation menus and managing media content are discussed, along with resources for further learning.