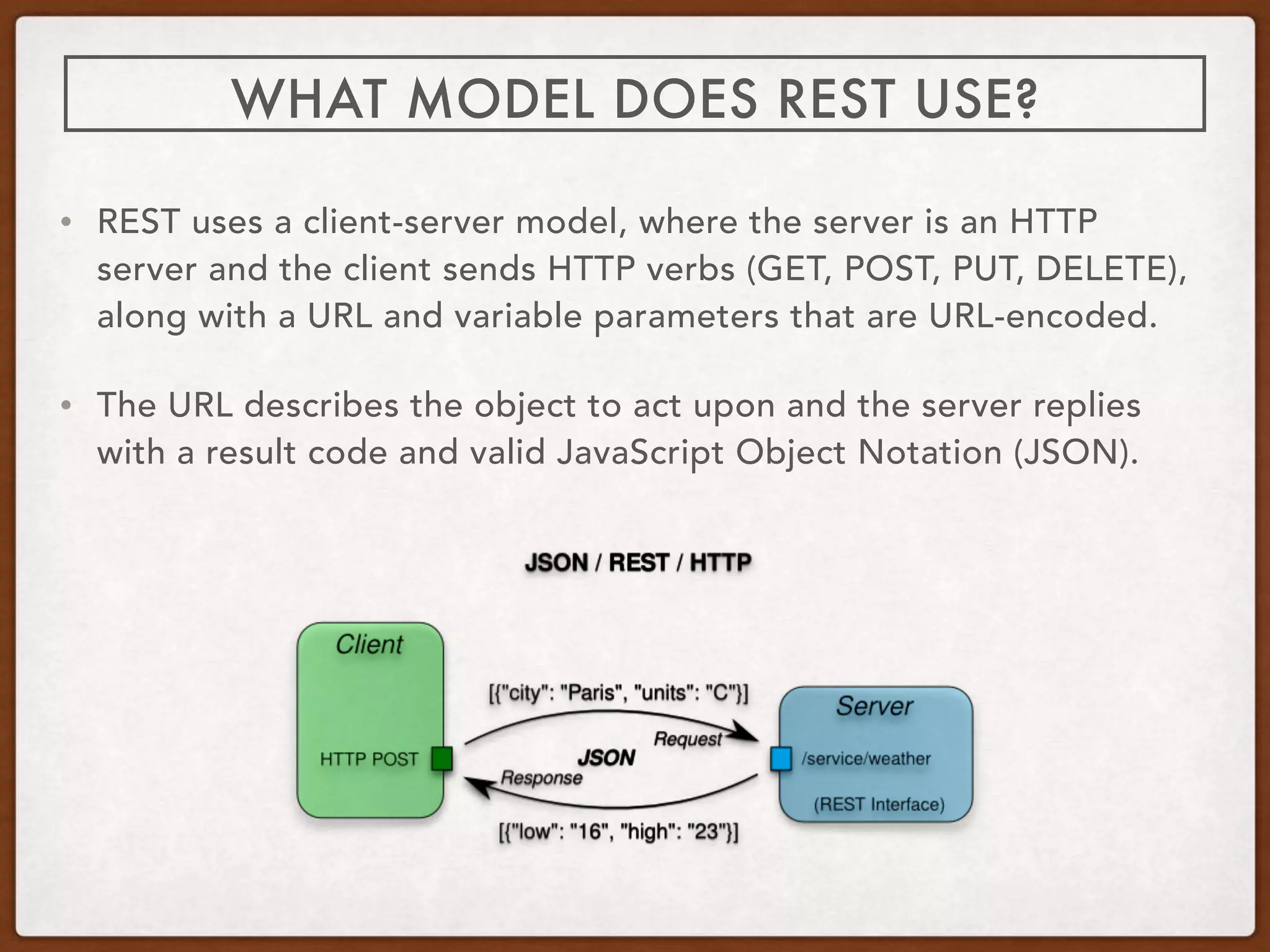
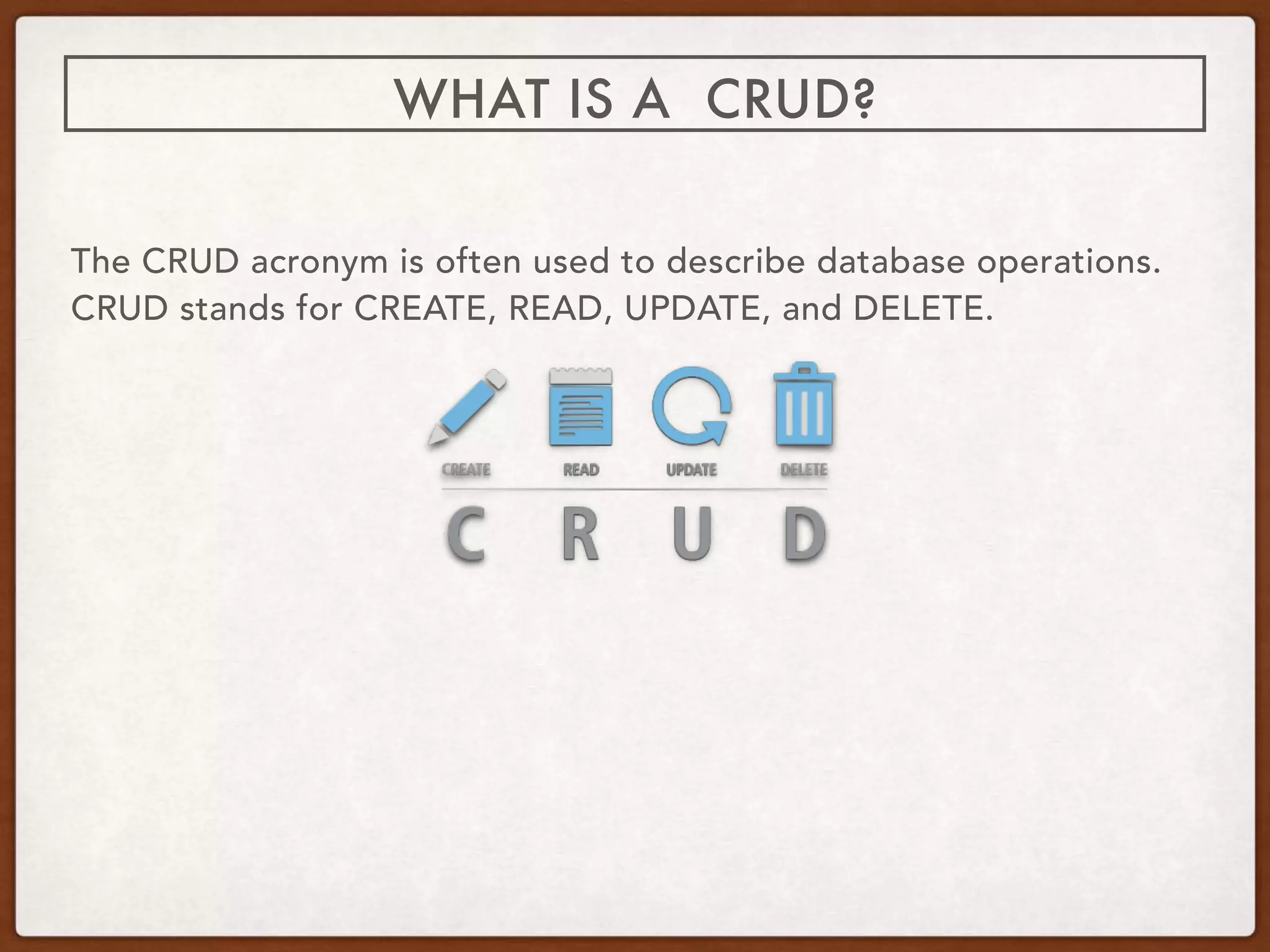
A REST API uses HTTP requests with verbs like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources identified by URLs. It provides a lightweight alternative to SOAP that returns data in JSON format and HTTP response codes. Well-known codes include 200 for OK, 201 for Created, 400 for Bad Request, and 404 for Not Found. REST enables building applications and platforms that can easily integrate new interfaces over time.