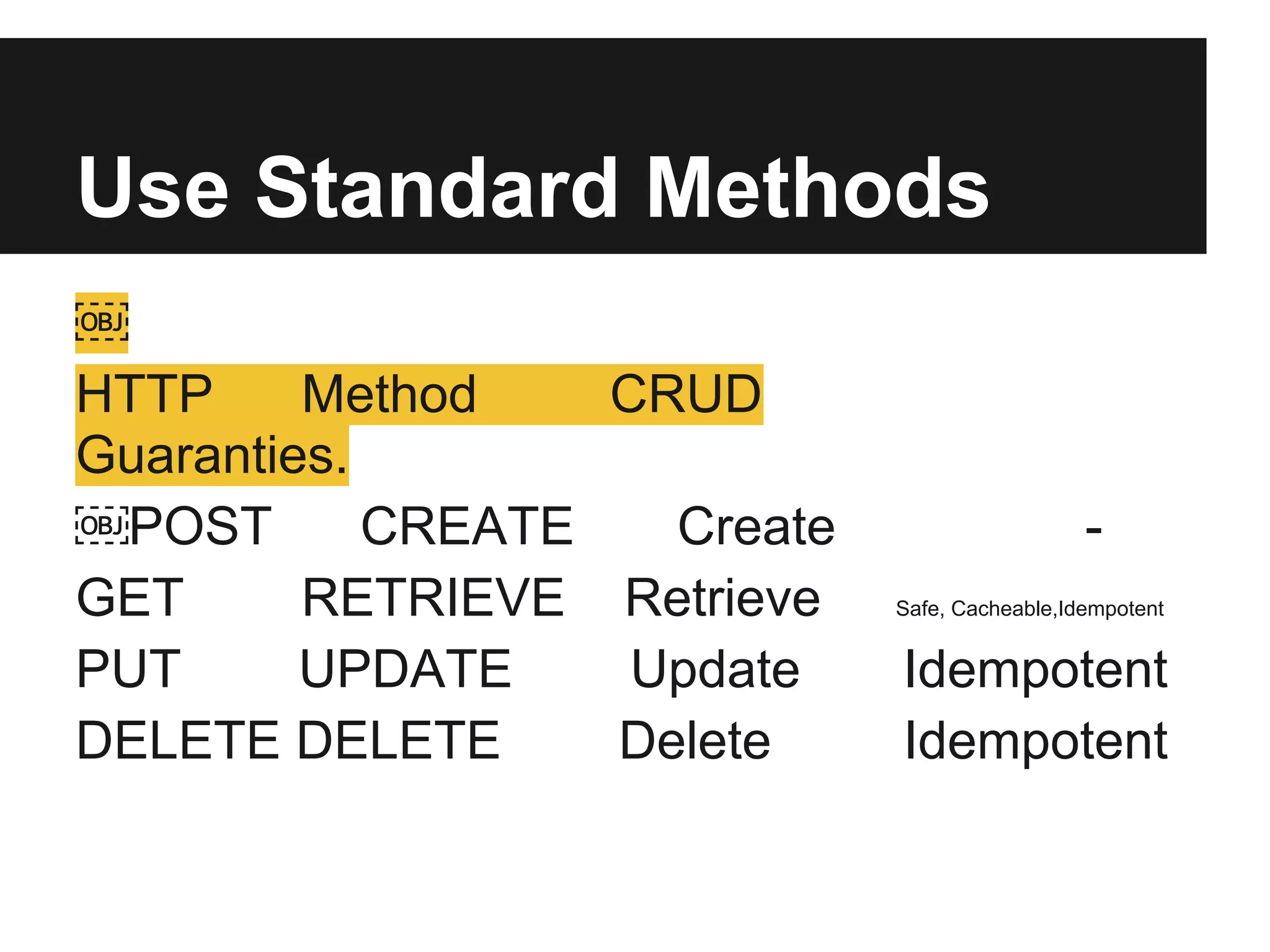
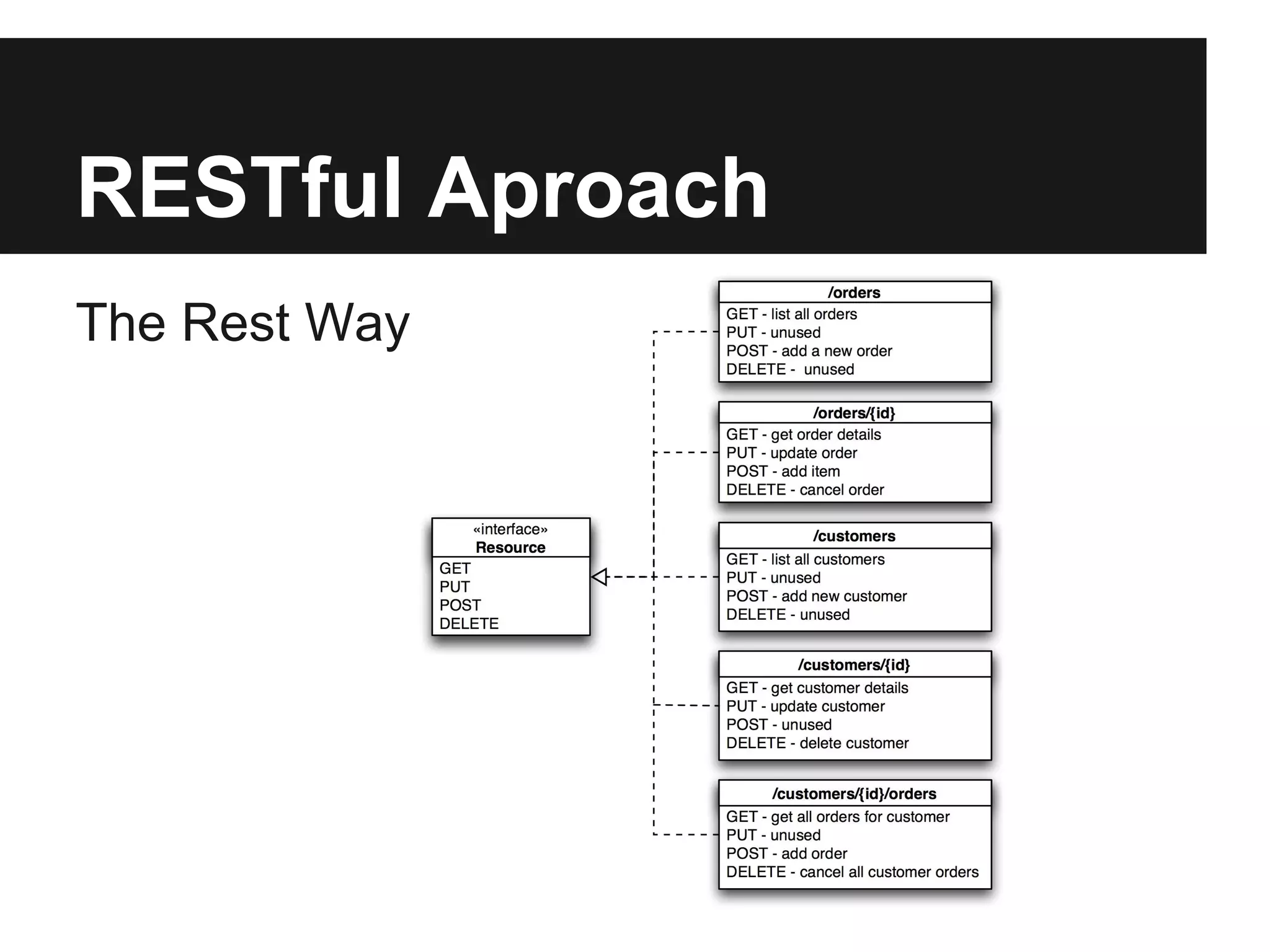
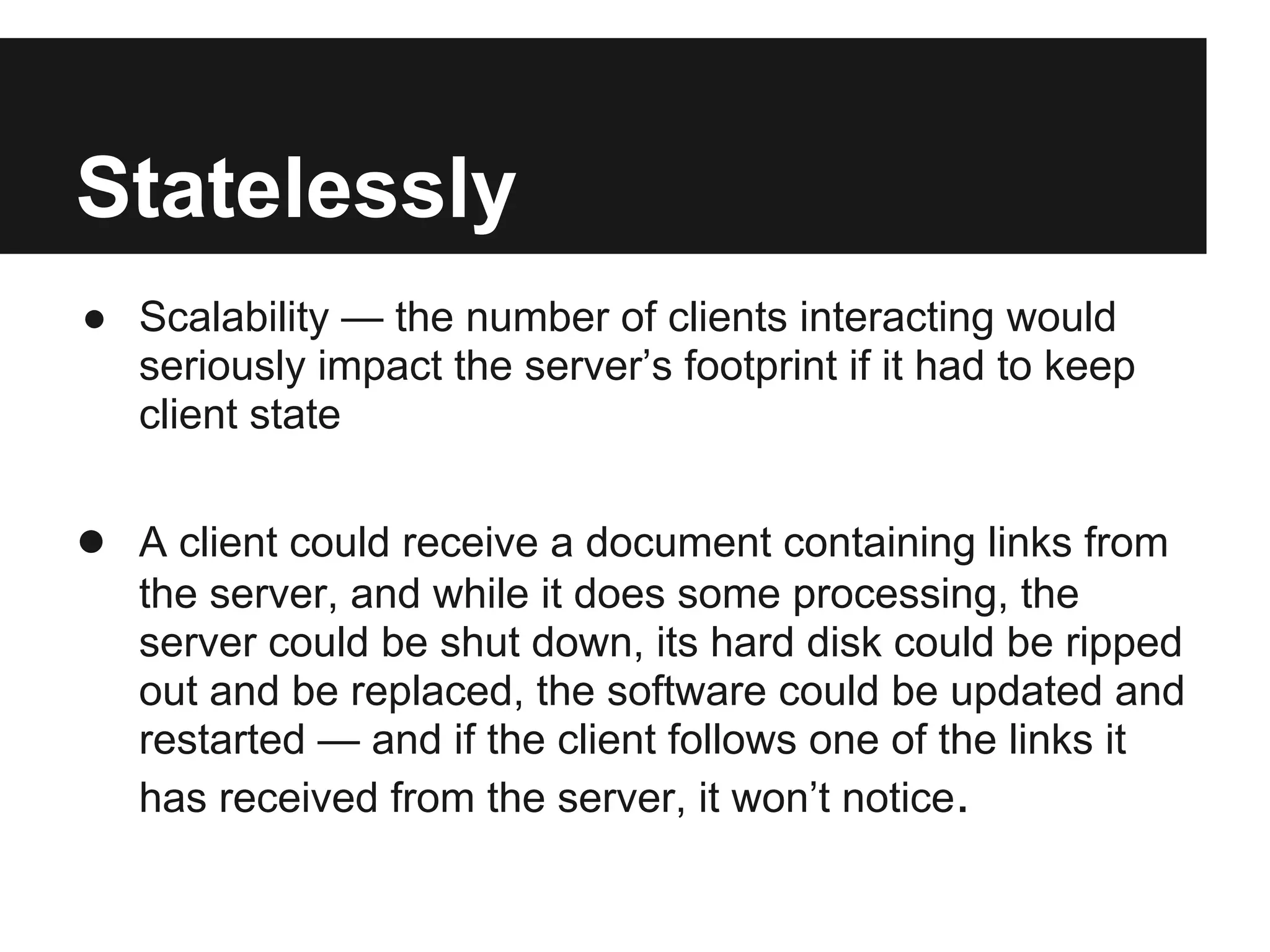
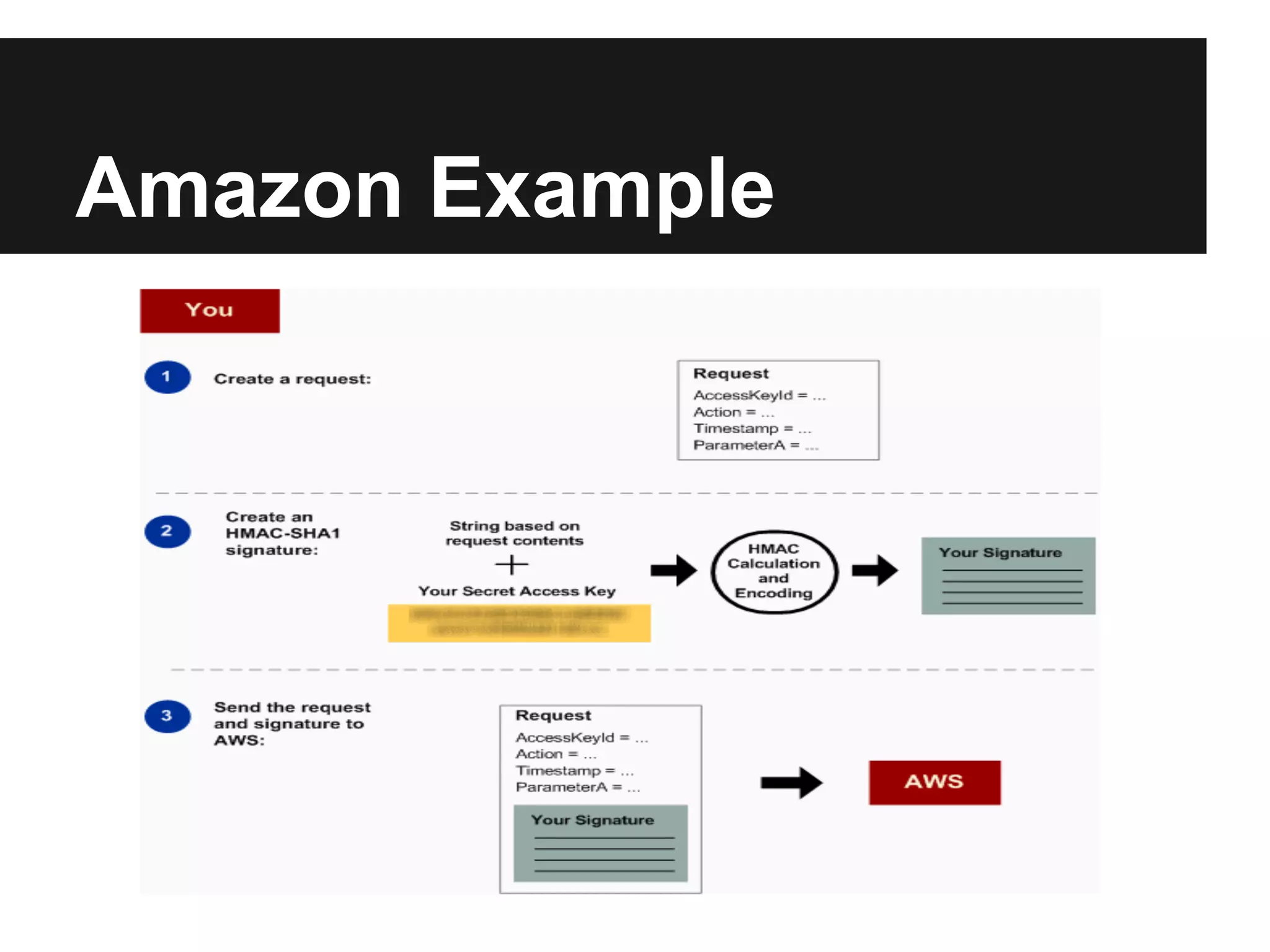
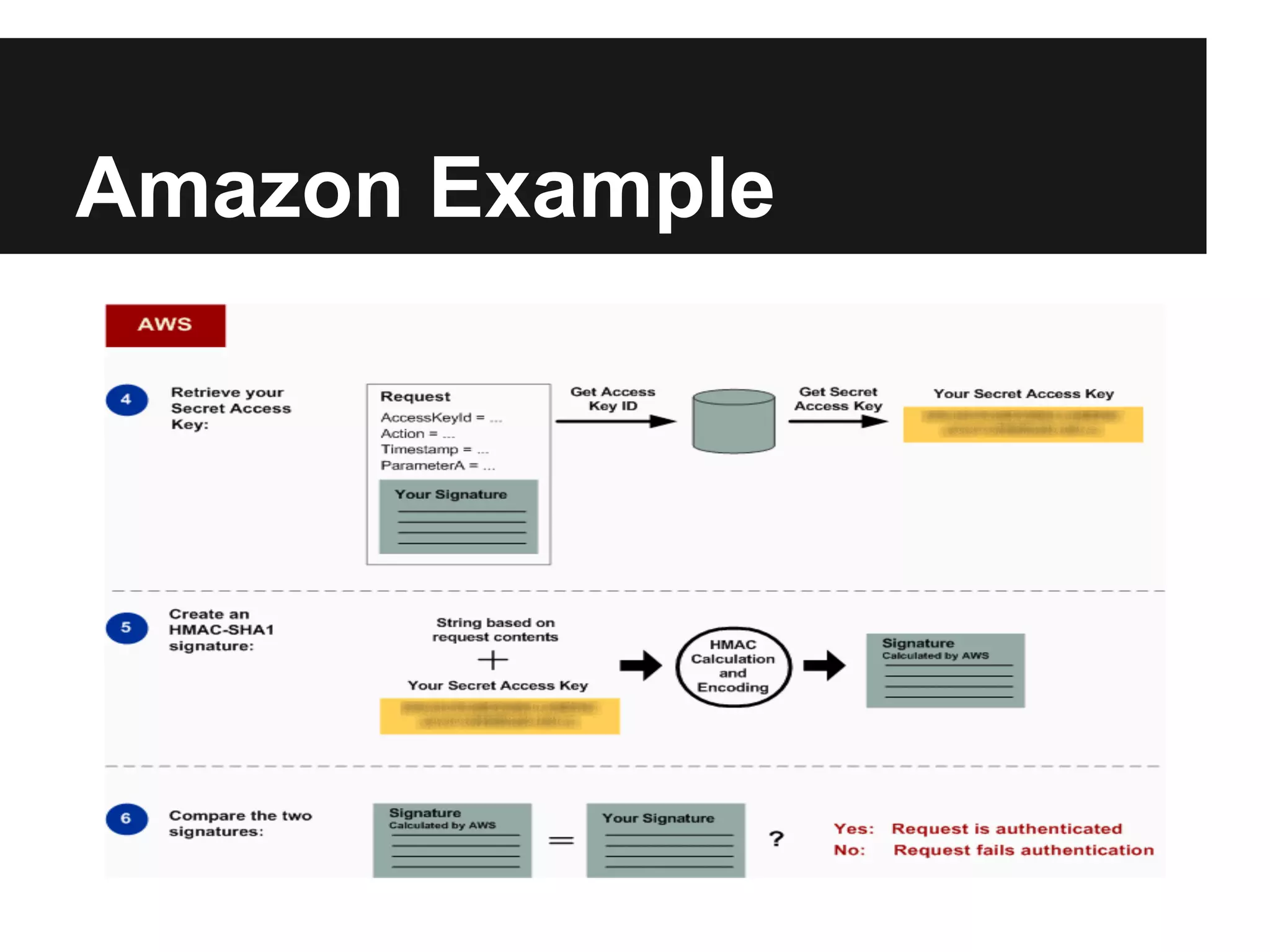
This document provides an overview of Representational State Transfer (REST), describing its key principles for designing web services. REST uses a stateless, client-server architecture where requests made to a resource's unique Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) can retrieve multiple representations of that resource (e.g. XML, JSON). The core REST operations are GET to retrieve a resource, POST to create, PUT to update, and DELETE to delete. Requests should be cacheable, idempotent and link resources together through hypermedia. State is managed by clients rather than servers to improve scalability. Authentication can be done through HTTP basic auth over HTTPS, cookies, or signing query parameters.