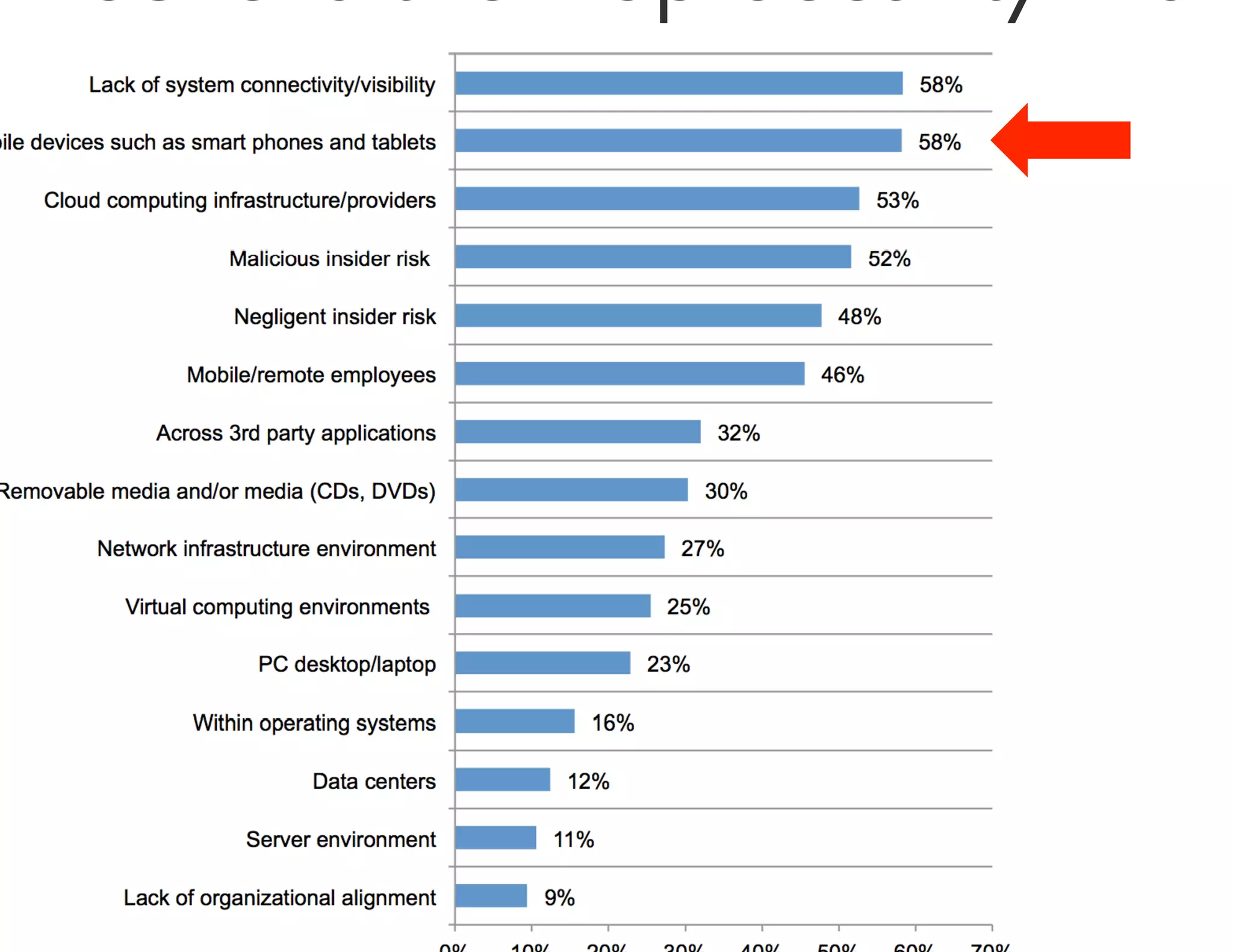
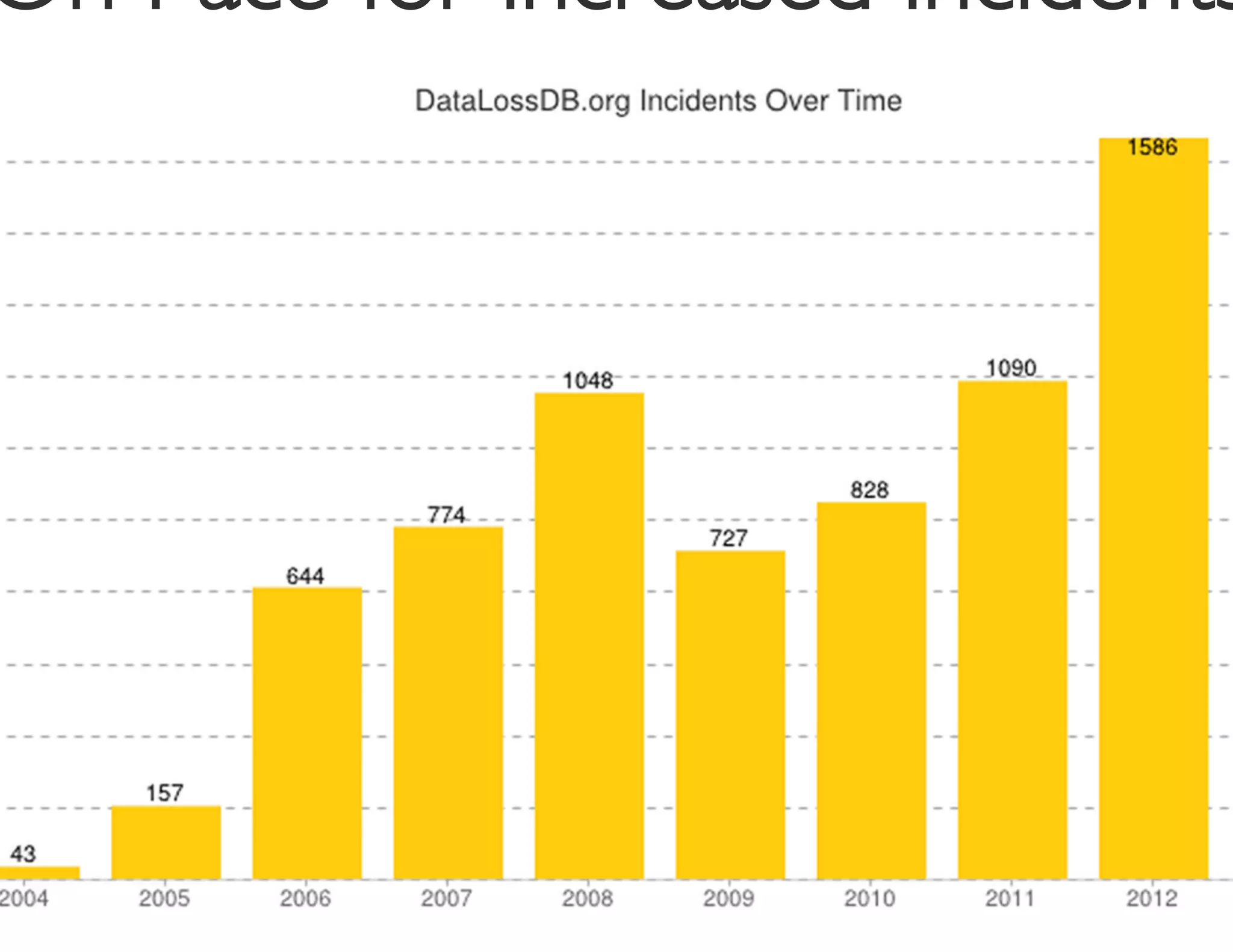
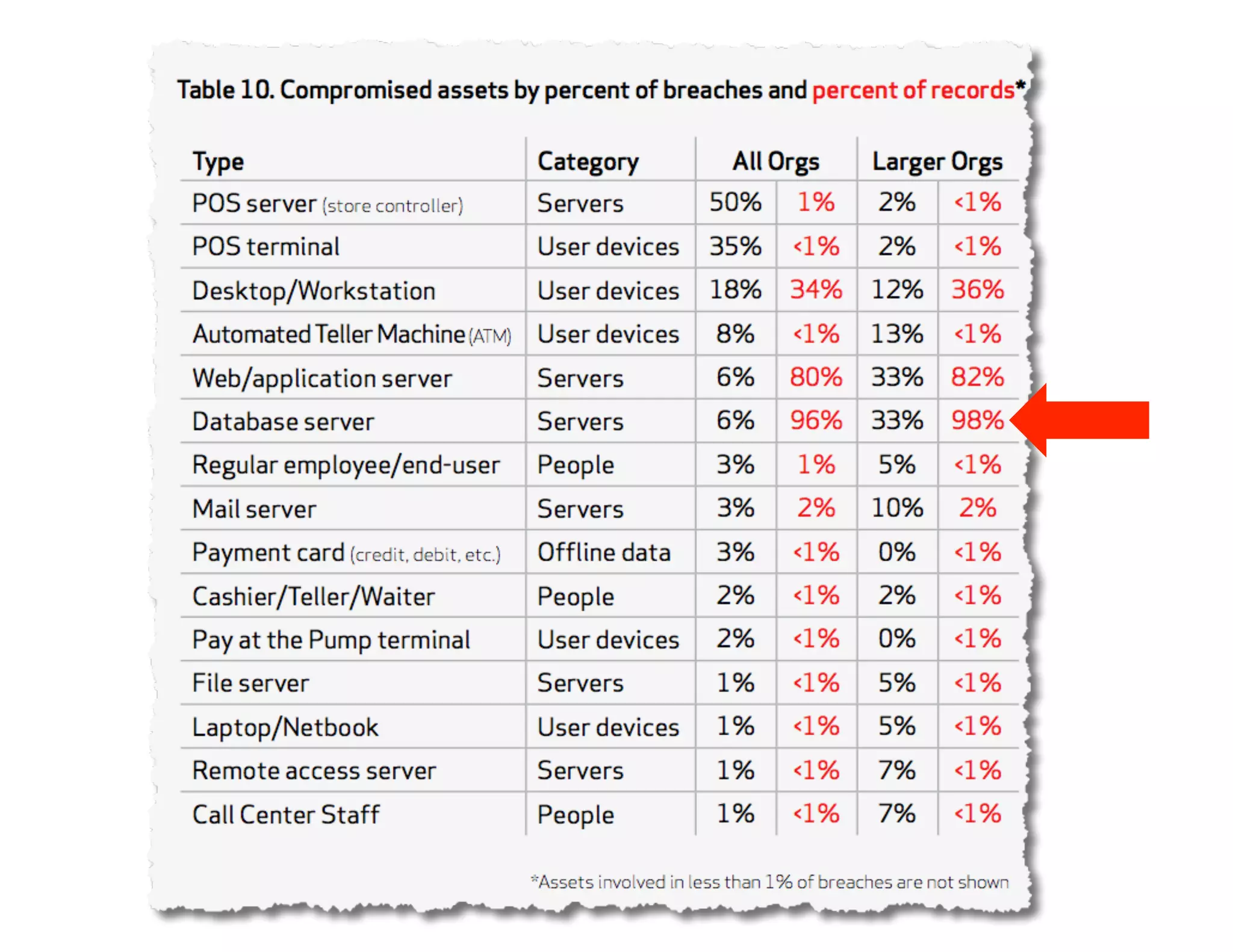
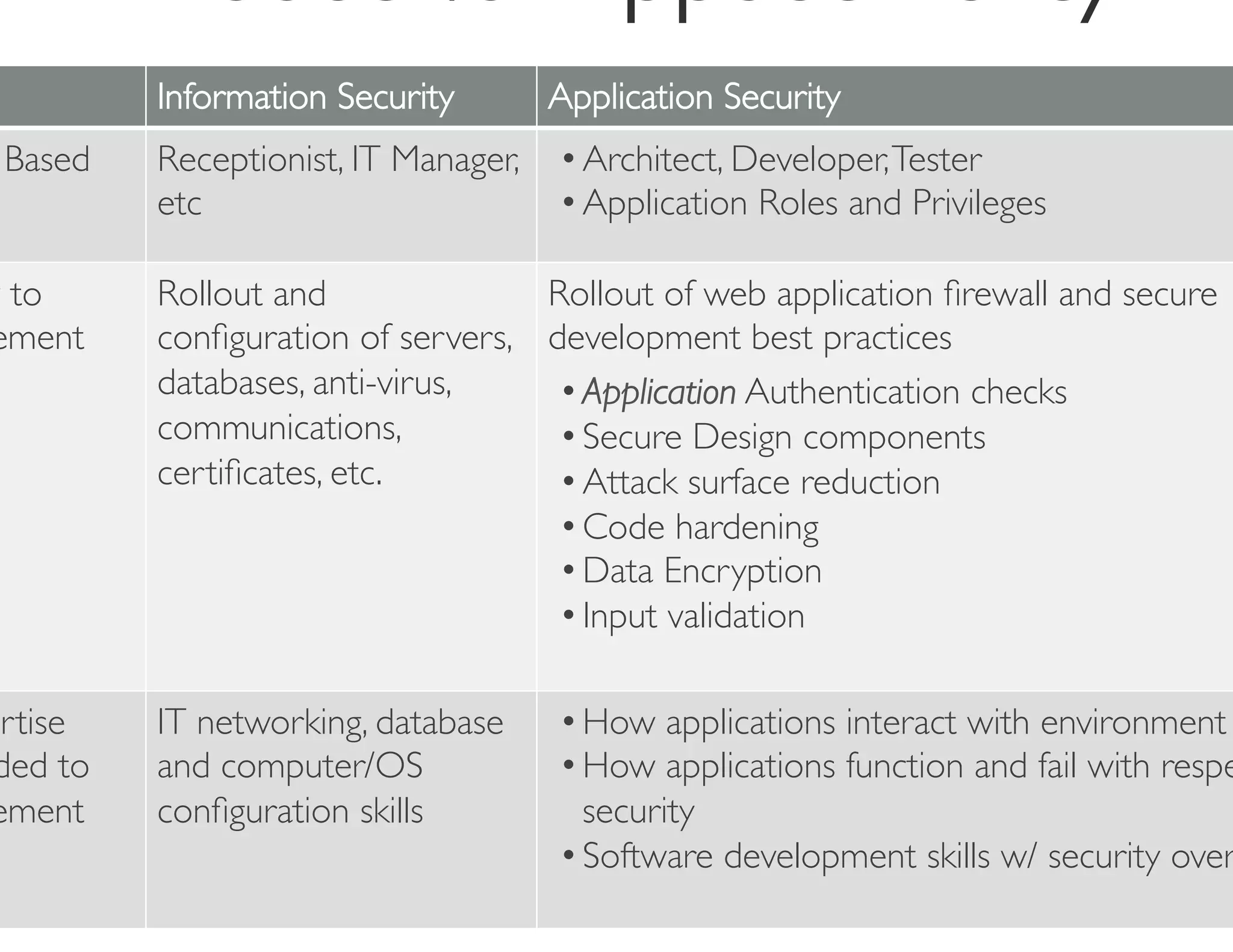
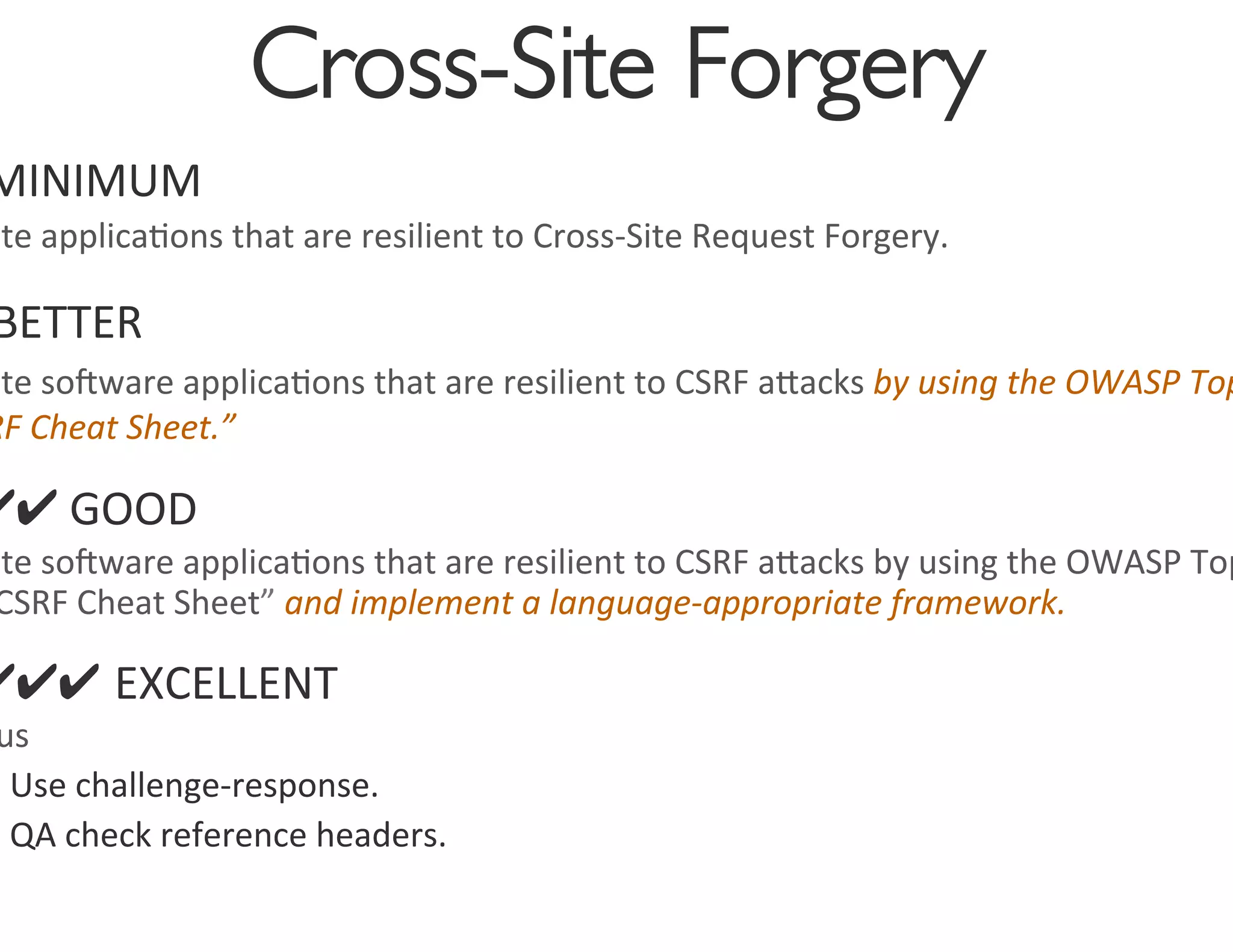
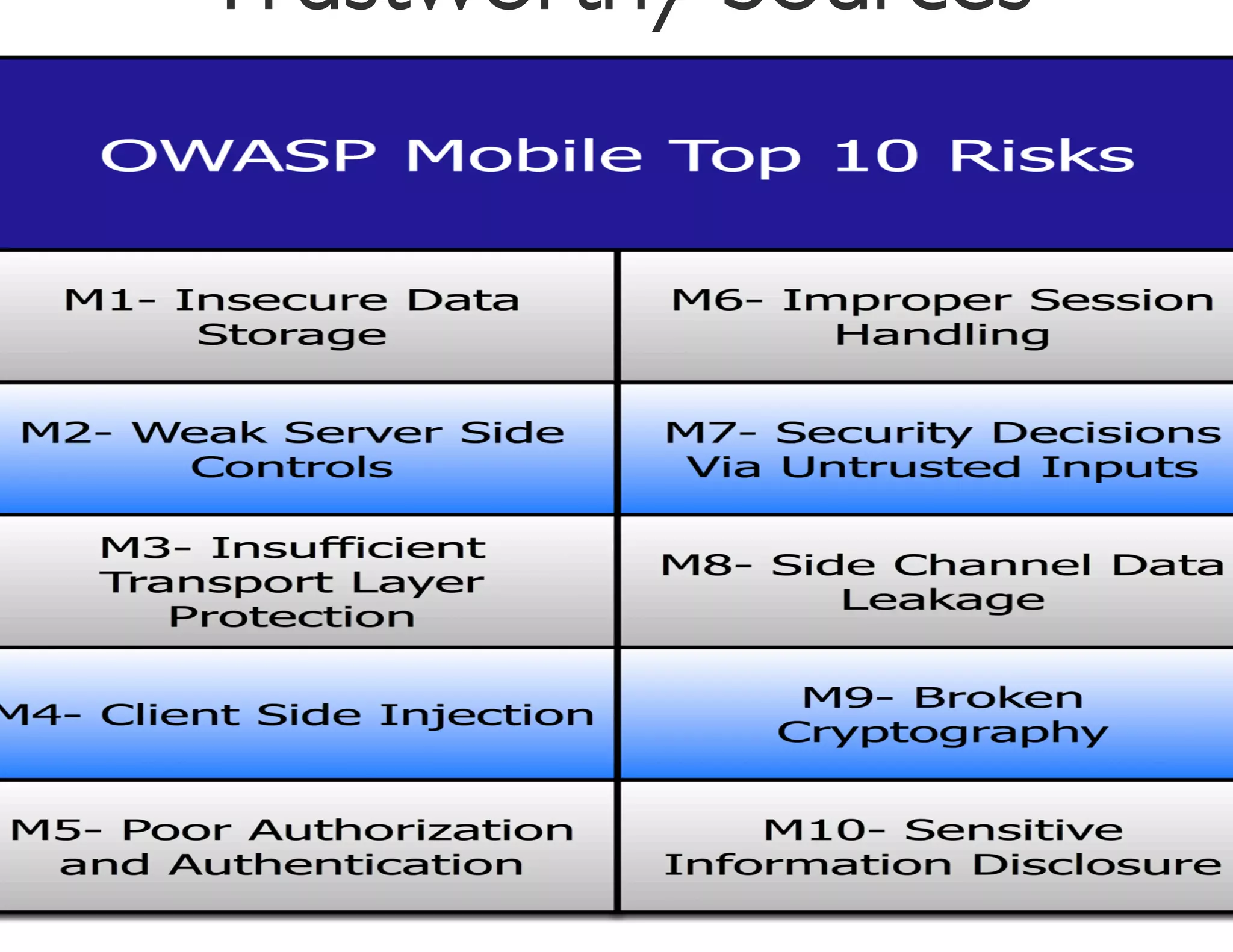
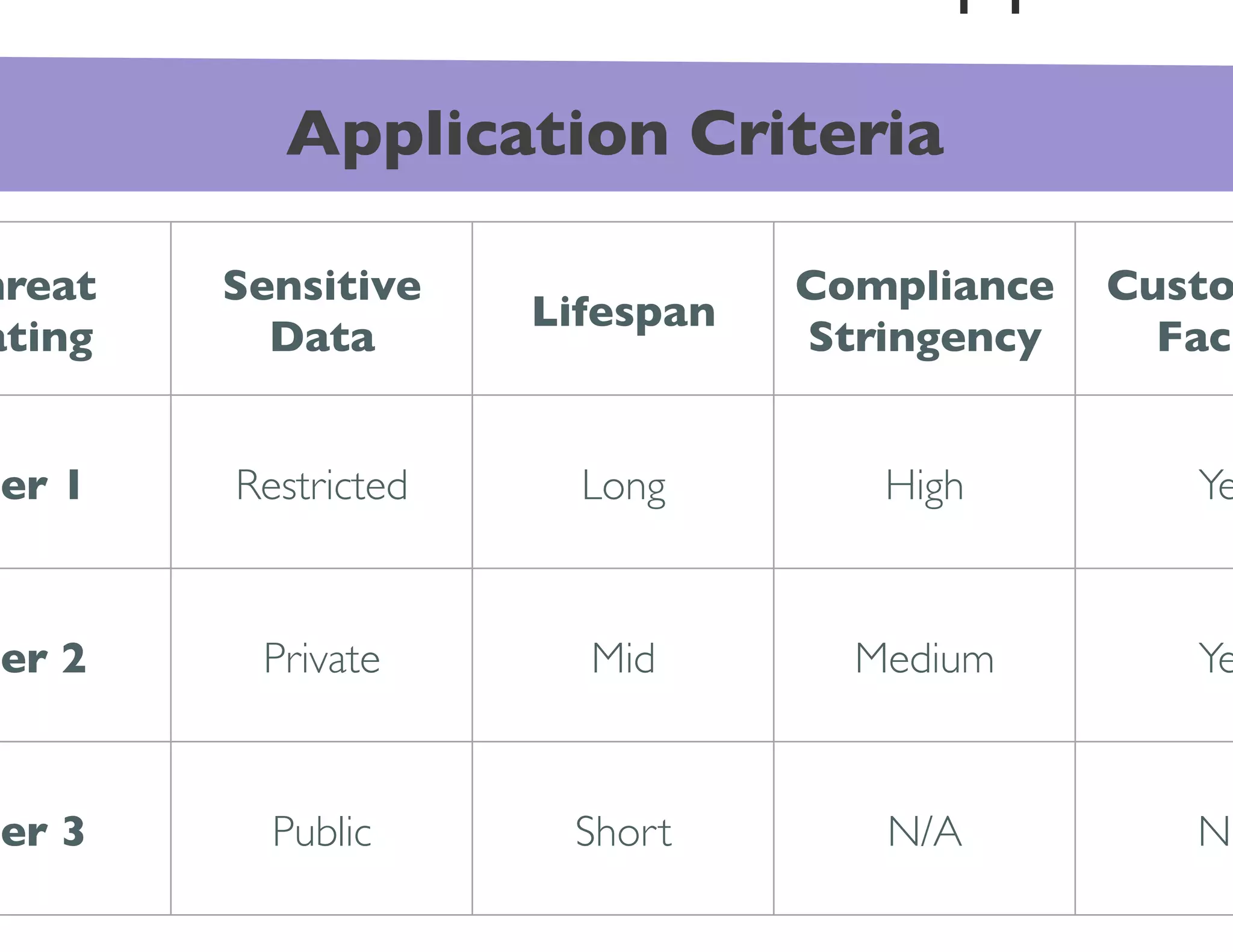
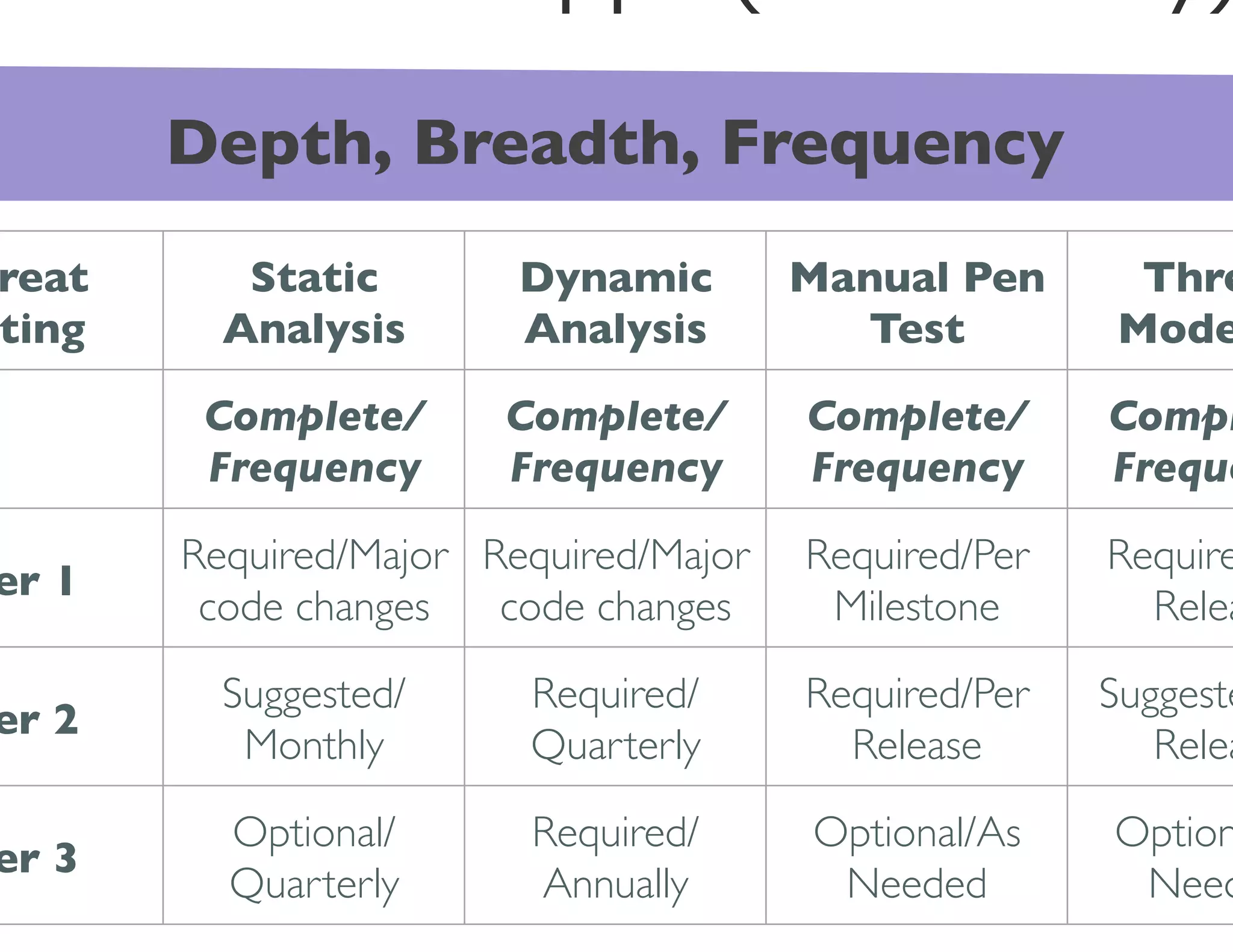
The document discusses the challenges and strategies for developing a mobile security policy amidst the growing trend of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) in the workplace. It highlights the importance of balancing security needs with employee autonomy and productivity, emphasizing risk assessment, compliance, and the need for comprehensive training. Additionally, it outlines best practices for application security, vulnerability management, and policy enforcement to mitigate security risks associated with personal devices used for work.