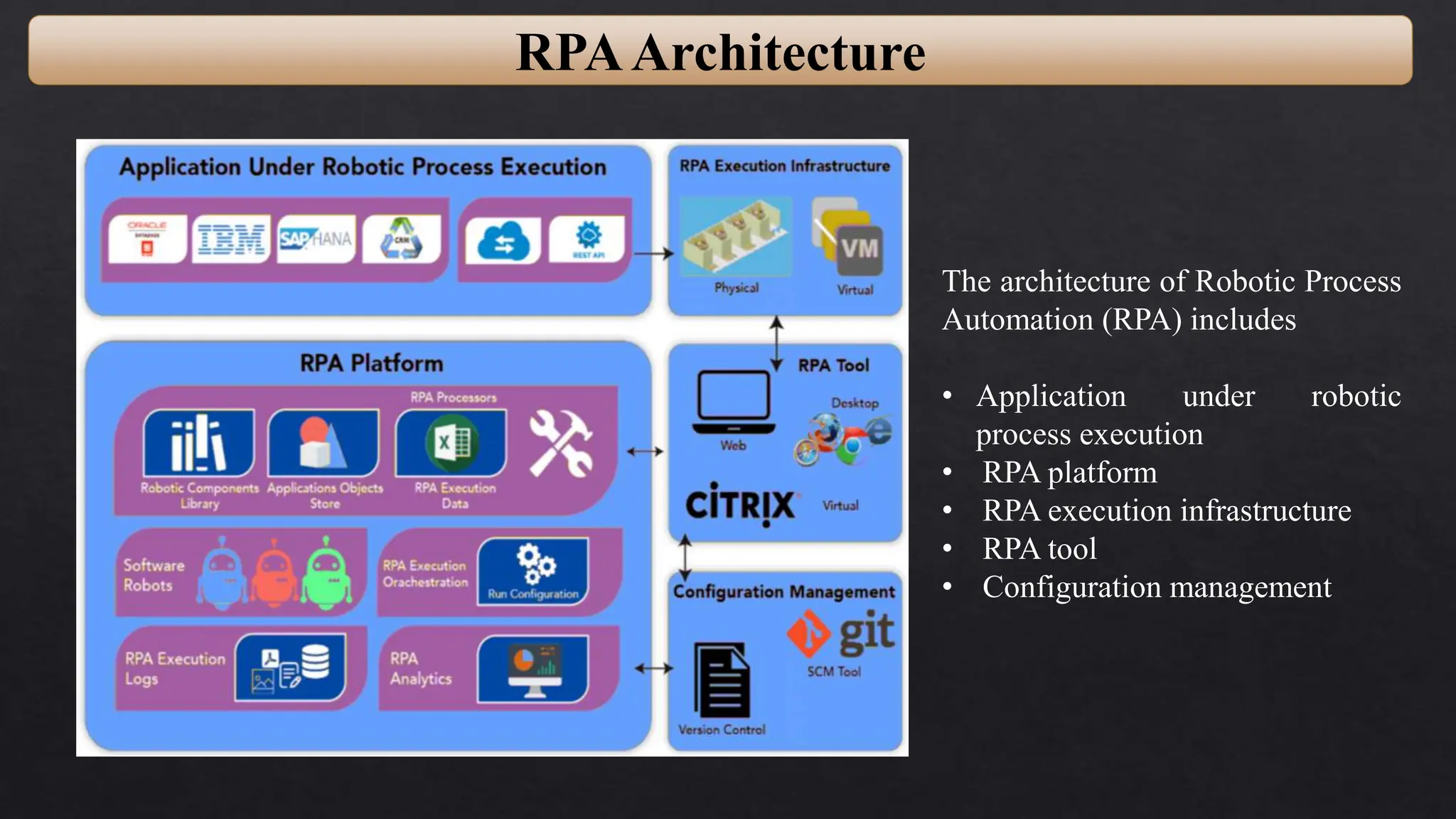
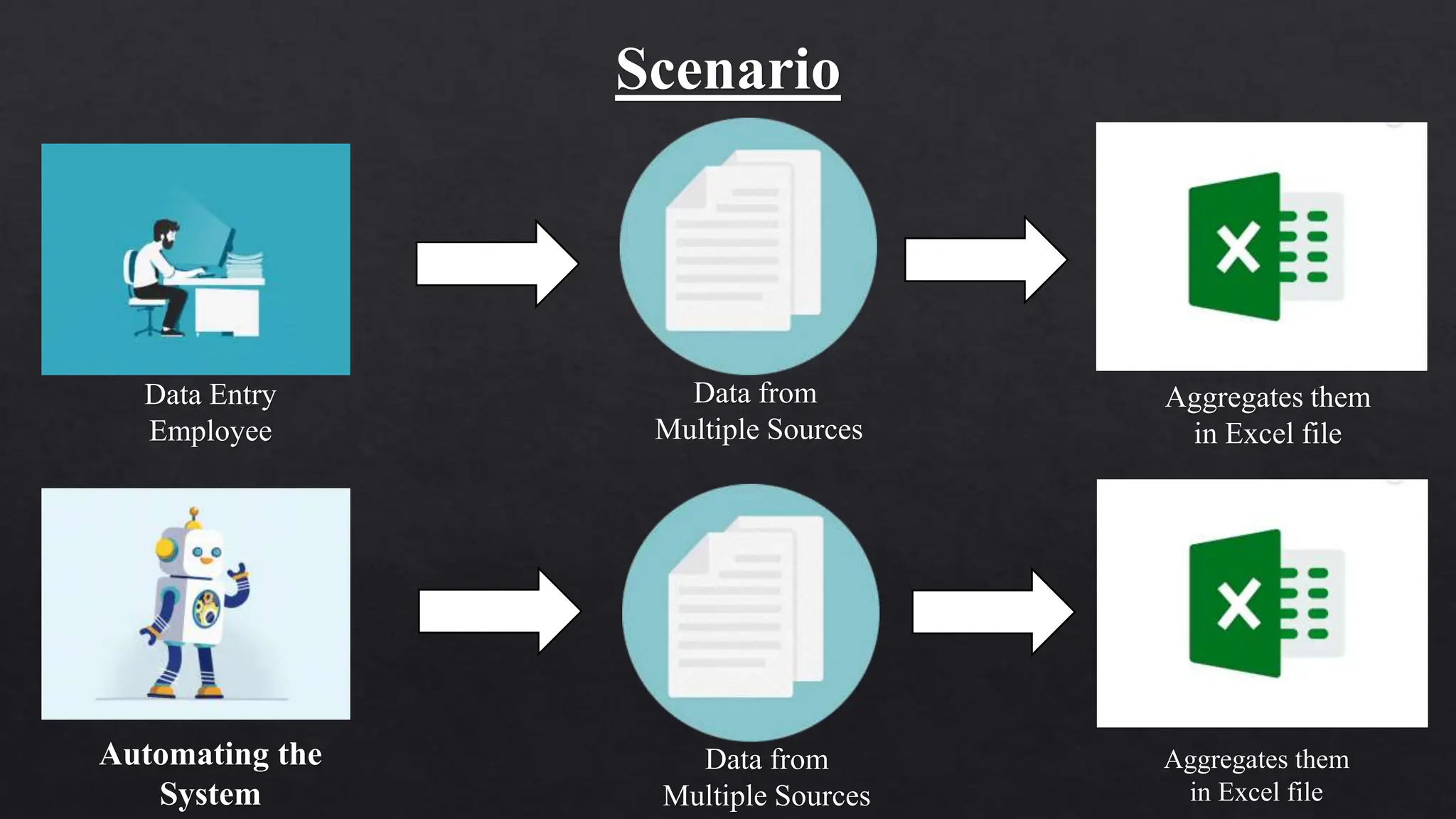
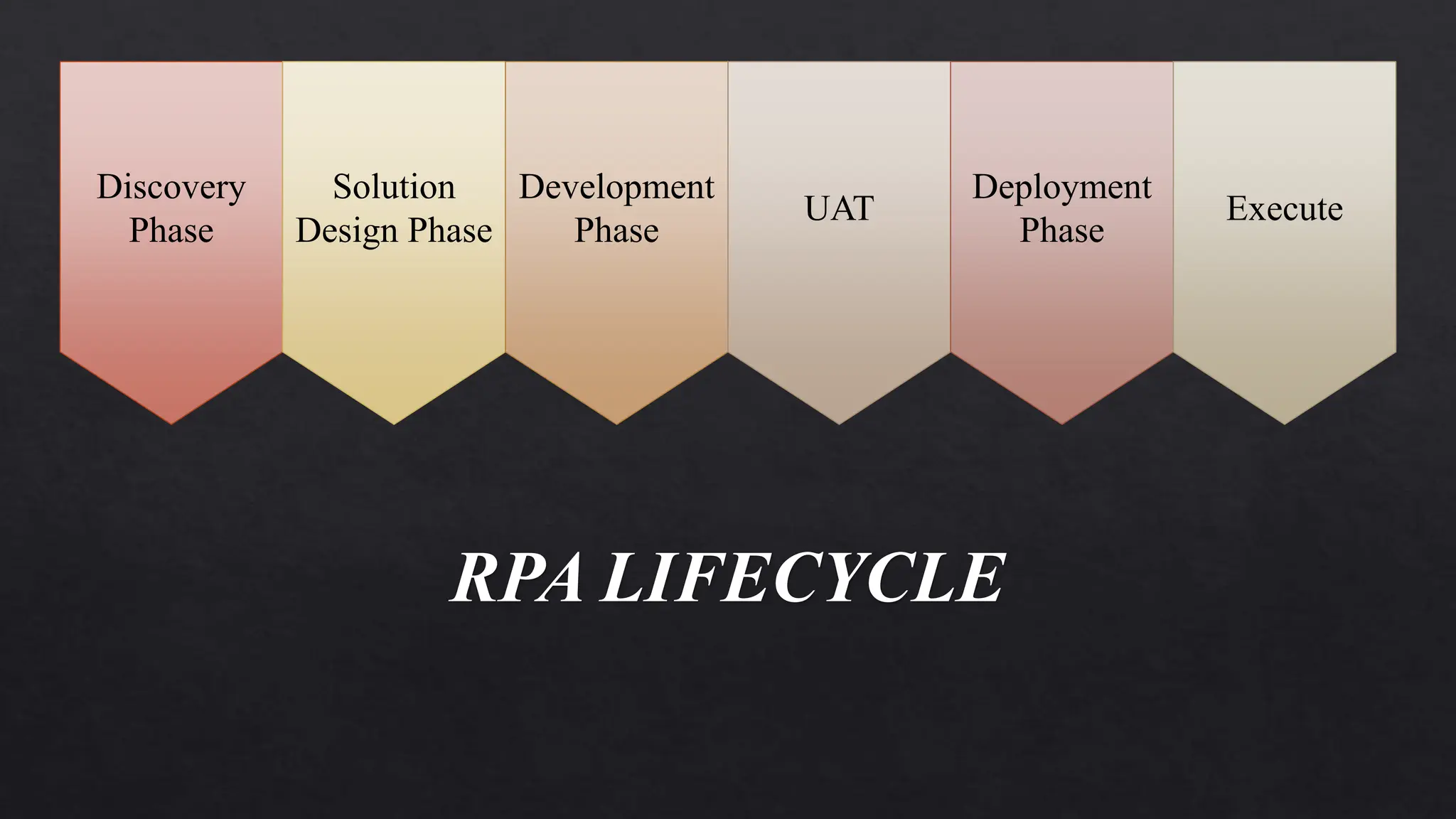
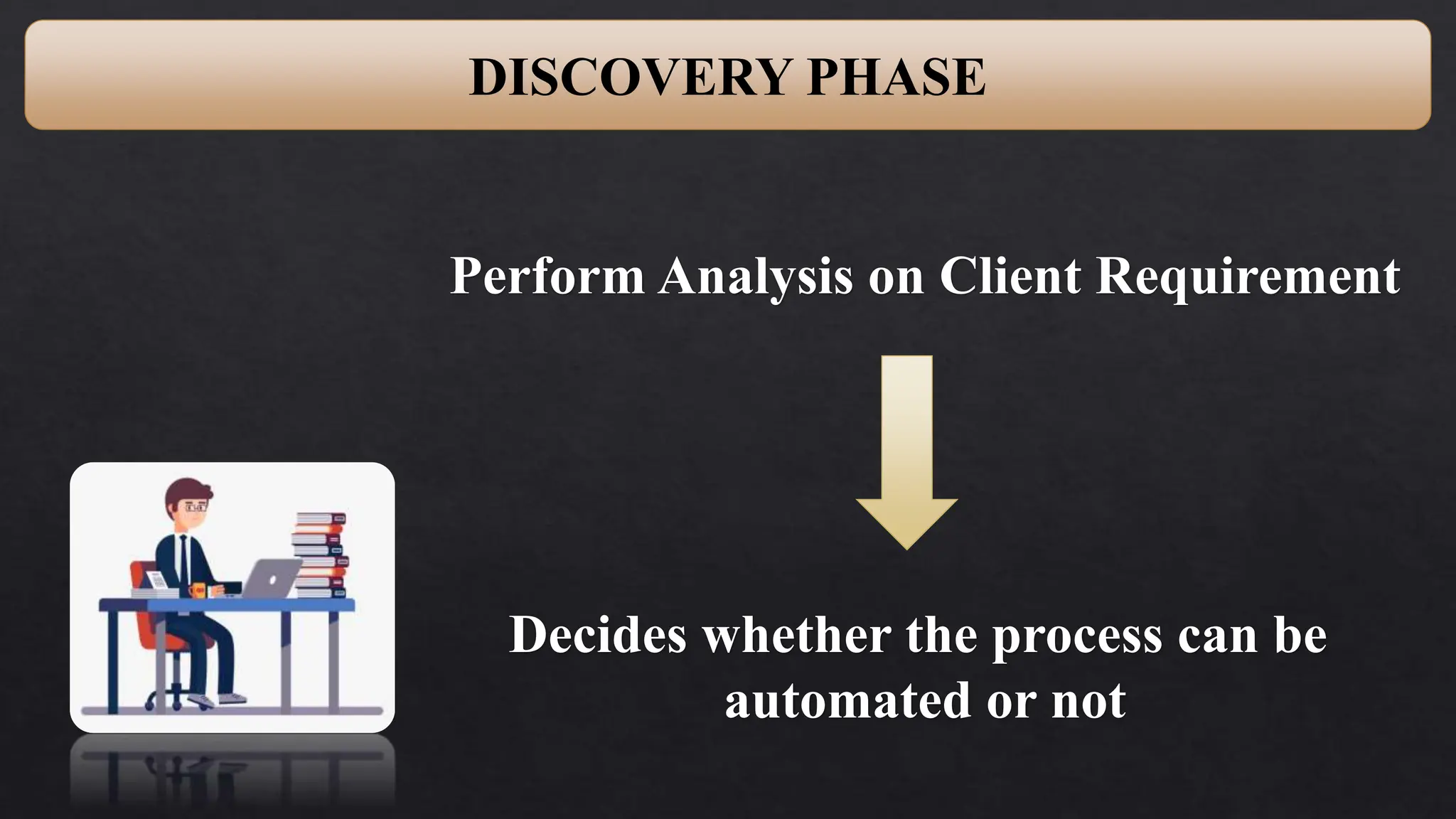
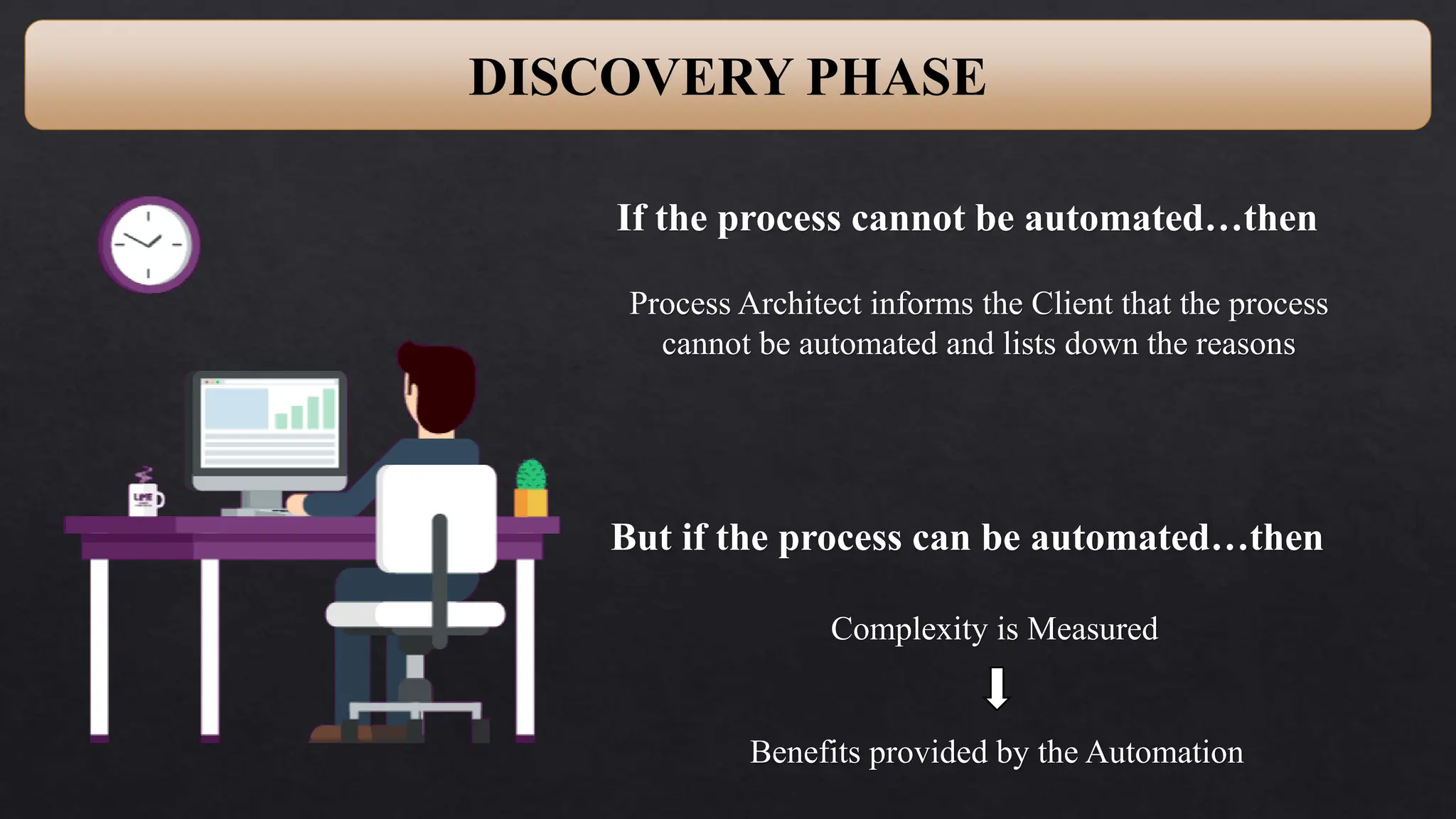
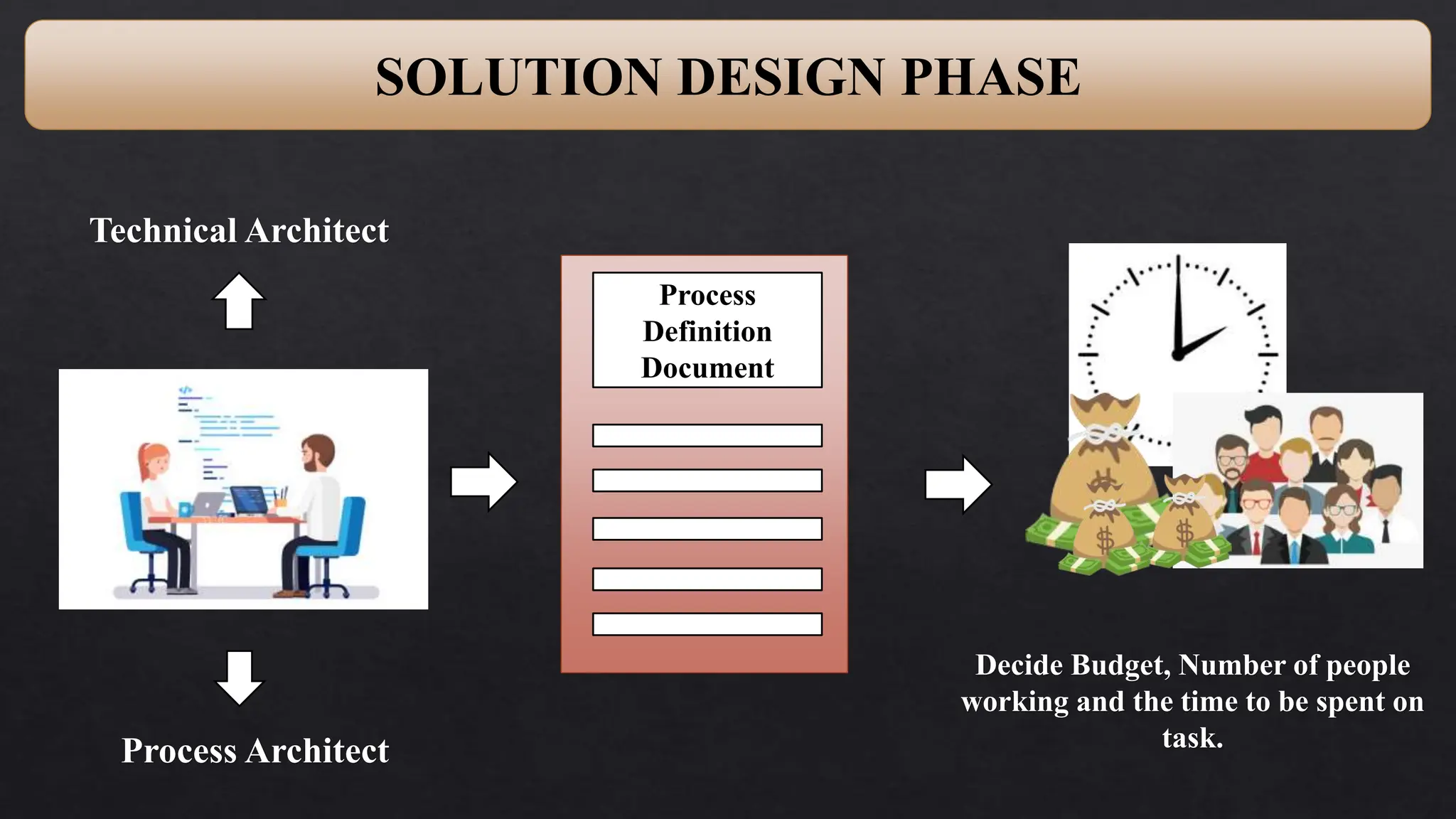
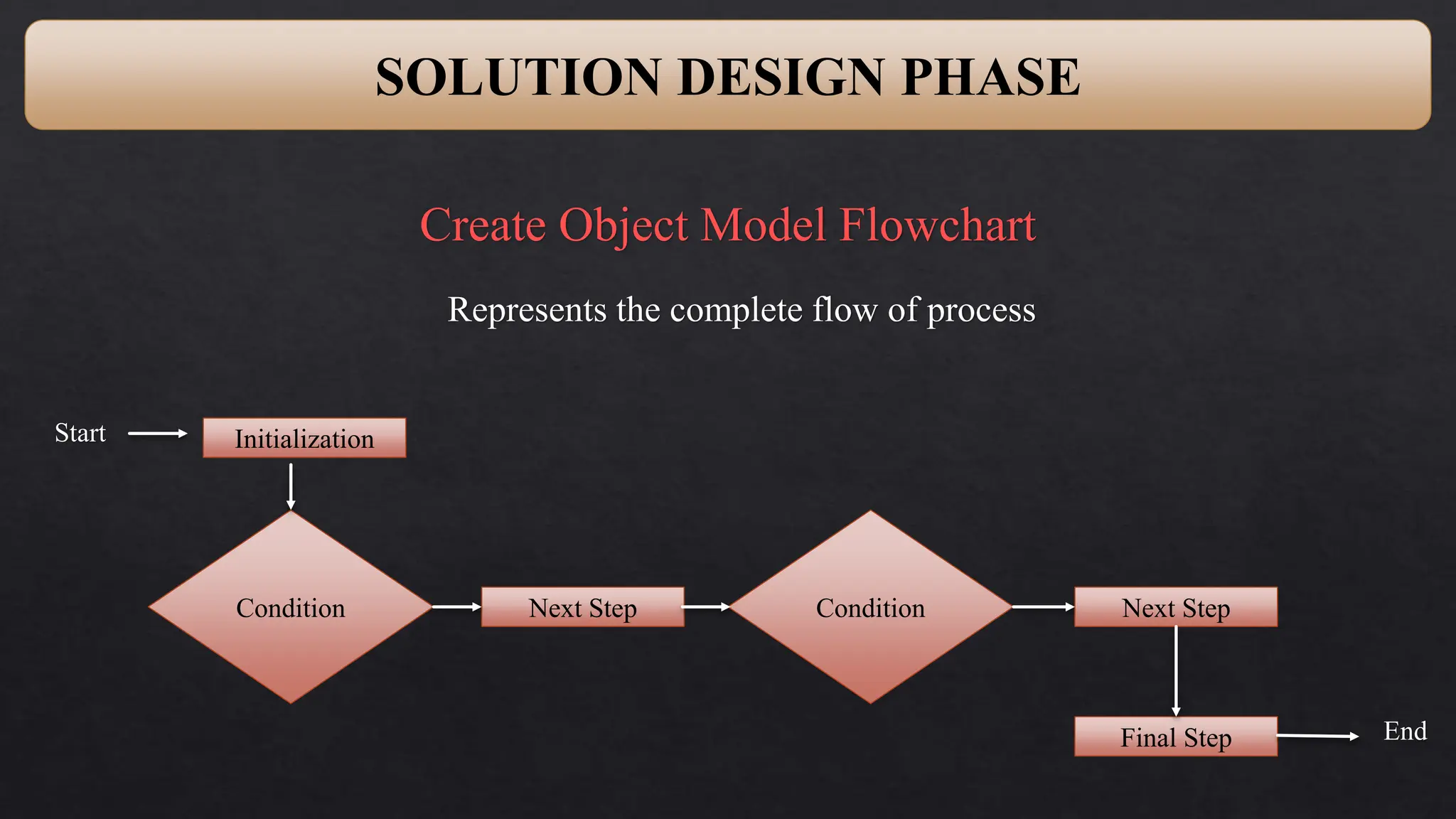
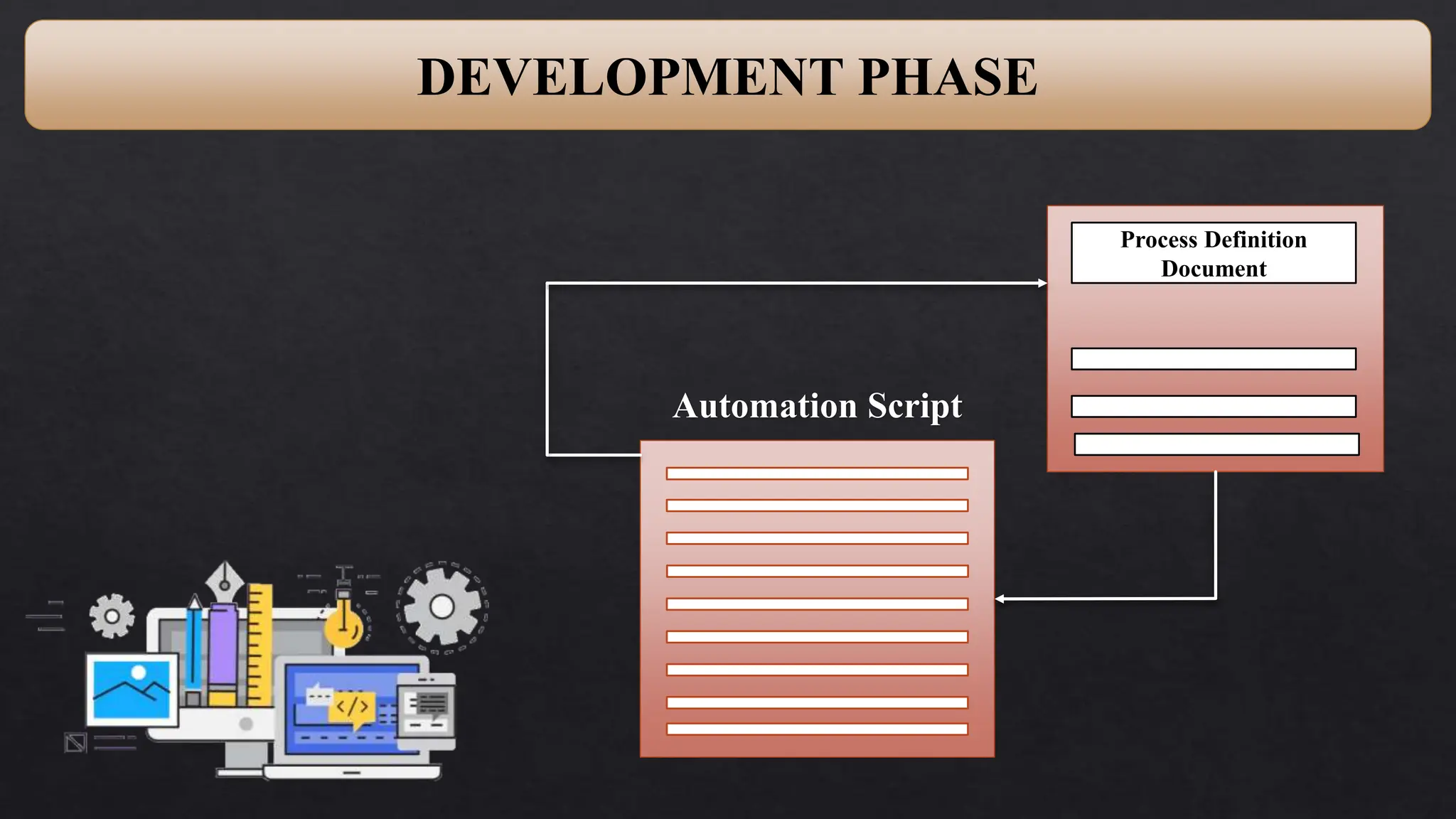
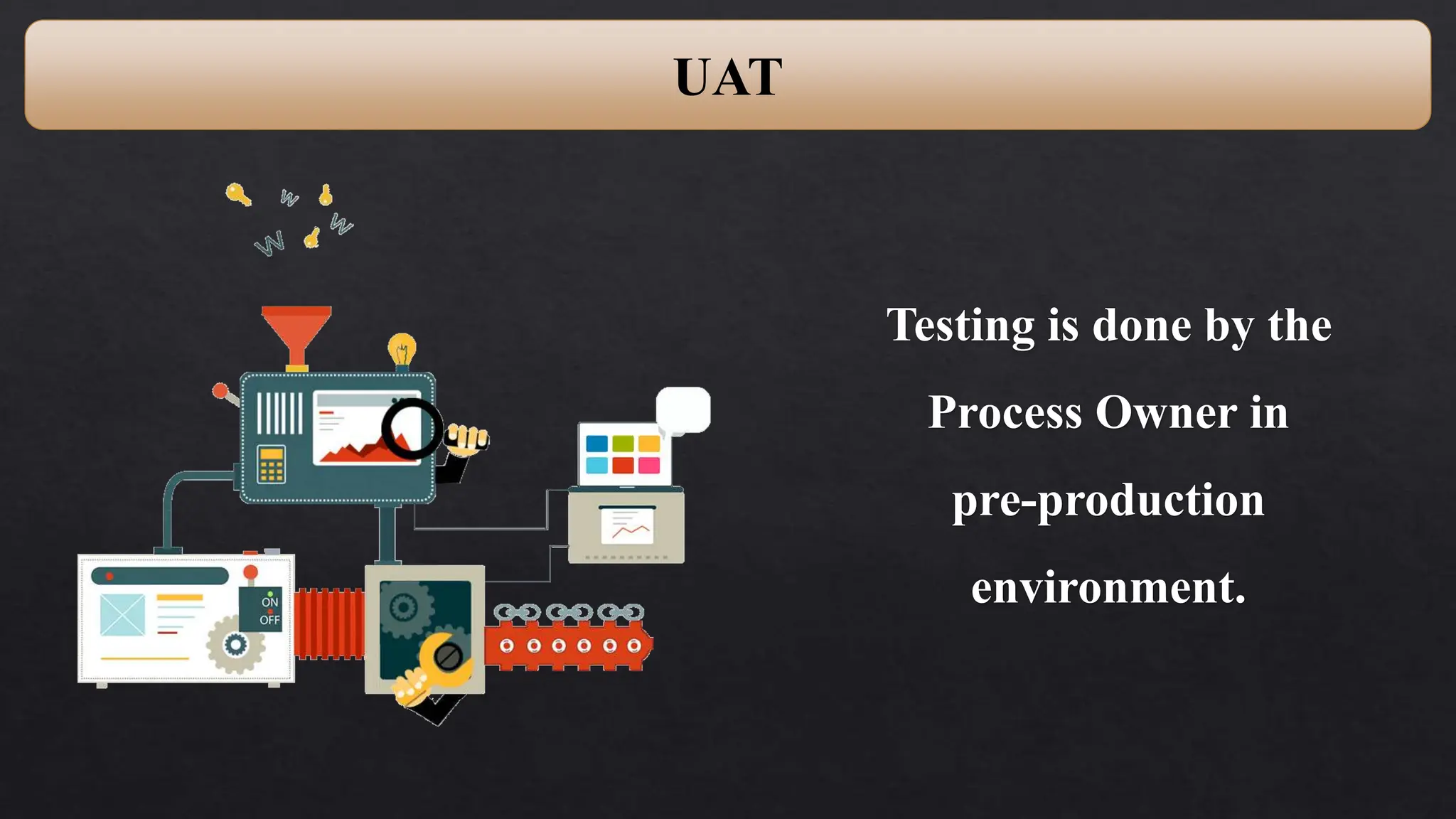
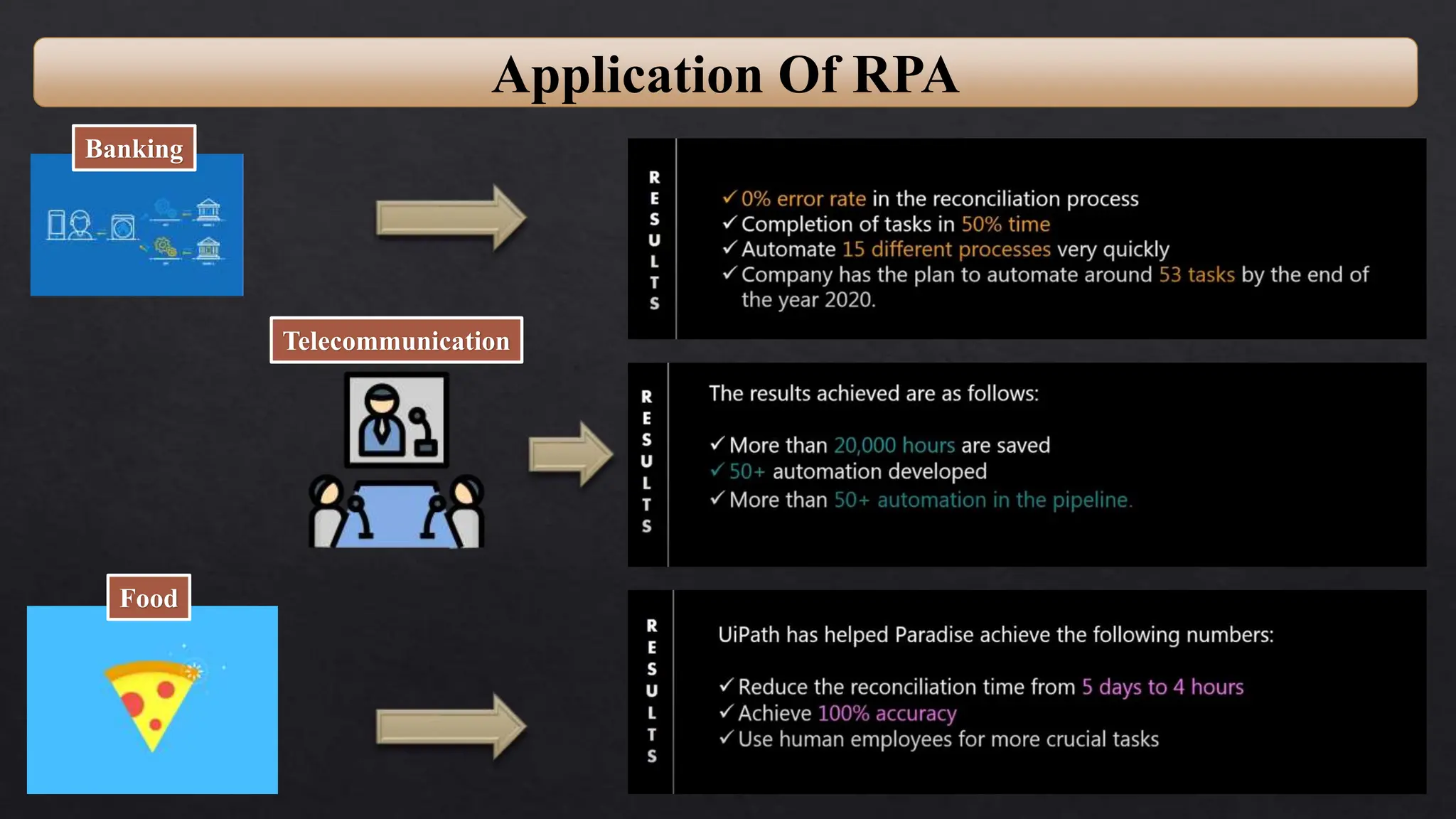
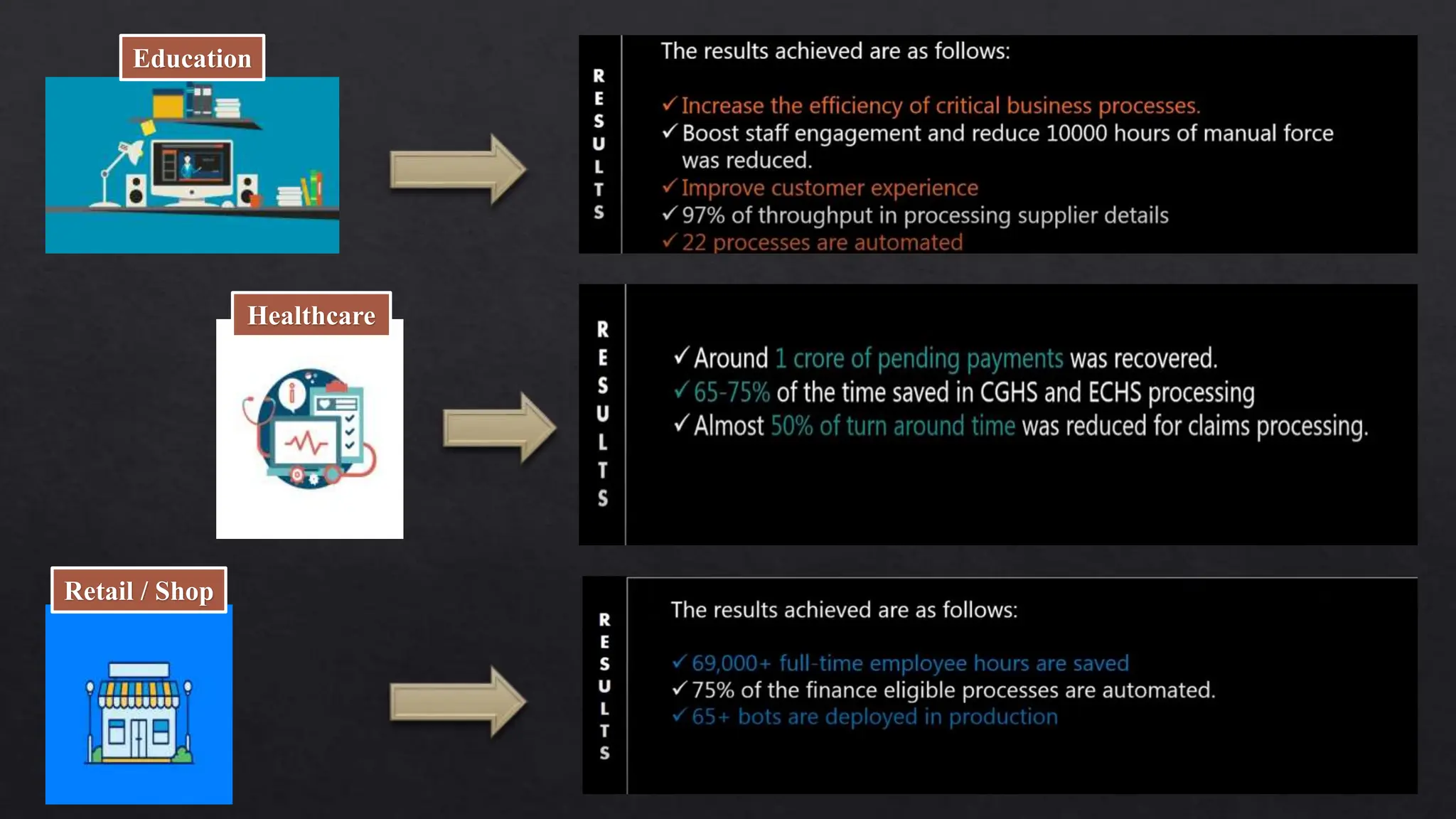
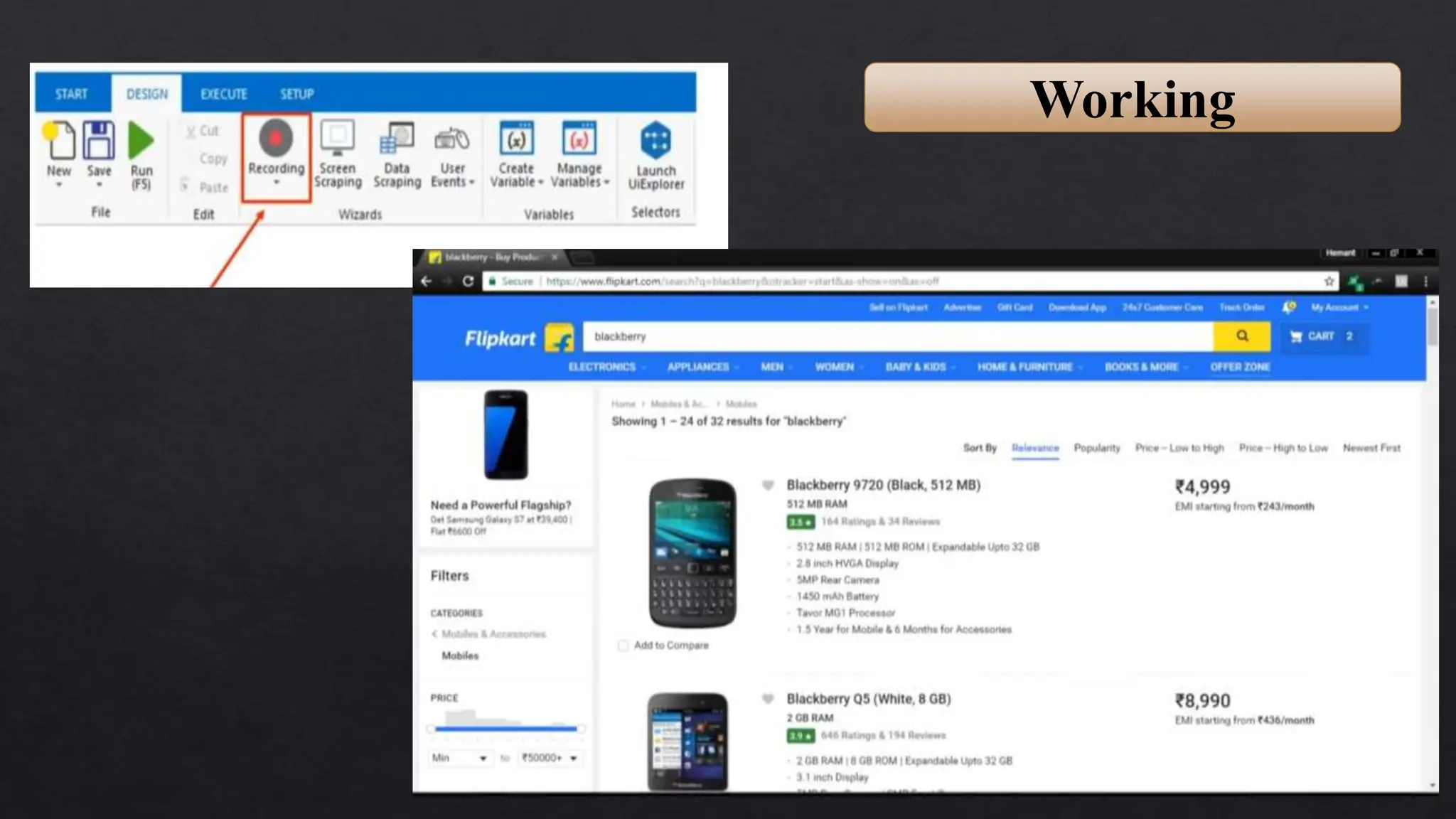
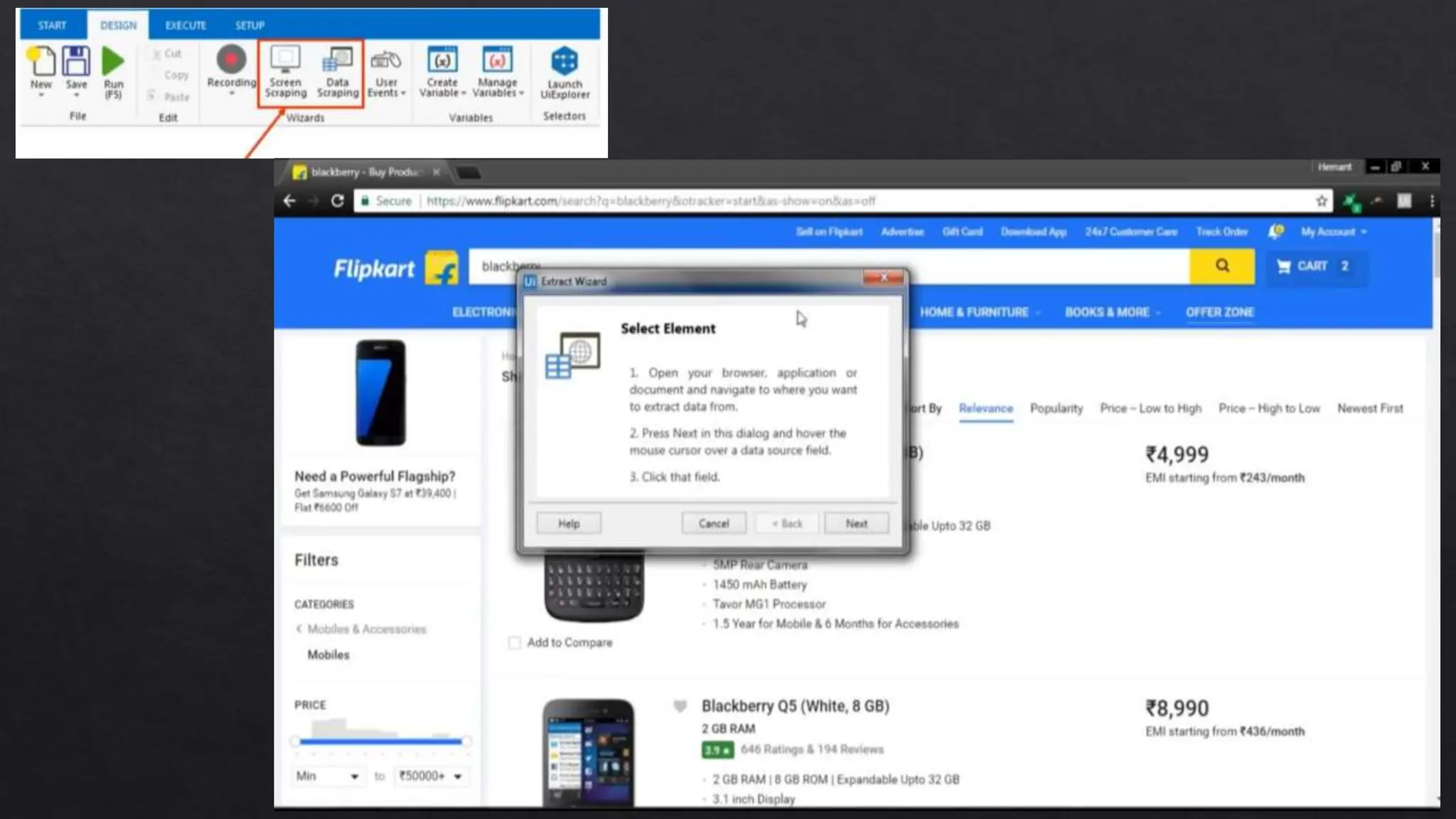
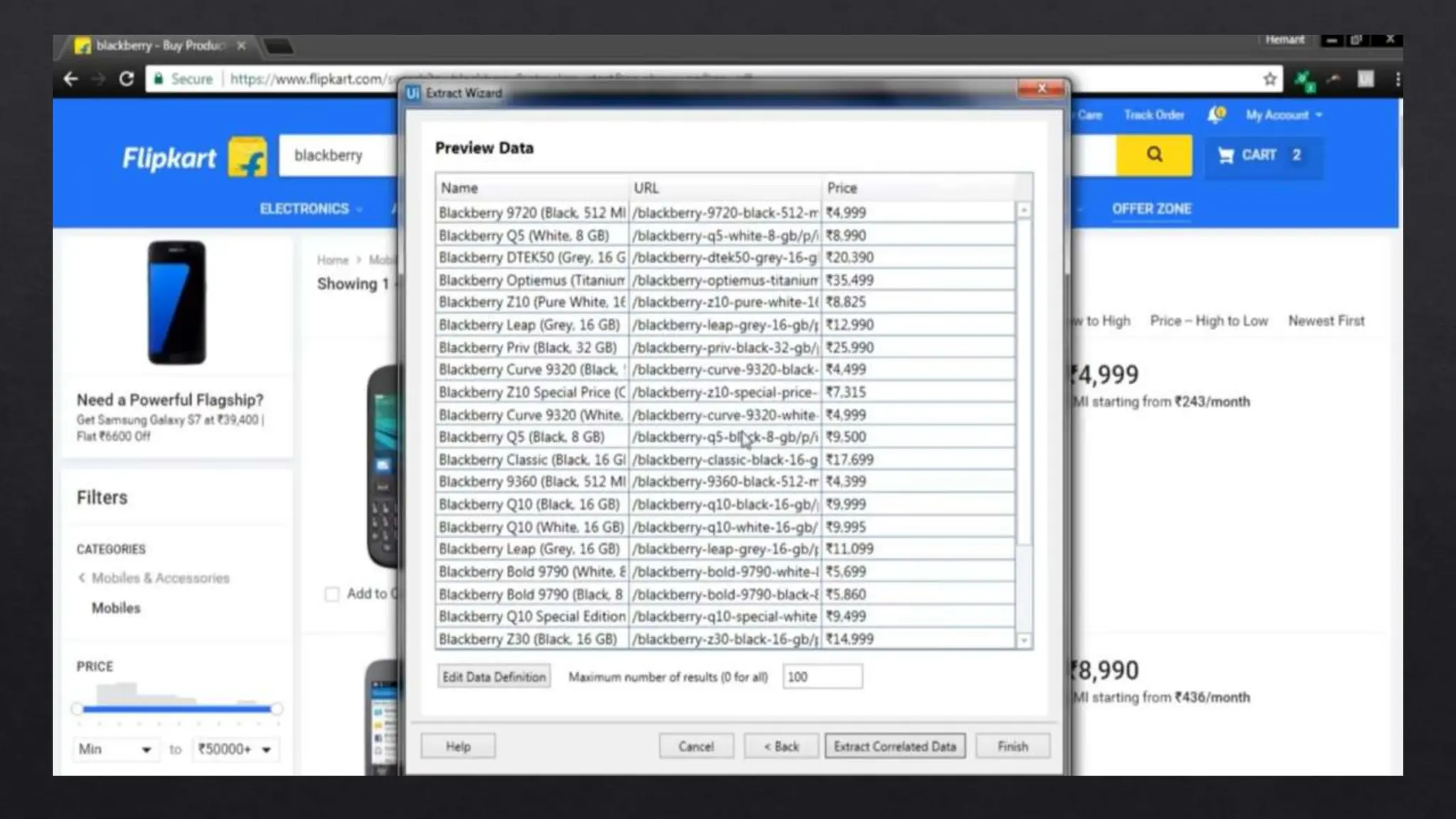
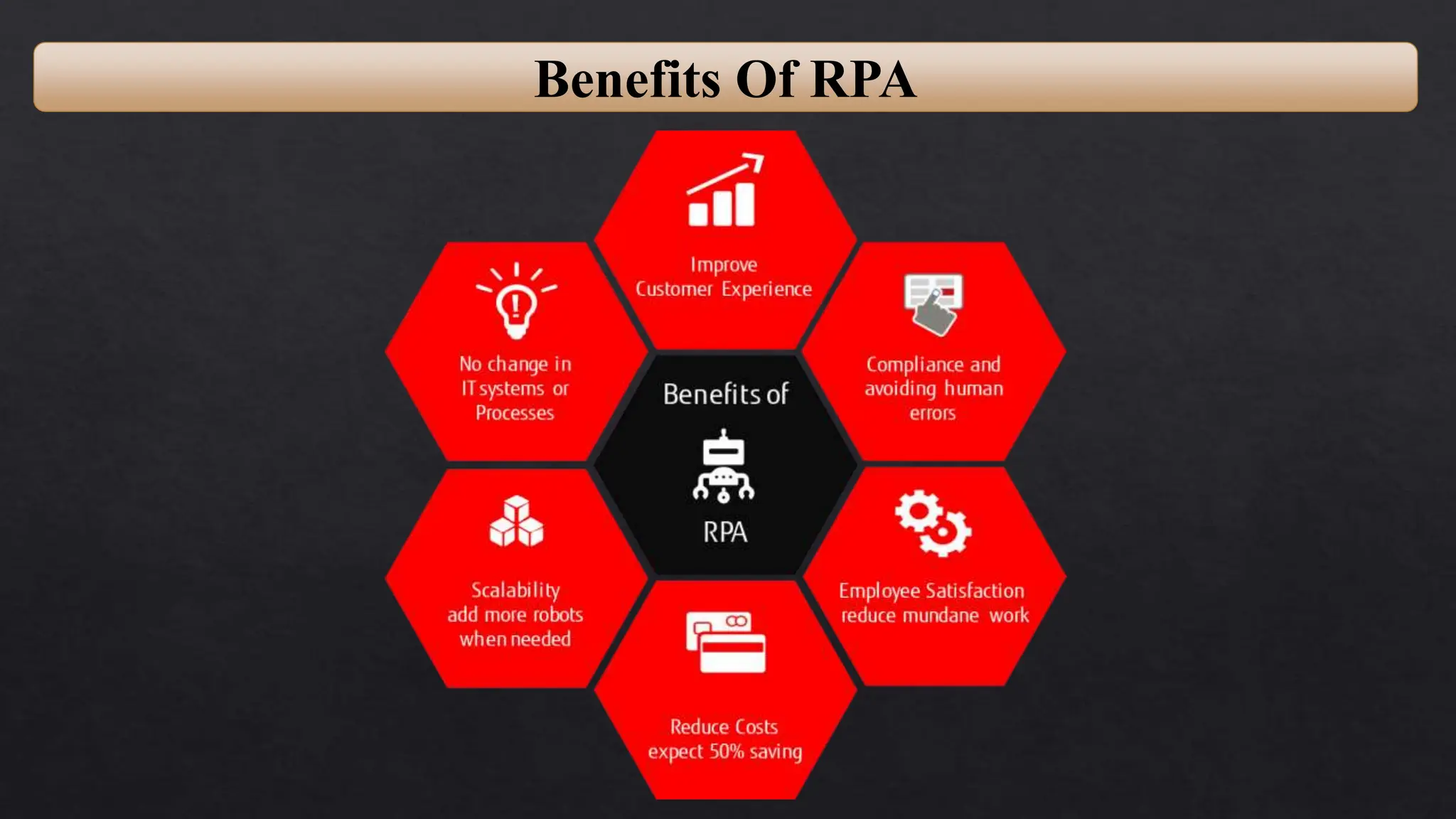
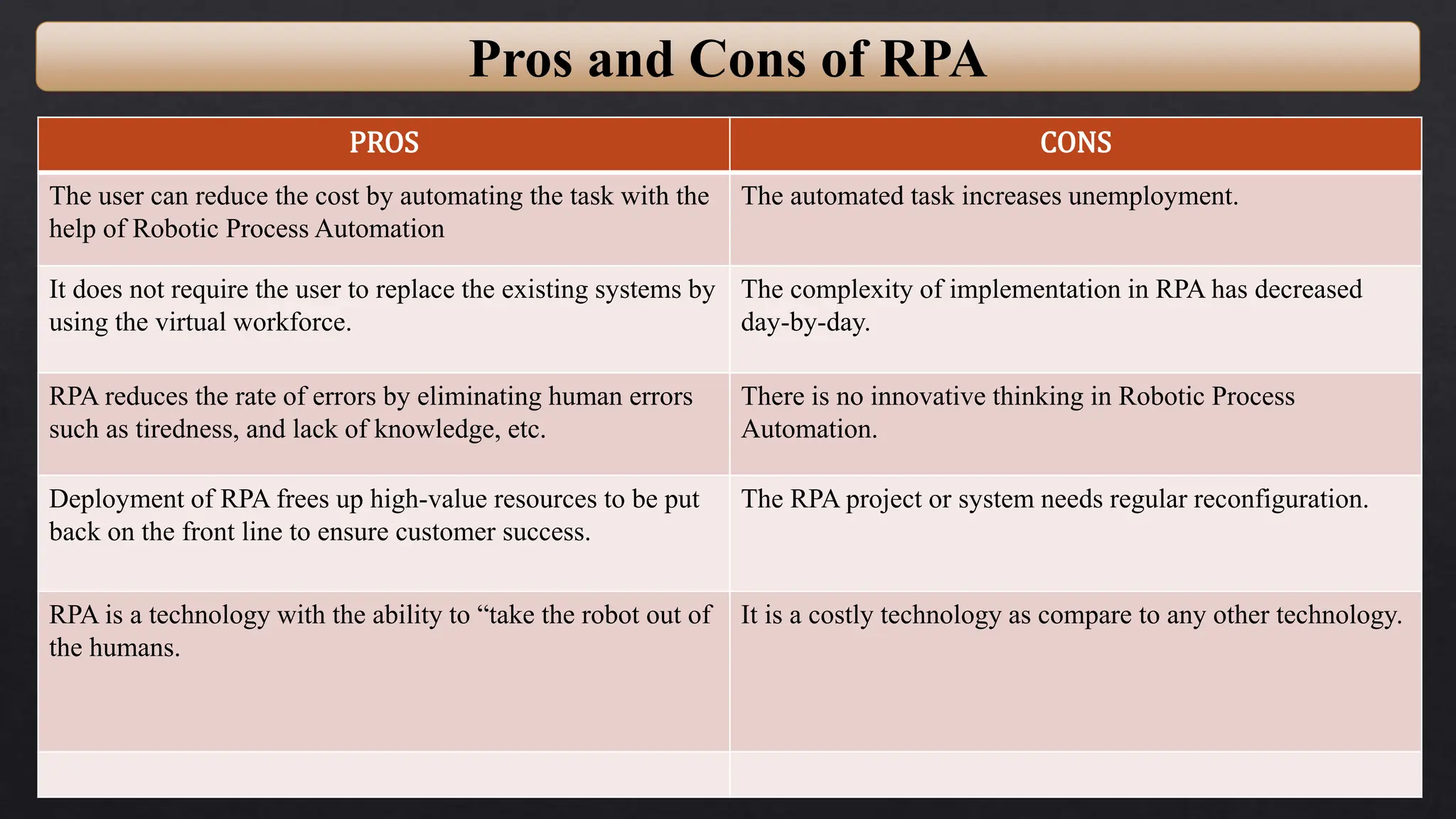
This document provides an overview of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) presented by Pramod C R. It discusses the introduction to RPA including definitions of robots, processes, and automation. The presentation describes the architecture of RPA including the application under execution, RPA platform, tools, and configuration management. It also outlines the RPA lifecycle including the discovery, design, development, testing, deployment, and execution phases. Examples of RPA applications in banking, healthcare, retail, and other industries are provided. The benefits of RPA including cost reduction, increased accuracy, and freeing up of human resources are summarized. The document concludes with pros and cons of RPA and summaries of two literature surveys on R