The document discusses and compares different routing algorithms:
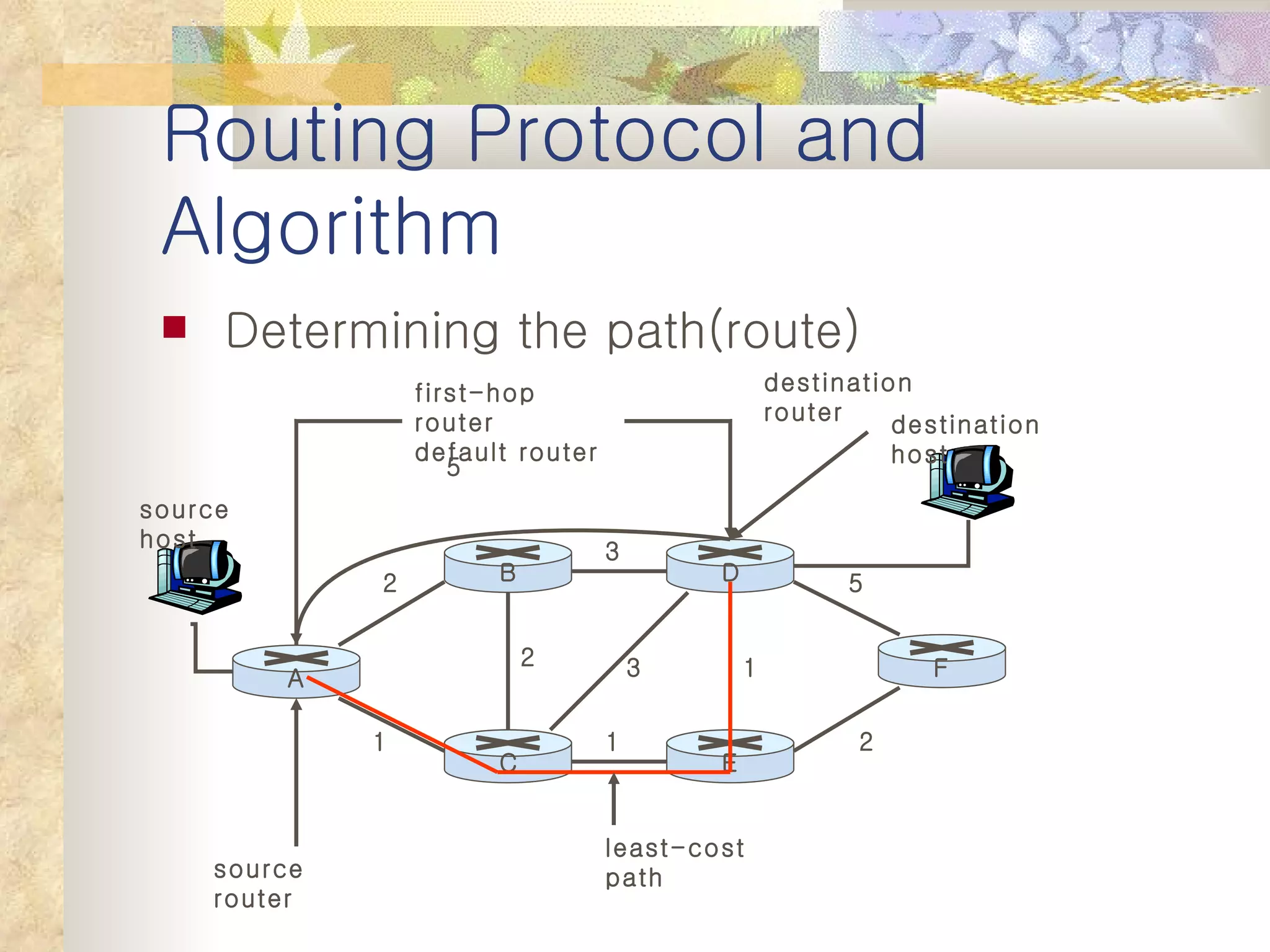
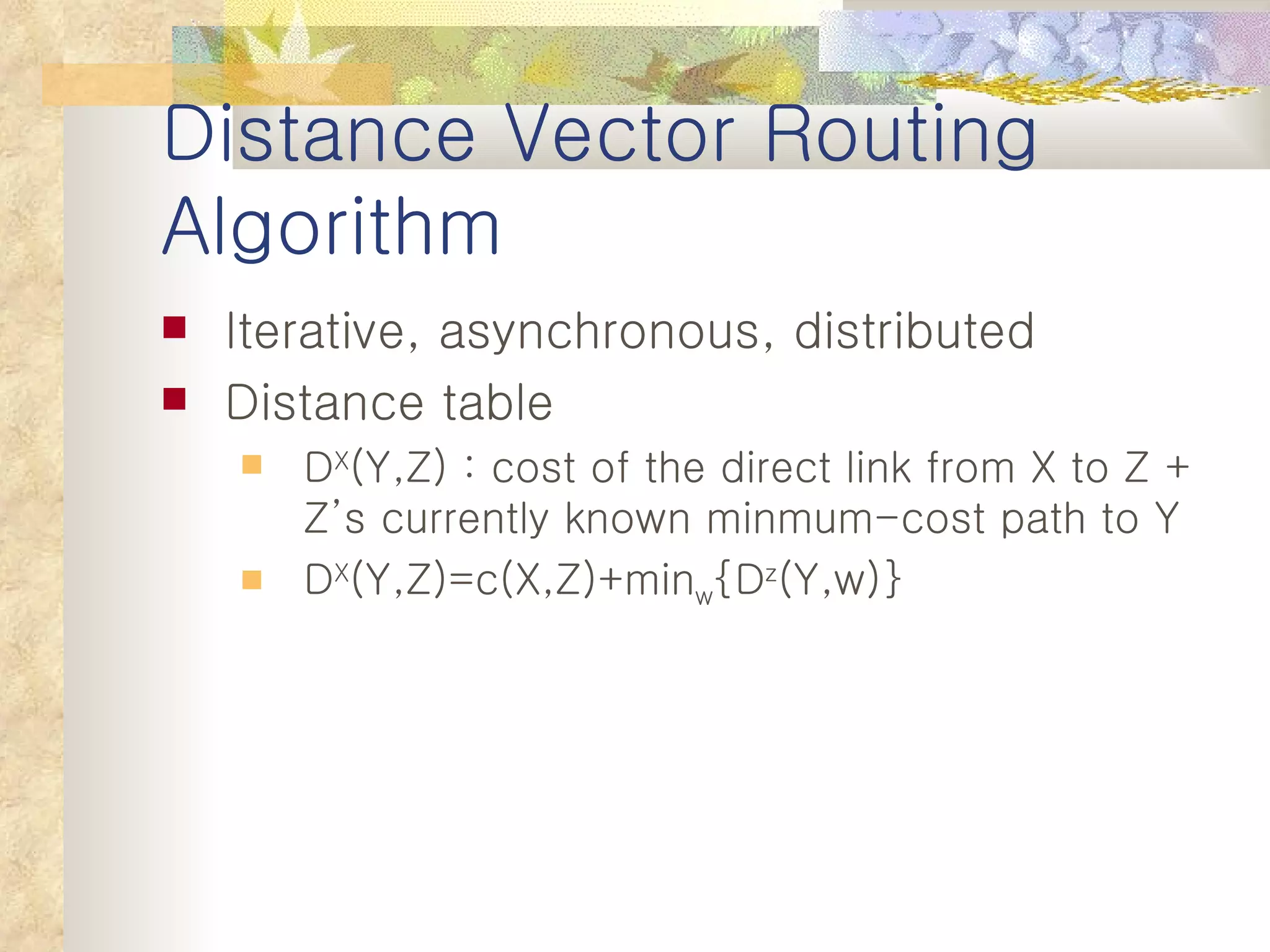
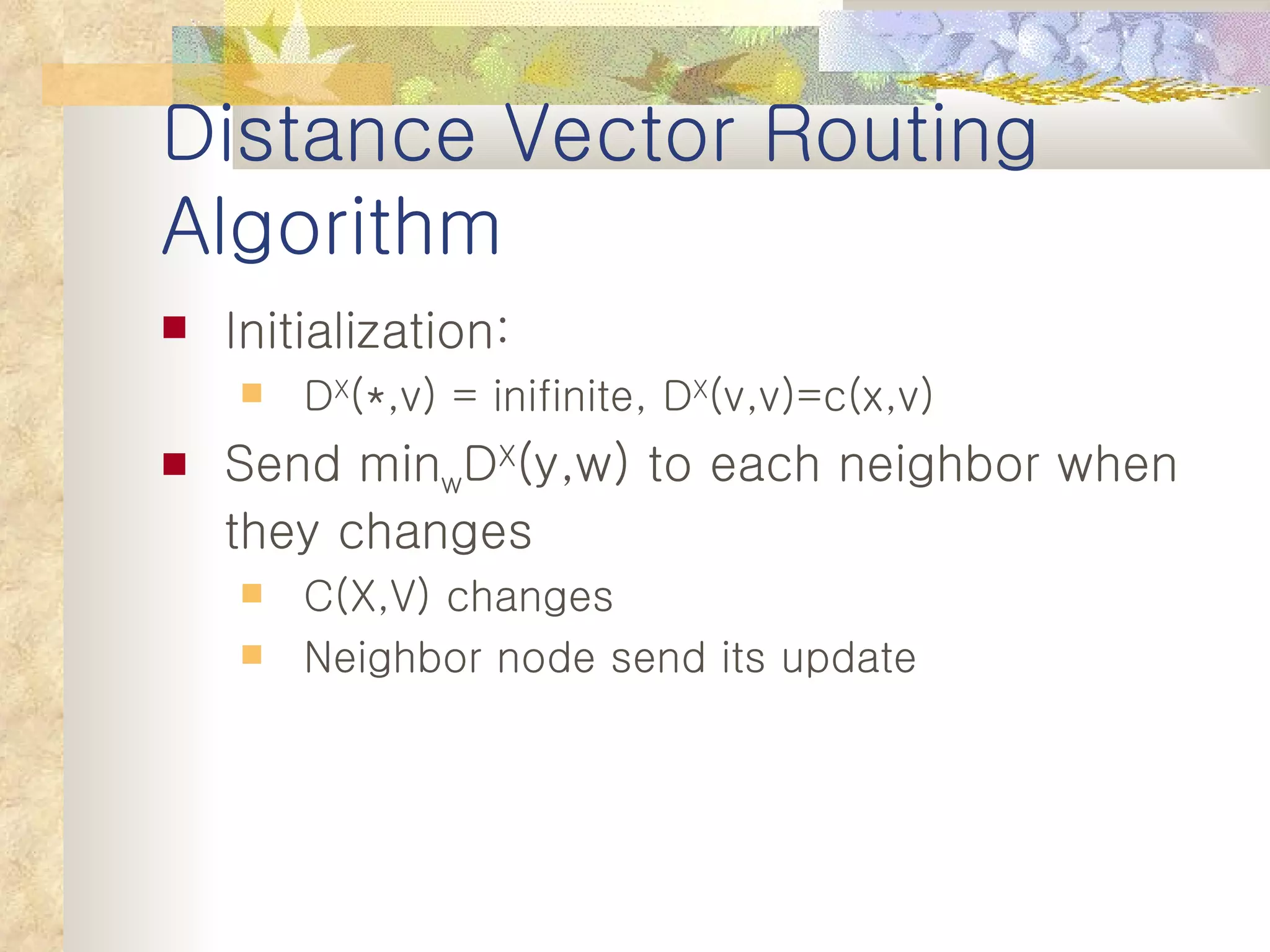
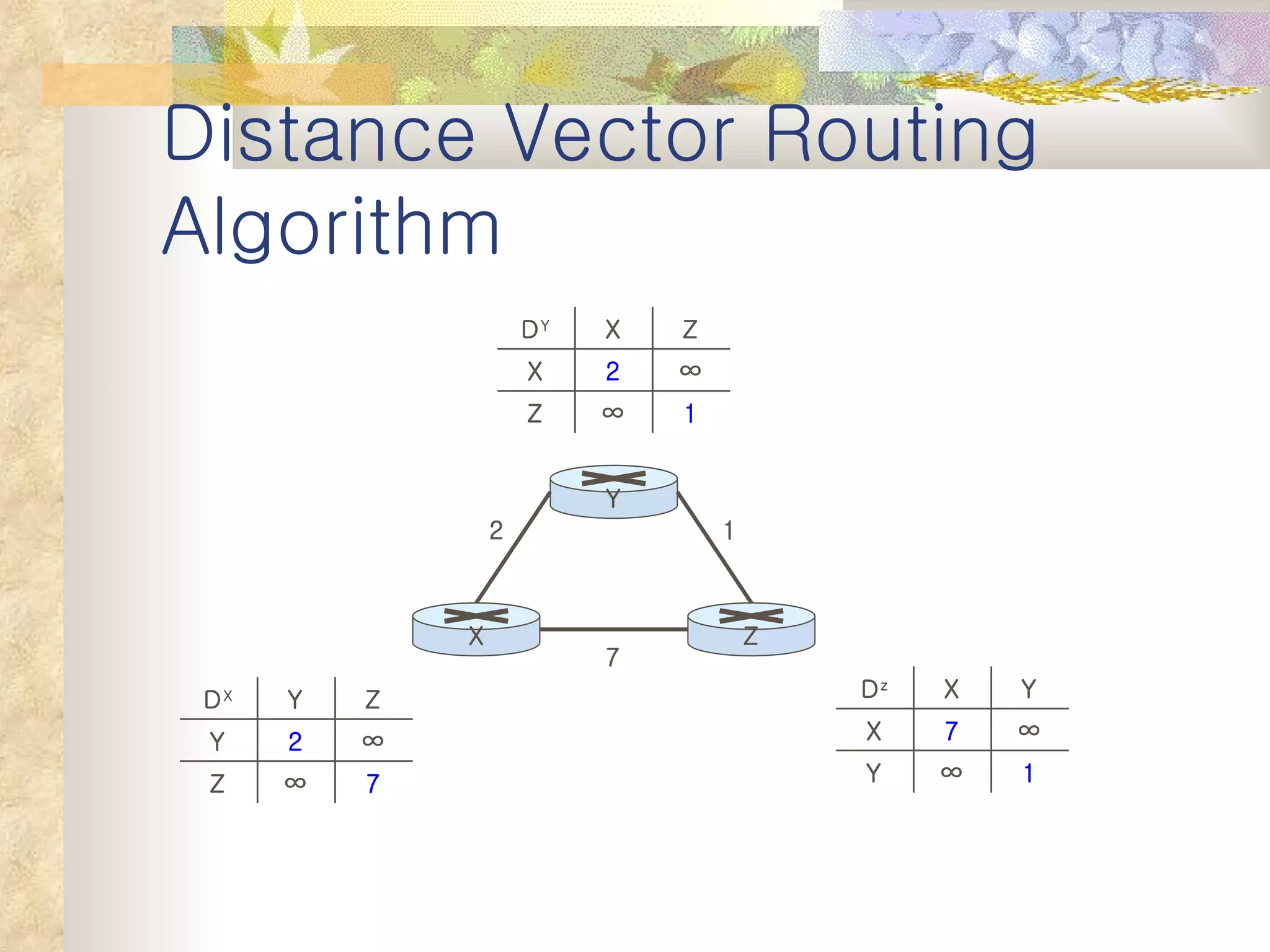
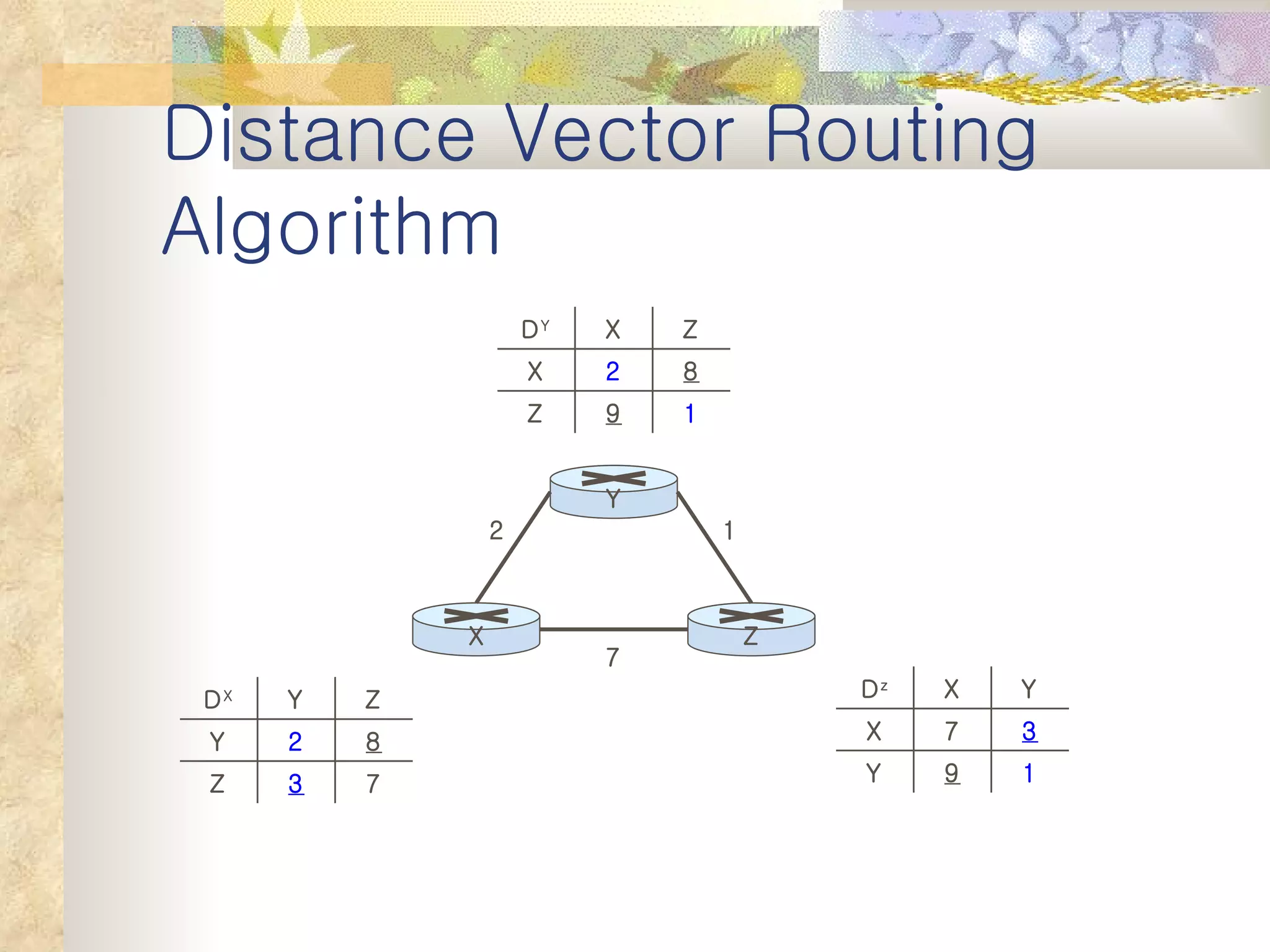
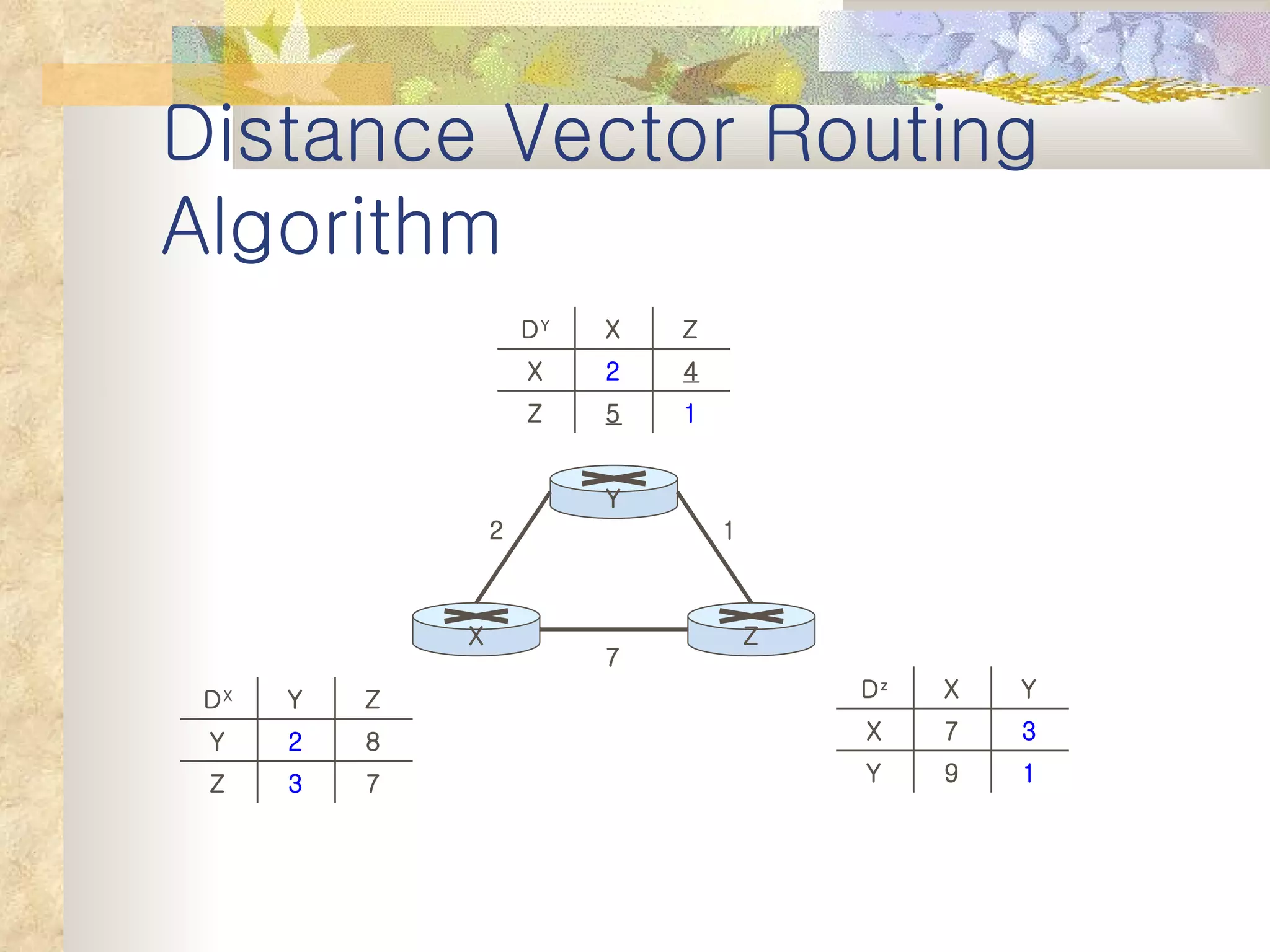
1. It classifies routing protocols as either link state or distance vector, and describes how each type works. Link state algorithms use flooding to share link information, while distance vector algorithms iteratively calculate the best paths.
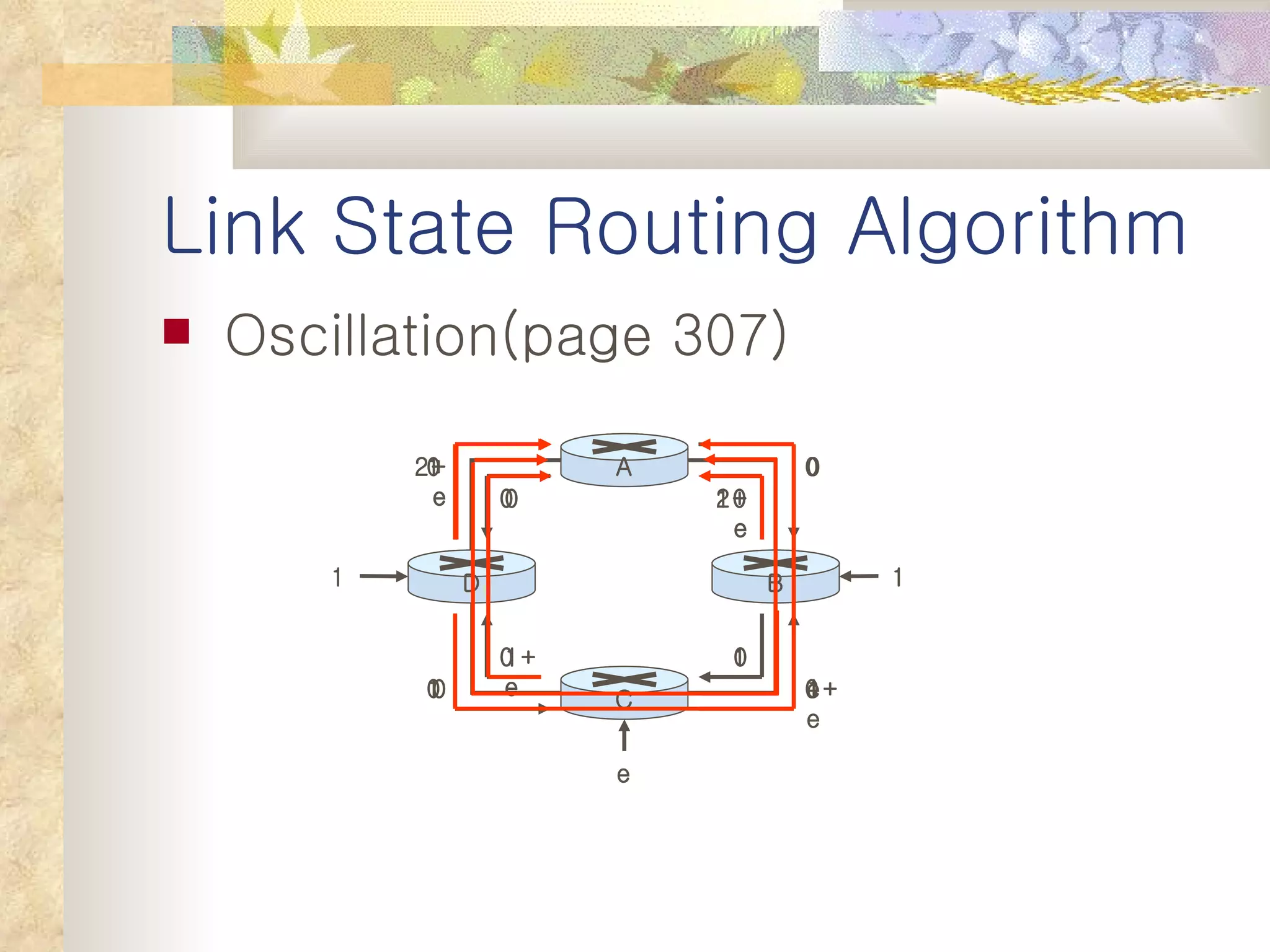
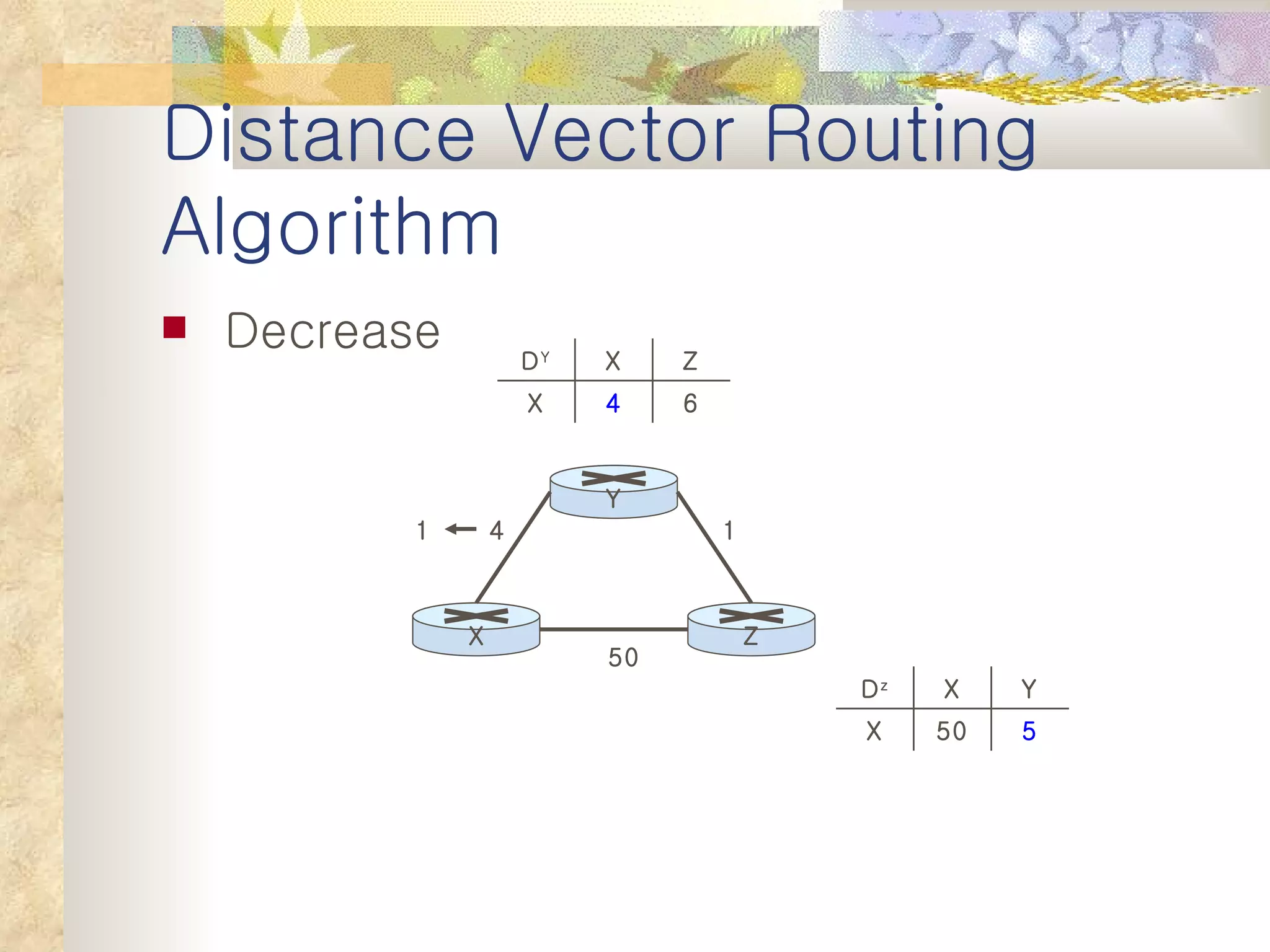
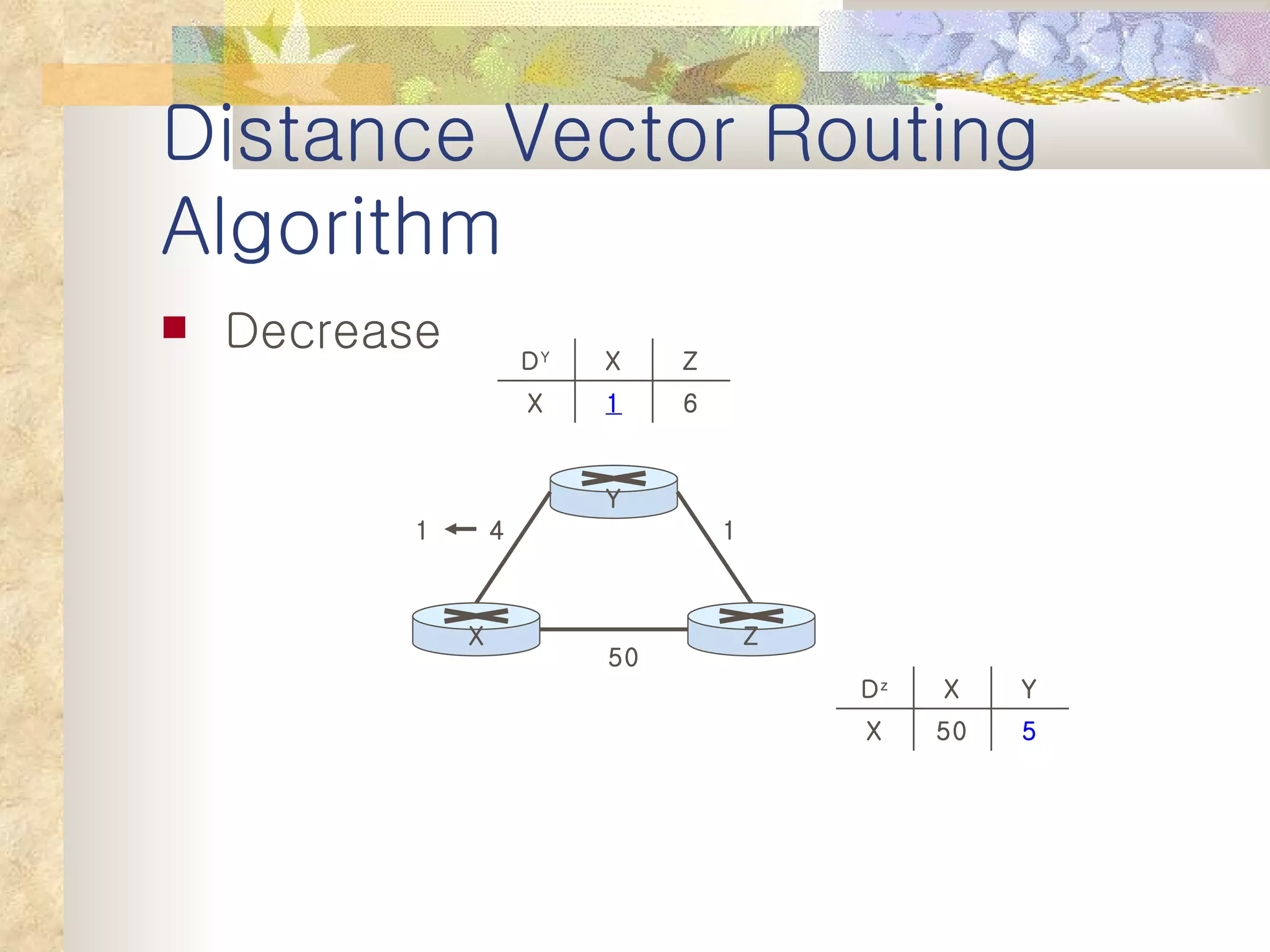
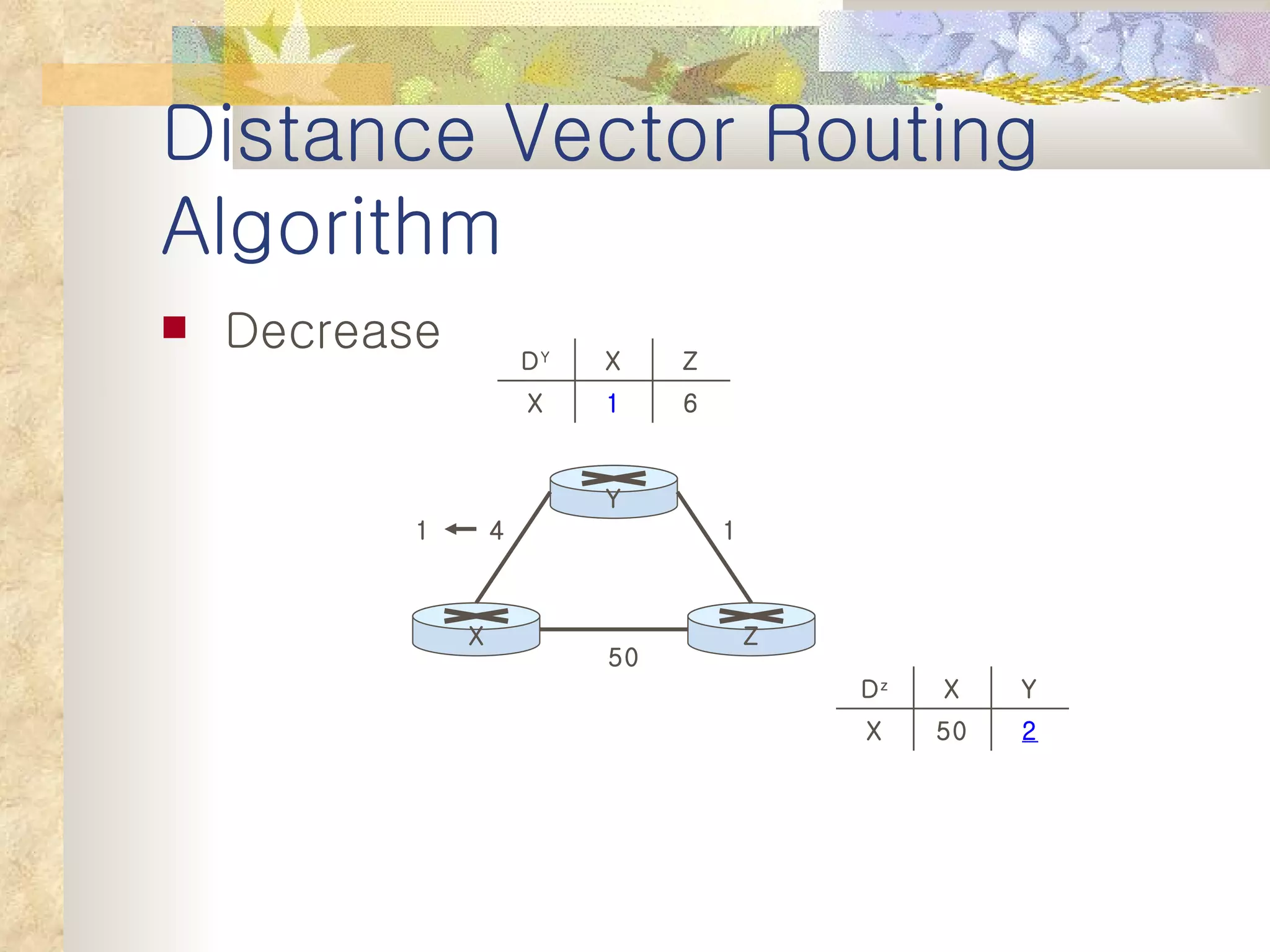
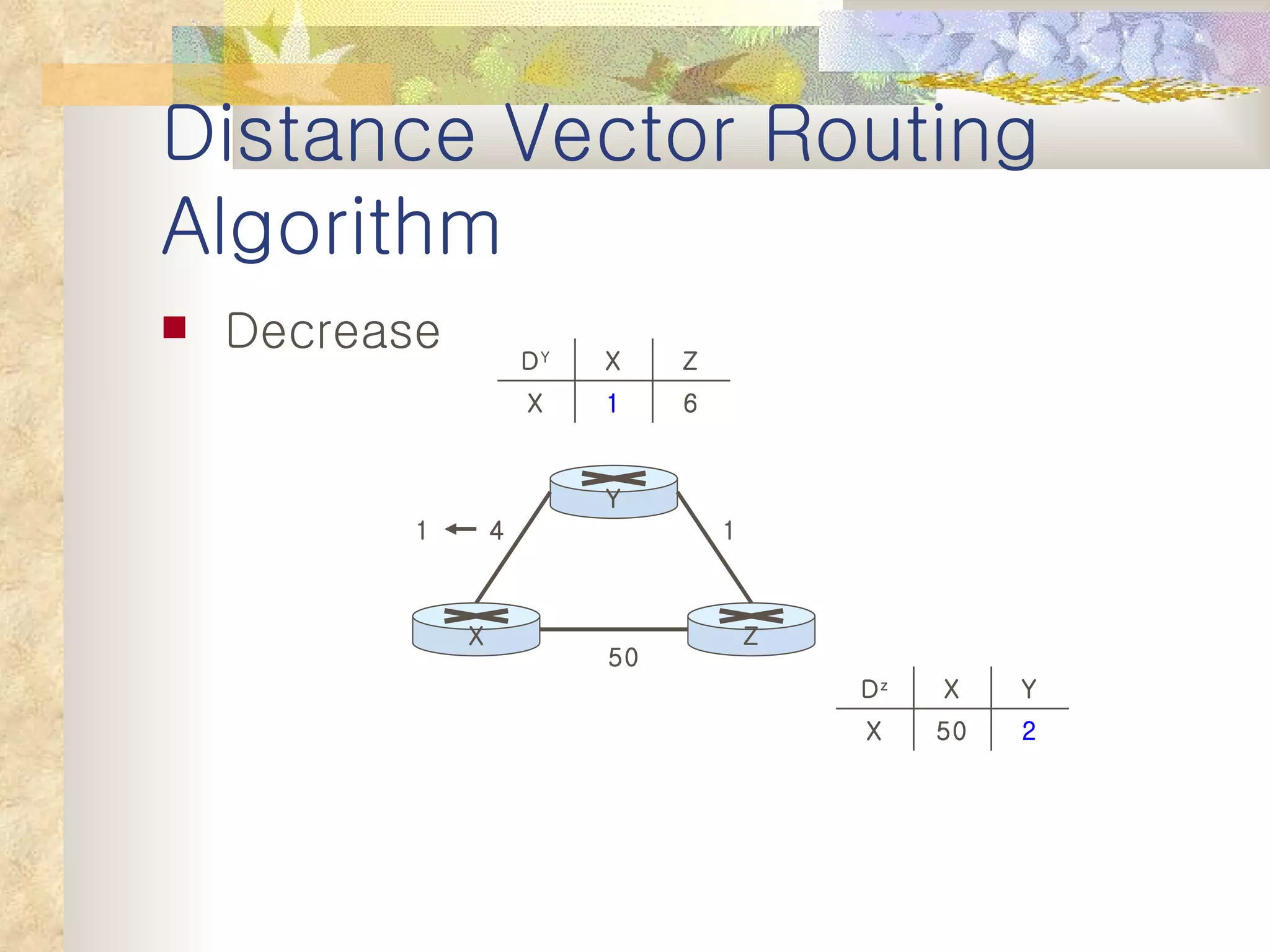
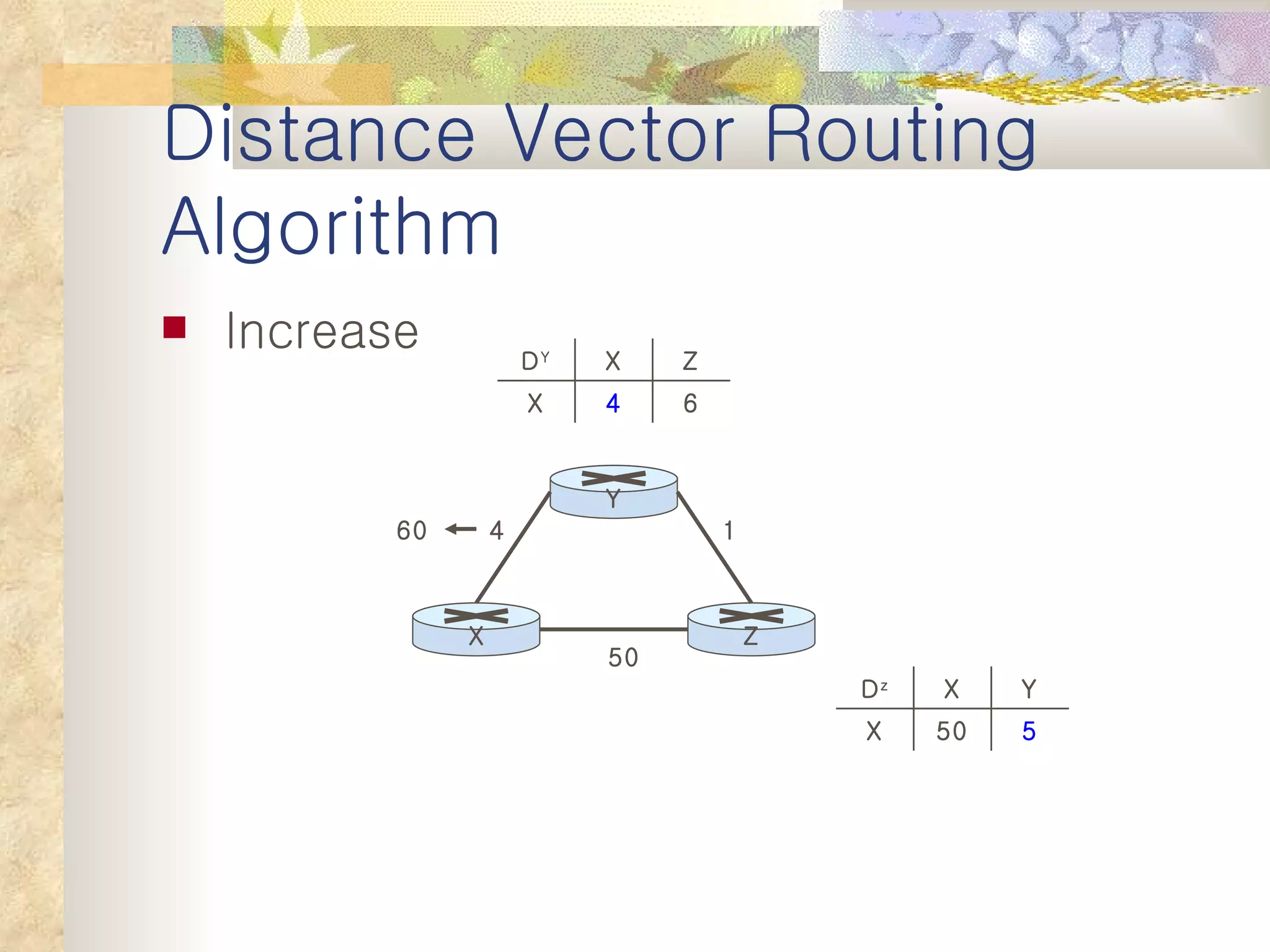
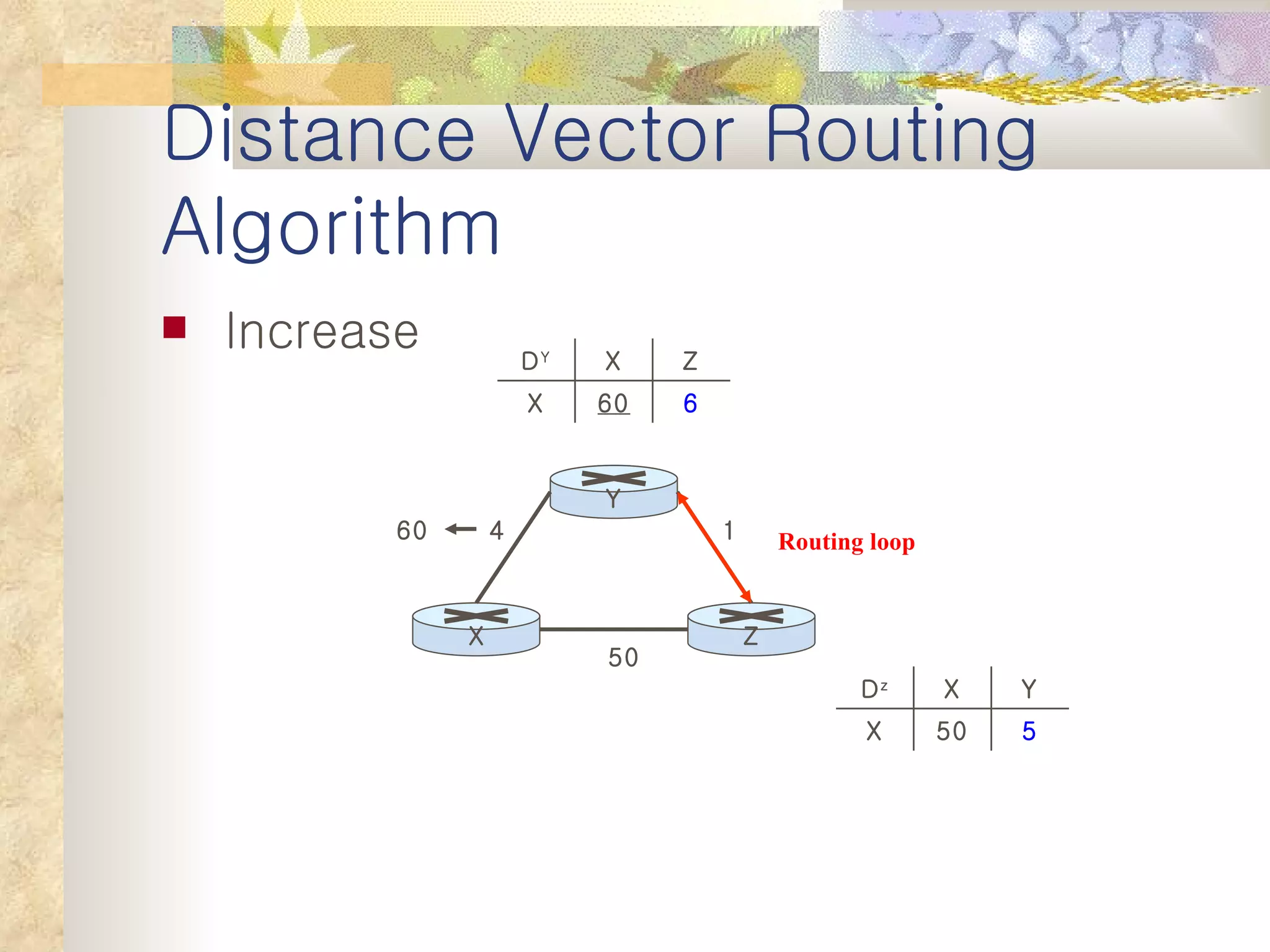
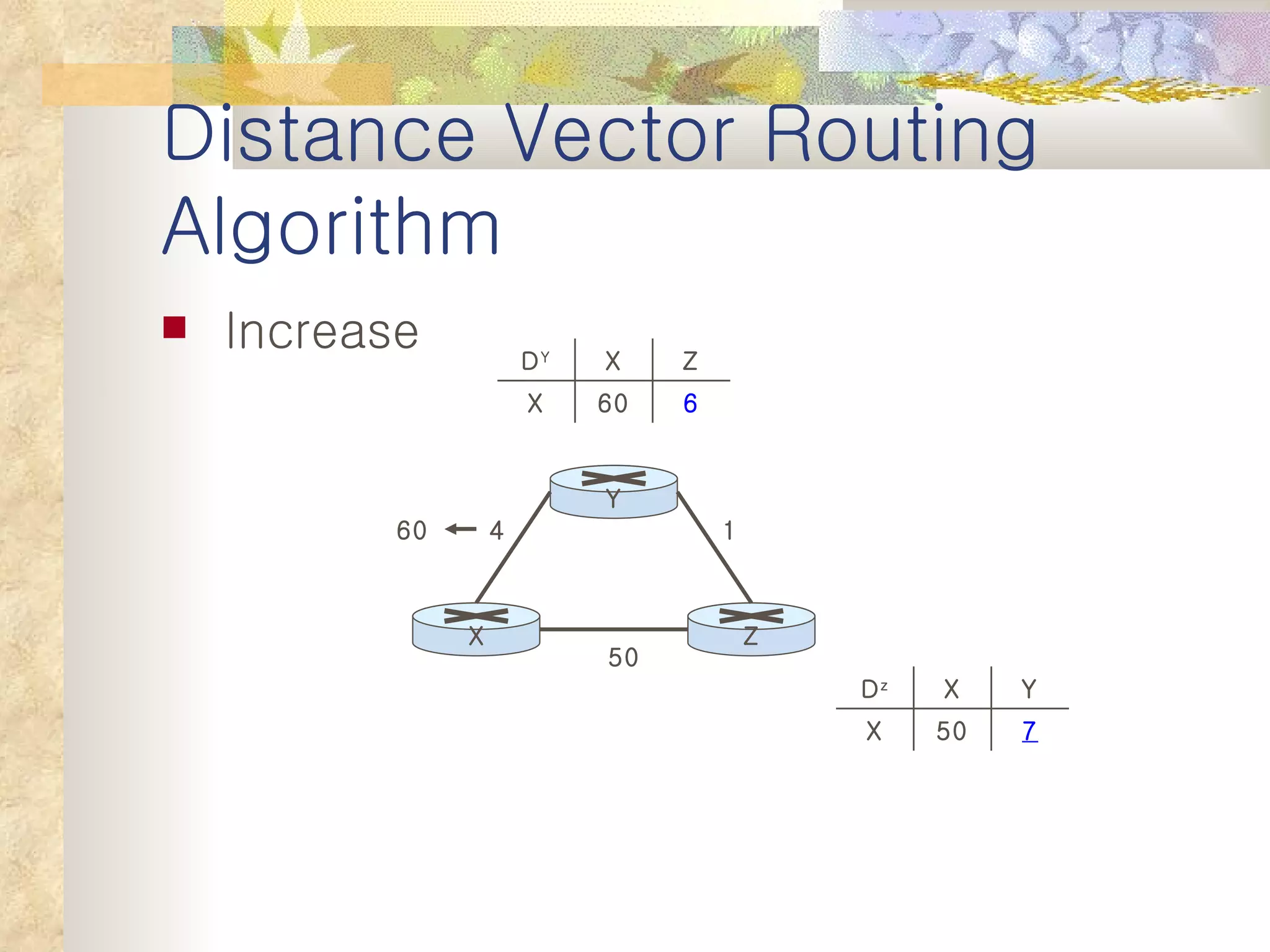
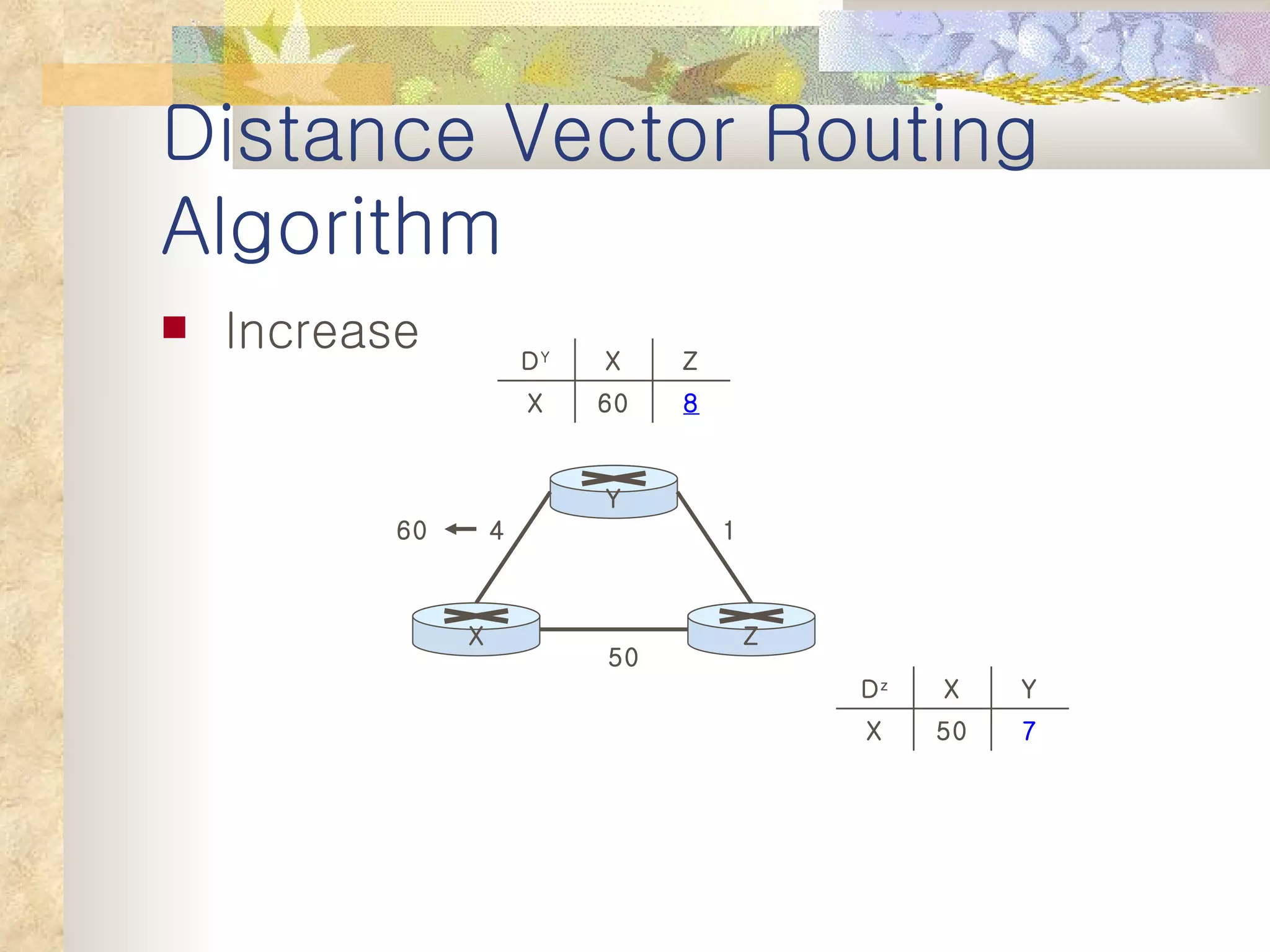
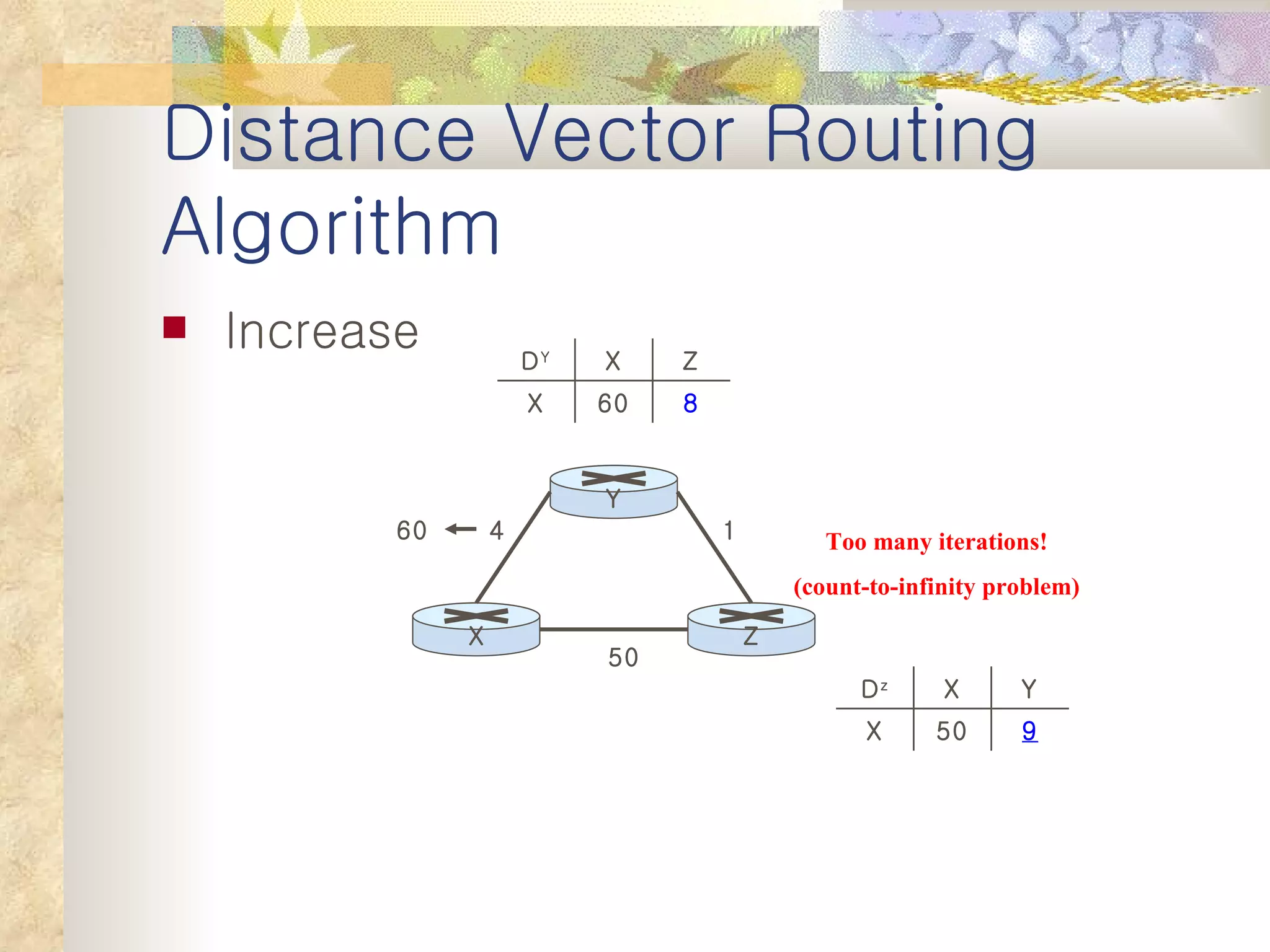
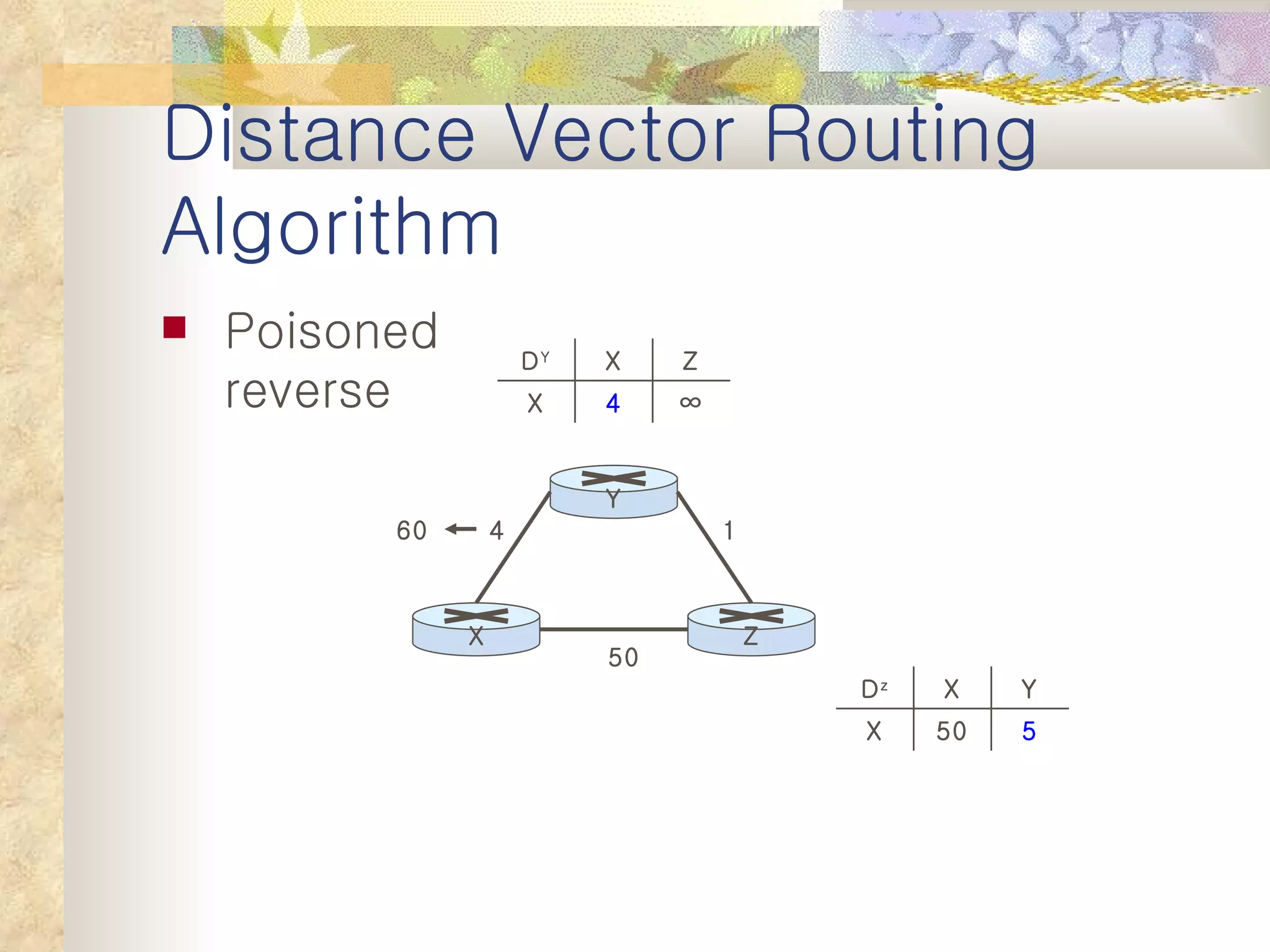
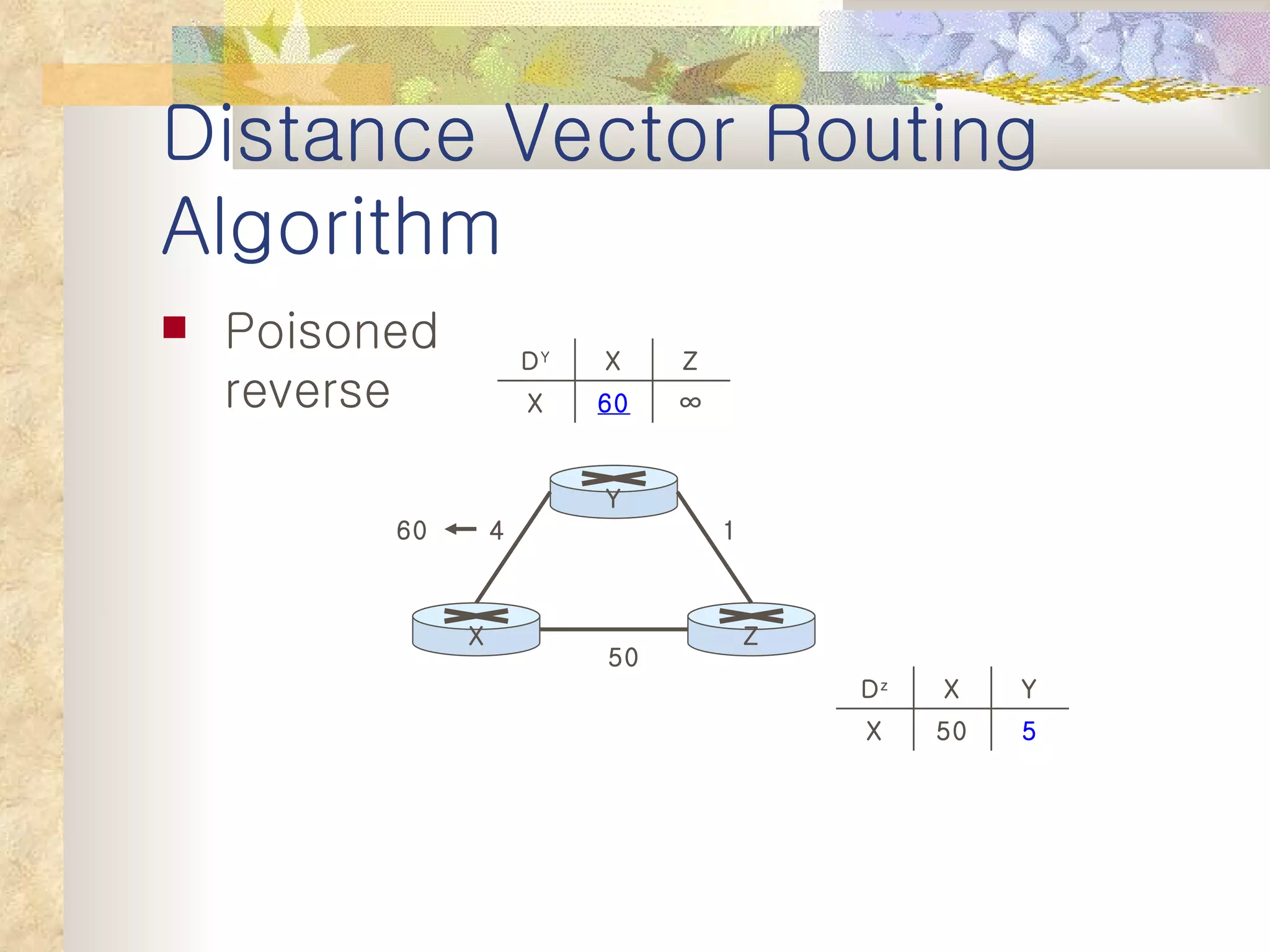
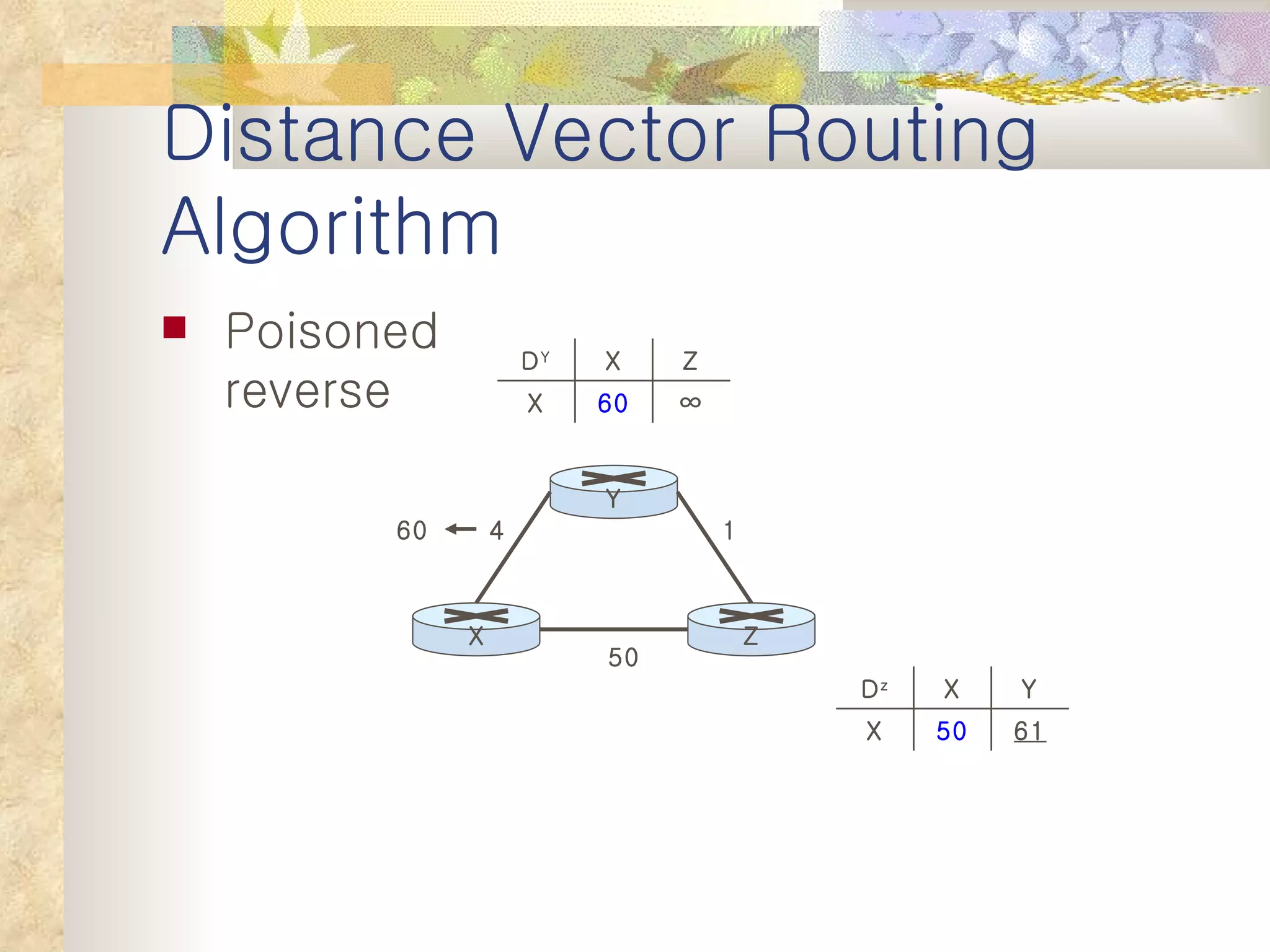
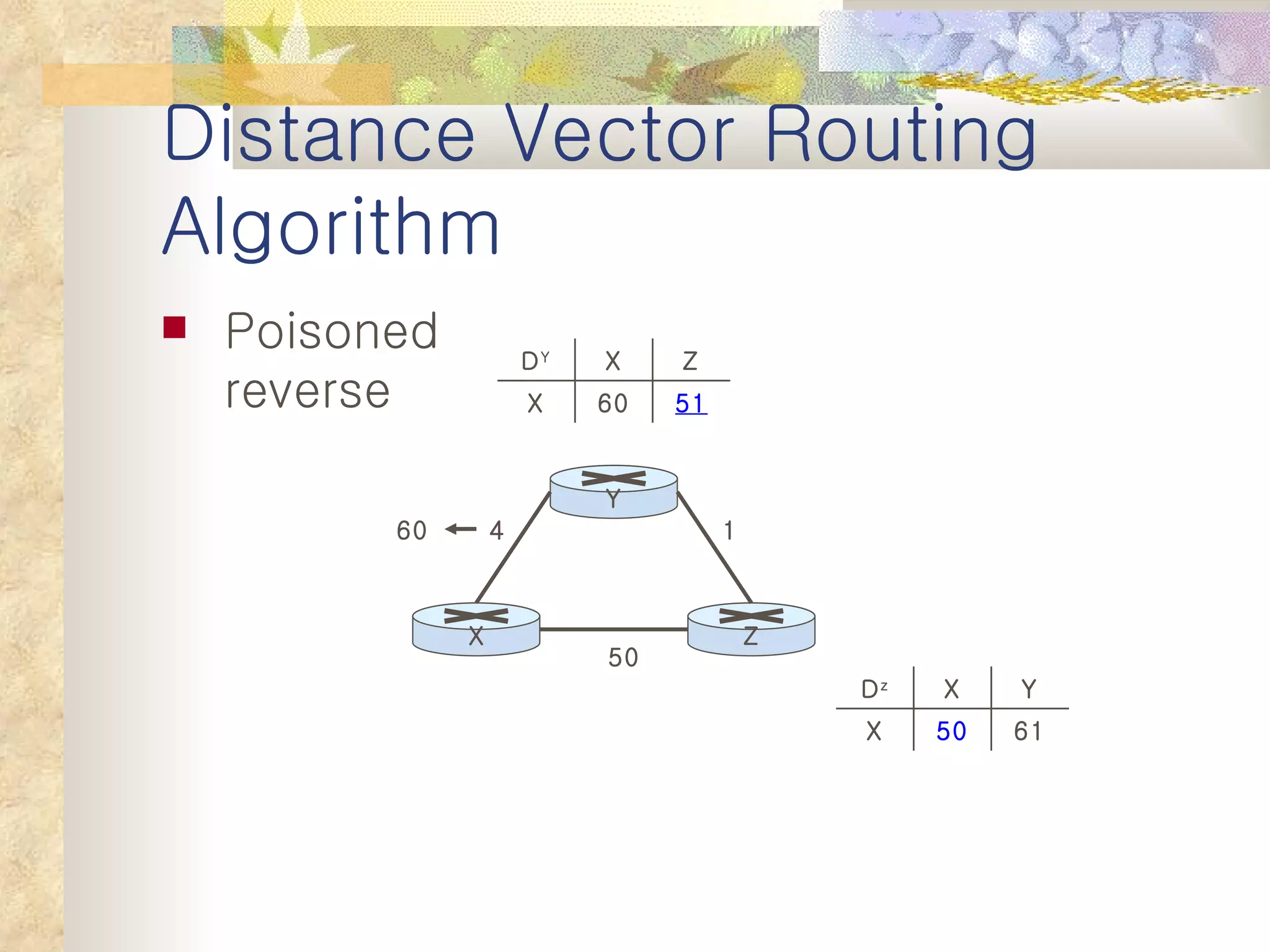
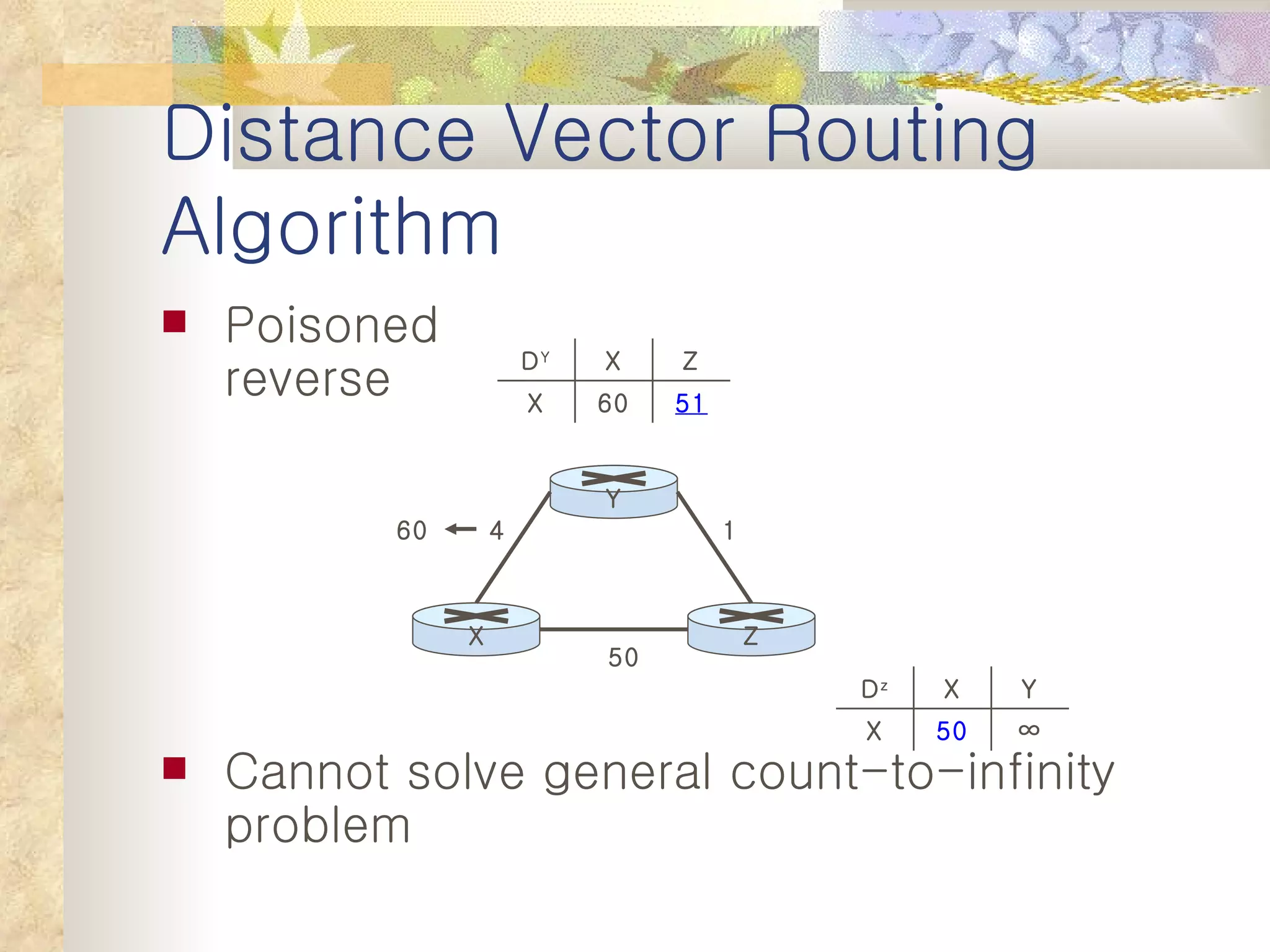
2. It explains that distance vector algorithms can have issues with counting to infinity and routing loops. Techniques like poison reverse are used to address this.
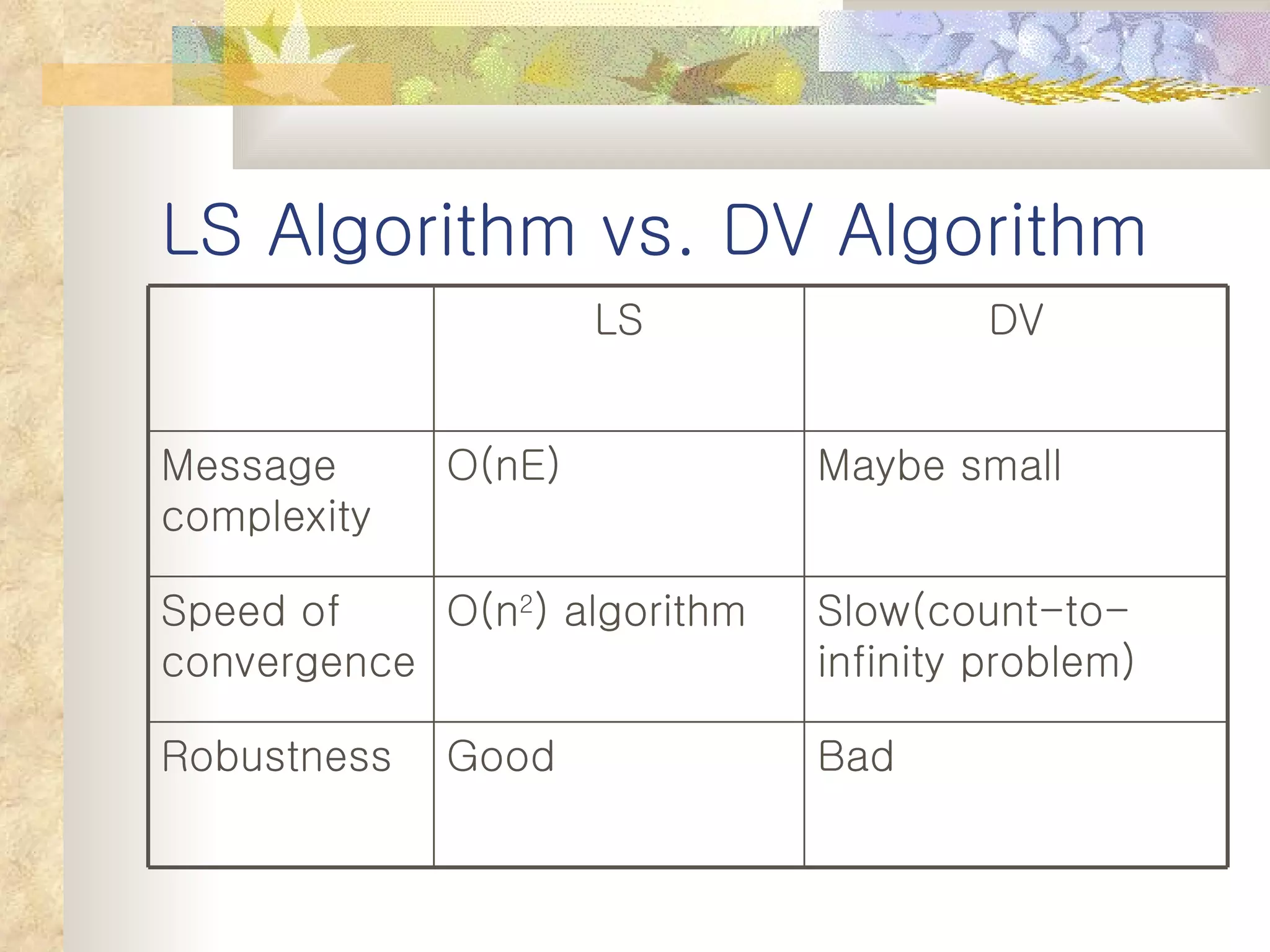
3. It notes that link state algorithms have faster convergence but require more overhead, while distance vector algorithms are simpler but can be slower to converge.
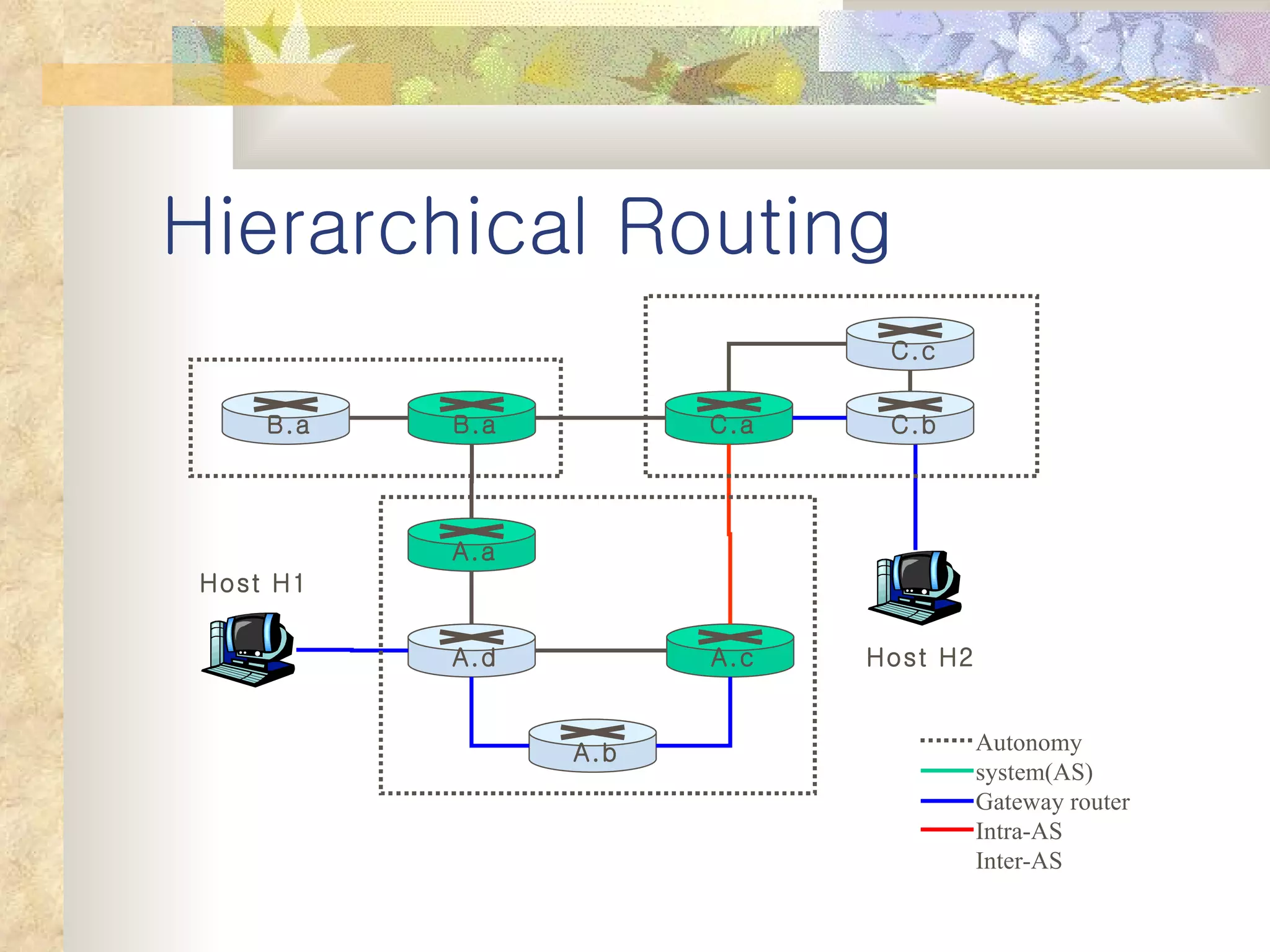
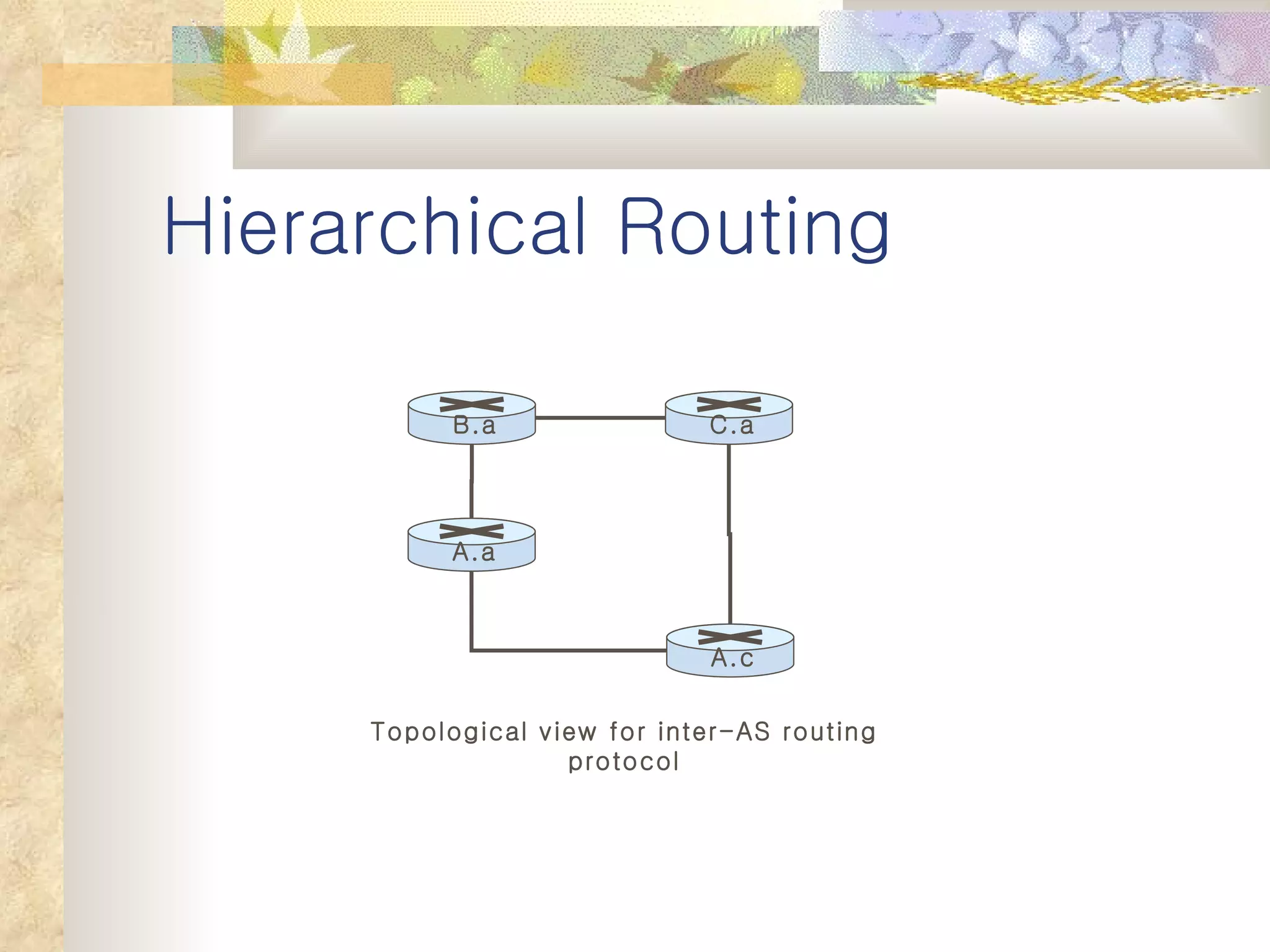
4. Hierarchical routing is introduced as a way to scale routing by organizing routers into autonomous systems (AS) with inter and intra-