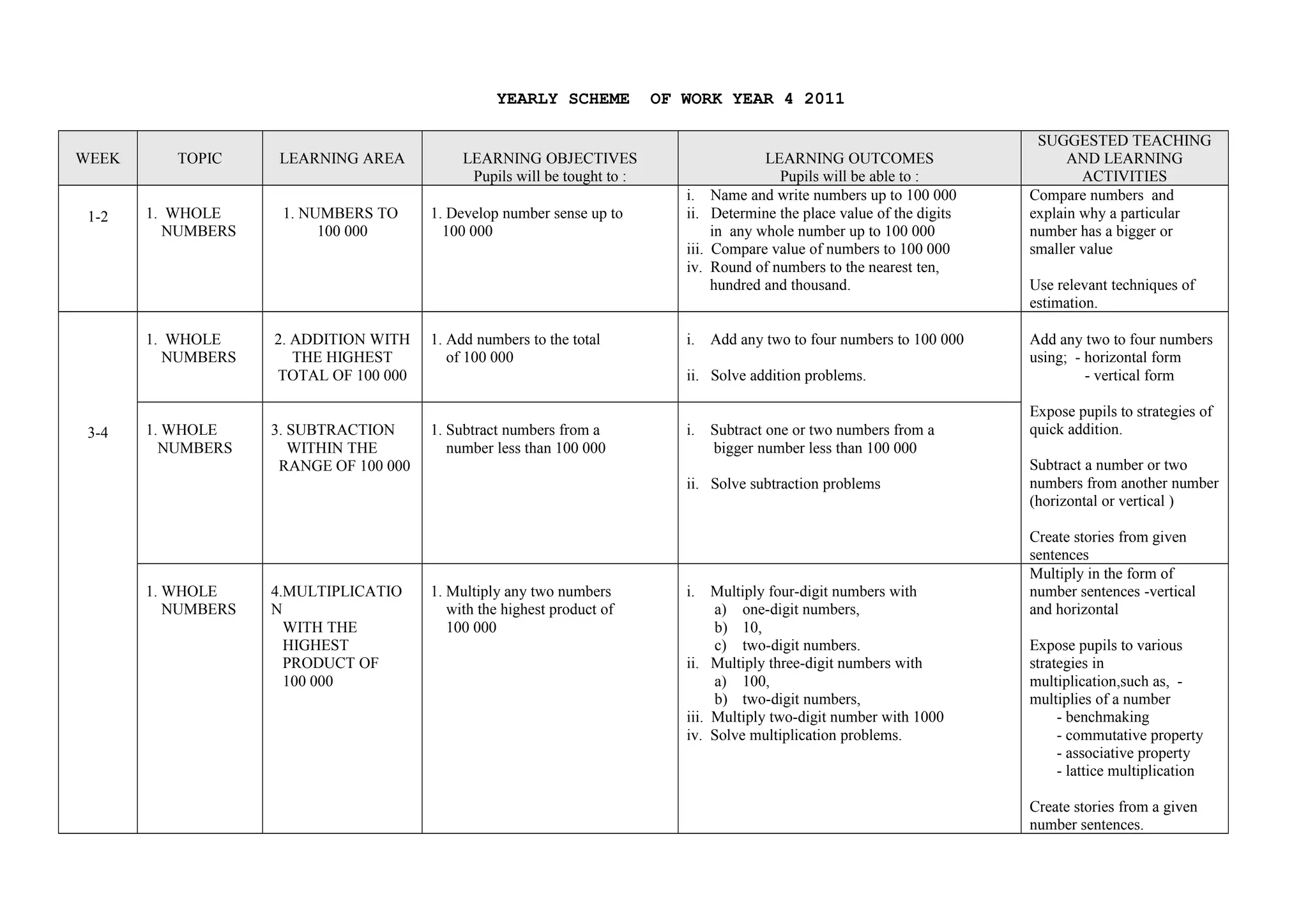
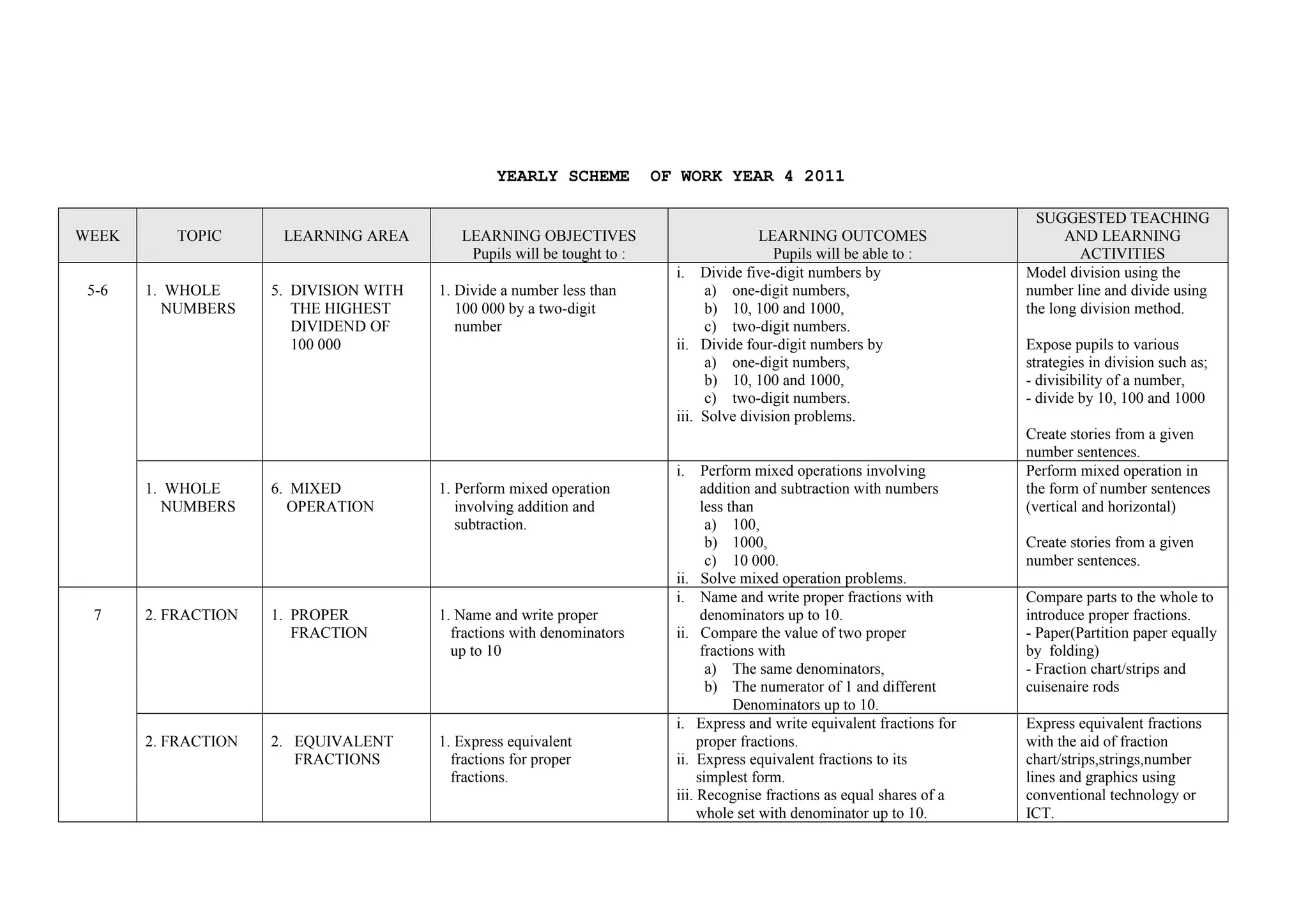
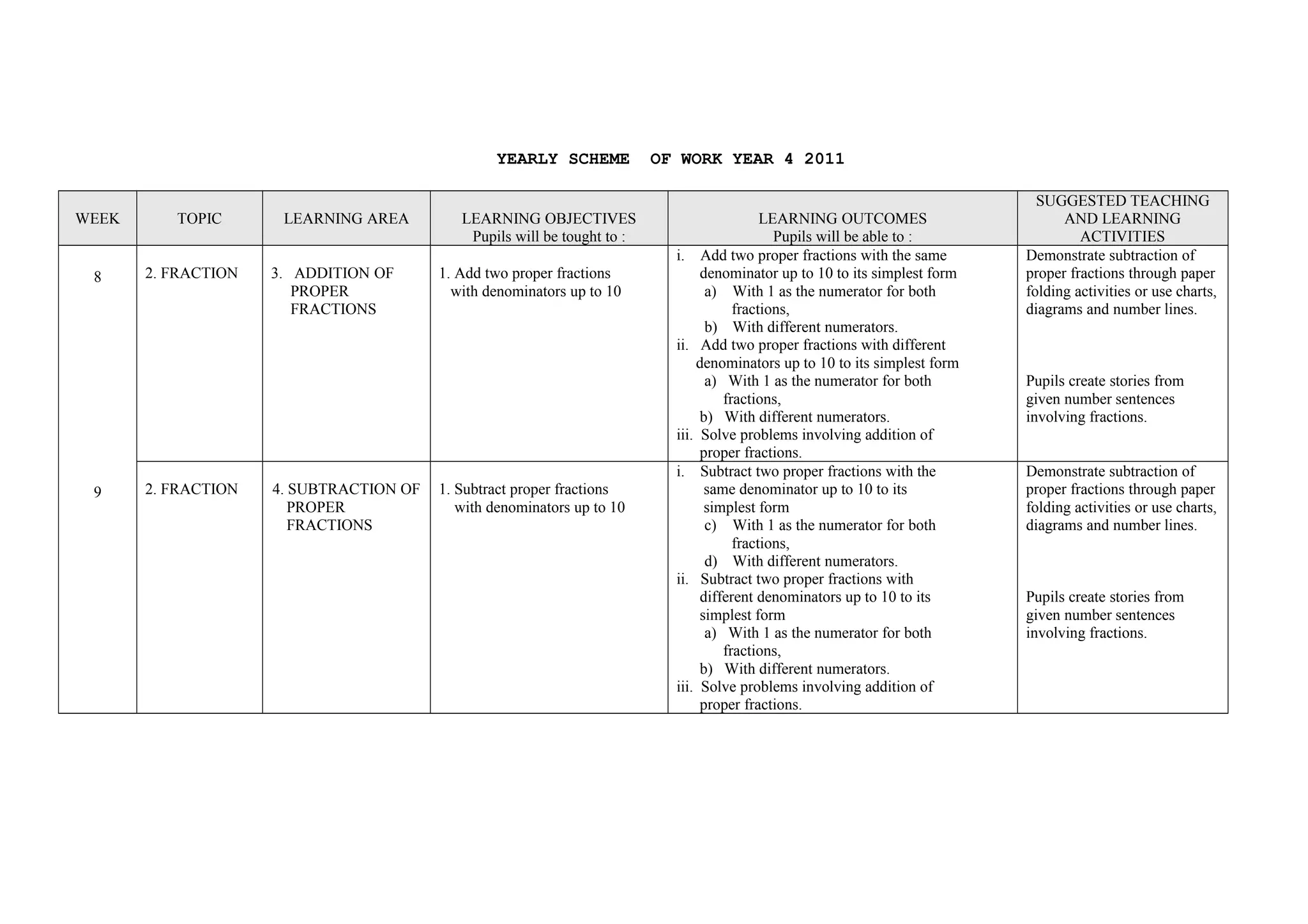
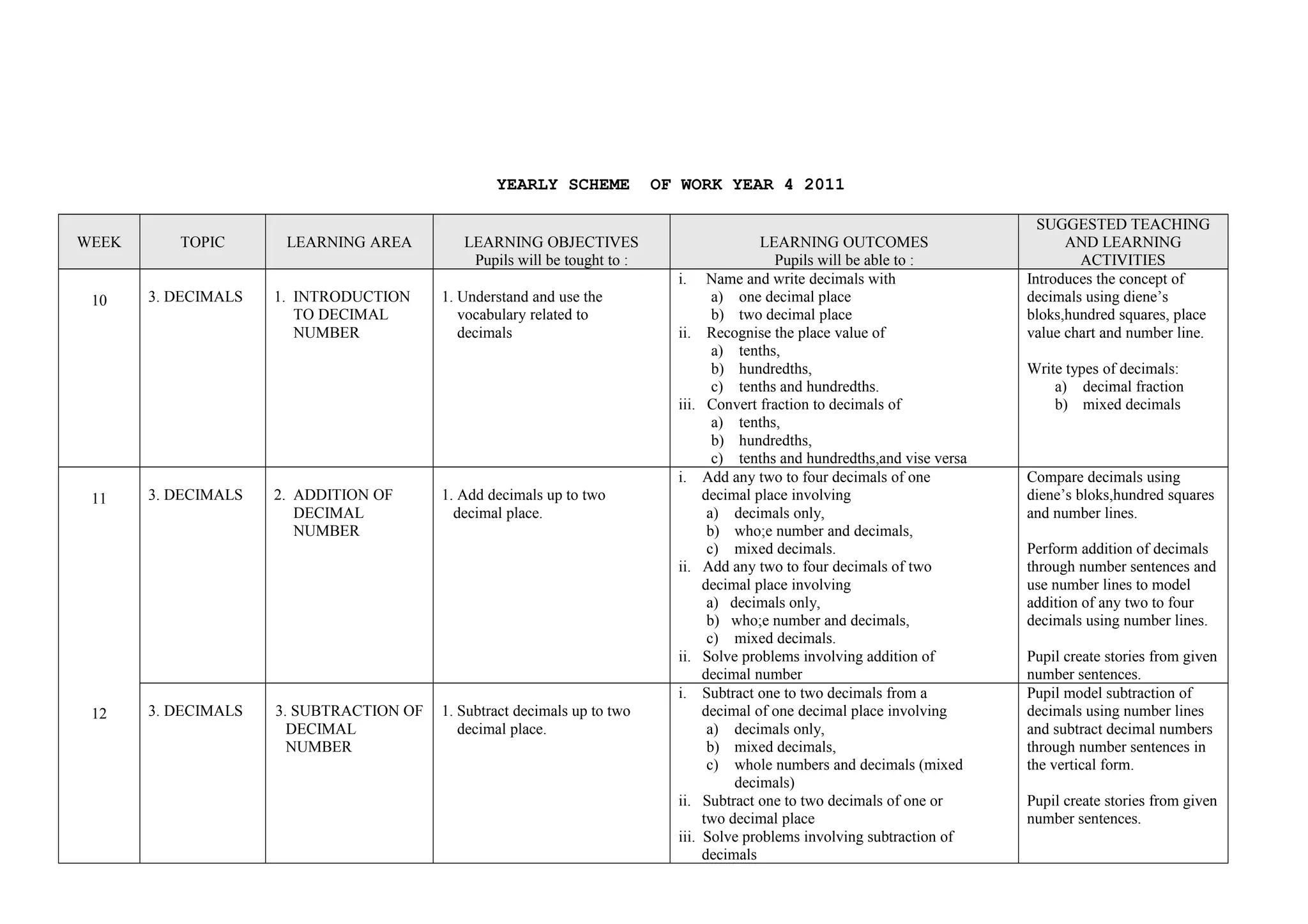
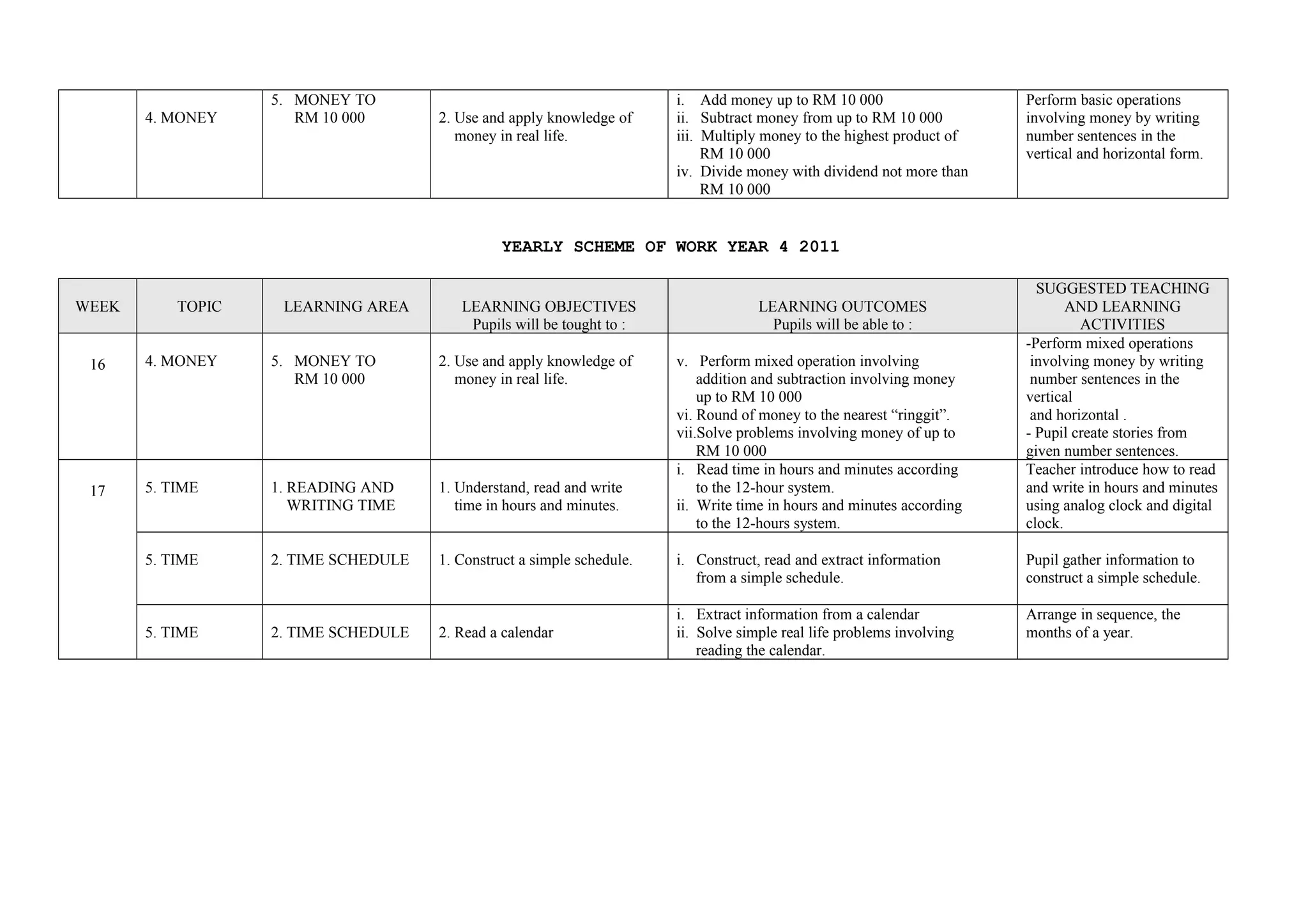
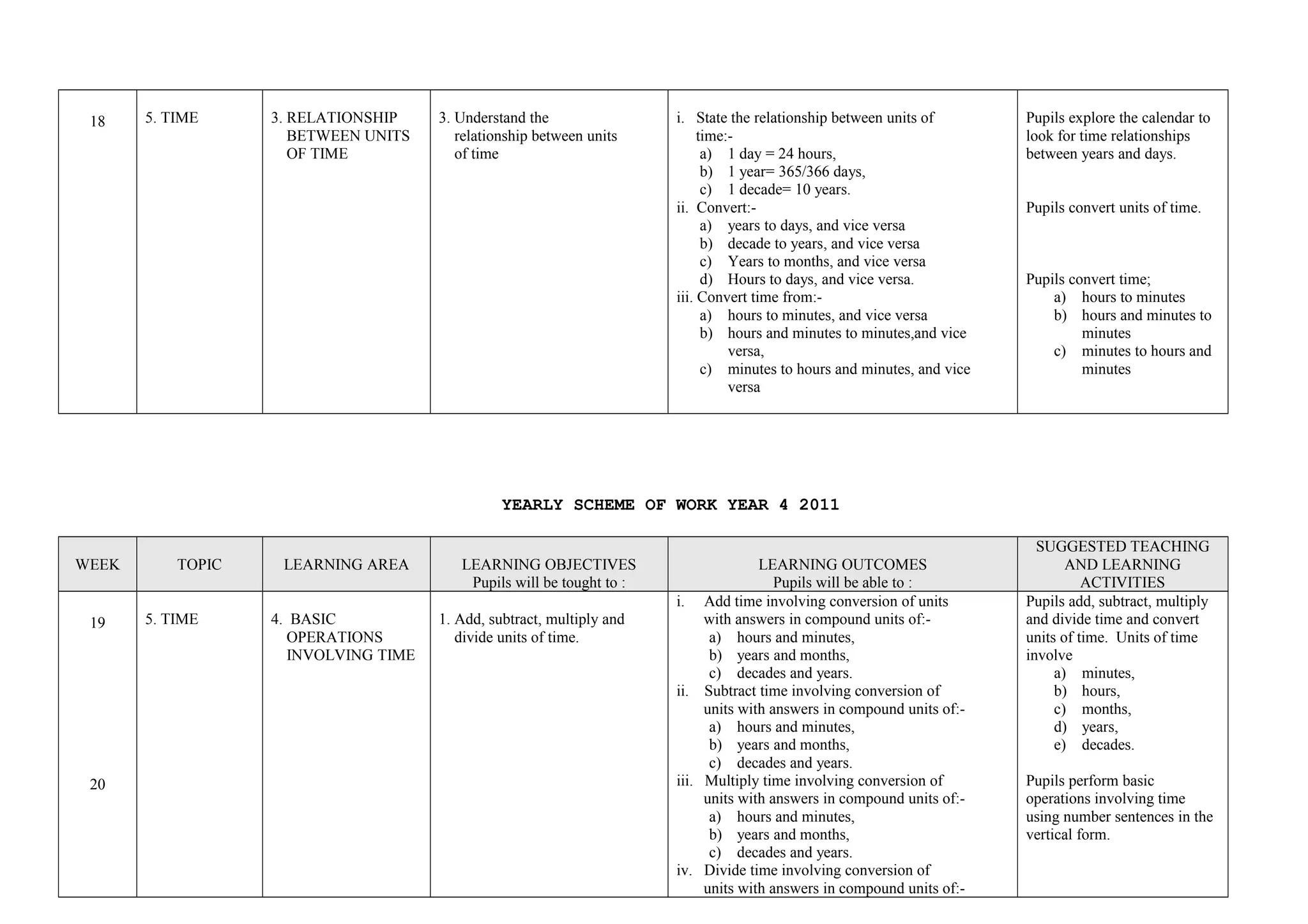
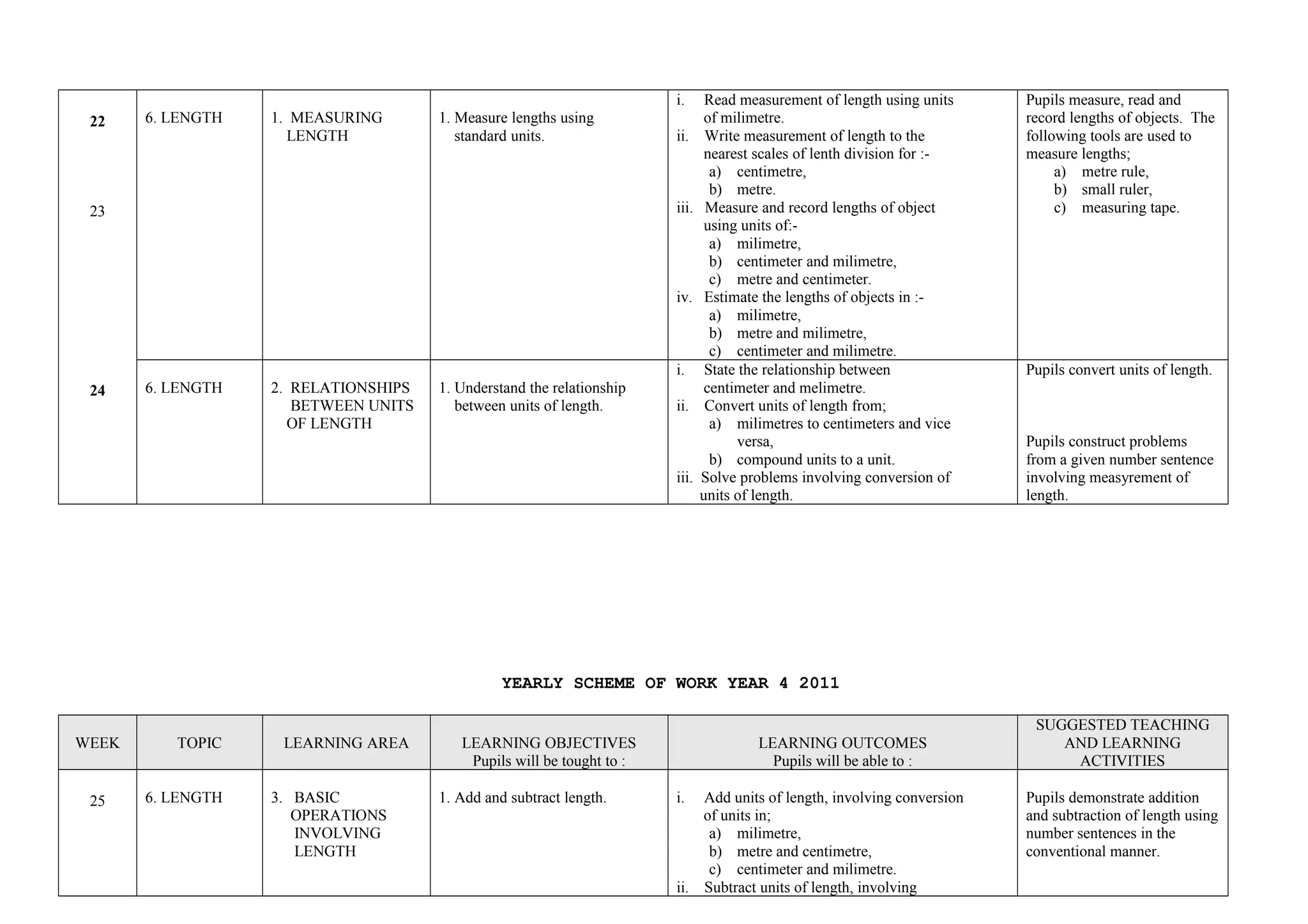
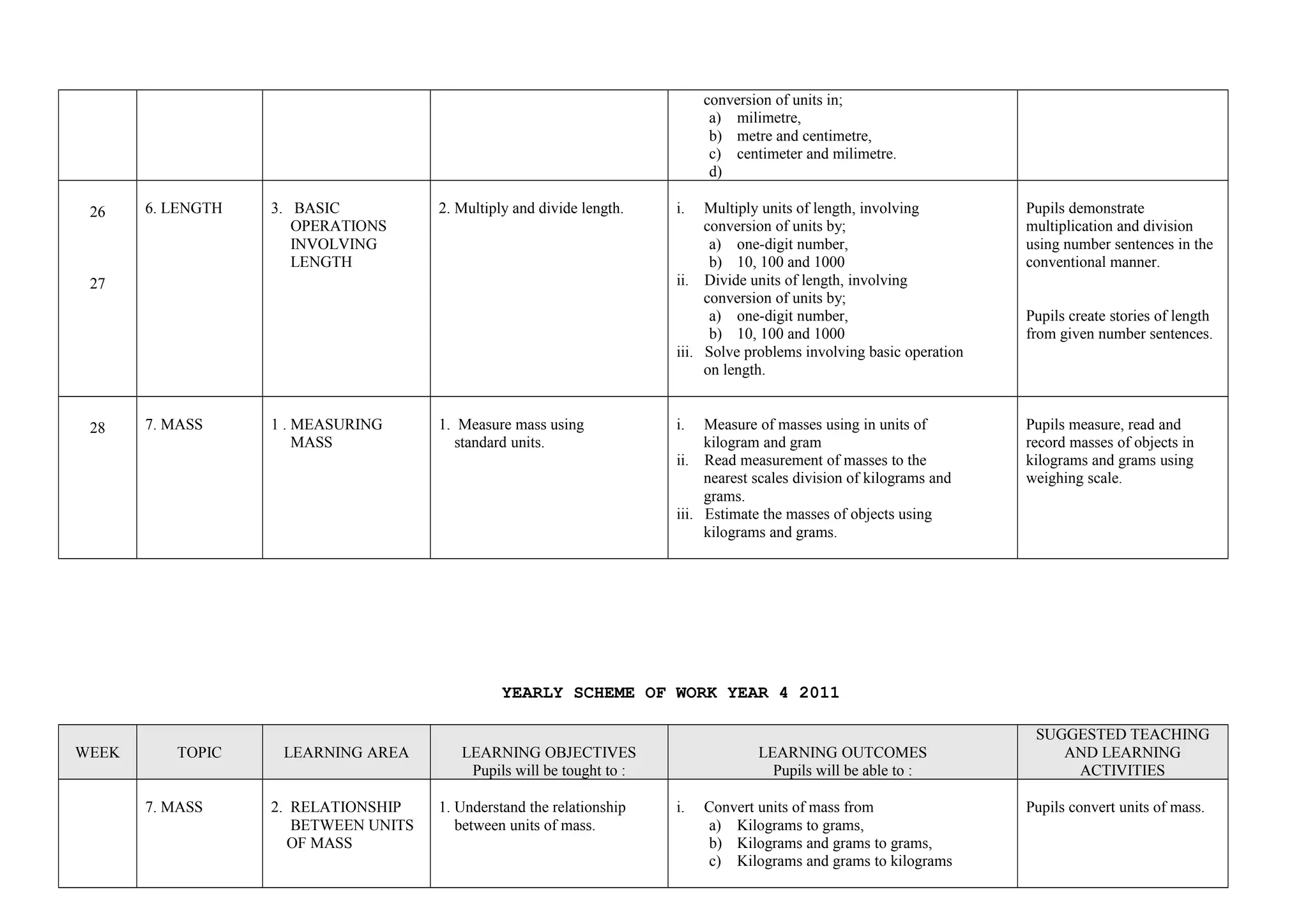
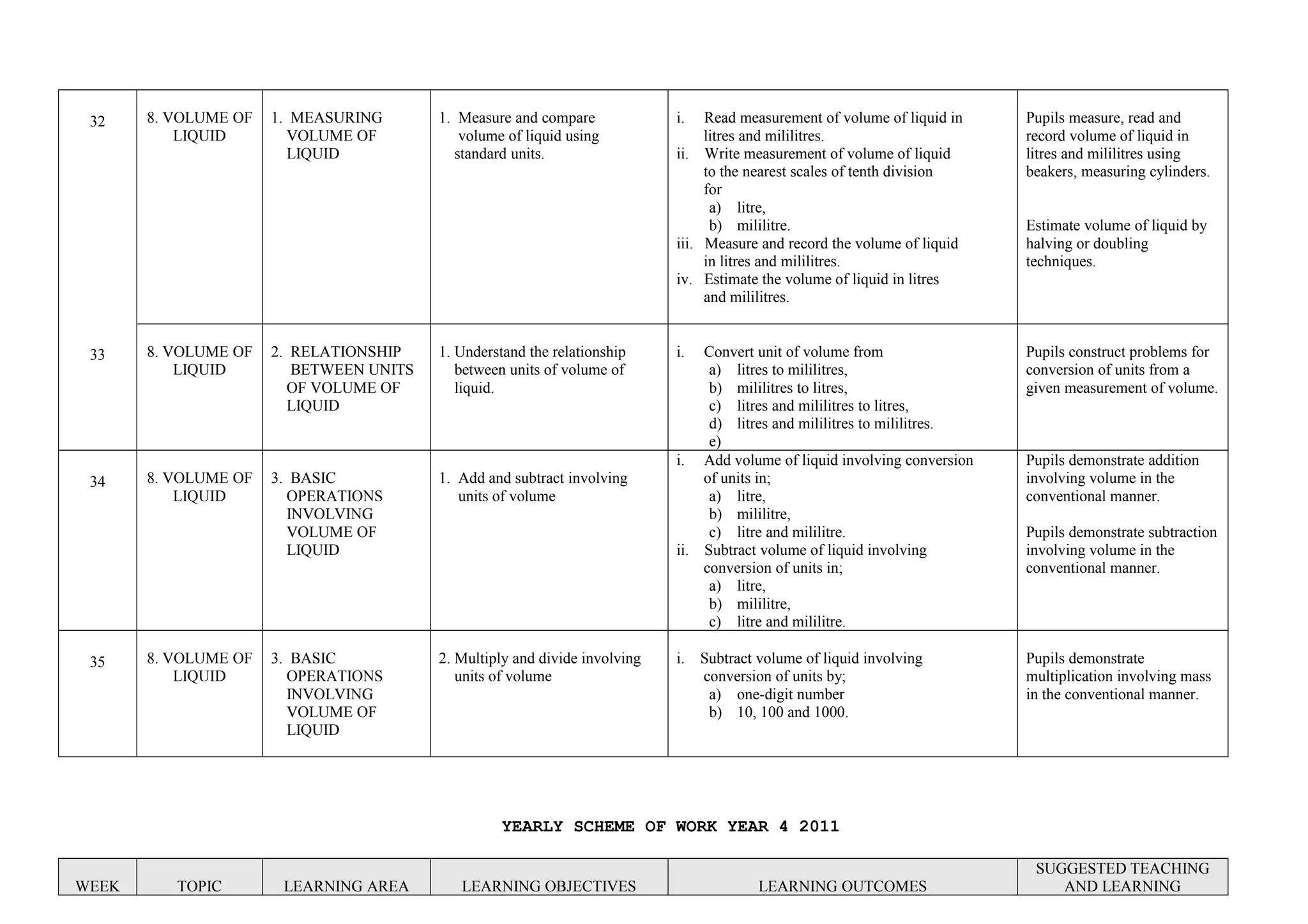
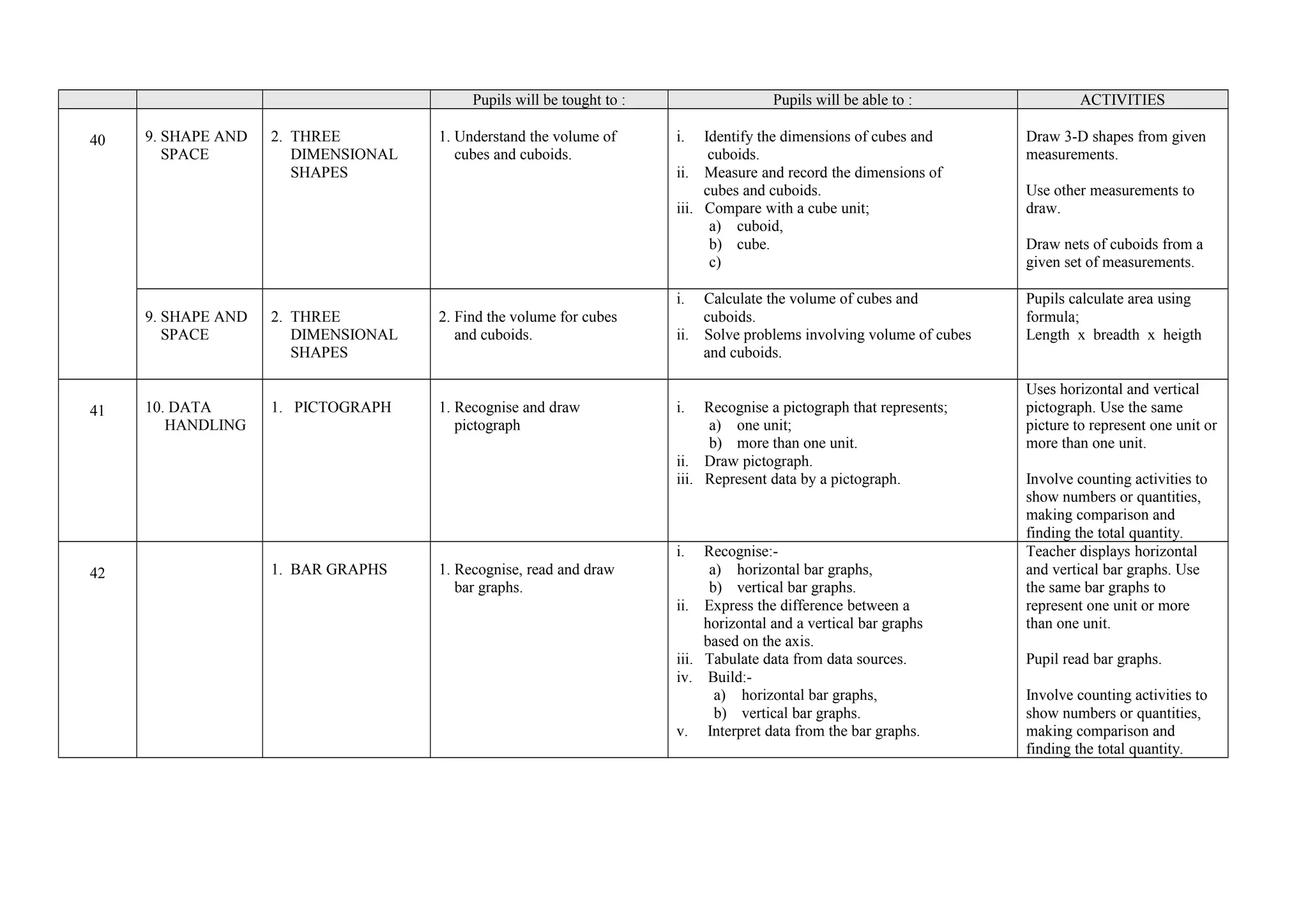
This document provides a yearly scheme of work for Year 4 students covering topics in numbers, fractions, decimals, money, and time. It outlines the learning objectives, outcomes, and suggested teaching activities for each week. The topics include whole numbers, fractions, decimals, money up to RM 10,000, and telling time in hours and minutes. The learning objectives focus on skills like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of whole numbers, fractions, and decimals. Suggested activities include using number lines, charts, and story problems. The scheme of work provides a full-year overview of the key mathematical concepts and skills to be taught each week.