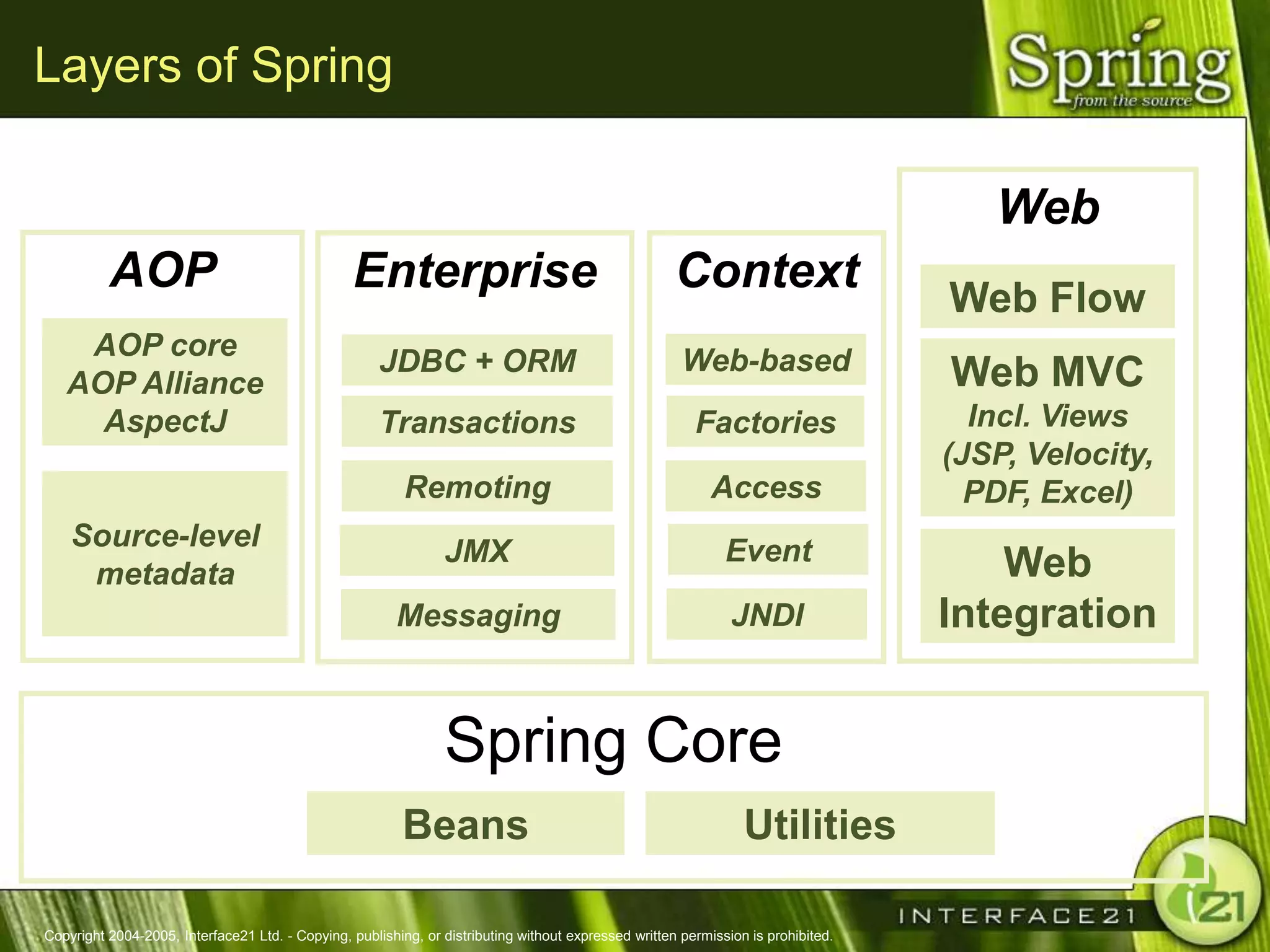
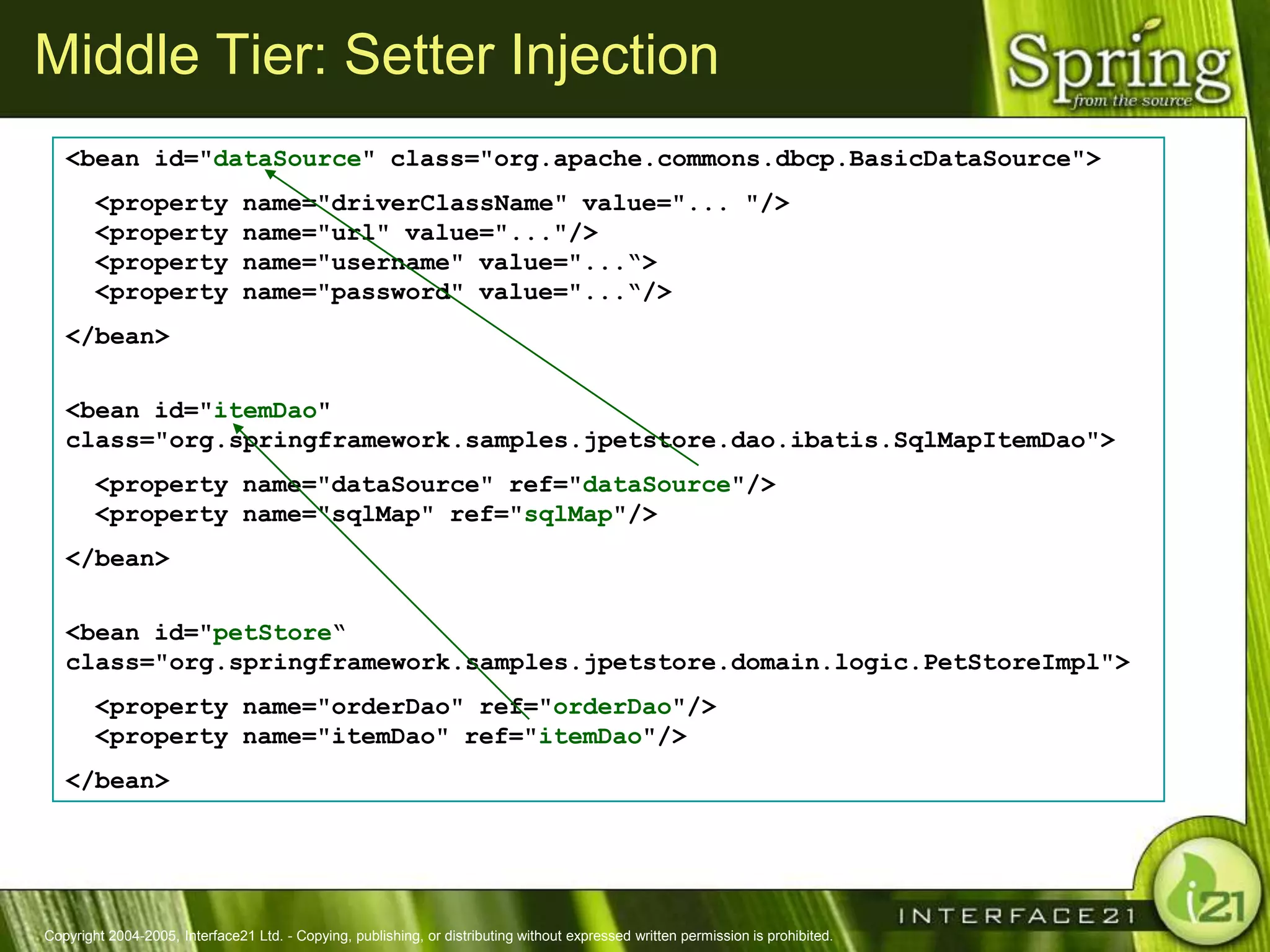
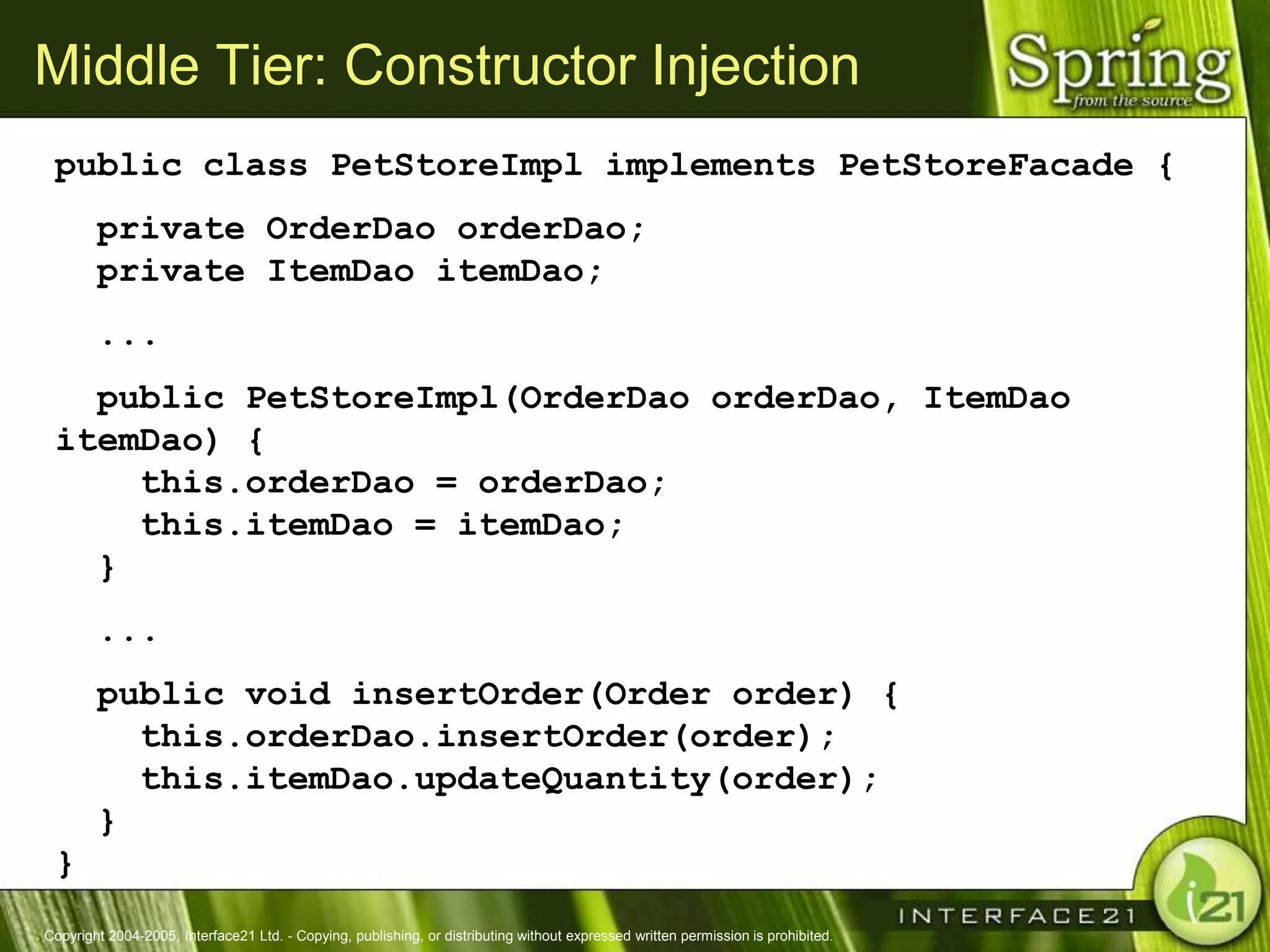
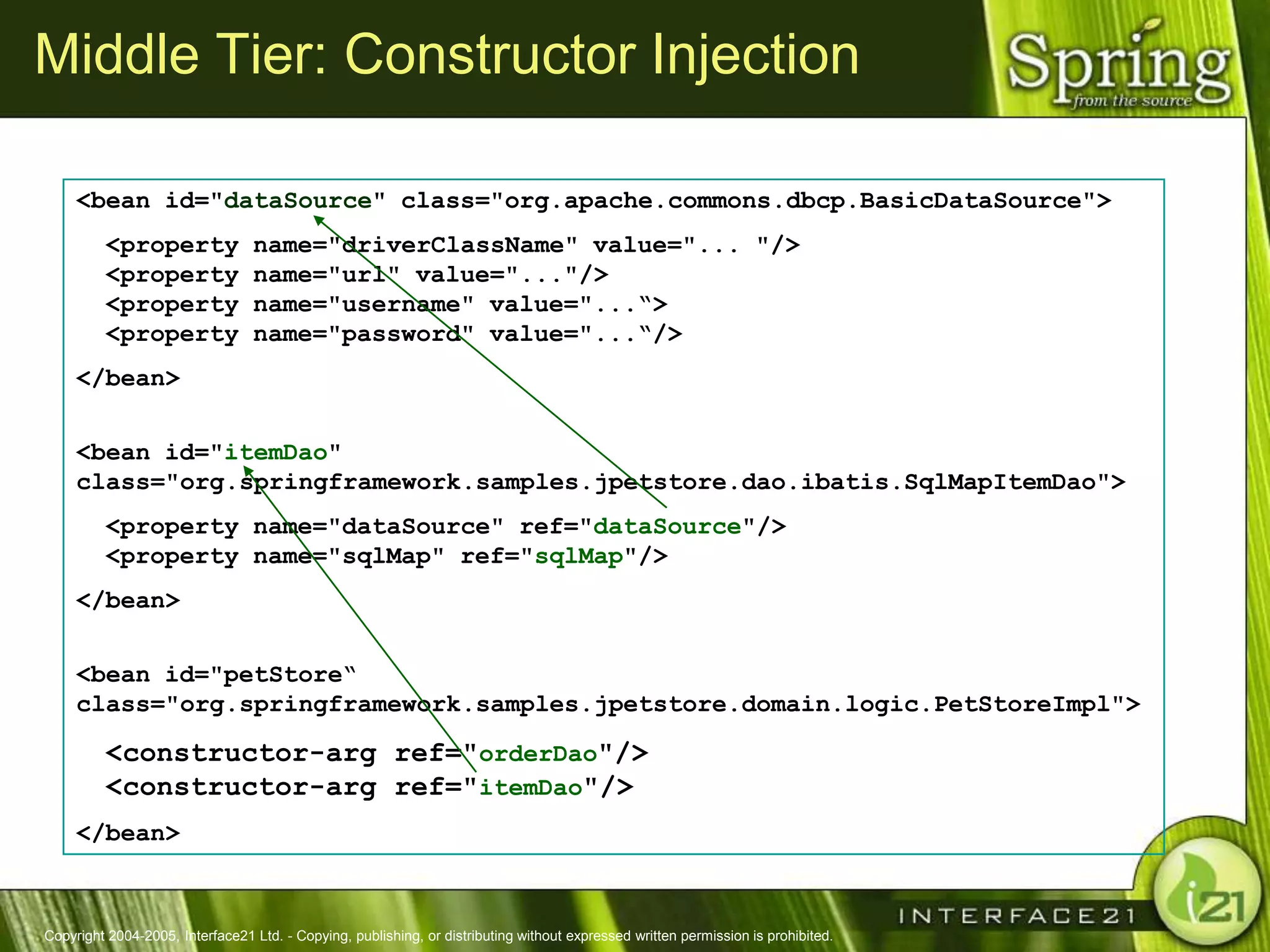
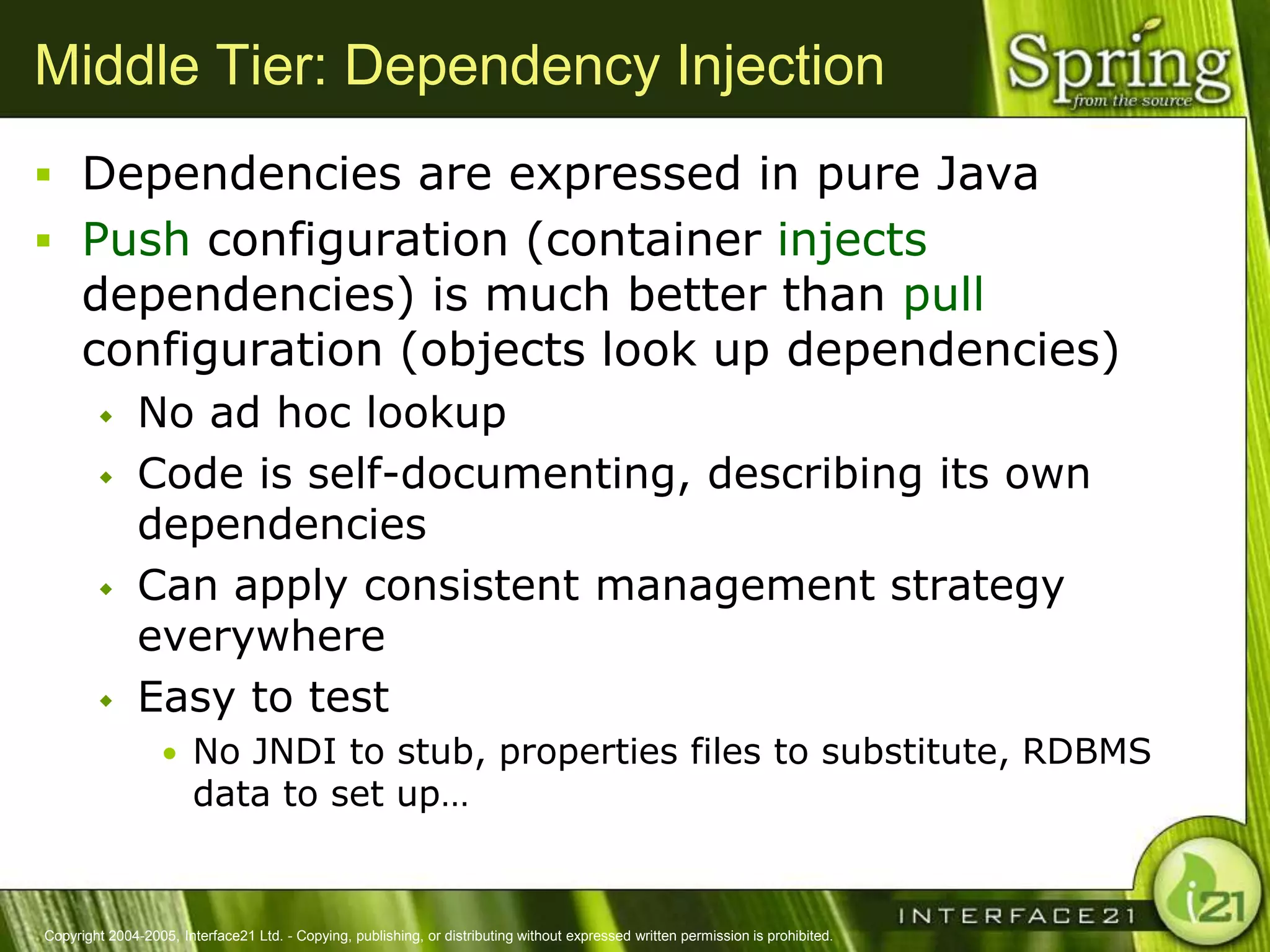
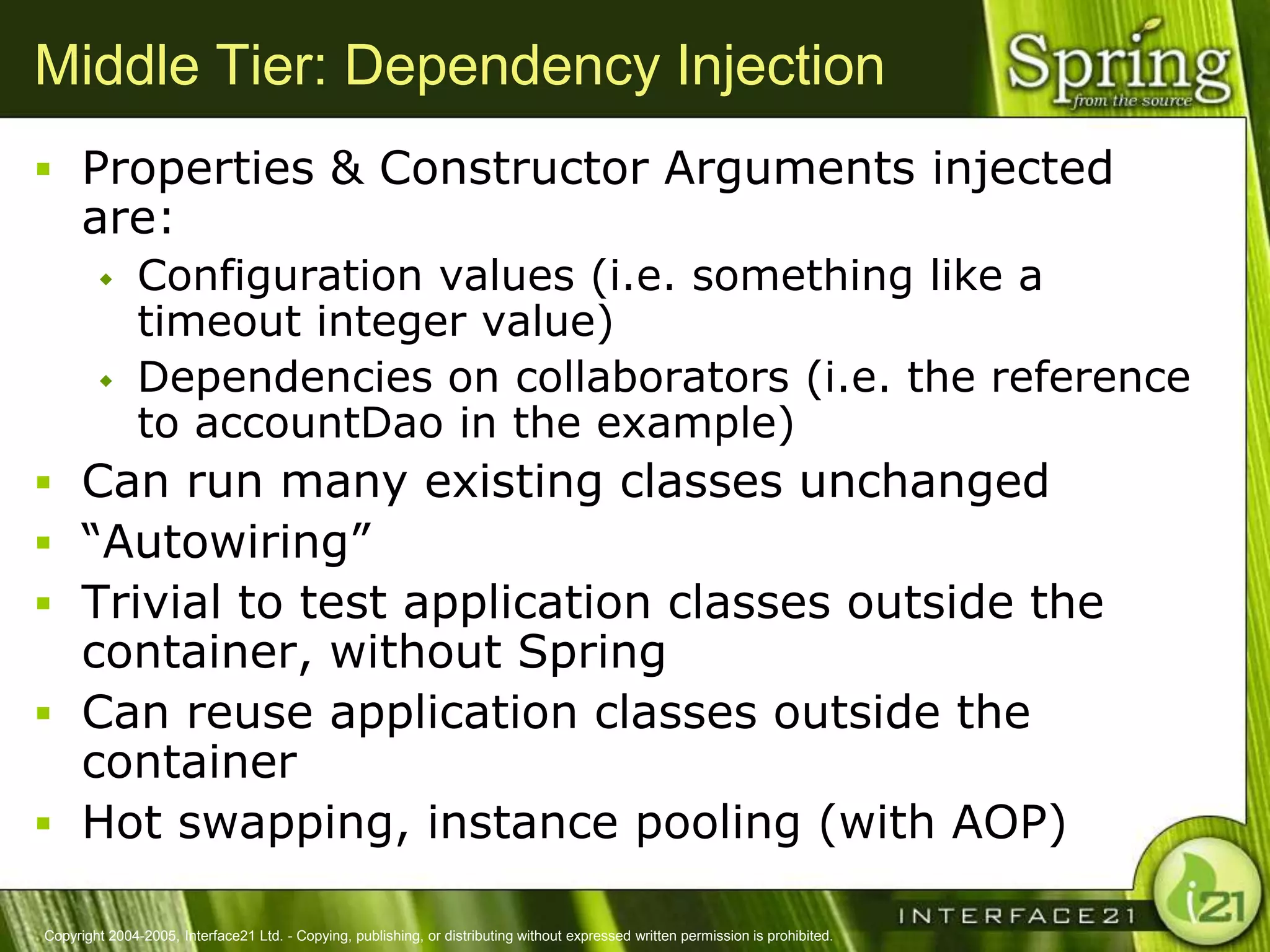
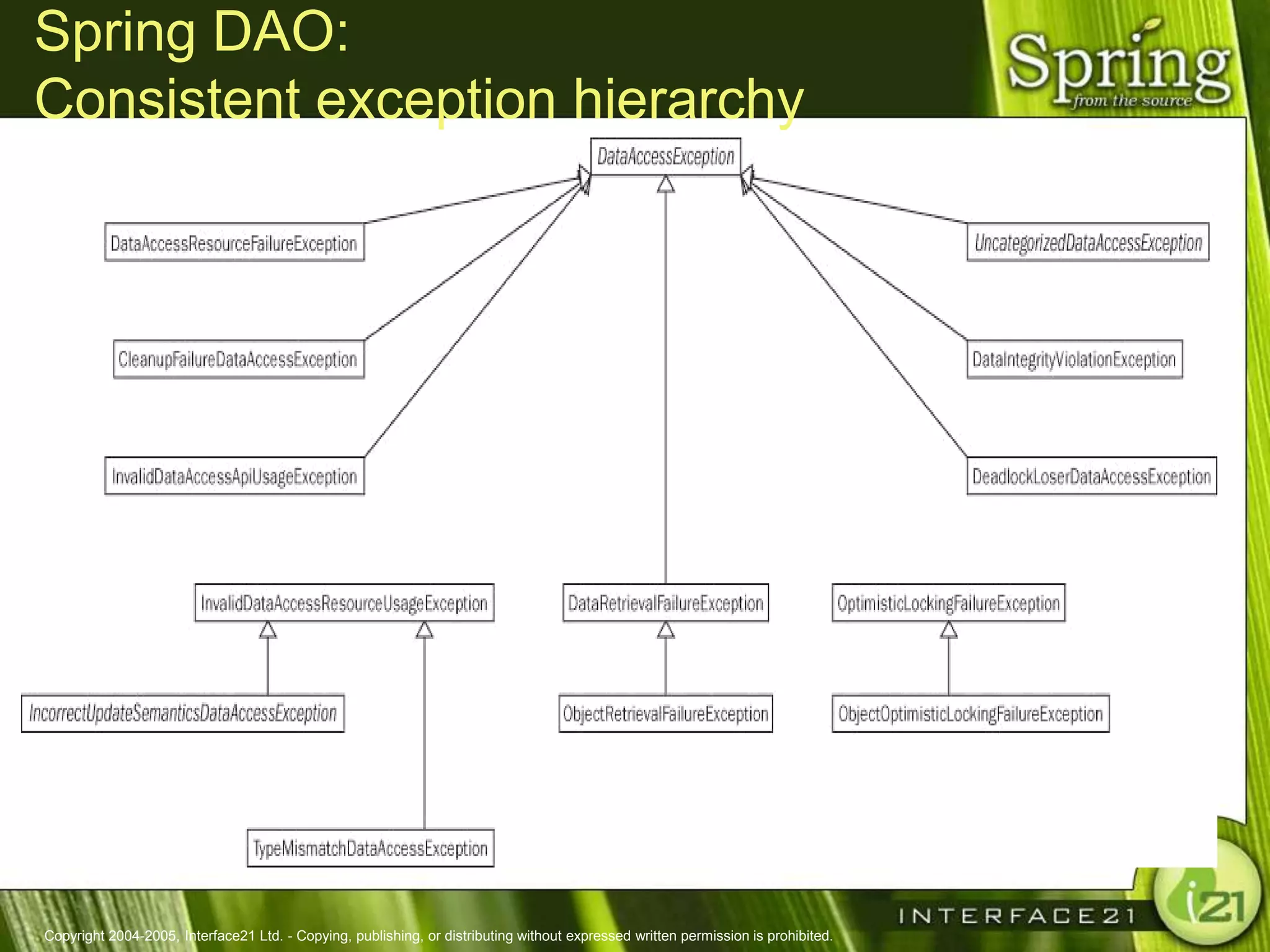
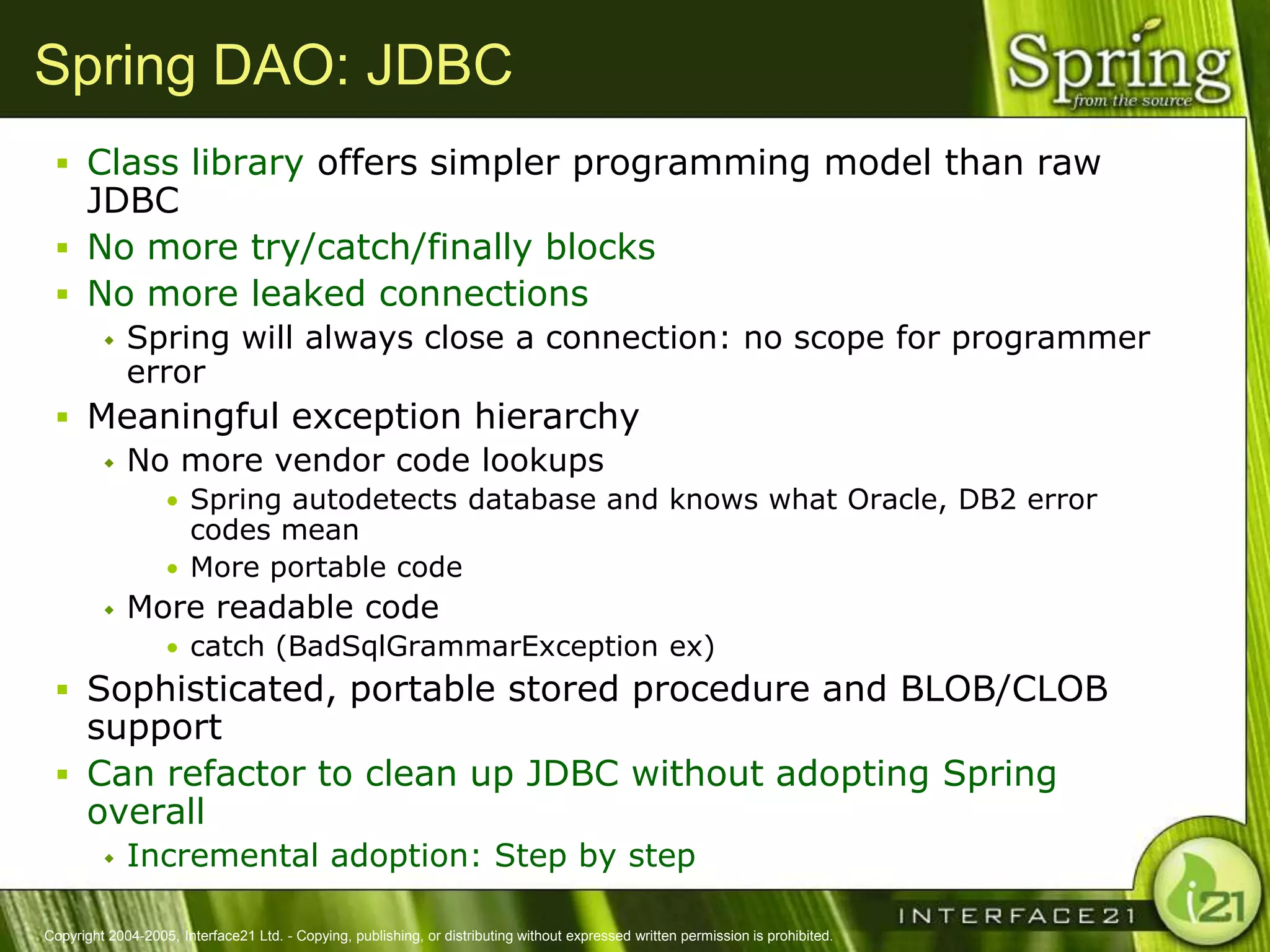
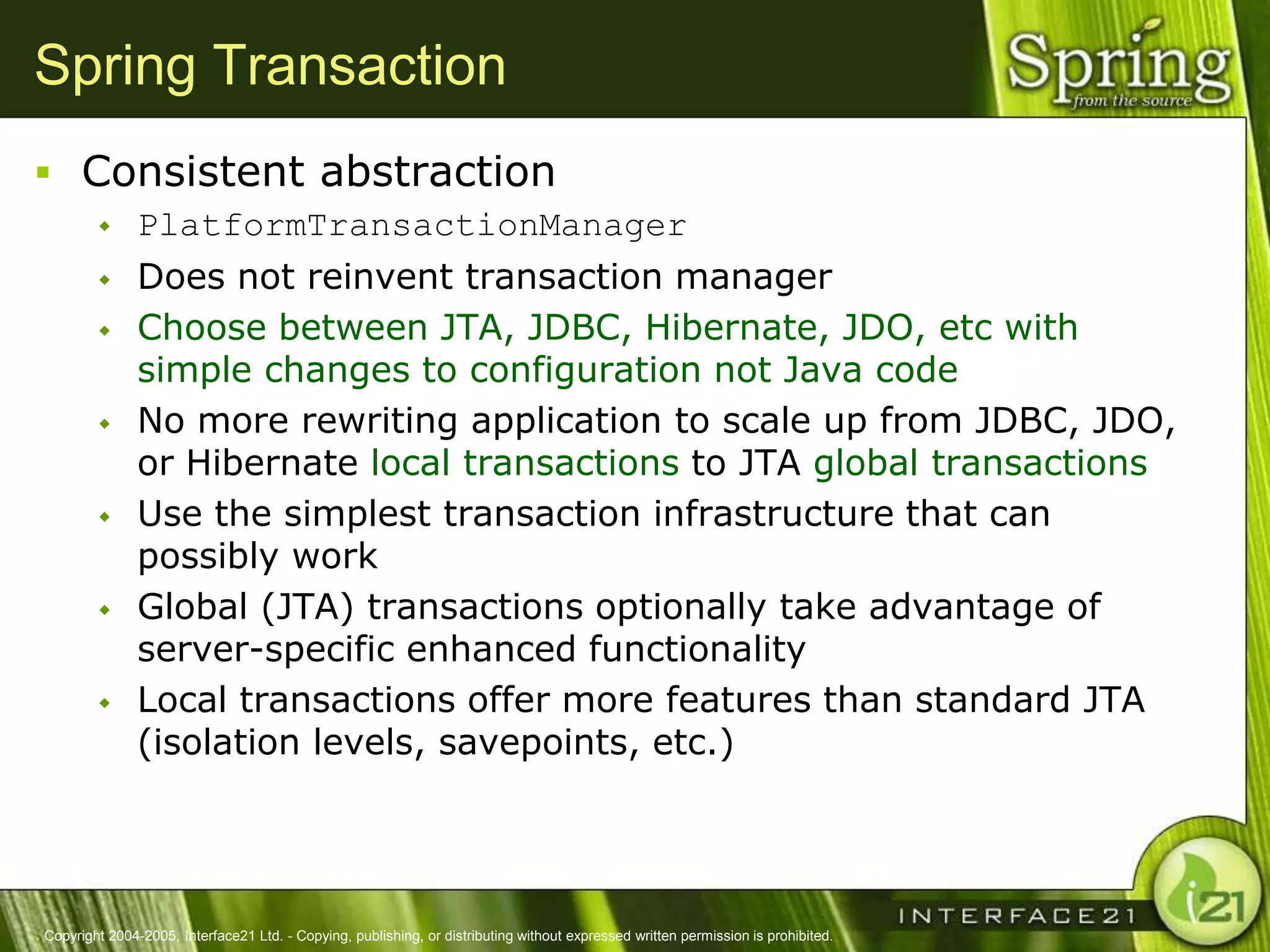
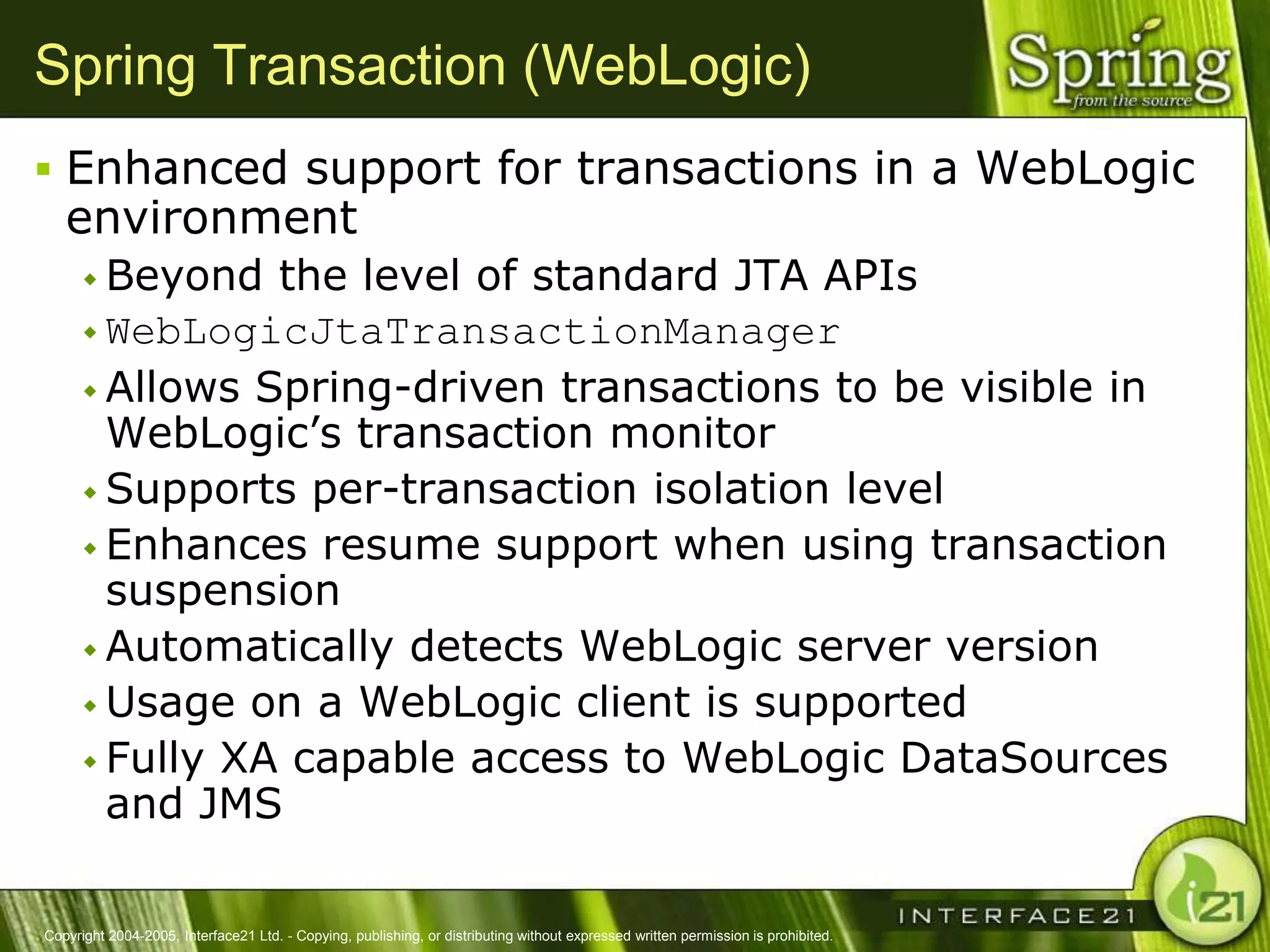
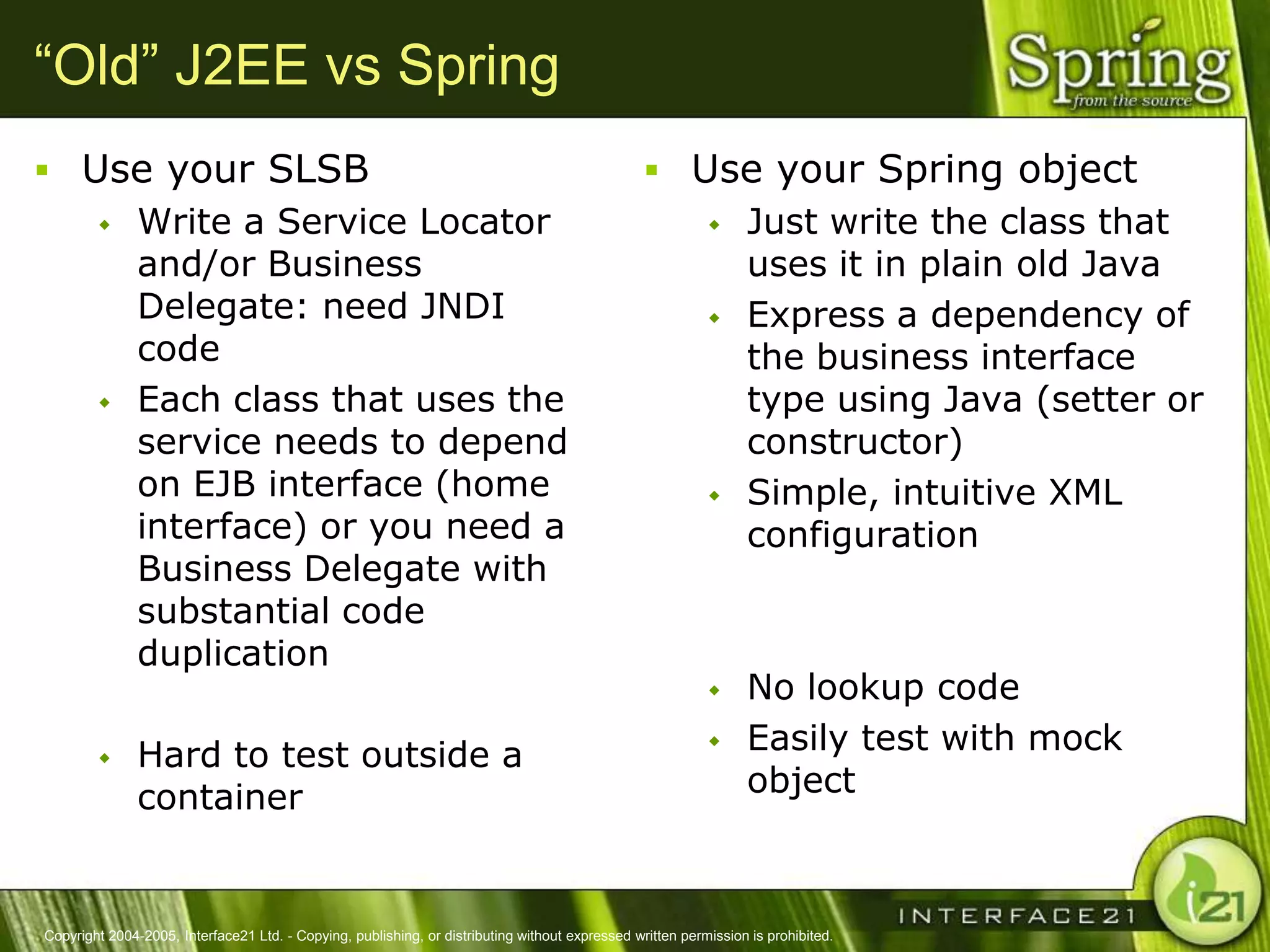
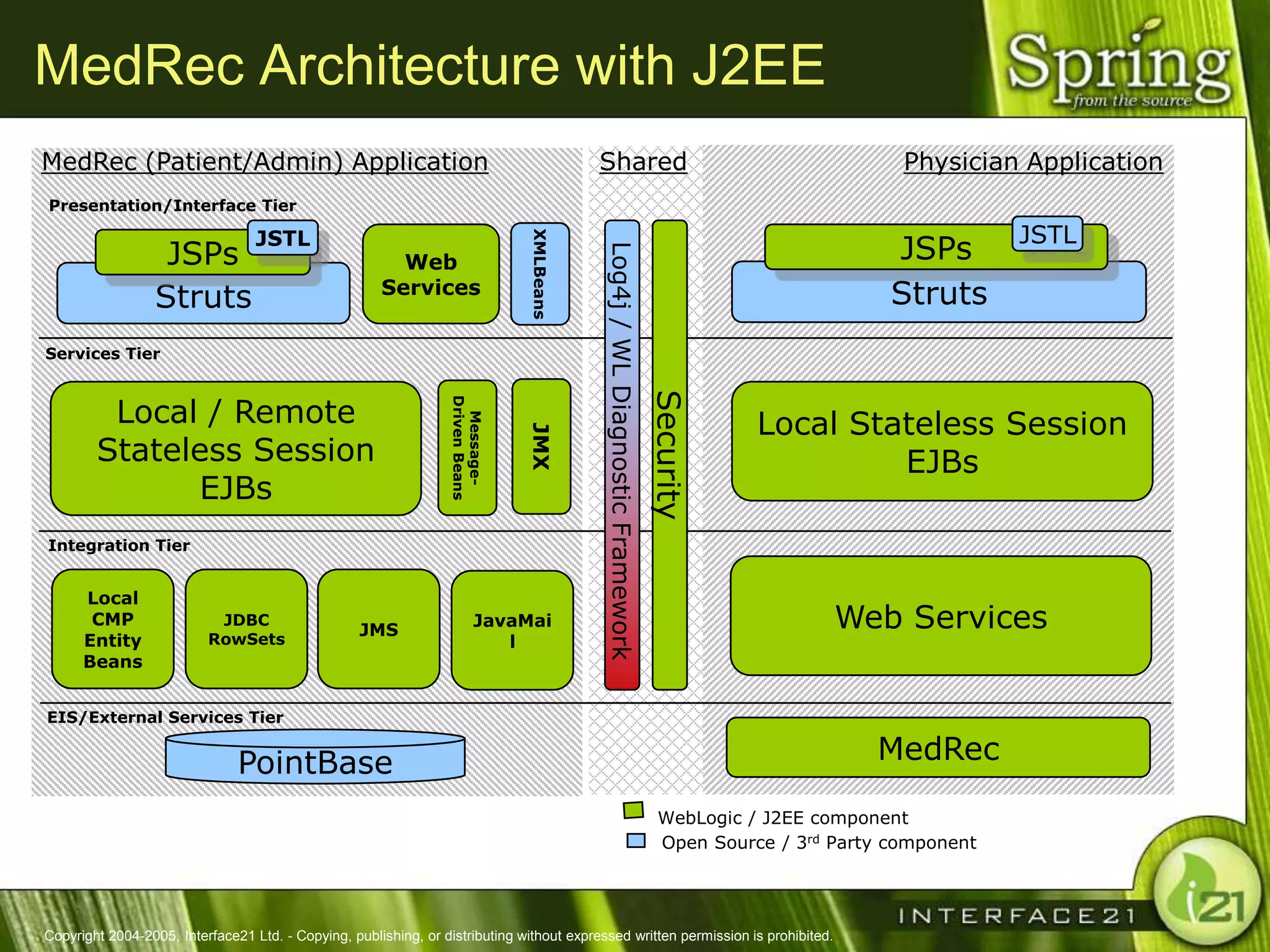
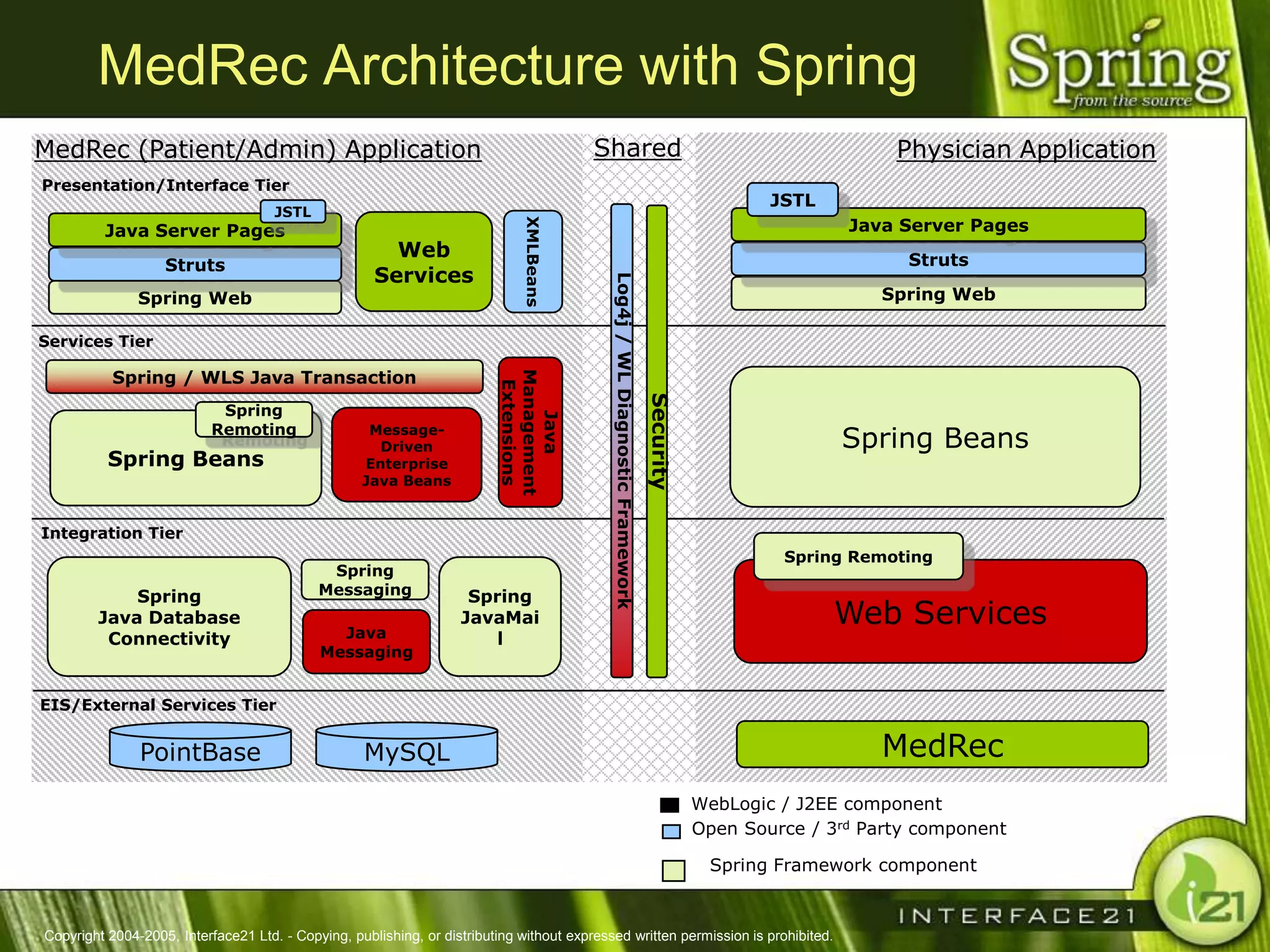
The Spring Framework aims to make J2EE development easier and more productive by providing an inversion of control container and aspect-oriented programming. It addresses requirements across application tiers rather than focusing on a single tier. The Spring Framework's goals include eliminating the need for "glue" code between tiers, facilitating unit testing and object-oriented best practices, and providing an alternative to Enterprise JavaBeans for many applications.