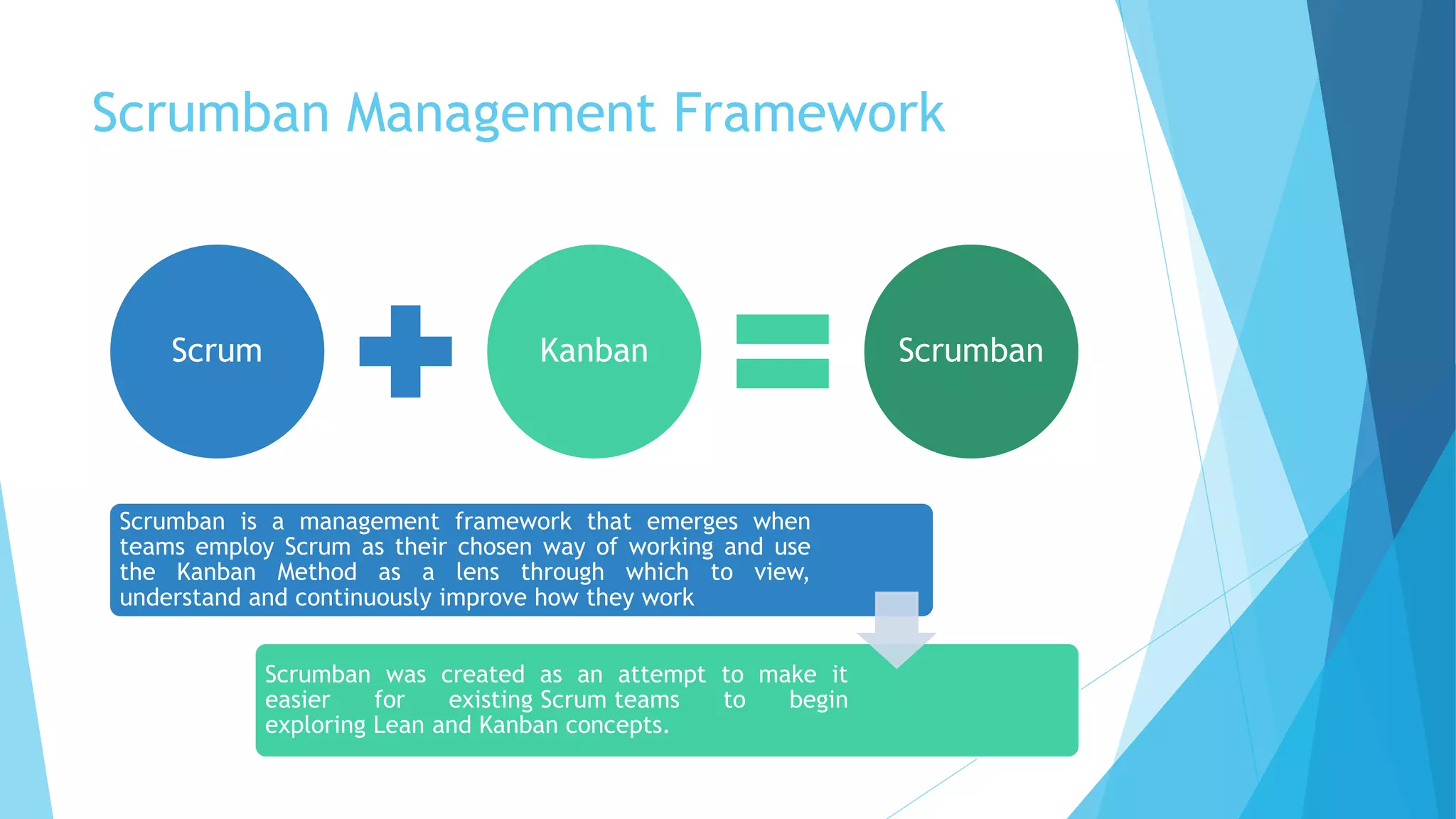
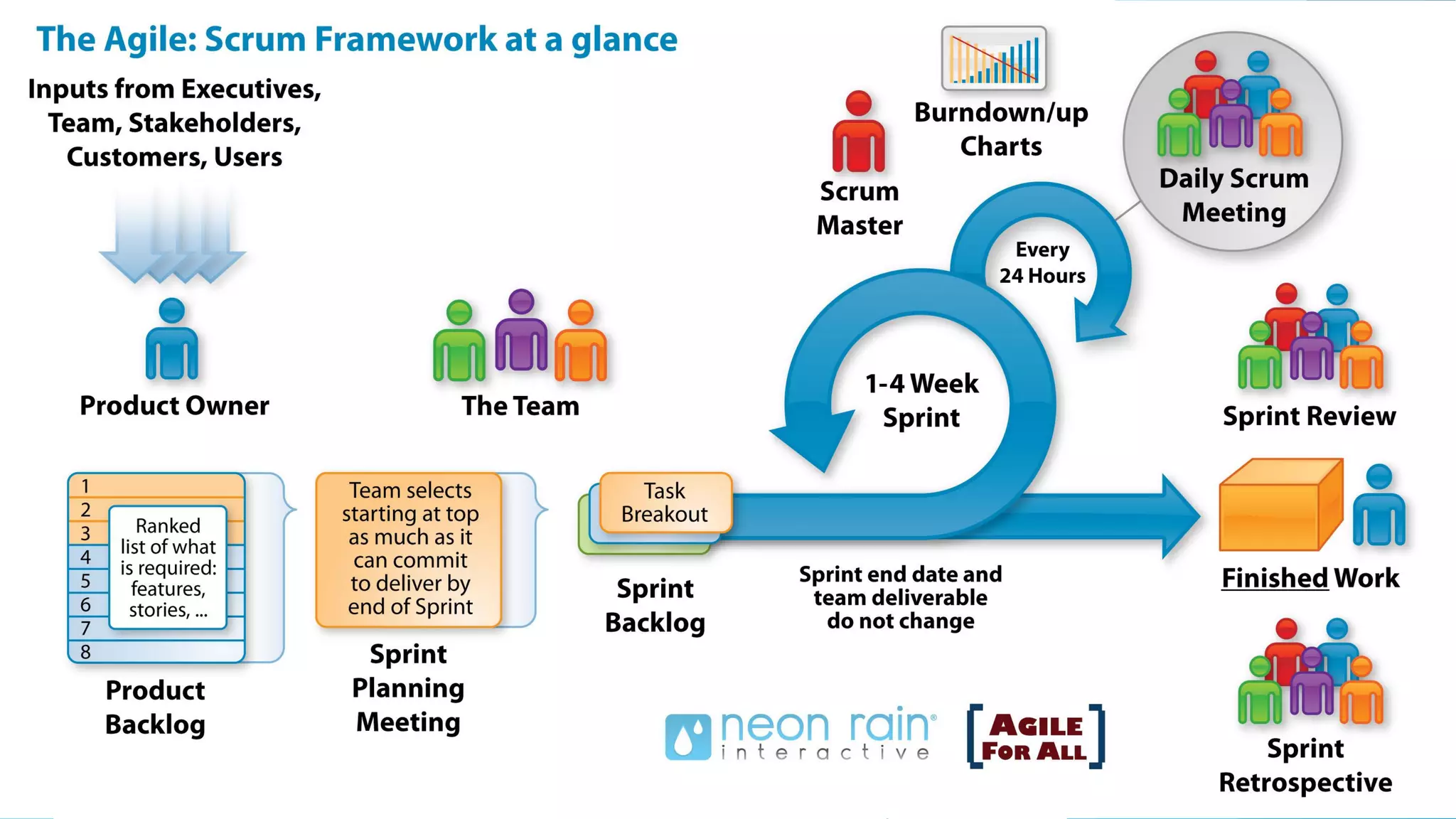
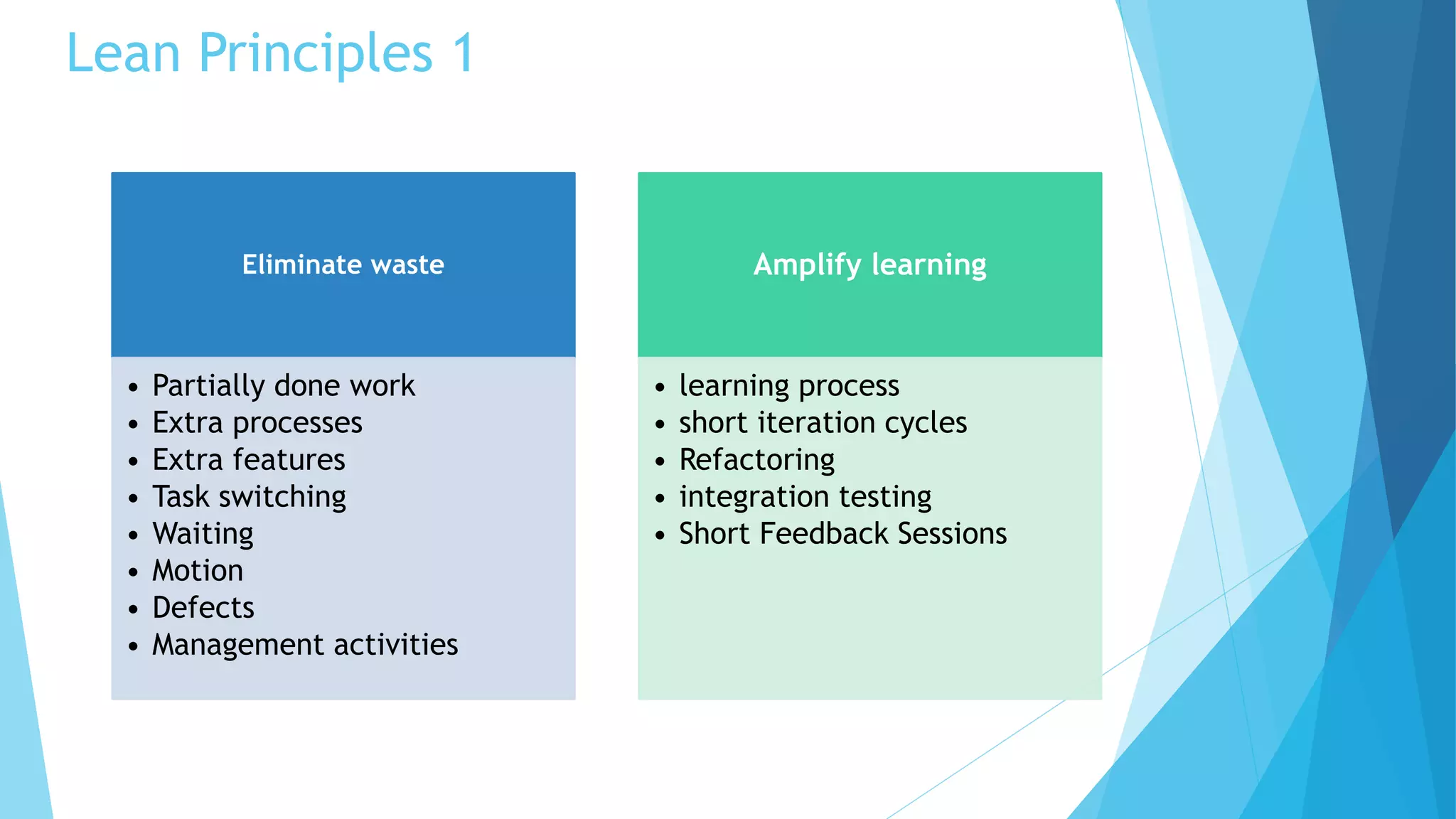
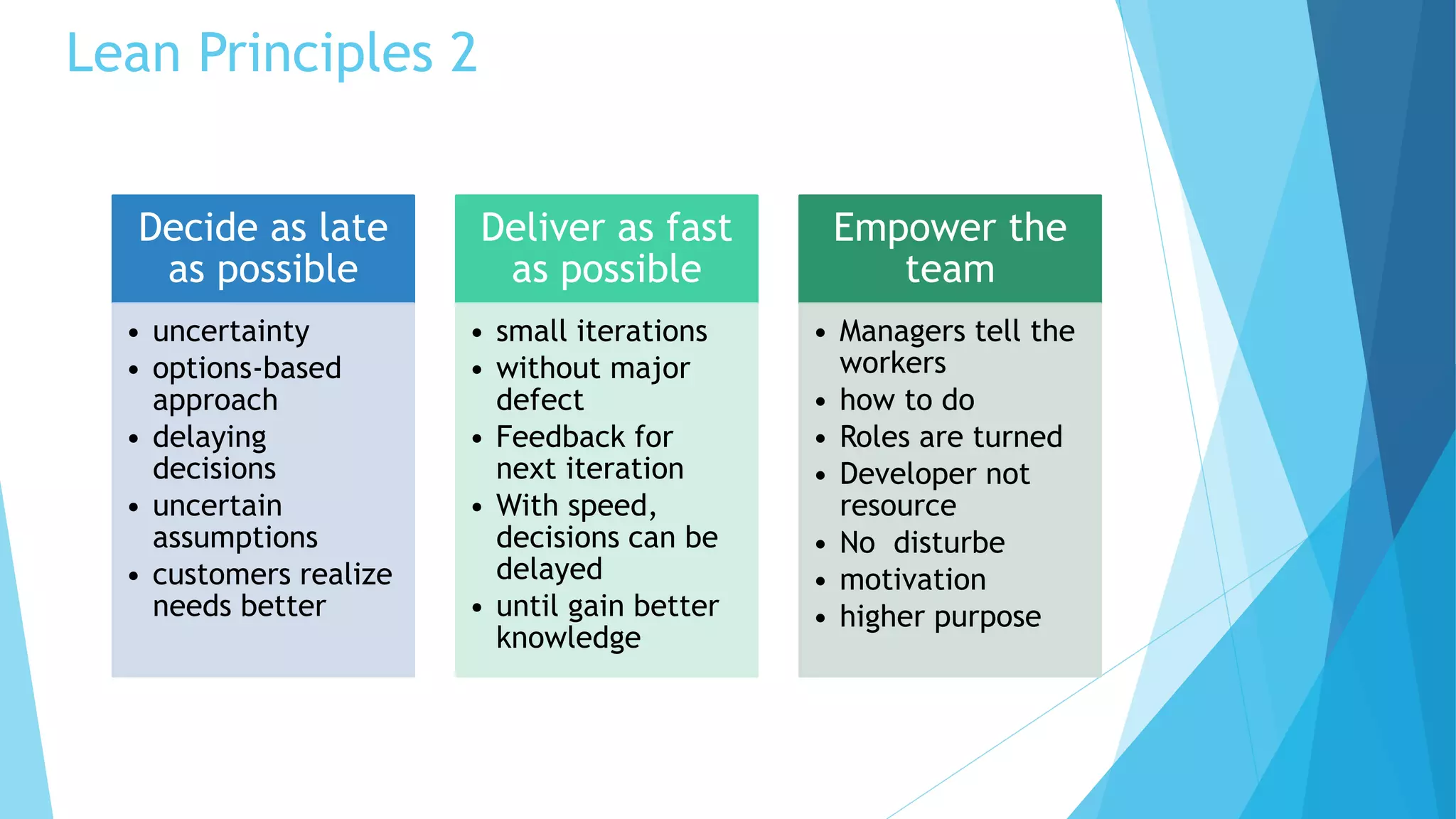
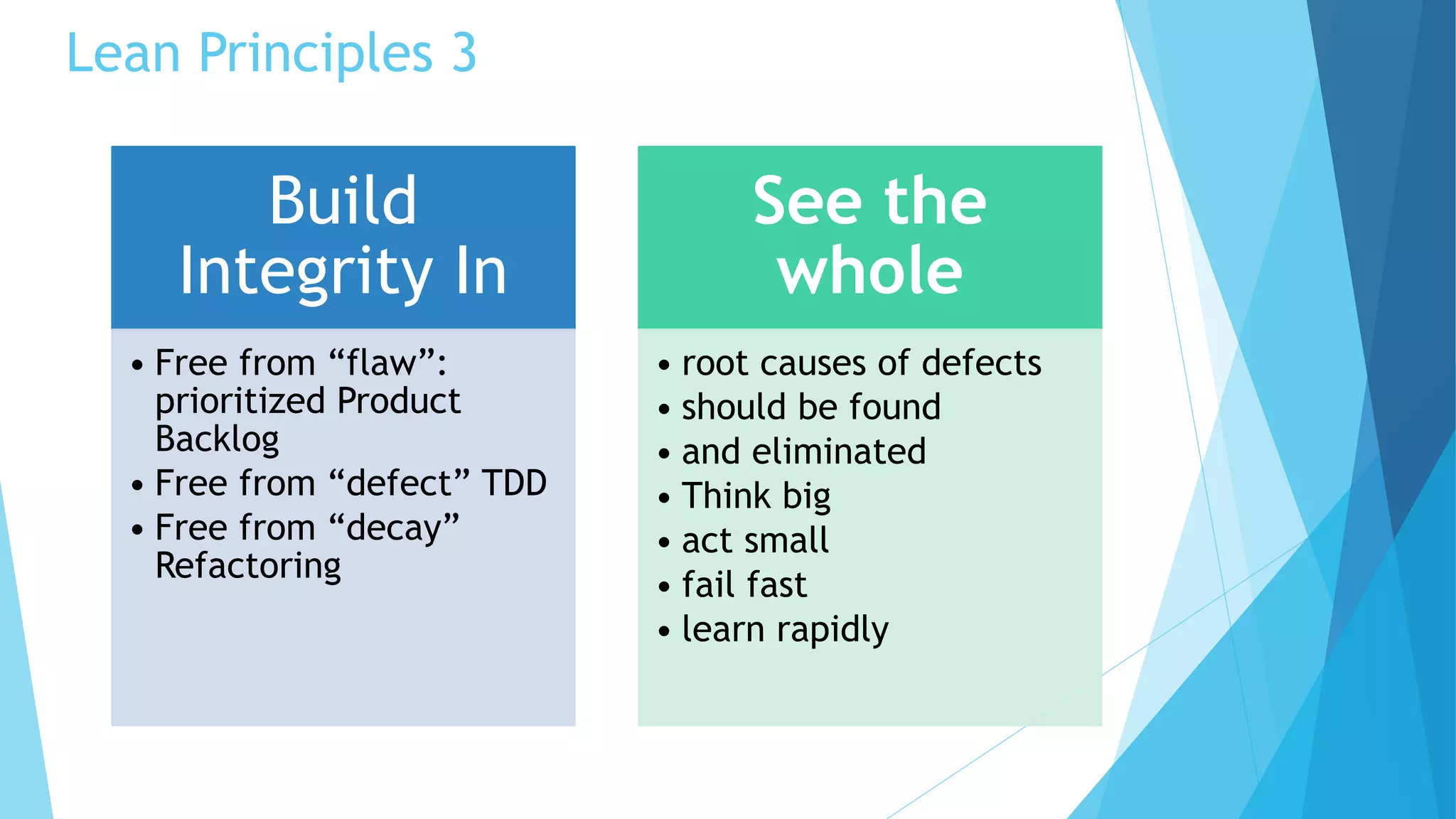
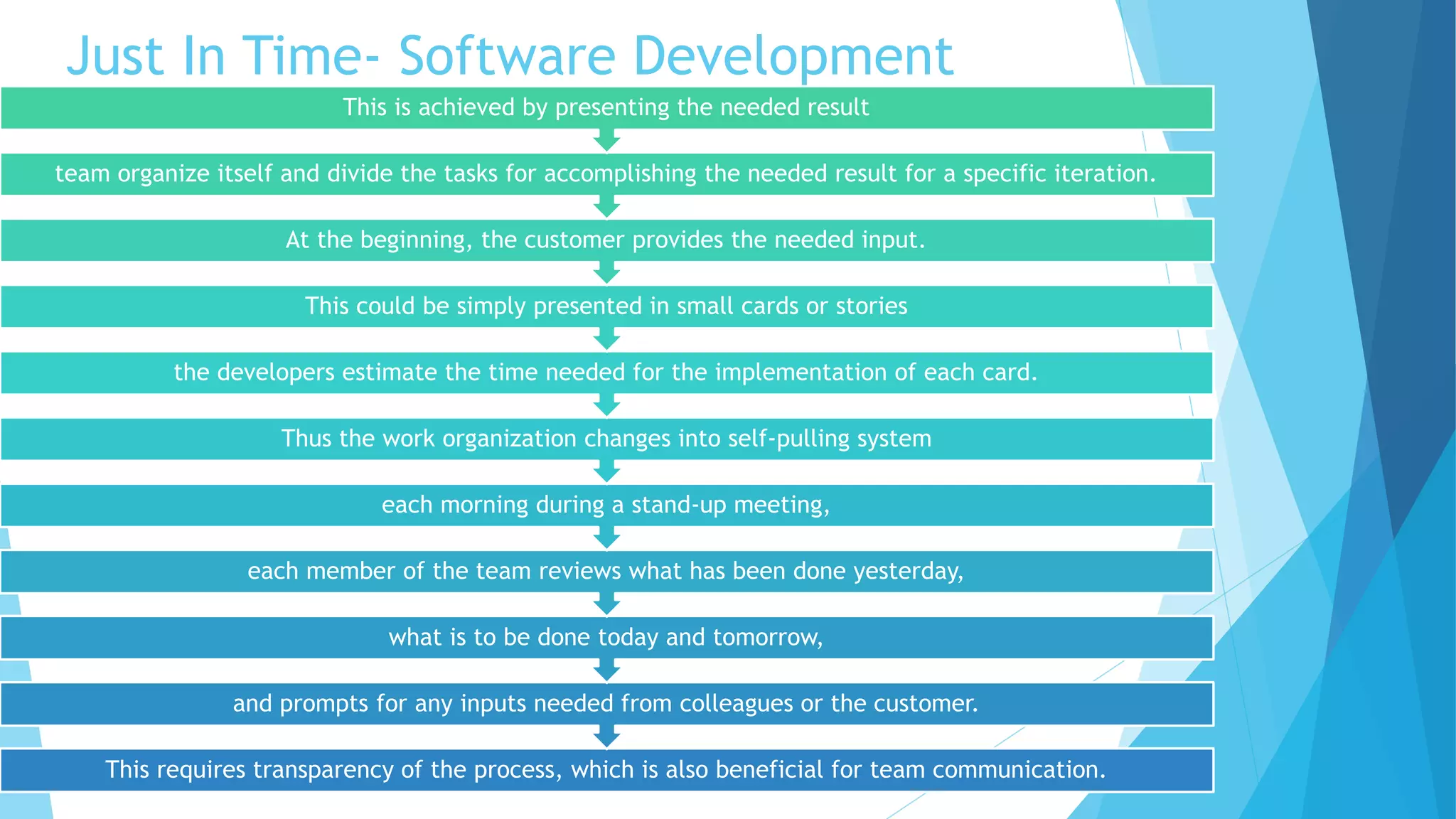
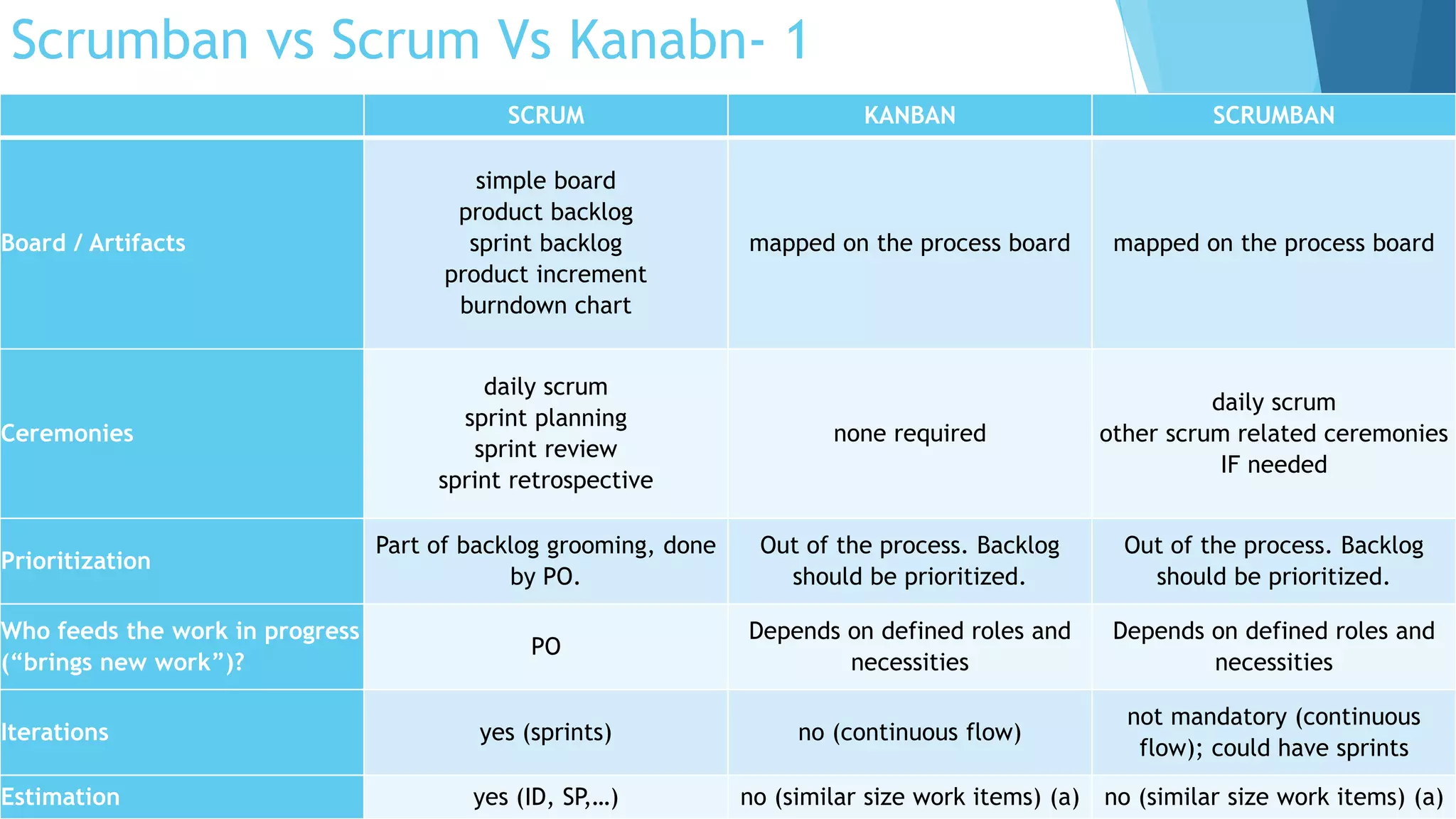
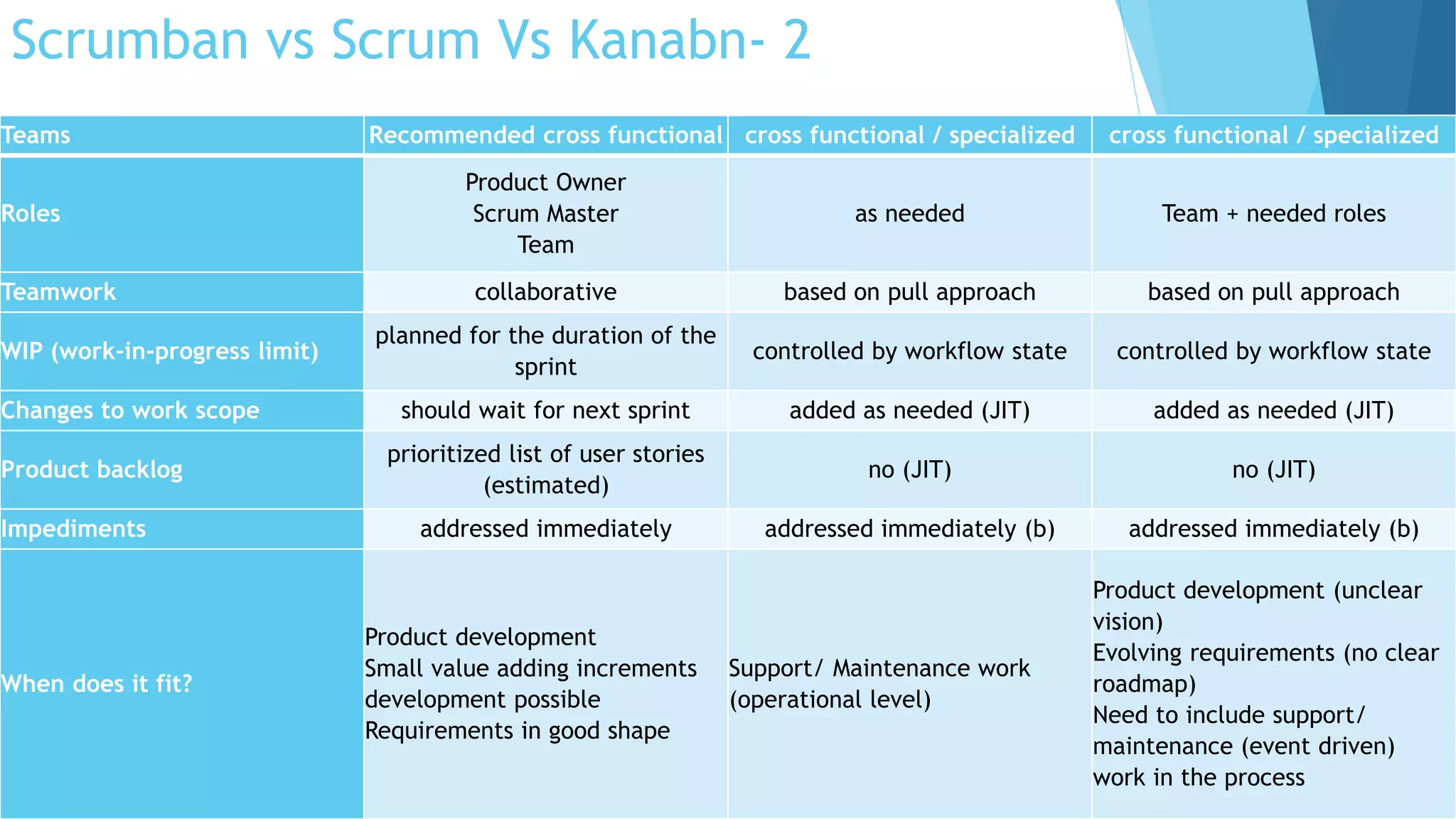
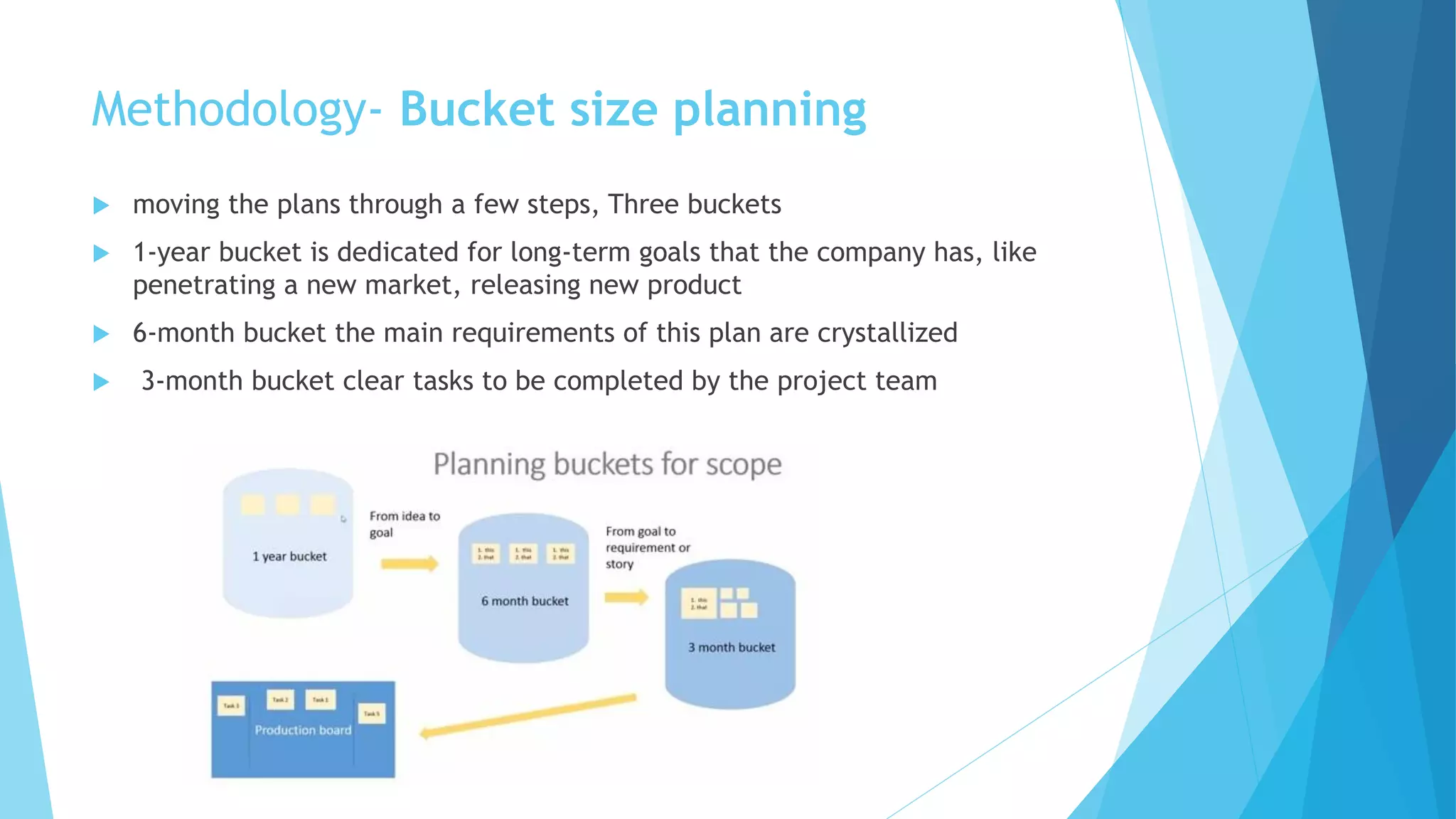
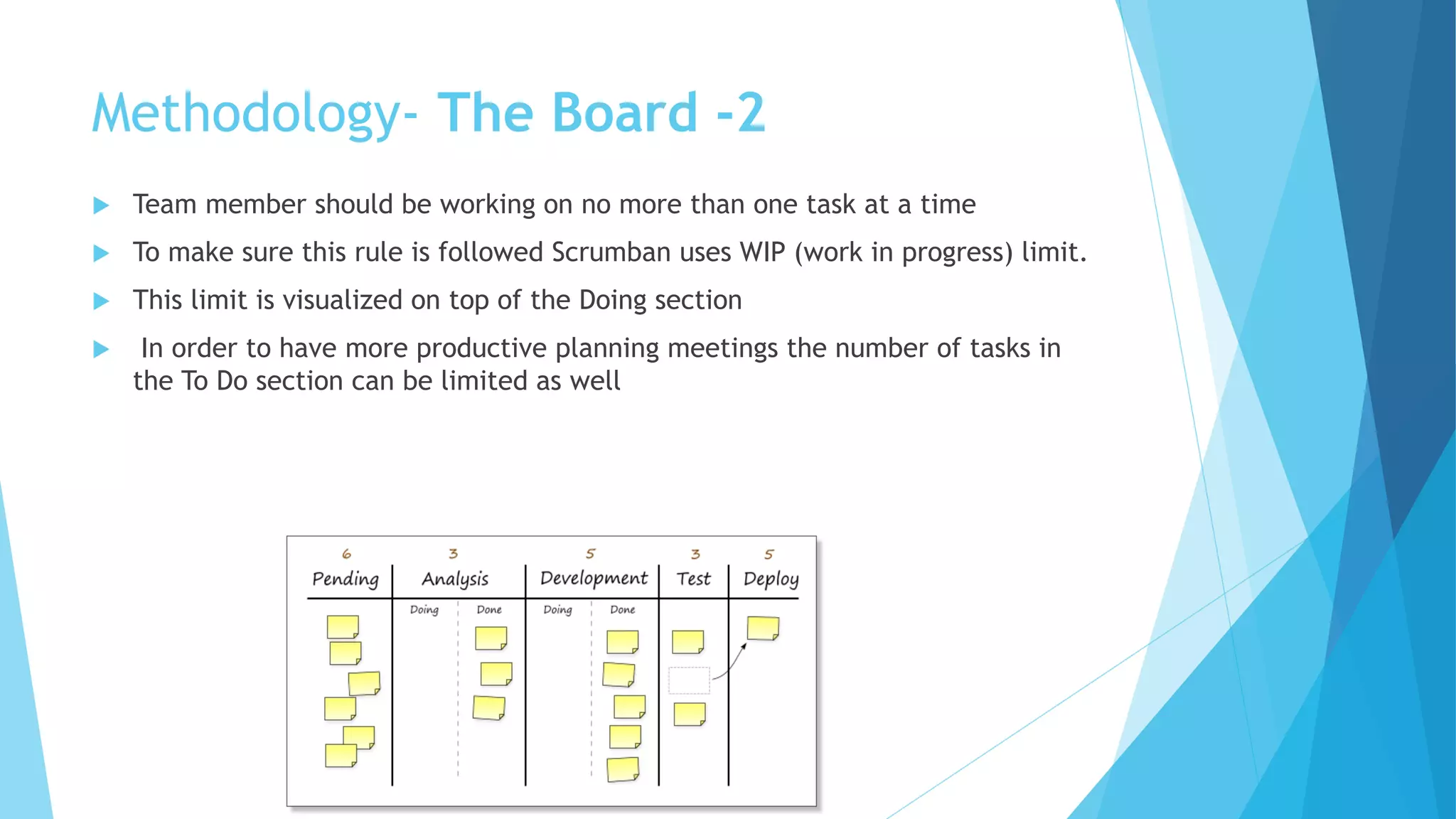
Scrumban is a management framework that integrates Scrum practices with Kanban principles to improve team workflow and operational efficiency. It emphasizes lean principles, such as eliminating waste, empowering teams, and maintaining a prioritized backlog to ensure timely delivery and adaptability. The framework accommodates continuous flow and on-demand planning, allowing teams to dynamically manage tasks based on project needs and priorities.