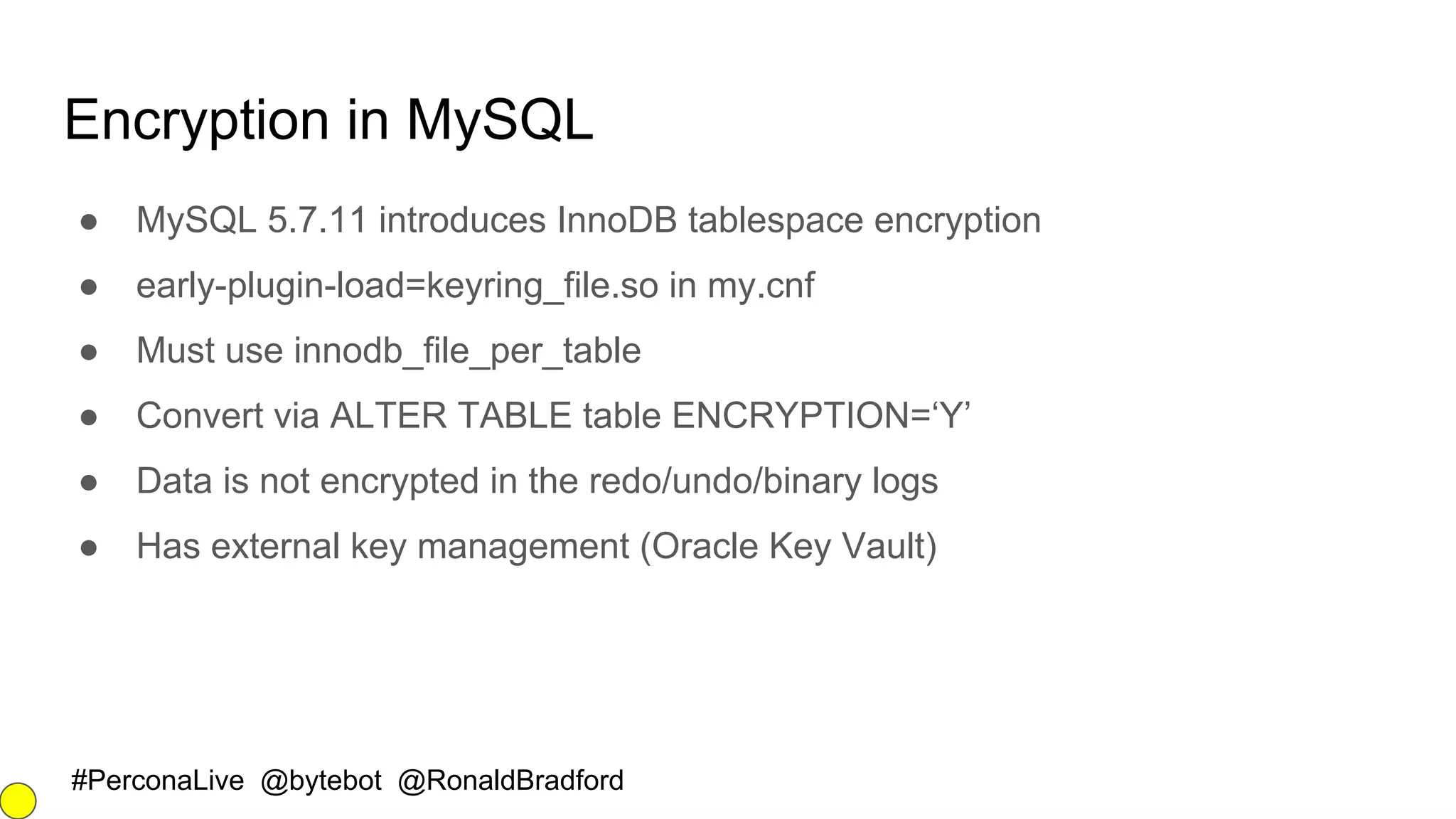
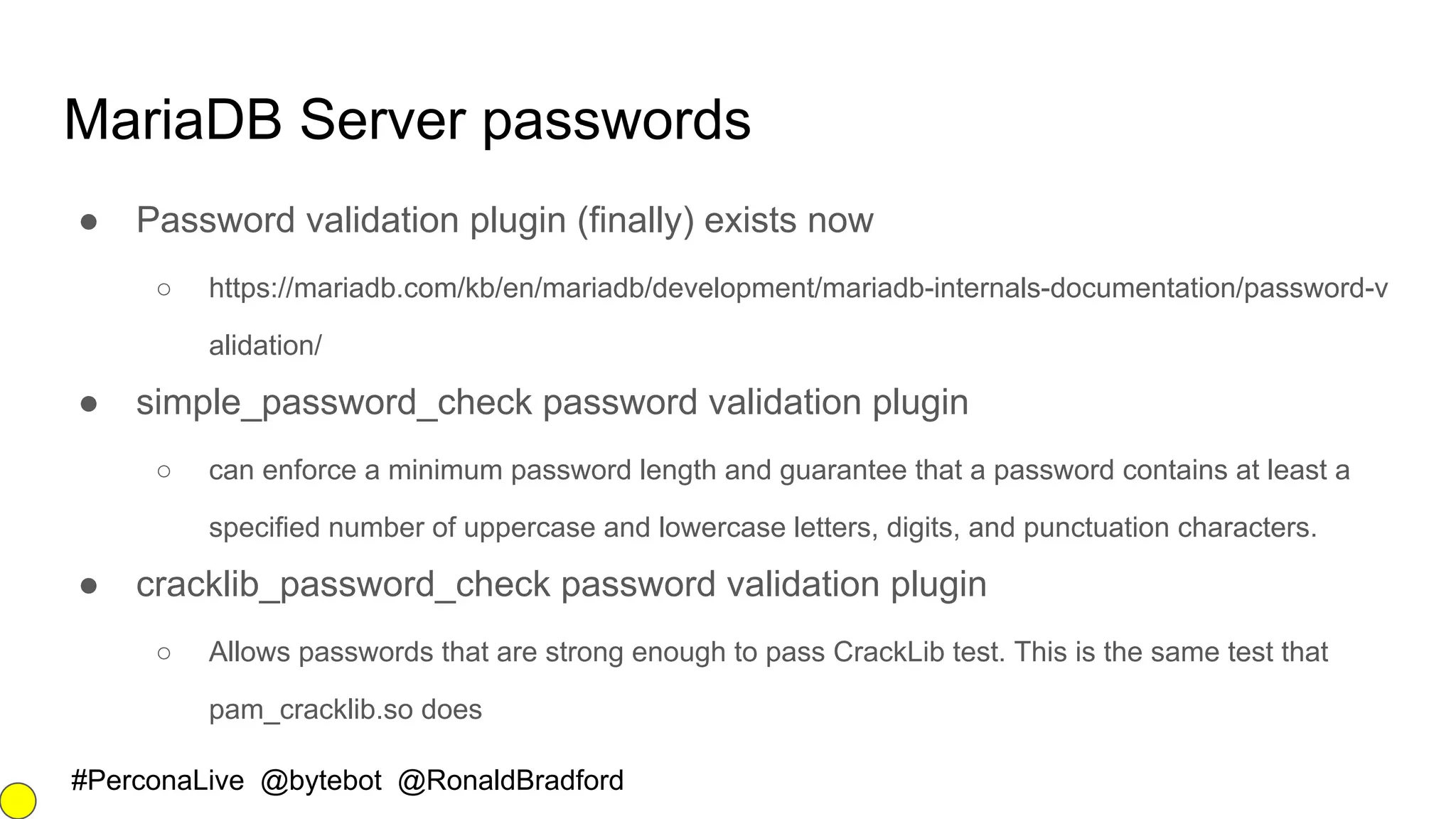
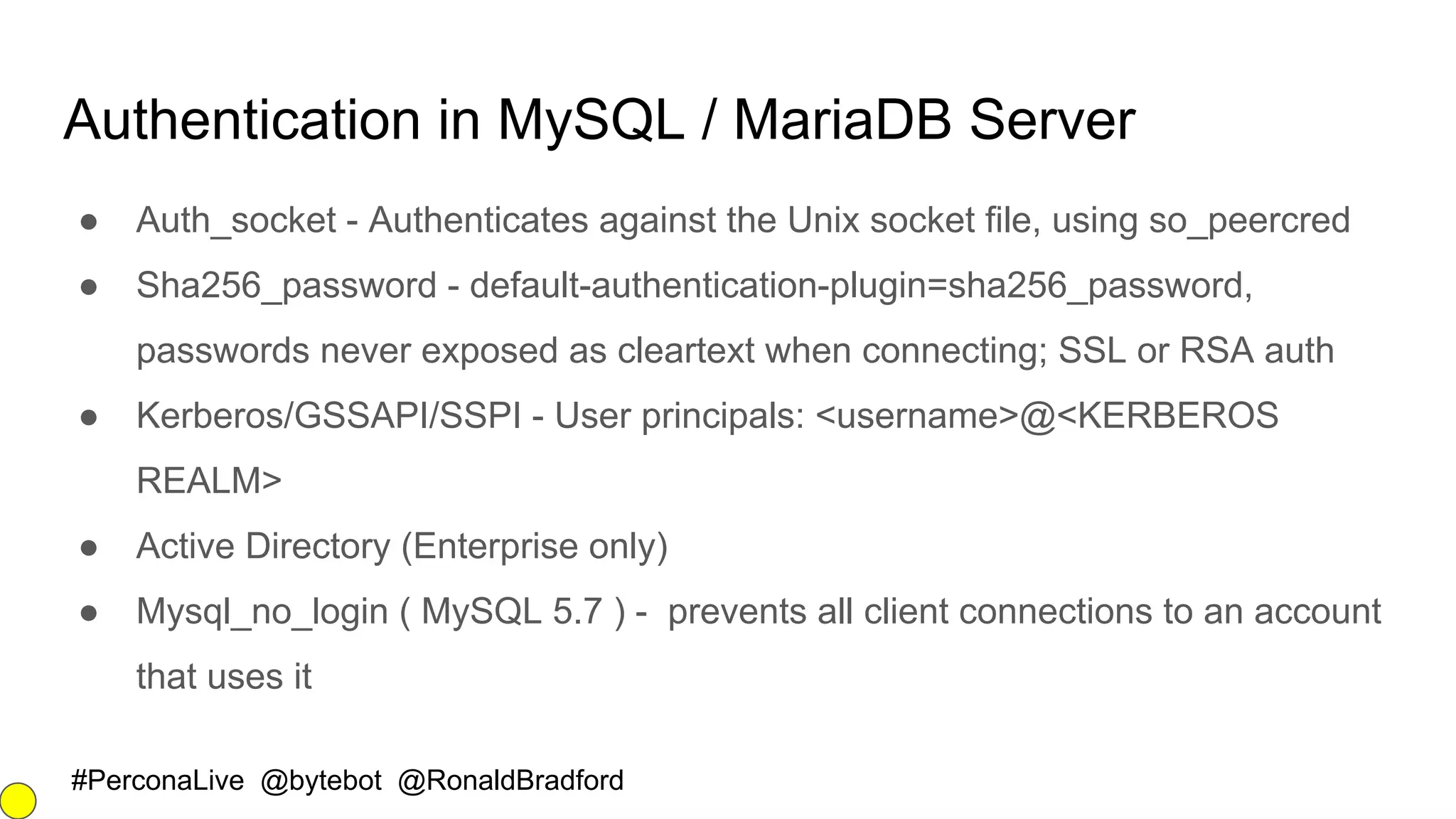
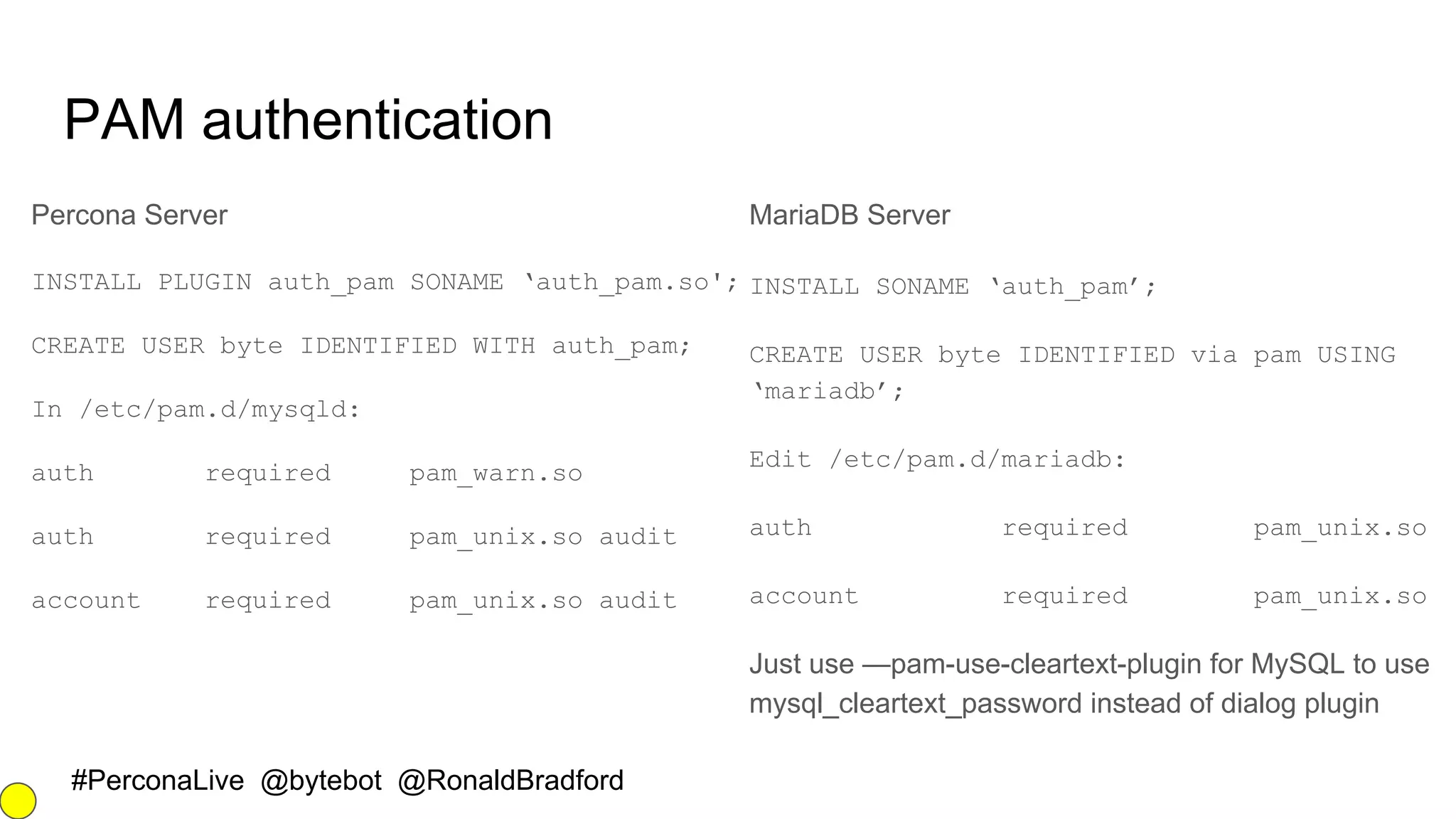
The document outlines security best practices for MySQL and MariaDB databases, focusing on securing data, communication, user accounts, and server access. It highlights poor security signs, the importance of encryption and key management, and various authentication mechanisms. Additionally, it covers installation security, the use of Docker containers, and recommended practices for maintaining a secure database environment.


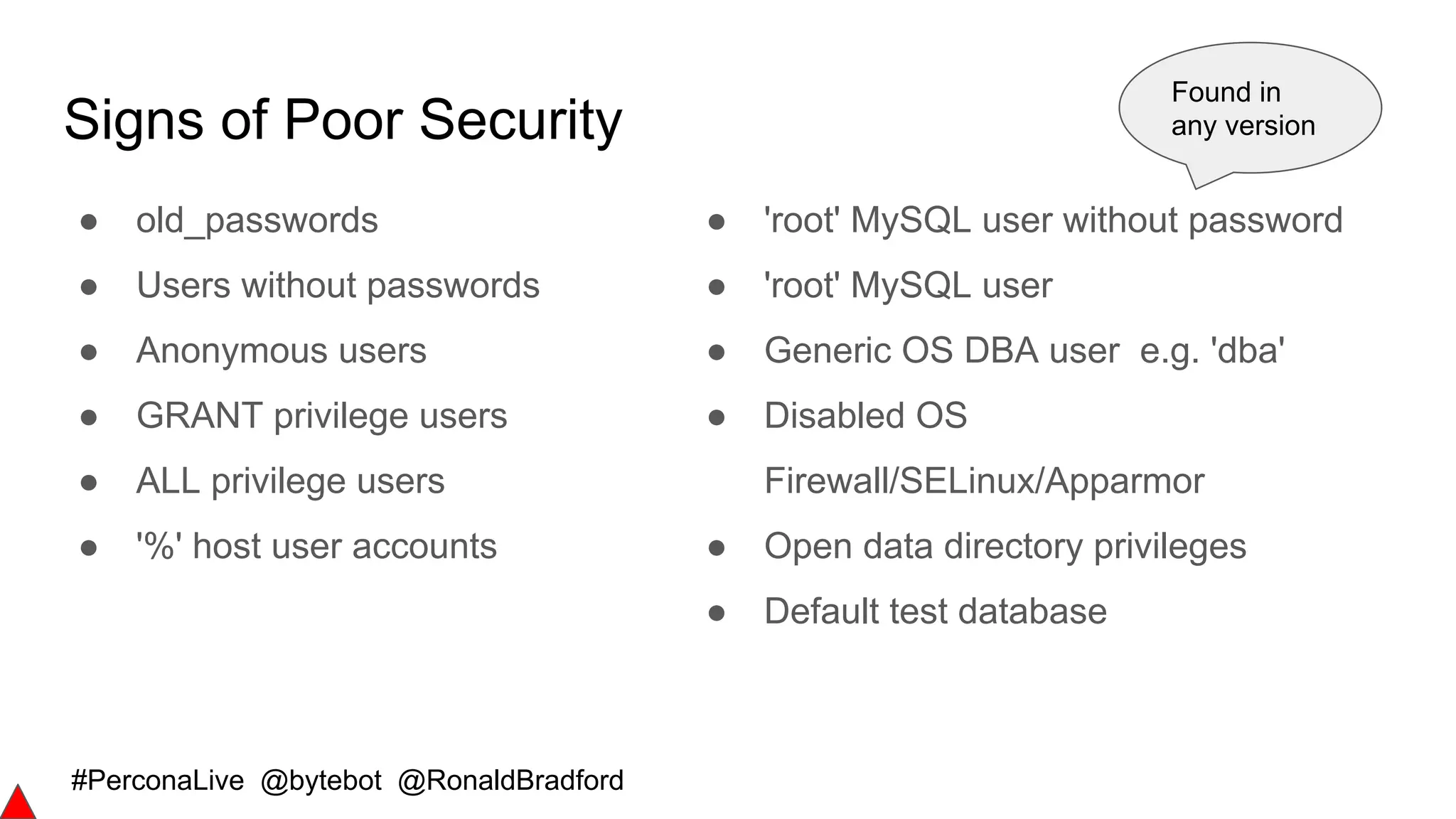




![#PerconaLive @bytebot @RonaldBradford
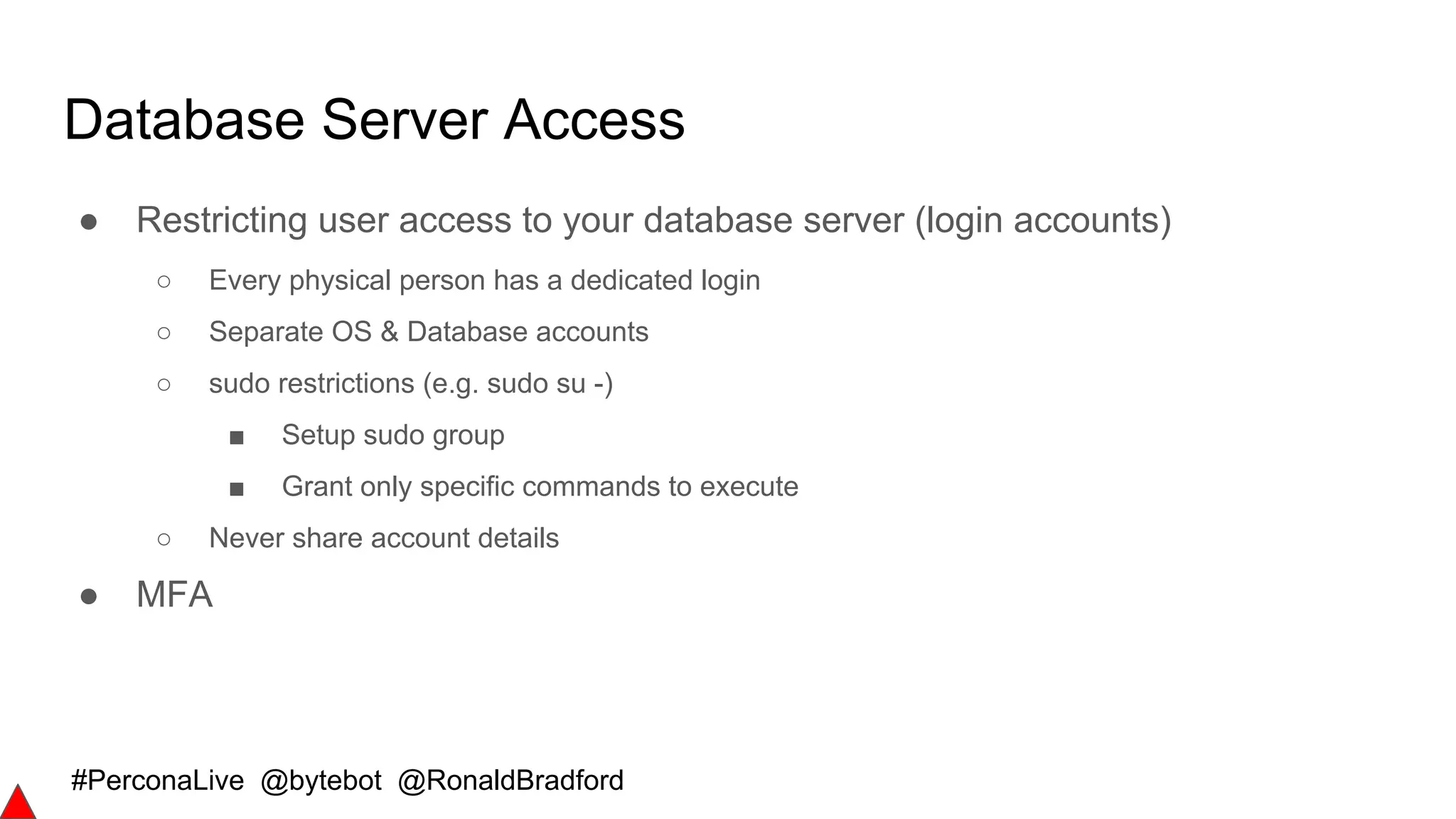
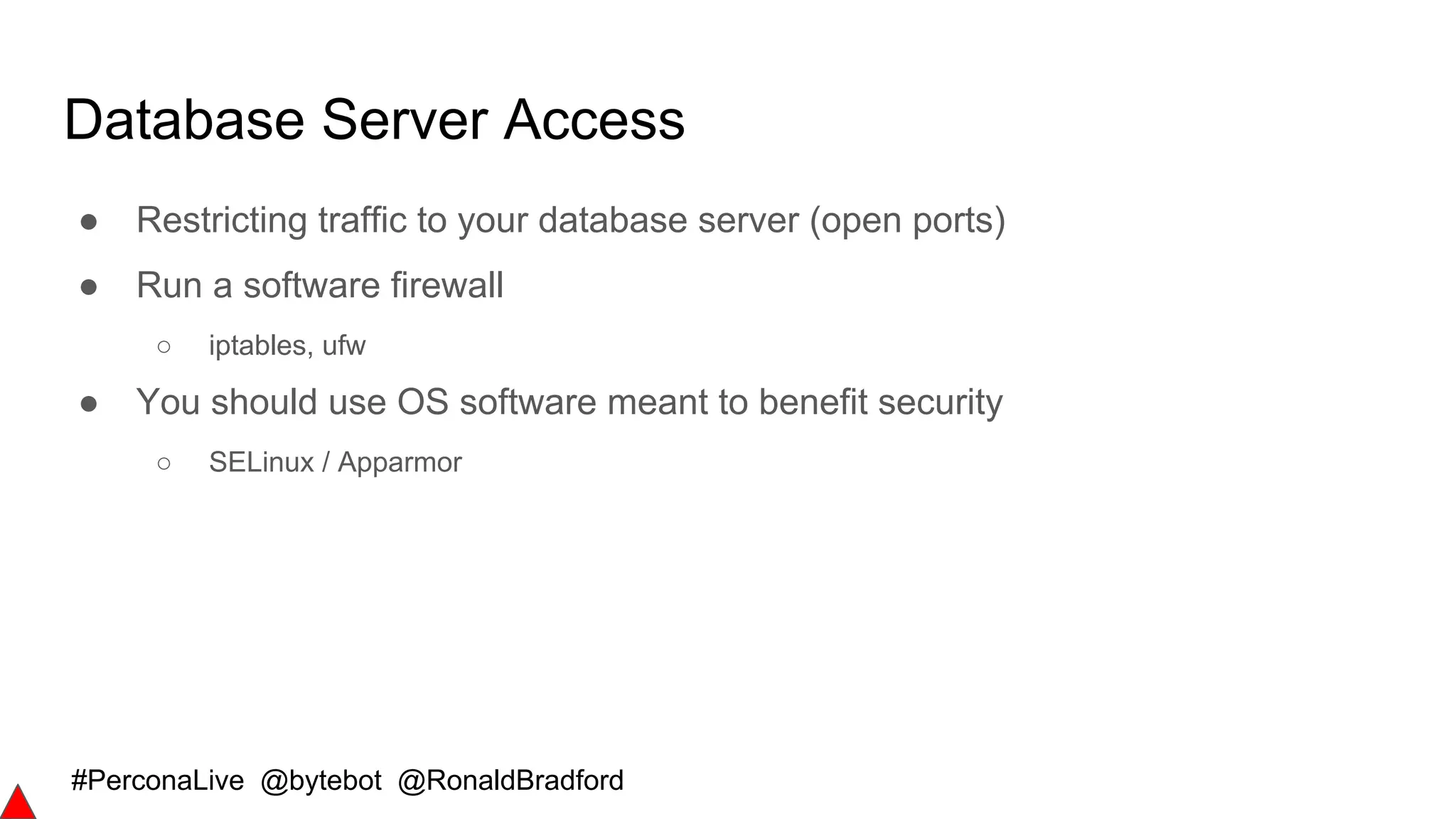
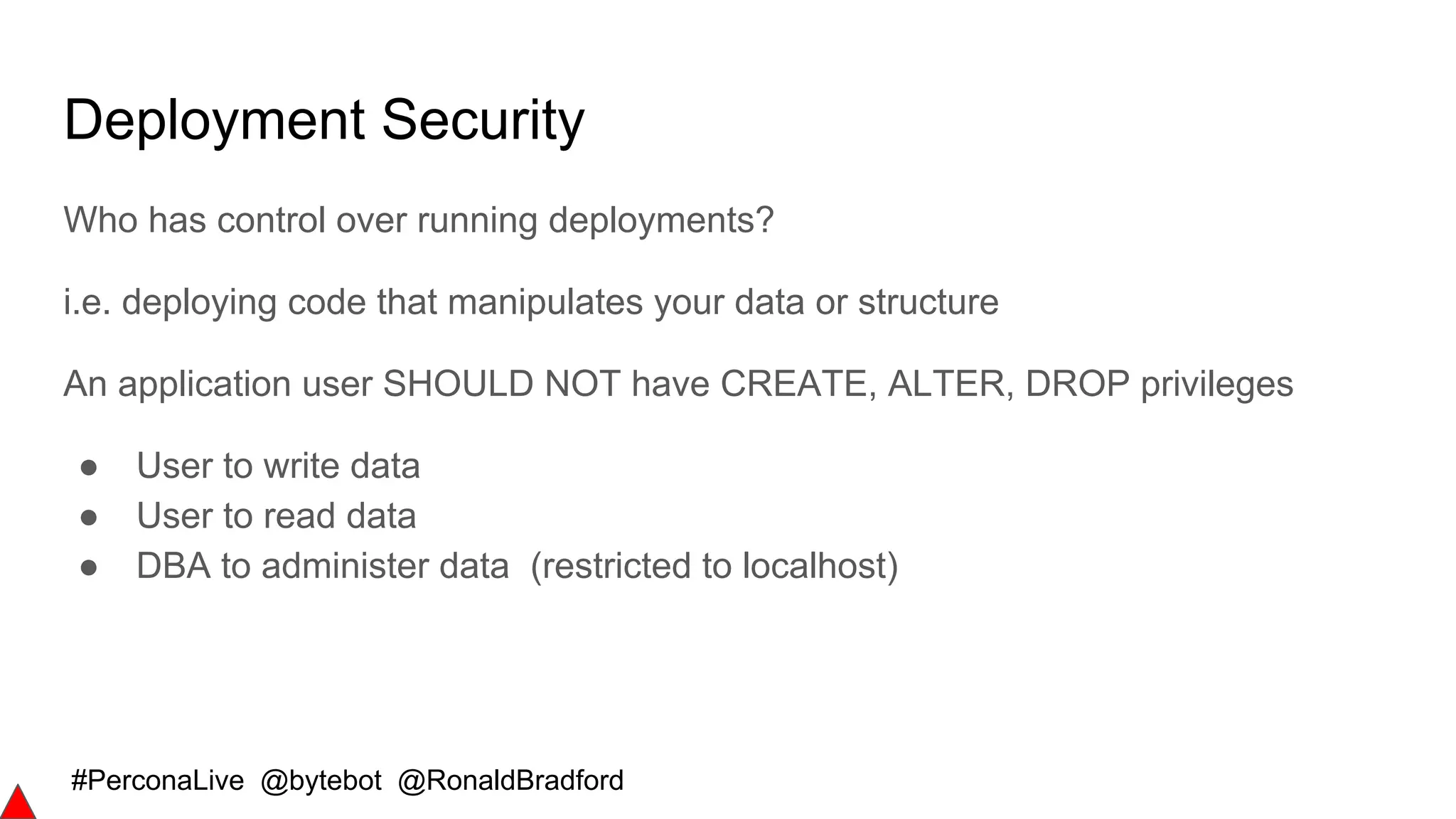
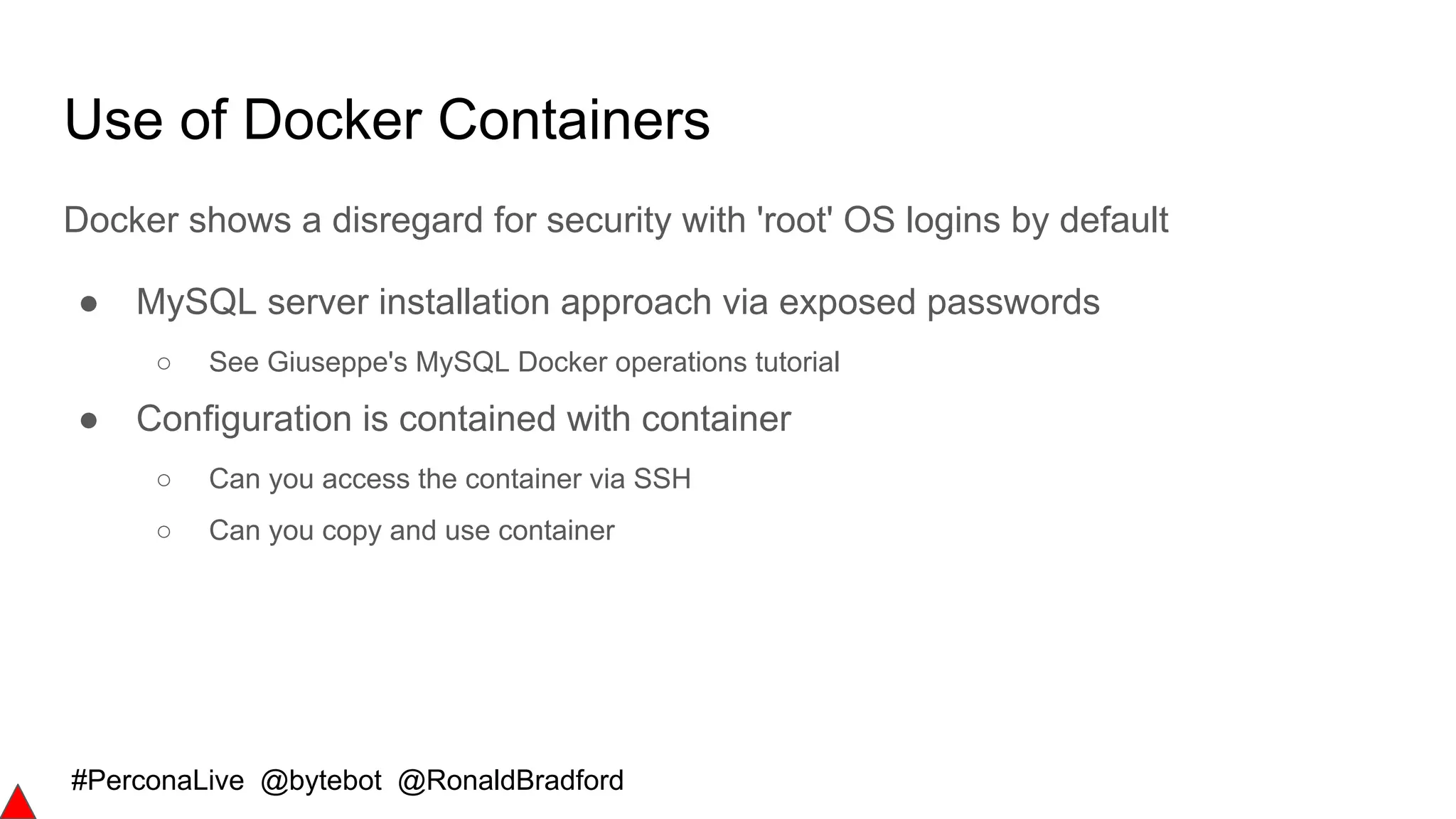
Secure Communications
[mysqld]
ssl-ca=ca.pem
ssl-cert=server-cert.pem
ssl-key=server-key.pem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securingyourmysql2fmariadbdata-161011021616/75/Securing-your-MySQL-MariaDB-Server-data-10-2048.jpg)
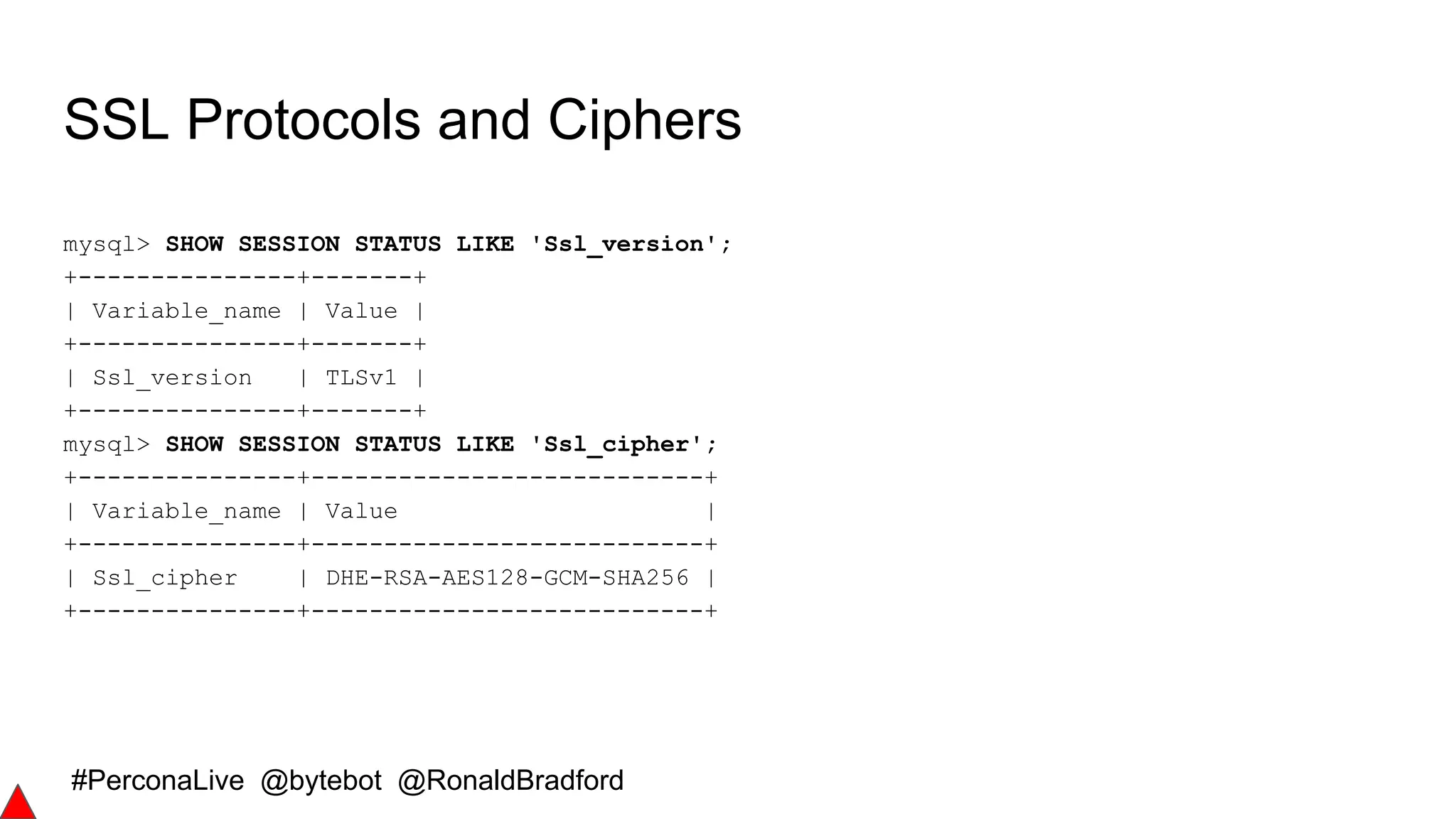
![#PerconaLive @bytebot @RonaldBradford
SSL Client Connections
Https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-python/en/connector-python-connectargs.html
import mysql.connector
from mysql.connector.constants import ClientFlag
config = {
'user': 'ssluser',
'password': 'asecret',
'host': '127.0.0.1',
'client_flags': [ClientFlag.SSL],
'ssl_ca': '/opt/mysql/ssl/ca.pem',
'ssl_cert': '/opt/mysql/ssl/client-cert.pem',
'ssl_key': '/opt/mysql/ssl/client-key.pem',
}
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connectors/en/connector-net-tutorials-ssl.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securingyourmysql2fmariadbdata-161011021616/75/Securing-your-MySQL-MariaDB-Server-data-12-2048.jpg)


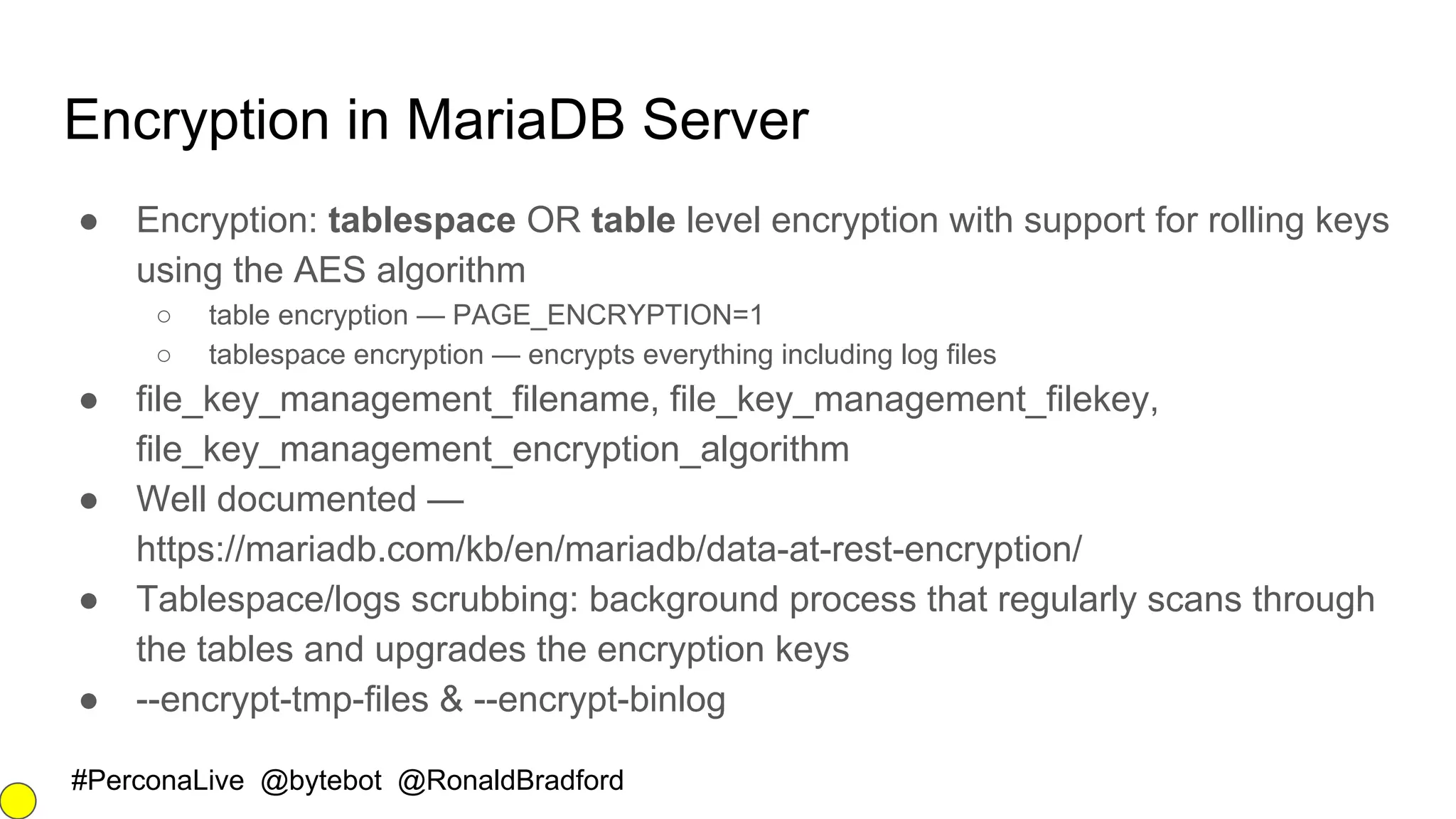
![#PerconaLive @bytebot @RonaldBradford
Encryption in MariaDB Server II
[mysqld]
plugin-load-add=file_key_management.so
file-key-management
file-key-management-filename = /home/mdb/keys.enc
innodb-encrypt-tables
innodb-encrypt-log
innodb-encryption-threads=4
aria-encrypt-tables=1 # PAGE row format
encrypt-tmp-disk-tables=1 # this is for Aria
CREATE TABLE customer (
customer_id bigint not null primary key,
customer_name varchar(80),
customer_creditcard varchar(20))
ENGINE=InnoDB
page_encryption=1
page_encryption_key=1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securingyourmysql2fmariadbdata-161011021616/75/Securing-your-MySQL-MariaDB-Server-data-16-2048.jpg)